 P D 1 D 3 D 2 S 3 Q “OK, I was wrong. It is a matter of supply and demand, and now I think you da “man”. and Demand S 1 S 2
P D 1 D 3 D 2 S 3 Q “OK, I was wrong. It is a matter of supply and demand, and now I think you da “man”. and Demand S 1 S 2
 Consumers and Producers Feel Differently About High and Low prices Producers supply more at the higher price because the opportunity cost increases if they don’t. Consumers consume less at the higher price because they now have less money to spend. Producers supply less at the lower prices because the opportunity cost decreases if they don’t. Consumers consume more at the lower price because they now have more money to spend. I was going to buy a Honda but this car is $4, 000 cheaper. I’m saving money at the lower price. I normally eat one, but at this low price, I’m having two.
Consumers and Producers Feel Differently About High and Low prices Producers supply more at the higher price because the opportunity cost increases if they don’t. Consumers consume less at the higher price because they now have less money to spend. Producers supply less at the lower prices because the opportunity cost decreases if they don’t. Consumers consume more at the lower price because they now have more money to spend. I was going to buy a Honda but this car is $4, 000 cheaper. I’m saving money at the lower price. I normally eat one, but at this low price, I’m having two.
![Supply (& Demand) “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] Direct – price Supply (& Demand) “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] Direct – price](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-3.jpg) Supply (& Demand) “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] Direct – price and QS move in the same direction. (increase together or decrease together) S The Law of Supply says QS varies directly with price. P 2 The Law Of Demand says QD varies inversely with price. P 1 QS 2
Supply (& Demand) “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] Direct – price and QS move in the same direction. (increase together or decrease together) S The Law of Supply says QS varies directly with price. P 2 The Law Of Demand says QD varies inversely with price. P 1 QS 2
![Supply (and Demand) “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] The law of Supply (and Demand) “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] The law of](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-4.jpg) Supply (and Demand) “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] The law of supply and demand is learned in infancy. Infants demand clean diapers and are willing to supply peace and quiet in exchange. Mothers demand peace and quiet and are willing to supply clean diapers in exchange. The terms of trade arranged. . “One scream equals one diaper. The price of one diaper is one scream. ” Supply – producers “willingness to sell. ” Or, the “amount of products offered at each price during a specific time period. ”
Supply (and Demand) “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] The law of supply and demand is learned in infancy. Infants demand clean diapers and are willing to supply peace and quiet in exchange. Mothers demand peace and quiet and are willing to supply clean diapers in exchange. The terms of trade arranged. . “One scream equals one diaper. The price of one diaper is one scream. ” Supply – producers “willingness to sell. ” Or, the “amount of products offered at each price during a specific time period. ”
![Supply (and Demand) Bread “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] Butter Law Supply (and Demand) Bread “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] Butter Law](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-5.jpg) Supply (and Demand) Bread “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] Butter Law of Supply – QS varies directly with price Suppliers offer more for sale at higher prices than at lower prices. The consumers, being consumers on the paying end, tend to buy a small amount of the product, but will buy more if the price is lowered. The supplier, on the lowered supplier receiving end, considers price as an incentive to sell a product. The higher the price, the more incentive he has.
Supply (and Demand) Bread “Bread & Butter” of Economics [“perfectly competitive markets”] Butter Law of Supply – QS varies directly with price Suppliers offer more for sale at higher prices than at lower prices. The consumers, being consumers on the paying end, tend to buy a small amount of the product, but will buy more if the price is lowered. The supplier, on the lowered supplier receiving end, considers price as an incentive to sell a product. The higher the price, the more incentive he has.
 SUPPLY DEFINED SUPPLY SCHEDULE Various Amounts CORN P QS $1 2 3 4 5 5 20 35 50 60 And why is talk so cheap? Supply is excessive. Cut Supply & you will increase demand.
SUPPLY DEFINED SUPPLY SCHEDULE Various Amounts CORN P QS $1 2 3 4 5 5 20 35 50 60 And why is talk so cheap? Supply is excessive. Cut Supply & you will increase demand.
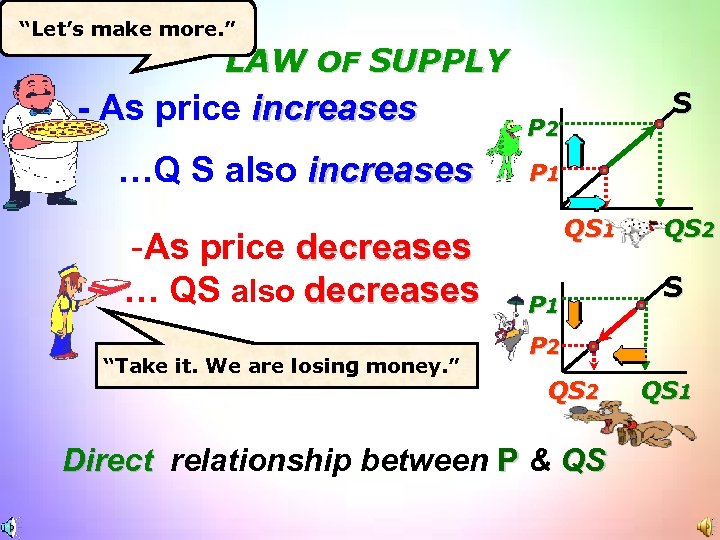 “Let’s make more. ” LAW OF SUPPLY - As price increases …Q S also increases -As price decreases … QS also decreases “Take it. We are losing money. ” S P 2 P 1 QS 1 P 1 QS 2 S P 2 QS 2 Direct relationship between P & QS QS 1
“Let’s make more. ” LAW OF SUPPLY - As price increases …Q S also increases -As price decreases … QS also decreases “Take it. We are losing money. ” S P 2 P 1 QS 1 P 1 QS 2 S P 2 QS 2 Direct relationship between P & QS QS 1
![I only have 200 acres Change in “Supply” [Curve] 1. “Non-price change” [RATNEST] 2. I only have 200 acres Change in “Supply” [Curve] 1. “Non-price change” [RATNEST] 2.](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-8.jpg) I only have 200 acres Change in “Supply” [Curve] 1. “Non-price change” [RATNEST] 2. Whole supply curve “shifts” [There was a QS change but it was not caused by a change in price] Corn Broccoli S P 2 P 1 P S 2 S 1 Alternative Output Price Change [ I N V ER S E] “Substitutes in production” S 1 S 2 P QS 1 QS 2 “Supply Shifters” [RATNEST] 1. Resource Cost [wages /raw materials ] [ I NV E RS E ] 2. Alternative Output Prices [INVERSE] 3. Technology [DIRECT] DIRECT. 4. Number of Suppliers [DIRECT] DIRECT [new football league- bigger “S” of games] 5. Expectations [about future price] [INVERSE] 6. Subsidies [DIRECT] DIRECT 3 1 S 2 7. Taxes [INVERSE] S S Don’t confuse these two with Chg in QS. “Suppliers produce smaller/ larger quantities at each price. ” QS 3 QS 1 QS 2
I only have 200 acres Change in “Supply” [Curve] 1. “Non-price change” [RATNEST] 2. Whole supply curve “shifts” [There was a QS change but it was not caused by a change in price] Corn Broccoli S P 2 P 1 P S 2 S 1 Alternative Output Price Change [ I N V ER S E] “Substitutes in production” S 1 S 2 P QS 1 QS 2 “Supply Shifters” [RATNEST] 1. Resource Cost [wages /raw materials ] [ I NV E RS E ] 2. Alternative Output Prices [INVERSE] 3. Technology [DIRECT] DIRECT. 4. Number of Suppliers [DIRECT] DIRECT [new football league- bigger “S” of games] 5. Expectations [about future price] [INVERSE] 6. Subsidies [DIRECT] DIRECT 3 1 S 2 7. Taxes [INVERSE] S S Don’t confuse these two with Chg in QS. “Suppliers produce smaller/ larger quantities at each price. ” QS 3 QS 1 QS 2
![Supply Shifters [“RATNEST”] • Resource Cost[wages & raw materials] [inverse] • Alternative Output price Supply Shifters [“RATNEST”] • Resource Cost[wages & raw materials] [inverse] • Alternative Output price](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-9.jpg) Supply Shifters [“RATNEST”] • Resource Cost[wages & raw materials] [inverse] • Alternative Output price changes [inverse] • Technology [direct] direct • Number of Suppliers [direct] • Expectation(Suppliers) about future price [inverse] • Subsidies [direct] Taxes [inverse] Decr in “S” of broccoli Bigger supply of games “Take this money. ” Up down
Supply Shifters [“RATNEST”] • Resource Cost[wages & raw materials] [inverse] • Alternative Output price changes [inverse] • Technology [direct] direct • Number of Suppliers [direct] • Expectation(Suppliers) about future price [inverse] • Subsidies [direct] Taxes [inverse] Decr in “S” of broccoli Bigger supply of games “Take this money. ” Up down
![DETERMINANTS [Shifters] OF SUPPLY [RATNEST – non PL] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 DETERMINANTS [Shifters] OF SUPPLY [RATNEST – non PL] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-10.jpg) DETERMINANTS [Shifters] OF SUPPLY [RATNEST – non PL] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 P • 1. Resource Cost [wages & raw materials] [inverse] • 58. Increase in wages (increases/decreases) supply. • Ex: A decrease in the price of computer chips (increases/decreases) the supply of computers. • 2. Alternative Output price changes [inverse] • 57. If the price of corn decreases, the supply of broccoli (increases/decreases). S 1 S 2 P Supply
DETERMINANTS [Shifters] OF SUPPLY [RATNEST – non PL] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 P • 1. Resource Cost [wages & raw materials] [inverse] • 58. Increase in wages (increases/decreases) supply. • Ex: A decrease in the price of computer chips (increases/decreases) the supply of computers. • 2. Alternative Output price changes [inverse] • 57. If the price of corn decreases, the supply of broccoli (increases/decreases). S 1 S 2 P Supply
 3. Technological Improvement “Can’t wait till milking time. ” This lowers production costs & increases “S”. Ex: Suppose a new milking machine called “The Invisible Hand” has a very soothing effect on cows; cows find the new machine so “udderly” delightful that they produce 30% more milk. This technological advance milk will cause a shift to the right 54
3. Technological Improvement “Can’t wait till milking time. ” This lowers production costs & increases “S”. Ex: Suppose a new milking machine called “The Invisible Hand” has a very soothing effect on cows; cows find the new machine so “udderly” delightful that they produce 30% more milk. This technological advance milk will cause a shift to the right 54
![4. Number of producers [direct] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 56. If more 4. Number of producers [direct] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 56. If more](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-12.jpg) 4. Number of producers [direct] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 56. If more firms enter an industry, the supply 56 curve will shift to the (left/right). • When the American Basketball League began play in 1968, there was a (bigger/smaller) supply of basketball games each week. 60. A new professional football league will 60 (increase/decrease) the supply of football games.
4. Number of producers [direct] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 56. If more firms enter an industry, the supply 56 curve will shift to the (left/right). • When the American Basketball League began play in 1968, there was a (bigger/smaller) supply of basketball games each week. 60. A new professional football league will 60 (increase/decrease) the supply of football games.
![5. Producer Expectations about Future Price [Inverse] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 59. 5. Producer Expectations about Future Price [Inverse] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 59.](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-13.jpg) 5. Producer Expectations about Future Price [Inverse] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 59. If oil producers expect future oil prices to 59 decline, they will (increase/decrease) current production. P Oil Prices Expected to decrease Supply
5. Producer Expectations about Future Price [Inverse] AS 3 AS 1 AS 2 59. If oil producers expect future oil prices to 59 decline, they will (increase/decrease) current production. P Oil Prices Expected to decrease Supply
 6. Subsidies – free money from “G” Free money from the government (subsidies) induces suppliers to supply more. 7. Taxes – take away business profits and decrease supply. 55. Businesses have their taxes increased which moves the supply curve to the (left/right).
6. Subsidies – free money from “G” Free money from the government (subsidies) induces suppliers to supply more. 7. Taxes – take away business profits and decrease supply. 55. Businesses have their taxes increased which moves the supply curve to the (left/right).
 Shortage of Face Masks for SARS S Young Hong Kong ballet dancers wear masks to protect themselves from SARS. 770 people died from this disease.
Shortage of Face Masks for SARS S Young Hong Kong ballet dancers wear masks to protect themselves from SARS. 770 people died from this disease.
 So What to use if there is a shortage?
So What to use if there is a shortage?
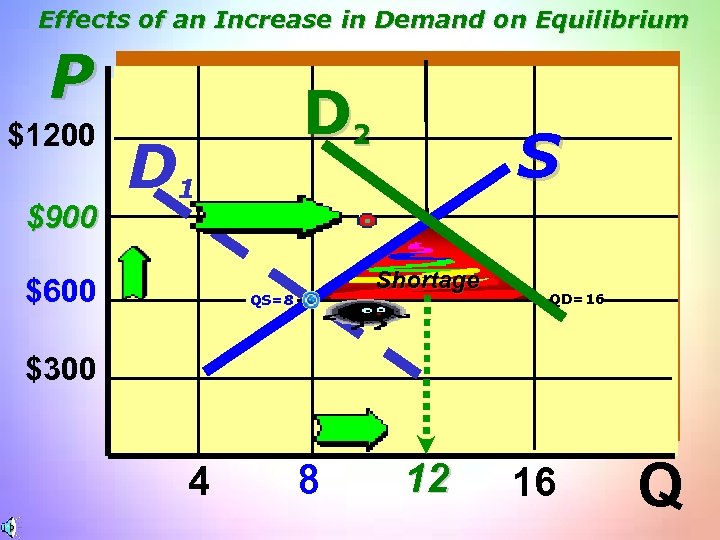 Effects of an Increase in Demand on Equilibrium P $1200 $900 D 2 D 1 $600 S Shortage QS=8 QD=16 $300 4 8 12 16 Q
Effects of an Increase in Demand on Equilibrium P $1200 $900 D 2 D 1 $600 S Shortage QS=8 QD=16 $300 4 8 12 16 Q
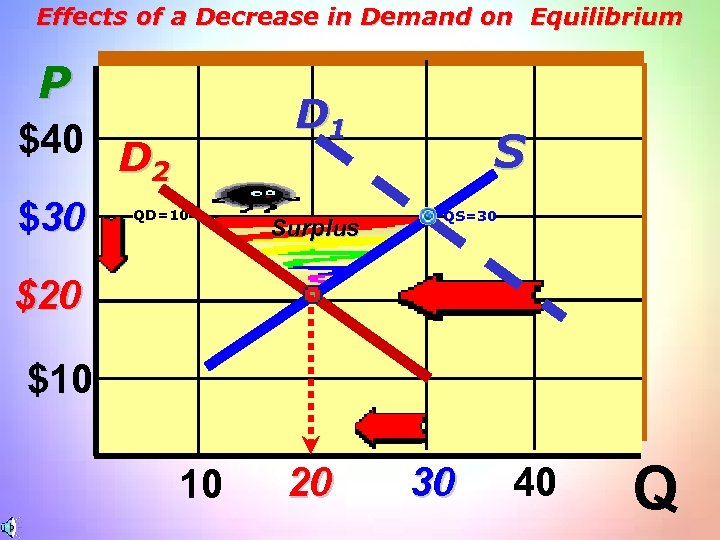 Effects of a Decrease in Demand on Equilibrium P D 1 $40 D 2 $30 QD=10 Surplus S QS=30 $20 $10 10 20 30 40 Q
Effects of a Decrease in Demand on Equilibrium P D 1 $40 D 2 $30 QD=10 Surplus S QS=30 $20 $10 10 20 30 40 Q
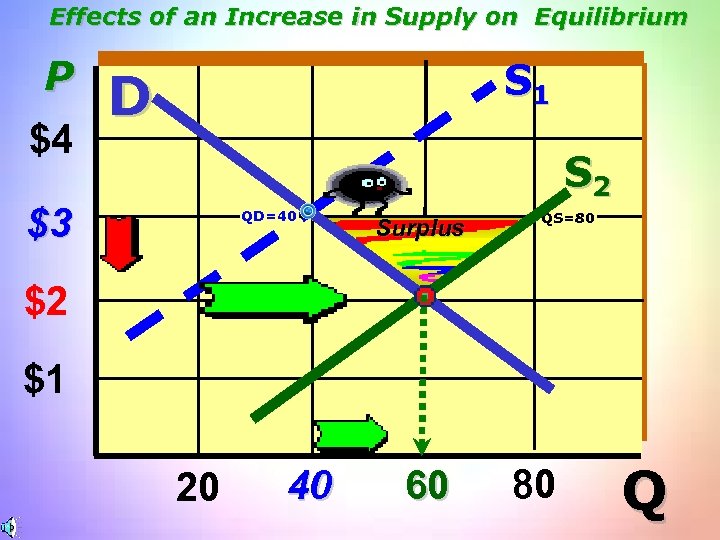 Effects of an Increase in Supply on Equilibrium P $4 S 1 D S 2 $3 QD=40 Surplus QS=80 $2 $1 20 40 60 80 Q
Effects of an Increase in Supply on Equilibrium P $4 S 1 D S 2 $3 QD=40 Surplus QS=80 $2 $1 20 40 60 80 Q
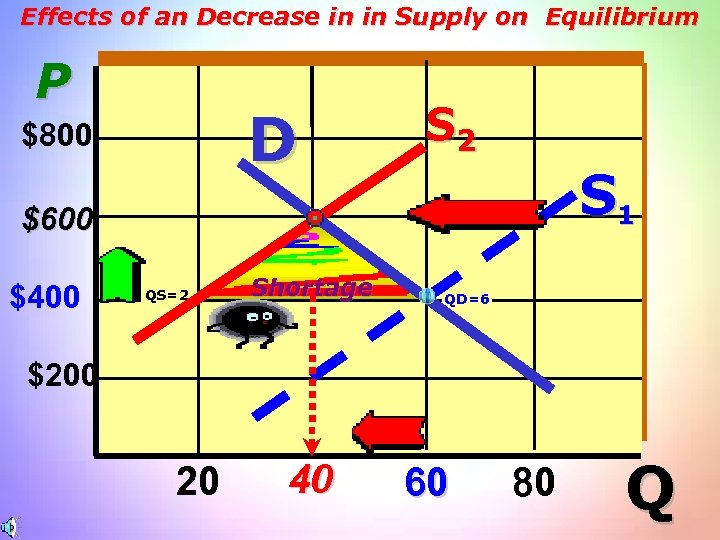 Effects of an Decrease in in Supply on Equilibrium P D $800 S 2 S 1 $600 $400 QS=2 Shortage QD=6 $200 20 40 60 80 Q
Effects of an Decrease in in Supply on Equilibrium P D $800 S 2 S 1 $600 $400 QS=2 Shortage QD=6 $200 20 40 60 80 Q
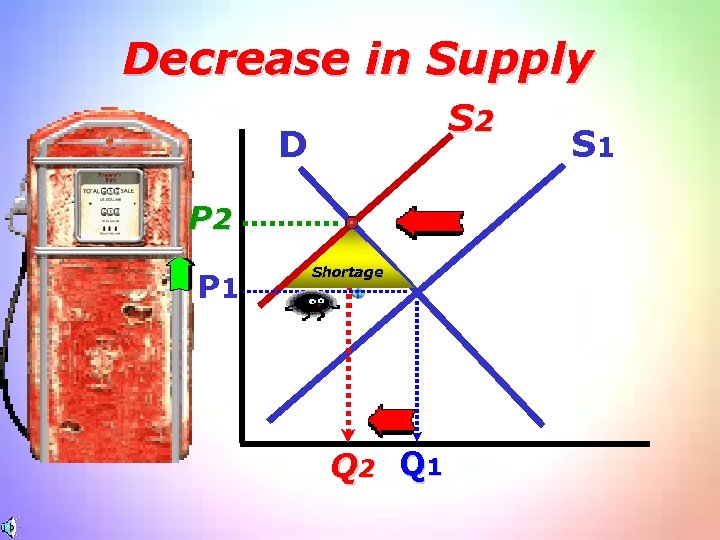 Decrease in Supply S 2 D P 2 P 1 Shortage Q 2 Q 1 S 1
Decrease in Supply S 2 D P 2 P 1 Shortage Q 2 Q 1 S 1
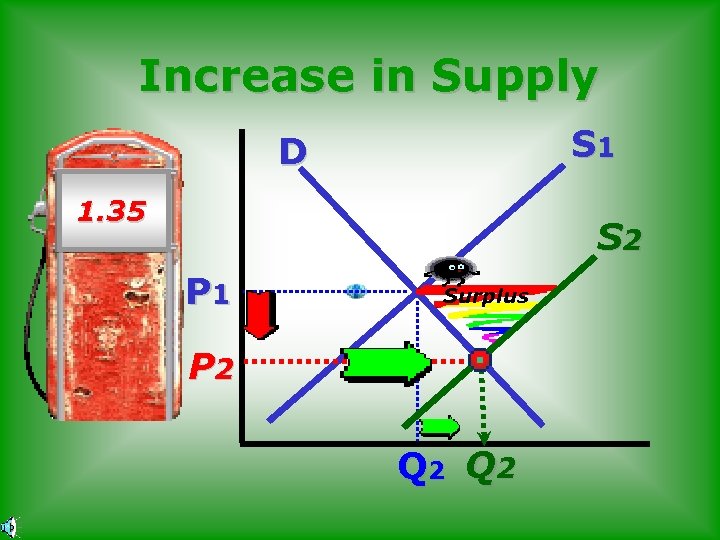 Increase in Supply S 1 D 1. 35 $2. 70 S 2 P 1 Surplus P 2 Q 2
Increase in Supply S 1 D 1. 35 $2. 70 S 2 P 1 Surplus P 2 Q 2
 Juicy “Orange” Prices Decide if the price of oranges is going to rise, fall, or stay the same rise fall R ___1. All of the growers meet & agree to grow fewer oranges next year. F ___2. Growers plant more acres of orange trees. R ___3. Orange growers run an advertising campaign promoting oranges as a symbol of good health. S ___4. One grower [out of thousands] retires and stops growing oranges. R ___5. Growers develop a bigger and better tasting orange. R ___6. Orange growers are struck by the disease-causing Mediterranean fruit fly. Quantity of Oranges
Juicy “Orange” Prices Decide if the price of oranges is going to rise, fall, or stay the same rise fall R ___1. All of the growers meet & agree to grow fewer oranges next year. F ___2. Growers plant more acres of orange trees. R ___3. Orange growers run an advertising campaign promoting oranges as a symbol of good health. S ___4. One grower [out of thousands] retires and stops growing oranges. R ___5. Growers develop a bigger and better tasting orange. R ___6. Orange growers are struck by the disease-causing Mediterranean fruit fly. Quantity of Oranges
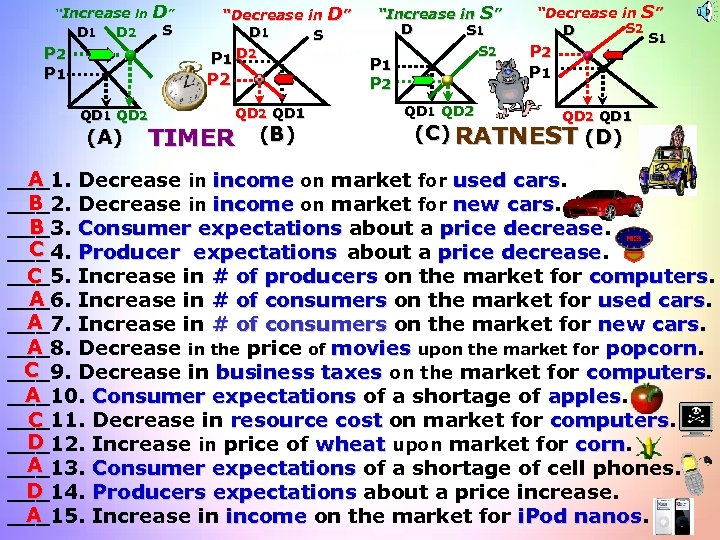 “Increase in D 1 D” S D 2 P 1 “Decrease in D 1 S P 1 D 2 P 2 QD 1 QD 2 (A) QD 2 QD 1 TIMER (B) D” “Increase in S” D S 1 S 2 P 1 P 2 “Decrease in S” S 2 D S 1 P 2 P 1 QD 2 QD 1 (C) RATNEST (D) A ___1. Decrease in income on market for used cars B ___2. Decrease in income on market for new cars B ___3. Consumer expectations about a price decrease C ___4. Producer expectations about a price decrease C ___5. Increase in # of producers on the market for computers A ___6. Increase in # of consumers on the market for used cars A ___7. Increase in # of consumers on the market for new cars A ___8. Decrease in the price of movies upon the market for popcorn C ___9. Decrease in business taxes on the market for computers A ___10. Consumer expectations of a shortage of apples C ___11. Decrease in resource cost on market for computers D ___12. Increase in price of wheat upon market for corn A ___13. Consumer expectations of a shortage of cell phones. D ___14. Producers expectations about a price increase. A ___15. Increase in income on the market for i. Pod nanos
“Increase in D 1 D” S D 2 P 1 “Decrease in D 1 S P 1 D 2 P 2 QD 1 QD 2 (A) QD 2 QD 1 TIMER (B) D” “Increase in S” D S 1 S 2 P 1 P 2 “Decrease in S” S 2 D S 1 P 2 P 1 QD 2 QD 1 (C) RATNEST (D) A ___1. Decrease in income on market for used cars B ___2. Decrease in income on market for new cars B ___3. Consumer expectations about a price decrease C ___4. Producer expectations about a price decrease C ___5. Increase in # of producers on the market for computers A ___6. Increase in # of consumers on the market for used cars A ___7. Increase in # of consumers on the market for new cars A ___8. Decrease in the price of movies upon the market for popcorn C ___9. Decrease in business taxes on the market for computers A ___10. Consumer expectations of a shortage of apples C ___11. Decrease in resource cost on market for computers D ___12. Increase in price of wheat upon market for corn A ___13. Consumer expectations of a shortage of cell phones. D ___14. Producers expectations about a price increase. A ___15. Increase in income on the market for i. Pod nanos
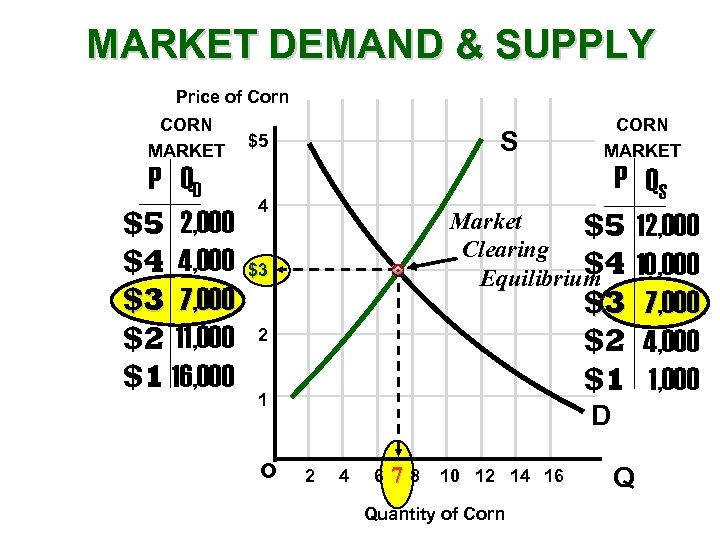 MARKET DEMAND & SUPPLY Price of Corn CORN MARKET P QD $5 2, 000 $4 4, 000 $3 7, 000 $2 11, 000 $1 16, 000 S $5 P QS Market $5 12, 000 Clearing $4 Equilibrium 10, 000 $3 7, 000 $2 4, 000 $1 1, 000 4 $3 2 1 o CORN MARKET D 2 4 6 78 10 12 14 16 Quantity of Corn Q
MARKET DEMAND & SUPPLY Price of Corn CORN MARKET P QD $5 2, 000 $4 4, 000 $3 7, 000 $2 11, 000 $1 16, 000 S $5 P QS Market $5 12, 000 Clearing $4 Equilibrium 10, 000 $3 7, 000 $2 4, 000 $1 1, 000 4 $3 2 1 o CORN MARKET D 2 4 6 78 10 12 14 16 Quantity of Corn Q
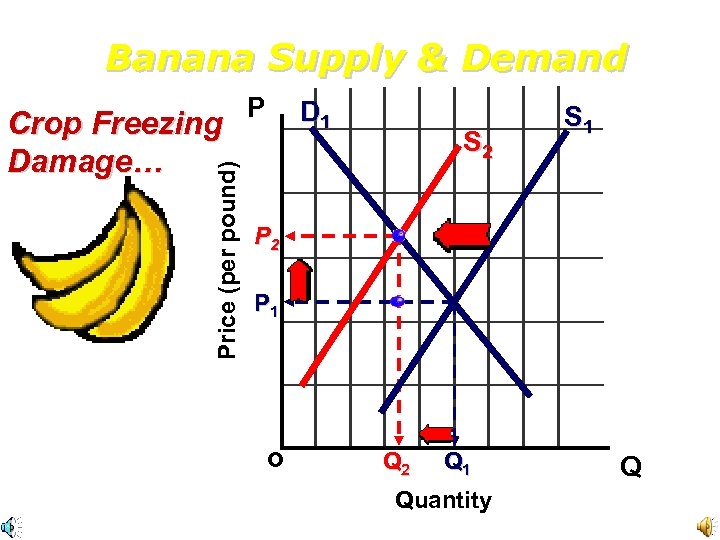 Banana Supply & Demand Price (per pound) Crop Freezing Damage… P D 1 S 2 S 1 P 2 P 1 o Q 2 Q 1 Quantity Q
Banana Supply & Demand Price (per pound) Crop Freezing Damage… P D 1 S 2 S 1 P 2 P 1 o Q 2 Q 1 Quantity Q
![Price Floor – minimum price [creates surpluses] surpluses Such as: Minimum Wage P Agricultural Price Floor – minimum price [creates surpluses] surpluses Such as: Minimum Wage P Agricultural](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-27.jpg) Price Floor – minimum price [creates surpluses] surpluses Such as: Minimum Wage P Agricultural Price Supports Price Floor-minimum price $2. 50 The price has to be IN the house. It can’t be below the floor. 1. 90 QS exceeds QD Surplus Equilibrium price for milk Price per gallon Some call agricultural price supports “udder insanity. ” S D . 0 14 19 24 Millions of gallons per month Q
Price Floor – minimum price [creates surpluses] surpluses Such as: Minimum Wage P Agricultural Price Supports Price Floor-minimum price $2. 50 The price has to be IN the house. It can’t be below the floor. 1. 90 QS exceeds QD Surplus Equilibrium price for milk Price per gallon Some call agricultural price supports “udder insanity. ” S D . 0 14 19 24 Millions of gallons per month Q
![Price Ceiling - maximum price [creates shortages] shortages Such as: Rent controls in NYC Price Ceiling - maximum price [creates shortages] shortages Such as: Rent controls in NYC](https://present5.com/presentation/b8d469f4ef0ee15cdb8acea65f227589/image-28.jpg) Price Ceiling - maximum price [creates shortages] shortages Such as: Rent controls in NYC Wartime price controls Rock concert prices Super Bowl tickets P S D The price has to be in the house. It can’t be above the ceiling. $2, 000 NYC 1, 200 Reliant Stadium Super Bowl Ticket Prices E-Bay 1967 - $12. 00 o 2004 - $500 $2 -6, 000 Price Ceiling-maximum price Rent Controls QD exceeds QS Shortage 2. 5 3 7 3. 5 Millions of Dwellings Rented NFL could raise the price & make another $150 M but the average man couldn’t attend.
Price Ceiling - maximum price [creates shortages] shortages Such as: Rent controls in NYC Wartime price controls Rock concert prices Super Bowl tickets P S D The price has to be in the house. It can’t be above the ceiling. $2, 000 NYC 1, 200 Reliant Stadium Super Bowl Ticket Prices E-Bay 1967 - $12. 00 o 2004 - $500 $2 -6, 000 Price Ceiling-maximum price Rent Controls QD exceeds QS Shortage 2. 5 3 7 3. 5 Millions of Dwellings Rented NFL could raise the price & make another $150 M but the average man couldn’t attend.



