9393587c18dad622d596cf78d90fd9b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Overview SA 3‐LI Oct. 2013 R. Taylor/J. Ing Public Safety Canada
Overview SA 3‐LI Oct. 2013 R. Taylor/J. Ing Public Safety Canada
 What is it • Web Real‐Time Communications • Standards to enable browser based sessions (voice, video, Collab, …) without the need of custom clients or plugins • Builds on HTLM 5 capabilities with Java. Script • Standardized by W 3 C and IETF – IETF RTCWeb WG ( Internet world, IP protocols) – W 3 C Web. RTC WG (web world, Browsers etc. ) • Intended for all browsers to support – Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Opera, IE … • MSFT being problematic – Have their own CU‐RTC‐Web framework • Apple (Safari) not at the table 3/19/2018 Unclassified 2
What is it • Web Real‐Time Communications • Standards to enable browser based sessions (voice, video, Collab, …) without the need of custom clients or plugins • Builds on HTLM 5 capabilities with Java. Script • Standardized by W 3 C and IETF – IETF RTCWeb WG ( Internet world, IP protocols) – W 3 C Web. RTC WG (web world, Browsers etc. ) • Intended for all browsers to support – Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Opera, IE … • MSFT being problematic – Have their own CU‐RTC‐Web framework • Apple (Safari) not at the table 3/19/2018 Unclassified 2
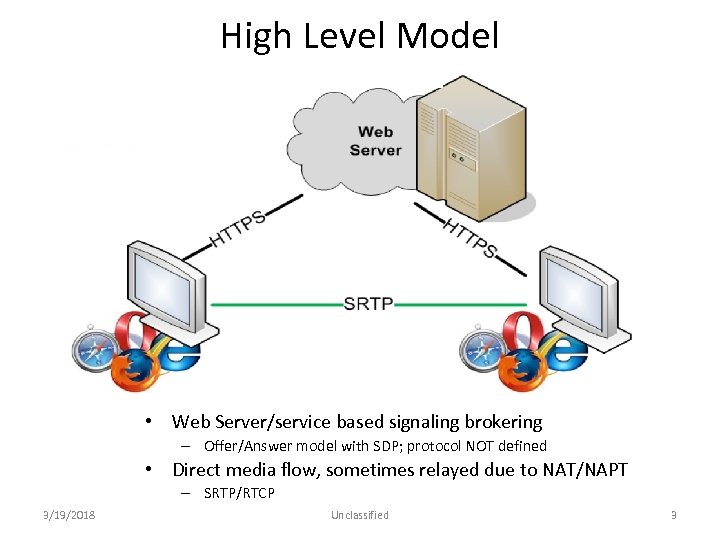 High Level Model • Web Server/service based signaling brokering – Offer/Answer model with SDP; protocol NOT defined • Direct media flow, sometimes relayed due to NAT/NAPT – SRTP/RTCP 3/19/2018 Unclassified 3
High Level Model • Web Server/service based signaling brokering – Offer/Answer model with SDP; protocol NOT defined • Direct media flow, sometimes relayed due to NAT/NAPT – SRTP/RTCP 3/19/2018 Unclassified 3
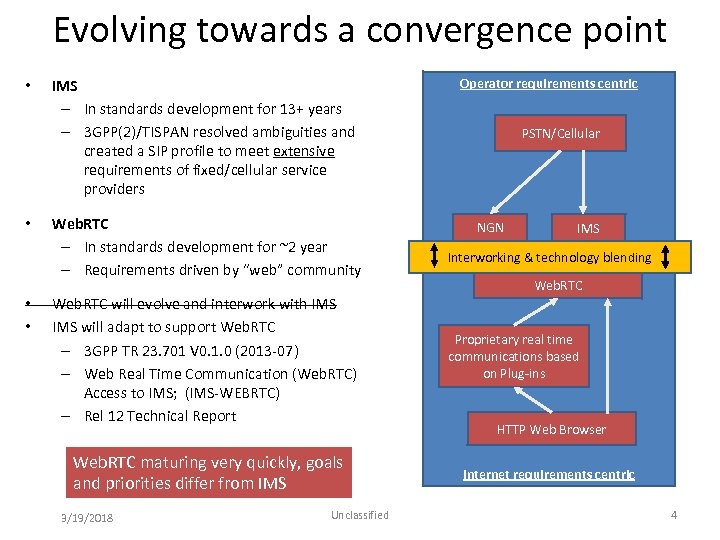 Evolving towards a convergence point • • IMS – In standards development for 13+ years – 3 GPP(2)/TISPAN resolved ambiguities and created a SIP profile to meet extensive requirements of fixed/cellular service providers Web. RTC – In standards development for ~2 year – Requirements driven by “web” community Web. RTC will evolve and interwork with IMS will adapt to support Web. RTC – 3 GPP TR 23. 701 V 0. 1. 0 (2013‐ 07) – Web Real Time Communication (Web. RTC) Access to IMS; (IMS‐WEBRTC) – Rel 12 Technical Report Web. RTC maturing very quickly, goals and priorities differ from IMS 3/19/2018 Unclassified Operator requirements centric PSTN/Cellular NGN IMS Interworking & technology blending Web. RTC Proprietary real time communications based on Plug‐ins HTTP Web Browser Internet requirements centric 4
Evolving towards a convergence point • • IMS – In standards development for 13+ years – 3 GPP(2)/TISPAN resolved ambiguities and created a SIP profile to meet extensive requirements of fixed/cellular service providers Web. RTC – In standards development for ~2 year – Requirements driven by “web” community Web. RTC will evolve and interwork with IMS will adapt to support Web. RTC – 3 GPP TR 23. 701 V 0. 1. 0 (2013‐ 07) – Web Real Time Communication (Web. RTC) Access to IMS; (IMS‐WEBRTC) – Rel 12 Technical Report Web. RTC maturing very quickly, goals and priorities differ from IMS 3/19/2018 Unclassified Operator requirements centric PSTN/Cellular NGN IMS Interworking & technology blending Web. RTC Proprietary real time communications based on Plug‐ins HTTP Web Browser Internet requirements centric 4
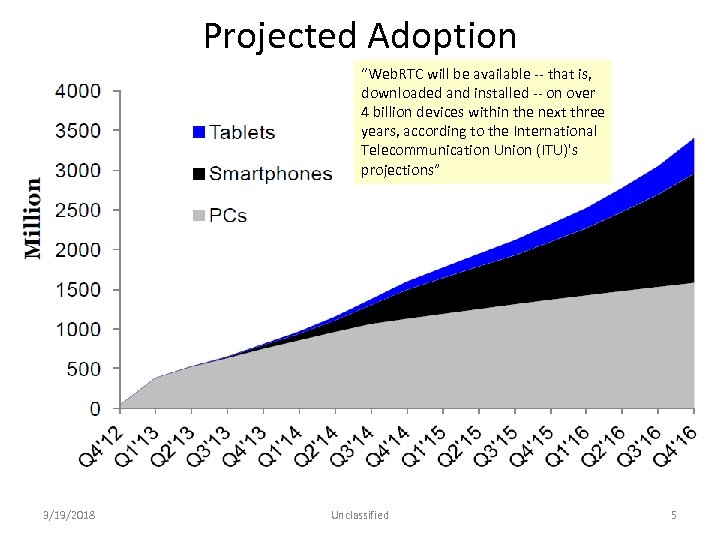 Projected Adoption “Web. RTC will be available ‐‐ that is, downloaded and installed ‐‐ on over 4 billion devices within the next three years, according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)'s projections” 3/19/2018 Unclassified 5
Projected Adoption “Web. RTC will be available ‐‐ that is, downloaded and installed ‐‐ on over 4 billion devices within the next three years, according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU)'s projections” 3/19/2018 Unclassified 5
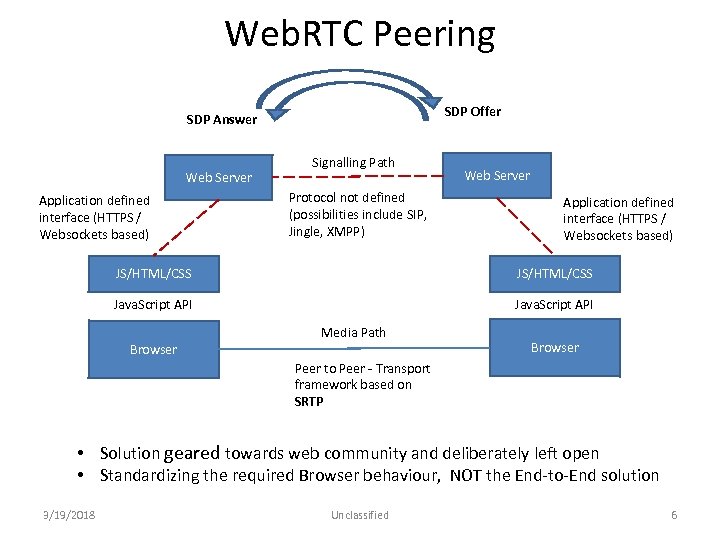 Web. RTC Peering SDP Offer SDP Answer Web Server Application defined interface (HTTPS / Websockets based) Signalling Path Protocol not defined (possibilities include SIP, Jingle, XMPP) Web Server Application defined interface (HTTPS / Websockets based) JS/HTML/CSS Java. Script API Browser Media Path Browser Peer to Peer ‐ Transport framework based on SRTP • Solution geared towards web community and deliberately left open • Standardizing the required Browser behaviour, NOT the End‐to‐End solution 3/19/2018 Unclassified 6
Web. RTC Peering SDP Offer SDP Answer Web Server Application defined interface (HTTPS / Websockets based) Signalling Path Protocol not defined (possibilities include SIP, Jingle, XMPP) Web Server Application defined interface (HTTPS / Websockets based) JS/HTML/CSS Java. Script API Browser Media Path Browser Peer to Peer ‐ Transport framework based on SRTP • Solution geared towards web community and deliberately left open • Standardizing the required Browser behaviour, NOT the End‐to‐End solution 3/19/2018 Unclassified 6
 Details 3/19/2018 Unclassified 7
Details 3/19/2018 Unclassified 7
 Under the covers Parts in blue are “a” TSP’s view, not part of Standards activities 3/19/2018 Unclassified 8
Under the covers Parts in blue are “a” TSP’s view, not part of Standards activities 3/19/2018 Unclassified 8
 Solution Details • • Web page invokes set of defined Java. Script's to request services from the browser Interface/Protocol between scripts and browser: JSEP – Java Session Establishment Protocol – Create an Offer, Create an Answer, get media details (SDP), Invoke ICE, etc. – Implements Offer/Answer model like used in SIP • Offers, Answers etc. sent to/via Web server – Uses HTTPS or secure Web. Sockets (RFC 6455) • Provides full‐duplex communications channels over a single TCP connection • Uses ICE for NAT traversal (RFC 5245) – Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE): • A Protocol for Network Address Translator (NAT) Traversal for Offer/Answer Protocols – Complicated set of procedures using STUN and TURN to discover best addresses to use for RTP streams • Web server pushes notification to “called” party – Requires browser to be open and excepting – Inter ‐Server protocol not defined • Secure RTP for media exchange – Using DTLS (Datagram TLS) • use of SDES (Session Description Protocol Security Descriptions ) has been disallowed by the IETF – RTP and RTCP multiplexed on same port (RTCP usually on RTP port plus one) – A media relay service (TURN) may be required 3/19/2018 Unclassified 9
Solution Details • • Web page invokes set of defined Java. Script's to request services from the browser Interface/Protocol between scripts and browser: JSEP – Java Session Establishment Protocol – Create an Offer, Create an Answer, get media details (SDP), Invoke ICE, etc. – Implements Offer/Answer model like used in SIP • Offers, Answers etc. sent to/via Web server – Uses HTTPS or secure Web. Sockets (RFC 6455) • Provides full‐duplex communications channels over a single TCP connection • Uses ICE for NAT traversal (RFC 5245) – Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE): • A Protocol for Network Address Translator (NAT) Traversal for Offer/Answer Protocols – Complicated set of procedures using STUN and TURN to discover best addresses to use for RTP streams • Web server pushes notification to “called” party – Requires browser to be open and excepting – Inter ‐Server protocol not defined • Secure RTP for media exchange – Using DTLS (Datagram TLS) • use of SDES (Session Description Protocol Security Descriptions ) has been disallowed by the IETF – RTP and RTCP multiplexed on same port (RTCP usually on RTP port plus one) – A media relay service (TURN) may be required 3/19/2018 Unclassified 9
 Now a word about Codecs • G 711 a/u (RFC 3551) – Mandated – supported by all the devices – Tends to use a lot of bandwidth • DTMF tones (RFC 4733, updates RFC 2833) – needed for interactions with legacy systems – Voice mail, IVRs, … • Opus (RFC 6716): – – Mandated Variable bitrate, low latency and high quality for human voice and music Specifically designed for real time communications Supposedly Patent unencumbered hence royalty free • Ongoing battle in video VP 8/9 vs H. 264/265 – Royalty free ? vs. MPEG world – No Flash • Proposals to support other Codecs if available on the device – E. g. , AMR‐wb 3/19/2018 Unclassified 10
Now a word about Codecs • G 711 a/u (RFC 3551) – Mandated – supported by all the devices – Tends to use a lot of bandwidth • DTMF tones (RFC 4733, updates RFC 2833) – needed for interactions with legacy systems – Voice mail, IVRs, … • Opus (RFC 6716): – – Mandated Variable bitrate, low latency and high quality for human voice and music Specifically designed for real time communications Supposedly Patent unencumbered hence royalty free • Ongoing battle in video VP 8/9 vs H. 264/265 – Royalty free ? vs. MPEG world – No Flash • Proposals to support other Codecs if available on the device – E. g. , AMR‐wb 3/19/2018 Unclassified 10
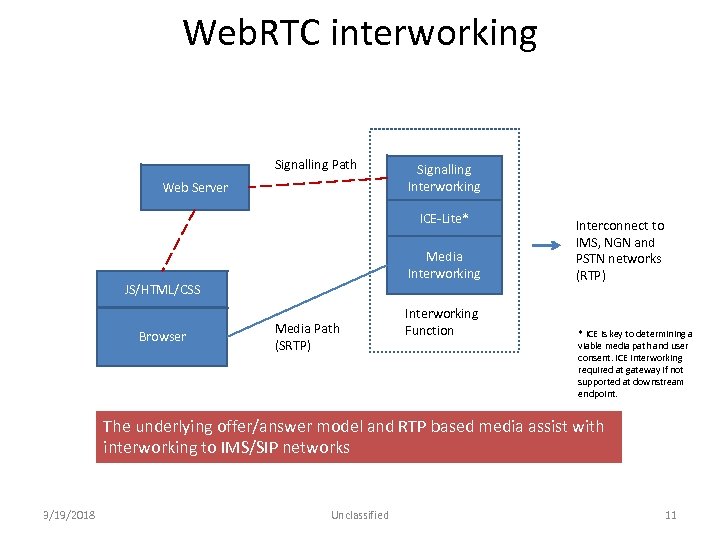 Web. RTC interworking Signalling Path Web Server Signalling Interworking ICE‐Lite* Media Interworking JS/HTML/CSS Browser Media Path (SRTP) Interworking Function Interconnect to IMS, NGN and PSTN networks (RTP) * ICE is key to determining a viable media path and user consent. ICE interworking required at gateway if not supported at downstream endpoint. The underlying offer/answer model and RTP based media assist with interworking to IMS/SIP networks 3/19/2018 Unclassified 11
Web. RTC interworking Signalling Path Web Server Signalling Interworking ICE‐Lite* Media Interworking JS/HTML/CSS Browser Media Path (SRTP) Interworking Function Interconnect to IMS, NGN and PSTN networks (RTP) * ICE is key to determining a viable media path and user consent. ICE interworking required at gateway if not supported at downstream endpoint. The underlying offer/answer model and RTP based media assist with interworking to IMS/SIP networks 3/19/2018 Unclassified 11
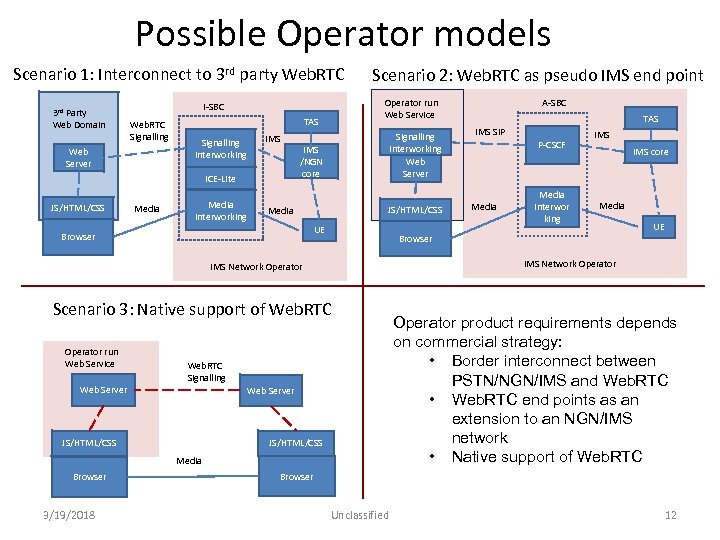 Possible Operator models Scenario 1: Interconnect to 3 rd party Web. RTC 3 rd Party Web Domain Web Server TAS Signalling Interworking IMS ICE‐Lite JS/HTML/CSS Operator run Web Service I‐SBC Web. RTC Signalling Media Interworking Scenario 2: Web. RTC as pseudo IMS end point Signalling Interworking Web Server IMS /NGN core JS/HTML/CSS Media UE Browser Web Server JS/HTML/CSS Media Browser 3/19/2018 P‐CSCF Media Interwor king IMS core Media UE IMS Network Operator Scenario 3: Native support of Web. RTC Signalling TAS IMS SIP Browser IMS Network Operator run Web Service A‐SBC Operator product requirements depends on commercial strategy: • Border interconnect between PSTN/NGN/IMS and Web. RTC • Web. RTC end points as an extension to an NGN/IMS network • Native support of Web. RTC Browser Unclassified 12
Possible Operator models Scenario 1: Interconnect to 3 rd party Web. RTC 3 rd Party Web Domain Web Server TAS Signalling Interworking IMS ICE‐Lite JS/HTML/CSS Operator run Web Service I‐SBC Web. RTC Signalling Media Interworking Scenario 2: Web. RTC as pseudo IMS end point Signalling Interworking Web Server IMS /NGN core JS/HTML/CSS Media UE Browser Web Server JS/HTML/CSS Media Browser 3/19/2018 P‐CSCF Media Interwor king IMS core Media UE IMS Network Operator Scenario 3: Native support of Web. RTC Signalling TAS IMS SIP Browser IMS Network Operator run Web Service A‐SBC Operator product requirements depends on commercial strategy: • Border interconnect between PSTN/NGN/IMS and Web. RTC • Web. RTC end points as an extension to an NGN/IMS network • Native support of Web. RTC Browser Unclassified 12
 W 3 C Web. RTC deliverables • Media Stream Functions • – API for connecting processing functions to media devices and network connections, including media manipulation functions. • • Video Stream Functions – An extension of the Media Stream Functions to process video streams (e. g. bandwidth limiting, image manipulation or "video mute“). • ‐ Web. RTC 1. 0: Real-time Communication Between Browsers Draft 3 June 2013 available ‐ Implementation Library: Web. RTC Native APIs ‐ Media Capture and Streams - Draft 16 May 2013 Audio Stream Functions – An extension of the Media Stream Functions to process audio streams (e. g. automatic gain control, mute functions and echo cancellation). API specification Availability • Supported by Chrome and Firefox NOW ‐ Pre-standard Functional Component Functions – API to query presence of Web. RTC components in an implementation, instantiate them, and connect them to media streams. • P 2 P Connection Functions – API functions to support establishing signalling protocol agnostic peer‐to‐peer connections between Web browsers 3/19/2018 Unclassified 13
W 3 C Web. RTC deliverables • Media Stream Functions • – API for connecting processing functions to media devices and network connections, including media manipulation functions. • • Video Stream Functions – An extension of the Media Stream Functions to process video streams (e. g. bandwidth limiting, image manipulation or "video mute“). • ‐ Web. RTC 1. 0: Real-time Communication Between Browsers Draft 3 June 2013 available ‐ Implementation Library: Web. RTC Native APIs ‐ Media Capture and Streams - Draft 16 May 2013 Audio Stream Functions – An extension of the Media Stream Functions to process audio streams (e. g. automatic gain control, mute functions and echo cancellation). API specification Availability • Supported by Chrome and Firefox NOW ‐ Pre-standard Functional Component Functions – API to query presence of Web. RTC components in an implementation, instantiate them, and connect them to media streams. • P 2 P Connection Functions – API functions to support establishing signalling protocol agnostic peer‐to‐peer connections between Web browsers 3/19/2018 Unclassified 13
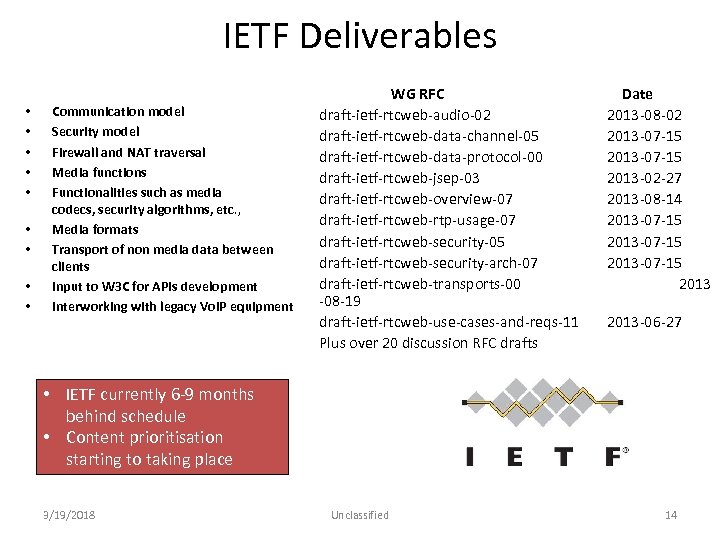 IETF Deliverables • • • Communication model Security model Firewall and NAT traversal Media functions Functionalities such as media codecs, security algorithms, etc. , Media formats Transport of non media data between clients Input to W 3 C for APIs development Interworking with legacy Vo. IP equipment WG RFC draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐audio‐ 02 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐data‐channel‐ 05 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐data‐protocol‐ 00 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐jsep‐ 03 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐overview‐ 07 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐rtp‐usage‐ 07 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐security‐ 05 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐security‐arch‐ 07 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐transports‐ 00 ‐ 08‐ 19 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐use‐cases‐and‐reqs‐ 11 Plus over 20 discussion RFC drafts Date 2013‐ 08‐ 02 2013‐ 07‐ 15 2013‐ 02‐ 27 2013‐ 08‐ 14 2013‐ 07‐ 15 2013‐ 06‐ 27 • IETF currently 6‐ 9 months behind schedule • Content prioritisation starting to taking place 3/19/2018 Unclassified 14
IETF Deliverables • • • Communication model Security model Firewall and NAT traversal Media functions Functionalities such as media codecs, security algorithms, etc. , Media formats Transport of non media data between clients Input to W 3 C for APIs development Interworking with legacy Vo. IP equipment WG RFC draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐audio‐ 02 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐data‐channel‐ 05 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐data‐protocol‐ 00 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐jsep‐ 03 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐overview‐ 07 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐rtp‐usage‐ 07 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐security‐ 05 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐security‐arch‐ 07 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐transports‐ 00 ‐ 08‐ 19 draft‐ietf‐rtcweb‐use‐cases‐and‐reqs‐ 11 Plus over 20 discussion RFC drafts Date 2013‐ 08‐ 02 2013‐ 07‐ 15 2013‐ 02‐ 27 2013‐ 08‐ 14 2013‐ 07‐ 15 2013‐ 06‐ 27 • IETF currently 6‐ 9 months behind schedule • Content prioritisation starting to taking place 3/19/2018 Unclassified 14
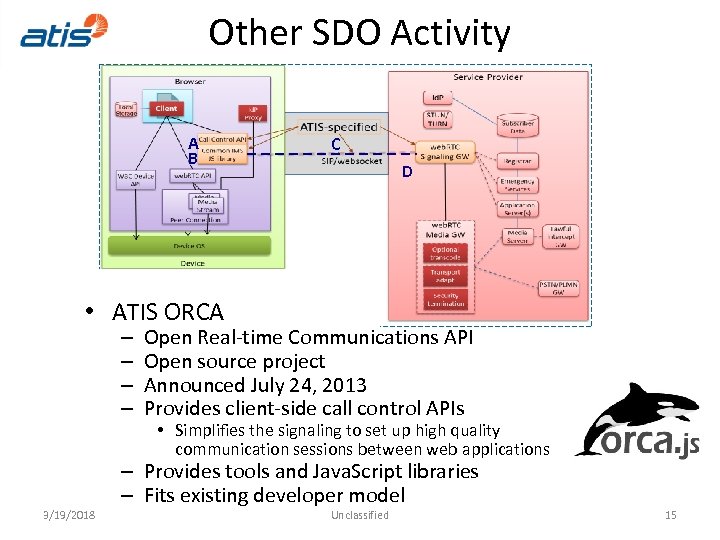 Other SDO Activity A B C D • ATIS ORCA – – 3/19/2018 Open Real‐time Communications API Open source project Announced July 24, 2013 Provides client‐side call control APIs • Simplifies the signaling to set up high quality communication sessions between web applications – Provides tools and Java. Script libraries – Fits existing developer model Unclassified 15
Other SDO Activity A B C D • ATIS ORCA – – 3/19/2018 Open Real‐time Communications API Open source project Announced July 24, 2013 Provides client‐side call control APIs • Simplifies the signaling to set up high quality communication sessions between web applications – Provides tools and Java. Script libraries – Fits existing developer model Unclassified 15
 The Tricky Bits • Identity resolution – Ok if in a wall‐garden solution (Facebook, Twitter, Google circles, …) – Ok for “Call Now” button on Personal & Business Web pages • Assuming there’s someone manning the website – But how can Alice “call” Bob just browser to browser ? • How to resolve Bob’s address to Web Server and Bob’s browser instance – Public ENUM (Phone # to URL) failed • NAT/NAPT traversal – ICE is heavy weight, not web developer “friendly” – If media relay is required, who supplies the TURN servers ? • Security – Lots of focus on the protocols – But browsers and Java. Script ripe with potential/real exploits – SPAM & Unwanted call control/mitigation • RTP stream multiplexing – RTP + RTCP – Multiple RTP streams • Interworking – – 3/19/2018 Between Web. RTC solutions With established OTT solutions (Skype, Viber, etc. ) With NGN/IMS Legacy PSTN and PLMN Unclassified 16
The Tricky Bits • Identity resolution – Ok if in a wall‐garden solution (Facebook, Twitter, Google circles, …) – Ok for “Call Now” button on Personal & Business Web pages • Assuming there’s someone manning the website – But how can Alice “call” Bob just browser to browser ? • How to resolve Bob’s address to Web Server and Bob’s browser instance – Public ENUM (Phone # to URL) failed • NAT/NAPT traversal – ICE is heavy weight, not web developer “friendly” – If media relay is required, who supplies the TURN servers ? • Security – Lots of focus on the protocols – But browsers and Java. Script ripe with potential/real exploits – SPAM & Unwanted call control/mitigation • RTP stream multiplexing – RTP + RTCP – Multiple RTP streams • Interworking – – 3/19/2018 Between Web. RTC solutions With established OTT solutions (Skype, Viber, etc. ) With NGN/IMS Legacy PSTN and PLMN Unclassified 16
 LI Concerns and/or Issues • Who’s providing the “Service” – Regulated, Unregulated, Mix ? – Depends a lot on the nature of the solution • TSP IMS controlled vs. just a “Call Me” button on a web page • What Ids are being used/resolved ? – By whom and how ? – In a regulatory domain ? • Detecting the service – Security posture is specifically around blocking man‐in‐the‐middle (“The Man”‐in‐the‐middle ? ) attacks – Is the signaling reasonably detectable ? – Protocols being used ? ? – Encryption • Location not part of the solution space: Jurisdiction – Where’s the client/browser vs. Web Server(s) • Media Interception – – • Where is the bearer really going, passing through ? Forcing media relays when not required ? RTP multiplexing Media Encryption (DTLS) • Who has the keys ? No LEA influence over lead SDOs – IETF and W 3 C not “LI friendly” 3/19/2018 Unclassified 17
LI Concerns and/or Issues • Who’s providing the “Service” – Regulated, Unregulated, Mix ? – Depends a lot on the nature of the solution • TSP IMS controlled vs. just a “Call Me” button on a web page • What Ids are being used/resolved ? – By whom and how ? – In a regulatory domain ? • Detecting the service – Security posture is specifically around blocking man‐in‐the‐middle (“The Man”‐in‐the‐middle ? ) attacks – Is the signaling reasonably detectable ? – Protocols being used ? ? – Encryption • Location not part of the solution space: Jurisdiction – Where’s the client/browser vs. Web Server(s) • Media Interception – – • Where is the bearer really going, passing through ? Forcing media relays when not required ? RTP multiplexing Media Encryption (DTLS) • Who has the keys ? No LEA influence over lead SDOs – IETF and W 3 C not “LI friendly” 3/19/2018 Unclassified 17
 Backup 3/19/2018 Unclassified 18
Backup 3/19/2018 Unclassified 18
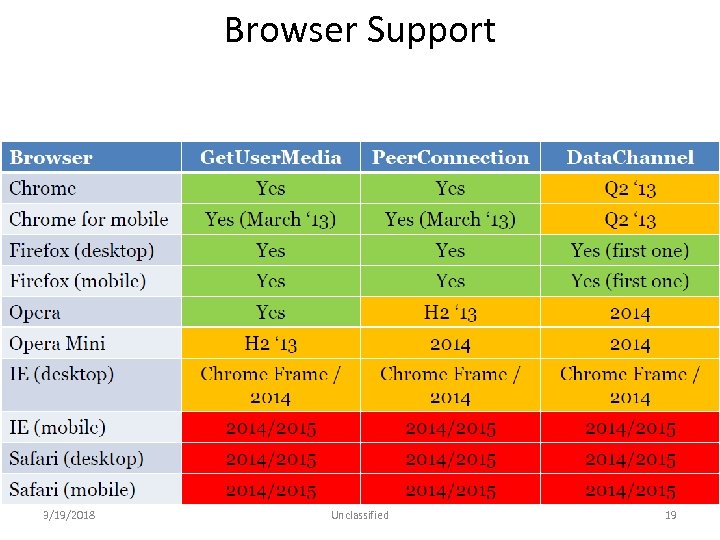 Browser Support 3/19/2018 Unclassified 19
Browser Support 3/19/2018 Unclassified 19
 End 3/19/2018 Unclassified 20
End 3/19/2018 Unclassified 20


