3e772a525f713d93e6937156819976a8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Overview of the Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process framework used by the PFSA Polish Financial Supervision Authority, Financial Services, Licensing and Functional Supervision Department
Overview of the Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process framework used by the PFSA Polish Financial Supervision Authority, Financial Services, Licensing and Functional Supervision Department
 AGENDA PART 1 Introduction PART 2 Organizational issues of SREP (BION) • Regulations • Basic definitions (ICAAP, SPEP, internal capital, regulatory capital) • • • BION of brokerage • houses in detail • PART 3 BION – cycle Rating Time requirements Technical aspects of BION Ongoing supervision Presentation Off/on-site Inspection
AGENDA PART 1 Introduction PART 2 Organizational issues of SREP (BION) • Regulations • Basic definitions (ICAAP, SPEP, internal capital, regulatory capital) • • • BION of brokerage • houses in detail • PART 3 BION – cycle Rating Time requirements Technical aspects of BION Ongoing supervision Presentation Off/on-site Inspection
 AGENDA PART 1 Introduction PART 2 Organizational issues of SREP (BION) • Regulations • Basic definitions (ICAAP, SPEP, internal capital, regulatory capital) • • • BION of brokerage • houses in detail • PART 3 BION – cycle Rating Time requirements Technical aspects of BION Ongoing supervision Presentation Off/on-site Inspection
AGENDA PART 1 Introduction PART 2 Organizational issues of SREP (BION) • Regulations • Basic definitions (ICAAP, SPEP, internal capital, regulatory capital) • • • BION of brokerage • houses in detail • PART 3 BION – cycle Rating Time requirements Technical aspects of BION Ongoing supervision Presentation Off/on-site Inspection
 SELECTED INFORMATION ON POLISH CAPITAL MARKET
SELECTED INFORMATION ON POLISH CAPITAL MARKET
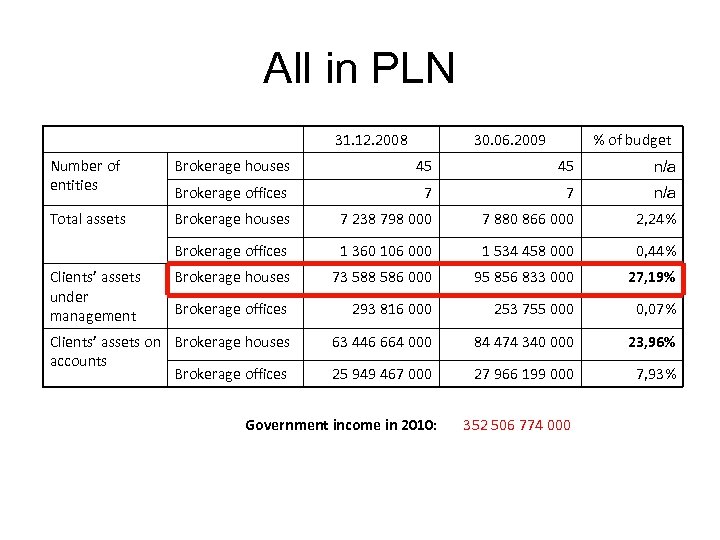 All in PLN 31. 12. 2008 30. 06. 2009 % of budget Number of entities Brokerage houses 45 45 n/a Brokerage offices 7 7 n/a Total assets Brokerage houses 7 238 798 000 7 880 866 000 2, 24% Brokerage offices 1 360 106 000 1 534 458 000 0, 44% Brokerage houses 73 588 586 000 95 856 833 000 27, 19% Brokerage offices 293 816 000 253 755 000 0, 07% Clients’ assets on Brokerage houses accounts Brokerage offices 63 446 664 000 84 474 340 000 23, 96% 25 949 467 000 27 966 199 000 7, 93% Clients’ assets under management Government income in 2010: 352 506 774 000
All in PLN 31. 12. 2008 30. 06. 2009 % of budget Number of entities Brokerage houses 45 45 n/a Brokerage offices 7 7 n/a Total assets Brokerage houses 7 238 798 000 7 880 866 000 2, 24% Brokerage offices 1 360 106 000 1 534 458 000 0, 44% Brokerage houses 73 588 586 000 95 856 833 000 27, 19% Brokerage offices 293 816 000 253 755 000 0, 07% Clients’ assets on Brokerage houses accounts Brokerage offices 63 446 664 000 84 474 340 000 23, 96% 25 949 467 000 27 966 199 000 7, 93% Clients’ assets under management Government income in 2010: 352 506 774 000

 Regulations • Directive 2006/48/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 June 2006 relating to the taking up and pursuit of the business of credit institutions • Directive 2006/49/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 June 2006 on the capital adequacy of investment firms and credit institutions • Act on Trading in Financial Instruments of 29 July 2005 (Dz. U. No. 183, item 1538) • Regulation of the Minister of Finance of 20 November 2009 on Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process of brokerage houses
Regulations • Directive 2006/48/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 June 2006 relating to the taking up and pursuit of the business of credit institutions • Directive 2006/49/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 June 2006 on the capital adequacy of investment firms and credit institutions • Act on Trading in Financial Instruments of 29 July 2005 (Dz. U. No. 183, item 1538) • Regulation of the Minister of Finance of 20 November 2009 on Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process of brokerage houses
 Directive 2006/48/EC Article 124 1. Taking into account the technical criteria set out in Annex XI, the competent authorities shall review the arrangements, strategies, processes and mechanisms implemented by the credit institutions to comply with this Directive and evaluate the risks to which the credit institutions are or might be exposed. 2. The scope of the review and evaluation referred to in paragraph 1 shall be that of the requirements of this Directive.
Directive 2006/48/EC Article 124 1. Taking into account the technical criteria set out in Annex XI, the competent authorities shall review the arrangements, strategies, processes and mechanisms implemented by the credit institutions to comply with this Directive and evaluate the risks to which the credit institutions are or might be exposed. 2. The scope of the review and evaluation referred to in paragraph 1 shall be that of the requirements of this Directive.
 Directive 2006/48/EC Article 124 3. On the basis of the review and evaluation (…), the competent authorities shall determine whether the arrangements, strategies, processes and mechanisms implemented by the credit institutions and the own funds held by these ensure a sound management and coverage of their risks. 4. Competent authorities shall establish the frequency and intensity of the review and evaluation (…) having regard to the size, systemic importance, nature, scale and complexity of the activities of the credit institution concerned and taking into account the principle of proportionality. The review and evaluation shall be updated at least on an annual basis.
Directive 2006/48/EC Article 124 3. On the basis of the review and evaluation (…), the competent authorities shall determine whether the arrangements, strategies, processes and mechanisms implemented by the credit institutions and the own funds held by these ensure a sound management and coverage of their risks. 4. Competent authorities shall establish the frequency and intensity of the review and evaluation (…) having regard to the size, systemic importance, nature, scale and complexity of the activities of the credit institution concerned and taking into account the principle of proportionality. The review and evaluation shall be updated at least on an annual basis.
 Basel II (Capital Requirement Directive, CRD) • Directive 2006/48/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 June 2006 relating to the taking up and pursuit of the business of credit institutions; and • Directive 2006/49/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 June 2006 on the capital adequacy of investment firms and credit institutions.
Basel II (Capital Requirement Directive, CRD) • Directive 2006/48/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 June 2006 relating to the taking up and pursuit of the business of credit institutions; and • Directive 2006/49/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 June 2006 on the capital adequacy of investment firms and credit institutions.
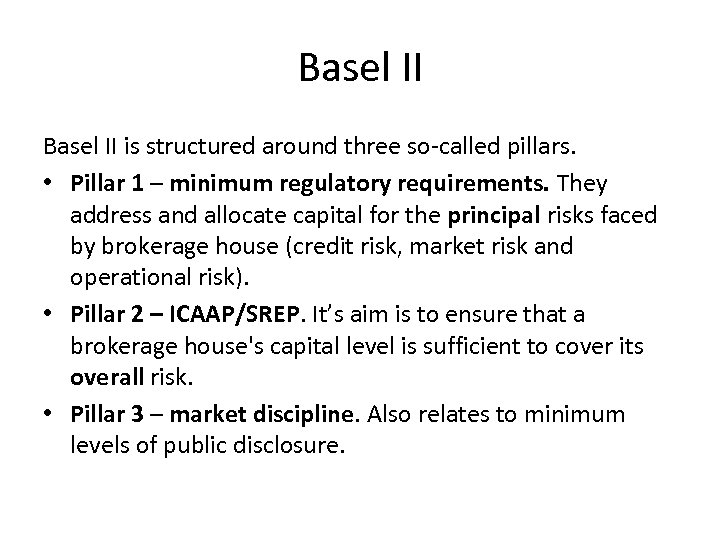 Basel II is structured around three so-called pillars. • Pillar 1 – minimum regulatory requirements. They address and allocate capital for the principal risks faced by brokerage house (credit risk, market risk and operational risk). • Pillar 2 – ICAAP/SREP. It’s aim is to ensure that a brokerage house's capital level is sufficient to cover its overall risk. • Pillar 3 – market discipline. Also relates to minimum levels of public disclosure.
Basel II is structured around three so-called pillars. • Pillar 1 – minimum regulatory requirements. They address and allocate capital for the principal risks faced by brokerage house (credit risk, market risk and operational risk). • Pillar 2 – ICAAP/SREP. It’s aim is to ensure that a brokerage house's capital level is sufficient to cover its overall risk. • Pillar 3 – market discipline. Also relates to minimum levels of public disclosure.
 ICAAP/SREP • The ICAAP is the firm’s own assessment of the internal capital it needs to hold against its risks. • The SREP is how supervisors assess the overall risks of firm/group, covering inherent business risk, control factors and internal governance. SREP includes a quantitative and qualitative assessment of the ICAAP.
ICAAP/SREP • The ICAAP is the firm’s own assessment of the internal capital it needs to hold against its risks. • The SREP is how supervisors assess the overall risks of firm/group, covering inherent business risk, control factors and internal governance. SREP includes a quantitative and qualitative assessment of the ICAAP.
 AGENDA PART 1 Introduction PART 2 Organizational issues of SREP (BION) • Regulations • Basic definitions (ICAAP, SPEP, internal capital, regulatory capital) • • • BION of brokerage • houses in detail • PART 3 BION – cycle Rating Time requirements Technical aspects of BION Ongoing supervision Presentation Off/on-site Inspection
AGENDA PART 1 Introduction PART 2 Organizational issues of SREP (BION) • Regulations • Basic definitions (ICAAP, SPEP, internal capital, regulatory capital) • • • BION of brokerage • houses in detail • PART 3 BION – cycle Rating Time requirements Technical aspects of BION Ongoing supervision Presentation Off/on-site Inspection
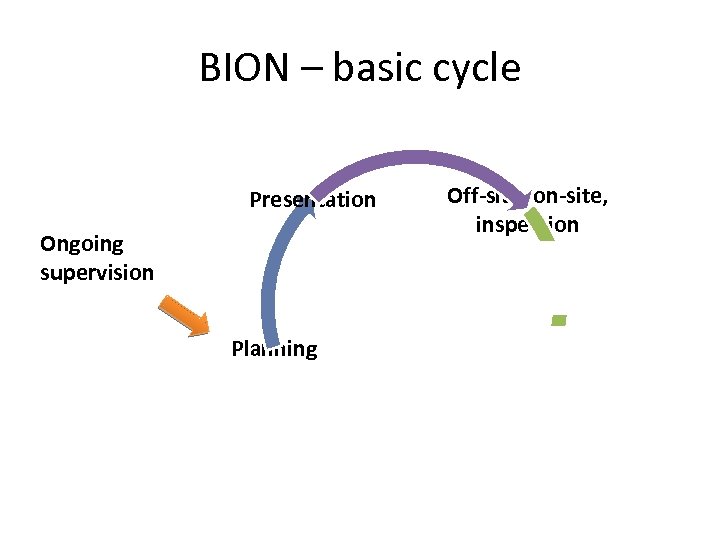
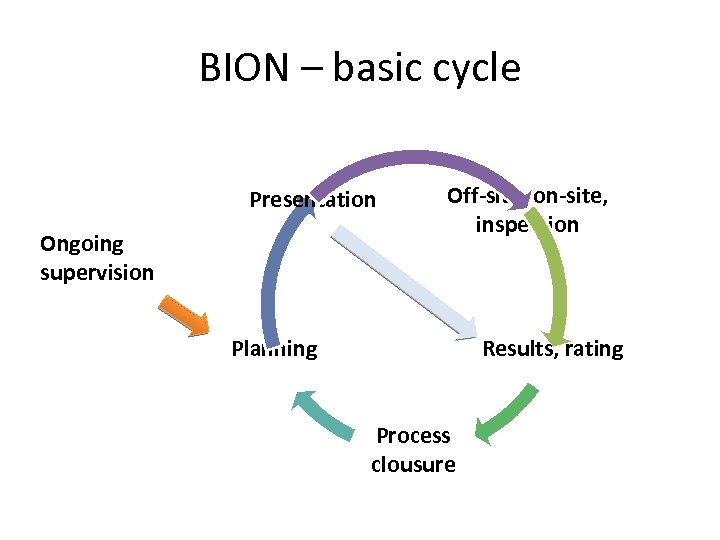 BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
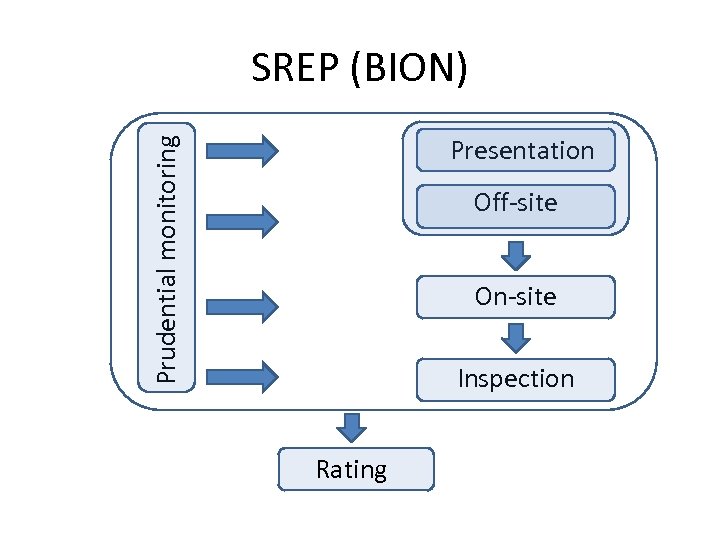 SREP (BION) Prudential monitoring Presentation Off-site On-site Inspection Rating
SREP (BION) Prudential monitoring Presentation Off-site On-site Inspection Rating
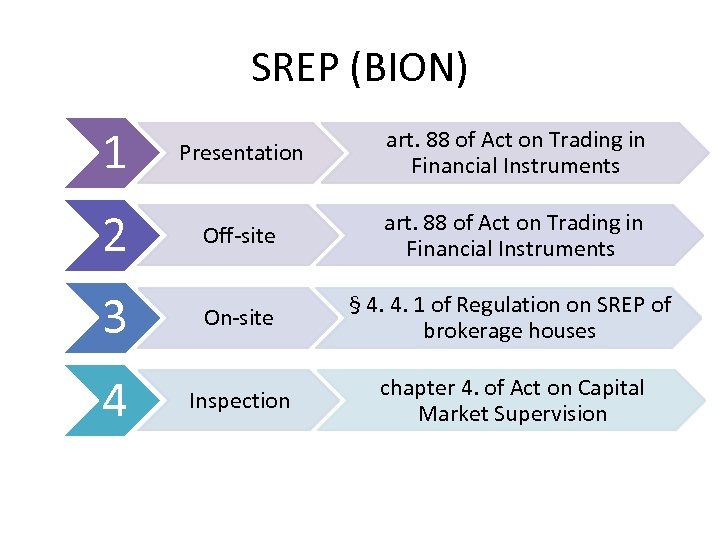 SREP (BION) 1 Presentation art. 88 of Act on Trading in Financial Instruments 2 Off-site art. 88 of Act on Trading in Financial Instruments 3 On-site § 4. 4. 1 of Regulation on SREP of brokerage houses 4 Inspection chapter 4. of Act on Capital Market Supervision
SREP (BION) 1 Presentation art. 88 of Act on Trading in Financial Instruments 2 Off-site art. 88 of Act on Trading in Financial Instruments 3 On-site § 4. 4. 1 of Regulation on SREP of brokerage houses 4 Inspection chapter 4. of Act on Capital Market Supervision
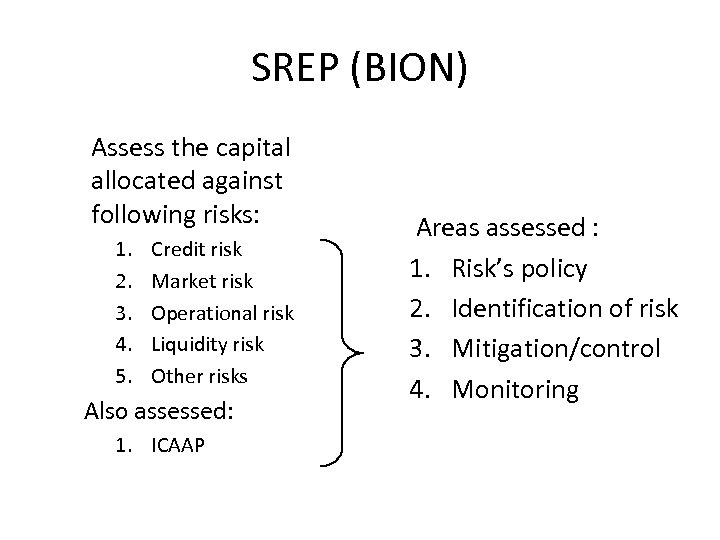 SREP (BION) Assess the capital allocated against following risks: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Credit risk Market risk Operational risk Liquidity risk Other risks Also assessed: 1. ICAAP Areas assessed : 1. Risk’s policy 2. Identification of risk 3. Mitigation/control 4. Monitoring
SREP (BION) Assess the capital allocated against following risks: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Credit risk Market risk Operational risk Liquidity risk Other risks Also assessed: 1. ICAAP Areas assessed : 1. Risk’s policy 2. Identification of risk 3. Mitigation/control 4. Monitoring
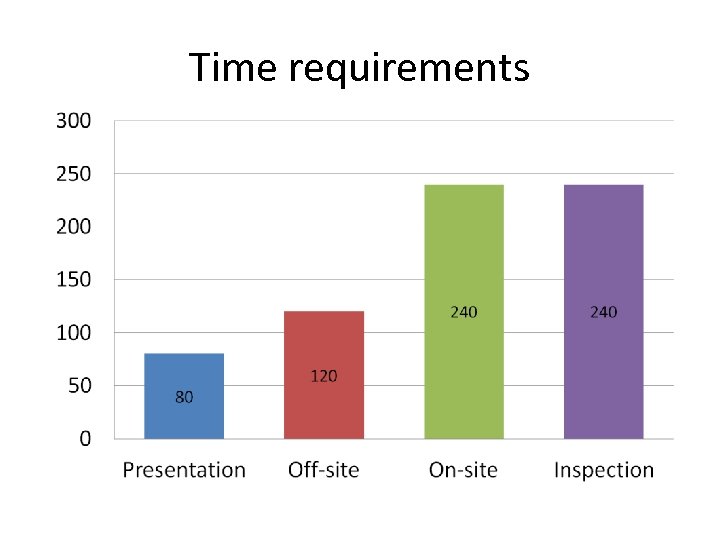 Time requirements
Time requirements
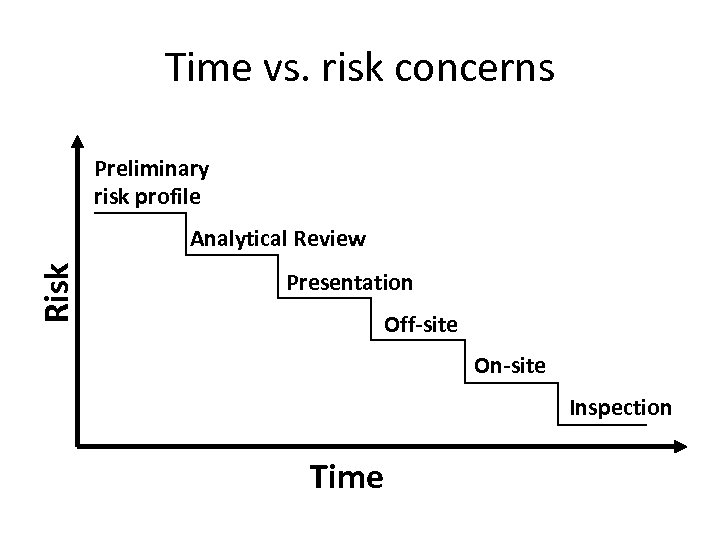 Time vs. risk concerns Preliminary risk profile Risk Analytical Review Presentation Off-site On-site Inspection Time
Time vs. risk concerns Preliminary risk profile Risk Analytical Review Presentation Off-site On-site Inspection Time
 Key boundaries 1. Every brokerage house has to be ranked 2. Team organization 3. Methodology basic level training – up to 10 working days 4. Balance between tools/time 5. Staff turnover ca. 1, 5 year 6. Skill level (employees who passed CFA level 1 are decision makers) 6. Transparency to the market 7. Simplicity before complexity
Key boundaries 1. Every brokerage house has to be ranked 2. Team organization 3. Methodology basic level training – up to 10 working days 4. Balance between tools/time 5. Staff turnover ca. 1, 5 year 6. Skill level (employees who passed CFA level 1 are decision makers) 6. Transparency to the market 7. Simplicity before complexity
 AGENDA PART 1 Introduction PART 2 Organizational issues of SREP (BION) • Regulations • Basic definitions (ICAAP, SPEP, internal capital, regulatory capital) • • • BION of brokerage • houses in detail • PART 3 BION – cycle Rating Time requirements Technical aspects of BION Ongoing supervision Presentation Off/on-site Inspection
AGENDA PART 1 Introduction PART 2 Organizational issues of SREP (BION) • Regulations • Basic definitions (ICAAP, SPEP, internal capital, regulatory capital) • • • BION of brokerage • houses in detail • PART 3 BION – cycle Rating Time requirements Technical aspects of BION Ongoing supervision Presentation Off/on-site Inspection
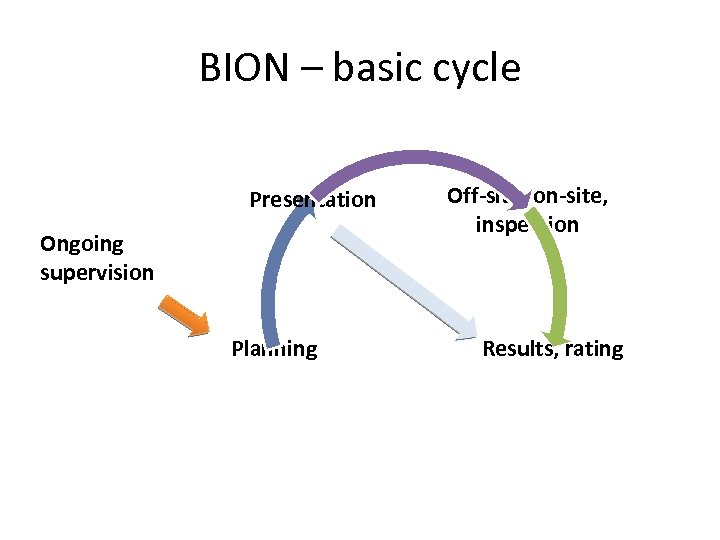
 BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
 Ongoing supervision • All available data and information, ranging from qualitative to quantitative, is taken into account • This includes, for example, data and information from: – corep, – regulatory reports (entity’s current data – S 01), – annual financial statements (audited), – the latest on-site examination report, – other relevant information.
Ongoing supervision • All available data and information, ranging from qualitative to quantitative, is taken into account • This includes, for example, data and information from: – corep, – regulatory reports (entity’s current data – S 01), – annual financial statements (audited), – the latest on-site examination report, – other relevant information.
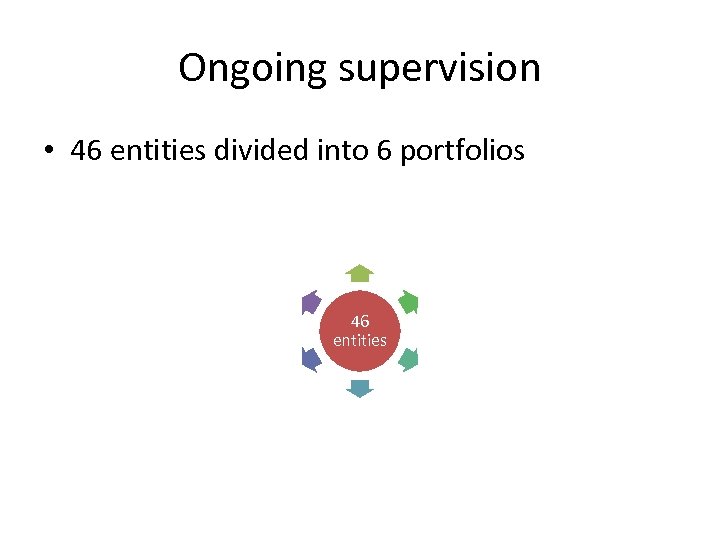 Ongoing supervision • 46 entities divided into 6 portfolios P 1 P 6 P 2 46 entities P 5 P 3 P 4
Ongoing supervision • 46 entities divided into 6 portfolios P 1 P 6 P 2 46 entities P 5 P 3 P 4
 Main table • Includes information about: – – – – the value of total assets, the value of total capital requirement, the value of assets under management, qualifications (if any), auditor, information from other departments, information from consolidating supervisor. • Key decision parameters, • Input for kick off meetings, • Rating can be assigned basing on Main table only.
Main table • Includes information about: – – – – the value of total assets, the value of total capital requirement, the value of assets under management, qualifications (if any), auditor, information from other departments, information from consolidating supervisor. • Key decision parameters, • Input for kick off meetings, • Rating can be assigned basing on Main table only.
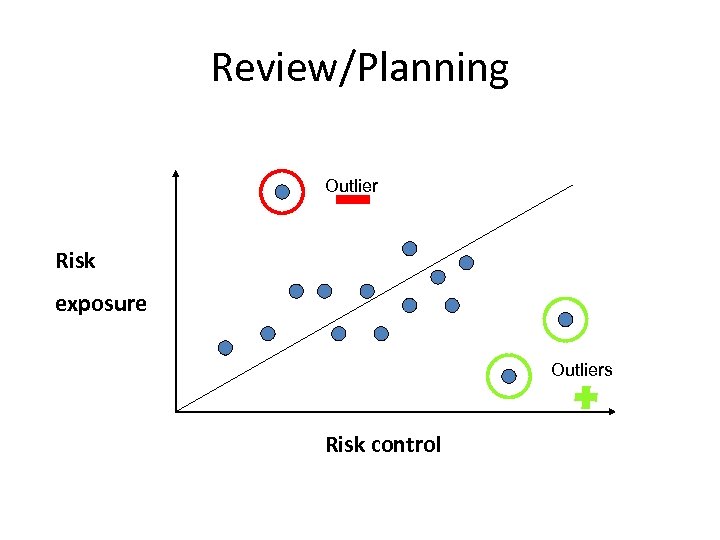 Review/Planning Outlier Risk exposure Outliers Risk control
Review/Planning Outlier Risk exposure Outliers Risk control
 BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
 Presentation Divided into: – Module A – Overview – standardized questions about an entity (shareholding structure, capital group, capital allocated for risks) – Module B – Risk profile – detailed questions (material risks, key employees, IT structure) • Two approaches
Presentation Divided into: – Module A – Overview – standardized questions about an entity (shareholding structure, capital group, capital allocated for risks) – Module B – Risk profile – detailed questions (material risks, key employees, IT structure) • Two approaches
 Standard presentation Pros + easy to aggregate results, + convenient for a supervisor (no additional analysis). Cons – preparation for such presentation is timeconsuming (extensive set), – some questions may not apply to a particular brokerage house.
Standard presentation Pros + easy to aggregate results, + convenient for a supervisor (no additional analysis). Cons – preparation for such presentation is timeconsuming (extensive set), – some questions may not apply to a particular brokerage house.
 Tailored presentation Pros + less burdensome for small brokerage houses. Cons – nearly impossible to aggregate results, – requires additional work of a supervisor, – some questions can be accidentally not included.
Tailored presentation Pros + less burdensome for small brokerage houses. Cons – nearly impossible to aggregate results, – requires additional work of a supervisor, – some questions can be accidentally not included.
 Presentation to-do list Supervisor – Notification (date, set of questions…) Company – Prepares and gives presentation – Communicates with a supervisor – Provides electronic deliverables
Presentation to-do list Supervisor – Notification (date, set of questions…) Company – Prepares and gives presentation – Communicates with a supervisor – Provides electronic deliverables
 We ask about… Structure of the capital group Ways of reporting within capital group Documentation flow (reports provided to the Board) Way of choosing members of Board of Directors and Supervisory Board (strategic plan, role in the ICAAP) • Dependencies delegation and scope of delegation • Experience and competence of managers • Organizational structure • •
We ask about… Structure of the capital group Ways of reporting within capital group Documentation flow (reports provided to the Board) Way of choosing members of Board of Directors and Supervisory Board (strategic plan, role in the ICAAP) • Dependencies delegation and scope of delegation • Experience and competence of managers • Organizational structure • •
 We ask about… Key employees Scale of capital and personal dependencies Amount of capital allocated on risk in Pillar I and II Types of risks estimated as material (policies and procedures…) • Measurement of risk materiality • Expenditures allocated on risk management • ICAAP (comprehensive…) • •
We ask about… Key employees Scale of capital and personal dependencies Amount of capital allocated on risk in Pillar I and II Types of risks estimated as material (policies and procedures…) • Measurement of risk materiality • Expenditures allocated on risk management • ICAAP (comprehensive…) • •
 BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating N/Y Planning /End/
BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating N/Y Planning /End/
 Off-site • • Requires additional communication with the brokerage house and further exchange of information. Off-site supervision uses additional information obtained from the brokerage house that was not included in the presentation but is necessary from the supervisor’s point of view to properly rank a brokerage house.
Off-site • • Requires additional communication with the brokerage house and further exchange of information. Off-site supervision uses additional information obtained from the brokerage house that was not included in the presentation but is necessary from the supervisor’s point of view to properly rank a brokerage house.
 On-site • An on-site examination focuses on detailed assessment of the brokerage house's business and financial condition • It involves looking at financial statements, systems and procedures, transactions and documentation, as well as meeting with management and staff • Reliable supervisory tool (low risk)
On-site • An on-site examination focuses on detailed assessment of the brokerage house's business and financial condition • It involves looking at financial statements, systems and procedures, transactions and documentation, as well as meeting with management and staff • Reliable supervisory tool (low risk)
 On-site limitations On-site examinations have some limitations, they: – involve significant supervisory resources, – can be costly and burdensome for brokerage houses, – relate to the assessment of a brokerage house at a specific point in time, – in addition, information contained in examination does not remain valid for long.
On-site limitations On-site examinations have some limitations, they: – involve significant supervisory resources, – can be costly and burdensome for brokerage houses, – relate to the assessment of a brokerage house at a specific point in time, – in addition, information contained in examination does not remain valid for long.
 Inspection • Similar to an on-site examination • Unlike an on-site examination, inspection also involves assessment of compliance
Inspection • Similar to an on-site examination • Unlike an on-site examination, inspection also involves assessment of compliance
 BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
 Rating • • Each component of risk is rated on a scale from 1 (best) through 4 (worst) based on supervisory criteria and guidelines Results are aggregated using weights (summing up to 1) Final rating – a number with two decimal points (only range is communicated i. e. 1 – 1, 5) Exception – when an on-site examination or inspection are conducted we communicate the exact number i. e. 2, 14
Rating • • Each component of risk is rated on a scale from 1 (best) through 4 (worst) based on supervisory criteria and guidelines Results are aggregated using weights (summing up to 1) Final rating – a number with two decimal points (only range is communicated i. e. 1 – 1, 5) Exception – when an on-site examination or inspection are conducted we communicate the exact number i. e. 2, 14
 Scale Rating Meaning 1 – 1, 5 Good general situation of the entity in the context of risk. Supervisory strategy determined as result of BION narrows down to monitoring reports and other information that are likely to influence the exposure and the level of risk. 1, 5 – 2, 5 Satisfying general situation of the entity in all of the assessed areas. Irregularities that appear (if any) aren't material from the point of view of safety of the entity. 2, 5 – 3, 5 General situation is not satisfying. Appearing irregularities aren't at present substantial from the point of view of safety of the entity, however if they aren't eliminated they can become a threat. 3, 5 – 4, 0 Critical situation of the assessed entity. Appearing irregularities are alarming – entity’s ability to continue it’s business is doubtful.
Scale Rating Meaning 1 – 1, 5 Good general situation of the entity in the context of risk. Supervisory strategy determined as result of BION narrows down to monitoring reports and other information that are likely to influence the exposure and the level of risk. 1, 5 – 2, 5 Satisfying general situation of the entity in all of the assessed areas. Irregularities that appear (if any) aren't material from the point of view of safety of the entity. 2, 5 – 3, 5 General situation is not satisfying. Appearing irregularities aren't at present substantial from the point of view of safety of the entity, however if they aren't eliminated they can become a threat. 3, 5 – 4, 0 Critical situation of the assessed entity. Appearing irregularities are alarming – entity’s ability to continue it’s business is doubtful.
 BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
BION – basic cycle Presentation Ongoing supervision Off-site, on-site, inspection Planning Results, rating Process clousure
 Communication • Communication with brokerage houses – Rating – Pointing out the weakest elements in the risk management process (Action Plan) – Correction Plan (if an inspection is conducted) • Taking up appropriate supervisory actions • Ongoing monitoring of entity’s rating (possible change of rating if the circumstances change)
Communication • Communication with brokerage houses – Rating – Pointing out the weakest elements in the risk management process (Action Plan) – Correction Plan (if an inspection is conducted) • Taking up appropriate supervisory actions • Ongoing monitoring of entity’s rating (possible change of rating if the circumstances change)
 Supervisory actions • Intensify the monitoring of the brokerage house • Require the brokerage house to raise additional capital • Restrict current activities • Prohibit new activities or acquisitions • Restrict or prohibit the payment of dividends • Fines • Legal action • Withdrawal of authorisation (license)
Supervisory actions • Intensify the monitoring of the brokerage house • Require the brokerage house to raise additional capital • Restrict current activities • Prohibit new activities or acquisitions • Restrict or prohibit the payment of dividends • Fines • Legal action • Withdrawal of authorisation (license)
 Process closure • • Next year’s issue Statistics & Research Feedback & technology update …
Process closure • • Next year’s issue Statistics & Research Feedback & technology update …


