b82f35c9997500d9d0654845c7f4b805.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Overview of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 For CWA Leaders April 2010

National Health Care Reform Finally Achieved n n n Not our bill, but it moves us forward. A tough fight. A fight to protect CWA members and retirees, to improve our bargaining position, and to achieve progress for all.

CWA Leads on Issues Critical to Our Members and Retirees n Retiree health care – Coalitions; ads; joint visits – Result: $5 billion reinsurance trust fund; premium rating limits n Tax on high-cost health plans – – Reports, briefings Labor & Coalition letters, visits & ads Patch thru calls & worksite calls Result: delayed effective date to 2018; reduced tax by 80%

Reform & CWA Negotiated Plans n We keep our plans: existing bargained-for plans are exempt from most changes through expiration. n Some good reforms apply after contract expiration: – No exclusions for pre-existing conditions. – No lifetime or annual limits on benefits. – Children covered until age 26. – Preventive care with no deductible or copay. – Waiting period for coverage limited to 90 days. n Implementation of reforms is subject of bargaining.

More on Reform & CWA Negotiated Plans n Limits pre-tax health FSA contributions to $2, 500 per year, indexed for inflation n Penalty increased to 20% if HSA funds used for non-medical claims n No reimbursement of over-the-counter meds in health accounts unless prescribed

Reform & Retirees n As of 1/1/11 Medicare covers prevention & screenings with no deductibles or co-pays n “Doughnut hole” in Medicare Rx plan closed by 2020 n $5 billion trust to help cover high-cost claims of retirees age 55 - 64

Reform & CWA Employers n Must negotiate over new benefit requirements after current bargaining agreements expire. n Waiting periods for new employees limited to no more than 90 -days. n Must provide vouchers to some low-income workers to purchase coverage through exchanges. n Must report value of health plan on employee W-2 s (not taxable. ) n Small employers can purchase health coverage through exchanges; may qualify for subsidies.

More on Reform and CWA Employers – Excise Tax on High-Value Plans n 40% tax on high-cost plans delayed to 2018 applies to cost above thresholds. n 2018 Thresholds: $10, 200 for single coverage; $27, 500 for family coverage. n Thresholds indexed to CPI + 1% in 2019; CPI only beginning in 2020. n Adjustments for age and gender and separate threshold for retirees will reduce the tax. n Separate vision and dental plans excluded; contributions to savings accounts included. n Negotiations between Labor and White House cut tax by 80% – from $149 billion to $32 billion.
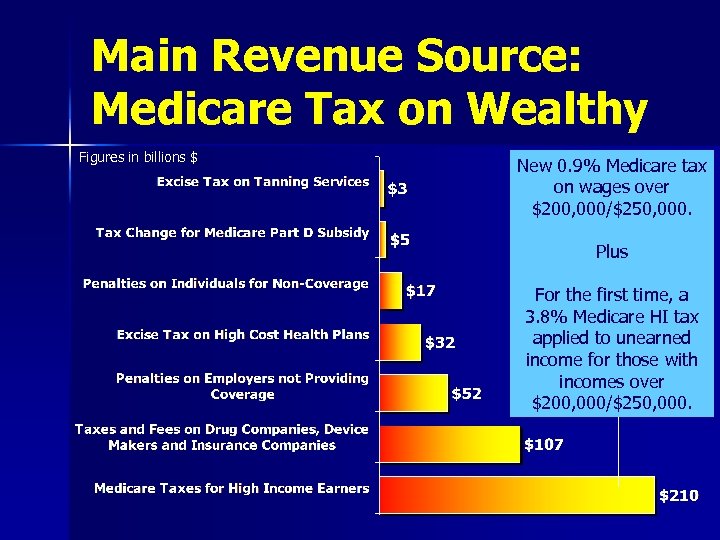
Main Revenue Source: Medicare Tax on Wealthy Figures in billions $ New 0. 9% Medicare tax on wages over $200, 000/$250, 000. Plus For the first time, a 3. 8% Medicare HI tax applied to unearned income for those with incomes over $200, 000/$250, 000.

More on Reform & CWA Employers – Medicare Retiree Drug Subsidy n Business deduction for retiree benefit expense remains in effect. n Medicare Retiree Drug Subsidy (RDS) for 28% of retiree Rx costs remains in effect. n Companies may no longer deduct the cost of benefits for which they have received a subsidy. n Provision eliminates windfall but reduces value of subsidy.

CWA Mobilizes Big Time! n n n 177 Coordinators 7, 372 Letters to Members of Congress 31, 218 Calls to MOCs from worksites 38, 739 Patch thru calls 300+ Visits to MOCs Plus Town Hall meetings, rallies, sit ins, fly ins, etc.

The Principles that Guided Our Work & the Progress We Made n Cover All Americans – 32 million uninsured covered; from 83% to 95% of population covered n Control Costs –federal deficit reduced $1. 3 trillion over 20 years; estimated to cut employer premium trend by 15% to 20% n Strong Government Role – rules and standards for insurance companies; health insurance exchanges; cost controls; quality oversight.

The Principles that Guided Our Work & the Progress We Made n Fair Financing – relies on wealthy, employers and health industry to pay their share n Improve Health Quality – 100% coverage of prevention; provider payments based on quality & outcomes.

Reform Addresses CWA Members’ Concerns n n Janet of Virginia Beach is concerned about her cousin, a self-employed, single dad who cannot afford the $400 a month needed for insurance coverage. He goes without, betting and hoping that he and his daughter do not become ill or get in an accident. Janet’s cousin will be able to buy affordable coverage through the health insurance exchanges at much lower rates. Individuals and small employers will band together to create a large insurance pool, and insurers will not be able to underwrite and charge more for small groups. The government will provide subsidies and tax credits for individuals and small businesses who have a hard time finding affordable coverage.

Reform Addresses CWA Members’ Concerns n n Veronica of Arkansas worried about her father who worked all of his life, but when he had a massive stroke, got shunted from hospital to hospital because he had no health insurance. Now, with the health care reform legislation, Veronica’s dad will be able to get coverage through the health insurance exchanges. No one will be denied coverage for a pre-existing condition. Subsidies are available to keep coverage affordable.

Reform Addresses CWA Members’ Concerns n n Pamela of Brooklyn worries about her grandmother who finds it hard to pay her Medicare deductible and prescription costs. Health care reform will benefit Pam’s grandmother by closing the Medicare prescription drug “doughnut hole” over time, making prescription drugs more affordable.

Key Implementation Dates Note: Bargained-for plans exempt from most new rules until expiration of current agreement. Implementation of most provisions is subject of bargaining.

Health Care Reform Timeline – 2010 n Companies must report impact of change in taxability of Retiree Drug Subsidy payments n Reinsurance trust for retiree medical coverage established n $250 rebate for seniors who hit Medicare Part D “doughnut hole”

Health Care Reform Timeline – 2011 n n n n Children covered to age 26 (CBA caveat) No lifetime and restricted annual limits (CBA caveat) No pre-existing condition exclusions for children 18 and younger (CBA caveat) Employers report health plan value on employee W -2 s (no tax) HSA withdrawal penalty increased to 20% No OTC drugs from account-based plans Long-term care benefit available Begin phase out of Medicare D doughnut hole

Health Care Reform Timeline – 2013 n Deduction for employer Medicare Part D Retiree Drug Subsidy eliminated n Medicare payroll tax increased for high wage employees (over $200, 000 single/$250, 000 joint filers) n Medicare tax applied to unearned income (dividends, sale of stock, etc) of the wealthiest taxpayers (over $200, 000 single/$250, 000 joint filers) n $2500 cap on health FSA contributions

Health Care Reform Timeline – 2014 n Individuals must have health coverage or pay a penalty n Health Insurance Exchanges operational n Premium and cost-sharing subsidies for low and middle income individuals available n Medicaid eligibility expanded n Insurance market reforms: guaranteed issue, premium rating restrictions, waiting period limits, no annual dollar limits, etc.

Health Care Reform Timeline – 2016 & 2018 n 2016 -- Cross-border sales of health insurance allowed n 2018 – Excise tax on high-cost health plans kicks in

Summary n Really good for family, friends, or laid off members without insurance, and small businesses. – And it’s primarily financed by taxing the rich n n n n We keep our plans – existing bargained-for plans are exempt from most changes through expiration. Some improvements in the bill may raise plan costs initially, But the hidden cost of 32 million uninsured in our plans will be removed. New regulations on insurance companies will create a fairer system. Long-range cost controls will moderate cost increases and lower the pressure we face at the bargaining table. Some aspects of health bill will raise our costs. Overall impact will be positive.

Next Steps for CWA n Inform members about facts of health care reform and safeguards in it. n Develop bargaining agendas for the new health care environment. n Analyze impact of changes and work with Congress to fix unintended consequences. n Engage with employers about impact of the legislation on our plans and on our members.
b82f35c9997500d9d0654845c7f4b805.ppt