74f084cbc99a3dfa3b5d1451947ec141.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 144
 Overview of the DEc. IDE Research Network Agency for Healthcare Research & Quality Center for Outcomes & Evidence December, 2005
Overview of the DEc. IDE Research Network Agency for Healthcare Research & Quality Center for Outcomes & Evidence December, 2005
 Terms of Use • This slide set was created to provide information that may be distributed and copied by AHRQ program affiliates, but it is requested that in subsequent use the Agency for Healthcare Research (AHRQ) be given appropriate acknowledgement. In addition, a disclaimer should be provided stating no official endorsement by AHRQ or DHHS is intended or should be inferred by these slides. • Media requests for information about the AHRQ programs should be directed to AHRQ’s Office of Communication & Knowledge Transfer. • Individuals not authorized to use the AHRQ logo or other images in these slides, should remove them prior to use. • If you use some or all of these slides, AHRQ would like to hear about the purpose and the audience so we can develop future slide sets that are useful to the public. • If you use some or all of these slides, please send a brief email to effectivehealthcare@ahrq. gov to let us know about the use, the audience, and your suggestions. Thank you! 2
Terms of Use • This slide set was created to provide information that may be distributed and copied by AHRQ program affiliates, but it is requested that in subsequent use the Agency for Healthcare Research (AHRQ) be given appropriate acknowledgement. In addition, a disclaimer should be provided stating no official endorsement by AHRQ or DHHS is intended or should be inferred by these slides. • Media requests for information about the AHRQ programs should be directed to AHRQ’s Office of Communication & Knowledge Transfer. • Individuals not authorized to use the AHRQ logo or other images in these slides, should remove them prior to use. • If you use some or all of these slides, AHRQ would like to hear about the purpose and the audience so we can develop future slide sets that are useful to the public. • If you use some or all of these slides, please send a brief email to effectivehealthcare@ahrq. gov to let us know about the use, the audience, and your suggestions. Thank you! 2
 New authorization by MMA. Authorizes AHRQ to conduct research to improve the quality, effectiveness, and efficiency of Medicare, Medicaid, and State Children Health Insurance (SCHIP) programs. A. Evidence synthesis – – Transparent process of systematically reviewing and synthesizing evidence on treatment effectiveness. Identifying relevant knowledge gaps. B. Evidence generation – Development of new scientific knowledge to address knowledge gaps. C. Evidence communication/translation – Communication of scientific information in plain language 3 to policymakers, patients, and providers.
New authorization by MMA. Authorizes AHRQ to conduct research to improve the quality, effectiveness, and efficiency of Medicare, Medicaid, and State Children Health Insurance (SCHIP) programs. A. Evidence synthesis – – Transparent process of systematically reviewing and synthesizing evidence on treatment effectiveness. Identifying relevant knowledge gaps. B. Evidence generation – Development of new scientific knowledge to address knowledge gaps. C. Evidence communication/translation – Communication of scientific information in plain language 3 to policymakers, patients, and providers.
 4
4
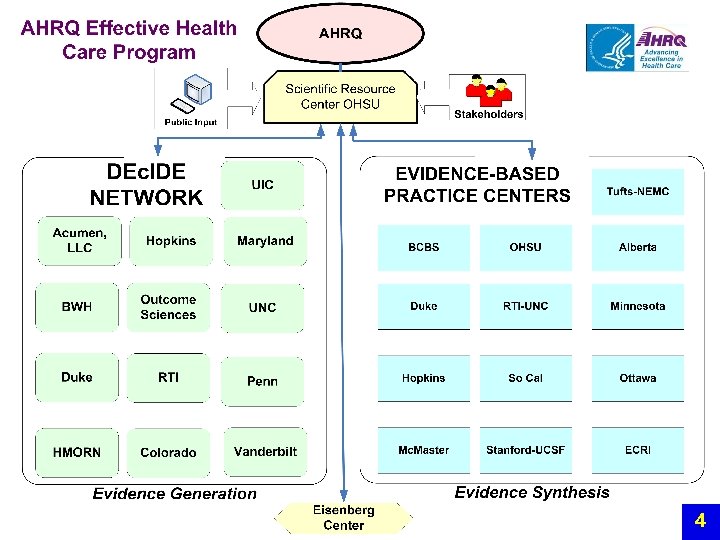
 Evidence Generation new DEc. IDE Research Network Developing Evidence to Inform Decisions about Effectiveness n The main purpose of the DEc. IDE network is to expeditiously develop valid scientific evidence about the outcomes, comparative clinical effectiveness, safety, and appropriateness of health care items and services n The network is comprised of academic, clinic, and practice-based centers with access to electronic health information databases and the capacity to conduct accelerated research. 5
Evidence Generation new DEc. IDE Research Network Developing Evidence to Inform Decisions about Effectiveness n The main purpose of the DEc. IDE network is to expeditiously develop valid scientific evidence about the outcomes, comparative clinical effectiveness, safety, and appropriateness of health care items and services n The network is comprised of academic, clinic, and practice-based centers with access to electronic health information databases and the capacity to conduct accelerated research. 5
 What Will DEc. IDE Do? Perform secondary database analysis to compare health outcomes Develop algorithms to identify inappropriate drug prescribing patterns Conduct methodological studies Evaluate the effects of benefit and formulary structure on health outcomes Conduct clinical economics studies Analyze existing disease registries or prescription databases Evaluate patient and prescriber decision-making tools Studies comparing the clinical effectiveness of common treatment options Conduct simulations and modeling Carry out evaluations of innovative healthcare services Design & implement prospective studies Examine clinical benefits of 6 genetics testing.
What Will DEc. IDE Do? Perform secondary database analysis to compare health outcomes Develop algorithms to identify inappropriate drug prescribing patterns Conduct methodological studies Evaluate the effects of benefit and formulary structure on health outcomes Conduct clinical economics studies Analyze existing disease registries or prescription databases Evaluate patient and prescriber decision-making tools Studies comparing the clinical effectiveness of common treatment options Conduct simulations and modeling Carry out evaluations of innovative healthcare services Design & implement prospective studies Examine clinical benefits of 6 genetics testing.
 2005 -06 Priority List • • • Arthritis and non-traumatic joint disorders Cancer Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/asthma. Dementia, including Alzheimer's disease Depression and other mood disorders Diabetes mellitus Ischemic heart disease Peptic ulcer/dyspepsia Pneumonia Stroke, including control of hypertension 7
2005 -06 Priority List • • • Arthritis and non-traumatic joint disorders Cancer Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease/asthma. Dementia, including Alzheimer's disease Depression and other mood disorders Diabetes mellitus Ischemic heart disease Peptic ulcer/dyspepsia Pneumonia Stroke, including control of hypertension 7
 Why the Need for Effectiveness Research? Interventions that are efficacious under a highly specific set of circumstances often fail to replicate across a wide variety of settings, conditions, patients. 8 Glasgow, 2003
Why the Need for Effectiveness Research? Interventions that are efficacious under a highly specific set of circumstances often fail to replicate across a wide variety of settings, conditions, patients. 8 Glasgow, 2003
 A Guiding Principle Within the Center for Outcomes & Evidence “Perhaps a more salient question is what we can do now, within the current infrastructure, to move effectiveness research forward so that everyone can reap the benefits of the most unprecedented bounty of biomedical research findings in our lifetime. ” Clancy C and Slutsky J. JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE MEDICINE • Volume 53 Number 2 • February 2005 9
A Guiding Principle Within the Center for Outcomes & Evidence “Perhaps a more salient question is what we can do now, within the current infrastructure, to move effectiveness research forward so that everyone can reap the benefits of the most unprecedented bounty of biomedical research findings in our lifetime. ” Clancy C and Slutsky J. JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE MEDICINE • Volume 53 Number 2 • February 2005 9
 Overview of Slide Series • For Each DEc. IDE Center, the following information is provided in the subsequent slides. – DEc. IDE Name – Core Personnel & Expertise – Affiliations and Partnerships – Research Interests & Center Strengths – Key Database Holdings – DEc. IDE Project(s) – Program & Center Goals 10
Overview of Slide Series • For Each DEc. IDE Center, the following information is provided in the subsequent slides. – DEc. IDE Name – Core Personnel & Expertise – Affiliations and Partnerships – Research Interests & Center Strengths – Key Database Holdings – DEc. IDE Project(s) – Program & Center Goals 10
 DEc. IDE Research Centers http: //effectivehealthcare. ahrq. gov/decide/index. cfm 11
DEc. IDE Research Centers http: //effectivehealthcare. ahrq. gov/decide/index. cfm 11
 DEc. IDE Centers • • • • Acumen, LLC. Brigham and Women’s Hospital Duke University Harvard Pilgrim Health Care, Inc. Johns Hopkins University Outcome Sciences RTI International University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center University of Illinois at Chicago University of Maryland at Baltimore University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Center 12
DEc. IDE Centers • • • • Acumen, LLC. Brigham and Women’s Hospital Duke University Harvard Pilgrim Health Care, Inc. Johns Hopkins University Outcome Sciences RTI International University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center University of Illinois at Chicago University of Maryland at Baltimore University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Center 12
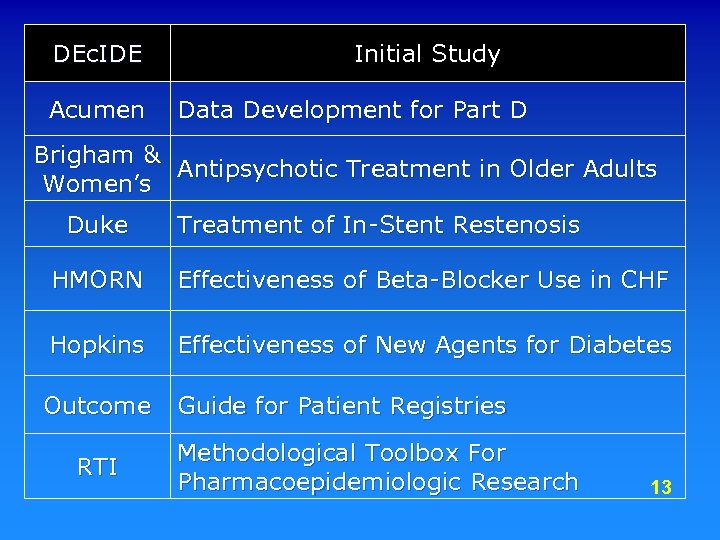 DEc. IDE Acumen Initial Study Data Development for Part D Brigham & Antipsychotic Treatment in Older Adults Women’s Duke Treatment of In-Stent Restenosis HMORN Effectiveness of Beta-Blocker Use in CHF Hopkins Effectiveness of New Agents for Diabetes Outcome Guide for Patient Registries RTI Methodological Toolbox For Pharmacoepidemiologic Research 13
DEc. IDE Acumen Initial Study Data Development for Part D Brigham & Antipsychotic Treatment in Older Adults Women’s Duke Treatment of In-Stent Restenosis HMORN Effectiveness of Beta-Blocker Use in CHF Hopkins Effectiveness of New Agents for Diabetes Outcome Guide for Patient Registries RTI Methodological Toolbox For Pharmacoepidemiologic Research 13
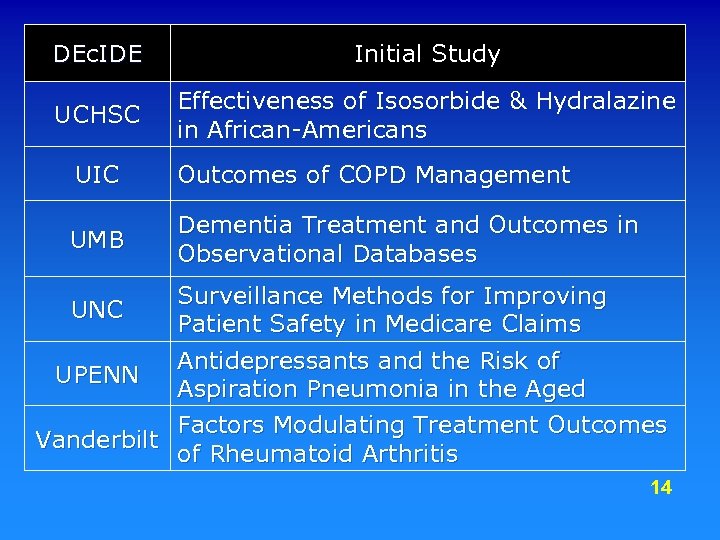 DEc. IDE Initial Study UCHSC Effectiveness of Isosorbide & Hydralazine in African-Americans UIC Outcomes of COPD Management UMB Dementia Treatment and Outcomes in Observational Databases Surveillance Methods for Improving UNC Patient Safety in Medicare Claims Antidepressants and the Risk of UPENN Aspiration Pneumonia in the Aged Factors Modulating Treatment Outcomes Vanderbilt of Rheumatoid Arthritis 14
DEc. IDE Initial Study UCHSC Effectiveness of Isosorbide & Hydralazine in African-Americans UIC Outcomes of COPD Management UMB Dementia Treatment and Outcomes in Observational Databases Surveillance Methods for Improving UNC Patient Safety in Medicare Claims Antidepressants and the Risk of UPENN Aspiration Pneumonia in the Aged Factors Modulating Treatment Outcomes Vanderbilt of Rheumatoid Arthritis 14
 Acumen DEc. IDE Center Thomas Ma. Curdy, Ph. D Principal Investigator
Acumen DEc. IDE Center Thomas Ma. Curdy, Ph. D Principal Investigator
 Acumen - Core Personnel & Expertise • Dr. Thomas Ma. Curdy, Ph. D. Economics: Health policy research, program evaluation using administrative and survey data, statistical modeling, behavioral research, economic analysis, financing of health care (Acumen LLC, Stanford University) • Dr. John Hornberger, M. D. , M. S. : Health economics, comparative effectiveness, decision analysis, technology assessment, cross-cultural medicine (Acumen LLC) • Dr. Sandra Wilson, Ph. D. Psychology : Design and assessment of care delivery systems, chronic disease care, vulnerable populations, caregiver-patient interaction (PAMFRI) 16
Acumen - Core Personnel & Expertise • Dr. Thomas Ma. Curdy, Ph. D. Economics: Health policy research, program evaluation using administrative and survey data, statistical modeling, behavioral research, economic analysis, financing of health care (Acumen LLC, Stanford University) • Dr. John Hornberger, M. D. , M. S. : Health economics, comparative effectiveness, decision analysis, technology assessment, cross-cultural medicine (Acumen LLC) • Dr. Sandra Wilson, Ph. D. Psychology : Design and assessment of care delivery systems, chronic disease care, vulnerable populations, caregiver-patient interaction (PAMFRI) 16
 Acumen - Core Personnel & Expertise (cont) • Dr. Mark Holodniy, M. D. : Infectious Disease. Outcomes research. Variation in practice patterns and outcomes. Epidemic preparedness and control. (Palo Alto VA) • Dr. Grecia Marrufo, Ph. D. Economics: Health policy research, econometrics, large database management, program evaluation (Acumen LLC) • Dr. Alan Garber, M. D. Ph. D. Econmics: Health economics. Guideline development, evidence reviews, cost-effectiveness analysis, assessment of innovative technologies and strategies (Stanford University) 17
Acumen - Core Personnel & Expertise (cont) • Dr. Mark Holodniy, M. D. : Infectious Disease. Outcomes research. Variation in practice patterns and outcomes. Epidemic preparedness and control. (Palo Alto VA) • Dr. Grecia Marrufo, Ph. D. Economics: Health policy research, econometrics, large database management, program evaluation (Acumen LLC) • Dr. Alan Garber, M. D. Ph. D. Econmics: Health economics. Guideline development, evidence reviews, cost-effectiveness analysis, assessment of innovative technologies and strategies (Stanford University) 17
 Acumen - Affiliations and Partnerships • VA Public Health Strategic Health Care Group (PHSHG), VA Palo Alto Health Care System • Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute. (Sutter Health affiliate) • Center for Primary Care and Outcomes Research, Stanford University 18
Acumen - Affiliations and Partnerships • VA Public Health Strategic Health Care Group (PHSHG), VA Palo Alto Health Care System • Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute. (Sutter Health affiliate) • Center for Primary Care and Outcomes Research, Stanford University 18
 Acumen - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Methodology – Development of research databases and computerized surveillance and monitoring systems – Econometrics, decision analyses, costeffectiveness analyses – Risk adjustment – Pay for performance, influence of incentives on behavior – Policy and program evaluation 19
Acumen - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Methodology – Development of research databases and computerized surveillance and monitoring systems – Econometrics, decision analyses, costeffectiveness analyses – Risk adjustment – Pay for performance, influence of incentives on behavior – Policy and program evaluation 19
 Acumen - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Programmatic – Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP, VA – State and county health agencies – Managed care organizations • Fields – Health service delivery & finance systems – Novel pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, & 20 devices
Acumen - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Programmatic – Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP, VA – State and county health agencies – Managed care organizations • Fields – Health service delivery & finance systems – Novel pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, & 20 devices
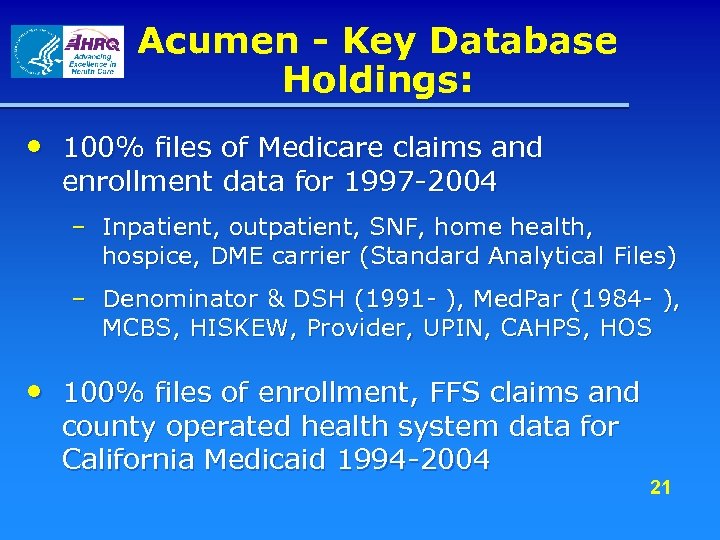 Acumen - Key Database Holdings: • 100% files of Medicare claims and enrollment data for 1997 -2004 – Inpatient, outpatient, SNF, home health, hospice, DME carrier (Standard Analytical Files) – Denominator & DSH (1991 - ), Med. Par (1984 - ), MCBS, HISKEW, Provider, UPIN, CAHPS, HOS • 100% files of enrollment, FFS claims and county operated health system data for California Medicaid 1994 -2004 21
Acumen - Key Database Holdings: • 100% files of Medicare claims and enrollment data for 1997 -2004 – Inpatient, outpatient, SNF, home health, hospice, DME carrier (Standard Analytical Files) – Denominator & DSH (1991 - ), Med. Par (1984 - ), MCBS, HISKEW, Provider, UPIN, CAHPS, HOS • 100% files of enrollment, FFS claims and county operated health system data for California Medicaid 1994 -2004 21
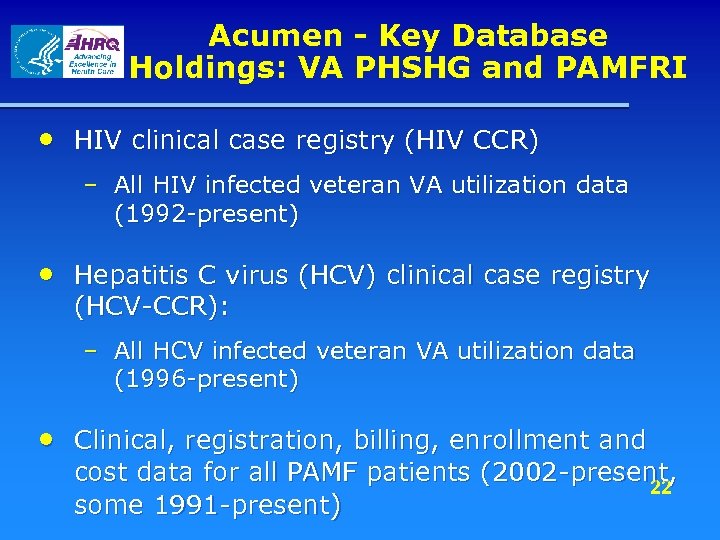 Acumen - Key Database Holdings: VA PHSHG and PAMFRI • HIV clinical case registry (HIV CCR) – All HIV infected veteran VA utilization data (1992 -present) • Hepatitis C virus (HCV) clinical case registry (HCV-CCR): – All HCV infected veteran VA utilization data (1996 -present) • Clinical, registration, billing, enrollment and cost data for all PAMF patients (2002 -present, 22 some 1991 -present)
Acumen - Key Database Holdings: VA PHSHG and PAMFRI • HIV clinical case registry (HIV CCR) – All HIV infected veteran VA utilization data (1992 -present) • Hepatitis C virus (HCV) clinical case registry (HCV-CCR): – All HCV infected veteran VA utilization data (1996 -present) • Clinical, registration, billing, enrollment and cost data for all PAMF patients (2002 -present, 22 some 1991 -present)
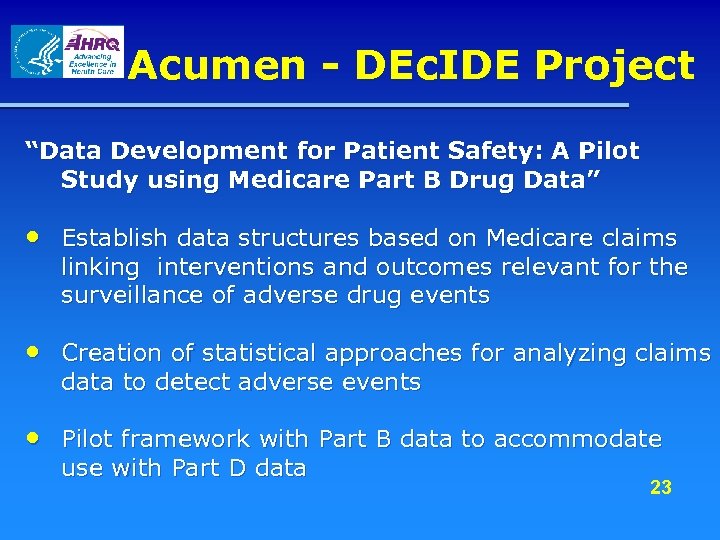 Acumen - DEc. IDE Project “Data Development for Patient Safety: A Pilot Study using Medicare Part B Drug Data” • Establish data structures based on Medicare claims linking interventions and outcomes relevant for the surveillance of adverse drug events • Creation of statistical approaches for analyzing claims data to detect adverse events • Pilot framework with Part B data to accommodate use with Part D data 23
Acumen - DEc. IDE Project “Data Development for Patient Safety: A Pilot Study using Medicare Part B Drug Data” • Establish data structures based on Medicare claims linking interventions and outcomes relevant for the surveillance of adverse drug events • Creation of statistical approaches for analyzing claims data to detect adverse events • Pilot framework with Part B data to accommodate use with Part D data 23
 ABSTRACT: Data Development for Patient Safety: A Pilot Study using Medicare Part B Drug Data Abstract: Medicare administrative claims data offer a valuable informational source for the surveillance of adverse drug events, but there are substantial challenges in exploiting these data to screen for potential patient safety problems. The merits of these data include large samples covering the spectrum of the elderly and disabled and data accessible at relatively low costs. Medicare claims provide a broad picture of the health services received by individuals, with considerable diagnosis information recorded across many provider types. As Medicare Part D records become available, the claims data will also incorporate the use of pharmaceuticals. In sharp contrast to clinical trials and experimental data, one can draw on claims data to assess potential safety problems on a rapid turnaround basis, investigating both current and recent past experiences to uncover adverse outcomes. There are two central challenges in using claims data for the surveillance of drug safety: (1) The development of frameworks to organize claims data into structures that link relevant interventions, outcomes and patient characteristics for the study of pharmaceuticals under investigation; and (2) The formulation of statistical approaches to analyze these data to detect adverse events. This project will develop a data system and empirical framework for identifying and capturing adverse drug events using elements contained in the Medicare claims files. The analysis will exploit information available in Part B claims on drugs, to produce a framework that can be readily adapted to incorporate Part D claims when they come on line next year. 24
ABSTRACT: Data Development for Patient Safety: A Pilot Study using Medicare Part B Drug Data Abstract: Medicare administrative claims data offer a valuable informational source for the surveillance of adverse drug events, but there are substantial challenges in exploiting these data to screen for potential patient safety problems. The merits of these data include large samples covering the spectrum of the elderly and disabled and data accessible at relatively low costs. Medicare claims provide a broad picture of the health services received by individuals, with considerable diagnosis information recorded across many provider types. As Medicare Part D records become available, the claims data will also incorporate the use of pharmaceuticals. In sharp contrast to clinical trials and experimental data, one can draw on claims data to assess potential safety problems on a rapid turnaround basis, investigating both current and recent past experiences to uncover adverse outcomes. There are two central challenges in using claims data for the surveillance of drug safety: (1) The development of frameworks to organize claims data into structures that link relevant interventions, outcomes and patient characteristics for the study of pharmaceuticals under investigation; and (2) The formulation of statistical approaches to analyze these data to detect adverse events. This project will develop a data system and empirical framework for identifying and capturing adverse drug events using elements contained in the Medicare claims files. The analysis will exploit information available in Part B claims on drugs, to produce a framework that can be readily adapted to incorporate Part D claims when they come on line next year. 24
 Acumen - Program Goals • Goals for Acumen DEc. IDE Center – Formulate empirical approaches to reliably conduct comparative effectiveness and patient safety analyses using medical claims/records – Structure findings to inform policy decisions – Develop practical computerized surveillance and monitoring systems for tracking adverse events associated with medical 25 interventions
Acumen - Program Goals • Goals for Acumen DEc. IDE Center – Formulate empirical approaches to reliably conduct comparative effectiveness and patient safety analyses using medical claims/records – Structure findings to inform policy decisions – Develop practical computerized surveillance and monitoring systems for tracking adverse events associated with medical 25 interventions
 Brigham and Women’s Hospital DEc. IDE Research Center at Harvard Medical School, Boston Sebastian Schneeweiss, MD, Sc. D
Brigham and Women’s Hospital DEc. IDE Research Center at Harvard Medical School, Boston Sebastian Schneeweiss, MD, Sc. D
 B&W - Core Personnel & Expertise Sebastian Schneeweiss, MD, Sc. D (Pharmacoepidemiology) Jerry Avorn, MD (Geriatric Health Services) David Bates, MD, MPH (Medication Safety) Robert Glynn, Ph. D, Sc. D (Biostatistics) Jennifer Haas, MD, MPH (Health Services) Peter Neumann, Sc. D, (Pharmacoeconomics) Daniel Solomon, MD, MPH (Antiinflammatories) Philip Wang, MD, DPH, (Psychotropics) 27
B&W - Core Personnel & Expertise Sebastian Schneeweiss, MD, Sc. D (Pharmacoepidemiology) Jerry Avorn, MD (Geriatric Health Services) David Bates, MD, MPH (Medication Safety) Robert Glynn, Ph. D, Sc. D (Biostatistics) Jennifer Haas, MD, MPH (Health Services) Peter Neumann, Sc. D, (Pharmacoeconomics) Daniel Solomon, MD, MPH (Antiinflammatories) Philip Wang, MD, DPH, (Psychotropics) 27
 B&W - Affiliations and Partnerships • Brigham & Women’s Hospital - Pharmacoepidemiology - General Internal Medicine • Harvard School of Public Health - Harvard Center for Risk Analysis • New England Medical Center - The Health Institute 28
B&W - Affiliations and Partnerships • Brigham & Women’s Hospital - Pharmacoepidemiology - General Internal Medicine • Harvard School of Public Health - Harvard Center for Risk Analysis • New England Medical Center - The Health Institute 28
 B&W - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Comparative effectiveness of – Psychotropics – NSAIDs – Biologic agents – and a range of other drugs • Developing methods for comparative effectiveness research using observational data • Drug policy evaluation and development • Academic outreach for improved prescribing 29
B&W - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Comparative effectiveness of – Psychotropics – NSAIDs – Biologic agents – and a range of other drugs • Developing methods for comparative effectiveness research using observational data • Drug policy evaluation and development • Academic outreach for improved prescribing 29
 B&W - Key Database Holdings • Medicare (2 states, linked to pharmacy assistance programs, deaths with causes, geocoded physician information) - Medicaid (1 state) - MCBS, MEPS • Province of British Columbia (all residents, drug use independent of payor, hospitalization, physician services and specialty deaths with causes, long-term care) • Partners Health Care: Longitudinal EMR of hospital and outpatient care 30
B&W - Key Database Holdings • Medicare (2 states, linked to pharmacy assistance programs, deaths with causes, geocoded physician information) - Medicaid (1 state) - MCBS, MEPS • Province of British Columbia (all residents, drug use independent of payor, hospitalization, physician services and specialty deaths with causes, long-term care) • Partners Health Care: Longitudinal EMR of hospital and outpatient care 30
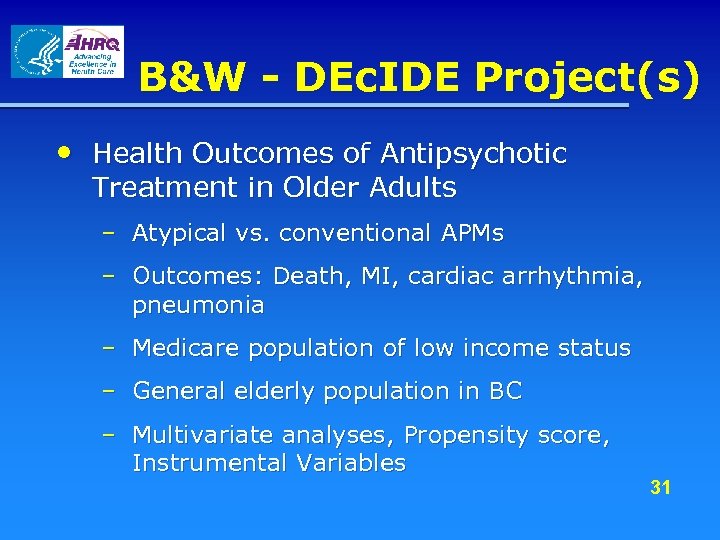 B&W - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Health Outcomes of Antipsychotic Treatment in Older Adults – Atypical vs. conventional APMs – Outcomes: Death, MI, cardiac arrhythmia, pneumonia – Medicare population of low income status – General elderly population in BC – Multivariate analyses, Propensity score, Instrumental Variables 31
B&W - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Health Outcomes of Antipsychotic Treatment in Older Adults – Atypical vs. conventional APMs – Outcomes: Death, MI, cardiac arrhythmia, pneumonia – Medicare population of low income status – General elderly population in BC – Multivariate analyses, Propensity score, Instrumental Variables 31
 Health Outcomes of Antipsychotic Treatment in Older Adults • Abstract: In April 2005 the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an Advisory that atypical antipsychotic medications (APMs) increase mortality in older patients with dementia. However, the Advisory and the ‘Black Box’ warnings added to the labels of atypical APMs did not cover older conventional APMs. Concerns have been raised that, in their search for therapeutic alternatives, physicians may simply switch their elderly patients from atypical APMs to these older conventional agents. Unfortunately, the safety of these conventional APMs in elderly populations is not well understood. Specific Aim: To investigate whether the risk of death as well as possible intermediary outcomes such as acute myocardial infarction (MI), cardiac arrhythmia, and pneumonia, differ for conventional vs. atypical APM use by elderly with dementia or in nursing homes. Study design: We propose two cohort studies of initiators of antipsychotics in a state Medicare and in British Columbia. Many individuals in the state Medicare population >65 are vulnerable elderly patients with low incomes and high levels of comorbid illness severity. To increase generalizability we will conduct a parallel analysis in British Columbia, which is truly population representative for patients 65 years or older. A 180 -day follow-up period was chosen based upon the duration of trials in the FDA’s reanalysis, which ranged from 4 -26 weeks. Study outcomes: Death as identified in vital statistics data including cause of death; acute MI, ventricular arrhythmia, and pneumonia as identified in claims data. Analysis: Unadjusted and multivariable Cox proportional hazards models will be constructed. In confirmatory analyses, we will repeat Cox models using propensity score adjustments to balance independent risk factors for outcomes between drug user groups. We will also use 32 instrumental variable analysis to provide unbiased estimates even if important confounding variables are unmeasured.
Health Outcomes of Antipsychotic Treatment in Older Adults • Abstract: In April 2005 the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an Advisory that atypical antipsychotic medications (APMs) increase mortality in older patients with dementia. However, the Advisory and the ‘Black Box’ warnings added to the labels of atypical APMs did not cover older conventional APMs. Concerns have been raised that, in their search for therapeutic alternatives, physicians may simply switch their elderly patients from atypical APMs to these older conventional agents. Unfortunately, the safety of these conventional APMs in elderly populations is not well understood. Specific Aim: To investigate whether the risk of death as well as possible intermediary outcomes such as acute myocardial infarction (MI), cardiac arrhythmia, and pneumonia, differ for conventional vs. atypical APM use by elderly with dementia or in nursing homes. Study design: We propose two cohort studies of initiators of antipsychotics in a state Medicare and in British Columbia. Many individuals in the state Medicare population >65 are vulnerable elderly patients with low incomes and high levels of comorbid illness severity. To increase generalizability we will conduct a parallel analysis in British Columbia, which is truly population representative for patients 65 years or older. A 180 -day follow-up period was chosen based upon the duration of trials in the FDA’s reanalysis, which ranged from 4 -26 weeks. Study outcomes: Death as identified in vital statistics data including cause of death; acute MI, ventricular arrhythmia, and pneumonia as identified in claims data. Analysis: Unadjusted and multivariable Cox proportional hazards models will be constructed. In confirmatory analyses, we will repeat Cox models using propensity score adjustments to balance independent risk factors for outcomes between drug user groups. We will also use 32 instrumental variable analysis to provide unbiased estimates even if important confounding variables are unmeasured.
 B&W - Program Goals • PI goals for BWH DEc. IDE Research Center – Develop comparative effectiveness research in older adults using health care utilization databases – Drug policy evaluation in light of MMA 33
B&W - Program Goals • PI goals for BWH DEc. IDE Research Center – Develop comparative effectiveness research in older adults using health care utilization databases – Drug policy evaluation in light of MMA 33
 http: //www. brighamandwomens. org/pharmacoepid/Faculty. asp 34
http: //www. brighamandwomens. org/pharmacoepid/Faculty. asp 34
 Duke University DEc. IDE Center David Matchar, MD SLIDES PENDING
Duke University DEc. IDE Center David Matchar, MD SLIDES PENDING
 Duke University Project: Treatment of In-Stent Restenosis SLIDES PENDING 36
Duke University Project: Treatment of In-Stent Restenosis SLIDES PENDING 36
 HMO Research Network CERTs DEc. IDE Center at Harvard Pilgrim / Harvard Medical School Richard Platt, MD
HMO Research Network CERTs DEc. IDE Center at Harvard Pilgrim / Harvard Medical School Richard Platt, MD
 HMORN - Core Personnel & Expertise • Richard Platt, MD, MS Pharmacoepidemiology, infectious disease epidemiology. • Alan Go, MD Internist, clinical epidemiologist focus on cardiovascular and renal disease. • Eric B. Larson, MD improving quality of care, technology assessment, aging and dementia. • Joe V. Selby, MD, MPH family physician, diabetes, primary care delivery, and quality improvement research. 38
HMORN - Core Personnel & Expertise • Richard Platt, MD, MS Pharmacoepidemiology, infectious disease epidemiology. • Alan Go, MD Internist, clinical epidemiologist focus on cardiovascular and renal disease. • Eric B. Larson, MD improving quality of care, technology assessment, aging and dementia. • Joe V. Selby, MD, MPH family physician, diabetes, primary care delivery, and quality improvement research. 38
 HMORN - Core Personnel & Expertise • Edward H. Wagner, MD, MPH -PI Cancer Research Network • Mark C. Hornbrook, Ph. D, health economics, health status measurement, and managed care data systems. • Stephen B. Soumerai, Sc. D effectiveness of interventions to improve drug prescribing; economic access to medications; effects of cost -containment and coverage policies among vulnerable populations. 39
HMORN - Core Personnel & Expertise • Edward H. Wagner, MD, MPH -PI Cancer Research Network • Mark C. Hornbrook, Ph. D, health economics, health status measurement, and managed care data systems. • Stephen B. Soumerai, Sc. D effectiveness of interventions to improve drug prescribing; economic access to medications; effects of cost -containment and coverage policies among vulnerable populations. 39
 HMORN - Core Personnel & Expertise • Tracy Lieu, MD, MPH pediatrician / health services researcher • Jerry H. Gurwitz, MD geriatric medicine and the use of drug therapy in the elderly • Michael Von Korff, Sc. D –chronic illness • Gregory Simon, MD, MPH psychiatry, psychotherapy • John Hsu, MD, MBA medical decision making, impact of prescription drug cost-sharing 40
HMORN - Core Personnel & Expertise • Tracy Lieu, MD, MPH pediatrician / health services researcher • Jerry H. Gurwitz, MD geriatric medicine and the use of drug therapy in the elderly • Michael Von Korff, Sc. D –chronic illness • Gregory Simon, MD, MPH psychiatry, psychotherapy • John Hsu, MD, MBA medical decision making, impact of prescription drug cost-sharing 40
 HMORN - Affiliations and Partnerships HMORN Multi-center collaborations: • NIH Collaborative Clinical Studies Network • CDC Vaccine Safety Datalink • NCI Cancer Research Network HMORN Participating HMOs: • Meyers Primary Care Institute UMass /Fallon Community Health Plan, Worcester MA • Group Health Cooperative, Seattle, WA • Kaiser Permanente: Hawaii, Northwest, Colorado, Southern California, Northern California and Georgia regions • Health. Partners Research Foundation, Minneapolis, MN • Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, MI • Lovelace Clinic Foundation, Albuquerque, New Mexico 41
HMORN - Affiliations and Partnerships HMORN Multi-center collaborations: • NIH Collaborative Clinical Studies Network • CDC Vaccine Safety Datalink • NCI Cancer Research Network HMORN Participating HMOs: • Meyers Primary Care Institute UMass /Fallon Community Health Plan, Worcester MA • Group Health Cooperative, Seattle, WA • Kaiser Permanente: Hawaii, Northwest, Colorado, Southern California, Northern California and Georgia regions • Health. Partners Research Foundation, Minneapolis, MN • Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, MI • Lovelace Clinic Foundation, Albuquerque, New Mexico 41
 HMORN - Research Interests & Center Strengths The HMORN DEc. IDE Center will maximize its access to health plans’ resources to develop information about therapeutic effectiveness within typical clinical settings. We will work directly with health plan decision makers, providers and health plan members to create and implement novel analytical tools and intervention capabilities to improve public health. 42
HMORN - Research Interests & Center Strengths The HMORN DEc. IDE Center will maximize its access to health plans’ resources to develop information about therapeutic effectiveness within typical clinical settings. We will work directly with health plan decision makers, providers and health plan members to create and implement novel analytical tools and intervention capabilities to improve public health. 42
 HMORN - Key Database Holdings Automated data of 11 health plans with 7. 7 million combined members. Accessible data includes: – electronic medical records, – claims systems (utilization, pharmacy, lab), and – membership demographic /eligibility data. 43
HMORN - Key Database Holdings Automated data of 11 health plans with 7. 7 million combined members. Accessible data includes: – electronic medical records, – claims systems (utilization, pharmacy, lab), and – membership demographic /eligibility data. 43
 HMORN - DEc. IDE Project(s) TO #1: Effectiveness of Β-Adrenergic Antagonists on the Risk of Rehospitalization in Adults with Diagnosed Heart Failure Among adults hospitalized for heart failure between 2001 - 2003 and followed through 2004 within two large health plans we will: • examine the rates and predictors of prescription of different β-blockers following discharge. • evaluate the association between different βblockers and the risks of heart failure-specific and all-cause re-hospitalization. 44
HMORN - DEc. IDE Project(s) TO #1: Effectiveness of Β-Adrenergic Antagonists on the Risk of Rehospitalization in Adults with Diagnosed Heart Failure Among adults hospitalized for heart failure between 2001 - 2003 and followed through 2004 within two large health plans we will: • examine the rates and predictors of prescription of different β-blockers following discharge. • evaluate the association between different βblockers and the risks of heart failure-specific and all-cause re-hospitalization. 44
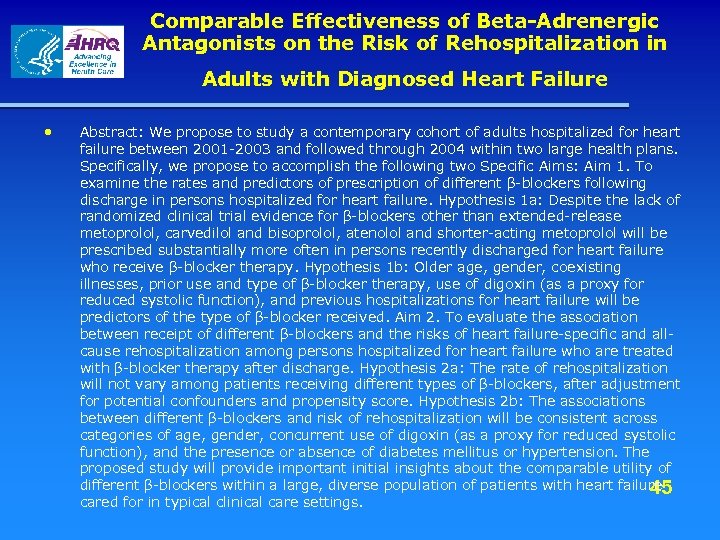 Comparable Effectiveness of Beta-Adrenergic Antagonists on the Risk of Rehospitalization in Adults with Diagnosed Heart Failure • Abstract: We propose to study a contemporary cohort of adults hospitalized for heart failure between 2001 -2003 and followed through 2004 within two large health plans. Specifically, we propose to accomplish the following two Specific Aims: Aim 1. To examine the rates and predictors of prescription of different β-blockers following discharge in persons hospitalized for heart failure. Hypothesis 1 a: Despite the lack of randomized clinical trial evidence for β-blockers other than extended-release metoprolol, carvedilol and bisoprolol, atenolol and shorter-acting metoprolol will be prescribed substantially more often in persons recently discharged for heart failure who receive β-blocker therapy. Hypothesis 1 b: Older age, gender, coexisting illnesses, prior use and type of β-blocker therapy, use of digoxin (as a proxy for reduced systolic function), and previous hospitalizations for heart failure will be predictors of the type of β-blocker received. Aim 2. To evaluate the association between receipt of different β-blockers and the risks of heart failure-specific and allcause rehospitalization among persons hospitalized for heart failure who are treated with β-blocker therapy after discharge. Hypothesis 2 a: The rate of rehospitalization will not vary among patients receiving different types of β-blockers, after adjustment for potential confounders and propensity score. Hypothesis 2 b: The associations between different β-blockers and risk of rehospitalization will be consistent across categories of age, gender, concurrent use of digoxin (as a proxy for reduced systolic function), and the presence or absence of diabetes mellitus or hypertension. The proposed study will provide important initial insights about the comparable utility of different β-blockers within a large, diverse population of patients with heart failure 45 cared for in typical clinical care settings.
Comparable Effectiveness of Beta-Adrenergic Antagonists on the Risk of Rehospitalization in Adults with Diagnosed Heart Failure • Abstract: We propose to study a contemporary cohort of adults hospitalized for heart failure between 2001 -2003 and followed through 2004 within two large health plans. Specifically, we propose to accomplish the following two Specific Aims: Aim 1. To examine the rates and predictors of prescription of different β-blockers following discharge in persons hospitalized for heart failure. Hypothesis 1 a: Despite the lack of randomized clinical trial evidence for β-blockers other than extended-release metoprolol, carvedilol and bisoprolol, atenolol and shorter-acting metoprolol will be prescribed substantially more often in persons recently discharged for heart failure who receive β-blocker therapy. Hypothesis 1 b: Older age, gender, coexisting illnesses, prior use and type of β-blocker therapy, use of digoxin (as a proxy for reduced systolic function), and previous hospitalizations for heart failure will be predictors of the type of β-blocker received. Aim 2. To evaluate the association between receipt of different β-blockers and the risks of heart failure-specific and allcause rehospitalization among persons hospitalized for heart failure who are treated with β-blocker therapy after discharge. Hypothesis 2 a: The rate of rehospitalization will not vary among patients receiving different types of β-blockers, after adjustment for potential confounders and propensity score. Hypothesis 2 b: The associations between different β-blockers and risk of rehospitalization will be consistent across categories of age, gender, concurrent use of digoxin (as a proxy for reduced systolic function), and the presence or absence of diabetes mellitus or hypertension. The proposed study will provide important initial insights about the comparable utility of different β-blockers within a large, diverse population of patients with heart failure 45 cared for in typical clinical care settings.
 HMORN - Program Goals • Develop and disseminate strategies for the appropriate and equitable delivery of therapeutics 46
HMORN - Program Goals • Develop and disseminate strategies for the appropriate and equitable delivery of therapeutics 46
 Johns Hopkins University DEc. IDE Center Albert W. Wu, MD, MPH, PI Eric B. Bass, MD, MPH, Co-PI
Johns Hopkins University DEc. IDE Center Albert W. Wu, MD, MPH, PI Eric B. Bass, MD, MPH, Co-PI
 JHU - Core Personnel & Expertise • • • Gerard Anderson, Ph. D – Health Policy Eric Bass, MD, MPH – Technology Assessment Sydney Dy, MD, MPH – Quality of Care Dan Ford, MD – Mental Health Outcomes Laura Morlock, Ph. D – Organization & Management Jodi Segal, MD – Clinical Epidemiology Don Steinwachs, Ph. D – Health Services Research Albert Wu, MD, MPH – Patient Outcomes Scott Zeger, Ph. D – Statistical Methods 48
JHU - Core Personnel & Expertise • • • Gerard Anderson, Ph. D – Health Policy Eric Bass, MD, MPH – Technology Assessment Sydney Dy, MD, MPH – Quality of Care Dan Ford, MD – Mental Health Outcomes Laura Morlock, Ph. D – Organization & Management Jodi Segal, MD – Clinical Epidemiology Don Steinwachs, Ph. D – Health Services Research Albert Wu, MD, MPH – Patient Outcomes Scott Zeger, Ph. D – Statistical Methods 48
 JHU - Affiliations and Partnerships Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Nursing Ingenix, Inc. 49
JHU - Affiliations and Partnerships Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Nursing Ingenix, Inc. 49
 JHU - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Analyses of utilization and outcomes using large administrative datasets • • • Analysis of clinical outcomes using cohort data Quality of care and patient safety Cost-effectiveness of medications and new technologies • Systematic reviews of evidence • Analytic methods for longitudinal data and risk adjustment • Chronic conditions including hypertension, cardiovascular dsease, diabetes mellitus, and hematologic disorders 50
JHU - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Analyses of utilization and outcomes using large administrative datasets • • • Analysis of clinical outcomes using cohort data Quality of care and patient safety Cost-effectiveness of medications and new technologies • Systematic reviews of evidence • Analytic methods for longitudinal data and risk adjustment • Chronic conditions including hypertension, cardiovascular dsease, diabetes mellitus, and hematologic disorders 50
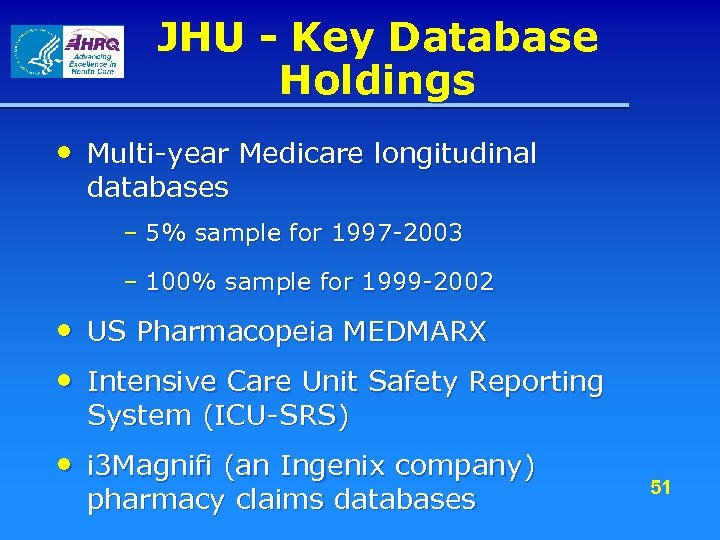 JHU - Key Database Holdings • Multi-year Medicare longitudinal databases – 5% sample for 1997 -2003 – 100% sample for 1999 -2002 • US Pharmacopeia MEDMARX • Intensive Care Unit Safety Reporting System (ICU-SRS) • i 3 Magnifi (an Ingenix company) pharmacy claims databases 51
JHU - Key Database Holdings • Multi-year Medicare longitudinal databases – 5% sample for 1997 -2003 – 100% sample for 1999 -2002 • US Pharmacopeia MEDMARX • Intensive Care Unit Safety Reporting System (ICU-SRS) • i 3 Magnifi (an Ingenix company) pharmacy claims databases 51
 JHU - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of New Therapies for Glucose Control in Diabetes Mellitus – Aims of this project are to develop methodology to allow for the rapid evaluation of new therapies, using large administrative databases; and to analyze such a dataset to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of inhaled insulin (or other new treatment) for diabetes. 52
JHU - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of New Therapies for Glucose Control in Diabetes Mellitus – Aims of this project are to develop methodology to allow for the rapid evaluation of new therapies, using large administrative databases; and to analyze such a dataset to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of inhaled insulin (or other new treatment) for diabetes. 52
 Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of New Therapies for Glucose Control in Diabetes Mellitus • Abstract: Investigators will be evaluating the comparative effectiveness and safety of a new therapy for treatment of diabetes mellitus (DM). To do so, the team will devise appropriate and novel methodology for the study of the effectiveness of inhaled insulin using large administrative datasets. The study team will include experts in the design of observational studies and analysis of large data sets, as well as experts in DM research. The project will use unique databases, which include information on patient characteristics, medication use, clinical outcomes, and resource utilization. The study will examine the initial pattern of use of inhaled insulin. The study will identify comparison groups of patients with DM, and estimate outcome rates during a three to six month period, focusing on clinical outcomes such as medication-related adverse events, and resource utilization including hospitalization rates and costs. The study will compare the outcome rates in the comparison populations to the rates among recipients of the new therapy. An important question will be to identify potential adverse events related to treatment, including pulmonary complications. As these will be observational studies, the investigators will carefully address risk adjustment by using propensity scores, sensitivity analyses or other methods. The study will be one of the first efforts to use a large administrative dataset to evaluate the diffusion, effectiveness and safety of a new medication in its first year of use. The methods developed and results 53 obtained should have wide applicability for future research, policy, and practice.
Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of New Therapies for Glucose Control in Diabetes Mellitus • Abstract: Investigators will be evaluating the comparative effectiveness and safety of a new therapy for treatment of diabetes mellitus (DM). To do so, the team will devise appropriate and novel methodology for the study of the effectiveness of inhaled insulin using large administrative datasets. The study team will include experts in the design of observational studies and analysis of large data sets, as well as experts in DM research. The project will use unique databases, which include information on patient characteristics, medication use, clinical outcomes, and resource utilization. The study will examine the initial pattern of use of inhaled insulin. The study will identify comparison groups of patients with DM, and estimate outcome rates during a three to six month period, focusing on clinical outcomes such as medication-related adverse events, and resource utilization including hospitalization rates and costs. The study will compare the outcome rates in the comparison populations to the rates among recipients of the new therapy. An important question will be to identify potential adverse events related to treatment, including pulmonary complications. As these will be observational studies, the investigators will carefully address risk adjustment by using propensity scores, sensitivity analyses or other methods. The study will be one of the first efforts to use a large administrative dataset to evaluate the diffusion, effectiveness and safety of a new medication in its first year of use. The methods developed and results 53 obtained should have wide applicability for future research, policy, and practice.
 JHU - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center – To develop the capacity to conduct rapid evaluations of the use, effectiveness and safety of new treatments using large administrative datasets – To foster policy relevant research involving scientists and clinicians across the University – To develop new research tools that can be used for effectiveness and outcomes research using large datasets 54
JHU - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center – To develop the capacity to conduct rapid evaluations of the use, effectiveness and safety of new treatments using large administrative datasets – To foster policy relevant research involving scientists and clinicians across the University – To develop new research tools that can be used for effectiveness and outcomes research using large datasets 54
 Outcome DEc. IDE Center at Outcome Sciences, Inc. Richard E. Gliklich, MD
Outcome DEc. IDE Center at Outcome Sciences, Inc. Richard E. Gliklich, MD
 Outcome - Core Personnel & Expertise • Richard Gliklich MD, Principal Investigator – 21 years experience in real-world observational and investigational studies. Designed and implemented more than 70 registries and high quality prospective data programs. • Nancy A. Dreyer, MPH, Ph. D, Program Director – 30 years experience in epidemiology and drug safety. • Fiona Smith, MPH Project Manager – 7 years experience working on projects with CMS 56 and AHRQ.
Outcome - Core Personnel & Expertise • Richard Gliklich MD, Principal Investigator – 21 years experience in real-world observational and investigational studies. Designed and implemented more than 70 registries and high quality prospective data programs. • Nancy A. Dreyer, MPH, Ph. D, Program Director – 30 years experience in epidemiology and drug safety. • Fiona Smith, MPH Project Manager – 7 years experience working on projects with CMS 56 and AHRQ.
 Outcome - Core Personnel & Expertise Additional core and collaborative personnel with expertise in – program design – informatics – privacy – quality – pharmacoeconomics and – analytics related to registries, postapproval studies, quality initiatives and safety surveillance programs. 57
Outcome - Core Personnel & Expertise Additional core and collaborative personnel with expertise in – program design – informatics – privacy – quality – pharmacoeconomics and – analytics related to registries, postapproval studies, quality initiatives and safety surveillance programs. 57
 Outcome - Affiliations and Partnerships • American Heart Association (AHA) – Largest independent supporter of cardiovascular disease research. Partner for Get With The Guidelines (sm) programs. • Primary Care Network (PCN) – Association of 72, 000 health care providers and professionals • Consortium of Rheumatology Researchers of North America (CORRONA) – Nationwide network of practicing rheumatologists Other Affiliations: Many additional partnerships and affiliations with large health 58 care provider networks and medical specialty associations
Outcome - Affiliations and Partnerships • American Heart Association (AHA) – Largest independent supporter of cardiovascular disease research. Partner for Get With The Guidelines (sm) programs. • Primary Care Network (PCN) – Association of 72, 000 health care providers and professionals • Consortium of Rheumatology Researchers of North America (CORRONA) – Nationwide network of practicing rheumatologists Other Affiliations: Many additional partnerships and affiliations with large health 58 care provider networks and medical specialty associations
 Outcome - Research Interests & Center Strengths The Outcome DEc. IDE Center is particularly well-suited to developing and implementing registries and other prospective data capture and surveillance programs. – Expertise and experience in developing and managing registries (more than 70 initiated) – Existing, productive networks in several of the Priority Conditions connected through a common information platform v >2500 hospitals and several thousand physician offices and pharmacies are currently participating in prospective data programs – Informatics expertise and infrastructure for collecting data directly from practitioners and patients via web, IVR, fax, and from existing health information systems – Rapid, large scale prospective study execution in real-world clinical 59 sites
Outcome - Research Interests & Center Strengths The Outcome DEc. IDE Center is particularly well-suited to developing and implementing registries and other prospective data capture and surveillance programs. – Expertise and experience in developing and managing registries (more than 70 initiated) – Existing, productive networks in several of the Priority Conditions connected through a common information platform v >2500 hospitals and several thousand physician offices and pharmacies are currently participating in prospective data programs – Informatics expertise and infrastructure for collecting data directly from practitioners and patients via web, IVR, fax, and from existing health information systems – Rapid, large scale prospective study execution in real-world clinical 59 sites
 Outcome - Key Database Holdings • Existing data from – Cardiovascular disease and stroke registries – Rheumatologic disease registries – Oncology registries 60
Outcome - Key Database Holdings • Existing data from – Cardiovascular disease and stroke registries – Rheumatologic disease registries – Oncology registries 60
 Outcome - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Establishing Registries for Evaluating Patient Outcomes – Defining Standards – Produce a reference for the design and use of successful registries both for registries that may be required by CMS and registries set up for other purposes in both the public and private sectors. It will focus on establishing standards for n Creation and operation of registries n Evaluation of registries n Scientific evaluation of outcomes using registry 61 data
Outcome - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Establishing Registries for Evaluating Patient Outcomes – Defining Standards – Produce a reference for the design and use of successful registries both for registries that may be required by CMS and registries set up for other purposes in both the public and private sectors. It will focus on establishing standards for n Creation and operation of registries n Evaluation of registries n Scientific evaluation of outcomes using registry 61 data
 Establishing Registries for Evaluating Patient Outcomes – Defining Standards • Abstract: The purpose of this project is to produce a reference for the design and use of successful registries. The project will produce a web-based reference document defining standards and best practices. It will be organized into three sections: creation and operation of registries designed to answer scientific questions about patient outcomes of treatment; evaluation of registries and scientific evaluation of outcomes using registry data. During the course of the project a workshop will be convened that will include scientists and technologists with expertise in the design, implementation and analysis of registries data. 62
Establishing Registries for Evaluating Patient Outcomes – Defining Standards • Abstract: The purpose of this project is to produce a reference for the design and use of successful registries. The project will produce a web-based reference document defining standards and best practices. It will be organized into three sections: creation and operation of registries designed to answer scientific questions about patient outcomes of treatment; evaluation of registries and scientific evaluation of outcomes using registry data. During the course of the project a workshop will be convened that will include scientists and technologists with expertise in the design, implementation and analysis of registries data. 62
 Outcome - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center – Promote rapid generation of high-quality prospective data to better evaluate health care products, therapies and services – Serve as a resource to and collaborator with other DEc. IDE Centers • PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network – Become the primary pathway for evidence development within HHS through a consistent track record of excellence, speed and efficiency 63
Outcome - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center – Promote rapid generation of high-quality prospective data to better evaluate health care products, therapies and services – Serve as a resource to and collaborator with other DEc. IDE Centers • PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network – Become the primary pathway for evidence development within HHS through a consistent track record of excellence, speed and efficiency 63
 201 Broadway Cambridge, MA 02139 64
201 Broadway Cambridge, MA 02139 64
 RTI DEc. IDE Center Kathleen N. Lohr, Ph. D. , Principal Investigator Lucy A. Savitz, Ph. D. , MBA, Co-PI RTI International (www. rti. org) 3040 Cornwallis Drive Research Triangle Park, NC USA
RTI DEc. IDE Center Kathleen N. Lohr, Ph. D. , Principal Investigator Lucy A. Savitz, Ph. D. , MBA, Co-PI RTI International (www. rti. org) 3040 Cornwallis Drive Research Triangle Park, NC USA
 RTI - Core Personnel and Expertise • Kathleen Lohr, Ph. D: evidence-based practice, quality of care, quality of life assessment, health policy • Lucy Savitz, Ph. D, MBA: patient safety, quality improvement, health informatics, organizational development, research translation • Linda Lux, MPA: evidence-based practice, chronic disease, project management 66
RTI - Core Personnel and Expertise • Kathleen Lohr, Ph. D: evidence-based practice, quality of care, quality of life assessment, health policy • Lucy Savitz, Ph. D, MBA: patient safety, quality improvement, health informatics, organizational development, research translation • Linda Lux, MPA: evidence-based practice, chronic disease, project management 66
 RTI - Affiliations and Partnerships • Intermountain Health Care: Brent James, MD, M. Stat. • Baylor Health Care System: David Ballard, MD, Ph. D. • Providence Health System: K. Bruce Bayley, Ph. D. • Health. Insight (UT-NV QIO): Scott Williams, MD, MPH • Utah Department of Health: Wu Xu, Ph. D. • VA IDEAS Center: Matthew Samore, MD, MPH • National Association of Health Data Organizations: Denise Love, MBA, RN • Governor Scott M. Matheson Center for Health Care Studies, University of Utah: Richard Sperry, Ph. D. 67
RTI - Affiliations and Partnerships • Intermountain Health Care: Brent James, MD, M. Stat. • Baylor Health Care System: David Ballard, MD, Ph. D. • Providence Health System: K. Bruce Bayley, Ph. D. • Health. Insight (UT-NV QIO): Scott Williams, MD, MPH • Utah Department of Health: Wu Xu, Ph. D. • VA IDEAS Center: Matthew Samore, MD, MPH • National Association of Health Data Organizations: Denise Love, MBA, RN • Governor Scott M. Matheson Center for Health Care Studies, University of Utah: Richard Sperry, Ph. D. 67
 RTI - Research Interests and Center Strengths • Research Interests – Clinical and therapeutic effectiveness studies – Quality of care and patient safety – Pharmaceutical and Medicare Part D studies – Strategies for improving the efficiency and effectiveness (organization, management, & delivery) of health care • Center Strengths – Cohesive research laboratory for registry and database analyses, using GIS and sophisticated statistical applications – Extensive network of health systems and public and private sector organizations – Special capabilities in clinical medicine, patient safety, quality improvement, evidence-based practice, and health information technology – Deep knowledge of, experience with related AHRQ programs – Keen grasp of pressing Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP issues 68
RTI - Research Interests and Center Strengths • Research Interests – Clinical and therapeutic effectiveness studies – Quality of care and patient safety – Pharmaceutical and Medicare Part D studies – Strategies for improving the efficiency and effectiveness (organization, management, & delivery) of health care • Center Strengths – Cohesive research laboratory for registry and database analyses, using GIS and sophisticated statistical applications – Extensive network of health systems and public and private sector organizations – Special capabilities in clinical medicine, patient safety, quality improvement, evidence-based practice, and health information technology – Deep knowledge of, experience with related AHRQ programs – Keen grasp of pressing Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP issues 68
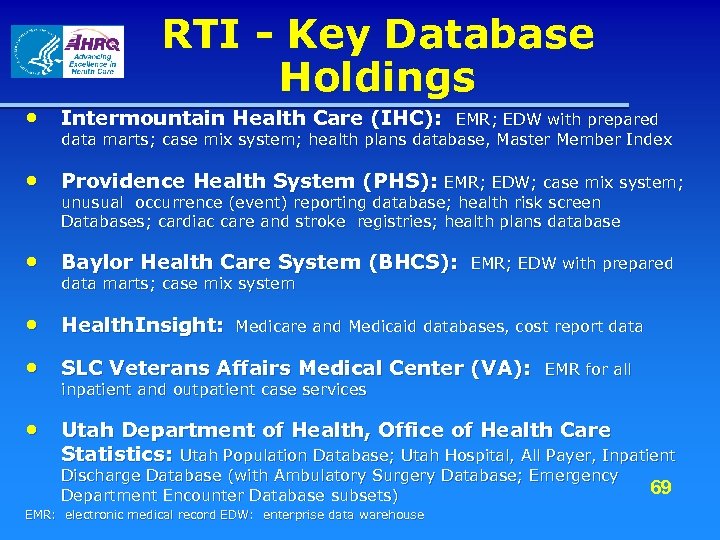 RTI - Key Database Holdings • Intermountain Health Care (IHC): EMR; EDW with prepared data marts; case mix system; health plans database, Master Member Index • Providence Health System (PHS): EMR; EDW; case mix system; unusual occurrence (event) reporting database; health risk screen Databases; cardiac care and stroke registries; health plans database • Baylor Health Care System (BHCS): data marts; case mix system EMR; EDW with prepared • Health. Insight: Medicare and Medicaid databases, cost report data • SLC Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VA): inpatient and outpatient case services EMR for all • Utah Department of Health, Office of Health Care Statistics: Utah Population Database; Utah Hospital, All Payer, Inpatient Discharge Database (with Ambulatory Surgery Database; Emergency 69 Department Encounter Database subsets) EMR: electronic medical record EDW: enterprise data warehouse
RTI - Key Database Holdings • Intermountain Health Care (IHC): EMR; EDW with prepared data marts; case mix system; health plans database, Master Member Index • Providence Health System (PHS): EMR; EDW; case mix system; unusual occurrence (event) reporting database; health risk screen Databases; cardiac care and stroke registries; health plans database • Baylor Health Care System (BHCS): data marts; case mix system EMR; EDW with prepared • Health. Insight: Medicare and Medicaid databases, cost report data • SLC Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VA): inpatient and outpatient case services EMR for all • Utah Department of Health, Office of Health Care Statistics: Utah Population Database; Utah Hospital, All Payer, Inpatient Discharge Database (with Ambulatory Surgery Database; Emergency 69 Department Encounter Database subsets) EMR: electronic medical record EDW: enterprise data warehouse
 RTI - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Medicare Prescription Drug Data Development: Methods for Improving Patient Safety and Pharmacovigilance Using Observational Data – – Critically assess current techniques and methods for pharmacoepidemiologic and pharmacovigilance research, standardize drug prescription statistics and drug safety measures, create simulated database, and conduct pilot studies Judith Shinogle, Ph. D. , Project Director • Effective Health Care: Patient Safety and Therapeutic Effectiveness – – Support the EHC program by planning a series of 3 DEc. IDE meetings and developing a journal supplement on these topics Lucy Savitz, Ph. D. , MBA, Project Director 70
RTI - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Medicare Prescription Drug Data Development: Methods for Improving Patient Safety and Pharmacovigilance Using Observational Data – – Critically assess current techniques and methods for pharmacoepidemiologic and pharmacovigilance research, standardize drug prescription statistics and drug safety measures, create simulated database, and conduct pilot studies Judith Shinogle, Ph. D. , Project Director • Effective Health Care: Patient Safety and Therapeutic Effectiveness – – Support the EHC program by planning a series of 3 DEc. IDE meetings and developing a journal supplement on these topics Lucy Savitz, Ph. D. , MBA, Project Director 70
 Medicare Prescription Drug Data Development: Methods for Improving Patient Safety and Pharmacovigilance Using Observational Data • Abstract: The Medicare Modernization Act and the Medicare Part D benefit offers new resources in pharmacoepidemiology. The investigators will develop a methodological toolbox and data analytical framework for pharmacoepidemiologic research using population-based claims and administrative data sources. The investigators will first perform a critical assessment of current techniques and methods used in pharmacoepidemiologic and pharmacovigilance research. From this literature review and with input stakeholders, the investigators will develop an evidence-based approach to standardizing drug prescription statistics and process or outcome measures of the safety of drugs or drug classes for specific clinical conditions. In conjunction with our DEc. IDE partners, we will develop a database that links pharmacy, outpatient, inpatient, physician office, and emergency department claims. This simulated database will be similar to the one that will be available from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services once the Medicare Prescription Drug Benefit is operable. Finally, using these data, the investigators will conduct pilot studies to examine the feasibility of prototypical measures pertaining to specific drugs or classes of drugs identified from the earlier tasks. 71
Medicare Prescription Drug Data Development: Methods for Improving Patient Safety and Pharmacovigilance Using Observational Data • Abstract: The Medicare Modernization Act and the Medicare Part D benefit offers new resources in pharmacoepidemiology. The investigators will develop a methodological toolbox and data analytical framework for pharmacoepidemiologic research using population-based claims and administrative data sources. The investigators will first perform a critical assessment of current techniques and methods used in pharmacoepidemiologic and pharmacovigilance research. From this literature review and with input stakeholders, the investigators will develop an evidence-based approach to standardizing drug prescription statistics and process or outcome measures of the safety of drugs or drug classes for specific clinical conditions. In conjunction with our DEc. IDE partners, we will develop a database that links pharmacy, outpatient, inpatient, physician office, and emergency department claims. This simulated database will be similar to the one that will be available from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services once the Medicare Prescription Drug Benefit is operable. Finally, using these data, the investigators will conduct pilot studies to examine the feasibility of prototypical measures pertaining to specific drugs or classes of drugs identified from the earlier tasks. 71
 Effective Health Care: Patients Safety and Therapeutic Effectiveness • Abstract: The investigators will carry out a three-faceted task on “Effective Health Care: Therapeutic Effectiveness and Patient Safety. ” Investigators will first attend and summarize three AHRQ meetings on “Genomics and Medicine, ” “Medication Therapy Management (MTM) Programs, ” and “Health Care for Older Adults with Multiple Health Conditions. ” Second, drawing on critical issues identified at these AHRQ meetings, the investigators will then plan and convene a major “evidence showcase” meeting on therapeutic effectiveness (particularly pharmaceuticals, especially in light of the Medicare Modernization Act and the onset of the Medicare Part D benefit for outpatient drugs) and patient safety. The third element of the project is to solicit or invite papers as possible manuscripts for a journal supplement to be published in late 2006 to early 2007. The overall theme of the journal supplement will be effective health care, particularly the links between therapeutic benefits and harms, on the one hand, and patient safety, on the other. Papers may come from the evidence showcase meeting, other DEc. IDE Centers, and other AHRQ 72 supported organizations.
Effective Health Care: Patients Safety and Therapeutic Effectiveness • Abstract: The investigators will carry out a three-faceted task on “Effective Health Care: Therapeutic Effectiveness and Patient Safety. ” Investigators will first attend and summarize three AHRQ meetings on “Genomics and Medicine, ” “Medication Therapy Management (MTM) Programs, ” and “Health Care for Older Adults with Multiple Health Conditions. ” Second, drawing on critical issues identified at these AHRQ meetings, the investigators will then plan and convene a major “evidence showcase” meeting on therapeutic effectiveness (particularly pharmaceuticals, especially in light of the Medicare Modernization Act and the onset of the Medicare Part D benefit for outpatient drugs) and patient safety. The third element of the project is to solicit or invite papers as possible manuscripts for a journal supplement to be published in late 2006 to early 2007. The overall theme of the journal supplement will be effective health care, particularly the links between therapeutic benefits and harms, on the one hand, and patient safety, on the other. Papers may come from the evidence showcase meeting, other DEc. IDE Centers, and other AHRQ 72 supported organizations.
 RTI - Program Goals • Goals for RTI DEc. IDE Center 1. Conduct rapid-cycle research in therapeutic effectiveness, patient safety, and quality of care issues with a focus on Medicare, Medicaid, and SCHIP Program populations. 2. Develop methods to advance data collection, database design, analysis, and information dissemination to improve quality of care and patient safety through applied health services research. 3. Working with our partners, AHRQ, other DEc. IDE Centers, and other AHRQ programs, create tools and analytic approaches to accomplish DEc. IDE program goals. • Suggested Goals for AHRQ DEc. IDE Network 1. Achieve fruitful collaborations between AHRQ and other federal agencies, across the DEc. IDE Centers, and across AHRQ programs in comparative effectiveness studies. 2. Identify and pursue mechanisms for shared learning and accelerated diffusion of research findings. 3. Translate research results into practical tools and strategies to 73 promote safe and high quality health care delivery.
RTI - Program Goals • Goals for RTI DEc. IDE Center 1. Conduct rapid-cycle research in therapeutic effectiveness, patient safety, and quality of care issues with a focus on Medicare, Medicaid, and SCHIP Program populations. 2. Develop methods to advance data collection, database design, analysis, and information dissemination to improve quality of care and patient safety through applied health services research. 3. Working with our partners, AHRQ, other DEc. IDE Centers, and other AHRQ programs, create tools and analytic approaches to accomplish DEc. IDE program goals. • Suggested Goals for AHRQ DEc. IDE Network 1. Achieve fruitful collaborations between AHRQ and other federal agencies, across the DEc. IDE Centers, and across AHRQ programs in comparative effectiveness studies. 2. Identify and pursue mechanisms for shared learning and accelerated diffusion of research findings. 3. Translate research results into practical tools and strategies to 73 promote safe and high quality health care delivery.
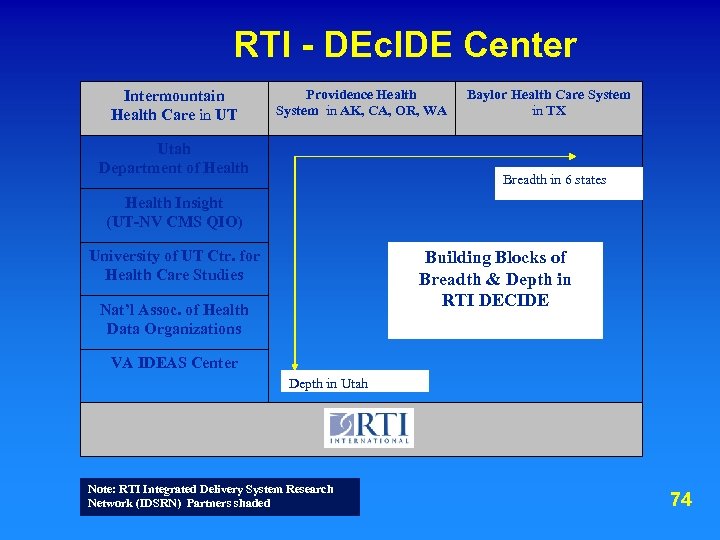 RTI - DEc. IDE Center Intermountain Health Care UT Health Care in UT Providence Health System in AK, CA, OR, WA Utah Department of Health Baylor Health Care System in TX Breadth in 6 states Health Insight (UT-NV CMS QIO) University of UT Ctr. for Health Care Studies Building Blocks of Breadth & Depth in RTI DECIDE Nat’l Assoc. of Health Data Organizations VA IDEAS Center Depth in Utah Note: RTI Integrated Delivery System Research Network (IDSRN) Partners shaded 74
RTI - DEc. IDE Center Intermountain Health Care UT Health Care in UT Providence Health System in AK, CA, OR, WA Utah Department of Health Baylor Health Care System in TX Breadth in 6 states Health Insight (UT-NV CMS QIO) University of UT Ctr. for Health Care Studies Building Blocks of Breadth & Depth in RTI DECIDE Nat’l Assoc. of Health Data Organizations VA IDEAS Center Depth in Utah Note: RTI Integrated Delivery System Research Network (IDSRN) Partners shaded 74
 CO-DEc. IDE Collaboration at the University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center John F. Steiner, MD, MPH Principal Investigator
CO-DEc. IDE Collaboration at the University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center John F. Steiner, MD, MPH Principal Investigator
 CO - Core Personnel & Expertise • John F. Steiner, MD, MPH – primary care, adherence • David West, Ph. D – Medicaid, primary care • Karl Hammermeister, MD – cardiovascular disease • William Henderson, Ph. D – surgical/ perioperative care • Andrew Kramer, MD – post-acute/nursing home care, Medicare policy • Richard Hamman, MD, Dr. PH – diabetes, epidemiology • Robert Valuck, Ph. D – Medicaid, mental health • Wilson Pace, MD – primary care, practice-based research • And others…. 76
CO - Core Personnel & Expertise • John F. Steiner, MD, MPH – primary care, adherence • David West, Ph. D – Medicaid, primary care • Karl Hammermeister, MD – cardiovascular disease • William Henderson, Ph. D – surgical/ perioperative care • Andrew Kramer, MD – post-acute/nursing home care, Medicare policy • Richard Hamman, MD, Dr. PH – diabetes, epidemiology • Robert Valuck, Ph. D – Medicaid, mental health • Wilson Pace, MD – primary care, practice-based research • And others…. 76
 CO - Affiliations and Partnerships • University of Colorado Health Sciences Center – Colorado Health Outcomes Program – Children’s Outcomes Research Program – SNOCAP Practice-based Research Network – Department of Preventive Medicine/Biometrics – School of Pharmacy – Division of Healthcare Policy and Research • • Abt Associates Medical Group Management Association Robert Graham Center American Academy of Family Physicians – National 77 Research Network
CO - Affiliations and Partnerships • University of Colorado Health Sciences Center – Colorado Health Outcomes Program – Children’s Outcomes Research Program – SNOCAP Practice-based Research Network – Department of Preventive Medicine/Biometrics – School of Pharmacy – Division of Healthcare Policy and Research • • Abt Associates Medical Group Management Association Robert Graham Center American Academy of Family Physicians – National 77 Research Network
 CO - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Quality and Safety of drugs and devices in: – Primary Care – Child Health (Medicaid, SCHIP) – Post-acute and Long-term Care – Mental Health Care – Cardiovascular Diseases – Diabetes – Underserved Populations – Palliative Care • Organization & delivery of pharmaceutical care 78
CO - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Quality and Safety of drugs and devices in: – Primary Care – Child Health (Medicaid, SCHIP) – Post-acute and Long-term Care – Mental Health Care – Cardiovascular Diseases – Diabetes – Underserved Populations – Palliative Care • Organization & delivery of pharmaceutical care 78
 CO - Key Database Holdings • National Surgical Quality Improvement Programs VA, Private Sector • Primary Care Research Unit – secondary dataset library (NAMCS, MEPS, HCUP, etc. ) • National Home Care and Hospice Survey • Medicare Datasets: MCBS, OASIS, Medicare claims, MEDPAR stroke data • PHARMetrics integrated outcomes database • Multi-state Medicaid database 79
CO - Key Database Holdings • National Surgical Quality Improvement Programs VA, Private Sector • Primary Care Research Unit – secondary dataset library (NAMCS, MEPS, HCUP, etc. ) • National Home Care and Hospice Survey • Medicare Datasets: MCBS, OASIS, Medicare claims, MEDPAR stroke data • PHARMetrics integrated outcomes database • Multi-state Medicaid database 79
 CO - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Task Order 1: Medical Management of Congestive Heart Failure and the Effectiveness of Isosorbide Dinitrate and Hydralazine 80
CO - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Task Order 1: Medical Management of Congestive Heart Failure and the Effectiveness of Isosorbide Dinitrate and Hydralazine 80
 Medical Management of Congestive Heart Failure and the Effectiveness of Isosorbide Dinitrate and Hydralazine • Abstract: Heart failure results in significant mortality and morbidity despite the benefits ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone inhibition. This has led to investigation of adjunctive therapies, including the combination of hydralazine and isosorbide. The recent A-He. FT trial found that this combination was effective in reducing mortality and heart failure hospitalizations in selfidentified African Americans receiving conventional therapy for heart failure. The study created additional questions about the effectiveness of this combination in unselected community-based African-American patients with systolic heart failure, its effect in other racial/ethnic subgroups, and the impact of co-administered agents for heart failure on this effect. The study aims for this task order are: 1) to assess the association between treatment with isosorbide/hydralazine and the outcomes of death and re-hospitalization in community-based populations with heart failure, after adjustment for patient, provider, and hospital characteristics; 2) to assess the strength of this association in patients treated with various combinations of evidence-based therapies, including ACE-inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists; and 3) to compare this association between African-American and patients from other racial groups. These aims will be explored using two datasets: national VA pharmacy and clinical data, and the CMS-sponsored National Heart Care Project. 81
Medical Management of Congestive Heart Failure and the Effectiveness of Isosorbide Dinitrate and Hydralazine • Abstract: Heart failure results in significant mortality and morbidity despite the benefits ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone inhibition. This has led to investigation of adjunctive therapies, including the combination of hydralazine and isosorbide. The recent A-He. FT trial found that this combination was effective in reducing mortality and heart failure hospitalizations in selfidentified African Americans receiving conventional therapy for heart failure. The study created additional questions about the effectiveness of this combination in unselected community-based African-American patients with systolic heart failure, its effect in other racial/ethnic subgroups, and the impact of co-administered agents for heart failure on this effect. The study aims for this task order are: 1) to assess the association between treatment with isosorbide/hydralazine and the outcomes of death and re-hospitalization in community-based populations with heart failure, after adjustment for patient, provider, and hospital characteristics; 2) to assess the strength of this association in patients treated with various combinations of evidence-based therapies, including ACE-inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists; and 3) to compare this association between African-American and patients from other racial groups. These aims will be explored using two datasets: national VA pharmacy and clinical data, and the CMS-sponsored National Heart Care Project. 81
 CO - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center Conduct pharmaceutical effectiveness research in areas of clinical expertise Develop and expand existing partnerships • PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network Identify and develop methodological “best practices” for effectiveness research 82
CO - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center Conduct pharmaceutical effectiveness research in areas of clinical expertise Develop and expand existing partnerships • PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network Identify and develop methodological “best practices” for effectiveness research 82
 Chicago-Area DEc. IDE Center Coordinating Site: Center for Pharmacoeconomic Research at the University of Illinois at Chicago Glen T. Schumock, Pharm. D, MBA (PI)
Chicago-Area DEc. IDE Center Coordinating Site: Center for Pharmacoeconomic Research at the University of Illinois at Chicago Glen T. Schumock, Pharm. D, MBA (PI)
 Chicago - Consortium Partners • University of Illinois at Chicago – Colleges of Pharmacy, Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, and School of Public Health • University of Chicago • Northwestern University • VA Midwest Center for Health Services and Policy Research • Blue Cross/Blue Shield Association Technology Assessment Center and EPC 84
Chicago - Consortium Partners • University of Illinois at Chicago – Colleges of Pharmacy, Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, and School of Public Health • University of Chicago • Northwestern University • VA Midwest Center for Health Services and Policy Research • Blue Cross/Blue Shield Association Technology Assessment Center and EPC 84
 Chicago - Center Organization • Steering Committee • Site Coordinators – UIC, NU, UC, BCBSA, VA MCHSRP • Cores – clinical support, data acquisition, data analysis and quality assurance • Management and support staff • Over 40 key personnel 85
Chicago - Center Organization • Steering Committee • Site Coordinators – UIC, NU, UC, BCBSA, VA MCHSRP • Cores – clinical support, data acquisition, data analysis and quality assurance • Management and support staff • Over 40 key personnel 85
 Chicago - Selected Key Personnel N Aronson, Ph. D BCBSA J Bauman, Pharm. D UIC Technology assessment Pharmacy practice W Beck, Ph. D UIC Pharmacogenomics C Bennett, MD, Ph. D NU D Meltzer, MD, Ph. D UC Adverse drug events Health economics G Schumock, Pharm. D, MBA K Weiss, MD, MPH Pharmacoeconomi cs Epidemiology J Zwanziger, Ph. D UIC VA & NU UIC 86 Health policy
Chicago - Selected Key Personnel N Aronson, Ph. D BCBSA J Bauman, Pharm. D UIC Technology assessment Pharmacy practice W Beck, Ph. D UIC Pharmacogenomics C Bennett, MD, Ph. D NU D Meltzer, MD, Ph. D UC Adverse drug events Health economics G Schumock, Pharm. D, MBA K Weiss, MD, MPH Pharmacoeconomi cs Epidemiology J Zwanziger, Ph. D UIC VA & NU UIC 86 Health policy
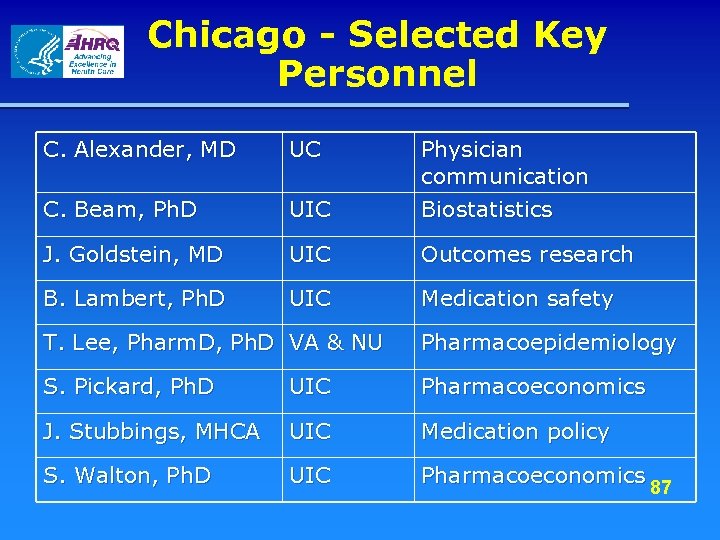 Chicago - Selected Key Personnel C. Alexander, MD UC C. Beam, Ph. D UIC Physician communication Biostatistics J. Goldstein, MD UIC Outcomes research B. Lambert, Ph. D UIC Medication safety T. Lee, Pharm. D, Ph. D VA & NU Pharmacoepidemiology S. Pickard, Ph. D UIC Pharmacoeconomics J. Stubbings, MHCA UIC Medication policy S. Walton, Ph. D UIC Pharmacoeconomics 87
Chicago - Selected Key Personnel C. Alexander, MD UC C. Beam, Ph. D UIC Physician communication Biostatistics J. Goldstein, MD UIC Outcomes research B. Lambert, Ph. D UIC Medication safety T. Lee, Pharm. D, Ph. D VA & NU Pharmacoepidemiology S. Pickard, Ph. D UIC Pharmacoeconomics J. Stubbings, MHCA UIC Medication policy S. Walton, Ph. D UIC Pharmacoeconomics 87
 Chicago - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Cost Effectiveness Analysis • Pharmacoeconomics • Medication Safety • Medication Use Policy • Pharmacoepidemiology • Pharmacy Practice 88
Chicago - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Cost Effectiveness Analysis • Pharmacoeconomics • Medication Safety • Medication Use Policy • Pharmacoepidemiology • Pharmacy Practice 88
 Chicago - Key Database Holdings • VA National Patient Database • VA Medicare Database • Walgreen’s Co Retail Database • Walgreen’s Co PBM Database • Marketscan Commercial Database • Marketscan Medicare Supplemental Database • Illinois Department of Healthcare and Family Services Database • Commercial Food Workers Union Database 89
Chicago - Key Database Holdings • VA National Patient Database • VA Medicare Database • Walgreen’s Co Retail Database • Walgreen’s Co PBM Database • Marketscan Commercial Database • Marketscan Medicare Supplemental Database • Illinois Department of Healthcare and Family Services Database • Commercial Food Workers Union Database 89
 Chicago - Key Database Holdings VA National Patient Db Veterans, medical and pharmacy data, laboratory results, mortality VA Medicare Db Medicare-eligible Veterans, medical and pharmacy data, mortality Walgreen’s Co Retail Db Retail prescriptions filled at 5, 000 stores nationwide Walgreen’s Co PBM Db Medical and pharmacy data for enrollees of plans serviced by WHI PBM 90
Chicago - Key Database Holdings VA National Patient Db Veterans, medical and pharmacy data, laboratory results, mortality VA Medicare Db Medicare-eligible Veterans, medical and pharmacy data, mortality Walgreen’s Co Retail Db Retail prescriptions filled at 5, 000 stores nationwide Walgreen’s Co PBM Db Medical and pharmacy data for enrollees of plans serviced by WHI PBM 90
 Chicago - Key Database Holdings Illinois Medicaid Medical and pharmacy data Db claims for 2 million citizens, includes Senior. Care program Commercial Pharmacy and medical claims Food Workers for 300, 000 Union members Union Db and families Marketscan Pharmacy and medical data for Commercial Db managed care population Marketscan Medical and pharmacy data for Medicare Supp 1 million individuals in 91 Db Medicare supp programs
Chicago - Key Database Holdings Illinois Medicaid Medical and pharmacy data Db claims for 2 million citizens, includes Senior. Care program Commercial Pharmacy and medical claims Food Workers for 300, 000 Union members Union Db and families Marketscan Pharmacy and medical data for Commercial Db managed care population Marketscan Medical and pharmacy data for Medicare Supp 1 million individuals in 91 Db Medicare supp programs
 Chicago - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Outcomes of COPD Management – administrative database evaluation of outcomes in COPD patients treated with beta-agonists and/or corticosteroids (proposed, lead investigator T. Lee). • Design and Evaluation of a Medication Therapy Management Program – comparative evaluation of 3 levels of MTM (proposed, lead investigator D. Touchette). 92
Chicago - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Outcomes of COPD Management – administrative database evaluation of outcomes in COPD patients treated with beta-agonists and/or corticosteroids (proposed, lead investigator T. Lee). • Design and Evaluation of a Medication Therapy Management Program – comparative evaluation of 3 levels of MTM (proposed, lead investigator D. Touchette). 92
 Outcomes of COPD Management • Abstract: The prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is high in the United States and continues to increase. Medication management is an integral part of treatment for patients with COPD. However, there remains a great deal of uncertainty in the optimal medication management of patients with COPD and a need for long-term evaluations of medication treatment outcomes in patients with COPD to better inform decisions when caring for these patients. The goal of this project is to identify and prioritize key questions related to the management of patients with COPD and conduct an analysis of the key question(s). The specific objectives for this project are: 1) Identify, review and assess major administrative, utilization, and/or claims databases, under the auspice of federal/state governments, third party payers, health plans/networks, or provider consortiums, that contain relevant prescription drug, surgical, outcome and utilization data for people with COPD; 2) Identify a set of clinically relevant key questions relating to effectiveness of medical therapy for patients with COPD which can be adequately evaluated using the identified data sets; and 3) Conduct a secondary data analysis to evaluate the key question(s), for outcomes including mortality, outpatient and inpatient hospitalization, and COPD-related hospitalizations and ED visits. The project will be completed in three phases, with a phase dedicated to each of the specific aims. The project has the potential to provide information relevant to health care provider organizations in policy formation about pharmacotherapy for 93 COPD.
Outcomes of COPD Management • Abstract: The prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is high in the United States and continues to increase. Medication management is an integral part of treatment for patients with COPD. However, there remains a great deal of uncertainty in the optimal medication management of patients with COPD and a need for long-term evaluations of medication treatment outcomes in patients with COPD to better inform decisions when caring for these patients. The goal of this project is to identify and prioritize key questions related to the management of patients with COPD and conduct an analysis of the key question(s). The specific objectives for this project are: 1) Identify, review and assess major administrative, utilization, and/or claims databases, under the auspice of federal/state governments, third party payers, health plans/networks, or provider consortiums, that contain relevant prescription drug, surgical, outcome and utilization data for people with COPD; 2) Identify a set of clinically relevant key questions relating to effectiveness of medical therapy for patients with COPD which can be adequately evaluated using the identified data sets; and 3) Conduct a secondary data analysis to evaluate the key question(s), for outcomes including mortality, outpatient and inpatient hospitalization, and COPD-related hospitalizations and ED visits. The project will be completed in three phases, with a phase dedicated to each of the specific aims. The project has the potential to provide information relevant to health care provider organizations in policy formation about pharmacotherapy for 93 COPD.
 Design & Evaluation of a Medication Therapy Management Program • Abstract: Nearly one third of Medicare beneficiaries have four or more chronic illnesses and 50% of patients over 65 receive 5 or more medications. Medication Therapy Management (MTM) programs may improve medication use and outcomes in beneficiaries with multiple medications and multiple chronic conditions. However, little is known about the effectiveness of MTM programs. The specific objectives of this project are to determine if different methods of delivering MTM services result in different outcomes and to identify what patient characteristics affect response to MTM programs. The aims of the study are: 1) to identify and describe existing MTM programs; 2) to develop, implement, and evaluate the impact of MTM programs of differing intensity on clinical, humanistic, and economic outcomes; and 3) to determine which patient factors have the greatest impact on MTM program success. This evaluation of the MTM programs will employ a randomized, single-blinded, controlled, prospective, parallel group design with three groups of varying intensity of intervention (controls, telephonic MTM, and face-to-face MTM). Endpoints include adherence to therapy, adverse drug events, clinical markers of chronic illnesses, potentially serious adverse events avoided, patient and provider satisfaction, and resource utilization. The impact of patient demographics and other characteristics on adherence and adverse drug events will be assessed. The long-term goal of our research program is to identify efficient practice models to improve outcomes in 94 complex patients with chronic conditions.
Design & Evaluation of a Medication Therapy Management Program • Abstract: Nearly one third of Medicare beneficiaries have four or more chronic illnesses and 50% of patients over 65 receive 5 or more medications. Medication Therapy Management (MTM) programs may improve medication use and outcomes in beneficiaries with multiple medications and multiple chronic conditions. However, little is known about the effectiveness of MTM programs. The specific objectives of this project are to determine if different methods of delivering MTM services result in different outcomes and to identify what patient characteristics affect response to MTM programs. The aims of the study are: 1) to identify and describe existing MTM programs; 2) to develop, implement, and evaluate the impact of MTM programs of differing intensity on clinical, humanistic, and economic outcomes; and 3) to determine which patient factors have the greatest impact on MTM program success. This evaluation of the MTM programs will employ a randomized, single-blinded, controlled, prospective, parallel group design with three groups of varying intensity of intervention (controls, telephonic MTM, and face-to-face MTM). Endpoints include adherence to therapy, adverse drug events, clinical markers of chronic illnesses, potentially serious adverse events avoided, patient and provider satisfaction, and resource utilization. The impact of patient demographics and other characteristics on adherence and adverse drug events will be assessed. The long-term goal of our research program is to identify efficient practice models to improve outcomes in 94 complex patients with chronic conditions.
 Chicago - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center – Assist AHRQ in conduct of research that is relevant and meaningful to health care consumers and decision-makers in the US – Create an environment that fosters collaborative, high quality, and innovative research for the benefit of the Consortium institutions and individuals 95
Chicago - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center – Assist AHRQ in conduct of research that is relevant and meaningful to health care consumers and decision-makers in the US – Create an environment that fosters collaborative, high quality, and innovative research for the benefit of the Consortium institutions and individuals 95
 Chicago - Program Goals • PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network – Develop a record of producing both high quality and quantity of useful research that influences health care policy and outcomes – Ensure that the success of the Network is communicated broadly 96
Chicago - Program Goals • PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network – Develop a record of producing both high quality and quantity of useful research that influences health care policy and outcomes – Ensure that the success of the Network is communicated broadly 96
 Chicago – Additional Information • University of Illinois at Chicago: http: //www. uic. edu/index. html/ – Center for Pharmacoeconomic Research: http: //www. uic. edu/pharmacy/research/cpr/ • University of Chicago: http: //www. uchicago. edu/ • Northwestern University: http: //www. northwestern. edu/ • VA Midwest Center for Health Services and Policy Research: http: //www. vard. org/links/gov. html • Blue Cross/Blue Shield Association Technology Assessment Center and EPC: http: //www. bcbs. com/tec/ 97
Chicago – Additional Information • University of Illinois at Chicago: http: //www. uic. edu/index. html/ – Center for Pharmacoeconomic Research: http: //www. uic. edu/pharmacy/research/cpr/ • University of Chicago: http: //www. uchicago. edu/ • Northwestern University: http: //www. northwestern. edu/ • VA Midwest Center for Health Services and Policy Research: http: //www. vard. org/links/gov. html • Blue Cross/Blue Shield Association Technology Assessment Center and EPC: http: //www. bcbs. com/tec/ 97
 The University of Maryland Baltimore (UMB) DEc. IDE Center Bruce Stuart, Ph. D (PI)
The University of Maryland Baltimore (UMB) DEc. IDE Center Bruce Stuart, Ph. D (PI)
 UMB The UMB DEc. IDE Center brings together the talents of more than 50 investigators and senior staff from: • School of Pharmacy • School of Medicine • School of Nursing 99
UMB The UMB DEc. IDE Center brings together the talents of more than 50 investigators and senior staff from: • School of Pharmacy • School of Medicine • School of Nursing 99
 UMB These UMB investigators are available to collaborate and provide data for this effort including: • Comparative Drug Effectiveness • Treatment Safety and Efficacy in Elderly and Disabled Patients • Innovative Research Designs using Observational Databases 100
UMB These UMB investigators are available to collaborate and provide data for this effort including: • Comparative Drug Effectiveness • Treatment Safety and Efficacy in Elderly and Disabled Patients • Innovative Research Designs using Observational Databases 100
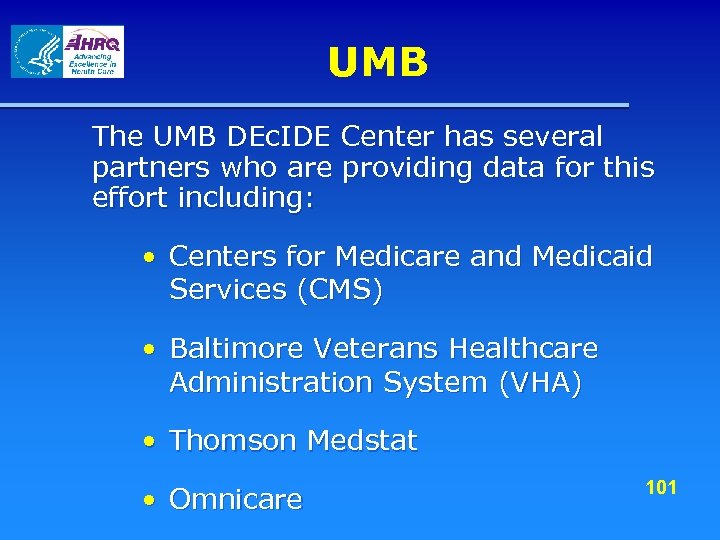 UMB The UMB DEc. IDE Center has several partners who are providing data for this effort including: • Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) • Baltimore Veterans Healthcare Administration System (VHA) • Thomson Medstat • Omnicare 101
UMB The UMB DEc. IDE Center has several partners who are providing data for this effort including: • Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) • Baltimore Veterans Healthcare Administration System (VHA) • Thomson Medstat • Omnicare 101
 UMB An Executive Management Team has overall program management responsibilities. This team will be led by Executive Director Bruce Stuart, Ph. D from the School of Pharmacy’s Peter Lamy Center. Executive Management Team Associate Directors are: • Ilene Zuckerman, Pharm. D, Ph. D from the School of Pharmacy’s Peter Lamy Center • Charlene Quinn, RN, Ph. D from the School of Medicine and the Baltimore Veterans Administration Medical Center (VAMC) 102
UMB An Executive Management Team has overall program management responsibilities. This team will be led by Executive Director Bruce Stuart, Ph. D from the School of Pharmacy’s Peter Lamy Center. Executive Management Team Associate Directors are: • Ilene Zuckerman, Pharm. D, Ph. D from the School of Pharmacy’s Peter Lamy Center • Charlene Quinn, RN, Ph. D from the School of Medicine and the Baltimore Veterans Administration Medical Center (VAMC) 102
 UMB The Center is structured around the Executive Management Team and 5 core groups: • • • Clinical Epidemiology Core Pharmacotherapy Core Data Core Methods and Statistics Core Information Dissemination Core 103
UMB The Center is structured around the Executive Management Team and 5 core groups: • • • Clinical Epidemiology Core Pharmacotherapy Core Data Core Methods and Statistics Core Information Dissemination Core 103
 UMB DEc. IDE Center Organizational Structure 104
UMB DEc. IDE Center Organizational Structure 104
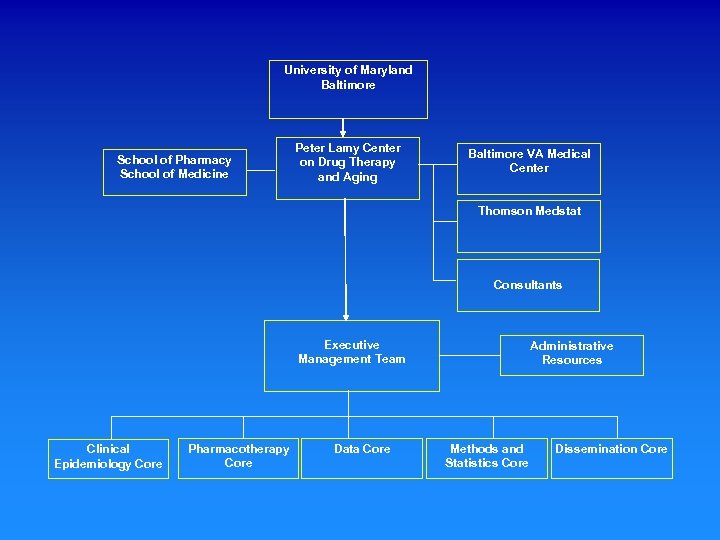 University of Maryland Baltimore School of Pharmacy School of Medicine Peter Lamy Center on Drug Therapy and Aging Baltimore VA Medical Center Thomson Medstat Consultants Executive Management Team Clinical Epidemiology Core Pharmacotherapy Core Data Core Administrative Resources Methods and Statistics Core Dissemination Core
University of Maryland Baltimore School of Pharmacy School of Medicine Peter Lamy Center on Drug Therapy and Aging Baltimore VA Medical Center Thomson Medstat Consultants Executive Management Team Clinical Epidemiology Core Pharmacotherapy Core Data Core Administrative Resources Methods and Statistics Core Dissemination Core
 UMB Task Order #1 Methods for Studying Dementia Treatment and Outcomes in Observational Databases 106
UMB Task Order #1 Methods for Studying Dementia Treatment and Outcomes in Observational Databases 106
 UMB This task order is being led by Ann Gruber -Baldini, Ph. D, an experienced researcher with a specialty in dementia diagnosis and outcomes in long-term care. Assisting Dr. Gruber-Baldini are: • clinical experts • methodological experts • a support network of administrative personnel dedicated to high performance and scientific integrity 107
UMB This task order is being led by Ann Gruber -Baldini, Ph. D, an experienced researcher with a specialty in dementia diagnosis and outcomes in long-term care. Assisting Dr. Gruber-Baldini are: • clinical experts • methodological experts • a support network of administrative personnel dedicated to high performance and scientific integrity 107
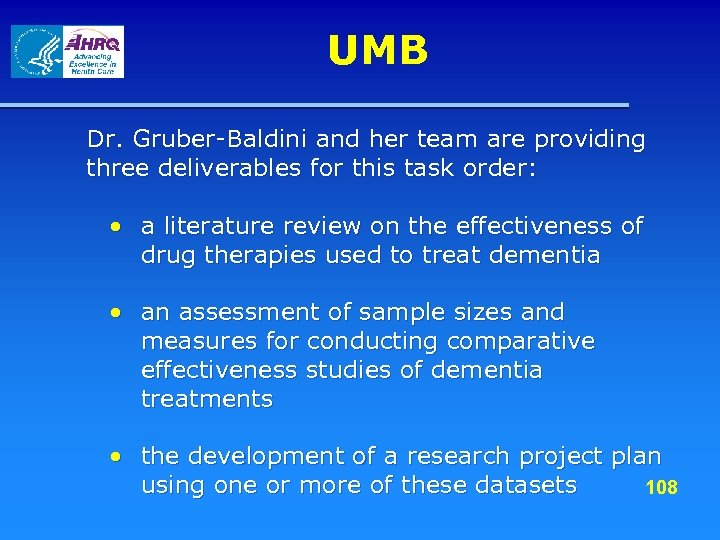 UMB Dr. Gruber-Baldini and her team are providing three deliverables for this task order: • a literature review on the effectiveness of drug therapies used to treat dementia • an assessment of sample sizes and measures for conducting comparative effectiveness studies of dementia treatments • the development of a research project plan using one or more of these datasets 108
UMB Dr. Gruber-Baldini and her team are providing three deliverables for this task order: • a literature review on the effectiveness of drug therapies used to treat dementia • an assessment of sample sizes and measures for conducting comparative effectiveness studies of dementia treatments • the development of a research project plan using one or more of these datasets 108
 Methods for Studying Dementia Treatment and Outcomes in Observational Databases • Abstract: The three main deliverables for this project are: (1) an update and evaluation of the scientific literature on the effectiveness of drug therapies used to treat dementia, (2) an assessment of sample sizes and measures for conducting comparative effectiveness studies of dementia treatments in each of the accessible datasets, and (3) the development of a research project plan using one or more of these datasets. The literature review and evaluation will serve both to update systematic reviews conducted by AHRQ and others and to inform the development and focus of our Research Project Plan and future work conducted by the DEc. IDE network. This will include an assessment of systematic reviews of studies conducted since 2000 augmented by a literature review of high quality observational studies conducted since 2000. The database assessment task is designed to establish the range of possible comparative effectiveness studies that could be conducted with data available to the investigating DEc. IDE Center. Since these datasets include overlapping source information (e. g. , Medicare claims) we are focusing this aspect of the study on data file types (e. g. , enrollment files, medical claims, pharmacy claims, Minimum Data Set (MDS), medical records, plan benefit design, and surveys), population coverage and sample sizes, and the unique opportunities provided through data linkages. • In the final phase of the study, we are using the knowledge gained in the literature review and database assessment tasks to design a research project focused on the effectiveness of drugs used to treat dementia. In order to provide a high quality comparative effectiveness study of dementia treatment options, we are splitting this task into two components: (1) a benchmarking study using the Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey (MCBS) data to establish prevalence rates for dementia and dementia treatments for community-dwelling and institutionalized Medicare beneficiaries, and (2) a fully fleshed out study design for future 109 comparative drug treatment studies using one or more of our databases.
Methods for Studying Dementia Treatment and Outcomes in Observational Databases • Abstract: The three main deliverables for this project are: (1) an update and evaluation of the scientific literature on the effectiveness of drug therapies used to treat dementia, (2) an assessment of sample sizes and measures for conducting comparative effectiveness studies of dementia treatments in each of the accessible datasets, and (3) the development of a research project plan using one or more of these datasets. The literature review and evaluation will serve both to update systematic reviews conducted by AHRQ and others and to inform the development and focus of our Research Project Plan and future work conducted by the DEc. IDE network. This will include an assessment of systematic reviews of studies conducted since 2000 augmented by a literature review of high quality observational studies conducted since 2000. The database assessment task is designed to establish the range of possible comparative effectiveness studies that could be conducted with data available to the investigating DEc. IDE Center. Since these datasets include overlapping source information (e. g. , Medicare claims) we are focusing this aspect of the study on data file types (e. g. , enrollment files, medical claims, pharmacy claims, Minimum Data Set (MDS), medical records, plan benefit design, and surveys), population coverage and sample sizes, and the unique opportunities provided through data linkages. • In the final phase of the study, we are using the knowledge gained in the literature review and database assessment tasks to design a research project focused on the effectiveness of drugs used to treat dementia. In order to provide a high quality comparative effectiveness study of dementia treatment options, we are splitting this task into two components: (1) a benchmarking study using the Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey (MCBS) data to establish prevalence rates for dementia and dementia treatments for community-dwelling and institutionalized Medicare beneficiaries, and (2) a fully fleshed out study design for future 109 comparative drug treatment studies using one or more of our databases.
 UNC DEc. IDE Center at The Cecil G. Sheps Center for Health Services Research The University of North Carolina Suzanne L. West, MPH, Ph. D Principal Investigator Michael (Mick) D. Murray, Pharm. D, MPH Co-Principal Investigator
UNC DEc. IDE Center at The Cecil G. Sheps Center for Health Services Research The University of North Carolina Suzanne L. West, MPH, Ph. D Principal Investigator Michael (Mick) D. Murray, Pharm. D, MPH Co-Principal Investigator
 UNC - Core Personnel & Expertise (1) • Suzanne West, MPH, Ph. D – Pharmacoepidemiology, systematic reviews, psychiatric epidemiology • Mick Murray, Pharm. D, MPH – Health outcomes of pharmaceutical interventions, medication adherence • Tim Carey, MD, MPH – Clinical epidemiology, internal medicine, evidencebased practice, back pain • Harry Guess, MD, Ph. D – Pediatrics, pharmacoepidemiology, patient reported 111 outcomes
UNC - Core Personnel & Expertise (1) • Suzanne West, MPH, Ph. D – Pharmacoepidemiology, systematic reviews, psychiatric epidemiology • Mick Murray, Pharm. D, MPH – Health outcomes of pharmaceutical interventions, medication adherence • Tim Carey, MD, MPH – Clinical epidemiology, internal medicine, evidencebased practice, back pain • Harry Guess, MD, Ph. D – Pediatrics, pharmacoepidemiology, patient reported 111 outcomes
 UNC - Core Personnel & Expertise (2) • Michele Jonsson Funk, Ph. D – HIV, advanced epidemiologic methods • Maryann Oertel, Pharm. D – Drug safety, drug information • John Paul, Ph. D – Healthcare policy, outcomes research • Susan Blalock, MPH, Ph. D – Adherence to treatment, inappropriate drug use • Nikki Mc. Koy, BS – Systematic reviews, project management 112
UNC - Core Personnel & Expertise (2) • Michele Jonsson Funk, Ph. D – HIV, advanced epidemiologic methods • Maryann Oertel, Pharm. D – Drug safety, drug information • John Paul, Ph. D – Healthcare policy, outcomes research • Susan Blalock, MPH, Ph. D – Adherence to treatment, inappropriate drug use • Nikki Mc. Koy, BS – Systematic reviews, project management 112
 UNC - Affiliations and Partnerships • Center for Health Services Research in Primary Care, VAMC, Durham, NC • Medicines Monitoring Unit at the University of Dundee, Scotland • NC Access. Care – not-for-profit Medicaid disease management coalition • Quality in Pediatric Subspecialty Care (QPSC) – Collaboration between the American Board of Pediatrics, American Academy of Pediatrics & UNC 113
UNC - Affiliations and Partnerships • Center for Health Services Research in Primary Care, VAMC, Durham, NC • Medicines Monitoring Unit at the University of Dundee, Scotland • NC Access. Care – not-for-profit Medicaid disease management coalition • Quality in Pediatric Subspecialty Care (QPSC) – Collaboration between the American Board of Pediatrics, American Academy of Pediatrics & UNC 113
 UNC - Research Interests & Center Strengths • • • Pharmacoepidemiologic methods Drug utilization review Systematic reviews Medication adherence Pharmacoeconomics Medical text information clustering and mining CERT focused on pediatrics Racial disparities Rural health 114
UNC - Research Interests & Center Strengths • • • Pharmacoepidemiologic methods Drug utilization review Systematic reviews Medication adherence Pharmacoeconomics Medical text information clustering and mining CERT focused on pediatrics Racial disparities Rural health 114
 UNC - Key Database Holdings • Veterans Administration data • NC State Employees Health Plan data • NC Medicaid data • Health Choice (NC SCHIP) 115
UNC - Key Database Holdings • Veterans Administration data • NC State Employees Health Plan data • NC Medicaid data • Health Choice (NC SCHIP) 115
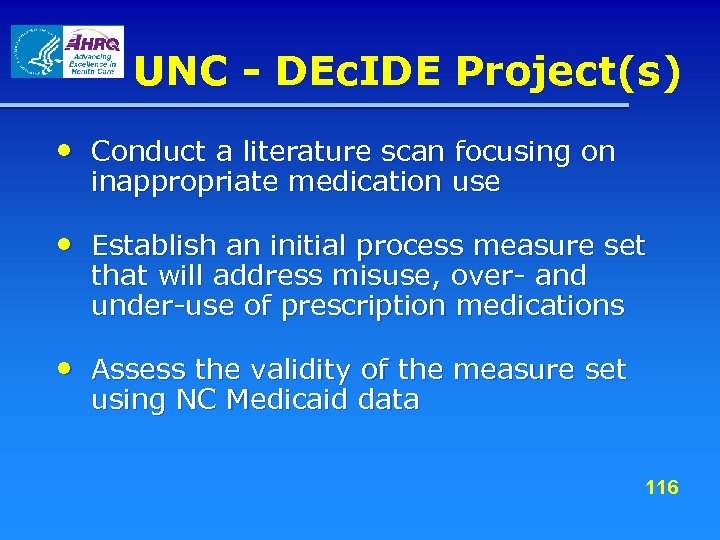 UNC - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Conduct a literature scan focusing on inappropriate medication use • Establish an initial process measure set that will address misuse, over- and under-use of prescription medications • Assess the validity of the measure set using NC Medicaid data 116
UNC - DEc. IDE Project(s) • Conduct a literature scan focusing on inappropriate medication use • Establish an initial process measure set that will address misuse, over- and under-use of prescription medications • Assess the validity of the measure set using NC Medicaid data 116
 Research and Surveillance Methods for Improving Patient Safety Through Medicare Claims Databases • Abstract: The specific objective of the project is to establish an initial measure set that will encompass surveillance for process measures such as misuse, over- and under-use of prescription medications based on dispensing claims in outpatient, inpatient, nursing home, and transitional settings such as rehabilitation centers. The process measures will be developed using an evidence-based approach, i. e. , by scanning the literature for published papers that have addressed these issues. We will consult with advisors to determine the integrity of the initial measure set selected and determine which indicators will be the focus of the validation phase. We will assess the validity of the measure set using state Medicaid data. The tasks for this project will be described in more detail below. The investigators will conduct a brief but focused literature scan to identify publications that have dealt with the conceptualization of medication safety using administrative databases as well as studies of specific misuse and underuse of medications. Our literature search will focus on Medical Subject Headings and text word searches as appropriate. A preliminary search identified over 600 articles using drug utilization review and health maintenance organization, insurance claim review, or health maintenance organization. Once we have assembled the literature, have identified examples of process measures (misuse, overuse, and underuse of medications) and have developed an initial measure set, we will share this information with collaborators and outside project advisors. We will seek constructive criticism on our conceptualization of the measures and the possible usage situations to evaluate based on the typical structure of Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP, and managed care administrative claims data. We will test the process measures using data from state Medicaid claims files. We will select a particular clinical situation for evaluation as informed by the literature scan and the suggestions of our collaborators and advisors. Investigators will begin with evidence-based clinical guidelines for the treatment of patients with the clinical issue being studied by reviewing websites and journals from the appropriate clinical society, in addition to the National Guideline Clearinghouse and other relevant sources. Based on the literature, we will develop algorithms for identifying usage patterns and their appropriateness for the condition under study along with highly prevalent co-morbidities. We will conduct sensitivity analyses to refine the algorithms and will characterize the patients in each use pattern after sensitivity analyses, by age and sex. Our final report will include a description of the literature scan and the evidence tables; processes for developing the algorithm(s); will discuss any problems encountered; and will provide an assessment of the algorithms’ overall robustness. 117
Research and Surveillance Methods for Improving Patient Safety Through Medicare Claims Databases • Abstract: The specific objective of the project is to establish an initial measure set that will encompass surveillance for process measures such as misuse, over- and under-use of prescription medications based on dispensing claims in outpatient, inpatient, nursing home, and transitional settings such as rehabilitation centers. The process measures will be developed using an evidence-based approach, i. e. , by scanning the literature for published papers that have addressed these issues. We will consult with advisors to determine the integrity of the initial measure set selected and determine which indicators will be the focus of the validation phase. We will assess the validity of the measure set using state Medicaid data. The tasks for this project will be described in more detail below. The investigators will conduct a brief but focused literature scan to identify publications that have dealt with the conceptualization of medication safety using administrative databases as well as studies of specific misuse and underuse of medications. Our literature search will focus on Medical Subject Headings and text word searches as appropriate. A preliminary search identified over 600 articles using drug utilization review and health maintenance organization, insurance claim review, or health maintenance organization. Once we have assembled the literature, have identified examples of process measures (misuse, overuse, and underuse of medications) and have developed an initial measure set, we will share this information with collaborators and outside project advisors. We will seek constructive criticism on our conceptualization of the measures and the possible usage situations to evaluate based on the typical structure of Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP, and managed care administrative claims data. We will test the process measures using data from state Medicaid claims files. We will select a particular clinical situation for evaluation as informed by the literature scan and the suggestions of our collaborators and advisors. Investigators will begin with evidence-based clinical guidelines for the treatment of patients with the clinical issue being studied by reviewing websites and journals from the appropriate clinical society, in addition to the National Guideline Clearinghouse and other relevant sources. Based on the literature, we will develop algorithms for identifying usage patterns and their appropriateness for the condition under study along with highly prevalent co-morbidities. We will conduct sensitivity analyses to refine the algorithms and will characterize the patients in each use pattern after sensitivity analyses, by age and sex. Our final report will include a description of the literature scan and the evidence tables; processes for developing the algorithm(s); will discuss any problems encountered; and will provide an assessment of the algorithms’ overall robustness. 117
 UNC - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center – Expand AHRQ capabilities in the analysis of claims data from CMS programs: Medicare, Medicaid, and State Children’s Health Insurance Programs – Develop capability in designing and conducting randomized database studies • PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network – Facilitating public-private partnerships for conducting comparative effectiveness studies – Improve linkages with EPC and CERT networks, also with the policy community – Improve research translation to the policy community in 118 terms understandable to them
UNC - Program Goals • PI goals for DEc. IDE Center – Expand AHRQ capabilities in the analysis of claims data from CMS programs: Medicare, Medicaid, and State Children’s Health Insurance Programs – Develop capability in designing and conducting randomized database studies • PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network – Facilitating public-private partnerships for conducting comparative effectiveness studies – Improve linkages with EPC and CERT networks, also with the policy community – Improve research translation to the policy community in 118 terms understandable to them
 University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine PI: Brian L. Strom, MD, MPH Co-PI: Sean Hennessy, Pharm. D, Ph. D
University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine PI: Brian L. Strom, MD, MPH Co-PI: Sean Hennessy, Pharm. D, Ph. D
 UPenn - Core Personnel & Expertise Brian L. Strom, MD, MPH: Pharmacoepidemiology, Clinical Epidemiology, General Internal Medicine, Clinical Pharmacology Sean Hennessy, Pharm. D, Ph. D: Pharmacoepidemiology, Clinical Epidemiology, Clinical Pharmacy Multidisciplinary Steering Committee Research Expertise: Epidemiology, Biostatistics, Health Services Research, Pharmacogenetics, etc. Clinical Expertise: Medicine, Surgery, Psychiatry, 120 Nursing, Pharmacy, etc.
UPenn - Core Personnel & Expertise Brian L. Strom, MD, MPH: Pharmacoepidemiology, Clinical Epidemiology, General Internal Medicine, Clinical Pharmacology Sean Hennessy, Pharm. D, Ph. D: Pharmacoepidemiology, Clinical Epidemiology, Clinical Pharmacy Multidisciplinary Steering Committee Research Expertise: Epidemiology, Biostatistics, Health Services Research, Pharmacogenetics, etc. Clinical Expertise: Medicine, Surgery, Psychiatry, 120 Nursing, Pharmacy, etc.
 UPenn - Affiliations and Partnerships • Geisinger Medical Center • Centers for Education and Research on Therapeutics • Other schools, departments, and centers of the University of Pennsylvania 121
UPenn - Affiliations and Partnerships • Geisinger Medical Center • Centers for Education and Research on Therapeutics • Other schools, departments, and centers of the University of Pennsylvania 121
 UPenn - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Epidemiologic studies of beneficial and adverse drug effects • Evaluations of efforts to improve medication use • Pharmacoepidemiology research methods • Pharmacogenetic epidemiology 122
UPenn - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Epidemiologic studies of beneficial and adverse drug effects • Evaluations of efforts to improve medication use • Pharmacoepidemiology research methods • Pharmacogenetic epidemiology 122
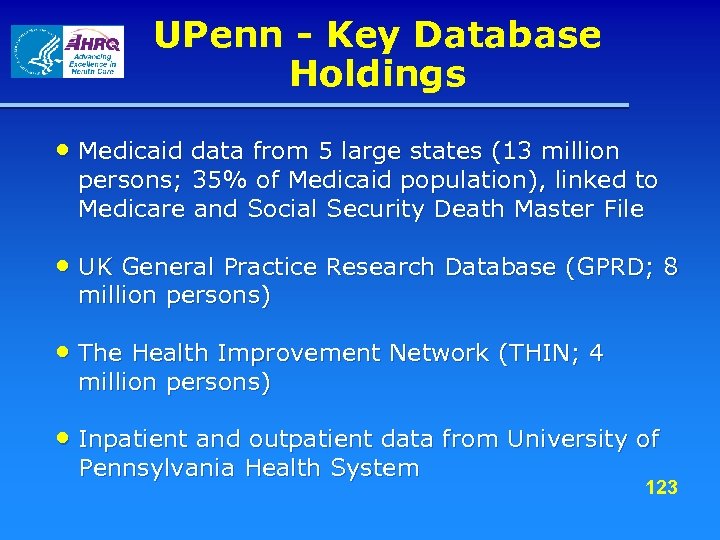 UPenn - Key Database Holdings • Medicaid data from 5 large states (13 million persons; 35% of Medicaid population), linked to Medicare and Social Security Death Master File • UK General Practice Research Database (GPRD; 8 million persons) • The Health Improvement Network (THIN; 4 million persons) • Inpatient and outpatient data from University of Pennsylvania Health System 123
UPenn - Key Database Holdings • Medicaid data from 5 large states (13 million persons; 35% of Medicaid population), linked to Medicare and Social Security Death Master File • UK General Practice Research Database (GPRD; 8 million persons) • The Health Improvement Network (THIN; 4 million persons) • Inpatient and outpatient data from University of Pennsylvania Health System 123
 UPenn - DEc. IDE Project • Antidepressants and Risk of Aspiration Pneumonia in the Aged 124
UPenn - DEc. IDE Project • Antidepressants and Risk of Aspiration Pneumonia in the Aged 124
 Antidepressants and Risk of Aspiration Pneumonia in the Aged • Abstract: Community-acquired pneumonia is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the elderly, with an estimated annual health care cost in the US of $4. 4 billion. Aspiration pneumonia occurs commonly in institutionalized elderly individuals, the number of whom is expected to grow as the population ages. Recent data suggest the possibility that antidepressant medications may increase the risk of aspiration pneumonia. Postulated mechanisms include effects on swallowing and lower esophageal sphincter pressure. However, the effects of antidepressant medications on these functions is not well studied, nor is the association between antidepressant medications and aspiration pneumonia. We propose to conduct an observational study within the UK General Practice Research Database to examine the association between use of antidepressant drug use and community acquired pneumonia in general, and community acquired aspiration pneumonia in particular. In addition, we will develop a proposal for a patient-oriented research study examining the effects of specific antidepressants on swallowing and on lower esophageal sphincter pressure. 125
Antidepressants and Risk of Aspiration Pneumonia in the Aged • Abstract: Community-acquired pneumonia is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the elderly, with an estimated annual health care cost in the US of $4. 4 billion. Aspiration pneumonia occurs commonly in institutionalized elderly individuals, the number of whom is expected to grow as the population ages. Recent data suggest the possibility that antidepressant medications may increase the risk of aspiration pneumonia. Postulated mechanisms include effects on swallowing and lower esophageal sphincter pressure. However, the effects of antidepressant medications on these functions is not well studied, nor is the association between antidepressant medications and aspiration pneumonia. We propose to conduct an observational study within the UK General Practice Research Database to examine the association between use of antidepressant drug use and community acquired pneumonia in general, and community acquired aspiration pneumonia in particular. In addition, we will develop a proposal for a patient-oriented research study examining the effects of specific antidepressants on swallowing and on lower esophageal sphincter pressure. 125
 UPenn - Program Goals • University of Pennsylvania DEc. IDE Center Goal: To improve the health of the public by producing correct answers to clinically important comparative effectiveness research questions. • Suggested Goal for DEc. IDE Network: To improve the health of the public by producing correct answers to clinically important comparative effectiveness research questions. 126
UPenn - Program Goals • University of Pennsylvania DEc. IDE Center Goal: To improve the health of the public by producing correct answers to clinically important comparative effectiveness research questions. • Suggested Goal for DEc. IDE Network: To improve the health of the public by producing correct answers to clinically important comparative effectiveness research questions. 126
 UPenn - Study Addressing a Clinically Relevant Research Question Clinical & Biologic Insight Medicine Cardiology Rheumatology Gastroenterology Oncology Neurology Endocrinology Pulmonology Psychiatry Genetics Pharmacology Pharmacy Nursing etc. Core Research Disciplines Pharmacoepidemiology Clinical epidemiology Biostatistics Health services research Health economics Health informatics Translational research Behavioral research Health assessment etc. Computing & Project Management Project Managers Programmers Fiscal Management Research Databases / Patient Populations Medicaid / Medicare GPRD THIN UPHS DVCCN Geisinger etc. 127
UPenn - Study Addressing a Clinically Relevant Research Question Clinical & Biologic Insight Medicine Cardiology Rheumatology Gastroenterology Oncology Neurology Endocrinology Pulmonology Psychiatry Genetics Pharmacology Pharmacy Nursing etc. Core Research Disciplines Pharmacoepidemiology Clinical epidemiology Biostatistics Health services research Health economics Health informatics Translational research Behavioral research Health assessment etc. Computing & Project Management Project Managers Programmers Fiscal Management Research Databases / Patient Populations Medicaid / Medicare GPRD THIN UPHS DVCCN Geisinger etc. 127
 DEc. IDE about Therapeutics at Vanderbilt Marie R. Griffin MD MPH
DEc. IDE about Therapeutics at Vanderbilt Marie R. Griffin MD MPH
 Vanderbilt - Core Personnel & Expertise • Marie R Griffin MD MPH, NSAIDs, vaccines • Wayne A Ray Ph. D, NSAIDs, psychotropic drugs • William O Cooper MD MPH, drugs for children • Carlos G Grijalva MD, public health, epidemiology • Patrick G Arbogast Ph. D, statistics • Edward F Mitchel MA, programming, data analysis • James R Daugherty Jr MS, programming • Rebecca Ding MA, statistician • Patricia S Gideon RN, data abstraction • Debbie Varnell, administration 129
Vanderbilt - Core Personnel & Expertise • Marie R Griffin MD MPH, NSAIDs, vaccines • Wayne A Ray Ph. D, NSAIDs, psychotropic drugs • William O Cooper MD MPH, drugs for children • Carlos G Grijalva MD, public health, epidemiology • Patrick G Arbogast Ph. D, statistics • Edward F Mitchel MA, programming, data analysis • James R Daugherty Jr MS, programming • Rebecca Ding MA, statistician • Patricia S Gideon RN, data abstraction • Debbie Varnell, administration 129
 Vanderbilt - Affiliations and Partnerships • Vanderbilt Center for Education and Research on Therapeutics (CERT) • Wayne A Ray PI • Tennessee Medicaid Program • VA Geriatric Research and Education Clinical Center (GRECC) • Robert Dittus PI • VA Translating Research into Practice • Theodore Speroff, PI • VA Clinical Research Center of Excellence • Marie R Griffin, PI 130
Vanderbilt - Affiliations and Partnerships • Vanderbilt Center for Education and Research on Therapeutics (CERT) • Wayne A Ray PI • Tennessee Medicaid Program • VA Geriatric Research and Education Clinical Center (GRECC) • Robert Dittus PI • VA Translating Research into Practice • Theodore Speroff, PI • VA Clinical Research Center of Excellence • Marie R Griffin, PI 130
 Vanderbilt - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Pharmacoepidemiology • NSAIDs and COX 2 inhibitors (“coxibs”) • Peptic ulcer disease • Vaccines and vaccine preventable diseases • Asthma • Sudden death • Child health 131
Vanderbilt - Research Interests & Center Strengths • Pharmacoepidemiology • NSAIDs and COX 2 inhibitors (“coxibs”) • Peptic ulcer disease • Vaccines and vaccine preventable diseases • Asthma • Sudden death • Child health 131
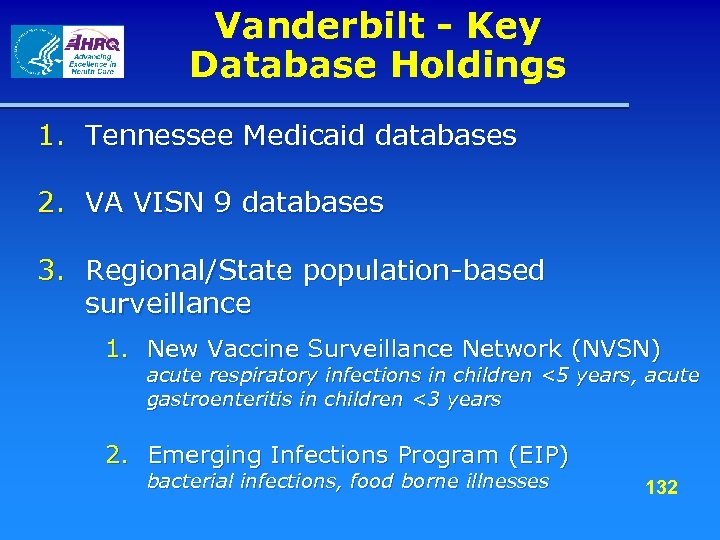 Vanderbilt - Key Database Holdings 1. Tennessee Medicaid databases 2. VA VISN 9 databases 3. Regional/State population-based surveillance 1. New Vaccine Surveillance Network (NVSN) acute respiratory infections in children <5 years, acute gastroenteritis in children <3 years 2. Emerging Infections Program (EIP) bacterial infections, food borne illnesses 132
Vanderbilt - Key Database Holdings 1. Tennessee Medicaid databases 2. VA VISN 9 databases 3. Regional/State population-based surveillance 1. New Vaccine Surveillance Network (NVSN) acute respiratory infections in children <5 years, acute gastroenteritis in children <3 years 2. Emerging Infections Program (EIP) bacterial infections, food borne illnesses 132
 Vanderbilt - DEc. IDE Project • Assessment of factors modulating treatment outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis Safety and relative effectiveness of biologics for rheumatoid arthritis as compared to older DMARDs 133
Vanderbilt - DEc. IDE Project • Assessment of factors modulating treatment outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis Safety and relative effectiveness of biologics for rheumatoid arthritis as compared to older DMARDs 133
 Relative Safety and Effectiveness of Therapies for Rheumatoid Arthritis • Abstract: The therapy of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is based on disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). The introduction of novel treatments, including biologics, offers hope for better prevention and control of pain and disability associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Although controlled clinical studies to help define optimal use of DMARDs in RA patients are in evolution, most clinical trials are of relatively short duration, and are performed in highly selected patients. RA is a life-long disease affecting one percent of the general population. Population-based studies are needed to help quantify important beneficial and adverse clinical outcomes associated with use of therapeutics in this disease. Populations that include lowincome persons, and members of racial and ethnic minorities, are of special interest, since these groups are typically under-represented in clinical trials. There is currently little information on effectiveness and safety of new DMARDs as compared to traditional DMARDs. We propose a sequence of epidemiologic studies aimed at addressing knowledge gaps in relative effectiveness (specific aim 1) and safety (specific aims 2 and 3) of specific DMARDs: 1. To define a cohort of patients with RA among state Medicaid enrollees to determine the prevalence of use of selected DMARDs. We will explore several outcomes as measures of relative effectiveness of specific agents/combinations: · Prevalence of co-therapy with a) corticosteroids, b) non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs), and c) narcotics. · Adherence to standard regimens and continuation of use · Health care utilization. 2. To determine the incidence of congestive heart failure in the RA cohort and test whether RA patients receiving anti TNF- á therapy (etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab) are at increased risk of developing congestive heart failure as compared to patients receiving conventional DMARDs. 3. To determine the incidence of selected infection outcomes in the RA cohort and test whether RA patients receiving anti TNF- á (etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab) or anti interleukin-1 (anakinra) are at increased risk of serious infections as compared to patients 134 receiving conventional DMARDs.
Relative Safety and Effectiveness of Therapies for Rheumatoid Arthritis • Abstract: The therapy of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is based on disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). The introduction of novel treatments, including biologics, offers hope for better prevention and control of pain and disability associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Although controlled clinical studies to help define optimal use of DMARDs in RA patients are in evolution, most clinical trials are of relatively short duration, and are performed in highly selected patients. RA is a life-long disease affecting one percent of the general population. Population-based studies are needed to help quantify important beneficial and adverse clinical outcomes associated with use of therapeutics in this disease. Populations that include lowincome persons, and members of racial and ethnic minorities, are of special interest, since these groups are typically under-represented in clinical trials. There is currently little information on effectiveness and safety of new DMARDs as compared to traditional DMARDs. We propose a sequence of epidemiologic studies aimed at addressing knowledge gaps in relative effectiveness (specific aim 1) and safety (specific aims 2 and 3) of specific DMARDs: 1. To define a cohort of patients with RA among state Medicaid enrollees to determine the prevalence of use of selected DMARDs. We will explore several outcomes as measures of relative effectiveness of specific agents/combinations: · Prevalence of co-therapy with a) corticosteroids, b) non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs), and c) narcotics. · Adherence to standard regimens and continuation of use · Health care utilization. 2. To determine the incidence of congestive heart failure in the RA cohort and test whether RA patients receiving anti TNF- á therapy (etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab) are at increased risk of developing congestive heart failure as compared to patients receiving conventional DMARDs. 3. To determine the incidence of selected infection outcomes in the RA cohort and test whether RA patients receiving anti TNF- á (etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab) or anti interleukin-1 (anakinra) are at increased risk of serious infections as compared to patients 134 receiving conventional DMARDs.
 Vanderbilt - Program Goals 1. To perform efficient studies of patterns of utilization and relative effectiveness in TN Medicaid population 2. To develop local and national VA databases to perform parallel studies 3. PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network • To develop uniform definitions for exposures, outcomes, and measures of relative effectiveness appropriate for observational studies 135
Vanderbilt - Program Goals 1. To perform efficient studies of patterns of utilization and relative effectiveness in TN Medicaid population 2. To develop local and national VA databases to perform parallel studies 3. PI suggested goals for the AHRQ DEc. IDE Network • To develop uniform definitions for exposures, outcomes, and measures of relative effectiveness appropriate for observational studies 135
 Other AHRQ Programs involved with Effective Health Care Initiative & Research in Therapeutics
Other AHRQ Programs involved with Effective Health Care Initiative & Research in Therapeutics
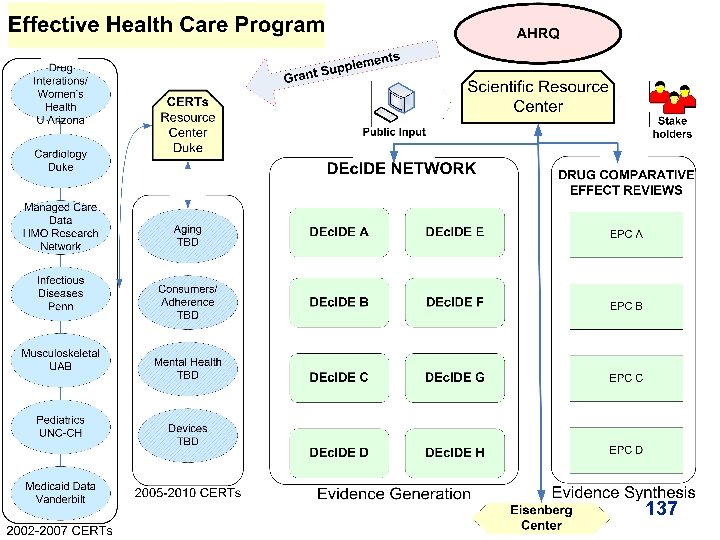 137
137
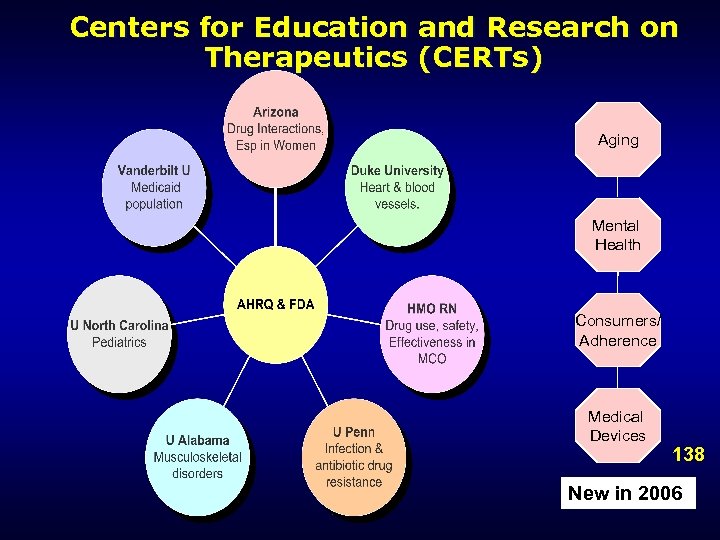 Centers for Education and Research on Therapeutics (CERTs) Aging Mental Health Consumers/ Adherence Medical Devices 138 New in 2006
Centers for Education and Research on Therapeutics (CERTs) Aging Mental Health Consumers/ Adherence Medical Devices 138 New in 2006
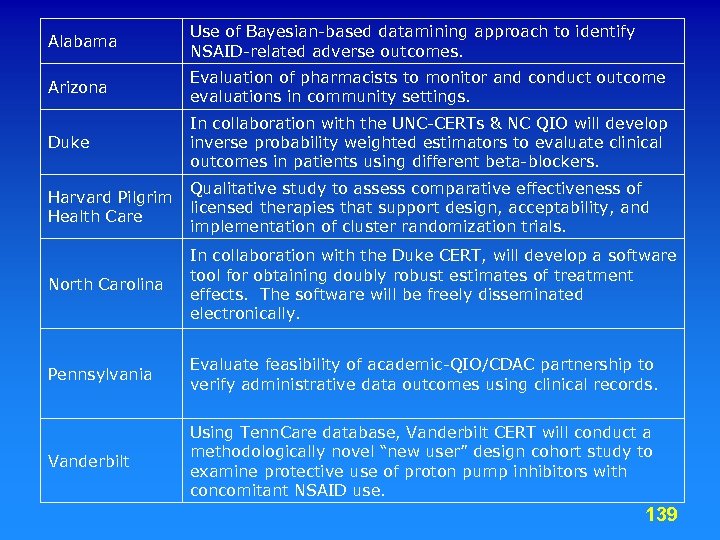 Alabama Use of Bayesian-based datamining approach to identify NSAID-related adverse outcomes. Arizona Evaluation of pharmacists to monitor and conduct outcome evaluations in community settings. Duke In collaboration with the UNC-CERTs & NC QIO will develop inverse probability weighted estimators to evaluate clinical outcomes in patients using different beta-blockers. Qualitative study to assess comparative effectiveness of Harvard Pilgrim licensed therapies that support design, acceptability, and Health Care implementation of cluster randomization trials. North Carolina In collaboration with the Duke CERT, will develop a software tool for obtaining doubly robust estimates of treatment effects. The software will be freely disseminated electronically. Pennsylvania Evaluate feasibility of academic-QIO/CDAC partnership to verify administrative data outcomes using clinical records. Vanderbilt Using Tenn. Care database, Vanderbilt CERT will conduct a methodologically novel “new user” design cohort study to examine protective use of proton pump inhibitors with concomitant NSAID use. 139
Alabama Use of Bayesian-based datamining approach to identify NSAID-related adverse outcomes. Arizona Evaluation of pharmacists to monitor and conduct outcome evaluations in community settings. Duke In collaboration with the UNC-CERTs & NC QIO will develop inverse probability weighted estimators to evaluate clinical outcomes in patients using different beta-blockers. Qualitative study to assess comparative effectiveness of Harvard Pilgrim licensed therapies that support design, acceptability, and Health Care implementation of cluster randomization trials. North Carolina In collaboration with the Duke CERT, will develop a software tool for obtaining doubly robust estimates of treatment effects. The software will be freely disseminated electronically. Pennsylvania Evaluate feasibility of academic-QIO/CDAC partnership to verify administrative data outcomes using clinical records. Vanderbilt Using Tenn. Care database, Vanderbilt CERT will conduct a methodologically novel “new user” design cohort study to examine protective use of proton pump inhibitors with concomitant NSAID use. 139
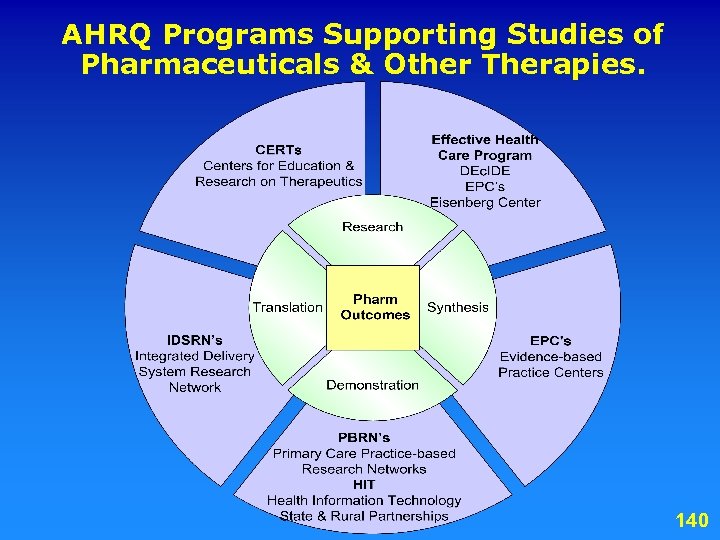 AHRQ Programs Supporting Studies of Pharmaceuticals & Other Therapies. 140
AHRQ Programs Supporting Studies of Pharmaceuticals & Other Therapies. 140
 More Information http: //effectivehealthcare. ahrq. gov/ Scott R. Smith, Ph. D DEc. IDE Director Ssmith@ahrq. gov Lia Snyder, MPH EHC Program Manager Lsnyder@ahrq. gov 141
More Information http: //effectivehealthcare. ahrq. gov/ Scott R. Smith, Ph. D DEc. IDE Director Ssmith@ahrq. gov Lia Snyder, MPH EHC Program Manager Lsnyder@ahrq. gov 141
 Acknowledgements & Thanks DEc. IDE Centers PI’s, Co-PI’s, and Affiliated Staff Jean Slutsky Director, AHRQ Center for Outcomes & Evidence Scott R. Smith, Ph. D Director, AHRQ Pharmaceutical Outcomes Research Programs Lia Snyder, MPH Program Manager, Effective Health Care Program Mark Helfand, MD Director, Scientific Resource Center David Hickham, MD Director, Eisenberg Center 142
Acknowledgements & Thanks DEc. IDE Centers PI’s, Co-PI’s, and Affiliated Staff Jean Slutsky Director, AHRQ Center for Outcomes & Evidence Scott R. Smith, Ph. D Director, AHRQ Pharmaceutical Outcomes Research Programs Lia Snyder, MPH Program Manager, Effective Health Care Program Mark Helfand, MD Director, Scientific Resource Center David Hickham, MD Director, Eisenberg Center 142
 Disclaimer This presentation and slide set does not represent the policy of either the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) or the US Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS). The views expressed herein are those of the presenter, and no official endorsement by AHRQ or DHHS is intended or should be inferred. Current information about the DEc. IDE program should be obtained from AHRQ or the DEc. IDE Program Director and not from these slides. 143
Disclaimer This presentation and slide set does not represent the policy of either the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) or the US Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS). The views expressed herein are those of the presenter, and no official endorsement by AHRQ or DHHS is intended or should be inferred. Current information about the DEc. IDE program should be obtained from AHRQ or the DEc. IDE Program Director and not from these slides. 143
 Thank you! 144
Thank you! 144


