e75bee49e8fceab5436ad5945bf399e4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Overview of PPP Edward Farquharson 28 September 2006

Agenda • Introduction • Types of PPP • UK Programme Scope • Institutional Issues • Does it Work? • Lessons Learnt

PPPs Are Not Standardised Internationally Each Country’s approach to PPP is: • Designed to meet the policy objectives of its Government • Developed to complement other public procurement and public service delivery methods • Implemented according to the available public and private sector resources Tailored and Unique

Relevance? ‘……a genie has been released from its bottle; the realisation that economic choices must be made based on risk-adjusted whole life costs and benefits will alter the nature of international economic competitiveness. In a sense, this is as fundamental as the discovery of gravity. When nations spend half their GDP on public services it was only a matter of time before the penny dropped…’ ‘PPP In-Depth’ - City and Financial – January 2006
Scope Total public service provision ‘Hard’ infrastructure Privatizations Concessions

PPPs are Not Just a Financing Tool Wider focus on issue of outcomes and procurement reform leads policy makers to address: – Project preparation, risk management and focus on whole life cost efficiencies – Sustainability - under-maintenance of public infrastructure – Value for money: optimum balance of cost and quality – Implications for institutions and processes

Types of PPP Concession Contract for Services - ‘PFI’ (UK) Joint Venture* Investment Programme Management * Partnerships UK is an example

Distinction between Privatisation and PPP? Where does accountability for public services delivery lie?
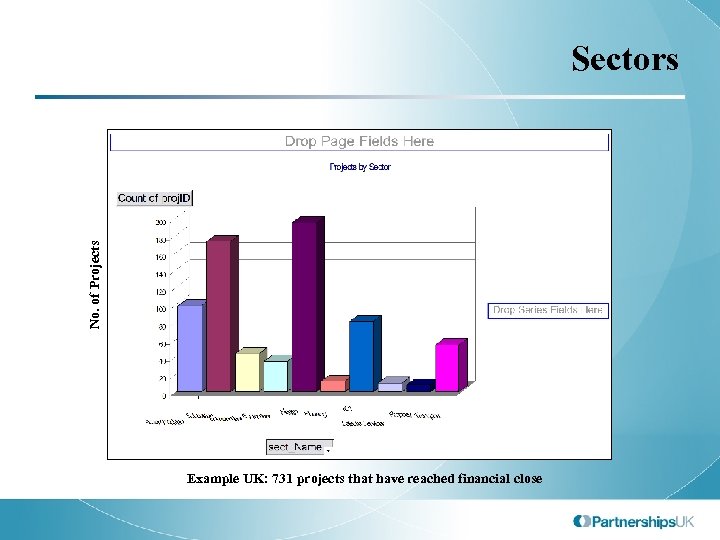
No. of Projects Sectors Example UK: 731 projects that have reached financial close
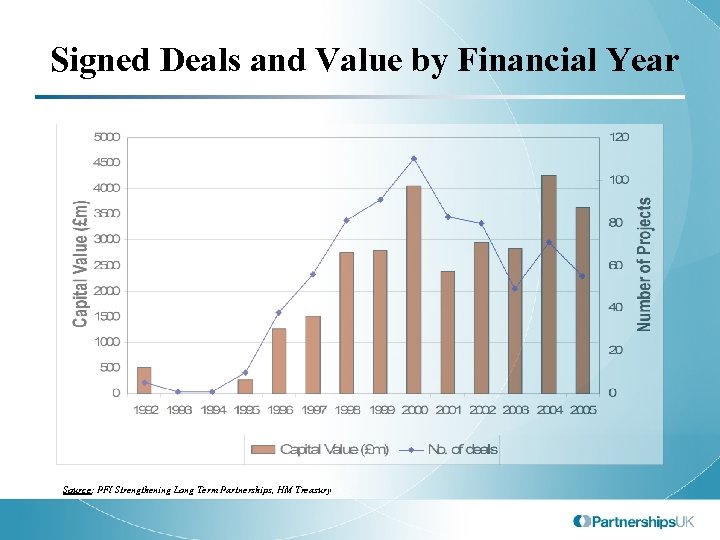
Signed Deals and Value by Financial Year Source: PFI Strengthening Long Term Partnerships, HM Treasury
Key features of PFI procurement • Output based contracts • Certainty of whole life-of-asset costings • Single point responsibility – integration / scope • Innovation • Competition • Capital at risk to long term performance • Optimal risk transfer • Private sector capital at risk to performance in the delivery of public services
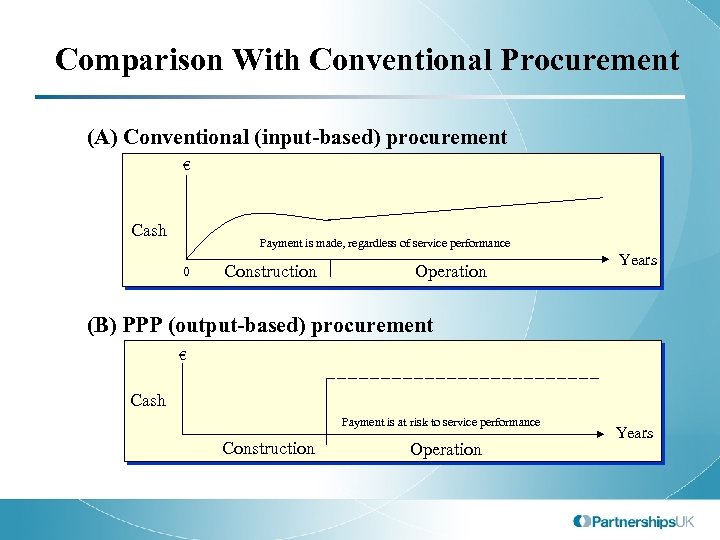
Comparison With Conventional Procurement (A) Conventional (input-based) procurement € Cash Payment is made, regardless of service performance 0 Construction Operation Years (B) PPP (output-based) procurement € Cash Payment is at risk to service performance Construction Operation Years

Importance of the Unitary Charge • Payments apportion risk: – – Availability Performance quality Usage / volume Additional revenue streams (where possible) – No guarantee of return • Composite total payment
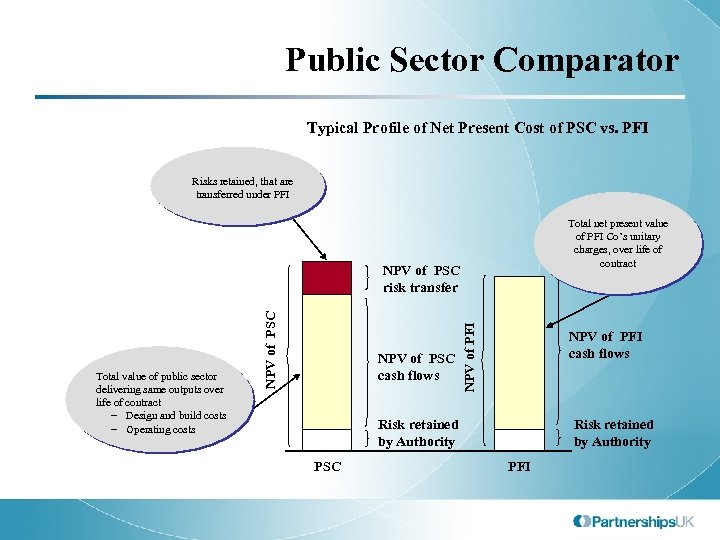
Public Sector Comparator Typical Profile of Net Present Cost of PSC vs. PFI Risks retained, that are transferred under PFI Total net present value of PFI Co’s unitary charges, over life of contract NPV of PSC cash flows NPV of PFI Total value of public sector delivering same outputs over life of contract – Design and build costs – Operating costs NPV of PSC risk transfer NPV of PFI cash flows Risk retained by Authority PSC Risk retained by Authority PFI

New Approaches to Vf. M Assessment • Quantitative analysis – Placed in context – Evidence based – Optimism bias • Qualitative tests – – – – Contractible Flexibility/cost Scope for cost/time overrun savings Innovation Length Capacity Competition ‘Viability’ ‘Desirability’ ‘Achievability’

Why Embark on a PFI Programme? • Improved value-for-money procurement of public services. • Reform / modernisation of public services. • Contestability in delivery of public services. • Antidote to short-termism in both public and private sectors. • Improved transparency of costs of public services delivery. • Overcome capital budget constraints.
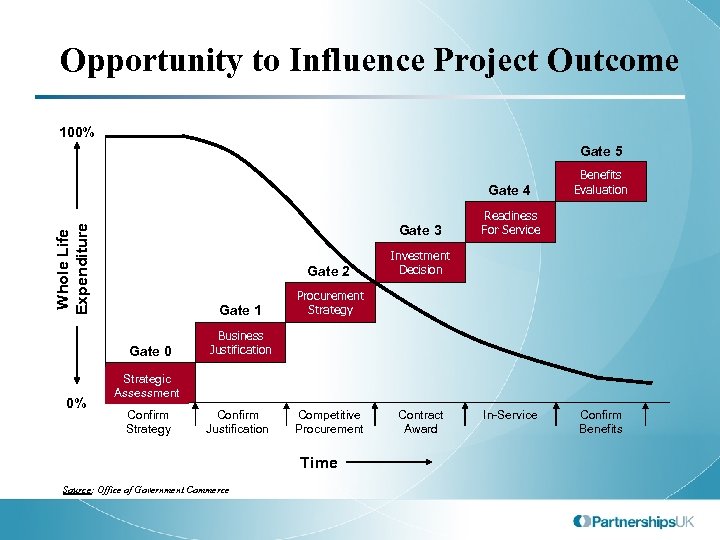
Opportunity to Influence Project Outcome 100% Gate 5 Gate 4 Whole Life Expenditure Gate 3 Gate 2 Gate 1 Gate 0 0% Benefits Evaluation Readiness For Service Investment Decision Procurement Strategy Business Justification Strategic Assessment Confirm Strategy Confirm Justification Competitive Procurement Time Source: Office of Government Commerce Contract Award In-Service Confirm Benefits

Public sector capacity issues • Joining up across time • Joining up across sectors • Asymmetry in experience/skills • Market knowledge • Role of the private sector • Independent scrutiny

Institutional challenges • Cuts across Government • Generic nature of issues • Resources scarce and expensive Central response
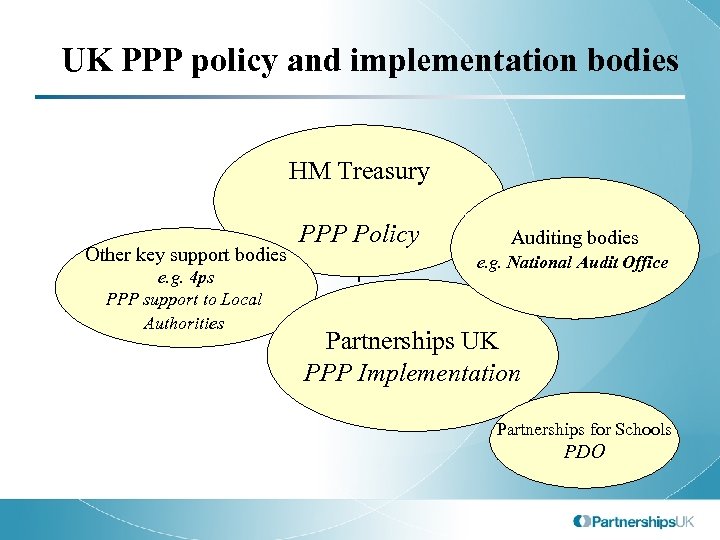
UK PPP policy and implementation bodies HM Treasury Other key support bodies e. g. 4 ps PPP support to Local Authorities PPP Policy Auditing bodies e. g. National Audit Office Partnerships UK PPP Implementation Partnerships for Schools PDO

PUK Activities • • Guidance, Standardisation, best practice, databases etc. • Help desk • Transaction Quality Control • Transaction Support • Programme/policy implementation Policy Support Investment programme management (Pf. H and Pf. S) • Co-sponsoring projects Partnership Agreements) • Commercialisation Investments Project support (Development
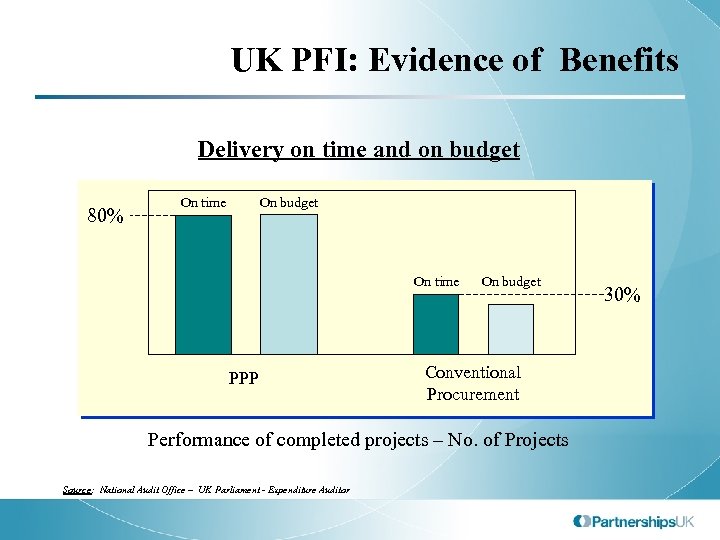
UK PFI: Evidence of Benefits Delivery on time and on budget 80% On time On budget On time PPP On budget Conventional Procurement Performance of completed projects – No. of Projects Source: National Audit Office – UK Parliament - Expenditure Auditor 30%
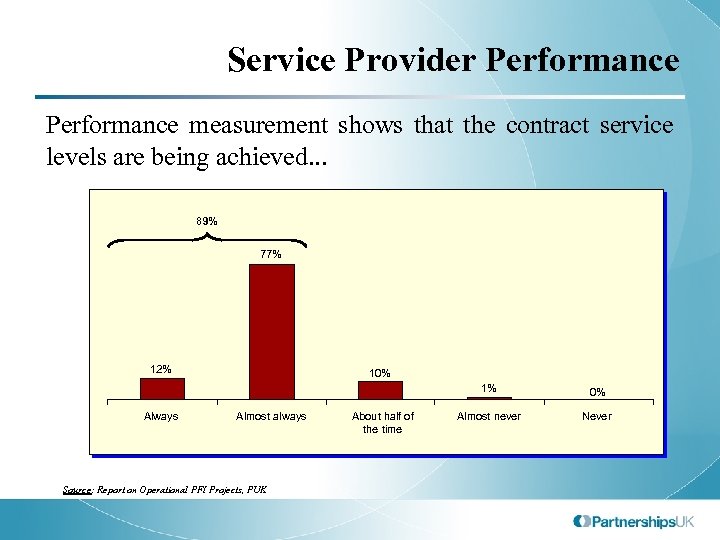
Service Provider Performance measurement shows that the contract service levels are being achieved. . . 89% 77% 12% 10% 1% Always Almost always Source: Report on Operational PFI Projects, PUK About half of the time 0% Almost never Never
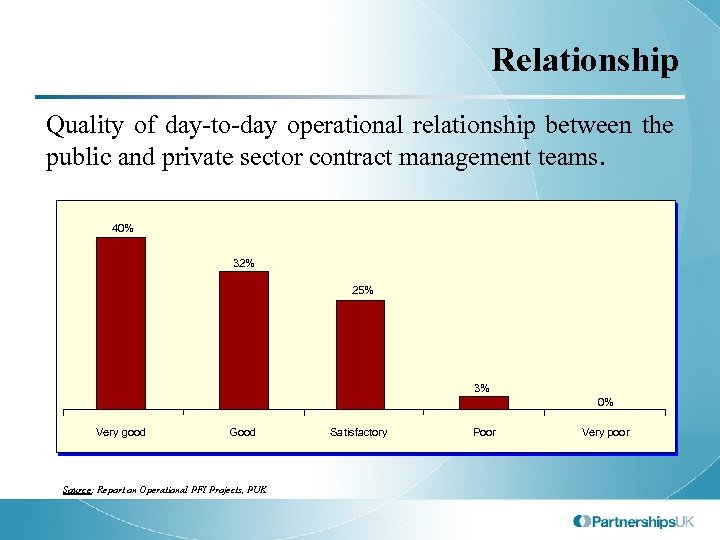
Relationship Quality of day-to-day operational relationship between the public and private sector contract management teams. 40% 32% 25% 3% 0% Very good Good Source: Report on Operational PFI Projects, PUK Satisfactory Poor Very poor
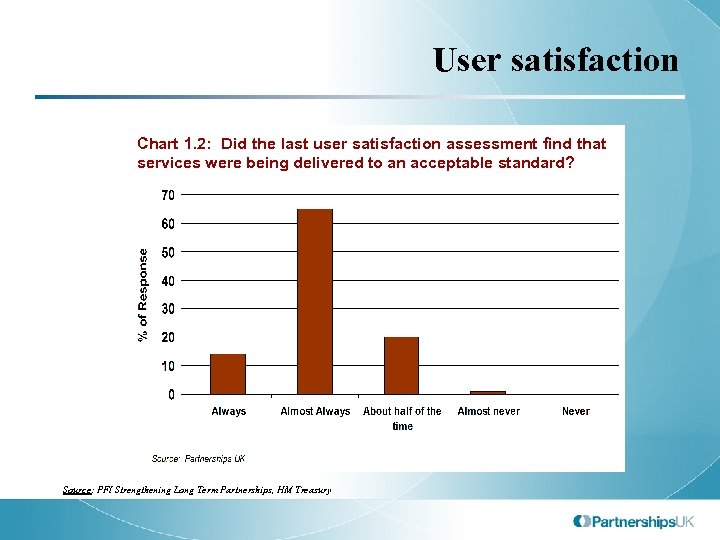
User satisfaction Chart 1. 2: Did the last user satisfaction assessment find that services were being delivered to an acceptable standard? Source: PFI Strengthening Long Term Partnerships, HM Treasury

Lessons Learnt • Legislative framework • Policy framework • Institutional reform • Capacity building: – – Public sector Private sector • Central support • Communication strategy • Programme development • Quality Control • … and above all, Political Commitment

edward. farquharson @partnershipsuk. org. uk +44 (0)20 7273 8040 www. partnershipsuk. org. uk
e75bee49e8fceab5436ad5945bf399e4.ppt