326f1c208337844cf5d0e790915ae577.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Overview of Navy Operational and Research SST Activities James Cummings Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey, CA Doug May and Bruce Mc. Kenzie Naval Oceanographic Office, Stennis Space Center, MS Sea Surface Temperature Science Team Meeting 8 -10 November 2010 Seattle, WA
Overview of Navy Operational and Research SST Activities James Cummings Naval Research Laboratory, Monterey, CA Doug May and Bruce Mc. Kenzie Naval Oceanographic Office, Stennis Space Center, MS Sea Surface Temperature Science Team Meeting 8 -10 November 2010 Seattle, WA
 Talk Outline: 1. NAVOCEANO SST Activities • SST retrievals • SST uncertainty estimates 2. SST Analysis Capabilities and Products 3. NRL SST Activities • aerosol contamination detection and correction • physical SST retrievals • diurnal skin SST model
Talk Outline: 1. NAVOCEANO SST Activities • SST retrievals • SST uncertainty estimates 2. SST Analysis Capabilities and Products 3. NRL SST Activities • aerosol contamination detection and correction • physical SST retrievals • diurnal skin SST model
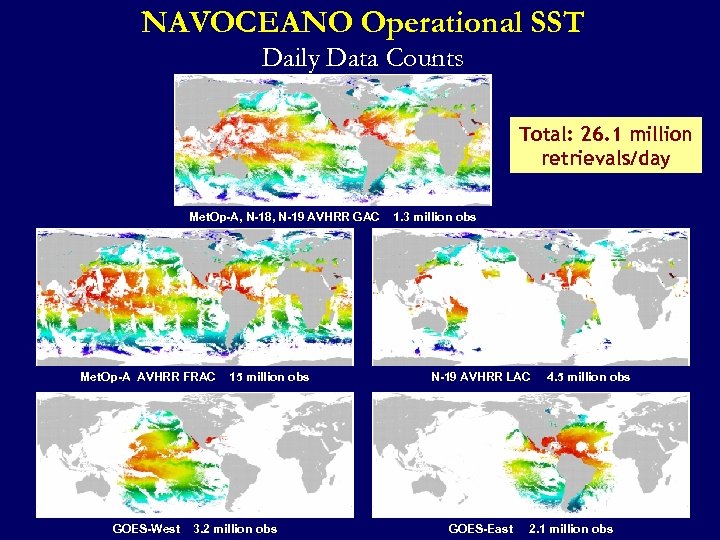 NAVOCEANO Operational SST Daily Data Counts Total: 26. 1 million retrievals/day Met. Op-A, N-18, N-19 AVHRR GAC Met. Op-A AVHRR FRAC GOES-West 15 million obs 3. 2 million obs 1. 3 million obs N-19 AVHRR LAC GOES-East 4. 5 million obs 2. 1 million obs
NAVOCEANO Operational SST Daily Data Counts Total: 26. 1 million retrievals/day Met. Op-A, N-18, N-19 AVHRR GAC Met. Op-A AVHRR FRAC GOES-West 15 million obs 3. 2 million obs 1. 3 million obs N-19 AVHRR LAC GOES-East 4. 5 million obs 2. 1 million obs
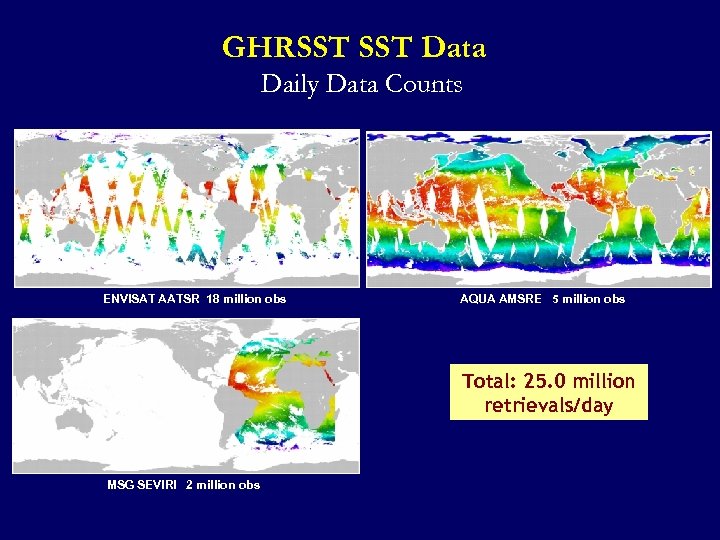 GHRSST Data Daily Data Counts ENVISAT AATSR 18 million obs AQUA AMSRE 5 million obs Total: 25. 0 million retrievals/day MSG SEVIRI 2 million obs
GHRSST Data Daily Data Counts ENVISAT AATSR 18 million obs AQUA AMSRE 5 million obs Total: 25. 0 million retrievals/day MSG SEVIRI 2 million obs
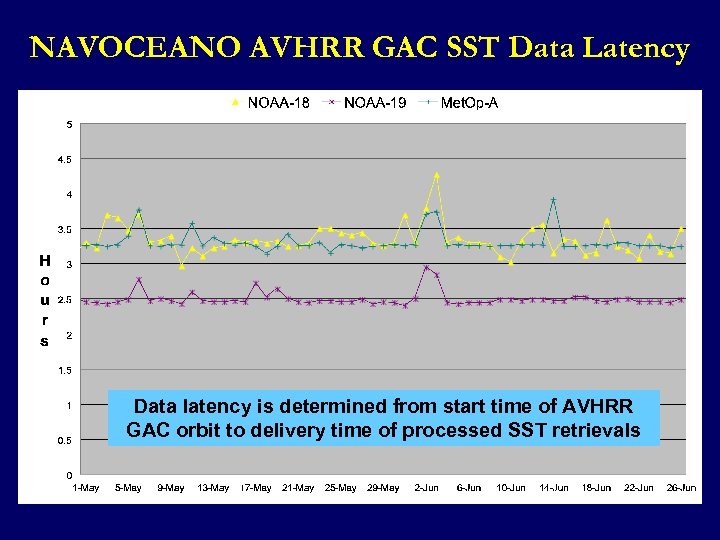 NAVOCEANO AVHRR GAC SST Data Latency Data latency is determined from start time of AVHRR GAC orbit to delivery time of processed SST retrievals
NAVOCEANO AVHRR GAC SST Data Latency Data latency is determined from start time of AVHRR GAC orbit to delivery time of processed SST retrievals
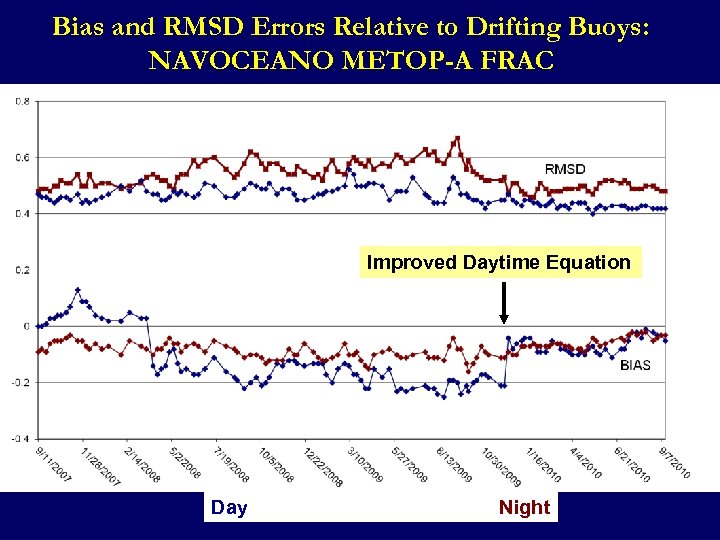 Bias and RMSD Errors Relative to Drifting Buoys: NAVOCEANO METOP-A FRAC Improved Daytime Equation Day Night
Bias and RMSD Errors Relative to Drifting Buoys: NAVOCEANO METOP-A FRAC Improved Daytime Equation Day Night
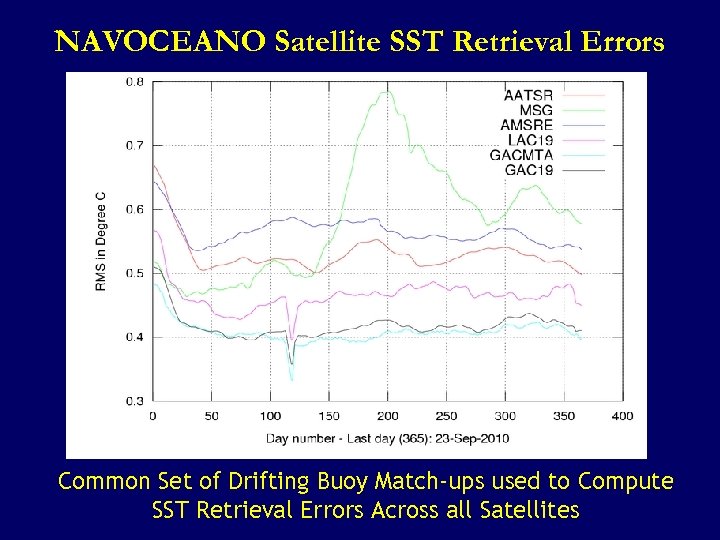 NAVOCEANO Satellite SST Retrieval Errors Common Set of Drifting Buoy Match-ups used to Compute SST Retrieval Errors Across all Satellites
NAVOCEANO Satellite SST Retrieval Errors Common Set of Drifting Buoy Match-ups used to Compute SST Retrieval Errors Across all Satellites
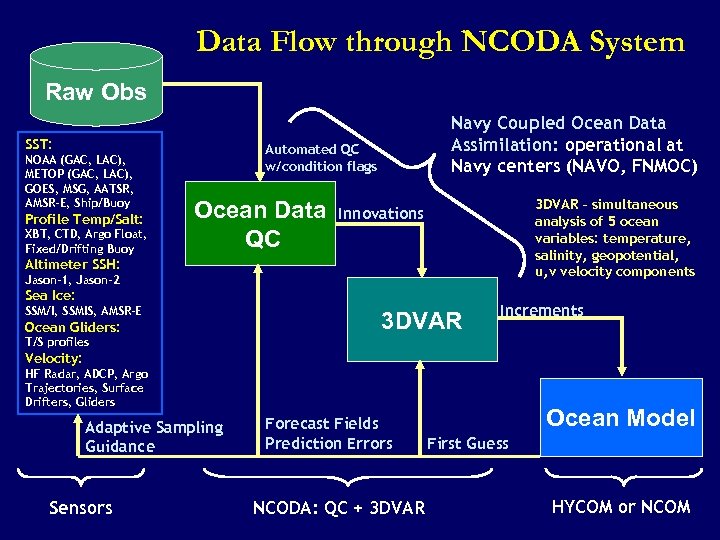 Data Flow through NCODA System Raw Obs SST: NOAA (GAC, LAC), METOP (GAC, LAC), GOES, MSG, AATSR, AMSR-E, Ship/Buoy Profile Temp/Salt: XBT, CTD, Argo Float, Fixed/Drifting Buoy Navy Coupled Ocean Data Assimilation: operational at Navy centers (NAVO, FNMOC) Automated QC w/condition flags Ocean Data QC 3 DVAR – simultaneous analysis of 5 ocean variables: temperature, salinity, geopotential, u, v velocity components Innovations Altimeter SSH: Jason-1, Jason-2 Sea Ice: SSM/I, SSMIS, AMSR-E Ocean Gliders: 3 DVAR Increments T/S profiles Velocity: HF Radar, ADCP, Argo Trajectories, Surface Drifters, Gliders Adaptive Sampling Guidance Sensors Forecast Fields Prediction Errors NCODA: QC + 3 DVAR Ocean Model First Guess HYCOM or NCOM
Data Flow through NCODA System Raw Obs SST: NOAA (GAC, LAC), METOP (GAC, LAC), GOES, MSG, AATSR, AMSR-E, Ship/Buoy Profile Temp/Salt: XBT, CTD, Argo Float, Fixed/Drifting Buoy Navy Coupled Ocean Data Assimilation: operational at Navy centers (NAVO, FNMOC) Automated QC w/condition flags Ocean Data QC 3 DVAR – simultaneous analysis of 5 ocean variables: temperature, salinity, geopotential, u, v velocity components Innovations Altimeter SSH: Jason-1, Jason-2 Sea Ice: SSM/I, SSMIS, AMSR-E Ocean Gliders: 3 DVAR Increments T/S profiles Velocity: HF Radar, ADCP, Argo Trajectories, Surface Drifters, Gliders Adaptive Sampling Guidance Sensors Forecast Fields Prediction Errors NCODA: QC + 3 DVAR Ocean Model First Guess HYCOM or NCOM
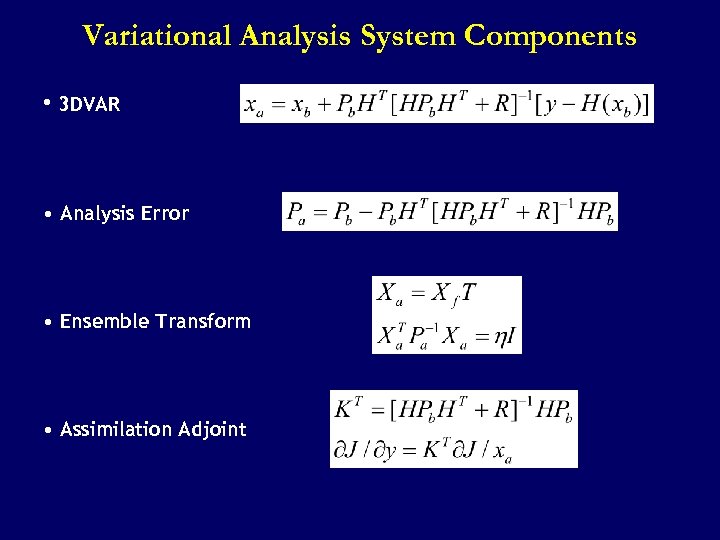 Variational Analysis System Components • 3 DVAR • Analysis Error • Ensemble Transform • Assimilation Adjoint
Variational Analysis System Components • 3 DVAR • Analysis Error • Ensemble Transform • Assimilation Adjoint
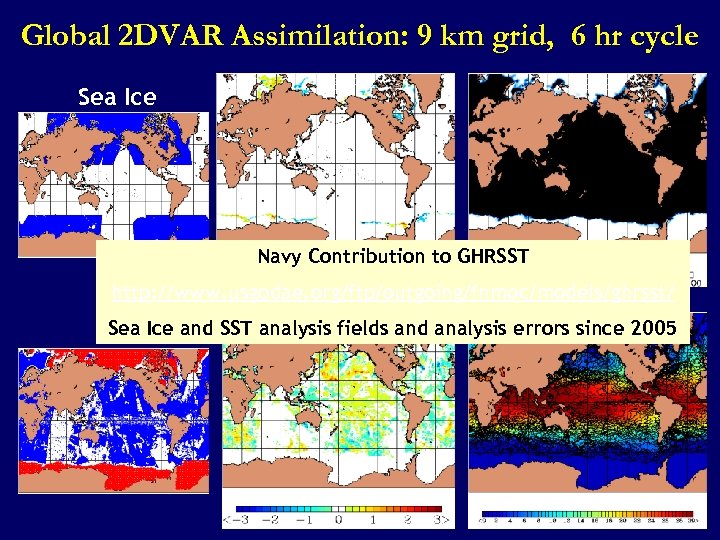 Global 2 DVAR Assimilation: 9 km grid, 6 hr cycle Sea Ice Navy Contribution to GHRSST http: //www. usgodae. org/ftp/outgoing/fnmoc/models/ghrsst/ Analysis Increments Updated Field Sea SST Ice and SST analysis fields and analysis errors since 2005
Global 2 DVAR Assimilation: 9 km grid, 6 hr cycle Sea Ice Navy Contribution to GHRSST http: //www. usgodae. org/ftp/outgoing/fnmoc/models/ghrsst/ Analysis Increments Updated Field Sea SST Ice and SST analysis fields and analysis errors since 2005
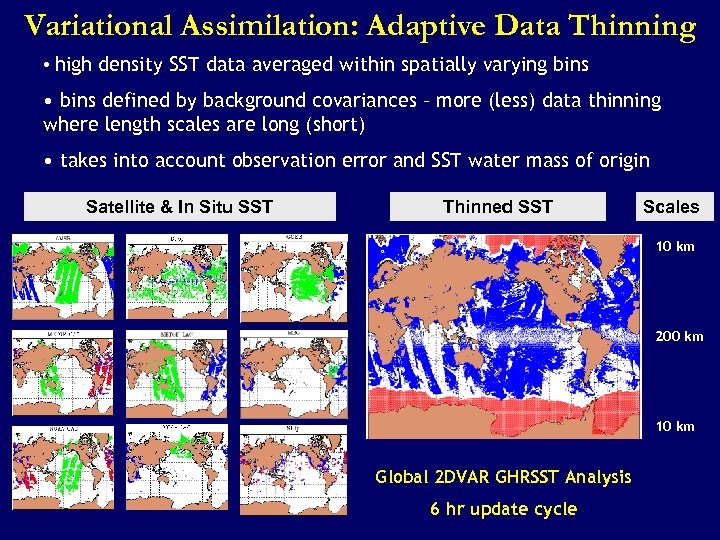 Variational Assimilation: Adaptive Data Thinning • high density SST data averaged within spatially varying bins • bins defined by background covariances – more (less) data thinning where length scales are long (short) • takes into account observation error and SST water mass of origin Satellite & In Situ SST Thinned SST Scales 10 km 200 km 10 km Global 2 DVAR GHRSST Analysis 6 hr update cycle
Variational Assimilation: Adaptive Data Thinning • high density SST data averaged within spatially varying bins • bins defined by background covariances – more (less) data thinning where length scales are long (short) • takes into account observation error and SST water mass of origin Satellite & In Situ SST Thinned SST Scales 10 km 200 km 10 km Global 2 DVAR GHRSST Analysis 6 hr update cycle
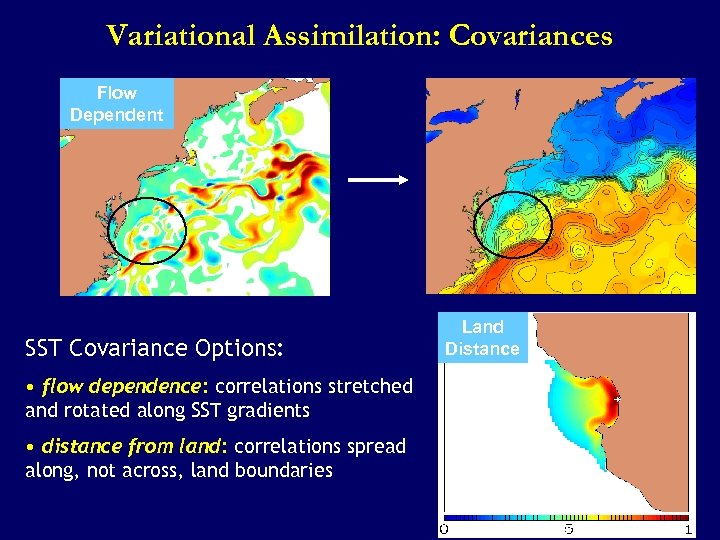 Variational Assimilation: Covariances Flow Dependent SST Covariance Options: • flow dependence: correlations stretched and rotated along SST gradients • distance from land: correlations spread along, not across, land boundaries Land Distance
Variational Assimilation: Covariances Flow Dependent SST Covariance Options: • flow dependence: correlations stretched and rotated along SST gradients • distance from land: correlations spread along, not across, land boundaries Land Distance
 Aerosol Plumes Obscure the Ocean Dust is optically active in the IR: elevated plumes appear cold Yellow Sea, Sea of Japan Need to first detect and then correct aerosol contamination of SST retrievals Tropical Atlantic Ocean West Pacific Ocean
Aerosol Plumes Obscure the Ocean Dust is optically active in the IR: elevated plumes appear cold Yellow Sea, Sea of Japan Need to first detect and then correct aerosol contamination of SST retrievals Tropical Atlantic Ocean West Pacific Ocean
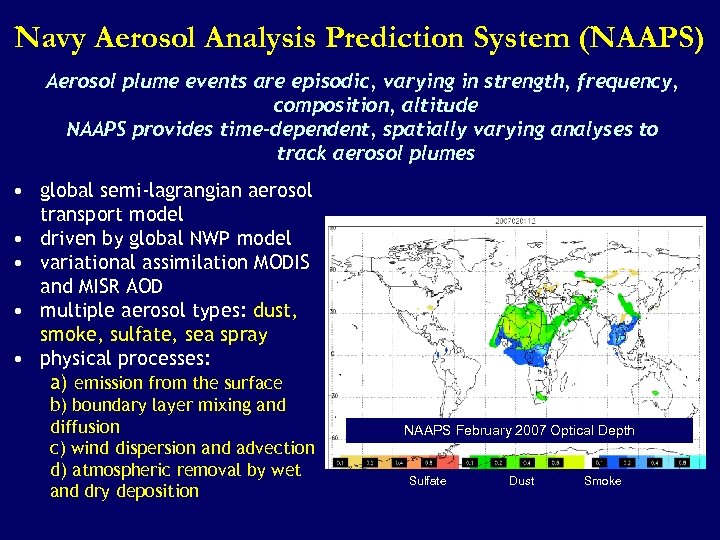 Navy Aerosol Analysis Prediction System (NAAPS) Aerosol plume events are episodic, varying in strength, frequency, composition, altitude NAAPS provides time-dependent, spatially varying analyses to track aerosol plumes • global semi-lagrangian aerosol transport model • driven by global NWP model • variational assimilation MODIS and MISR AOD • multiple aerosol types: dust, smoke, sulfate, sea spray • physical processes: a) emission from the surface b) boundary layer mixing and diffusion c) wind dispersion and advection d) atmospheric removal by wet and dry deposition NAAPS February 2007 Optical Depth Sulfate Dust Smoke
Navy Aerosol Analysis Prediction System (NAAPS) Aerosol plume events are episodic, varying in strength, frequency, composition, altitude NAAPS provides time-dependent, spatially varying analyses to track aerosol plumes • global semi-lagrangian aerosol transport model • driven by global NWP model • variational assimilation MODIS and MISR AOD • multiple aerosol types: dust, smoke, sulfate, sea spray • physical processes: a) emission from the surface b) boundary layer mixing and diffusion c) wind dispersion and advection d) atmospheric removal by wet and dry deposition NAAPS February 2007 Optical Depth Sulfate Dust Smoke
 Detection Aerosol Contamination: Canonical Variate Analysis • discriminate among groups of SST retrievals contaminated by aerosols and SST retrievals free from aerosols B = between group and W = within group covariance matrices. Eigenvalues of W-1 B and eigenvectors ( ) are the canonical variates. • • • predictors are AVHRR channel BTs and wavelength dependent NAAPS AOD components (x) projected onto r canonical variates SST is classified as contaminated if the Euclidean distance is closest to the contaminated group mean (μj) group assignment (k) is probabilistic ( 2) – allows for uncertainties in NAAPS model predictions and satellite IR BTs
Detection Aerosol Contamination: Canonical Variate Analysis • discriminate among groups of SST retrievals contaminated by aerosols and SST retrievals free from aerosols B = between group and W = within group covariance matrices. Eigenvalues of W-1 B and eigenvectors ( ) are the canonical variates. • • • predictors are AVHRR channel BTs and wavelength dependent NAAPS AOD components (x) projected onto r canonical variates SST is classified as contaminated if the Euclidean distance is closest to the contaminated group mean (μj) group assignment (k) is probabilistic ( 2) – allows for uncertainties in NAAPS model predictions and satellite IR BTs
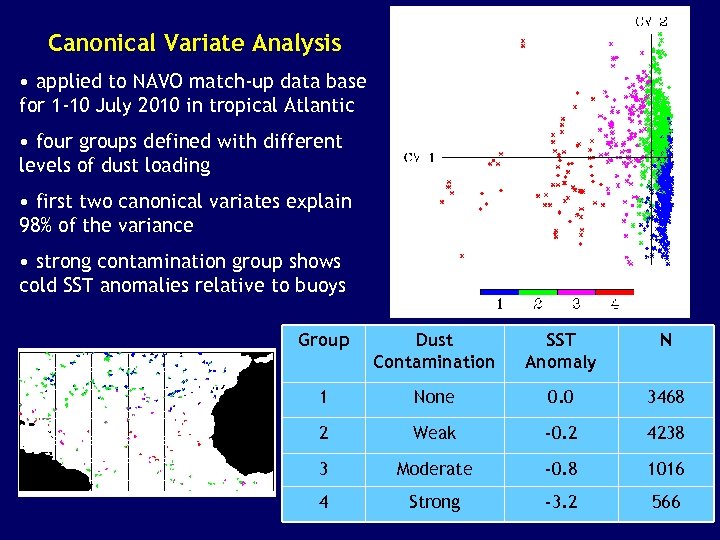 Canonical Variate Analysis • applied to NAVO match-up data base for 1 -10 July 2010 in tropical Atlantic • four groups defined with different levels of dust loading • first two canonical variates explain 98% of the variance • strong contamination group shows cold SST anomalies relative to buoys Group Dust Contamination SST Anomaly N 1 None 0. 0 3468 2 Weak -0. 2 4238 3 Moderate -0. 8 1016 4 Strong -3. 2 566
Canonical Variate Analysis • applied to NAVO match-up data base for 1 -10 July 2010 in tropical Atlantic • four groups defined with different levels of dust loading • first two canonical variates explain 98% of the variance • strong contamination group shows cold SST anomalies relative to buoys Group Dust Contamination SST Anomaly N 1 None 0. 0 3468 2 Weak -0. 2 4238 3 Moderate -0. 8 1016 4 Strong -3. 2 566
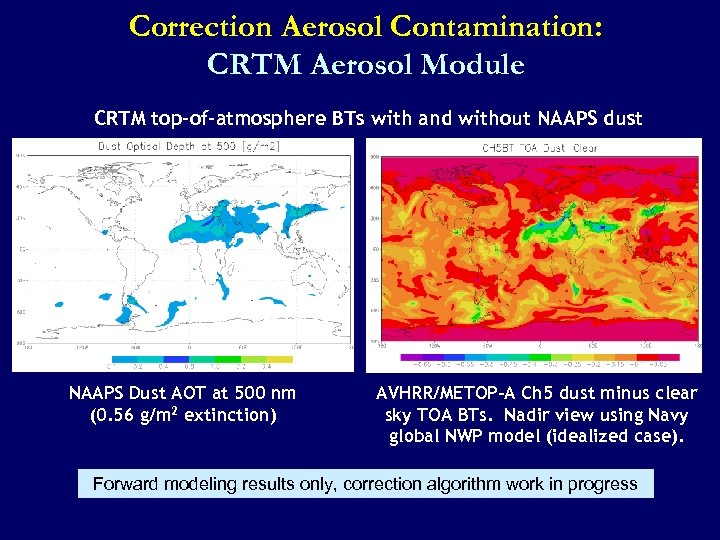 Correction Aerosol Contamination: CRTM Aerosol Module CRTM top-of-atmosphere BTs with and without NAAPS dust NAAPS Dust AOT at 500 nm (0. 56 g/m 2 extinction) AVHRR/METOP-A Ch 5 dust minus clear sky TOA BTs. Nadir view using Navy global NWP model (idealized case). Forward modeling results only, correction algorithm work in progress
Correction Aerosol Contamination: CRTM Aerosol Module CRTM top-of-atmosphere BTs with and without NAAPS dust NAAPS Dust AOT at 500 nm (0. 56 g/m 2 extinction) AVHRR/METOP-A Ch 5 dust minus clear sky TOA BTs. Nadir view using Navy global NWP model (idealized case). Forward modeling results only, correction algorithm work in progress
 Physical Satellite Skin SST Retrievals • incorporates impact of real atmosphere above the SST field • removes atmospheric signals in the data • assumes observed changes in SST BTs are due to 3 atmospheric model state variables: • atmospheric water vapor content • atmospheric temperature • sea surface temperature Two Step Process • CRTM forward modeling: innovations of AVHRR BTs wrt NWP model BTs • CRTM inverse modeling: sensitivities of SST BTs to model state vector and SST BT response to state perturbations
Physical Satellite Skin SST Retrievals • incorporates impact of real atmosphere above the SST field • removes atmospheric signals in the data • assumes observed changes in SST BTs are due to 3 atmospheric model state variables: • atmospheric water vapor content • atmospheric temperature • sea surface temperature Two Step Process • CRTM forward modeling: innovations of AVHRR BTs wrt NWP model BTs • CRTM inverse modeling: sensitivities of SST BTs to model state vector and SST BT response to state perturbations
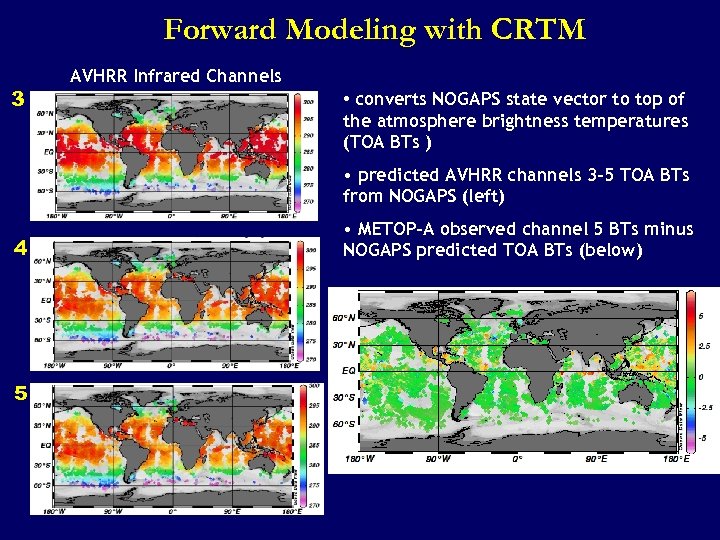 Forward Modeling with CRTM 3 AVHRR Infrared Channels • converts NOGAPS state vector to top of the atmosphere brightness temperatures (TOA BTs ) • predicted AVHRR channels 3 -5 TOA BTs from NOGAPS (left) 4 5 • METOP-A observed channel 5 BTs minus NOGAPS predicted TOA BTs (below)
Forward Modeling with CRTM 3 AVHRR Infrared Channels • converts NOGAPS state vector to top of the atmosphere brightness temperatures (TOA BTs ) • predicted AVHRR channels 3 -5 TOA BTs from NOGAPS (left) 4 5 • METOP-A observed channel 5 BTs minus NOGAPS predicted TOA BTs (below)
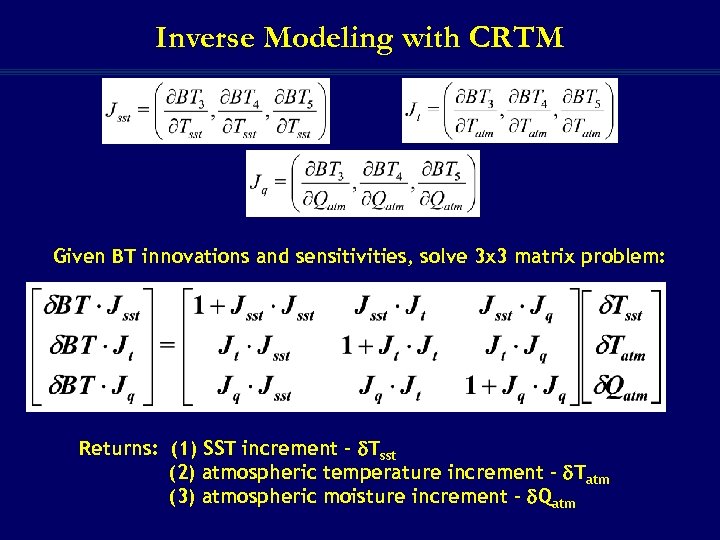 Inverse Modeling with CRTM Given BT innovations and sensitivities, solve 3 x 3 matrix problem: Returns: (1) SST increment - Tsst (2) atmospheric temperature increment - Tatm (3) atmospheric moisture increment - Qatm
Inverse Modeling with CRTM Given BT innovations and sensitivities, solve 3 x 3 matrix problem: Returns: (1) SST increment - Tsst (2) atmospheric temperature increment - Tatm (3) atmospheric moisture increment - Qatm
 Navy NWP Requirements for Physical Skin SST Skin vs. Bulk • empirical SST algorithms compute bulk SST from drifting buoys • skill limited to latitude / longitude range of buoy observations • unknown sampling depth of drifting buoys (cm to m) • daily averaged bulk SST analysis inadequate for NWP • Navy atmospheric 4 D-VAR rejects data from satellite sounding channels that peak at or near the surface Diurnal SST Cycle • need to resolve ocean diurnal cycle • essential weather variation • required for physical SST assimilation (6 -hr update cycle) • diurnal SST influences NWP convection and mixing • affects clouds, low level humidity, visibility, EM/EO propagation • NWP model improvements lead directly to improvements in ocean circulation and wave models
Navy NWP Requirements for Physical Skin SST Skin vs. Bulk • empirical SST algorithms compute bulk SST from drifting buoys • skill limited to latitude / longitude range of buoy observations • unknown sampling depth of drifting buoys (cm to m) • daily averaged bulk SST analysis inadequate for NWP • Navy atmospheric 4 D-VAR rejects data from satellite sounding channels that peak at or near the surface Diurnal SST Cycle • need to resolve ocean diurnal cycle • essential weather variation • required for physical SST assimilation (6 -hr update cycle) • diurnal SST influences NWP convection and mixing • affects clouds, low level humidity, visibility, EM/EO propagation • NWP model improvements lead directly to improvements in ocean circulation and wave models
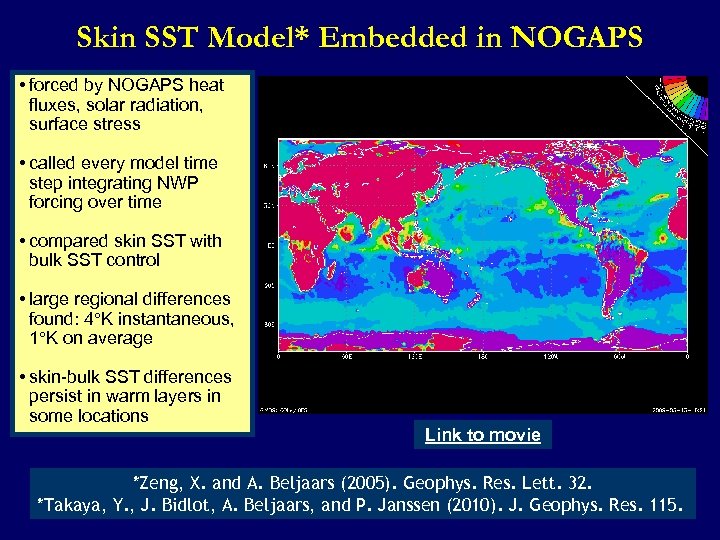 Skin SST Model* Embedded in NOGAPS • forced by NOGAPS heat fluxes, solar radiation, surface stress • called every model time step integrating NWP forcing over time • compared skin SST with bulk SST control • large regional differences found: 4 K instantaneous, 1 K on average • skin-bulk SST differences persist in warm layers in some locations Link to movie *Zeng, X. and A. Beljaars (2005). Geophys. Res. Lett. 32. *Takaya, Y. , J. Bidlot, A. Beljaars, and P. Janssen (2010). J. Geophys. Res. 115.
Skin SST Model* Embedded in NOGAPS • forced by NOGAPS heat fluxes, solar radiation, surface stress • called every model time step integrating NWP forcing over time • compared skin SST with bulk SST control • large regional differences found: 4 K instantaneous, 1 K on average • skin-bulk SST differences persist in warm layers in some locations Link to movie *Zeng, X. and A. Beljaars (2005). Geophys. Res. Lett. 32. *Takaya, Y. , J. Bidlot, A. Beljaars, and P. Janssen (2010). J. Geophys. Res. 115.
 Summary and Conclusions Navy Operations: • NOAA/METOP/GOES SST data provider • consistent SSES for all satellite SST observing systems • range of SST assimilation activities: • global, regional, coastal • analysis-only, model based forecasting systems Navy Research and Development: • physical SST retrieval algorithms • aerosol contamination detection and (eventually) correction • diurnal SST modeling, direct SST radiance assimilation Navy activities encompass many Science Team tasks
Summary and Conclusions Navy Operations: • NOAA/METOP/GOES SST data provider • consistent SSES for all satellite SST observing systems • range of SST assimilation activities: • global, regional, coastal • analysis-only, model based forecasting systems Navy Research and Development: • physical SST retrieval algorithms • aerosol contamination detection and (eventually) correction • diurnal SST modeling, direct SST radiance assimilation Navy activities encompass many Science Team tasks
 END
END
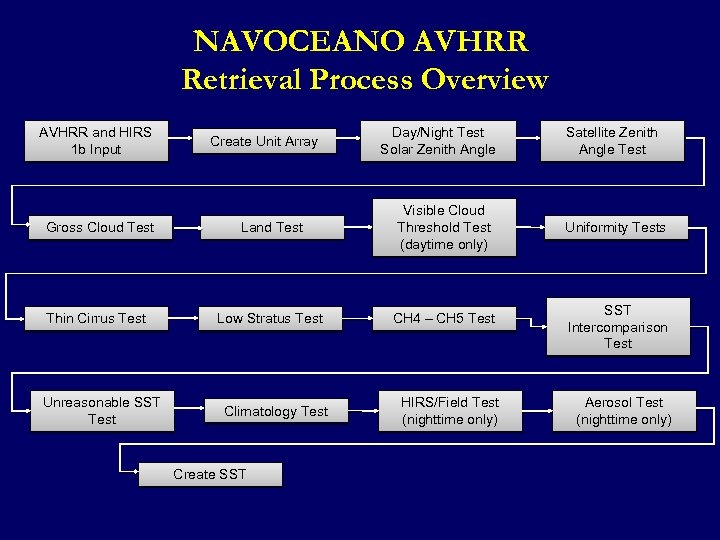 NAVOCEANO AVHRR Retrieval Process Overview AVHRR and HIRS 1 b Input Create Unit Array Day/Night Test Solar Zenith Angle Gross Cloud Test Land Test Visible Cloud Threshold Test (daytime only) Thin Cirrus Test Low Stratus Test CH 4 – CH 5 Test Unreasonable SST Test Climatology Test Create SST HIRS/Field Test (nighttime only) Satellite Zenith Angle Test Uniformity Tests SST Intercomparison Test Aerosol Test (nighttime only)
NAVOCEANO AVHRR Retrieval Process Overview AVHRR and HIRS 1 b Input Create Unit Array Day/Night Test Solar Zenith Angle Gross Cloud Test Land Test Visible Cloud Threshold Test (daytime only) Thin Cirrus Test Low Stratus Test CH 4 – CH 5 Test Unreasonable SST Test Climatology Test Create SST HIRS/Field Test (nighttime only) Satellite Zenith Angle Test Uniformity Tests SST Intercomparison Test Aerosol Test (nighttime only)


