7c27b96f310e0a3e13af01fbbf519ed7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Overview of CAAT A Partnership of Macomb Community College and Wayne State University July, 2012

What is CAAT? • Center for Advanced Automotive Technology at Macomb Community College and Wayne State University • Grant awarded for four years in September, 2010, by the NSF as a Regional Advanced Technological Education (ATE) Center – Focus on two-year colleges and cultivating partnerships: • Across academic institutions • Between academic institutions and employers – Key role is curriculum reform, development, and dissemination 2

Purpose of CAAT • Purpose: Advance the preparation of skilled technicians for the automotive industry which are now developing and producing more fuel efficient, environmentally friendly vehicles. The technologies, growing rapidly with implications for the nation’s electrical infrastructure, include: – Hybrid Electric, (HEV), Plug-in/Extended Range Electric (PEV) and Electric Vehicles (EV) – Alternative Fuel Vehicles (Advanced Clean Diesel, CNG, LPG) – Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCV) – Vehicle Lightweighting
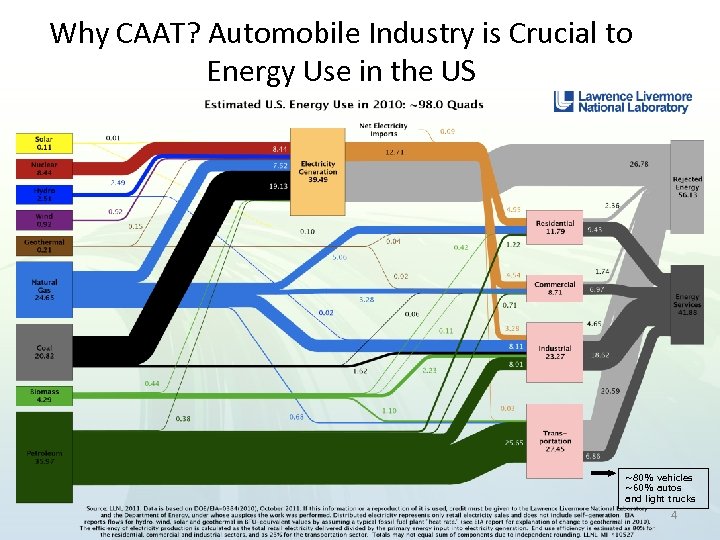
Why CAAT? Automobile Industry is Crucial to Energy Use in the US ~80% vehicles ~60% autos and light trucks 4
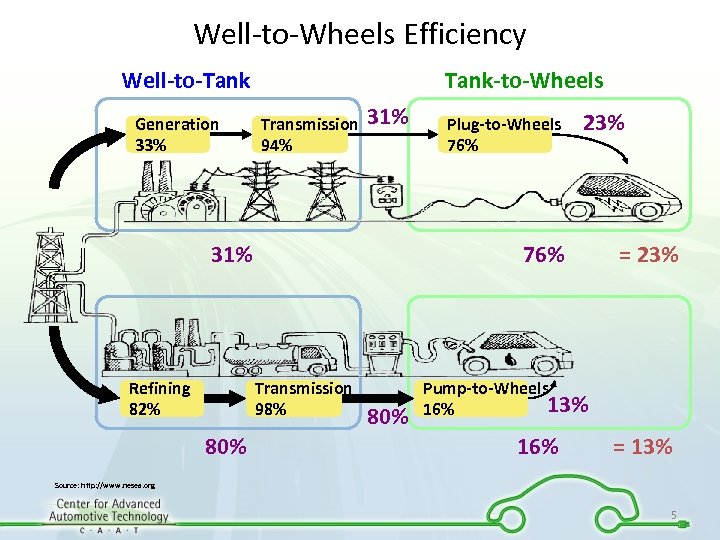
Well-to-Wheels Efficiency Well-to-Tank Generation 33% Tank-to-Wheels Transmission 94% 31% Refining 82% 23% 76% Transmission 98% 80% Plug-to-Wheels 76% 80% = 23% Pump-to-Wheels 13% 16% = 13% Source: http: //www. nesea. org 5
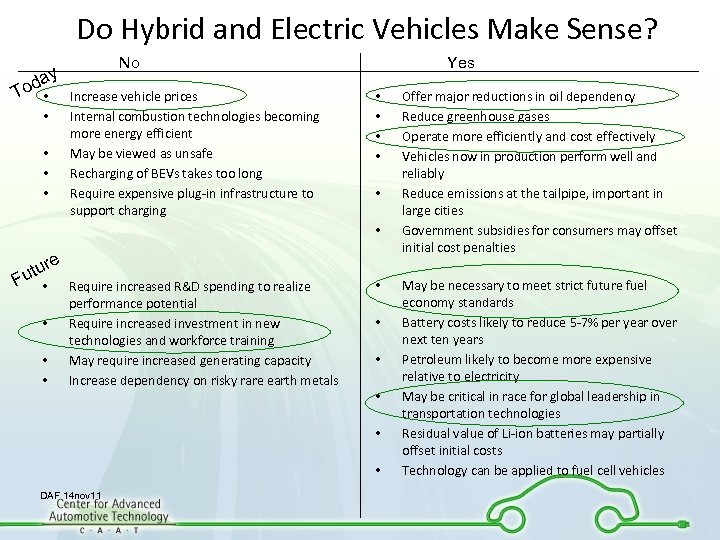
Do Hybrid and Electric Vehicles Make Sense? ay od • T • • No Increase vehicle prices Internal combustion technologies becoming more energy efficient May be viewed as unsafe Recharging of BEVs takes too long Require expensive plug-in infrastructure to support charging Yes • • • e tur u F • • Require increased R&D spending to realize performance potential Require increased investment in new technologies and workforce training May require increased generating capacity Increase dependency on risky rare earth metals • • • DAF 14 nov 11 Offer major reductions in oil dependency Reduce greenhouse gases Operate more efficiently and cost effectively Vehicles now in production perform well and reliably Reduce emissions at the tailpipe, important in large cities Government subsidies for consumers may offset initial cost penalties May be necessary to meet strict future fuel economy standards Battery costs likely to reduce 5 -7% per year over next ten years Petroleum likely to become more expensive relative to electricity May be critical in race for global leadership in transportation technologies Residual value of Li-ion batteries may partially offset initial costs Technology can be applied to fuel cell vehicles
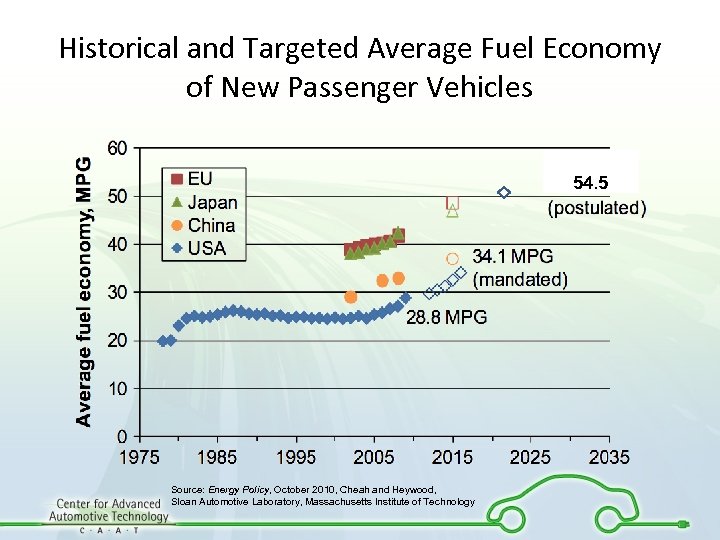
Historical and Targeted Average Fuel Economy of New Passenger Vehicles 54. 5 Source: Energy Policy, October 2010, Cheah and Heywood, Sloan Automotive Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
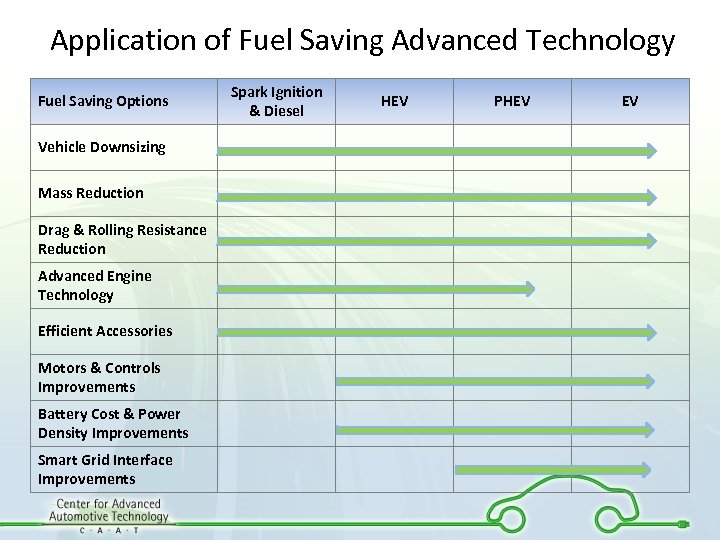
Application of Fuel Saving Advanced Technology Fuel Saving Options Vehicle Downsizing Mass Reduction Drag & Rolling Resistance Reduction Advanced Engine Technology Efficient Accessories Motors & Controls Improvements Battery Cost & Power Density Improvements Smart Grid Interface Improvements Spark Ignition & Diesel HEV PHEV EV
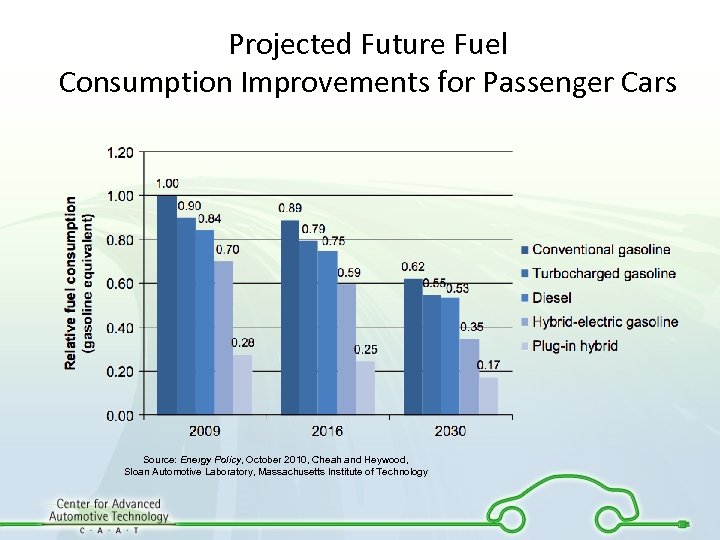
Projected Future Fuel Consumption Improvements for Passenger Cars Source: Energy Policy, October 2010, Cheah and Heywood, Sloan Automotive Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology

Long-Term Automotive Sales Forecasts: Key Industry Assumptions • Fuel costs • Cost and performance of advanced technologies, especially batteries • Electricity costs • Public acceptance of downsizing, advanced technologies, plugging-in, etc.
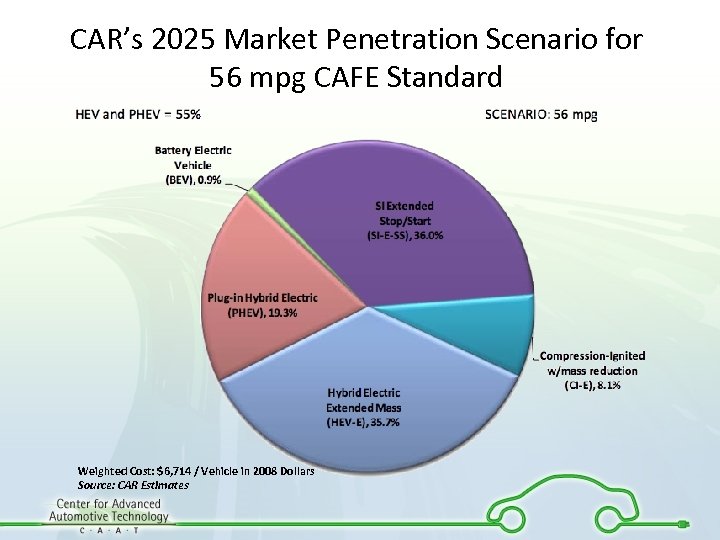
CAR’s 2025 Market Penetration Scenario for 56 mpg CAFE Standard Weighted Cost: $6, 714 / Vehicle in 2008 Dollars Source: CAR Estimates
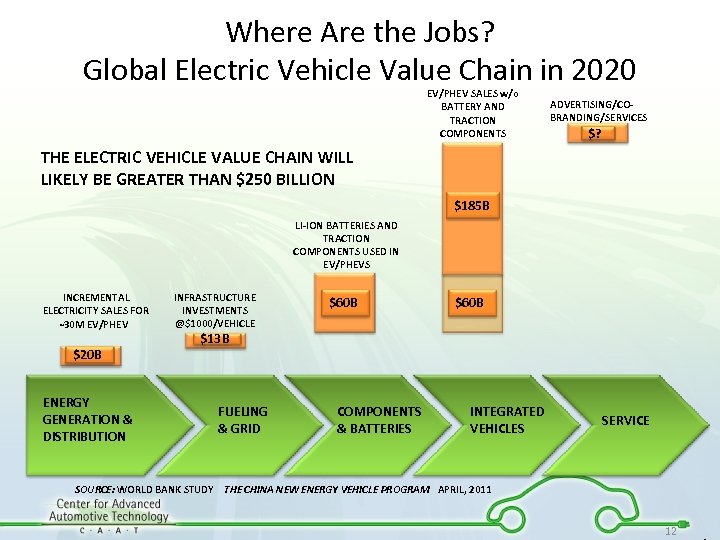
Where Are the Jobs? Global Electric Vehicle Value Chain in 2020 EV/PHEV SALES w/o BATTERY AND TRACTION COMPONENTS ADVERTISING/COBRANDING/SERVICES $? THE ELECTRIC VEHICLE VALUE CHAIN WILL LIKELY BE GREATER THAN $250 BILLION $185 B LI-ION BATTERIES AND TRACTION COMPONENTS USED IN EV/PHEVS INCREMENTAL ELECTRICITY SALES FOR 30 M EV/PHEV $20 B ENERGY GENERATION & DISTRIBUTION INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTMENTS @$1000/VEHICLE $60 B $13 B FUELING & GRID COMPONENTS & BATTERIES INTEGRATED VEHICLES SERVICE SOURCE: WORLD BANK STUDY THE CHINA NEW ENERGY VEHICLE PROGRAM APRIL, 2011 12

Why CAAT at Macomb/WSU? • Located in the heart of the rejuvenated US auto industry • Long history of serving the industry • Leaders of advanced automotive curriculum development • Executing a number of related Energy and Automotive grants 13

Advanced Automotive Grants Macomb Community College • Why is Macomb CC pursuing and winning grants in advanced automotive technology? Jobs, Skills, Careers Actions – Partnering with industry to identify educational needs and job opportunities – Preparing students for advanced auto work also prepares them for work in other advanced technologies – Builds the capability of MCC’s faculty and supporting resources to stay on the cutting edge of future technology developments – Partnering with Wayne State University on several auto-related grants broadens career opportunities for students 14
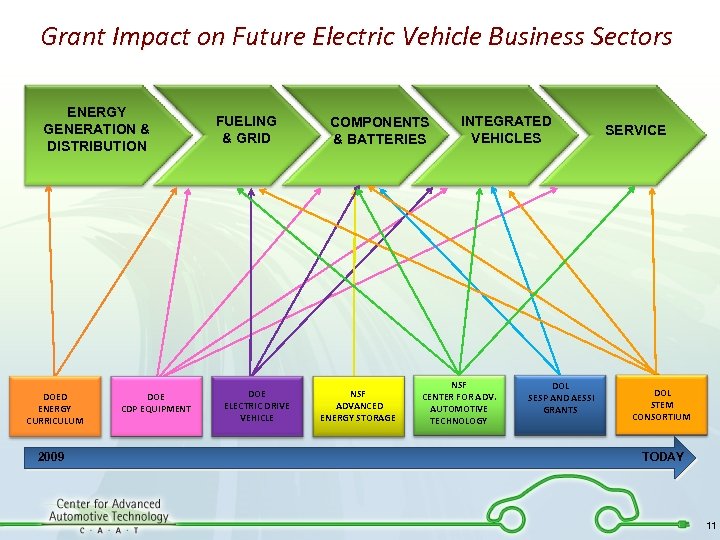
Grant Impact on Future Electric Vehicle Business Sectors ENERGY GENERATION & DISTRIBUTION DOED ENERGY CURRICULUM 2009 DOE CDP EQUIPMENT FUELING & GRID DOE ELECTRIC DRIVE VEHICLE COMPONENTS & BATTERIES NSF ADVANCED ENERGY STORAGE INTEGRATED VEHICLES NSF CENTER FOR ADV. AUTOMOTIVE TECHNOLOGY DOL SESP AND AESSI GRANTS SERVICE DOL STEM CONSORTIUM TODAY 11

Surveys of Industry Needs • MCC and WSU conducted, in 2008, a workforce needs survey in Advanced Automotive Technology as part of an ATE Center planning grant: – Workforce demand over next 5 years “high” (66. 7% for engineers and 57. 1% for technicians) – Community Colleges are meeting industry needs at least “moderately well” only 45% of the time • Two new surveys went out this month in partnership Workforce Intelligence Network for Southeast Michigan (WIN): – Data on industry skills needs for engineers, designers, and technicians – Specific gaps between industry expectations and the preparation of the workforce pool

What’s in It for Our Industry Partners? • Resource for: – Creating a technician pipeline (graduate or certified) – Increasing skills of current employees/technicians • Partner to: – Plan for future technical needs – Educate the general public
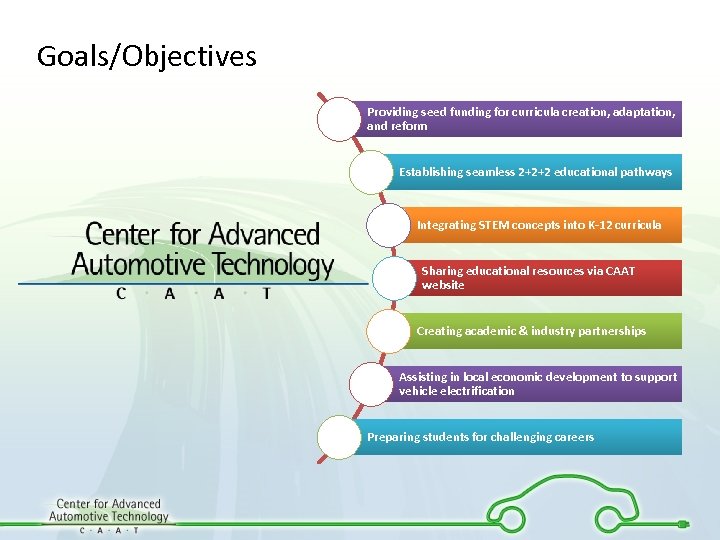
Goals/Objectives Providing seed funding for curricula creation, adaptation, and reform Establishing seamless 2+2+2 educational pathways Integrating STEM concepts into K-12 curricula Sharing educational resources via CAAT website Creating academic & industry partnerships Assisting in local economic development to support vehicle electrification Preparing students for challenging careers
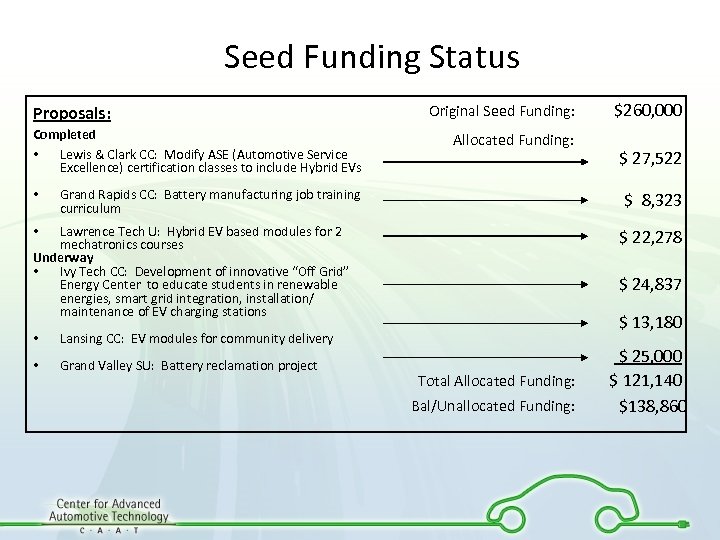
Seed Funding Status Proposals: Completed • Lewis & Clark CC: Modify ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) certification classes to include Hybrid EVs • Original Seed Funding: Allocated Funding: Grand Rapids CC: Battery manufacturing job training curriculum Lawrence Tech U: Hybrid EV based modules for 2 mechatronics courses Underway • Ivy Tech CC: Development of innovative “Off Grid” Energy Center to educate students in renewable energies, smart grid integration, installation/ maintenance of EV charging stations Grand Valley SU: Battery reclamation project $ 22, 278 $ 24, 837 $ 13, 180 Lansing CC: EV modules for community delivery • $ 27, 522 $ 8, 323 • • $260, 000 Total Allocated Funding: Bal/Unallocated Funding: $ 25, 000 $ 121, 140 $138, 860
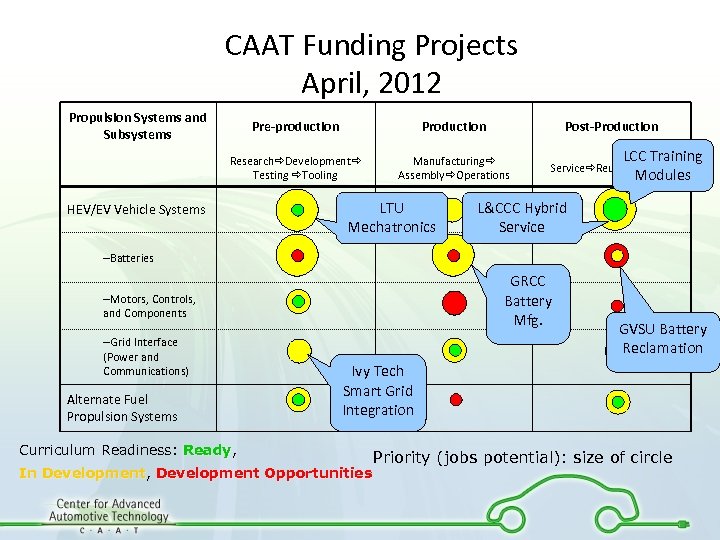
CAAT Funding Projects April, 2012 Propulsion Systems and Subsystems Pre-production Post-Production Research Development Testing Tooling Manufacturing Assembly Operations Service Reuse Recycle HEV/EV Vehicle Systems LTU Mechatronics LCC Training Modules L&CCC Hybrid Service –Batteries GRCC Battery Mfg. –Motors, Controls, and Components –Grid Interface (Power and Communications) Alternate Fuel Propulsion Systems GVSU Battery Reclamation Ivy Tech Smart Grid Integration Curriculum Readiness: Ready, Ready In Development, Development Opportunities Development Priority (jobs potential): size of circle

CAAT Seed Funding • Funding available on a first come, first serve basis for educational institutions to develop and/or adapt materials: • From modules and artifacts to courses and complete curricula • Equipment not to exceed 20% of funding request • CAAT and its partners will identify priority development needs 21

CAAT Seed Funding Process • Submit funding request using Proposal Template (following 5 slides) • Proposal approved by CAAT • Contract issued with key milestones for: – Deliverables – Payments – Reports 22

Proposal Template Section 1: Organization Info Name of Organization: Contact Person: Address: Phone: Email: Section 2: Abstract Brief overview (50 -100 words) of funding proposal including purpose, planned activities, resources, and expected results. Section 3: Project Purpose, Objectives, & Outcomes Describe what needs the proposal seeks to address, the specific objectives of the project, and how the project aligns with the overall mission of the CAAT. 23

Proposal Template Section 4: Project Scope Describe the educational project: - Adaptation of an existing course? - Development of a new course, course module or educational artifact? What Impact will project have on articulation agreements? On credit or non-credit courses. If credit, for what certificate(s) or degree progam(s)? Section 5: Target Audience Who will be the targeted students – Community college students, incumbent workers? How many students will be impacted? For degree, non-degree or certificate programs? 24

Proposal Template Section 6: Qualifications Describe skills, experiences, and organizational resources you and others engaged in the seed funding bring to the project. Include capabilities of partners and collaborators and brief bios. Section 7: Project Plan How will you gather and organize the requirements and resources for the project? What is your plan, including major milestones for developing all educational materials* funded under the project? *Submitted in editable format for sharing on the CAAT website with other educational institutions and organizations. Includes course description, objectives, outcomes, syllabus, instructor materials by class period, and other artifacts (student materials, lab activities and objectives, lab equipment, pre- and post-tests and exams). 25

Proposal Template Section 8: Quality Assurance - What outcomes will be specified for the curriculum/educational materials? - What evidence will you collect to demonstrate that the curriculum is effective? - What steps will you take to pilot or test your proposal and make adjustments to reflect the pilot results? Sections 9/10: Timeline & Budget - A timeline of important milestones in completing the project. - Your project budget detailing other sources of support and specify labor, materials, travel, equipment, and administrative costs (with justification for each). 26

Proposal Template Section 11: Reports - Submit brief progress reports coinciding with the project’s major milestone dates, agreed upon at funding and comprehended in the project plan. - For the calendar year(s) in which your project is being developed and implemented, you will be asked to submit data via a short survey immediately following the close of the calendar year. * *The NSF Advanced Technological Education (ATE) Program requires all ATE centers to submit this data annually. 27

CAAT SEED FUNDING Progress ____ or Final ____ Report (please check as applicable) Please submit this progress report to coincide with your project’s major milestone dates, as agreed upon at funding. Responses should be brief, totaling one or two pages, at most. College or Institution: _______________________ Name, Position & Phone Number: __________________ Reporting Period: ________________________ 1. Summary of Accomplishments (products, outputs, outcomes, etc. ): 2. Challenges, issues or concerns pertaining to the program, participants, project support, etc. and action plans to address these: 3. Scheduled events or anticipated activities (provide event/activity name, date, projected number of participants, etc. ) 4. Suggested improvements/feedback regarding the seed funding process. 28
Center for Advanced Automotive Technology Resources Available • Seed Funding Money Available • Curricula Resource Library Available on CAAT Website • Marketing of Your Program on CAAT Website • Source for Voice of Industry Needs • Industry Needs Survey Results • Development of Regional Strategy to Address Engineering & Technician Talent/Skills Needs • Existing & Future Internship Database 29
7c27b96f310e0a3e13af01fbbf519ed7.ppt