2ccaf908a5ebc235fa638f2c5d827b41.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

 Overview 1
Overview 1
 E-Government 2
E-Government 2
 Government to Citizens, Customers, and Businesses 3
Government to Citizens, Customers, and Businesses 3
 Government-to-Government Source: e. Gov. gov 4
Government-to-Government Source: e. Gov. gov 4
 Challenges & Expectations EXPECTATIONS Governance - IT Governance – IT Risk Management 5
Challenges & Expectations EXPECTATIONS Governance - IT Governance – IT Risk Management 5
 IT Governance 6
IT Governance 6
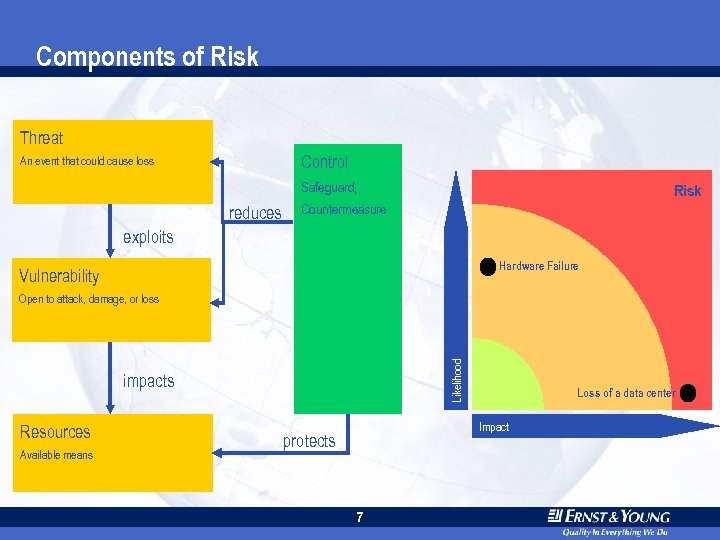 Components of Risk Threat Control An event that could cause loss Safeguard, reduces Risk Countermeasure exploits Hardware Failure Vulnerability Likelihood Open to attack, damage, or loss impacts Resources Available means Loss of a data center Impact protects 7
Components of Risk Threat Control An event that could cause loss Safeguard, reduces Risk Countermeasure exploits Hardware Failure Vulnerability Likelihood Open to attack, damage, or loss impacts Resources Available means Loss of a data center Impact protects 7
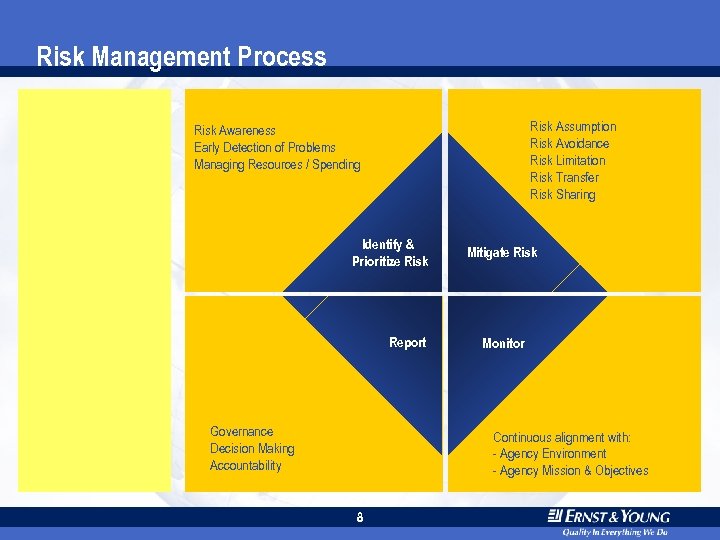 Risk Management Process Risk Assumption Risk Avoidance Risk Limitation Risk Transfer Risk Sharing Risk Awareness Early Detection of Problems Managing Resources / Spending Identify & Prioritize Risk Report Governance Decision Making Accountability Mitigate Risk Monitor Continuous alignment with: - Agency Environment - Agency Mission & Objectives 8
Risk Management Process Risk Assumption Risk Avoidance Risk Limitation Risk Transfer Risk Sharing Risk Awareness Early Detection of Problems Managing Resources / Spending Identify & Prioritize Risk Report Governance Decision Making Accountability Mitigate Risk Monitor Continuous alignment with: - Agency Environment - Agency Mission & Objectives 8
 Regulatory Environment 9
Regulatory Environment 9
 Control Requirements Drive requirements regarding …. . Which drive control objectives within…. To define or assess controls, these components need to be linked 10
Control Requirements Drive requirements regarding …. . Which drive control objectives within…. To define or assess controls, these components need to be linked 10
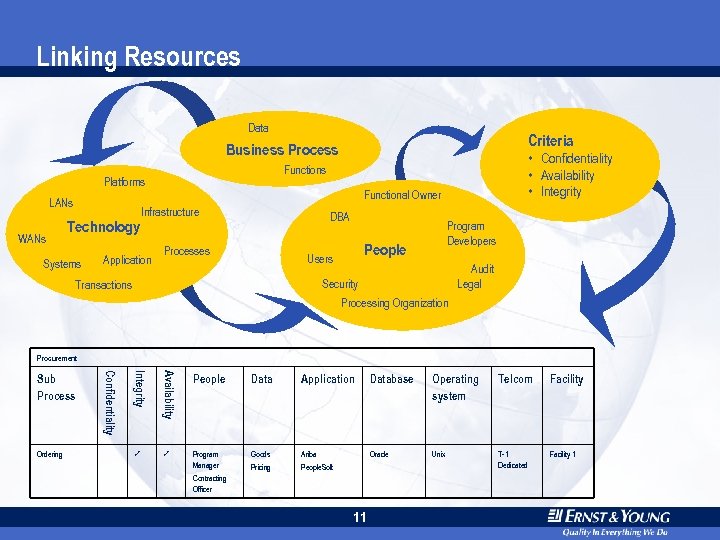 Linking Resources Data Criteria Business Process Platforms LANs WANs Technology Systems Functional Owner Infrastructure Application • Confidentiality • Availability • Integrity Functions DBA Processes Program Developers People Users Audit Legal Security Transactions Processing Organization Procurement Integrity Availability Ordering Confidentiality Sub Process People Program Manager Data Application Database Operating system Telcom Facility Goods Ariba Oracle Unix People. Soft T-1 Dedicated Facility 1 Pricing Contracting Officer 11
Linking Resources Data Criteria Business Process Platforms LANs WANs Technology Systems Functional Owner Infrastructure Application • Confidentiality • Availability • Integrity Functions DBA Processes Program Developers People Users Audit Legal Security Transactions Processing Organization Procurement Integrity Availability Ordering Confidentiality Sub Process People Program Manager Data Application Database Operating system Telcom Facility Goods Ariba Oracle Unix People. Soft T-1 Dedicated Facility 1 Pricing Contracting Officer 11
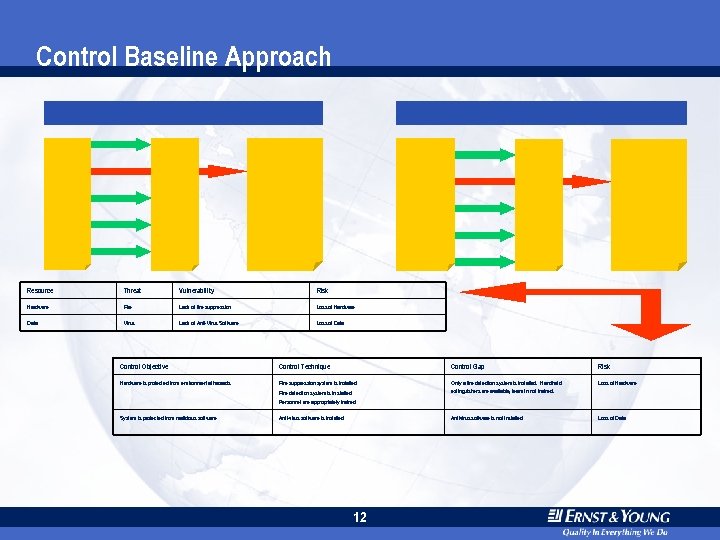 Control Baseline Approach Resource Threat Vulnerability Risk Hardware Fire Lack of fire suppression Loss of Hardware Data Virus Lack of Anti-Virus Software Loss of Data Control Objective Control Technique Control Gap Risk Hardware is protected from environmental hazards Fire suppression system is installed Only a fire detection system is installed. Handheld extinguishers are available, team in not trained. Loss of Hardware Antivirus software is not installed. Loss of Data Fire detection system is in stalled Personnel are appropriately trained System is protected from malicious software Anti-virus software is installed 12
Control Baseline Approach Resource Threat Vulnerability Risk Hardware Fire Lack of fire suppression Loss of Hardware Data Virus Lack of Anti-Virus Software Loss of Data Control Objective Control Technique Control Gap Risk Hardware is protected from environmental hazards Fire suppression system is installed Only a fire detection system is installed. Handheld extinguishers are available, team in not trained. Loss of Hardware Antivirus software is not installed. Loss of Data Fire detection system is in stalled Personnel are appropriately trained System is protected from malicious software Anti-virus software is installed 12
 Control Objectives 13
Control Objectives 13
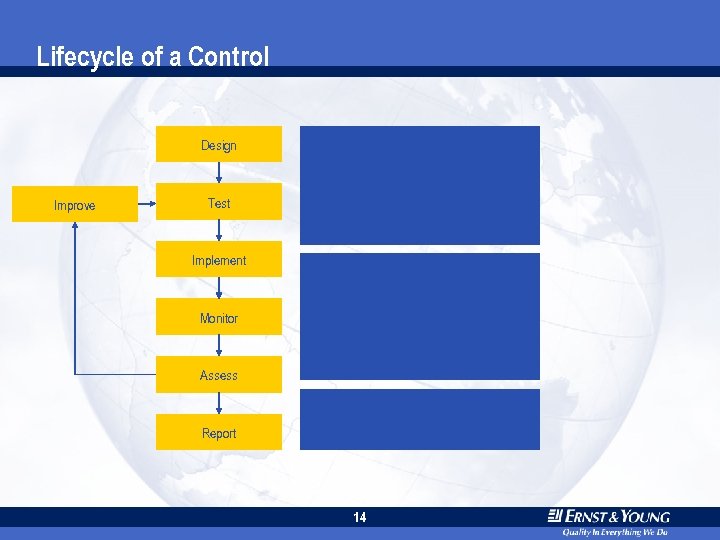 Lifecycle of a Control Design Improve Test Implement Monitor Assess Report 14
Lifecycle of a Control Design Improve Test Implement Monitor Assess Report 14
 Risk Considerations – New System Initiative 15
Risk Considerations – New System Initiative 15
 Risk Management Challenges 16
Risk Management Challenges 16
 Defining a Framework Approach and Methodology 17
Defining a Framework Approach and Methodology 17
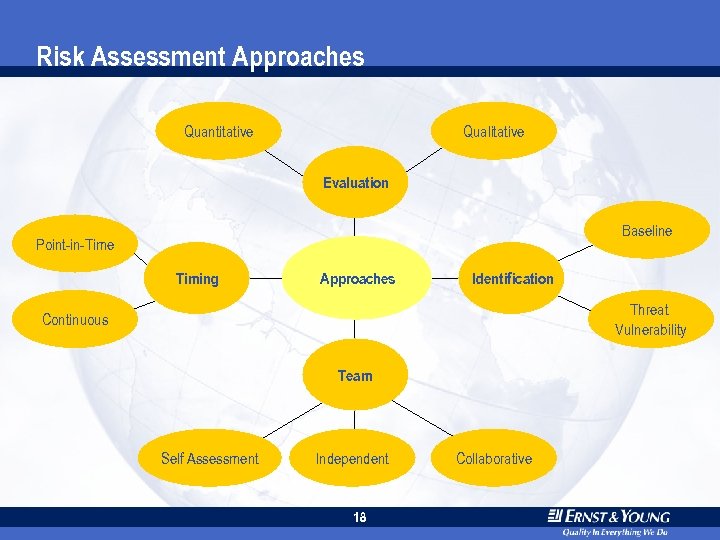 Risk Assessment Approaches Quantitative Qualitative Evaluation Baseline Point-in-Time Timing Approaches Identification Threat Vulnerability Continuous Team Self Assessment Independent 18 Collaborative
Risk Assessment Approaches Quantitative Qualitative Evaluation Baseline Point-in-Time Timing Approaches Identification Threat Vulnerability Continuous Team Self Assessment Independent 18 Collaborative
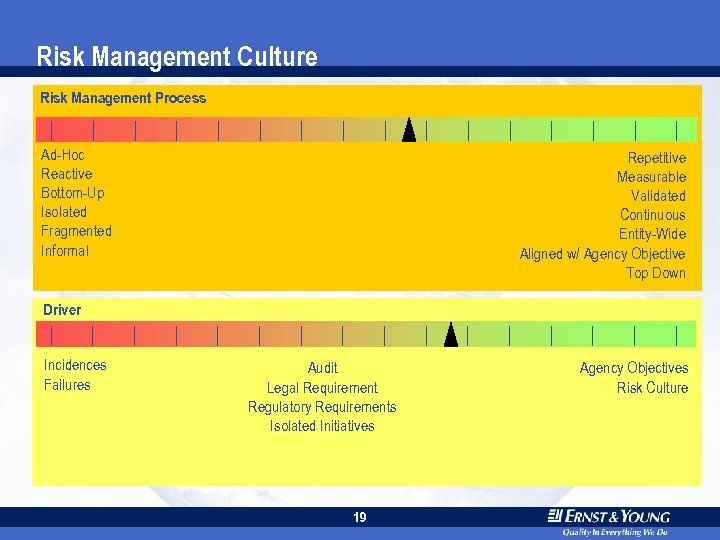 Risk Management Culture Risk Management Process Ad-Hoc Reactive Bottom-Up Isolated Fragmented Informal Repetitive Measurable Validated Continuous Entity-Wide Aligned w/ Agency Objective Top Down Driver Incidences Failures Audit Legal Requirement Regulatory Requirements Isolated Initiatives 19 Agency Objectives Risk Culture
Risk Management Culture Risk Management Process Ad-Hoc Reactive Bottom-Up Isolated Fragmented Informal Repetitive Measurable Validated Continuous Entity-Wide Aligned w/ Agency Objective Top Down Driver Incidences Failures Audit Legal Requirement Regulatory Requirements Isolated Initiatives 19 Agency Objectives Risk Culture
 Risk Management Program – Lessons Learned 20
Risk Management Program – Lessons Learned 20
 Risk Management Program – Lessons Learned 21
Risk Management Program – Lessons Learned 21
 Risk Management Program – Lessons Learned 22
Risk Management Program – Lessons Learned 22
 Risk Management Program – Lessons Learned 23
Risk Management Program – Lessons Learned 23
 Conclusion Risk management activities are, consciously or unconsciously, executed by various functions within an agency. Linking these activities through coordination and communication vastly enhances the effectiveness of the overall risk management program. 24
Conclusion Risk management activities are, consciously or unconsciously, executed by various functions within an agency. Linking these activities through coordination and communication vastly enhances the effectiveness of the overall risk management program. 24
 Contact Information: Werner Lippuner Ernst & Young LLP Washington, D. C. 202 -327 -8389 Werner. Lippuner@ey. com
Contact Information: Werner Lippuner Ernst & Young LLP Washington, D. C. 202 -327 -8389 Werner. Lippuner@ey. com


