356287d33193f093022cf4a1cb2ffbec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 OUTLINE: • The telescope • Dark Matter searches • Extragalactic sources • Gamma Ray Bursts Barbara De Lotto INFN and Univ. of Udine – Italy C 2 CR 07 – Lake Tahoe on behalf of the MAGIC collaboration De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Selected topics & results
OUTLINE: • The telescope • Dark Matter searches • Extragalactic sources • Gamma Ray Bursts Barbara De Lotto INFN and Univ. of Udine – Italy C 2 CR 07 – Lake Tahoe on behalf of the MAGIC collaboration De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Selected topics & results
 MAGIC De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Current generation Cherenkov telescopes HESS VERITAS CANGAROO-III 2
MAGIC De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Current generation Cherenkov telescopes HESS VERITAS CANGAROO-III 2
 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe The MAGIC site MAGIC La Palma, IAC 28° North, 18° West MAGIC and its Control House 2200 m asl 3
De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe The MAGIC site MAGIC La Palma, IAC 28° North, 18° West MAGIC and its Control House 2200 m asl 3
 Barcelona IFAE, UA Barcelona, U. Barcelona, HU Berlin, Instituto Astrofisica Canarias, U. C. Davis, U. Dortmund, U. Lodz, UCM Madrid, MPI München, INFN/ U. Padua, INFN/ U. Siena, INR Sofia, Tuorla Observatory, Yerevan Phys. Institute, INFN/ U. Udine, U. Würzburg, ETH Zürich • Largest Cherenkov Telescope: 17 m Ø mirror dish • 3. 5° Fo. V Camera with 576 enhanced QE PMT’s • Fast repositioning for GRBs: average < 40 s • Trigger threshold: 50 Ge. V • Sensitivity: 2. 5% Crab / 50 h • -PSF: ~ 0. 1° • Energy resolution: 20 - 30% De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe The MAGIC -ray telescope 4
Barcelona IFAE, UA Barcelona, U. Barcelona, HU Berlin, Instituto Astrofisica Canarias, U. C. Davis, U. Dortmund, U. Lodz, UCM Madrid, MPI München, INFN/ U. Padua, INFN/ U. Siena, INR Sofia, Tuorla Observatory, Yerevan Phys. Institute, INFN/ U. Udine, U. Würzburg, ETH Zürich • Largest Cherenkov Telescope: 17 m Ø mirror dish • 3. 5° Fo. V Camera with 576 enhanced QE PMT’s • Fast repositioning for GRBs: average < 40 s • Trigger threshold: 50 Ge. V • Sensitivity: 2. 5% Crab / 50 h • -PSF: ~ 0. 1° • Energy resolution: 20 - 30% De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe The MAGIC -ray telescope 4
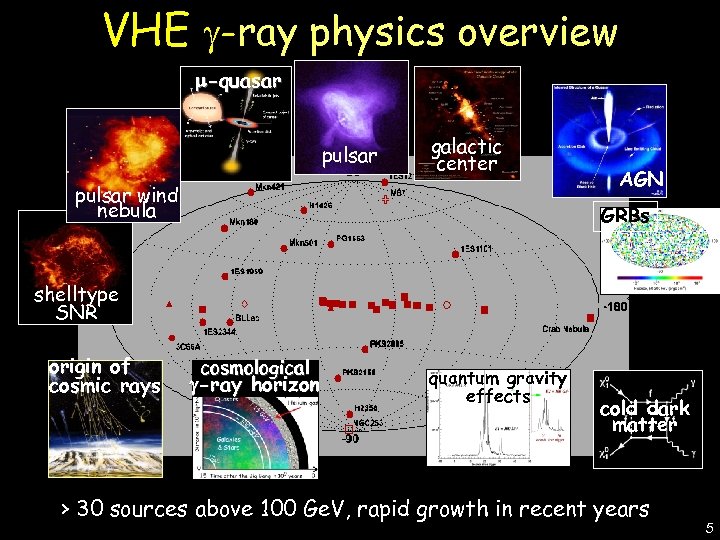 -quasar pulsar galactic center pulsar wind nebula AGN GRBs De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe VHE -ray physics overview shelltype SNR origin of cosmic rays cosmological -ray horizon quantum gravity effects cold dark matter > 30 sources above 100 Ge. V, rapid growth in recent years 5
-quasar pulsar galactic center pulsar wind nebula AGN GRBs De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe VHE -ray physics overview shelltype SNR origin of cosmic rays cosmological -ray horizon quantum gravity effects cold dark matter > 30 sources above 100 Ge. V, rapid growth in recent years 5
 n Standard Cosmological scenario of Cold Dark Matter n Neutralino (lightest SUSY particle) attractive candidate -flux from annihilations: Z, H Particle physics: CDM density: q De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe -ray emission from Dark Matter q signature for IACTs: ~ r 2 Eg search -ray flux -line =>= mc for CDM clumps -lines suppressed -line Eg = mc- m. Z 2/4 mc observe: galactic center (high diffuse bkg), -continuum with E << m other dense objects continuum dominates 6
n Standard Cosmological scenario of Cold Dark Matter n Neutralino (lightest SUSY particle) attractive candidate -flux from annihilations: Z, H Particle physics: CDM density: q De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe -ray emission from Dark Matter q signature for IACTs: ~ r 2 Eg search -ray flux -line =>= mc for CDM clumps -lines suppressed -line Eg = mc- m. Z 2/4 mc observe: galactic center (high diffuse bkg), -continuum with E << m other dense objects continuum dominates 6
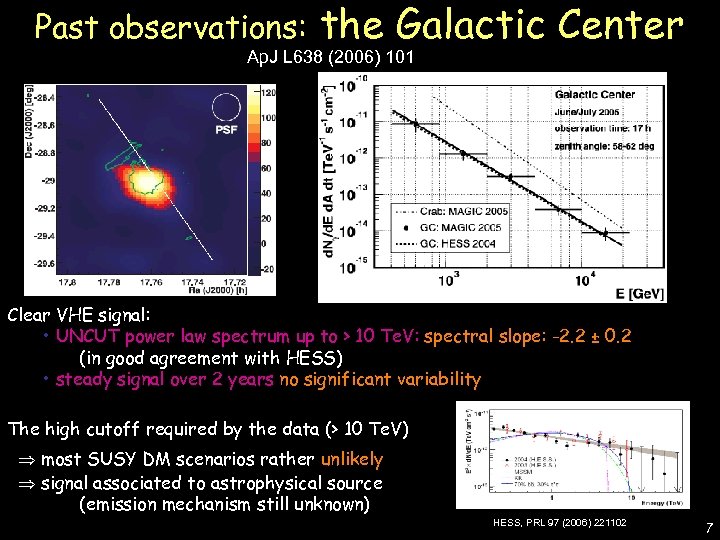 the Galactic Center Ap. J L 638 (2006) 101 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Past observations: Clear VHE signal: • UNCUT power law spectrum up to > 10 Te. V: spectral slope: -2. 2 ± 0. 2 (in good agreement with HESS) • steady signal over 2 years no significant variability The high cutoff required by the data (> 10 Te. V) most SUSY DM scenarios rather unlikely signal associated to astrophysical source (emission mechanism still unknown) HESS, PRL 97 (2006) 221102 7
the Galactic Center Ap. J L 638 (2006) 101 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Past observations: Clear VHE signal: • UNCUT power law spectrum up to > 10 Te. V: spectral slope: -2. 2 ± 0. 2 (in good agreement with HESS) • steady signal over 2 years no significant variability The high cutoff required by the data (> 10 Te. V) most SUSY DM scenarios rather unlikely signal associated to astrophysical source (emission mechanism still unknown) HESS, PRL 97 (2006) 221102 7
 Nearby galaxies with: “Mini-spike” model • high mass, low luminosity (M/L) possible large DM content • low stellar gas, dust content reduced background • northern hemisphere low Zd Possible formation of high r DM regions in association with Intermediate-Mass Black Holes in the galactic halo High M/L dwarf spheroid galaxies Draco [Bertone, Zentner, Silk, Phys. Rev. D 72 (2005) 103517] De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Proposals of candidates for observations (> June 2006) Unidentified EGRET sources (>100): • high galactic latitude (more clean signal) • stable flux • no counterpart at large wavelengths Look for identical cut-offs (DM mass) and similar spectra ~20 h Draco and ~30 h 3 EG_J 1835+5918 observed up to now 8
Nearby galaxies with: “Mini-spike” model • high mass, low luminosity (M/L) possible large DM content • low stellar gas, dust content reduced background • northern hemisphere low Zd Possible formation of high r DM regions in association with Intermediate-Mass Black Holes in the galactic halo High M/L dwarf spheroid galaxies Draco [Bertone, Zentner, Silk, Phys. Rev. D 72 (2005) 103517] De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Proposals of candidates for observations (> June 2006) Unidentified EGRET sources (>100): • high galactic latitude (more clean signal) • stable flux • no counterpart at large wavelengths Look for identical cut-offs (DM mass) and similar spectra ~20 h Draco and ~30 h 3 EG_J 1835+5918 observed up to now 8
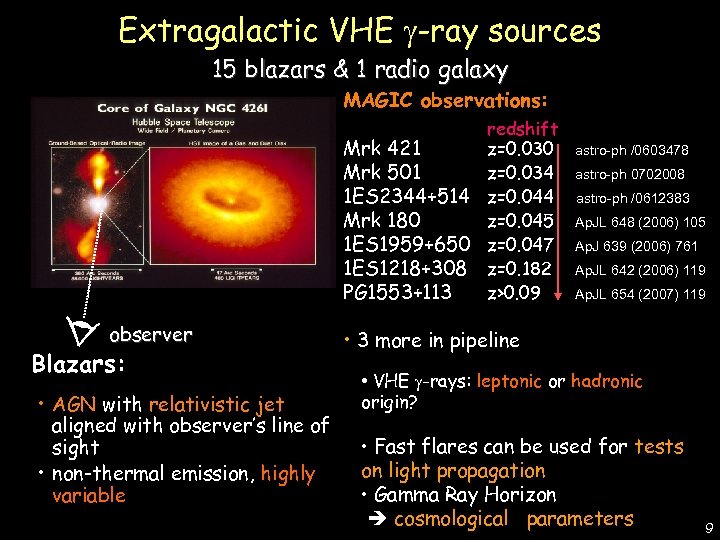 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Extragalactic VHE -ray sources 15 blazars & 1 radio galaxy MAGIC observations: redshift Mrk 421 z=0. 030 Mrk 501 z=0. 034 1 ES 2344+514 z=0. 044 Mrk 180 z=0. 045 1 ES 1959+650 z=0. 047 1 ES 1218+308 z=0. 182 PG 1553+113 z>0. 09 observer Blazars: • AGN with relativistic jet aligned with observer’s line of sight • non-thermal emission, highly variable astro-ph /0603478 astro-ph 0702008 astro-ph /0612383 Ap. JL 648 (2006) 105 Ap. J 639 (2006) 761 Ap. JL 642 (2006) 119 Ap. JL 654 (2007) 119 • 3 more in pipeline • VHE -rays: leptonic or hadronic origin? • Fast flares can be used for tests on light propagation • Gamma Ray Horizon cosmological parameters 9
De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Extragalactic VHE -ray sources 15 blazars & 1 radio galaxy MAGIC observations: redshift Mrk 421 z=0. 030 Mrk 501 z=0. 034 1 ES 2344+514 z=0. 044 Mrk 180 z=0. 045 1 ES 1959+650 z=0. 047 1 ES 1218+308 z=0. 182 PG 1553+113 z>0. 09 observer Blazars: • AGN with relativistic jet aligned with observer’s line of sight • non-thermal emission, highly variable astro-ph /0603478 astro-ph 0702008 astro-ph /0612383 Ap. JL 648 (2006) 105 Ap. J 639 (2006) 761 Ap. JL 642 (2006) 119 Ap. JL 654 (2007) 119 • 3 more in pipeline • VHE -rays: leptonic or hadronic origin? • Fast flares can be used for tests on light propagation • Gamma Ray Horizon cosmological parameters 9
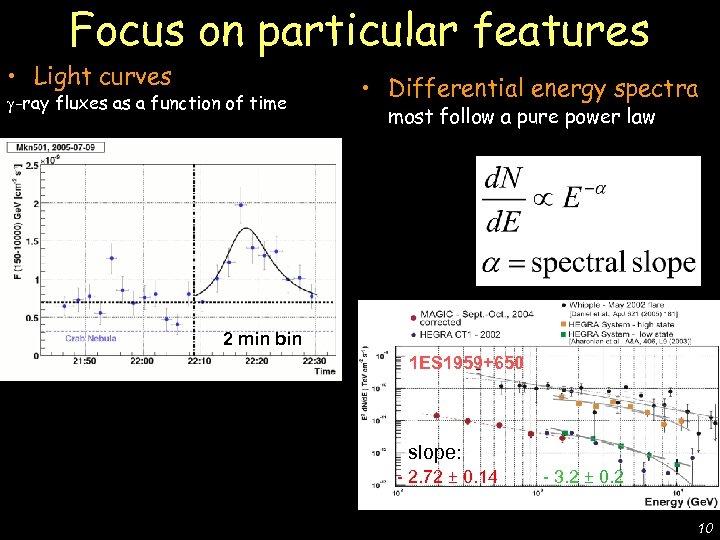 • Light curves -ray fluxes as a function of time • Differential energy spectra most follow a pure power law De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Focus on particular features 2 min bin 1 ES 1959+650 slope: - 2. 72 ± 0. 14 - 3. 2 ± 0. 2 10
• Light curves -ray fluxes as a function of time • Differential energy spectra most follow a pure power law De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Focus on particular features 2 min bin 1 ES 1959+650 slope: - 2. 72 ± 0. 14 - 3. 2 ± 0. 2 10
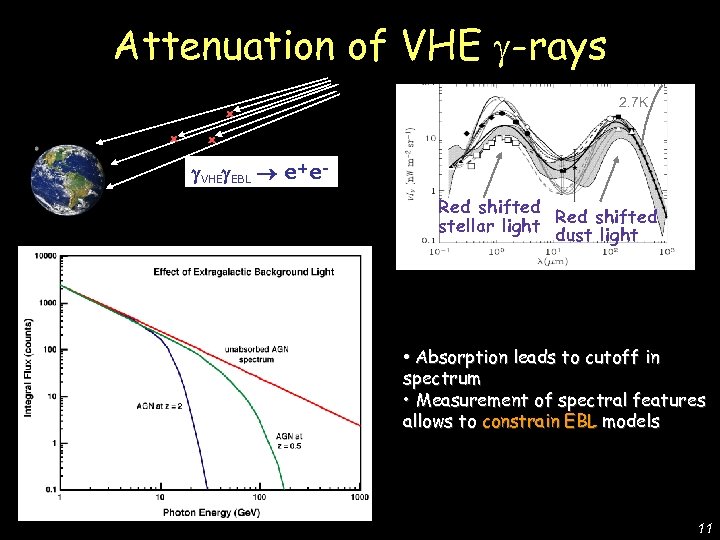 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Attenuation of VHE -rays x x 2. 7 K x VHE EBL e+e. Red shifted stellar light dust light • Absorption leads to cutoff in spectrum • Measurement of spectral features allows to constrain EBL models 11
De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Attenuation of VHE -rays x x 2. 7 K x VHE EBL e+e. Red shifted stellar light dust light • Absorption leads to cutoff in spectrum • Measurement of spectral features allows to constrain EBL models 11
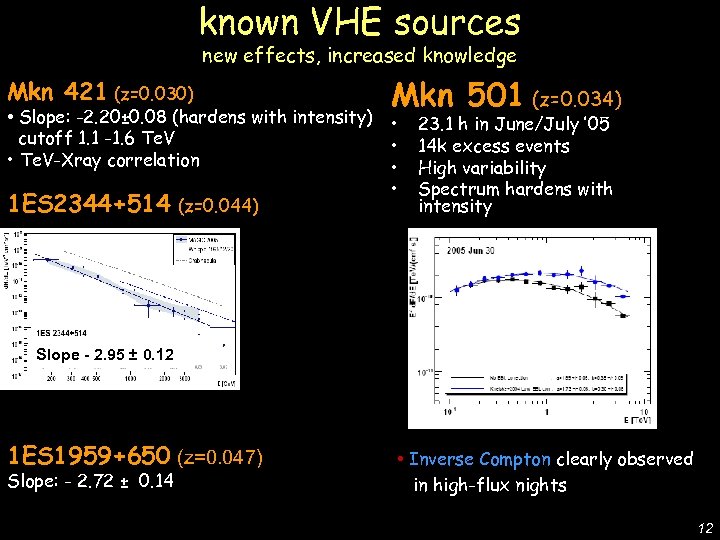 new effects, increased knowledge Mkn 421 (z=0. 030) Mkn 501 (z=0. 034) • Slope: -2. 20± 0. 08 (hardens with intensity) • cutoff 1. 1 -1. 6 Te. V • • Te. V-Xray correlation • • 1 ES 2344+514 (z=0. 044) 23. 1 h in June/July ’ 05 14 k excess events High variability Spectrum hardens with intensity De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe known VHE sources Slope - 2. 95 ± 0. 12 1 ES 1959+650 (z=0. 047) Slope: - 2. 72 ± 0. 14 • Inverse Compton clearly observed in high-flux nights 12
new effects, increased knowledge Mkn 421 (z=0. 030) Mkn 501 (z=0. 034) • Slope: -2. 20± 0. 08 (hardens with intensity) • cutoff 1. 1 -1. 6 Te. V • • Te. V-Xray correlation • • 1 ES 2344+514 (z=0. 044) 23. 1 h in June/July ’ 05 14 k excess events High variability Spectrum hardens with intensity De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe known VHE sources Slope - 2. 95 ± 0. 12 1 ES 1959+650 (z=0. 047) Slope: - 2. 72 ± 0. 14 • Inverse Compton clearly observed in high-flux nights 12
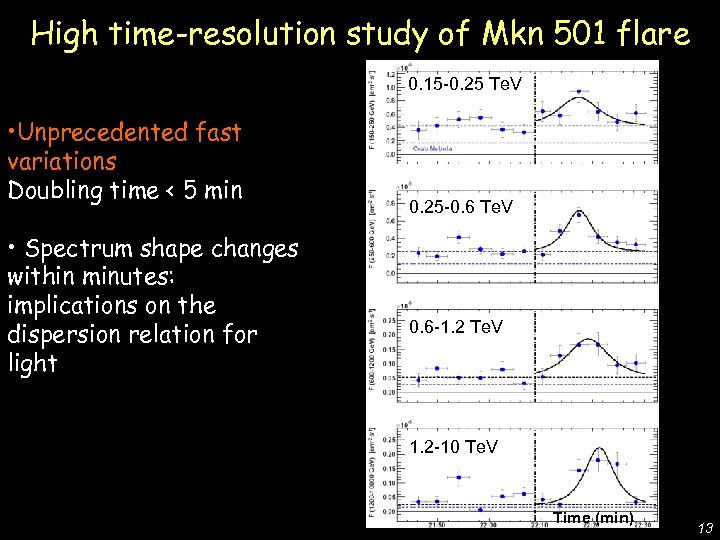 0. 15 -0. 25 Te. V • Unprecedented fast variations Doubling time < 5 min • Spectrum shape changes within minutes: implications on the dispersion relation for light 0. 25 -0. 6 Te. V De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe High time-resolution study of Mkn 501 flare 0. 6 -1. 2 Te. V 1. 2 -10 Te. V Time (min) 13
0. 15 -0. 25 Te. V • Unprecedented fast variations Doubling time < 5 min • Spectrum shape changes within minutes: implications on the dispersion relation for light 0. 25 -0. 6 Te. V De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe High time-resolution study of Mkn 501 flare 0. 6 -1. 2 Te. V 1. 2 -10 Te. V Time (min) 13
![• In some QG approaches [Amelino-Camelia 1998] : Dv/c ~ E / EQG, • In some QG approaches [Amelino-Camelia 1998] : Dv/c ~ E / EQG,](https://present5.com/presentation/356287d33193f093022cf4a1cb2ffbec/image-14.jpg) • In some QG approaches [Amelino-Camelia 1998] : Dv/c ~ E / EQG, EQG~EP ~ 1019 Ge. V • At 1 st order, the arrival delay of -rays emitted simultaneously from a distant source should be proportional to their energy difference and the path L to the source: De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Dispersion of light in vacuo • The expected delay is very small and to make it measurable one needs to observe very high energy rays coming from sources at cosmological distances. => new, stronger constraints on emission mechanism and light-speed dispersion relations could come from high time-resolution studies of AGN flares. Caveat: flare: physical mechanisms at the e- acceleration Mkn 501 blazarsassuming all produced(gradualsame moment in the emitting (0. 6 ± 0. 2) 1017 Ge. V the time delays EQG = plasma) could explain 14
• In some QG approaches [Amelino-Camelia 1998] : Dv/c ~ E / EQG, EQG~EP ~ 1019 Ge. V • At 1 st order, the arrival delay of -rays emitted simultaneously from a distant source should be proportional to their energy difference and the path L to the source: De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Dispersion of light in vacuo • The expected delay is very small and to make it measurable one needs to observe very high energy rays coming from sources at cosmological distances. => new, stronger constraints on emission mechanism and light-speed dispersion relations could come from high time-resolution studies of AGN flares. Caveat: flare: physical mechanisms at the e- acceleration Mkn 501 blazarsassuming all produced(gradualsame moment in the emitting (0. 6 ± 0. 2) 1017 Ge. V the time delays EQG = plasma) could explain 14
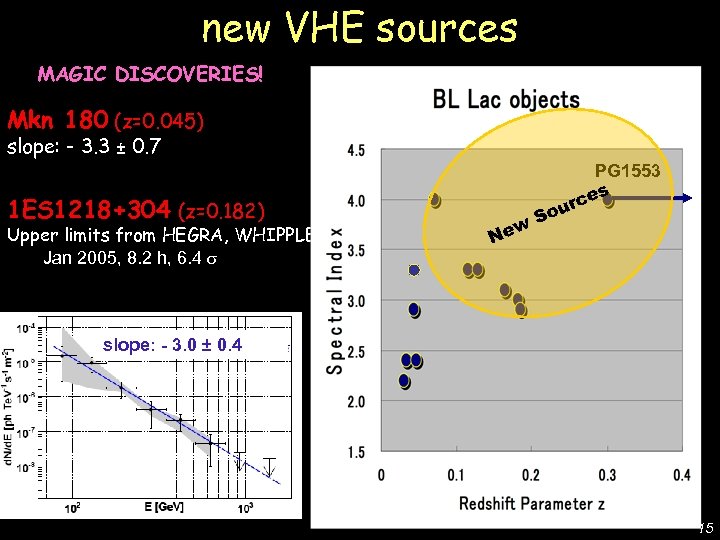 MAGIC DISCOVERIES! Mkn 180 (z=0. 045) slope: - 3. 3 ± 0. 7 1 ES 1218+304 (z=0. 182) Upper limits from HEGRA, WHIPPLE Jan 2005, 8. 2 h, 6. 4 PG 1553+113 (z>0. 09) HESS: 4. 0 hint (A&A 448 L (2006)) • MAGIC: 8. 8 from 19 h observation in 2005 -06 • Steepest observed -ray spectrum: PG 1553 s rce u So w Ne De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe new VHE sources slope: - 3. 0 ± 0. 4 slope: - 4. 2 ± 0. 3 • Upper limit of z < 0. 42 using MAGIC+HESS spectra [Mazin & Goebel Ap. JL 655 (2007) 13] 15
MAGIC DISCOVERIES! Mkn 180 (z=0. 045) slope: - 3. 3 ± 0. 7 1 ES 1218+304 (z=0. 182) Upper limits from HEGRA, WHIPPLE Jan 2005, 8. 2 h, 6. 4 PG 1553+113 (z>0. 09) HESS: 4. 0 hint (A&A 448 L (2006)) • MAGIC: 8. 8 from 19 h observation in 2005 -06 • Steepest observed -ray spectrum: PG 1553 s rce u So w Ne De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe new VHE sources slope: - 3. 0 ± 0. 4 slope: - 4. 2 ± 0. 3 • Upper limit of z < 0. 42 using MAGIC+HESS spectra [Mazin & Goebel Ap. JL 655 (2007) 13] 15
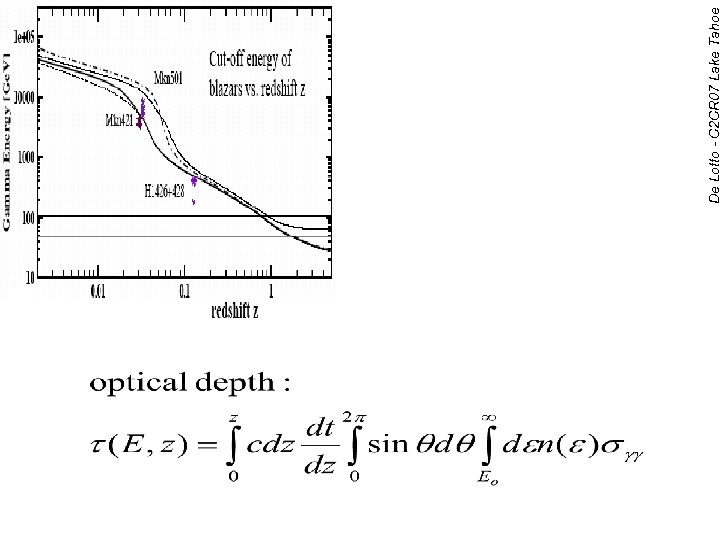
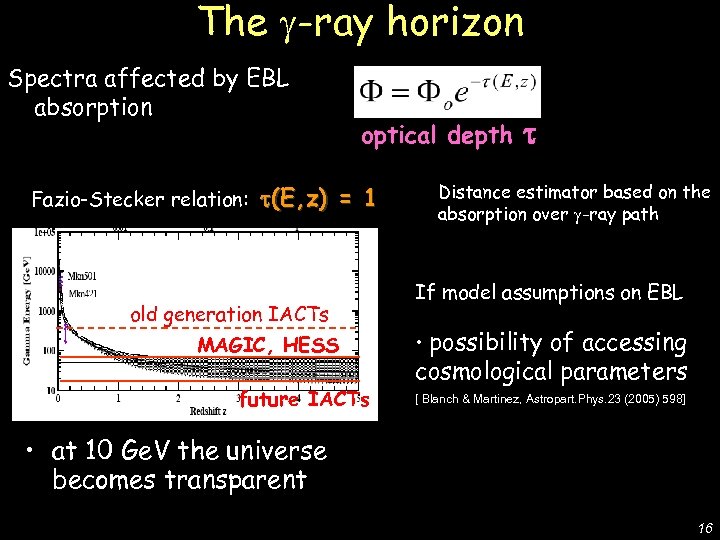 Spectra affected by EBL absorption Fazio-Stecker relation: optical depth (E, z) = 1 old generation IACTs MAGIC, HESS future IACTs De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe The -ray horizon Distance estimator based on the absorption over -ray path If model assumptions on EBL • possibility of accessing cosmological parameters [ Blanch & Martinez, Astropart. Phys. 23 (2005) 598] • at 10 Ge. V the universe becomes transparent 16
Spectra affected by EBL absorption Fazio-Stecker relation: optical depth (E, z) = 1 old generation IACTs MAGIC, HESS future IACTs De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe The -ray horizon Distance estimator based on the absorption over -ray path If model assumptions on EBL • possibility of accessing cosmological parameters [ Blanch & Martinez, Astropart. Phys. 23 (2005) 598] • at 10 Ge. V the universe becomes transparent 16
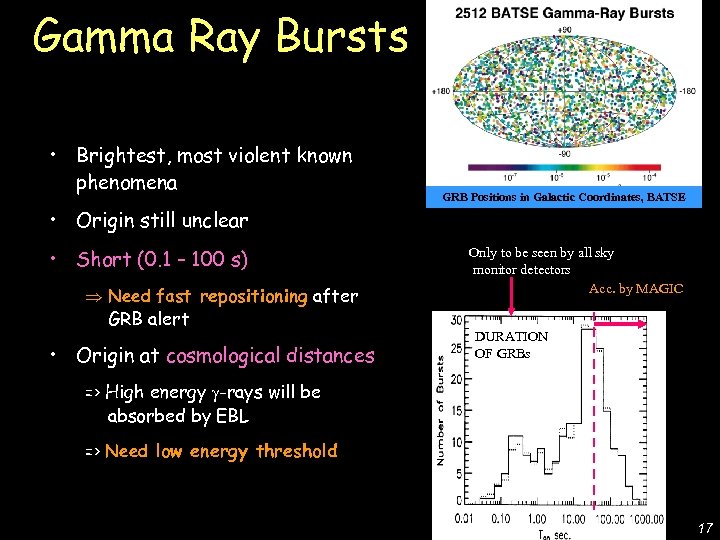 • Brightest, most violent known phenomena GRB Positions in Galactic Coordinates, BATSE De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Gamma Ray Bursts • Origin still unclear • Short (0. 1 – 100 s) Need fast repositioning after GRB alert • Origin at cosmological distances Only to be seen by all sky monitor detectors Acc. by MAGIC DURATION OF GRBs => High energy -rays will be absorbed by EBL => Need low energy threshold 17
• Brightest, most violent known phenomena GRB Positions in Galactic Coordinates, BATSE De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Gamma Ray Bursts • Origin still unclear • Short (0. 1 – 100 s) Need fast repositioning after GRB alert • Origin at cosmological distances Only to be seen by all sky monitor detectors Acc. by MAGIC DURATION OF GRBs => High energy -rays will be absorbed by EBL => Need low energy threshold 17
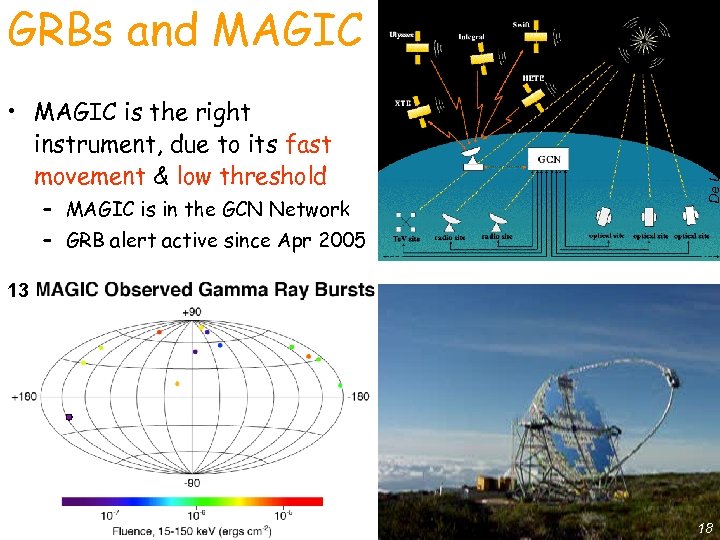 • MAGIC is the right instrument, due to its fast movement & low threshold – MAGIC is in the GCN Network De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe GRBs and MAGIC – GRB alert active since Apr 2005 13 18
• MAGIC is the right instrument, due to its fast movement & low threshold – MAGIC is in the GCN Network De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe GRBs and MAGIC – GRB alert active since Apr 2005 13 18
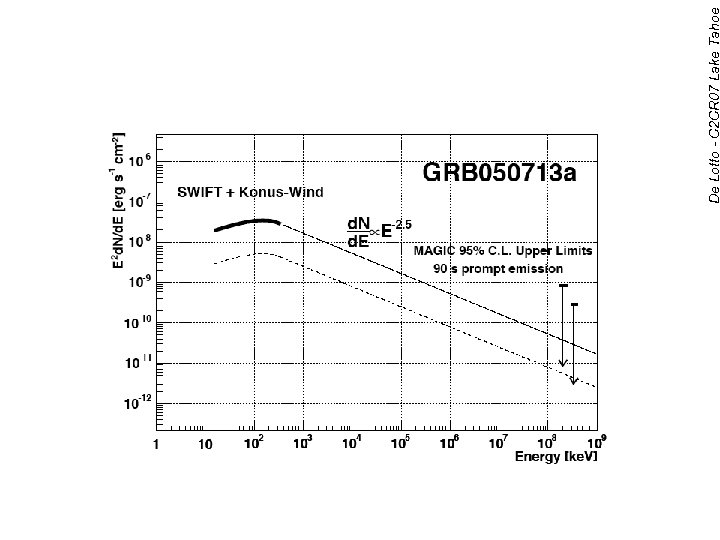
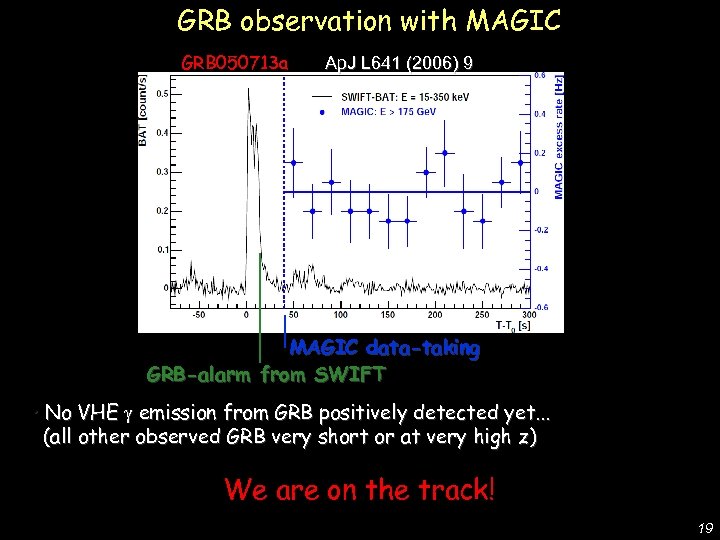 GRB 050713 a Ap. J L 641 (2006) 9 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe GRB observation with MAGIC data-taking GRB-alarm from SWIFT • No VHE emission from GRB positively detected yet. . . (all other observed GRB very short or at very high z) We are on the track! 19
GRB 050713 a Ap. J L 641 (2006) 9 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe GRB observation with MAGIC data-taking GRB-alarm from SWIFT • No VHE emission from GRB positively detected yet. . . (all other observed GRB very short or at very high z) We are on the track! 19
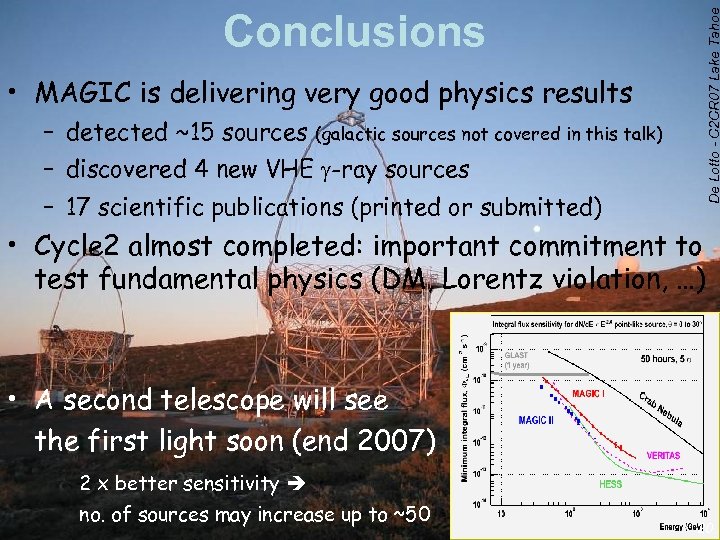 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Conclusions • MAGIC is delivering very good physics results – detected ~15 sources (galactic sources not covered in this talk) – discovered 4 new VHE -ray sources – 17 scientific publications (printed or submitted) • Cycle 2 almost completed: important commitment to test fundamental physics (DM, Lorentz violation, …) • A second telescope will see the first light soon (end 2007) 2 x better sensitivity no. of sources may increase up to ~50 20
De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Conclusions • MAGIC is delivering very good physics results – detected ~15 sources (galactic sources not covered in this talk) – discovered 4 new VHE -ray sources – 17 scientific publications (printed or submitted) • Cycle 2 almost completed: important commitment to test fundamental physics (DM, Lorentz violation, …) • A second telescope will see the first light soon (end 2007) 2 x better sensitivity no. of sources may increase up to ~50 20
 BACKUP 21 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe
BACKUP 21 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe
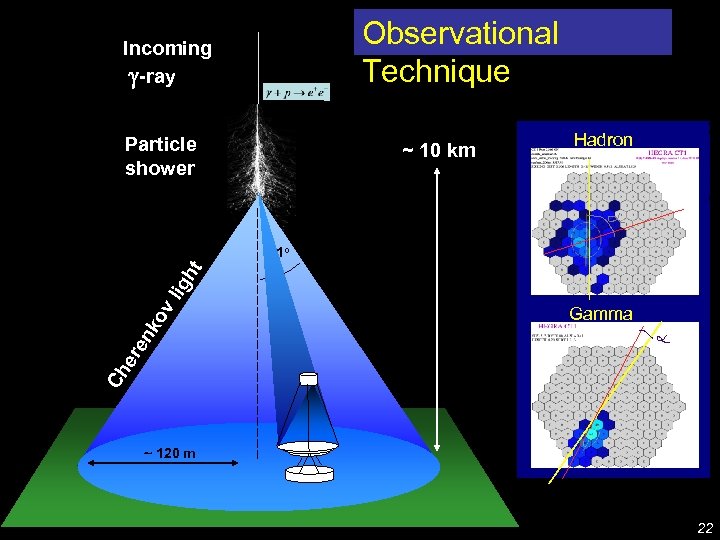 Particle shower ~ 10 km Hadron De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Observational Technique Incoming -ray Gamma Ch er en ko vl ig ht ~ 1 o ~ 120 m 22
Particle shower ~ 10 km Hadron De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Observational Technique Incoming -ray Gamma Ch er en ko vl ig ht ~ 1 o ~ 120 m 22
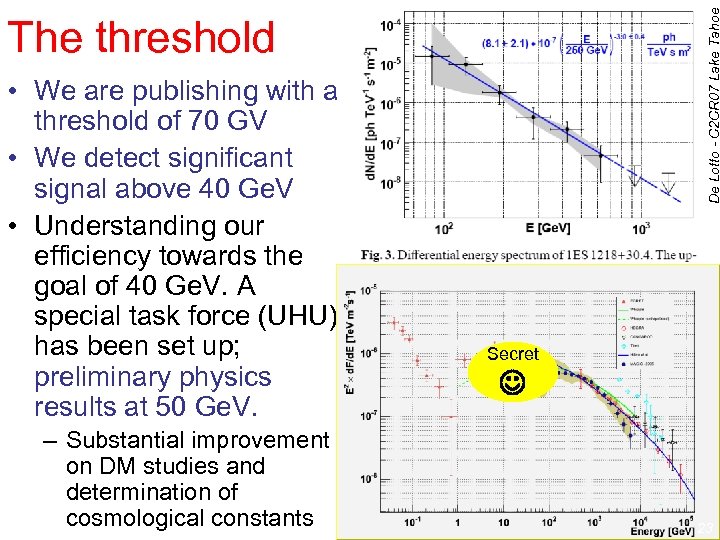 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe The threshold • We are publishing with a threshold of 70 GV • We detect significant signal above 40 Ge. V • Understanding our efficiency towards the goal of 40 Ge. V. A special task force (UHU) has been set up; preliminary physics results at 50 Ge. V. – Substantial improvement on DM studies and determination of cosmological constants Secret 23
De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe The threshold • We are publishing with a threshold of 70 GV • We detect significant signal above 40 Ge. V • Understanding our efficiency towards the goal of 40 Ge. V. A special task force (UHU) has been set up; preliminary physics results at 50 Ge. V. – Substantial improvement on DM studies and determination of cosmological constants Secret 23
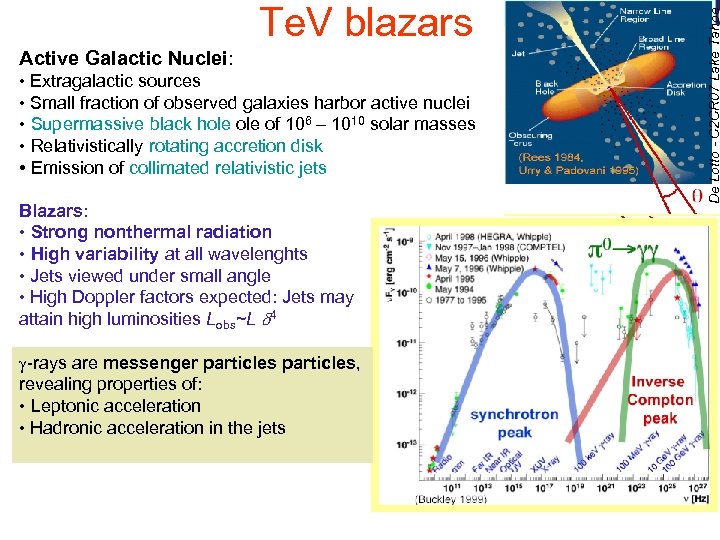 Active Galactic Nuclei: • Extragalactic sources • Small fraction of observed galaxies harbor active nuclei • Supermassive black hole of 106 – 1010 solar masses • Relativistically rotating accretion disk • Emission of collimated relativistic jets Blazars: • Strong nonthermal radiation • High variability at all wavelenghts • Jets viewed under small angle • High Doppler factors expected: Jets may attain high luminosities Lobs~L d 4 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Te. V blazars -rays are messenger particles, revealing properties of: • Leptonic acceleration • Hadronic acceleration in the jets 24
Active Galactic Nuclei: • Extragalactic sources • Small fraction of observed galaxies harbor active nuclei • Supermassive black hole of 106 – 1010 solar masses • Relativistically rotating accretion disk • Emission of collimated relativistic jets Blazars: • Strong nonthermal radiation • High variability at all wavelenghts • Jets viewed under small angle • High Doppler factors expected: Jets may attain high luminosities Lobs~L d 4 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Te. V blazars -rays are messenger particles, revealing properties of: • Leptonic acceleration • Hadronic acceleration in the jets 24
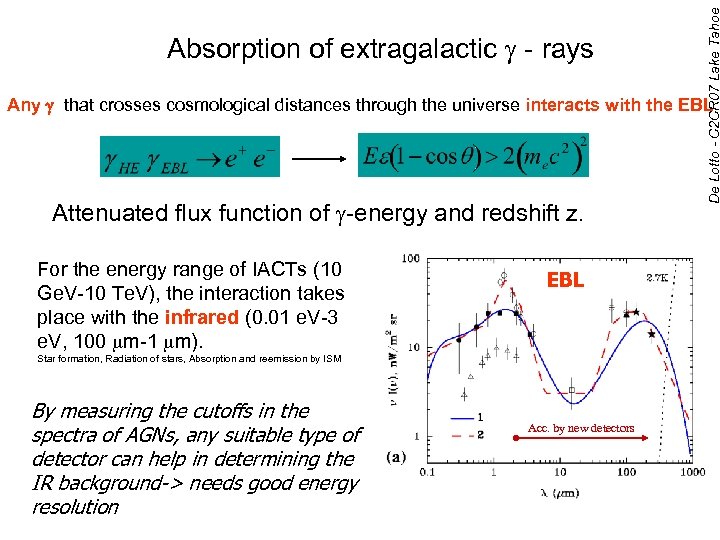 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Absorption of extragalactic - rays Any that crosses cosmological distances through the universe interacts with the EBL Attenuated flux function of -energy and redshift z. For the energy range of IACTs (10 Ge. V-10 Te. V), the interaction takes place with the infrared (0. 01 e. V-3 e. V, 100 m-1 m). EBL Star formation, Radiation of stars, Absorption and reemission by ISM By measuring the cutoffs in the spectra of AGNs, any suitable type of detector can help in determining the IR background-> needs good energy resolution Acc. by new detectors 25
De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Absorption of extragalactic - rays Any that crosses cosmological distances through the universe interacts with the EBL Attenuated flux function of -energy and redshift z. For the energy range of IACTs (10 Ge. V-10 Te. V), the interaction takes place with the infrared (0. 01 e. V-3 e. V, 100 m-1 m). EBL Star formation, Radiation of stars, Absorption and reemission by ISM By measuring the cutoffs in the spectra of AGNs, any suitable type of detector can help in determining the IR background-> needs good energy resolution Acc. by new detectors 25
 26 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe
26 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe
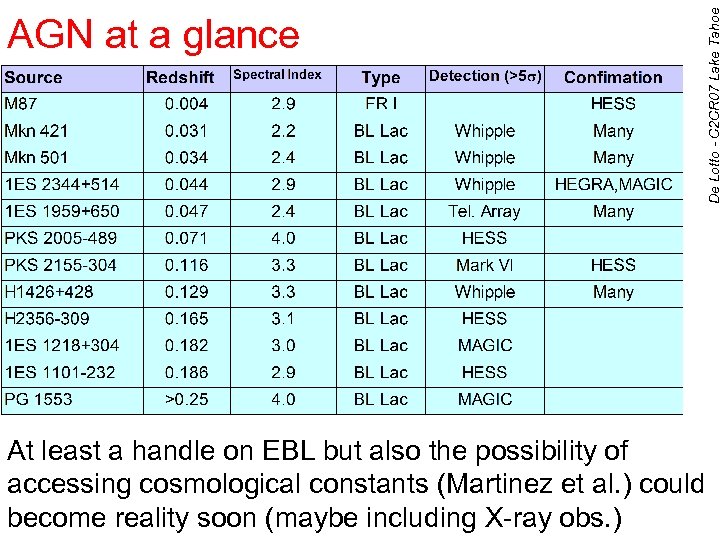 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe AGN at a glance At least a handle on EBL but also the possibility of accessing cosmological constants (Martinez et al. ) could become reality soon (maybe including X-ray obs. ) 27
De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe AGN at a glance At least a handle on EBL but also the possibility of accessing cosmological constants (Martinez et al. ) could become reality soon (maybe including X-ray obs. ) 27
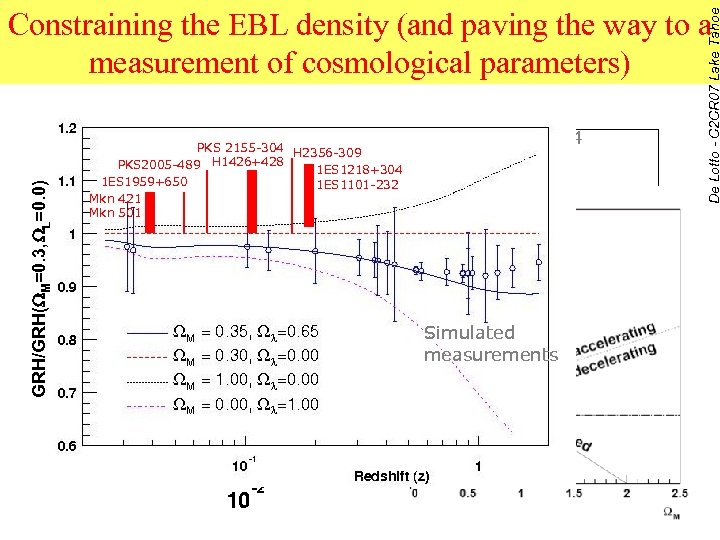 GRH/GRH(WM=0. 3, WL=0. 0) Blanch & Martinez 2004 PKS 2155 -304 H 2356 -309 PKS 2005 -489 H 1426+428 1 ES 1218+304 1 ES 1959+650 1 ES 1101 -232 Different Mkn 421 EBL models Mkn 501 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Constraining the EBL density (and paving the way to a measurement of cosmological parameters) Simulated measurements Mkn 421 Mkn 501 1 ES 1959+650 PKS 2005 -489 PKS 2155 -304 H 1426+428 H 2356 -309 Simulated measurements 1 ES 1218+304 1 ES 1101 -232 28
GRH/GRH(WM=0. 3, WL=0. 0) Blanch & Martinez 2004 PKS 2155 -304 H 2356 -309 PKS 2005 -489 H 1426+428 1 ES 1218+304 1 ES 1959+650 1 ES 1101 -232 Different Mkn 421 EBL models Mkn 501 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Constraining the EBL density (and paving the way to a measurement of cosmological parameters) Simulated measurements Mkn 421 Mkn 501 1 ES 1959+650 PKS 2005 -489 PKS 2155 -304 H 1426+428 H 2356 -309 Simulated measurements 1 ES 1218+304 1 ES 1101 -232 28
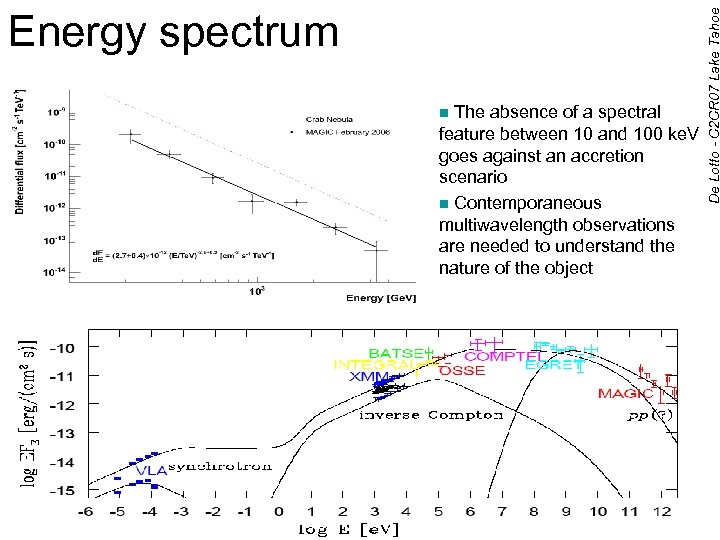 The absence of a spectral feature between 10 and 100 ke. V goes against an accretion scenario n Contemporaneous multiwavelength observations are needed to understand the nature of the object n De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Energy spectrum Albert et al. 2006 29
The absence of a spectral feature between 10 and 100 ke. V goes against an accretion scenario n Contemporaneous multiwavelength observations are needed to understand the nature of the object n De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe Energy spectrum Albert et al. 2006 29
 30 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe
30 De Lotto - C 2 CR 07 Lake Tahoe


