 Outline
Outline
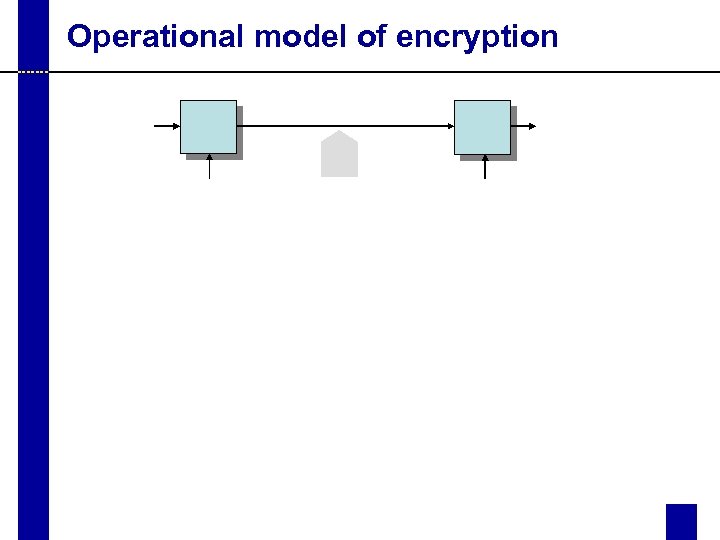 Operational model of encryption
Operational model of encryption
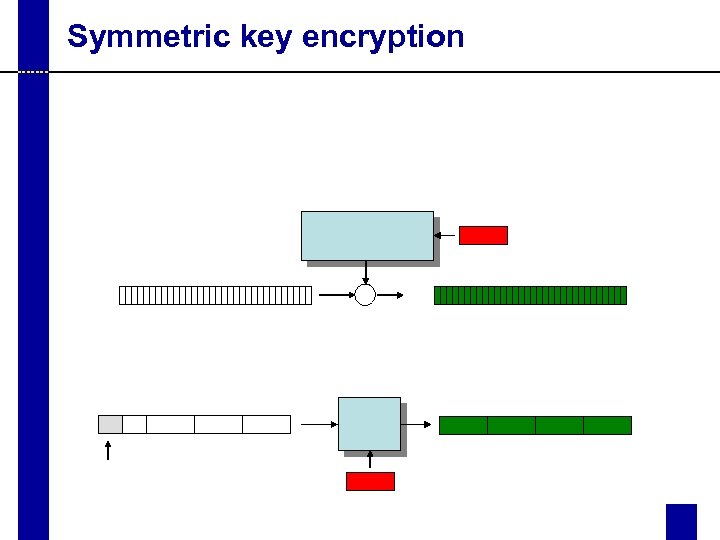 Symmetric key encryption
Symmetric key encryption
 One-time pad – theoretical vs. practical security
One-time pad – theoretical vs. practical security
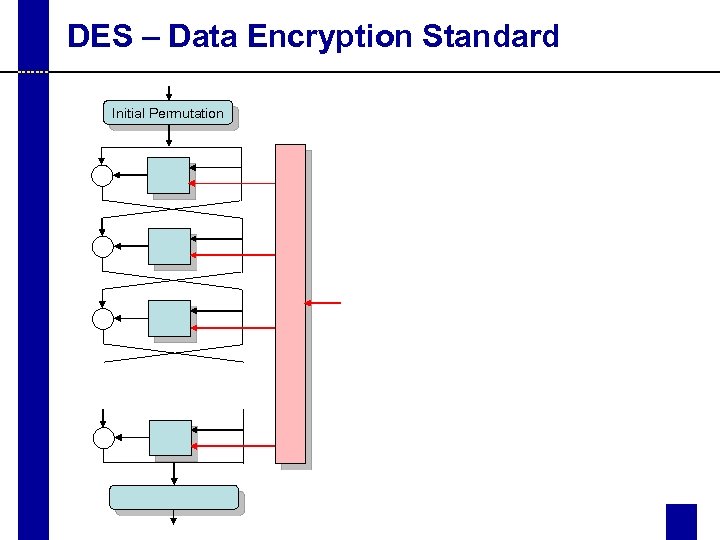 DES – Data Encryption Standard Initial Permutation
DES – Data Encryption Standard Initial Permutation
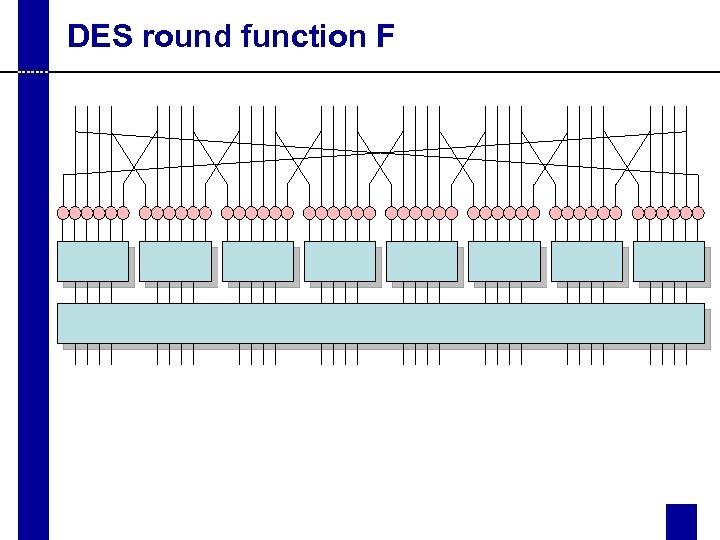 DES round function F
DES round function F
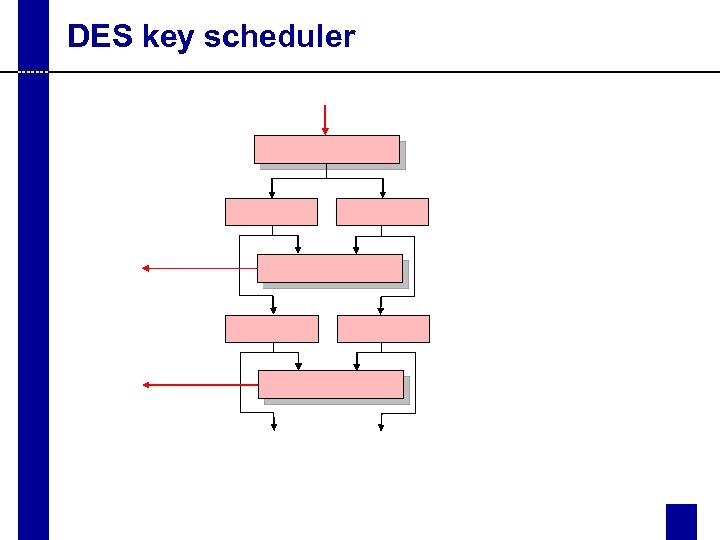 DES key scheduler
DES key scheduler
 AES – Advanced Encryption Standard
AES – Advanced Encryption Standard
![General structure of Rijndael encryption/decryption plaintext w[0. . 3] w[4. . 7] w[36. . General structure of Rijndael encryption/decryption plaintext w[0. . 3] w[4. . 7] w[36. .](https://present5.com/presentation/d3b20ef4b0fb960b1e8b09354191a8cc/image-10.jpg) General structure of Rijndael encryption/decryption plaintext w[0. . 3] w[4. . 7] w[36. . 39] w[40. . 43] ciphertext
General structure of Rijndael encryption/decryption plaintext w[0. . 3] w[4. . 7] w[36. . 39] w[40. . 43] ciphertext
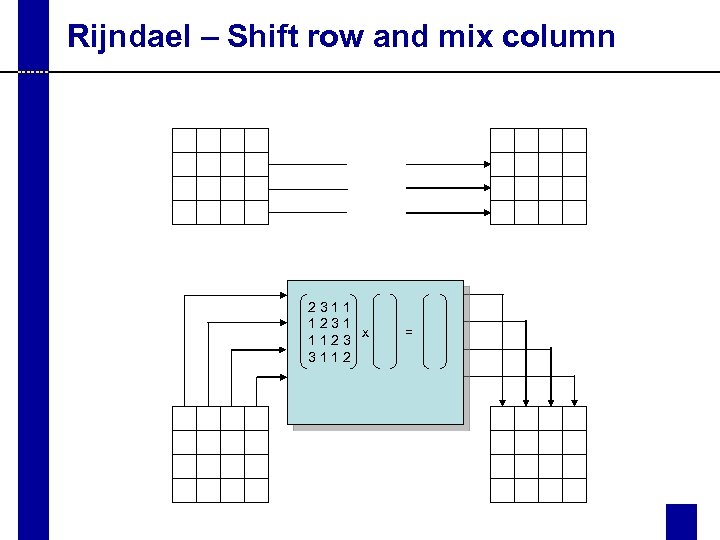 Rijndael – Shift row and mix column 2311 1231 x 1123 3112 =
Rijndael – Shift row and mix column 2311 1231 x 1123 3112 =
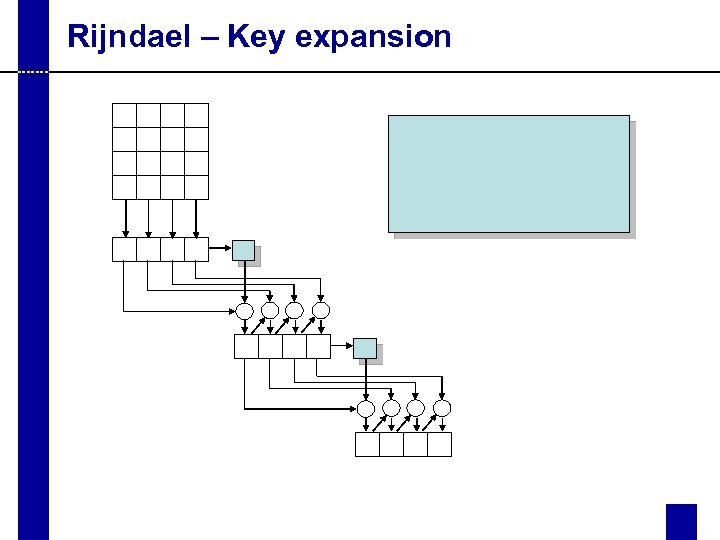 Rijndael – Key expansion
Rijndael – Key expansion
 RC 4 stream cipher
RC 4 stream cipher
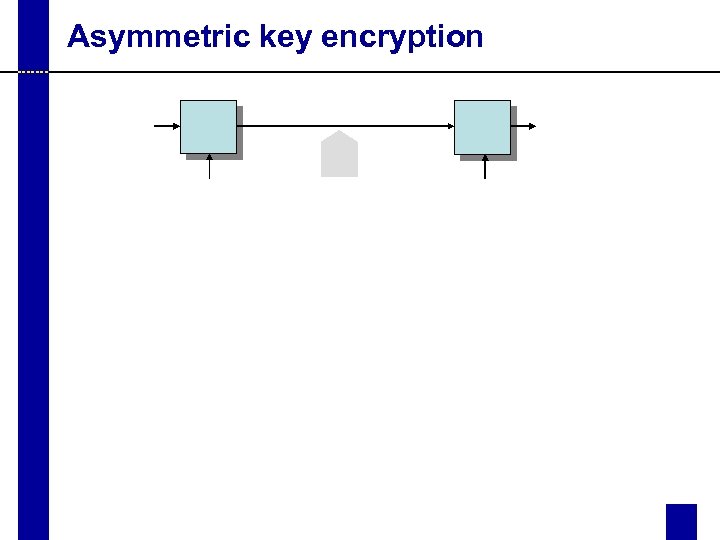 Asymmetric key encryption
Asymmetric key encryption
 RSA (Rivest, Shamir, Adleman, 1978)
RSA (Rivest, Shamir, Adleman, 1978)
 Proof of RSA decryption
Proof of RSA decryption
 Proof of RSA decryption cont’d
Proof of RSA decryption cont’d
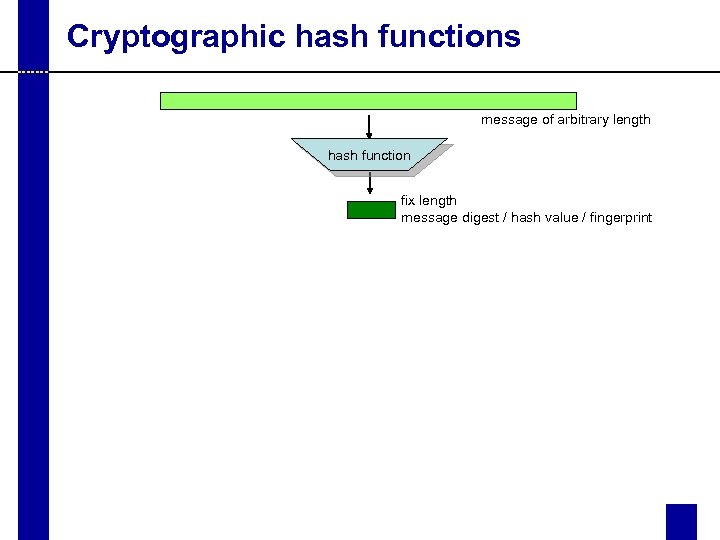 Cryptographic hash functions message of arbitrary length hash function fix length message digest / hash value / fingerprint
Cryptographic hash functions message of arbitrary length hash function fix length message digest / hash value / fingerprint
 How long should a hash value be?
How long should a hash value be?
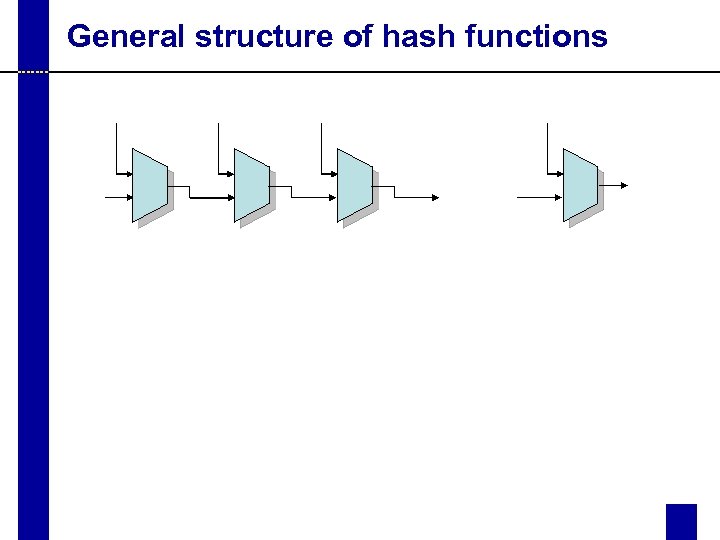 General structure of hash functions
General structure of hash functions
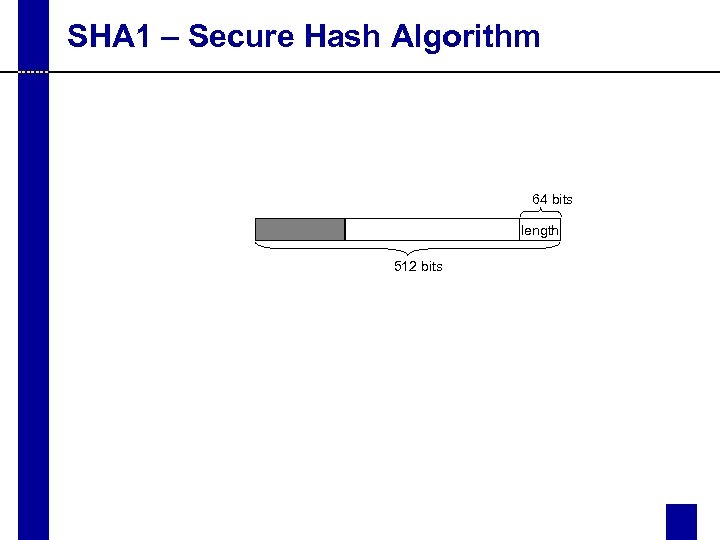 SHA 1 – Secure Hash Algorithm 64 bits length 512 bits
SHA 1 – Secure Hash Algorithm 64 bits length 512 bits
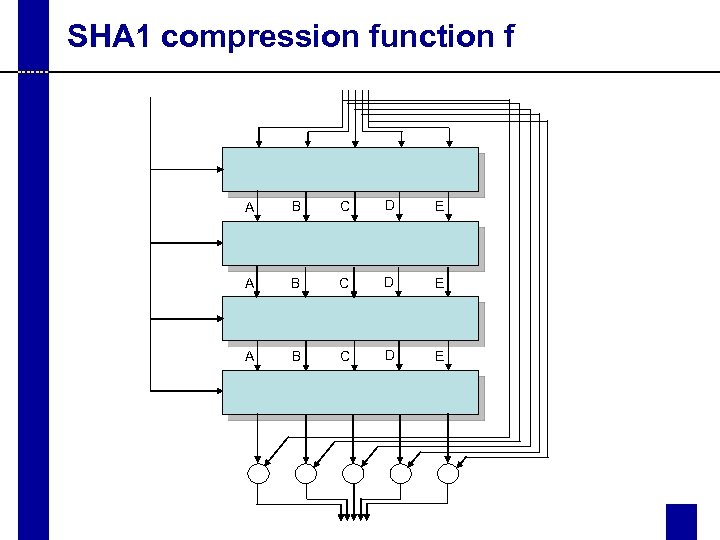 SHA 1 compression function f A B C D E
SHA 1 compression function f A B C D E
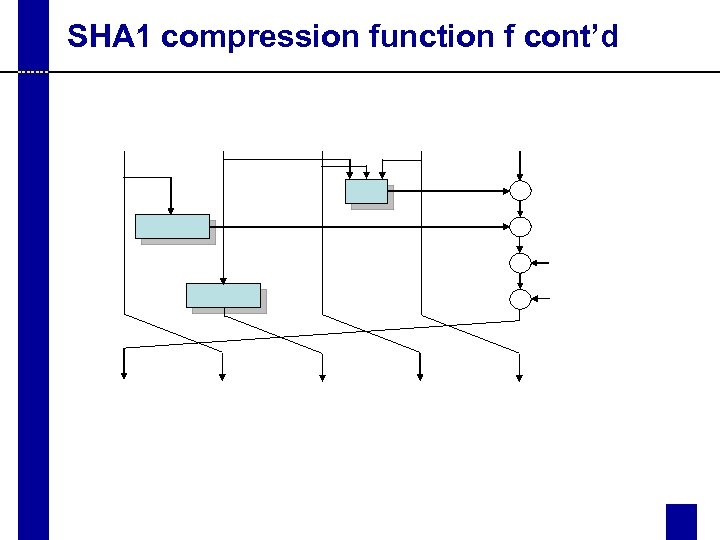 SHA 1 compression function f cont’d
SHA 1 compression function f cont’d
 SHA 1 compression function f cont’d
SHA 1 compression function f cont’d
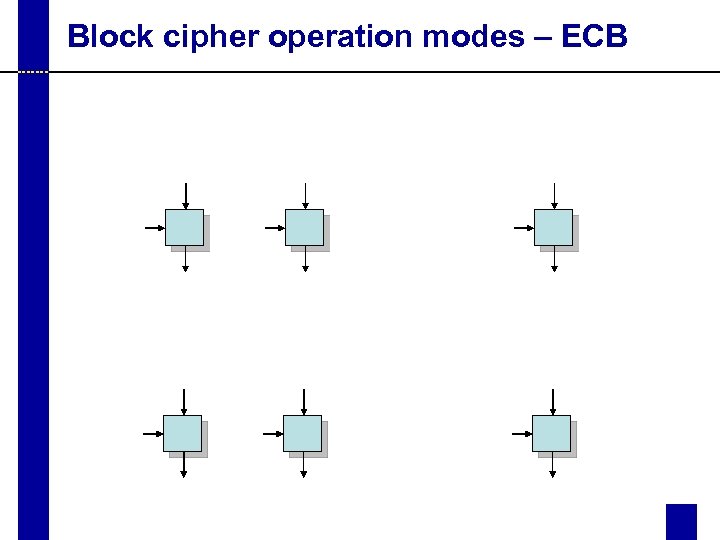 Block cipher operation modes – ECB
Block cipher operation modes – ECB
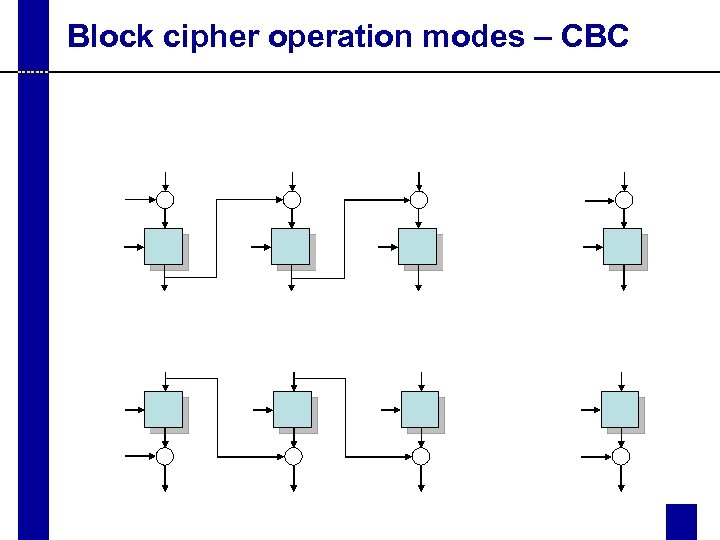 Block cipher operation modes – CBC
Block cipher operation modes – CBC
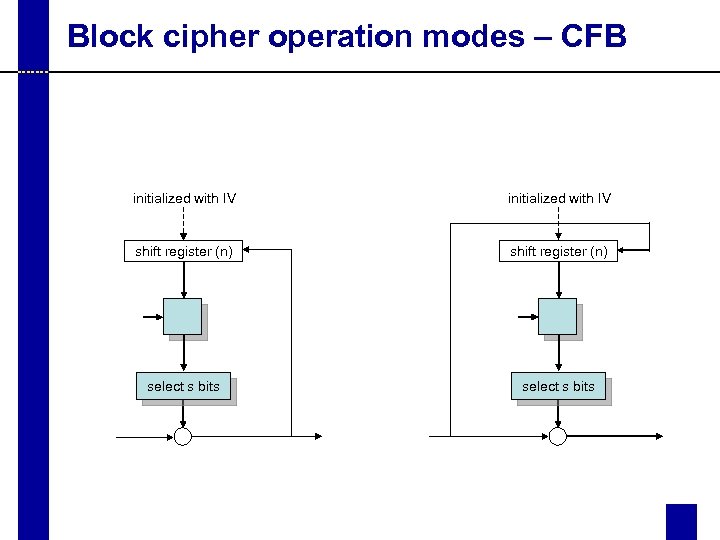 Block cipher operation modes – CFB initialized with IV shift register (n) select s bits
Block cipher operation modes – CFB initialized with IV shift register (n) select s bits
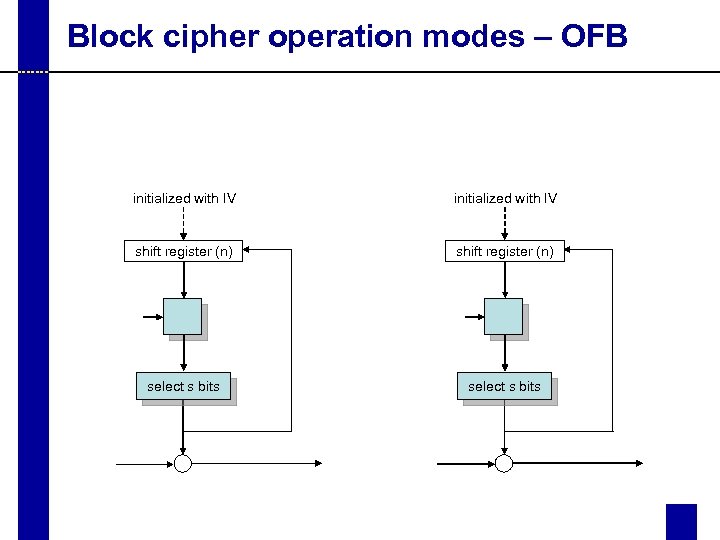 Block cipher operation modes – OFB initialized with IV shift register (n) select s bits
Block cipher operation modes – OFB initialized with IV shift register (n) select s bits
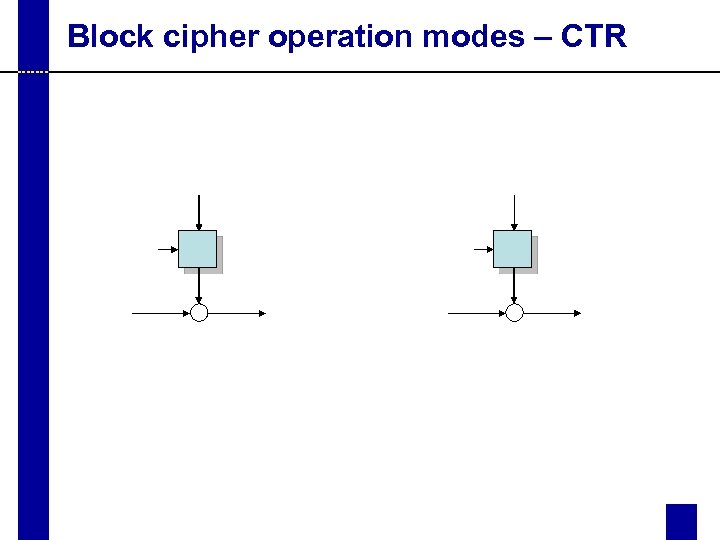 Block cipher operation modes – CTR
Block cipher operation modes – CTR
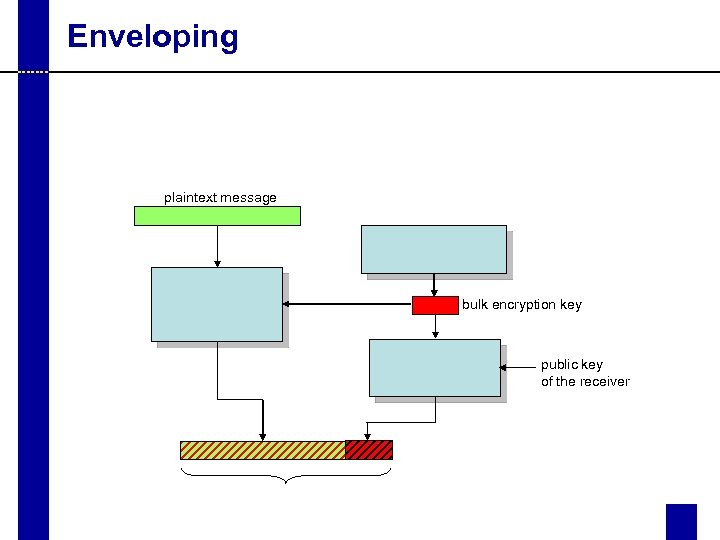 Enveloping plaintext message bulk encryption key public key of the receiver
Enveloping plaintext message bulk encryption key public key of the receiver
 Message Authentication Codes (MAC)
Message Authentication Codes (MAC)
 HMAC
HMAC
 Digital signatures
Digital signatures
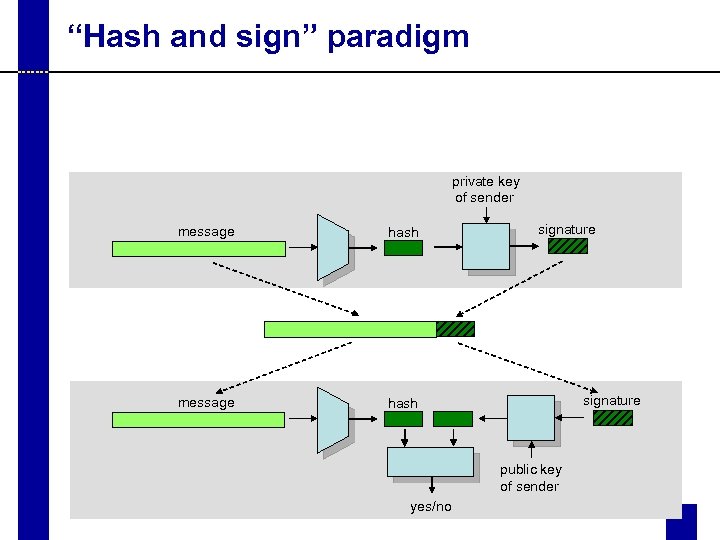 “Hash and sign” paradigm private key of sender message hash message signature hash signature public key of sender yes/no
“Hash and sign” paradigm private key of sender message hash message signature hash signature public key of sender yes/no
 El. Gamal signature scheme
El. Gamal signature scheme
 El. Gamal signature scheme cont’d
El. Gamal signature scheme cont’d
 How to establish a shared symmetric key?
How to establish a shared symmetric key?
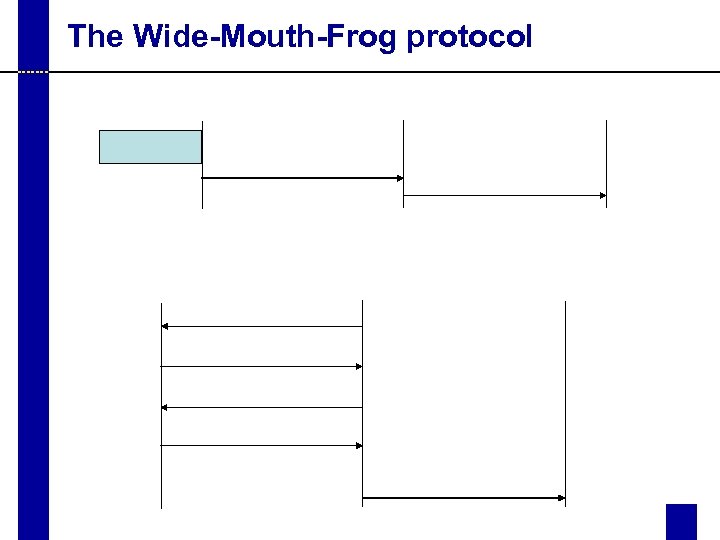 The Wide-Mouth-Frog protocol
The Wide-Mouth-Frog protocol
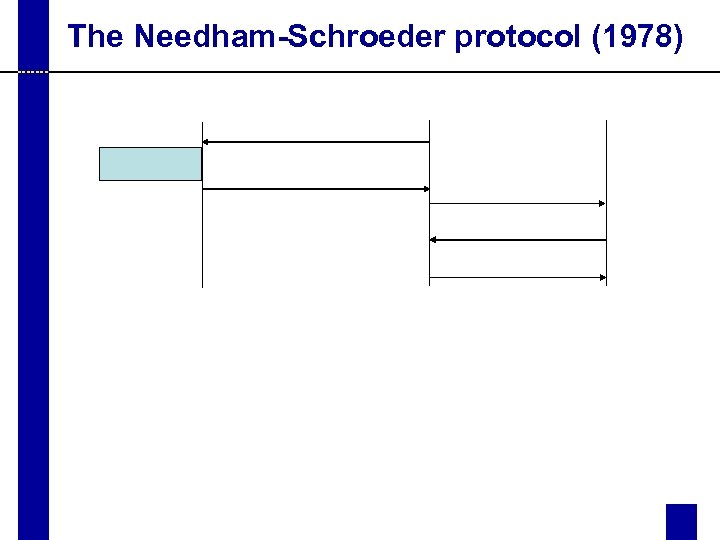 The Needham-Schroeder protocol (1978)
The Needham-Schroeder protocol (1978)
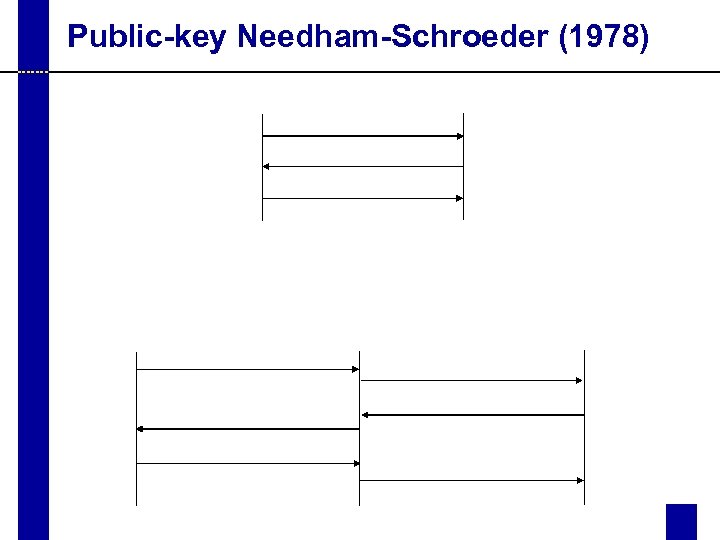 Public-key Needham-Schroeder (1978)
Public-key Needham-Schroeder (1978)
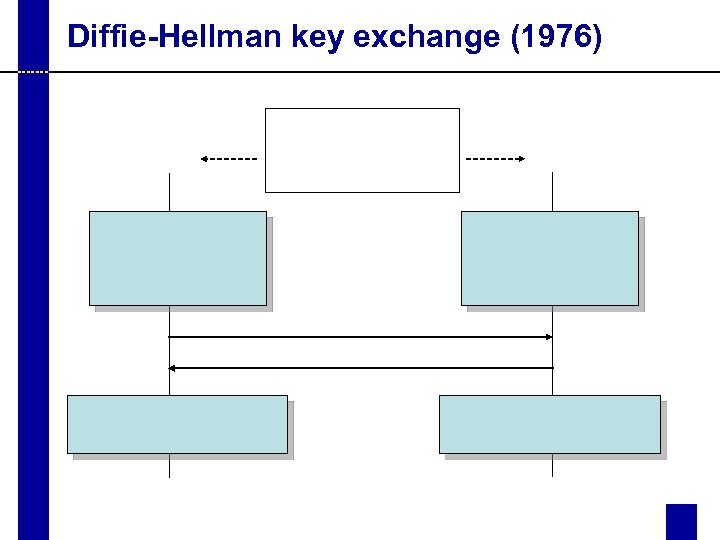 Diffie-Hellman key exchange (1976)
Diffie-Hellman key exchange (1976)
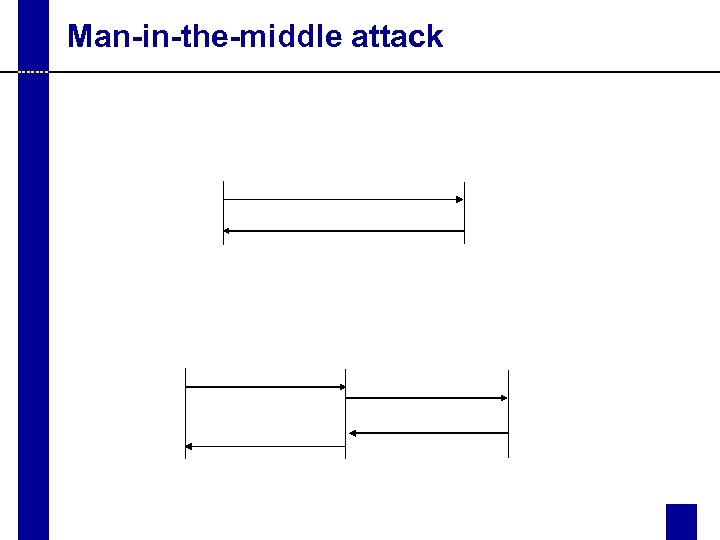 Man-in-the-middle attack
Man-in-the-middle attack
 Public-key certificates
Public-key certificates
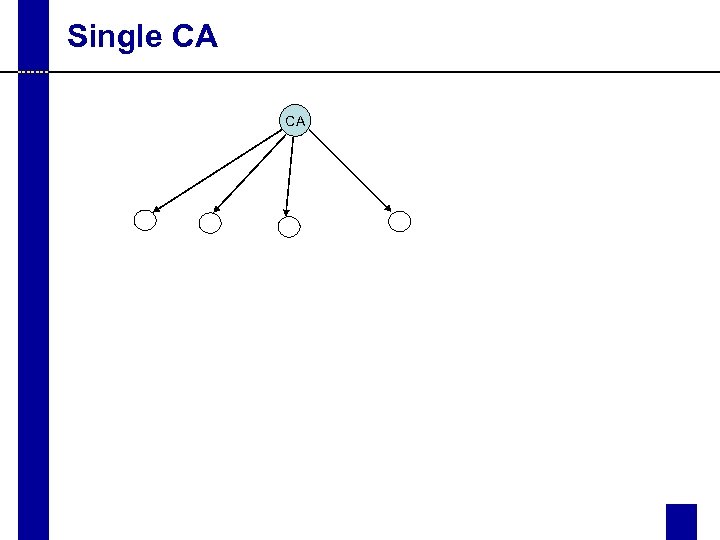 Single CA CA
Single CA CA
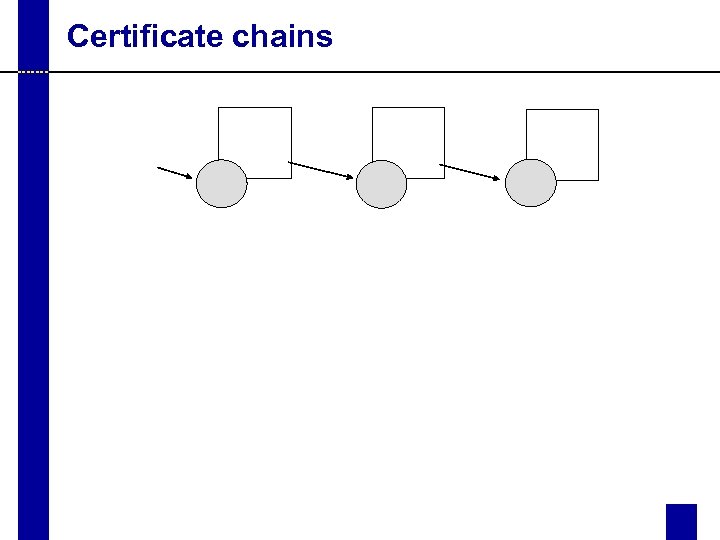 Certificate chains
Certificate chains
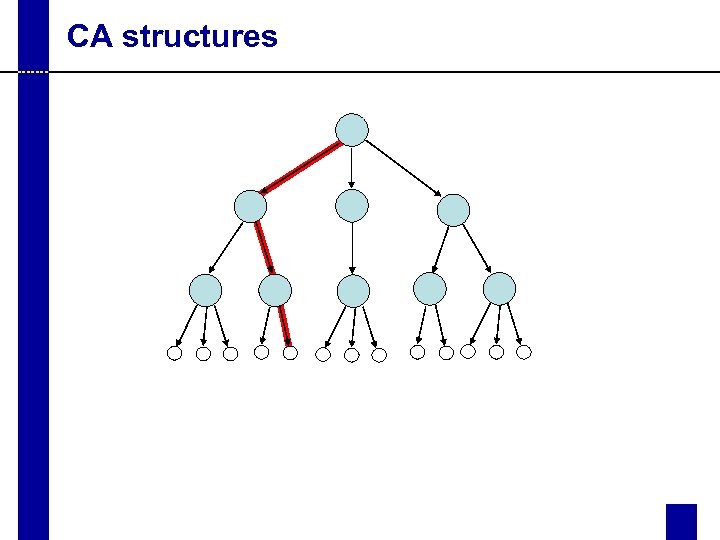 CA structures
CA structures
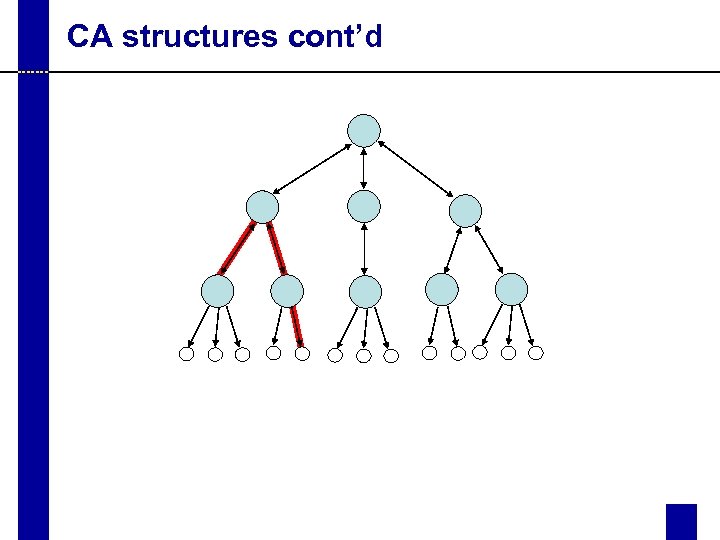 CA structures cont’d
CA structures cont’d
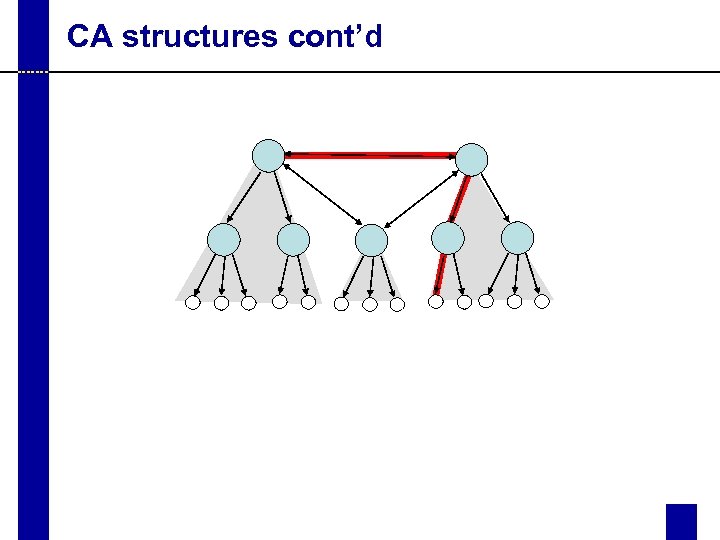 CA structures cont’d
CA structures cont’d