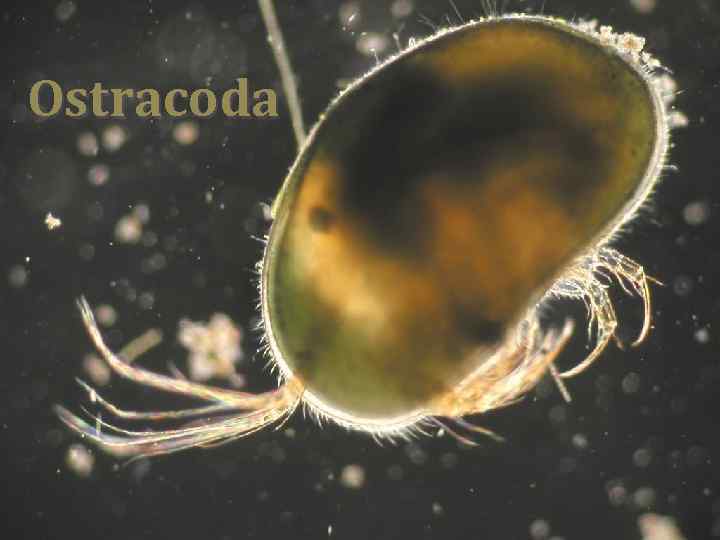
 Ostracoda
Ostracoda
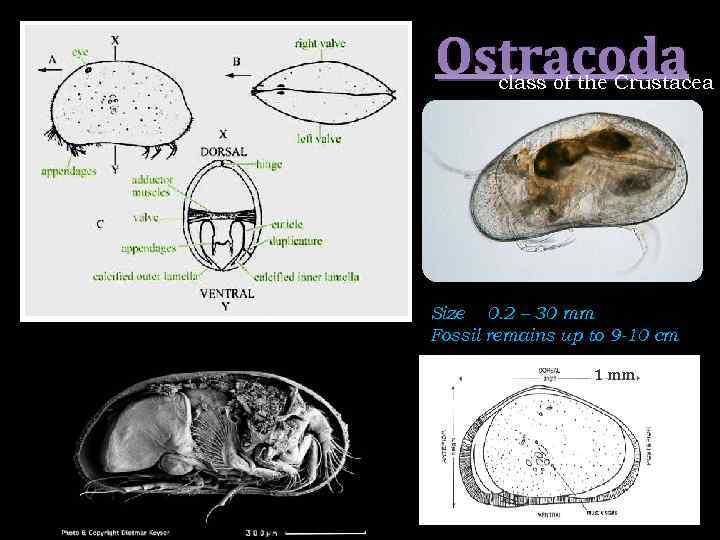 Ostracoda class of the Crustacea Size 0. 2 – 30 mm Fossil remains up to 9 -10 cm 1 mm
Ostracoda class of the Crustacea Size 0. 2 – 30 mm Fossil remains up to 9 -10 cm 1 mm
 Ostracoda Fresh and brackish water (lake, river, groundwater etc) Habitat Terrestrial (humid forest soils) Seawater (ocean floor and surface layer )
Ostracoda Fresh and brackish water (lake, river, groundwater etc) Habitat Terrestrial (humid forest soils) Seawater (ocean floor and surface layer )
 Factors of abundance Habitat characteristics: • Size, energy level, permanence of waterbody, depth of the site • Presence and types of aquatic plants • Availability of food • Predation Water characteristics: • • Temperature Salinity ad ionic composition p. H Dissolved oxygen content
Factors of abundance Habitat characteristics: • Size, energy level, permanence of waterbody, depth of the site • Presence and types of aquatic plants • Availability of food • Predation Water characteristics: • • Temperature Salinity ad ionic composition p. H Dissolved oxygen content
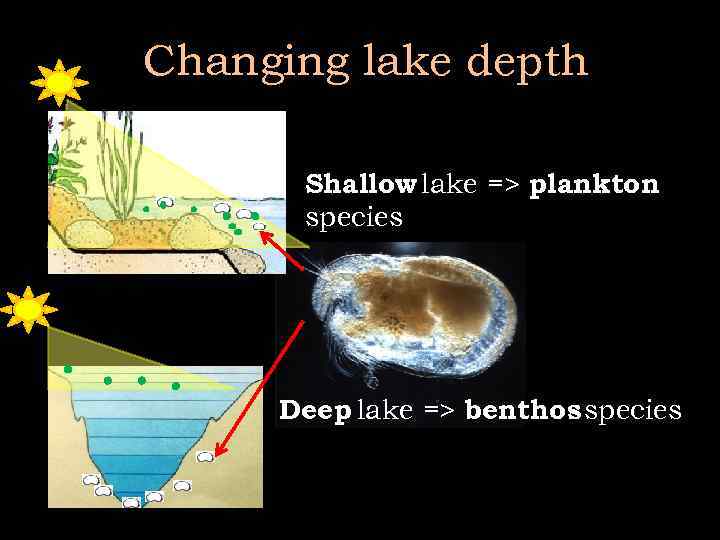 Changing lake depth Shallow lake => plankton species Deep lake => benthos species
Changing lake depth Shallow lake => plankton species Deep lake => benthos species
 Water energy regime • Ostracods have about 8 -9 moult stages during their life 1. Young and adult valves together => no strong current 2. Young absent => flows exist 3. Adult absent => unfavourable conditions for maturing
Water energy regime • Ostracods have about 8 -9 moult stages during their life 1. Young and adult valves together => no strong current 2. Young absent => flows exist 3. Adult absent => unfavourable conditions for maturing
 Salinity and ionic composition • Salinity and ionic composition of host waterbody are indicated by degree of tolerance of ostracoda species to this variables • In temperate deep lakes benthic ostracode shell chemistry is related to isotopic water composition • In margunal marine settings ostracode shell chemistry is related to salinities
Salinity and ionic composition • Salinity and ionic composition of host waterbody are indicated by degree of tolerance of ostracoda species to this variables • In temperate deep lakes benthic ostracode shell chemistry is related to isotopic water composition • In margunal marine settings ostracode shell chemistry is related to salinities
 Geochemical analysis • Trace element content (Mg, Sr) => water temperature and water chemistry in both lakes and oceans • Stable isotope ratios (18 O/16 O, 13 C/12 C) – lake sediments, temperature and precipitation regime of the waterbody, CO 2 and dissolved inorganic carbon processes in the water • Indicator of past heavy metal pollution • Radiometric dating (radiocarbon and uranium series)
Geochemical analysis • Trace element content (Mg, Sr) => water temperature and water chemistry in both lakes and oceans • Stable isotope ratios (18 O/16 O, 13 C/12 C) – lake sediments, temperature and precipitation regime of the waterbody, CO 2 and dissolved inorganic carbon processes in the water • Indicator of past heavy metal pollution • Radiometric dating (radiocarbon and uranium series)
 Thank you for attention!
Thank you for attention!