35313b61729e625c676be93ac4710def.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 ORIGIN AND NATURE OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP
ORIGIN AND NATURE OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP
 Evolution of Entrepreneurship Entrepreneur or Entrepreneurship originated in Europe sometime in the Middle Ages. Entrepreneur originated from the French word “Entreprendre” which means to undertake.
Evolution of Entrepreneurship Entrepreneur or Entrepreneurship originated in Europe sometime in the Middle Ages. Entrepreneur originated from the French word “Entreprendre” which means to undertake.
 Evolution of Entrepreneurship ◦ The ability of the individual to determine and come up with the proper combination of the resources available in his environment and transform this into an output of either goods or services, and obtain a fair profit at the price the entrepreneur sets.
Evolution of Entrepreneurship ◦ The ability of the individual to determine and come up with the proper combination of the resources available in his environment and transform this into an output of either goods or services, and obtain a fair profit at the price the entrepreneur sets.
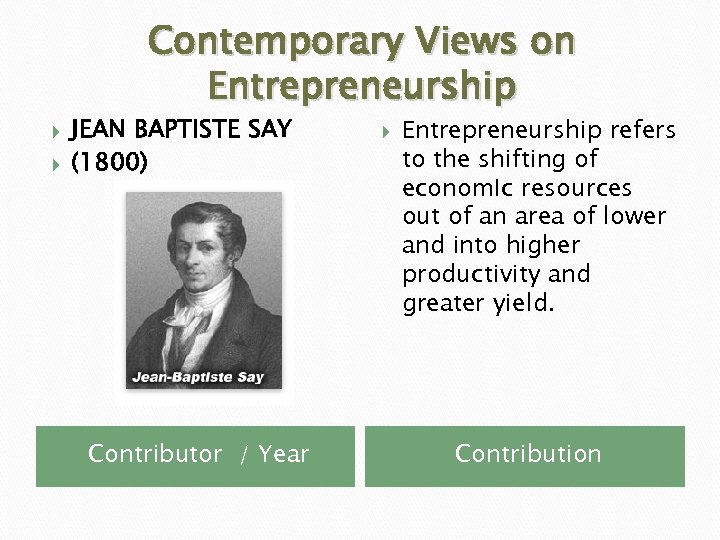 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship JEAN BAPTISTE SAY (1800) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship refers to the shifting of econom. Ic resources out of an area of lower and into higher productivity and greater yield. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship JEAN BAPTISTE SAY (1800) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship refers to the shifting of econom. Ic resources out of an area of lower and into higher productivity and greater yield. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship CARL MENGER (1871) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship involves obtaining information, calculations, an act of will and supervision. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship CARL MENGER (1871) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship involves obtaining information, calculations, an act of will and supervision. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship HARVEY LEIBENSTEIN (1970) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the reduction of organizational inefficency. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship HARVEY LEIBENSTEIN (1970) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the reduction of organizational inefficency. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship JOSEPH SCHUMPETER (1910) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is, in its essence, the finding and promoting new combinations of productive factors. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship JOSEPH SCHUMPETER (1910) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is, in its essence, the finding and promoting new combinations of productive factors. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship ISRAEL KIRZNER (1975) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is identification of market arbitrage opportunity. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship ISRAEL KIRZNER (1975) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is identification of market arbitrage opportunity. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship ALBERT SHAPIRO (1975) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship involves a kind of behavior that includes initiative taking, organizing and recognizing social mechanism to turn resources and situations so practical account, and the acceptance of risk and failures. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship ALBERT SHAPIRO (1975) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship involves a kind of behavior that includes initiative taking, organizing and recognizing social mechanism to turn resources and situations so practical account, and the acceptance of risk and failures. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship KARL VESPER (1980) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the dynamic process of creating incremental wealth. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship KARL VESPER (1980) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the dynamic process of creating incremental wealth. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship W. ED MC MULLAN AND WAYNE A. LONG (1990) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the building of new growth organization. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship W. ED MC MULLAN AND WAYNE A. LONG (1990) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the building of new growth organization. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship HOWARD STEVENSON (1992) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the pursuit of opportunity beyond the resources currently under one’s control. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship HOWARD STEVENSON (1992) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the pursuit of opportunity beyond the resources currently under one’s control. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship JEFFRY TIMMONS (1994) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the ability to create and build a vision from practically nothing. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship JEFFRY TIMMONS (1994) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the ability to create and build a vision from practically nothing. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship PETER DRUCKER (1998) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the process of starting one’s own new and small business. It is also the process of innovation and new venture creation through four major dimensions – individual, organizational, environmental, process – aided by collaborative networks in government, education and institutions. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship PETER DRUCKER (1998) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship is the process of starting one’s own new and small business. It is also the process of innovation and new venture creation through four major dimensions – individual, organizational, environmental, process – aided by collaborative networks in government, education and institutions. Contribution
 Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship ROBERT HISRICH (2001) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship involves the creation process, requires the devotion of the necessary time and effort, assumes the accompanying financial, psychic and social risks, and receives the resulting rewards of monetary and personal satisfaction and independence. Contribution
Contemporary Views on Entrepreneurship ROBERT HISRICH (2001) Contributor / Year Entrepreneurship involves the creation process, requires the devotion of the necessary time and effort, assumes the accompanying financial, psychic and social risks, and receives the resulting rewards of monetary and personal satisfaction and independence. Contribution
 Entrepreneurship as a Process and Approach ◦ The entrepreneur considers the opportunity to solve the problem rather than solving the problem itself. Process ◦ Entrepreneurship is a dynamic process of innovation and new – venture creation through the five major dimensions: individuals, organizations, environment, process and intuitions.
Entrepreneurship as a Process and Approach ◦ The entrepreneur considers the opportunity to solve the problem rather than solving the problem itself. Process ◦ Entrepreneurship is a dynamic process of innovation and new – venture creation through the five major dimensions: individuals, organizations, environment, process and intuitions.
 The Filipino Entrepreneur Findings in the 2006 Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) Research Consortium: ◦ Four out of ten adult Filipino are engaged in business. ◦ About half are in the early – stage entrepreneurial activity (Total Early Stage Activity – TEA). ◦ 19. 7% (9. 5 million) comprise the country’s established business. ◦ Mindanao has the higher TEA while Northern Luzon has the lowest. ◦ Most of the businesses are in consumer oriented with 35%.
The Filipino Entrepreneur Findings in the 2006 Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) Research Consortium: ◦ Four out of ten adult Filipino are engaged in business. ◦ About half are in the early – stage entrepreneurial activity (Total Early Stage Activity – TEA). ◦ 19. 7% (9. 5 million) comprise the country’s established business. ◦ Mindanao has the higher TEA while Northern Luzon has the lowest. ◦ Most of the businesses are in consumer oriented with 35%.
 The Filipino Entrepreneur Findings in the 2006 Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) Research Consortium: ◦ Motivated by Necessity (54%) and opportunity motivations (37%). ◦ Face stiff competition (75%), lack novelty (71%), lack new technology (67%), not employing (63%), and not exporting (77%). ◦ Only 8 out of 10 have discontinued a business in the past 12 months. ◦ Only 34% have dealings with banks. ◦ Only 17 who receive remittances use then to finance business. ◦ Only 1% are non – owner investors.
The Filipino Entrepreneur Findings in the 2006 Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) Research Consortium: ◦ Motivated by Necessity (54%) and opportunity motivations (37%). ◦ Face stiff competition (75%), lack novelty (71%), lack new technology (67%), not employing (63%), and not exporting (77%). ◦ Only 8 out of 10 have discontinued a business in the past 12 months. ◦ Only 34% have dealings with banks. ◦ Only 17 who receive remittances use then to finance business. ◦ Only 1% are non – owner investors.
 The Challenge to Entrepreneurs “Borderless World” – globalized trading system ◦ The Filipino entrepreneur who used to develop and market products locally is now faced with local competition with both Filipino and foreign products and services which are now available in the market. ◦ The Filipino entrepreneur has to contend with casting out the colonial mentality of the local market with its preferences for imported goods. ◦ Filipino entrepreneurs have the chance of developing and marketing export – quality products awing to the various incentives and support available.
The Challenge to Entrepreneurs “Borderless World” – globalized trading system ◦ The Filipino entrepreneur who used to develop and market products locally is now faced with local competition with both Filipino and foreign products and services which are now available in the market. ◦ The Filipino entrepreneur has to contend with casting out the colonial mentality of the local market with its preferences for imported goods. ◦ Filipino entrepreneurs have the chance of developing and marketing export – quality products awing to the various incentives and support available.
 The Challenge to Entrepreneurs “Cyber space or information highway” ◦ The resurgence and constantly improving information technology sector is a development to watch and its benefit for entrepreneurs to grab and exploit. ◦ By exploiting the benefits of information technology, and the various software available in the market, one can easily network with the foreign markets. ◦ The proliferation of computers both in offices and households has revolutionized business operations and system, allowing every place practically a base for business operations.
The Challenge to Entrepreneurs “Cyber space or information highway” ◦ The resurgence and constantly improving information technology sector is a development to watch and its benefit for entrepreneurs to grab and exploit. ◦ By exploiting the benefits of information technology, and the various software available in the market, one can easily network with the foreign markets. ◦ The proliferation of computers both in offices and households has revolutionized business operations and system, allowing every place practically a base for business operations.
 Entrepreneurship and Philippine Education The inclusion of entrepreneurship education at the secondary level. Vocational courses/subjects and books at the secondary level include chapters dealing with entrepreneurship. Courses leading to specialization on entrepreneurship or major area of study subsumed under the course leading to a degree in business management or business administration.
Entrepreneurship and Philippine Education The inclusion of entrepreneurship education at the secondary level. Vocational courses/subjects and books at the secondary level include chapters dealing with entrepreneurship. Courses leading to specialization on entrepreneurship or major area of study subsumed under the course leading to a degree in business management or business administration.
 Entrepreneurship and Philippine Education The Council of Management Educators (COME), comprising of academicians, has some way acknowledged entrepreneurship as part of the management education. The Society for Entrepreneurship Education, Inc. (SEED) has come into the arena of further promoting entrepreneurship education both in formal and nonformal sectors and a number of entrepreneurs themselves who continually talked it and unwillingly share their experiences and expertise, hoping that doers and believers of entrepreneurship will multiply in number.
Entrepreneurship and Philippine Education The Council of Management Educators (COME), comprising of academicians, has some way acknowledged entrepreneurship as part of the management education. The Society for Entrepreneurship Education, Inc. (SEED) has come into the arena of further promoting entrepreneurship education both in formal and nonformal sectors and a number of entrepreneurs themselves who continually talked it and unwillingly share their experiences and expertise, hoping that doers and believers of entrepreneurship will multiply in number.
 Entrepreneurship and Philippine Education The Commission on Higher Education (CHED) has pushed the formal integration of entrepreneurship education pursuant to Republic Act No. 7722 as embodied Memorandum Order No. 17 (CMO # 17) series of 2005 – Curriculum Requirement for Bachelor of Science in Entrepreneurship (BS Entrepreneurship). Some schools have integrated entrepreneurship as a track or major subject.
Entrepreneurship and Philippine Education The Commission on Higher Education (CHED) has pushed the formal integration of entrepreneurship education pursuant to Republic Act No. 7722 as embodied Memorandum Order No. 17 (CMO # 17) series of 2005 – Curriculum Requirement for Bachelor of Science in Entrepreneurship (BS Entrepreneurship). Some schools have integrated entrepreneurship as a track or major subject.
 Socio-economic Benefits of Entrepreneurship Promotes self-help and employment Mobilize capital Provides taxes to economy Empowers individual Enhances national identity and pride Enhances competitive consciousness Improves quality of life Enhances equitable distribution of income and wealth.
Socio-economic Benefits of Entrepreneurship Promotes self-help and employment Mobilize capital Provides taxes to economy Empowers individual Enhances national identity and pride Enhances competitive consciousness Improves quality of life Enhances equitable distribution of income and wealth.


