cc3d5d59c803bc348a1ac75131777004.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Orientation for fresh VDTT Students Introduction to UNIX July 28, 2001 Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 1 Anup Gangwar
Orientation for fresh VDTT Students Introduction to UNIX July 28, 2001 Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 1 Anup Gangwar
 Overview Prerequisites and goals of this course Differences between UNIX and Windows Overview of unices Basic UNIX commands and utilities Lunch Break File editors in UNIX Programming and Shell Scripting Document formatting using UNIX References and further study Thank You Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 2 • • •
Overview Prerequisites and goals of this course Differences between UNIX and Windows Overview of unices Basic UNIX commands and utilities Lunch Break File editors in UNIX Programming and Shell Scripting Document formatting using UNIX References and further study Thank You Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 2 • • •
 Prerequisites and Goals • What you should know – Basic familiarity with computers – Working Knowledge of atleast one operating system – A will to learn • What you will know This is not a complete UNIX tutorial Don’t try to learn the whole UNIX in one day How to do the most common set of tasks with UNIX Self-Help is the best help Pointers for further information Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 3 – – –
Prerequisites and Goals • What you should know – Basic familiarity with computers – Working Knowledge of atleast one operating system – A will to learn • What you will know This is not a complete UNIX tutorial Don’t try to learn the whole UNIX in one day How to do the most common set of tasks with UNIX Self-Help is the best help Pointers for further information Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 3 – – –
 Differences: UNIX and Windows • • The UNIX and Windows philosophies Client-Server model of Computation Multi-User and Multi-Tasking. Login? Concept of the Kernel and User Shell Concept of file ownership and groups GUI on UNIX and X windows Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 4 – UNIX is the most used OS in scientific and industrial community – Instead of avoiding UNIX take it heads on – Learning UNIX now will help you save precious time later on
Differences: UNIX and Windows • • The UNIX and Windows philosophies Client-Server model of Computation Multi-User and Multi-Tasking. Login? Concept of the Kernel and User Shell Concept of file ownership and groups GUI on UNIX and X windows Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 4 – UNIX is the most used OS in scientific and industrial community – Instead of avoiding UNIX take it heads on – Learning UNIX now will help you save precious time later on
 Overview of Unices-1 • • • The ? original? UNIX The AT&T SVR and BSD Others: HP-UX, Solaris, Linux, AIX, IRIX etc. Why are there so many unices? Vendor Wars! How do I understand all of them? POSIX! Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 5 – Learn the common set of commands for all the unices – Linux utilities will contain enhancements not found in others – Try to clear trivial doubts like command syntax yourself
Overview of Unices-1 • • • The ? original? UNIX The AT&T SVR and BSD Others: HP-UX, Solaris, Linux, AIX, IRIX etc. Why are there so many unices? Vendor Wars! How do I understand all of them? POSIX! Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 5 – Learn the common set of commands for all the unices – Linux utilities will contain enhancements not found in others – Try to clear trivial doubts like command syntax yourself
 Overview of Unices-2 • HP-UX – Processors: HP PA-RISC and Intel Itanium – Vendors: HP – Markets: High End Servers and Workstations • Solaris/Sun. OS Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 6 – Processors: Sun Ultra Sparc – Vendors: Sun Microsystems – Markets: All ranges of Servers and Workstations
Overview of Unices-2 • HP-UX – Processors: HP PA-RISC and Intel Itanium – Vendors: HP – Markets: High End Servers and Workstations • Solaris/Sun. OS Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 6 – Processors: Sun Ultra Sparc – Vendors: Sun Microsystems – Markets: All ranges of Servers and Workstations
 Overview of Unices-3 • Linux/GNU Systems – Processors: Intel 386 and up, Sun Ultra Sparc, IBM Power. PC etc. – Vendors: Free/GNU GPL – Markets: Low End Servers and Workstations • AIX (Advanced UNIX) Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 7 – Processors: IBM Power PC – Vendors: IBM – Markets: All ranges of Servers and Workstations
Overview of Unices-3 • Linux/GNU Systems – Processors: Intel 386 and up, Sun Ultra Sparc, IBM Power. PC etc. – Vendors: Free/GNU GPL – Markets: Low End Servers and Workstations • AIX (Advanced UNIX) Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 7 – Processors: IBM Power PC – Vendors: IBM – Markets: All ranges of Servers and Workstations
 Overview of Unices-4 • IRIX – Processors: MIPS – Vendors: SGI (Silicon Graphics International) – Markets: High End Graphics Servers and Workstations • Others Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 8 – Be. OS, Free. BSD etc. – RTOS’s: PSo. S, QNX, RTEMS, ? RTLinux? etc.
Overview of Unices-4 • IRIX – Processors: MIPS – Vendors: SGI (Silicon Graphics International) – Markets: High End Graphics Servers and Workstations • Others Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 8 – Be. OS, Free. BSD etc. – RTOS’s: PSo. S, QNX, RTEMS, ? RTLinux? etc.
 What we have • Philips VLSI Design Lab – HP Server running HP-UX – Sun Workstation – Linux Workstations • VDTT Lab – Linux Workstations – Windows NT Workstations • New VLSI Lab Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 9 – Sun Workstations – Windows NT Workstations
What we have • Philips VLSI Design Lab – HP Server running HP-UX – Sun Workstation – Linux Workstations • VDTT Lab – Linux Workstations – Windows NT Workstations • New VLSI Lab Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 9 – Sun Workstations – Windows NT Workstations
 Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-1 • Files and Directories – – – – File Types: Windows and UNIX File and Directory creation (Editors, mkdir, ln etc. ) Listing contents of a directory (ls) File and Directory deletion (rmdir, rm etc. ) File and Directory permissions (chmod) File and Directory ownership (chown, chgrp) Organizing your work in directories (mv) • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 10 – UNIX doesn’t have a recycle bin! – Try not to make the mistake of rm -rf * command
Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-1 • Files and Directories – – – – File Types: Windows and UNIX File and Directory creation (Editors, mkdir, ln etc. ) Listing contents of a directory (ls) File and Directory deletion (rmdir, rm etc. ) File and Directory permissions (chmod) File and Directory ownership (chown, chgrp) Organizing your work in directories (mv) • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 10 – UNIX doesn’t have a recycle bin! – Try not to make the mistake of rm -rf * command
 Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-2 • Managing your account – – – – What is meant by managing your account? Concept of setup files Why are there so many different Shells? Environment variables. bashrc and. cshrc files Customizing your environment with. bashrc and. cshrc files Example: The TERM environment variable and stty Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 11 • Try an environment variable on command-line first • Always set the PATH variable properly
Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-2 • Managing your account – – – – What is meant by managing your account? Concept of setup files Why are there so many different Shells? Environment variables. bashrc and. cshrc files Customizing your environment with. bashrc and. cshrc files Example: The TERM environment variable and stty Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 11 • Try an environment variable on command-line first • Always set the PATH variable properly
 Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-3 • Remote process execution – Why do we need remote process execution? – Telnet and rlogin – Remote execution of graphics programs • X-Security, granting permissions and colormap • The DISPLAY environment variable – dot-rhosts (. rhosts), xon – Moving files between computers: FTP (? anonymous? FTP login) – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 12 • Graphics performance suffers in remote graphics execution • xhost+ is the worst thing to do! • Ncftp is a better ftp client than the vanilla default UNIX ftp
Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-3 • Remote process execution – Why do we need remote process execution? – Telnet and rlogin – Remote execution of graphics programs • X-Security, granting permissions and colormap • The DISPLAY environment variable – dot-rhosts (. rhosts), xon – Moving files between computers: FTP (? anonymous? FTP login) – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 12 • Graphics performance suffers in remote graphics execution • xhost+ is the worst thing to do! • Ncftp is a better ftp client than the vanilla default UNIX ftp
 Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-4 • Taking printouts – – – Concept of network and local printers Printer languages: Postscript and PCL Ghost. View and Acroread programs Spooling, Deleting and Checking a printer job Duplex printing and mpage • Taking backups – Tarring, zipping, gzipping and compressing – Comparison with winzip and common filename extensions • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 13 – Do not issue the command tar -cvf
Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-4 • Taking printouts – – – Concept of network and local printers Printer languages: Postscript and PCL Ghost. View and Acroread programs Spooling, Deleting and Checking a printer job Duplex printing and mpage • Taking backups – Tarring, zipping, gzipping and compressing – Comparison with winzip and common filename extensions • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 13 – Do not issue the command tar -cvf
 Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-5 • Miscellaneous stuff – – – Forcing a process in background (&, fg, bg) Setting aliases Online manual pages, man Concept of NIS and NFS Changing password, passwd (? yppasswd? ) Searching for patterns, grep and regular expressions – – – Working with files with special characters in names The file utility finger, who and rwho ps and kill Mail and mail clients, netscape, pine, emacs and mail startx, . Xclients and. xinitrc files • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 14 – Instead of asking someone try man -k – It is a good practice to stick to one shell (csh is available on all)
Basic UNIX Commands and Utilities-5 • Miscellaneous stuff – – – Forcing a process in background (&, fg, bg) Setting aliases Online manual pages, man Concept of NIS and NFS Changing password, passwd (? yppasswd? ) Searching for patterns, grep and regular expressions – – – Working with files with special characters in names The file utility finger, who and rwho ps and kill Mail and mail clients, netscape, pine, emacs and mail startx, . Xclients and. xinitrc files • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 14 – Instead of asking someone try man -k – It is a good practice to stick to one shell (csh is available on all)
 Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 15 Lunch Break
Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 15 Lunch Break
 Editors in UNIX-1 • What all is available, Vi, Emacs, Pico, Joe? , Nedit? • Vi: The king of all editors? Tutorial? – Why learn vi? – Getting in and out? – Basic keys for editing • Moving around, deleting, joining lines • Repeating commands • Search and replace – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 16 • Vim is not Vi • Learn the keypad scroll key combinations instead of arrow keys • Vi is fast, try to make the best use of its capabilities
Editors in UNIX-1 • What all is available, Vi, Emacs, Pico, Joe? , Nedit? • Vi: The king of all editors? Tutorial? – Why learn vi? – Getting in and out? – Basic keys for editing • Moving around, deleting, joining lines • Repeating commands • Search and replace – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 16 • Vim is not Vi • Learn the keypad scroll key combinations instead of arrow keys • Vi is fast, try to make the best use of its capabilities
 Editors in UNIX-2 • Emacs: Much more than an editor? – Why learn Emacs? History, Tutorial – Getting in and out? – Basic keys for editing • • Moving around, deleting a line Search and replace Formatted text, postscript spooling mail in emacs – Syntax highlighting and templates – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 17 • Emacs recognizes 20+ languages out of the box • Emacs is slow • Emacs is not available by default on all unices
Editors in UNIX-2 • Emacs: Much more than an editor? – Why learn Emacs? History, Tutorial – Getting in and out? – Basic keys for editing • • Moving around, deleting a line Search and replace Formatted text, postscript spooling mail in emacs – Syntax highlighting and templates – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 17 • Emacs recognizes 20+ languages out of the box • Emacs is slow • Emacs is not available by default on all unices
 Editors in UNIX-3 • Pico: Is there really a need? – Pico and Pine – Editor Keys • Joe? , Nedit? – Keys similar to Norton Editor – Nedit has some features similar to Emacs • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 18 – Don’t fall for Pico or Nedit – Learn Vi and Emacs if you really want to get into UNIX – In the end it is a matter of choice
Editors in UNIX-3 • Pico: Is there really a need? – Pico and Pine – Editor Keys • Joe? , Nedit? – Keys similar to Norton Editor – Nedit has some features similar to Emacs • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 18 – Don’t fall for Pico or Nedit – Learn Vi and Emacs if you really want to get into UNIX – In the end it is a matter of choice
 Programming on UNIX-1 • • Is programming on UNIX tough? What all is available? Concept of IDE and differences with Turbo. C++ Compilers, Linkers, Debuggers and front-ends Managing big projects: make and comparison with TC project file Example of a simple makefile GUI development on UNIX Java Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 19 – UNIX is a programmers paradise
Programming on UNIX-1 • • Is programming on UNIX tough? What all is available? Concept of IDE and differences with Turbo. C++ Compilers, Linkers, Debuggers and front-ends Managing big projects: make and comparison with TC project file Example of a simple makefile GUI development on UNIX Java Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 19 – UNIX is a programmers paradise
 Programming on UNIX-2 • Gcc, The GNU C/C++ compiler – Simplest possible way to use: gcc
Programming on UNIX-2 • Gcc, The GNU C/C++ compiler – Simplest possible way to use: gcc
 Programming on UNIX-3 • Ld, The Linker – – What exactly are libraries? Shared and static libraries Is there a need to call Ld explicitly? Passing options to Ld from gcc • • The -l option The -L option The LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable The LD_RUN_PATH environment variable – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 21 • Always check the Ld on the system, HP-UX doesn’t use GNU Ld • Environment variables are different with non GNU Ld
Programming on UNIX-3 • Ld, The Linker – – What exactly are libraries? Shared and static libraries Is there a need to call Ld explicitly? Passing options to Ld from gcc • • The -l option The -L option The LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable The LD_RUN_PATH environment variable – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 21 • Always check the Ld on the system, HP-UX doesn’t use GNU Ld • Environment variables are different with non GNU Ld
 Programming on UNIX-4 • Gdb, The GNU C/C++ debugger – Why is a debugger needed? – gdb and ? core? File – Common commands • list • run, break, resume • backtrace and where – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 22 • Using gdb directly might be tedious • Try the various front-ends to gdb: emacs, xxgdb, mxgdb etc. • Not every system will have gdb, you just might have to use ? dbx?
Programming on UNIX-4 • Gdb, The GNU C/C++ debugger – Why is a debugger needed? – gdb and ? core? File – Common commands • list • run, break, resume • backtrace and where – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 22 • Using gdb directly might be tedious • Try the various front-ends to gdb: emacs, xxgdb, mxgdb etc. • Not every system will have gdb, you just might have to use ? dbx?
 Programming on UNIX-5 • Gmake or GNU make • What is the need for a Makefile? – – – Dependencies Targets in a makefile Patterns in makefile Automatic variables in a makefile Pattern substitution Common target names: all, clean, docs • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 23 – Never forget the TAB – Make is language independent!
Programming on UNIX-5 • Gmake or GNU make • What is the need for a Makefile? – – – Dependencies Targets in a makefile Patterns in makefile Automatic variables in a makefile Pattern substitution Common target names: all, clean, docs • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 23 – Never forget the TAB – Make is language independent!
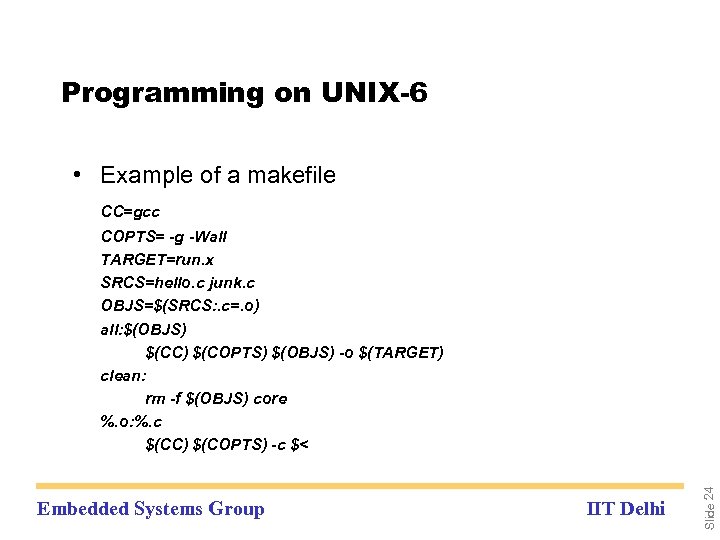 Programming on UNIX-6 • Example of a makefile CC=gcc Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 24 COPTS= -g -Wall TARGET=run. x SRCS=hello. c junk. c OBJS=$(SRCS: . c=. o) all: $(OBJS) $(CC) $(COPTS) $(OBJS) -o $(TARGET) clean: rm -f $(OBJS) core %. o: %. c $(CC) $(COPTS) -c $<
Programming on UNIX-6 • Example of a makefile CC=gcc Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 24 COPTS= -g -Wall TARGET=run. x SRCS=hello. c junk. c OBJS=$(SRCS: . c=. o) all: $(OBJS) $(CC) $(COPTS) $(OBJS) -o $(TARGET) clean: rm -f $(OBJS) core %. o: %. c $(CC) $(COPTS) -c $<
 Programming on UNIX-7 • GUI in UNIX? – – Differences with Turbo. C++ Vanilla X windows programming, why not? TCL/Tk Widget libraries • Motif • GTK • QT, etc. – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 25 • Always provide a command line interface to your programs • Using a GUI is slow
Programming on UNIX-7 • GUI in UNIX? – – Differences with Turbo. C++ Vanilla X windows programming, why not? TCL/Tk Widget libraries • Motif • GTK • QT, etc. – Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 25 • Always provide a command line interface to your programs • Using a GUI is slow
 Programming on UNIX-8 • Java – What is really different with the windows version? – Is Jfc, Java 2 D, Java 3 D available? – IDE’s for Java over UNIX? • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 26 – Don’t try to use a %. class dependency with make – If you run Java from a server, graphics would be slow
Programming on UNIX-8 • Java – What is really different with the windows version? – Is Jfc, Java 2 D, Java 3 D available? – IDE’s for Java over UNIX? • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 26 – Don’t try to use a %. class dependency with make – If you run Java from a server, graphics would be slow
 Introduction to Shell Programming-1 • • What is the need for shell programming? Bourne shell (sh, ksh, zsh and bash) c shell (csh, tcsh) Examples of shell programming – Moving all a. {i}. txt files to a. {i+1}. txt – Cleaning up your directory at the end of a day • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 27 – Perl just might be a better option – Don’t forget ? sed? and ? awk?
Introduction to Shell Programming-1 • • What is the need for shell programming? Bourne shell (sh, ksh, zsh and bash) c shell (csh, tcsh) Examples of shell programming – Moving all a. {i}. txt files to a. {i+1}. txt – Cleaning up your directory at the end of a day • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 27 – Perl just might be a better option – Don’t forget ? sed? and ? awk?
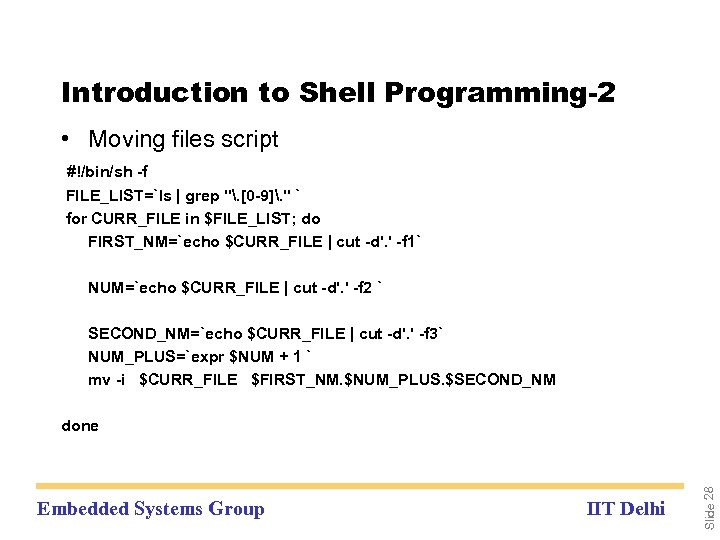 Introduction to Shell Programming-2 • Moving files script #!/bin/sh -f FILE_LIST=`ls | grep ". [0 -9]. " ` for CURR_FILE in $FILE_LIST; do FIRST_NM=`echo $CURR_FILE | cut -d'. ' -f 1` NUM=`echo $CURR_FILE | cut -d'. ' -f 2 ` SECOND_NM=`echo $CURR_FILE | cut -d'. ' -f 3` NUM_PLUS=`expr $NUM + 1 ` mv -i $CURR_FILE $FIRST_NM. $NUM_PLUS. $SECOND_NM Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 28 done
Introduction to Shell Programming-2 • Moving files script #!/bin/sh -f FILE_LIST=`ls | grep ". [0 -9]. " ` for CURR_FILE in $FILE_LIST; do FIRST_NM=`echo $CURR_FILE | cut -d'. ' -f 1` NUM=`echo $CURR_FILE | cut -d'. ' -f 2 ` SECOND_NM=`echo $CURR_FILE | cut -d'. ' -f 3` NUM_PLUS=`expr $NUM + 1 ` mv -i $CURR_FILE $FIRST_NM. $NUM_PLUS. $SECOND_NM Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 28 done
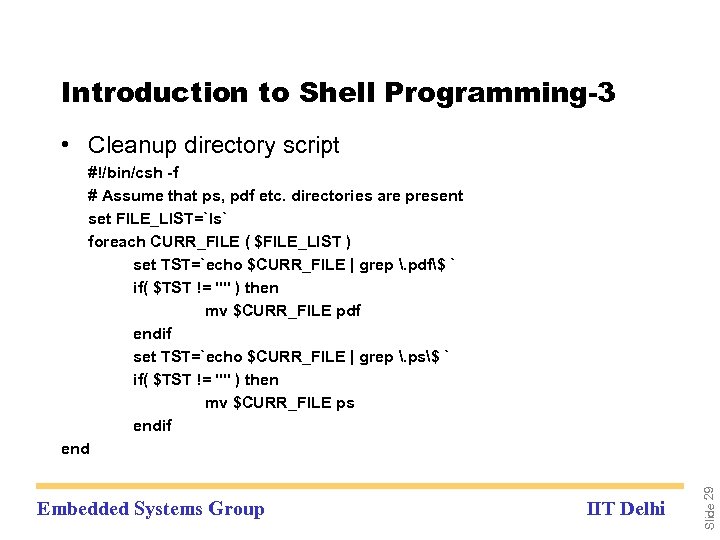 Introduction to Shell Programming-3 • Cleanup directory script Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 29 #!/bin/csh -f # Assume that ps, pdf etc. directories are present set FILE_LIST=`ls` foreach CURR_FILE ( $FILE_LIST ) set TST=`echo $CURR_FILE | grep . pdf$ ` if( $TST != "" ) then mv $CURR_FILE pdf endif set TST=`echo $CURR_FILE | grep . ps$ ` if( $TST != "" ) then mv $CURR_FILE ps endif end
Introduction to Shell Programming-3 • Cleanup directory script Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 29 #!/bin/csh -f # Assume that ps, pdf etc. directories are present set FILE_LIST=`ls` foreach CURR_FILE ( $FILE_LIST ) set TST=`echo $CURR_FILE | grep . pdf$ ` if( $TST != "" ) then mv $CURR_FILE pdf endif set TST=`echo $CURR_FILE | grep . ps$ ` if( $TST != "" ) then mv $CURR_FILE ps endif end
 Text formatting using UNIX-1 • • What is the need for text formatting? WYSWYG or NOT? La. Te. X & Emacs PS renderer La. Te. X WYSWYG front-end Lyx Other text formatters: ? troff? How to make Presentations? Slides? Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 30 – Power. Point is still the best software for making presentations – It is easy to convert Power. Point slides to html
Text formatting using UNIX-1 • • What is the need for text formatting? WYSWYG or NOT? La. Te. X & Emacs PS renderer La. Te. X WYSWYG front-end Lyx Other text formatters: ? troff? How to make Presentations? Slides? Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 30 – Power. Point is still the best software for making presentations – It is easy to convert Power. Point slides to html
 Text formatting using UNIX-2 • La. Te. X – origin: La. Te. X and Te. X – usage – La. Te. X tutorials and manuals • A not so short introduction to La. Te. X • The La. Te. X manual • La. Te. X by Lesslie Lamport • Lyx a WYSWIG interface to La. Te. X • Emacs ps-renderer and troff • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 31 – For small formatted text Emacs is still the best
Text formatting using UNIX-2 • La. Te. X – origin: La. Te. X and Te. X – usage – La. Te. X tutorials and manuals • A not so short introduction to La. Te. X • The La. Te. X manual • La. Te. X by Lesslie Lamport • Lyx a WYSWIG interface to La. Te. X • Emacs ps-renderer and troff • Tips: Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 31 – For small formatted text Emacs is still the best
 Before wrapping up Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 32 Any questions/doubts which you would like to clarify?
Before wrapping up Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 32 Any questions/doubts which you would like to clarify?
 Wrapping up • Self help is the best help! – The UNIX man pages. ? Manual sections? – Using man, whatis etc. – Experiment. You can never kill the system. • Links – – http: //www. gnu. org, for GNU tools and manuals http: //sunsite. unc. edu, world’s largest collection of free software http: //upavan. cse. iitd. ernet. in, Philips Lab. internal page http: //poorvi. cse. iitd. ernet. in/local, Intel cluster archives • Books Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 33 – The UNIX programming environment, Kernighan & Pike
Wrapping up • Self help is the best help! – The UNIX man pages. ? Manual sections? – Using man, whatis etc. – Experiment. You can never kill the system. • Links – – http: //www. gnu. org, for GNU tools and manuals http: //sunsite. unc. edu, world’s largest collection of free software http: //upavan. cse. iitd. ernet. in, Philips Lab. internal page http: //poorvi. cse. iitd. ernet. in/local, Intel cluster archives • Books Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 33 – The UNIX programming environment, Kernighan & Pike
 Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 34 Thank You
Embedded Systems Group IIT Delhi Slide 34 Thank You


