f540a227356d9d8f80b6165f1b5ae01e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Organizational Factors in Selecting and Supporting a VLE Roger Matthews Deputy Director of Information Services University of Wales Aberystwyth Patras 2003 1
Organizational Factors in Selecting and Supporting a VLE Roger Matthews Deputy Director of Information Services University of Wales Aberystwyth Patras 2003 1
 Useful URLs www. inf. aber. ac. uk/vle alto. aber. ac. uk Patras 2003 2
Useful URLs www. inf. aber. ac. uk/vle alto. aber. ac. uk Patras 2003 2
 Background - UWA University of Wales, Aberystwyth (UWA) was founded in 1872; The first university institution to be established in Wales; Today, it has over 7, 000 registered students, including over 1, 100 postgraduates; Eighteen academic departments. There is a strong bilingual policy Patras 2003 3
Background - UWA University of Wales, Aberystwyth (UWA) was founded in 1872; The first university institution to be established in Wales; Today, it has over 7, 000 registered students, including over 1, 100 postgraduates; Eighteen academic departments. There is a strong bilingual policy Patras 2003 3
 Background – Information Services Formed in 1995 as a fully converged service covering – Library Services; Central Computer Services; Microcomputer Services; Management Information Services; Learning Technology Services; Media Services. Patras 2003 4
Background – Information Services Formed in 1995 as a fully converged service covering – Library Services; Central Computer Services; Microcomputer Services; Management Information Services; Learning Technology Services; Media Services. Patras 2003 4
 Background – Learning & Teaching Strategy Institutional report produced during 1999 by one of our Pro Vice Chancellors required departments. To promote the use of learning technology…. in respect of the delivery, administration and management of courses (Staff Development Office, Academic Affairs Committee, Information Services); To review their means of assessment (Departmental Learning Committees / Deans / Academic Affairs Committee). Patras 2003 5
Background – Learning & Teaching Strategy Institutional report produced during 1999 by one of our Pro Vice Chancellors required departments. To promote the use of learning technology…. in respect of the delivery, administration and management of courses (Staff Development Office, Academic Affairs Committee, Information Services); To review their means of assessment (Departmental Learning Committees / Deans / Academic Affairs Committee). Patras 2003 5
 What happened next? Well this is a University isn’t it? We set up a Working Party comprising – Learning and Teaching Champions; Web Developers; CAL Developers; Central Administration (SDO/Marketing) Information Services Support Staff (including Librarians). Patras 2003 6
What happened next? Well this is a University isn’t it? We set up a Working Party comprising – Learning and Teaching Champions; Web Developers; CAL Developers; Central Administration (SDO/Marketing) Information Services Support Staff (including Librarians). Patras 2003 6
 Providing a Virtual Learning Environment? Advantages anticipated in 1999 Enables good teaching to be “captured” and improved on and presented repeatedly; Fitted with modern British student lifestyles where many have to work to support themselves; Allows “Learner-centred” teaching. Patras 2003 7
Providing a Virtual Learning Environment? Advantages anticipated in 1999 Enables good teaching to be “captured” and improved on and presented repeatedly; Fitted with modern British student lifestyles where many have to work to support themselves; Allows “Learner-centred” teaching. Patras 2003 7
 Providing a Virtual Learning Environment? Disadvantages (User Survey 2003) Some students feel that this is just a device to allow teachers to avoid lecturing and personal contact; Some students feel that the VLE experience is condescending, devaluing the learning experience; Some students and staff lack the IT skills to get the best from a VLE. Patras 2003 8
Providing a Virtual Learning Environment? Disadvantages (User Survey 2003) Some students feel that this is just a device to allow teachers to avoid lecturing and personal contact; Some students feel that the VLE experience is condescending, devaluing the learning experience; Some students and staff lack the IT skills to get the best from a VLE. Patras 2003 8
 Choosing a VLE (1999) Write your own VLE? Control of the design & interfaces; But, you depend upon in-house expertise, resource issues & staff retention. Buy a VLE? Out-of-box solution, easier inter-collegiate collaboration; But, high capital cost & lack of control. Patras 2003 9
Choosing a VLE (1999) Write your own VLE? Control of the design & interfaces; But, you depend upon in-house expertise, resource issues & staff retention. Buy a VLE? Out-of-box solution, easier inter-collegiate collaboration; But, high capital cost & lack of control. Patras 2003 9
 We decided to pilot a VLE We decided to buy one; Funded by Information Services (regrettably); We chose, largely on price, Web. CT running on a Windows NT server; We started in Summer 2000 with a target of 20 modules being live by May 2001. Patras 2003 10
We decided to pilot a VLE We decided to buy one; Funded by Information Services (regrettably); We chose, largely on price, Web. CT running on a Windows NT server; We started in Summer 2000 with a target of 20 modules being live by May 2001. Patras 2003 10
 Conducting the Pilot Without institutional level support we needed to “cascade-train” others We targeted a small group of Academics; Explained the principles behind a VLE; Explained how to plan a course for a VLE; Explained how to input the teaching materials; Gave them individual & group training. Patras 2003 11
Conducting the Pilot Without institutional level support we needed to “cascade-train” others We targeted a small group of Academics; Explained the principles behind a VLE; Explained how to plan a course for a VLE; Explained how to input the teaching materials; Gave them individual & group training. Patras 2003 11
 Outcomes – Pilot 1 (May 2001) Target number of modules exceeded by a factor of 3; High degree of satisfaction from Academics & Students; Tutors didn’t like the two stage content uploading process; We had concerns about content portability; Emerging Welsh Higher Education Blackboard community. Patras 2003 12
Outcomes – Pilot 1 (May 2001) Target number of modules exceeded by a factor of 3; High degree of satisfaction from Academics & Students; Tutors didn’t like the two stage content uploading process; We had concerns about content portability; Emerging Welsh Higher Education Blackboard community. Patras 2003 12
 Conclusions – Pilot 1 (May 2001) We should offer a VLE; But Blackboard seemed to offer a more attractive solution with a similar toolset; CHEST deal had made Blackboard software affordable; The Hardware from the Pilot was reuseable; Our users agreed to change (reluctantly). Patras 2003 13
Conclusions – Pilot 1 (May 2001) We should offer a VLE; But Blackboard seemed to offer a more attractive solution with a similar toolset; CHEST deal had made Blackboard software affordable; The Hardware from the Pilot was reuseable; Our users agreed to change (reluctantly). Patras 2003 13
 Pilot 2 (2001 -Present) We purchased Blackboard Level One (IS paid for it again); We promoted it initially (but it took off on its own); We provided staff effort to help Academics migrate their existing Web. CT courses; We provided training materials & training (so far more than 100 Academics have been trained in VLE and Front. Page). Patras 2003 14
Pilot 2 (2001 -Present) We purchased Blackboard Level One (IS paid for it again); We promoted it initially (but it took off on its own); We provided staff effort to help Academics migrate their existing Web. CT courses; We provided training materials & training (so far more than 100 Academics have been trained in VLE and Front. Page). Patras 2003 14
 Pilot 2 (2001 -Present) We had more than 200 active modules by July 2002 (initial target in 1999 had been 50 by then); Today we have 379 active modules; This figure grows almost every day; We have 299 registered instructors; Our Blackboard system has slightly less than 300, 000 hits a month. Patras 2003 15
Pilot 2 (2001 -Present) We had more than 200 active modules by July 2002 (initial target in 1999 had been 50 by then); Today we have 379 active modules; This figure grows almost every day; We have 299 registered instructors; Our Blackboard system has slightly less than 300, 000 hits a month. Patras 2003 15
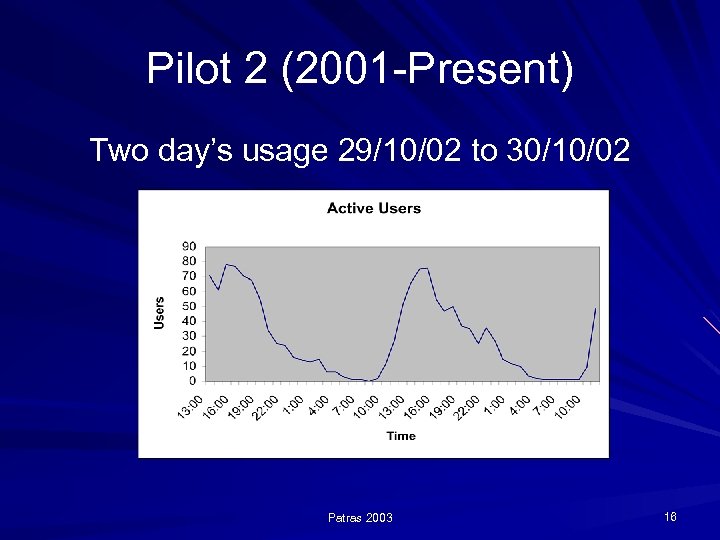 Pilot 2 (2001 -Present) Two day’s usage 29/10/02 to 30/10/02 Patras 2003 16
Pilot 2 (2001 -Present) Two day’s usage 29/10/02 to 30/10/02 Patras 2003 16
 Issues (1) – Project Ownership To embed a VLE into a University’s Learning & Teaching, the project must be “owned” by the Institution; It’s governance and funding must be at Institution level rather than at an IS (or Library) level; The top level Teaching & Learning committee must be fully involved; The VLE must be run as a central service. Patras 2003 17
Issues (1) – Project Ownership To embed a VLE into a University’s Learning & Teaching, the project must be “owned” by the Institution; It’s governance and funding must be at Institution level rather than at an IS (or Library) level; The top level Teaching & Learning committee must be fully involved; The VLE must be run as a central service. Patras 2003 17
 Issues (2) - Level of Support Training & Retraining Support Academic Staff – Training in teaching using Technology, IT skills training, assistance with design; Administrators – Course management; Library & IT Support Staff – Project concepts, Helpdesk training, accessing the VLE, liaison with Academic departments; Students – IT Skills training (but often little more than an induction to the system). Patras 2003 18
Issues (2) - Level of Support Training & Retraining Support Academic Staff – Training in teaching using Technology, IT skills training, assistance with design; Administrators – Course management; Library & IT Support Staff – Project concepts, Helpdesk training, accessing the VLE, liaison with Academic departments; Students – IT Skills training (but often little more than an induction to the system). Patras 2003 18
 Issues (2) - Level of Support Systems Support Software – Keeping the server O/S and the VLE software up-to-date; Hardware – You need servers which have high performance and reliability; You need to run 24 x 7 availability; Backup – You need to protect your users content, they have invested heavily. Patras 2003 19
Issues (2) - Level of Support Systems Support Software – Keeping the server O/S and the VLE software up-to-date; Hardware – You need servers which have high performance and reliability; You need to run 24 x 7 availability; Backup – You need to protect your users content, they have invested heavily. Patras 2003 19
 Issues (2) - Level of Support Systems Support (2) Systems Architecture – Your systems will be used in a time critical way, so you need to design in redundancy and automatic fail -over; Supplier Relations – you need to set aside effort to liaise with your suppliers to handle planning and fault resolution. Patras 2003 20
Issues (2) - Level of Support Systems Support (2) Systems Architecture – Your systems will be used in a time critical way, so you need to design in redundancy and automatic fail -over; Supplier Relations – you need to set aside effort to liaise with your suppliers to handle planning and fault resolution. Patras 2003 20
 Issues (3) - User Registration Course Tutors at Aberystwyth were not prepared to handle user registration and demanded an automatic process; We didn’t wish them to do this anyway; We wanted to synchronize registration and authentication between the Blackboard system and the rest of our services; Tutors often want freedom to make their courses available to others. Patras 2003 21
Issues (3) - User Registration Course Tutors at Aberystwyth were not prepared to handle user registration and demanded an automatic process; We didn’t wish them to do this anyway; We wanted to synchronize registration and authentication between the Blackboard system and the rest of our services; Tutors often want freedom to make their courses available to others. Patras 2003 21
 Issues (4) - Module Descriptors Our Academic Registry “own” the module descriptors which are held in an authoritative database; They insist that the module descriptors in Blackboard match their data exactly; They do not have the resource to enter these data again; And neither does Information Services. Patras 2003 22
Issues (4) - Module Descriptors Our Academic Registry “own” the module descriptors which are held in an authoritative database; They insist that the module descriptors in Blackboard match their data exactly; They do not have the resource to enter these data again; And neither does Information Services. Patras 2003 22
 Issues (5) - VLE Design Problems Example VLE Top Level Page Patras 2003 23
Issues (5) - VLE Design Problems Example VLE Top Level Page Patras 2003 23
 Issues (5) - VLE Design Problems Summary VLE suppliers tend to want to provide a full range of communications tools but these are often inferior; We want to provide “best-of-breed” tools in a seamless fashion; We want to “pick-and-mix” facilities not buy wholesale from one supplier. Patras 2003 24
Issues (5) - VLE Design Problems Summary VLE suppliers tend to want to provide a full range of communications tools but these are often inferior; We want to provide “best-of-breed” tools in a seamless fashion; We want to “pick-and-mix” facilities not buy wholesale from one supplier. Patras 2003 24
 Conclusions (1) VLEs are valuable tools to support Learning and Teaching; To get best use of a VLE you must eventually embed it in an MLE; Interoperability with your Library management and other MIS systems is crucial; You must pilot your project to find out what factors are important to your organization; If you want a bilingual system, you must select your VLE with this in mind. Patras 2003 25
Conclusions (1) VLEs are valuable tools to support Learning and Teaching; To get best use of a VLE you must eventually embed it in an MLE; Interoperability with your Library management and other MIS systems is crucial; You must pilot your project to find out what factors are important to your organization; If you want a bilingual system, you must select your VLE with this in mind. Patras 2003 25
 Conclusions (2) To allow access to the VLE environment with “best-of-breed” tools rather than inferior ones, some advise considering overlaying the system with a “Portal”; It is claimed that this will give many benefits - seamless integration, personalization and customization; However, a “Portal” is not, as yet very welldefined. Patras 2003 26
Conclusions (2) To allow access to the VLE environment with “best-of-breed” tools rather than inferior ones, some advise considering overlaying the system with a “Portal”; It is claimed that this will give many benefits - seamless integration, personalization and customization; However, a “Portal” is not, as yet very welldefined. Patras 2003 26
 Conclusions (3) Institutional backing is crucial to progress beyond a Pilot; Support quickly becomes a resource issue; The total cost of ownership is higher than you expect; Whichever VLE you buy will be wrong; So you must plan your development strategy. Patras 2003 27
Conclusions (3) Institutional backing is crucial to progress beyond a Pilot; Support quickly becomes a resource issue; The total cost of ownership is higher than you expect; Whichever VLE you buy will be wrong; So you must plan your development strategy. Patras 2003 27
 So what of the future - Patras 2003 28
So what of the future - Patras 2003 28
 Aberystwyth – Next Steps (1) We need to develop a fully integrated MLE; But, we are considering stepping back from trying to base that MLE development on Blackboard due to restrictive licensing conditions; But, we accept that we cannot do a step change again, so we will need to continue supporting our Blackboard system for now. Patras 2003 29
Aberystwyth – Next Steps (1) We need to develop a fully integrated MLE; But, we are considering stepping back from trying to base that MLE development on Blackboard due to restrictive licensing conditions; But, we accept that we cannot do a step change again, so we will need to continue supporting our Blackboard system for now. Patras 2003 29
 Aberystwyth – Next Steps (2) As indicated earlier, e-assessment is an integral part of e-learning and we haven’t been able to address it; A spin-off company from UWA has developed an e-assessment system which will serve this need; It is being enhanced and extended to incorporate a VLE – which might meet a lot of our requirements. Patras 2003 30
Aberystwyth – Next Steps (2) As indicated earlier, e-assessment is an integral part of e-learning and we haven’t been able to address it; A spin-off company from UWA has developed an e-assessment system which will serve this need; It is being enhanced and extended to incorporate a VLE – which might meet a lot of our requirements. Patras 2003 30
 Aberystwyth – Next Steps (3) It might address most of the issues raised by our two pilots; We will consider running it as a pilot alongside Blackboard from September 2003; We hope that, if it is successful, most users will eventually migrate to it (with our encouragement); Let’s hope! Patras 2003 31
Aberystwyth – Next Steps (3) It might address most of the issues raised by our two pilots; We will consider running it as a pilot alongside Blackboard from September 2003; We hope that, if it is successful, most users will eventually migrate to it (with our encouragement); Let’s hope! Patras 2003 31
 Acknowledgements Kate Wright (kaw@aber. ac. uk); Andra Bloomfield (adb@aber. ac. uk); Kerr Gardiner (akg@aber. ac. uk); Roger Matthews (rfm@aber. ac. uk). Patras 2003 32
Acknowledgements Kate Wright (kaw@aber. ac. uk); Andra Bloomfield (adb@aber. ac. uk); Kerr Gardiner (akg@aber. ac. uk); Roger Matthews (rfm@aber. ac. uk). Patras 2003 32
 The End Patras 2003 33
The End Patras 2003 33


