 Organizational Design, Diagnosis, and Development Session 7 Departmentation, II
Organizational Design, Diagnosis, and Development Session 7 Departmentation, II
 Objectives • To examine mixed and multinational structures • To consider design from an enterprise perspective • To consider design from an operational perspective
Objectives • To examine mixed and multinational structures • To consider design from an enterprise perspective • To consider design from an operational perspective
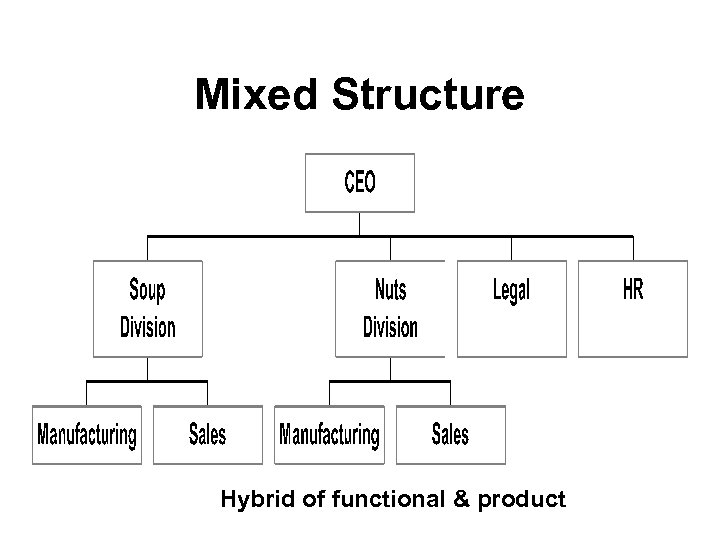 Mixed Structure Hybrid of functional & product
Mixed Structure Hybrid of functional & product
 Value of Mixed Design • Advantage – Uses divisional to be responsive to core enterprises and functional for staff areas which need to allow expertise to develop • Disadvantage – Conflicts can erupt between divisional units and centralized ones due to different perspectives and needs.
Value of Mixed Design • Advantage – Uses divisional to be responsive to core enterprises and functional for staff areas which need to allow expertise to develop • Disadvantage – Conflicts can erupt between divisional units and centralized ones due to different perspectives and needs.
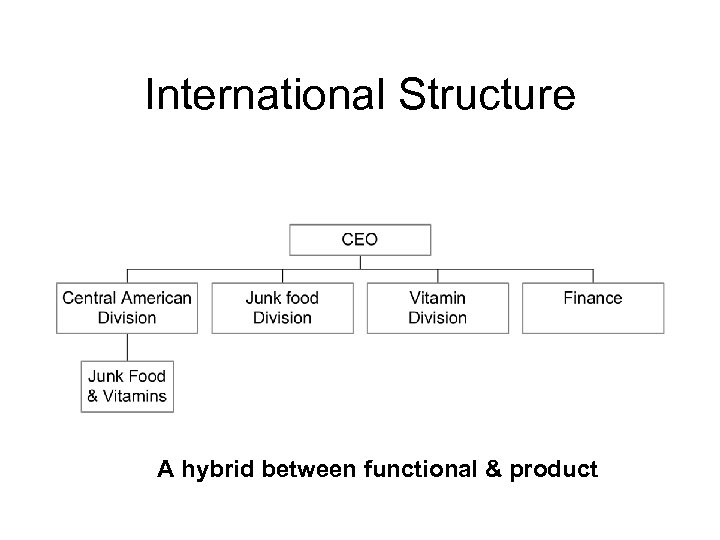 International Structure A hybrid between functional & product
International Structure A hybrid between functional & product
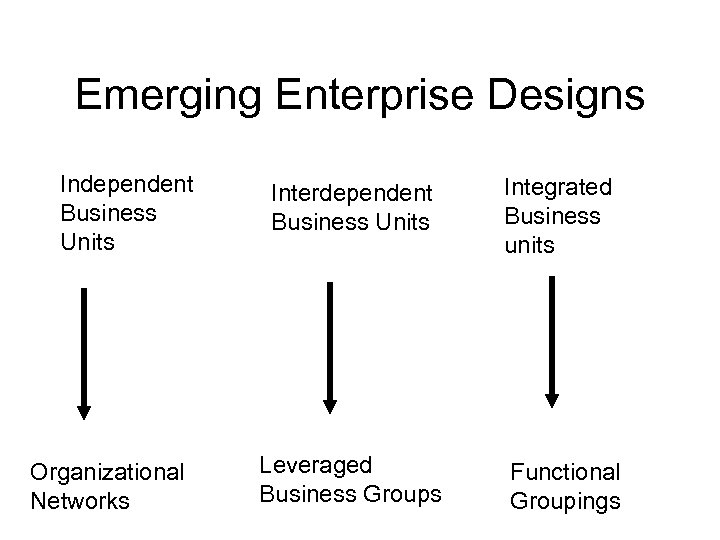 Emerging Enterprise Designs Independent Business Units Organizational Networks Interdependent Business Units Leveraged Business Groups Integrated Business units Functional Groupings
Emerging Enterprise Designs Independent Business Units Organizational Networks Interdependent Business Units Leveraged Business Groups Integrated Business units Functional Groupings
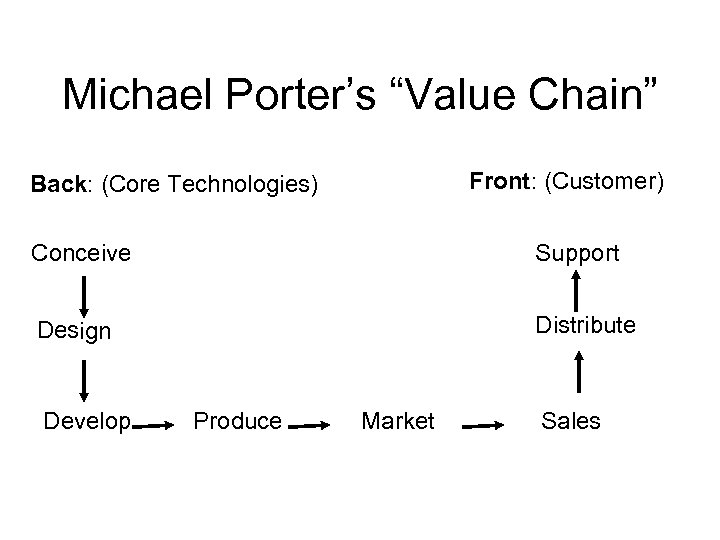 Michael Porter’s “Value Chain” Front: (Customer) Back: (Core Technologies) Conceive Support Design Distribute Develop Produce Market Sales
Michael Porter’s “Value Chain” Front: (Customer) Back: (Core Technologies) Conceive Support Design Distribute Develop Produce Market Sales
 Focus & Leverage • Focus: – “zoomed” : a close-up perspective on a segment of the process (traditional) – “telephotoed” or long range perspective on the entire process (emerging) • Leverage: the ability of the company to take advantage of economies of scale by using common resources
Focus & Leverage • Focus: – “zoomed” : a close-up perspective on a segment of the process (traditional) – “telephotoed” or long range perspective on the entire process (emerging) • Leverage: the ability of the company to take advantage of economies of scale by using common resources
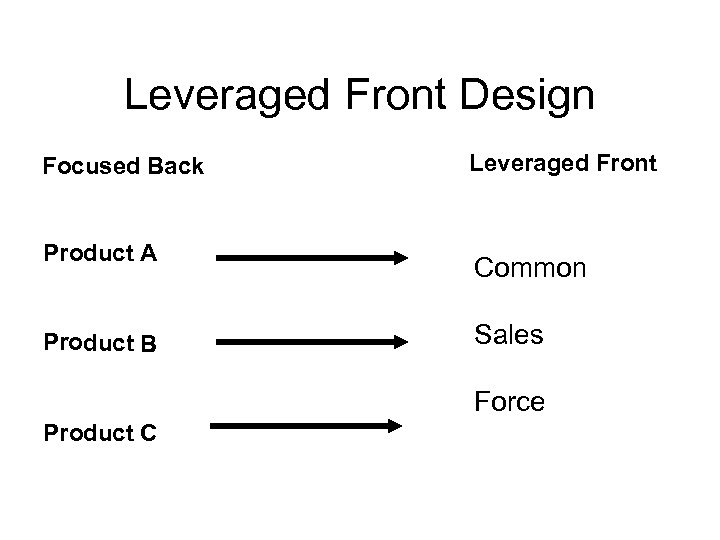 Leveraged Front Design Focused Back Product A Product B Leveraged Front Common Sales Force Product C
Leveraged Front Design Focused Back Product A Product B Leveraged Front Common Sales Force Product C
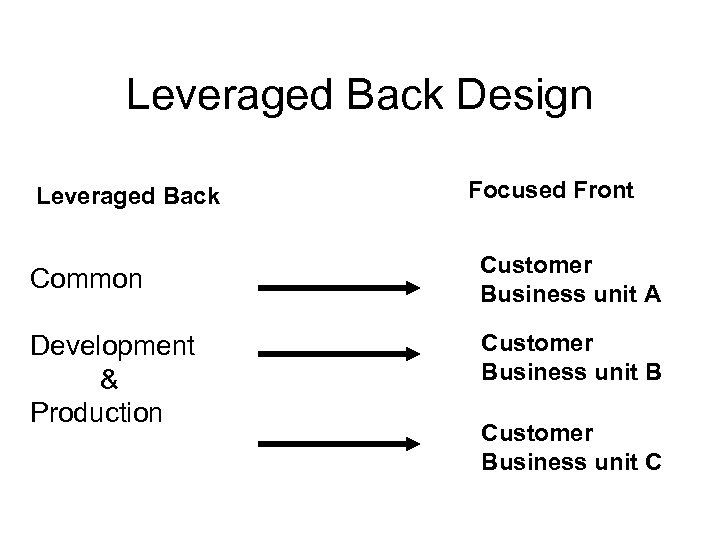 Leveraged Back Design Leveraged Back Focused Front Common Customer Business unit A Development & Production Customer Business unit B Customer Business unit C
Leveraged Back Design Leveraged Back Focused Front Common Customer Business unit A Development & Production Customer Business unit B Customer Business unit C
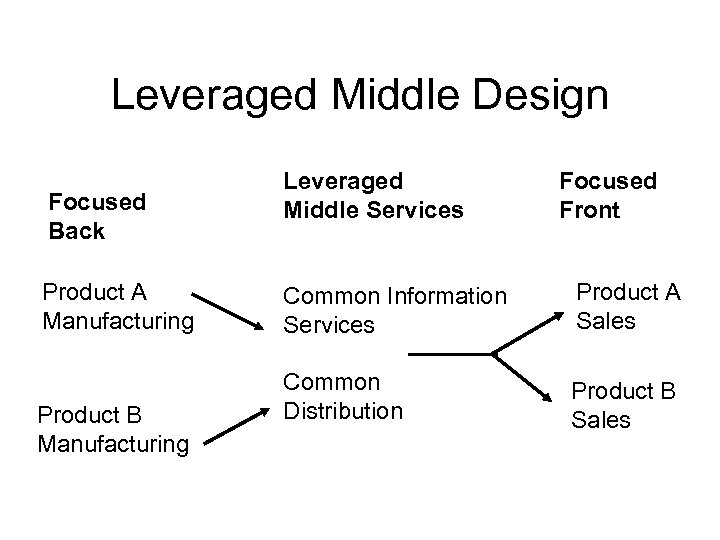 Leveraged Middle Design Focused Back Product A Manufacturing Product B Manufacturing Leveraged Middle Services Focused Front Common Information Services Product A Sales Common Distribution Product B Sales
Leveraged Middle Design Focused Back Product A Manufacturing Product B Manufacturing Leveraged Middle Services Focused Front Common Information Services Product A Sales Common Distribution Product B Sales
 Strategic Alliance • Two independent companies come together to plan the product and its delivery. – MSNBC is the joint venture of Microsoft & GE. • Requirements: – clear objectives – compatible cultures – commitment
Strategic Alliance • Two independent companies come together to plan the product and its delivery. – MSNBC is the joint venture of Microsoft & GE. • Requirements: – clear objectives – compatible cultures – commitment
 Socio-Technical Systems • Organization’s social system should match the technical systems – Design roles and tasks to complement social and technical needs – Build ability redundancy into the system – Utilize autonomous work groups with members who are cross-trained.
Socio-Technical Systems • Organization’s social system should match the technical systems – Design roles and tasks to complement social and technical needs – Build ability redundancy into the system – Utilize autonomous work groups with members who are cross-trained.
 High Performance Work Systems • Design the process starting with customer • Design work around autonomous work groups • Provide clear goals and performance standards • Provide quality control at the source • Align all systems • Provide information freely • Provide enriched jobs • HR practices which are aligned with HPWS • Management & culture must support HPWS • There needs to be flexibility built in
High Performance Work Systems • Design the process starting with customer • Design work around autonomous work groups • Provide clear goals and performance standards • Provide quality control at the source • Align all systems • Provide information freely • Provide enriched jobs • HR practices which are aligned with HPWS • Management & culture must support HPWS • There needs to be flexibility built in
 Backwards & Forwards • Summing up: Today we reviewed mixed and multinational structures. Then we explored some strategic issues for designs using Nadler and Tushman’s concepts of focus and leverage. This gave the opportunity to explore designs with areas of focus and leverage. Finally we looked at redesign at the operational level using notions of socio-technical systems and high performance work systems. • Looking ahead: Next time we conclude our module on design by looking at team organizations and virtual organizations.
Backwards & Forwards • Summing up: Today we reviewed mixed and multinational structures. Then we explored some strategic issues for designs using Nadler and Tushman’s concepts of focus and leverage. This gave the opportunity to explore designs with areas of focus and leverage. Finally we looked at redesign at the operational level using notions of socio-technical systems and high performance work systems. • Looking ahead: Next time we conclude our module on design by looking at team organizations and virtual organizations.