Topic_10.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 33

Organization of Remuneration and Motivation of Labor 1. Motivation of Labor: Definition &Meaning. 2. Organization of Remuneration: Meaning, Functions and Principles. Structure of Payroll on enterprise. 3. Base-rate remuneration. 4. Basic compensation systems and payment methods. 1

1. Motivation of Labor: Definition &Meaning. 2

? MOTIVATION & INCENTIVES 3
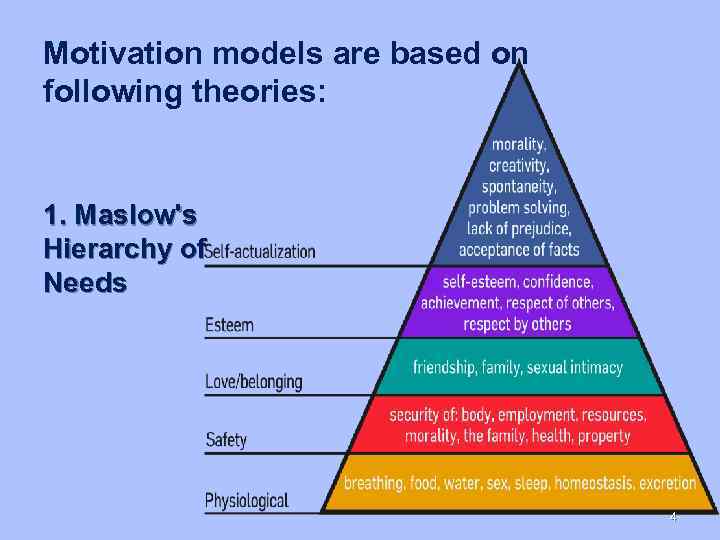
Motivation models are based on following theories: 1. Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs 4

Motivation models are based on following theories: 2. Mc. Clelland's Need Theory Need for achievement – People typically prefer to master a task or situation. Need for affiliation: People prefer to spend time creating and maintaining social relationships Need for power: person's desire to influence, teach or encourage others. 5
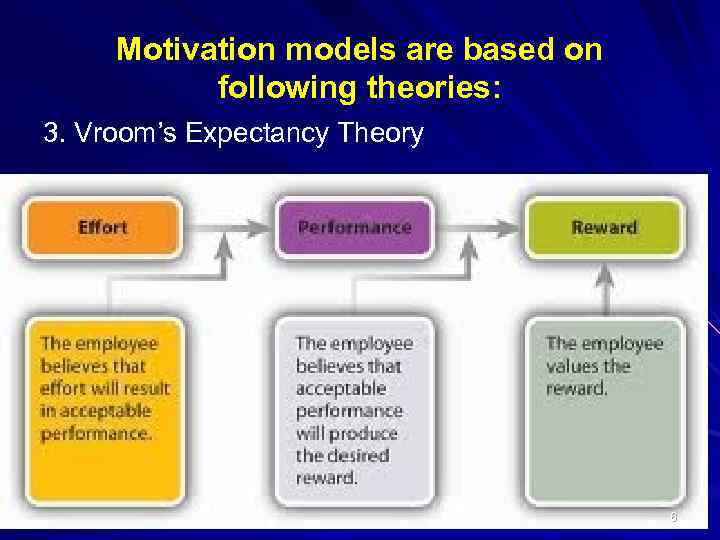
Motivation models are based on following theories: 3. Vroom’s Expectancy Theory 6
Motivation models are based on theories: 4. Equity Theory - (Carrell and Dittrich, 1978) : equity norm - Employees expect a fair return for what they contribute to their jobs. social comparison - Employees determine what their equitable return should be after comparing their inputs and outcomes with those of their coworkers. cognitive distortion - Employees who perceive themselves as being in an inequitable situation will seek to reduce the inequity either by distorting inputs and/or outcomes in their own minds, by directly altering inputs and/or outputs, or by leaving the organization. 7

Motivation Methods 1. Economic (direct): Piece rate & hourly pay Innovator’s allowance Profit sharing Payment of educational courses Bonuses for no absenteeism (100% present). 8

Motivation Methods 2. Economical (indirect): Privilege meal Additional payment for working experience Privilege housing accommodation, privilege transport 9

Motivation Methods 3. Non monetary: Flexible working time Labour safety Programs for enhancement of labor quality Carrier Participation in decision making and policy making. 10

2. Organization of Remuneration: Meaning, Functions and Principles. Structure of Payroll on enterprise. . 11

Remuneration - Reward for employment in the form of pay, salary, or wage, including allowances, benefits (such as company car, medical plan, pension plan), bonuses, cash incentives, and monetary value of the noncash incentives. (Definition from Business dictionary) - Any earning usually calculated in monetary value, that proprietor or authorized body pays to employee for his work performed according to employment contract. (definition of Low of Ukraine“About remuneration “) 12

Functions of Remuneration : reproducing Incentive (stimulating) coordinating social 13

Principles of Remuneration organization (1) Leading LP growth rate comparing to remuneration growth rate; Bridging the state regulation of remuneration with employment contract regulation (depending on the level: the state, the branch, the region, and finally the level of enterprise); Distribution according to labor results (after allowing for quantity and quality); 14

Principles of Remuneration organization (2) Incentive bonuses for high final results and limitlessness of salary; Bridging individual interest with collective ones; Continuous raising of salary; Simplicity, visualization, “transparency” of remuneration systems. 15

State Regulation of Remuneration in Ukraine Fixing of the minimum-wage level Establishment of the state norms and guarantees for remuneration Determination of conditions and remuneration calculations for heads of the state and the utility enterprises Determination of conditions and remuneration calculations for employees of the enterprises and organizations financing from the state budget 16

Payroll q In a company, payroll is the sum of all financial records of salaries for an employee, wages, bonuses and deductions. q In accounting, payroll refers to the amount paid to employees for services they provided during a certain period of time. 17
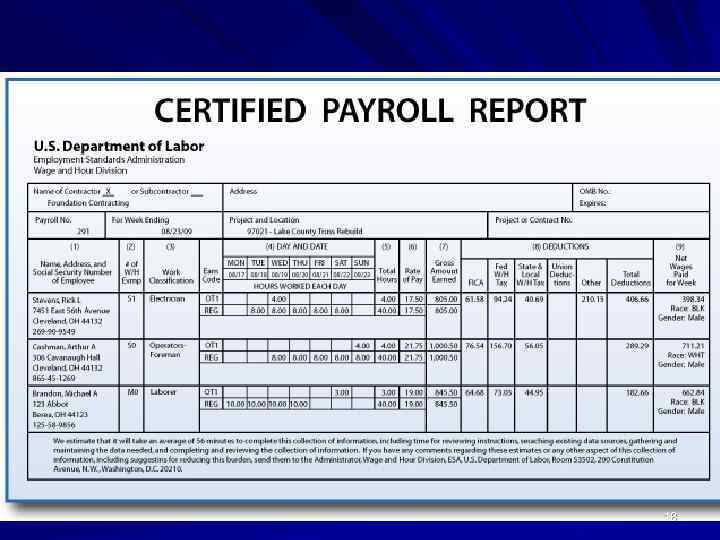
18
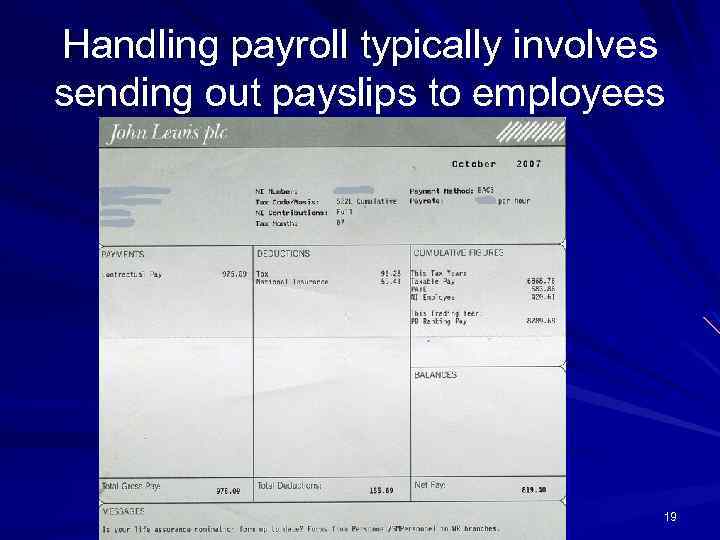
Handling payroll typically involves sending out payslips to employees 19

Payroll Structure in Ukraine Main salary and wages payroll; Additional salary and wages payroll; Other reimbursement and motivation payments. Instruction for the salary and wages statistics (2004) 20

Правова основа оплати праці Законодавчі та інші нормативні акти (Конституція України, Кодекс законів про працю, Господарський кодекс України, Закон України „Про оплату праці” тощо) Тарифні угоди (генеральна, галузева та регіональна, колективний договір) Employment contracts 21

3. Base-rate remuneration. 22

Base Rate Remuneration System – it is a set of specifications that differentiate, regulate, and control the earnings of different employees (workers) depending on complexity, labor conditions, features and importance of certain production and employee’s groups. 23

Base Pay describes the minimum compensation that one employee can expect to make on your job. Base pay can be expressed in terms of an hourly rate of pay, such as $10. 15 per hour, or it can be expressed in a number of other different forms. 24
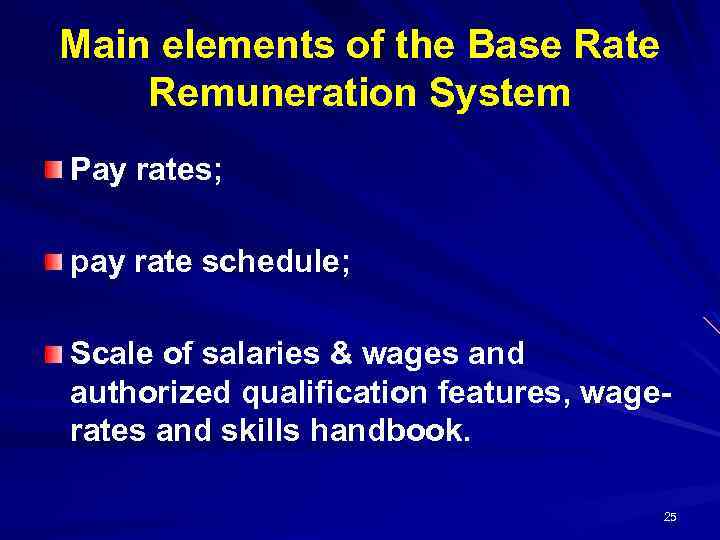
Main elements of the Base Rate Remuneration System Pay rates; pay rate schedule; schedule Scale of salaries & wages and authorized qualification features, wagerates and skills handbook 25
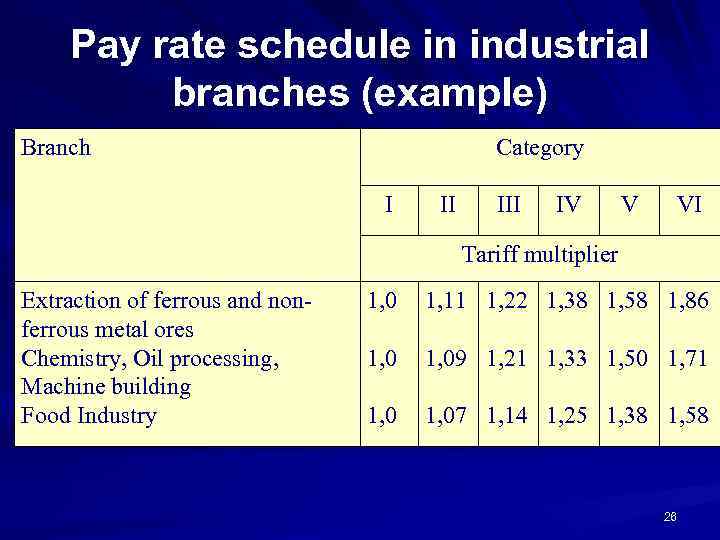
Pay rate schedule in industrial branches (example) Branch Category I II IV V VI Tariff multiplier Extraction of ferrous and nonferrous metal ores Chemistry, Oil processing, Machine building Food Industry 1, 0 1, 11 1, 22 1, 38 1, 58 1, 86 1, 09 1, 21 1, 33 1, 50 1, 71 1, 07 1, 14 1, 25 1, 38 1, 58 26

4. Basic compensation systems and payment methods. 27
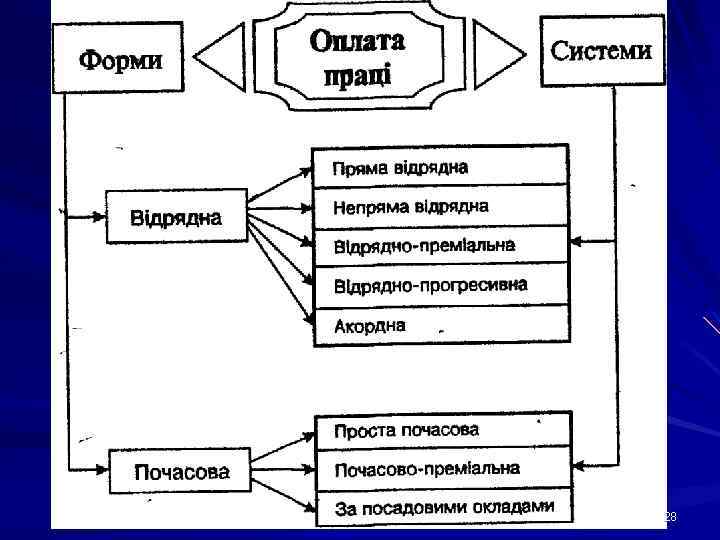
28
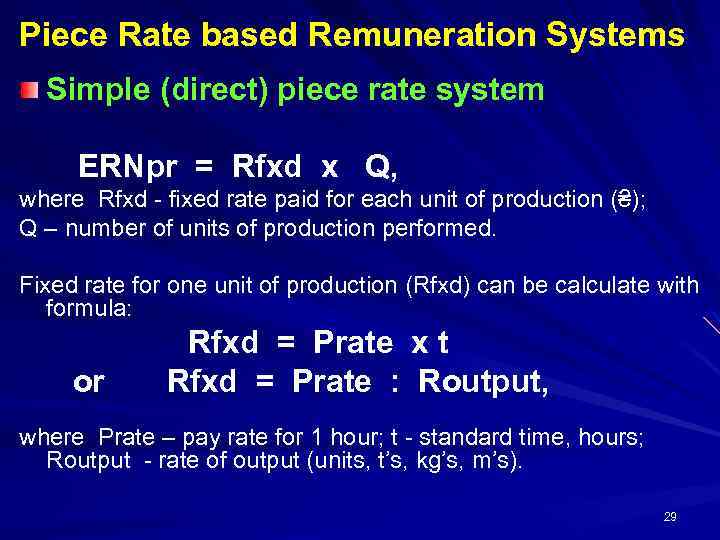
Piece Rate based Remuneration Systems Simple (direct) piece rate system ERNpr = Rfxd х Q, where Rfxd - fixed rate paid for each unit of production (₴); (₴) Q – number of units of production performed. Fixed rate for one unit of production (Rfxd) can be calculate with formula: or Rfxd = Prate х t Rfxd = Prate : Routput, where Prate – pay rate for 1 hour; t - standard time, hours; time Routput - rate of output (units, t’s, kg’s, m’s). 29
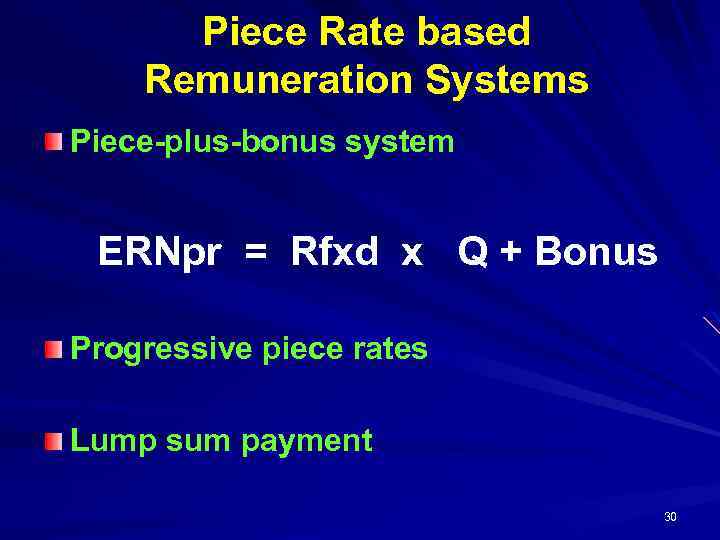
Piece Rate based Remuneration Systems Piece-plus-bonus system ERNpr = Rfxd х Q + Bonus Progressive piece rates Lump sum payment 30
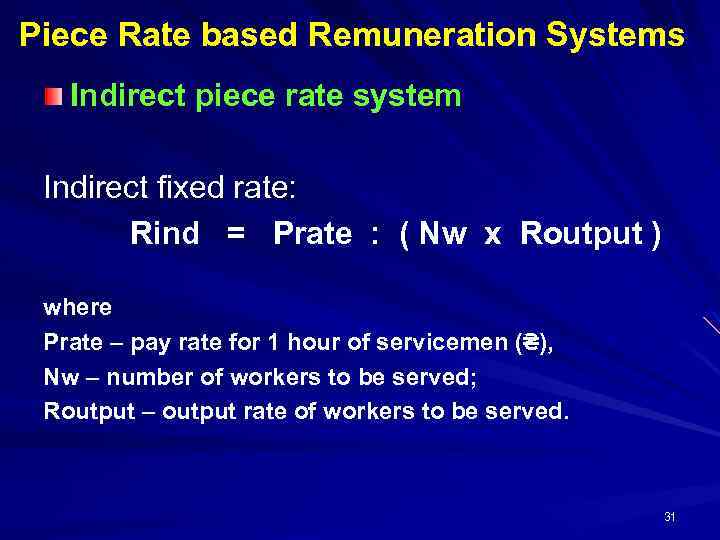
Piece Rate based Remuneration Systems Indirect piece rate system Indirect fixed rate: Rind = Prate : ( Nw х Routput ) where Prate – pay rate for 1 hour of servicemen (₴), Nw – number of workers to be served; Routput – output rate of workers to be served. 31
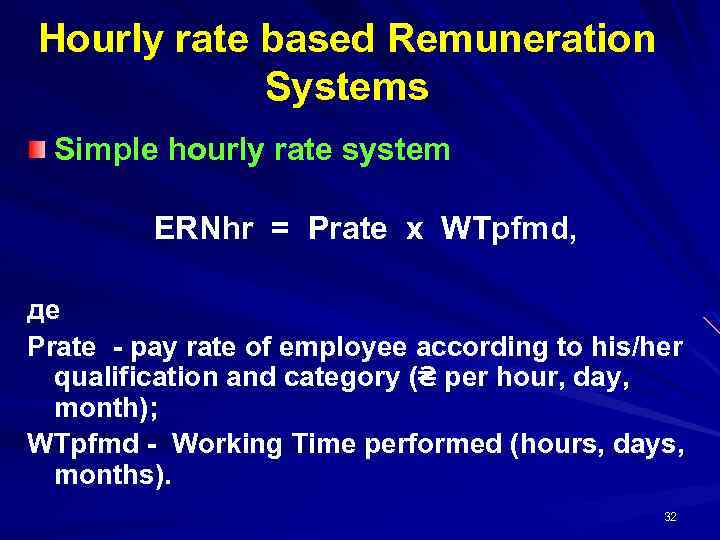
Hourly rate based Remuneration Systems Simple hourly rate system ERNhr = Prate х WTpfmd, де Prate - pay rate of employee according to his/her qualification and category (₴ per hour, day, month); WTpfmd - Working Time performed (hours, days, months). 32

Hourly rate based Remuneration Systems Time plus-bonus wage system, ERNhr = Prate х WTpfmd + Bonuses 33
Topic_10.pptx