Organization and structure of the system of education
















7952-organization_and_structure_of_the_system_of_education.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Organization and structure of the system of education in the USA
Organization and structure of the system of education in the USA
 The school year is usually nine months, from early September to mid-June.
The school year is usually nine months, from early September to mid-June.
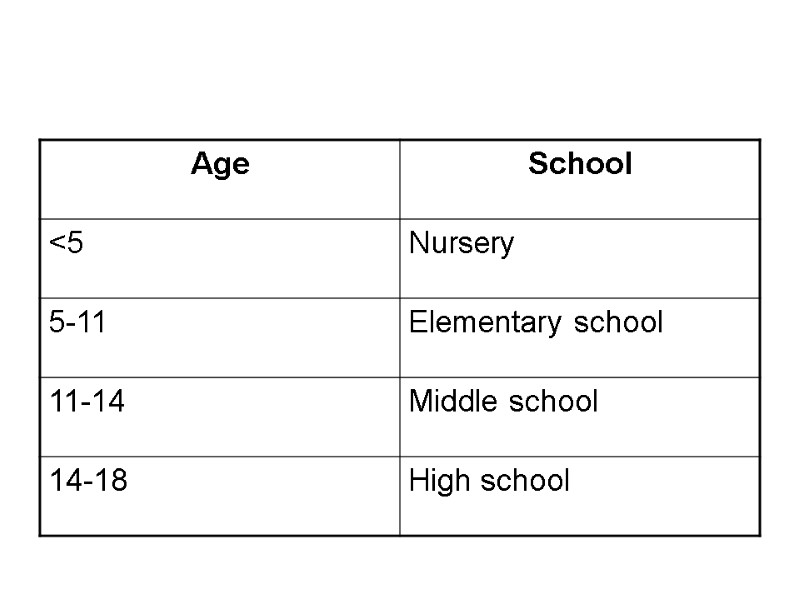
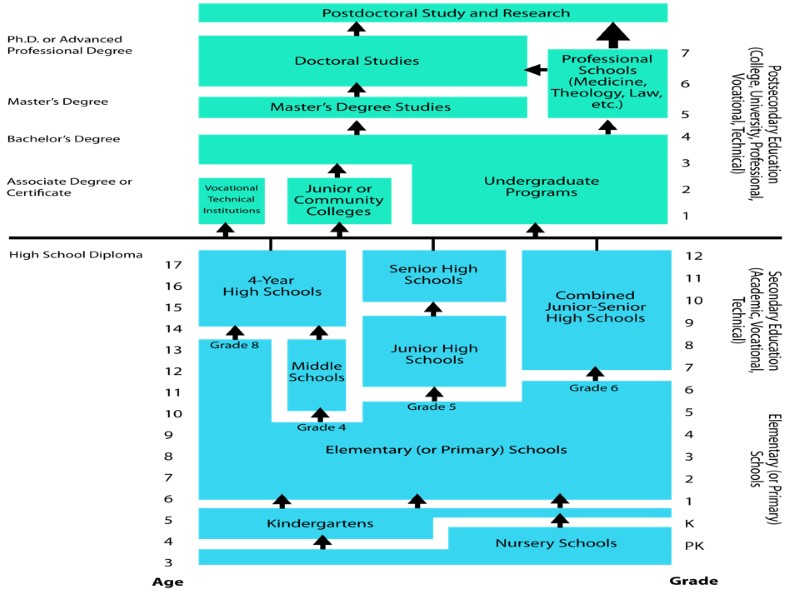
 Nursery school or preschool In the USA, children start school when they are five or six years old. Depending on the state, schooling is compulsory until the age of 16 or 18. Children younger than five can go to a nursery school or preschool.
Nursery school or preschool In the USA, children start school when they are five or six years old. Depending on the state, schooling is compulsory until the age of 16 or 18. Children younger than five can go to a nursery school or preschool.
 Preschool education A child's introduction to formal education is usually in kindergarten classes operated in most public school systems. Many systems also provide nursery schools. The age group is commonly four and five years. These preschool education programs maintain a close relationship with the home and parents, and aim to give children useful experiences which will prepare them for elementary school. The programs are flexible and are designed to help the child grow in self-reliance, learn to get along with others, and form good work and play habits.
Preschool education A child's introduction to formal education is usually in kindergarten classes operated in most public school systems. Many systems also provide nursery schools. The age group is commonly four and five years. These preschool education programs maintain a close relationship with the home and parents, and aim to give children useful experiences which will prepare them for elementary school. The programs are flexible and are designed to help the child grow in self-reliance, learn to get along with others, and form good work and play habits.
 At the age of five or six, the children attend elementary school (also known as grade school or grammar school), which last six years. The fist year at elementary school is called kindergarten.
At the age of five or six, the children attend elementary school (also known as grade school or grammar school), which last six years. The fist year at elementary school is called kindergarten.
 Elementary school The main purpose of the elementary school is the general intellectual and social development of the child from 6 to 12 or 15 years of age. Curricula vary with the organization and educational aims of individual schools and communities.
Elementary school The main purpose of the elementary school is the general intellectual and social development of the child from 6 to 12 or 15 years of age. Curricula vary with the organization and educational aims of individual schools and communities.
 After elementary school, students attend middle school for three years. Then they continue at high school. In some states, students have to stay in school until they are 18 years old. In other states they may leave school at 16 or 17 with parental permission.
After elementary school, students attend middle school for three years. Then they continue at high school. In some states, students have to stay in school until they are 18 years old. In other states they may leave school at 16 or 17 with parental permission.
 High school Most young Americans graduate from school with a high school diploma upon satisfactory completion of a specified number of courses.
High school Most young Americans graduate from school with a high school diploma upon satisfactory completion of a specified number of courses.

 Classes At elementary school pupils primarily learn how to read, write and count. There are about 20 to 30 pupils in one class.
Classes At elementary school pupils primarily learn how to read, write and count. There are about 20 to 30 pupils in one class.
 Classes At junior and senior high school, main subjects are English, maths, biology, chemistry, physics, physical education and history. Schools also offer optional courses from which the students can choose, e. g. art, modern languages, computers.
Classes At junior and senior high school, main subjects are English, maths, biology, chemistry, physics, physical education and history. Schools also offer optional courses from which the students can choose, e. g. art, modern languages, computers.
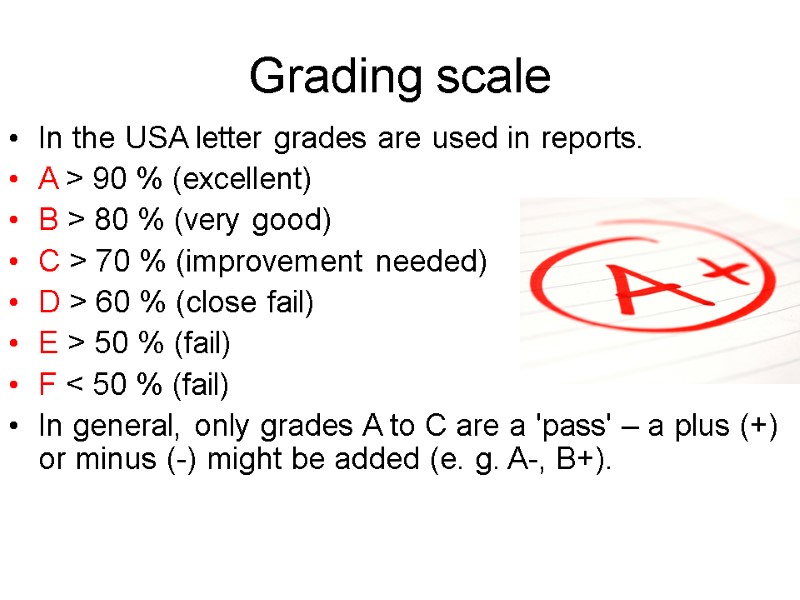
 Grading scale In the USA letter grades are used in reports. A > 90 % (excellent) B > 80 % (very good) C > 70 % (improvement needed) D > 60 % (close fail) E > 50 % (fail) F < 50 % (fail) In general, only grades A to C are a 'pass' – a plus (+) or minus (-) might be added (e. g. A-, B+).
Grading scale In the USA letter grades are used in reports. A > 90 % (excellent) B > 80 % (very good) C > 70 % (improvement needed) D > 60 % (close fail) E > 50 % (fail) F < 50 % (fail) In general, only grades A to C are a 'pass' – a plus (+) or minus (-) might be added (e. g. A-, B+).
 Different Kinds of Schools Most students in the USA are enrolled in public schools. These are financed through taxes, so parents do not have to pay for their children's education. About 10 % of US students attend private schools, where parents have to pay a yearly fee.
Different Kinds of Schools Most students in the USA are enrolled in public schools. These are financed through taxes, so parents do not have to pay for their children's education. About 10 % of US students attend private schools, where parents have to pay a yearly fee.
 Another option is homeschooling: approximately 1-2 % of parents in the USA educate their children at home. Some reasons for homeschooling are religious views, special needs (e. g. handicapped children), or problems in traditional schools (bullying, drugs etc.).
Another option is homeschooling: approximately 1-2 % of parents in the USA educate their children at home. Some reasons for homeschooling are religious views, special needs (e. g. handicapped children), or problems in traditional schools (bullying, drugs etc.).
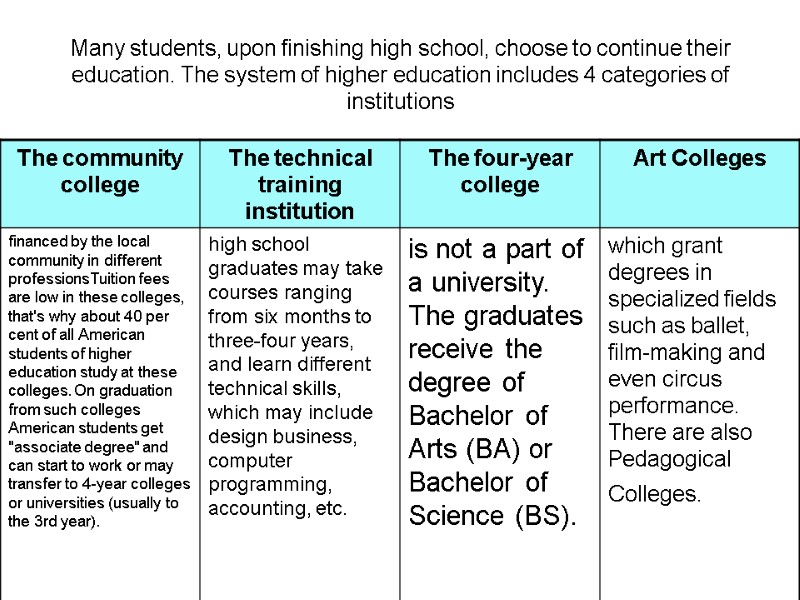
 Many students, upon finishing high school, choose to continue their education. The system of higher education includes 4 categories of institutions
Many students, upon finishing high school, choose to continue their education. The system of higher education includes 4 categories of institutions
 Universities There is no National University in the USA. Each state controls and supports at least one University. The National Government gives no direct financial aid to these state schools. The students do not go to the University free of charge. Everyone must pay a tuition fee. The amount varies from state to state. Students' total expenses throughout the year are very high. And though each University offers a number of scholarships many of the students have to work to pay their expenses.
Universities There is no National University in the USA. Each state controls and supports at least one University. The National Government gives no direct financial aid to these state schools. The students do not go to the University free of charge. Everyone must pay a tuition fee. The amount varies from state to state. Students' total expenses throughout the year are very high. And though each University offers a number of scholarships many of the students have to work to pay their expenses.
 Most of the US Universities have a central campus. Colleges of Law, Business, Medicine, Engineering, Music, Journalism can be found on one campus. Thus a student can attend courses at various colleges.
Most of the US Universities have a central campus. Colleges of Law, Business, Medicine, Engineering, Music, Journalism can be found on one campus. Thus a student can attend courses at various colleges.
 The students do not take the same courses. During the first two years they follow a basic programme. It means that every student must select at least one course from each of the basic fields of study: English, science, modern languages, history or physical education. After the first two years every student majors in one subject and minors in another. A student can major in history and minor in sociality. In addition to these major and minor courses he can select other subjects according to his professional interest.
The students do not take the same courses. During the first two years they follow a basic programme. It means that every student must select at least one course from each of the basic fields of study: English, science, modern languages, history or physical education. After the first two years every student majors in one subject and minors in another. A student can major in history and minor in sociality. In addition to these major and minor courses he can select other subjects according to his professional interest.
 After completing four years of study the students receive a Bachelor's Degree (either BA or B.Sc.). With an additional year of study one may get a Master's Degree and after two or three years of graduate work and writing of the dissertation it is possible to obtain a doctoral degree. For four years at the end of each year students have a final written examination. They take oral exams and write a dissertation only for advanced degrees.
After completing four years of study the students receive a Bachelor's Degree (either BA or B.Sc.). With an additional year of study one may get a Master's Degree and after two or three years of graduate work and writing of the dissertation it is possible to obtain a doctoral degree. For four years at the end of each year students have a final written examination. They take oral exams and write a dissertation only for advanced degrees.


