37ea0d77576e9be564540dd4454c2784.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

Organ Printer By Michael Da. Silva

What is the organ printer • An organ printer incorporates 2 technologies, tissue engineering and a 3 D printer. • Instead of paper, Petri dishes are used. • Instead of ink, cells and chemical called a “crosslinker” are used. • The cells are individually made for the patient.
Tissue Engineering • Basis of the organ printer. • Tissue engineering is the manipulation of cells in order to fix or replace a biological function. • Main goal is to create artificial organs. • This is what lead to the development of the organ printer.
3 D Printer • A printer that basically makes a 3 D model. • Used a lot for rapid prototyping. • Can construct objects out of a given material. • Used to make prototypes of new products. • Some machines are even used to make the final product.
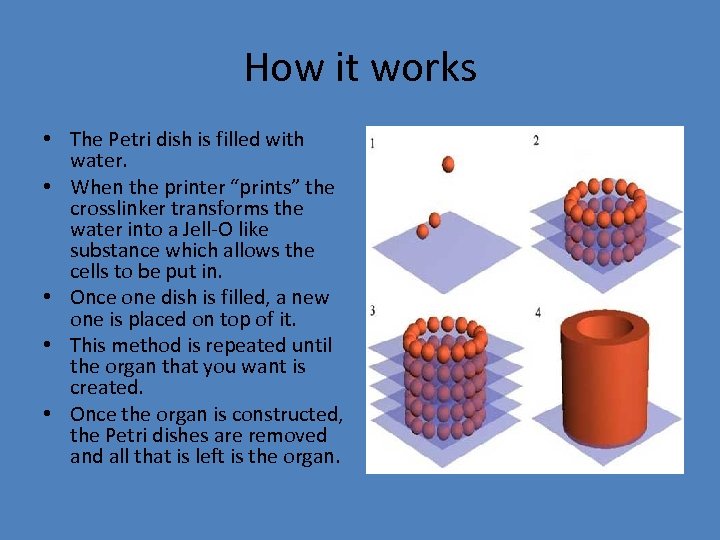
How it works • The Petri dish is filled with water. • When the printer “prints” the crosslinker transforms the water into a Jell-O like substance which allows the cells to be put in. • Once one dish is filled, a new one is placed on top of it. • This method is repeated until the organ that you want is created. • Once the organ is constructed, the Petri dishes are removed and all that is left is the organ.
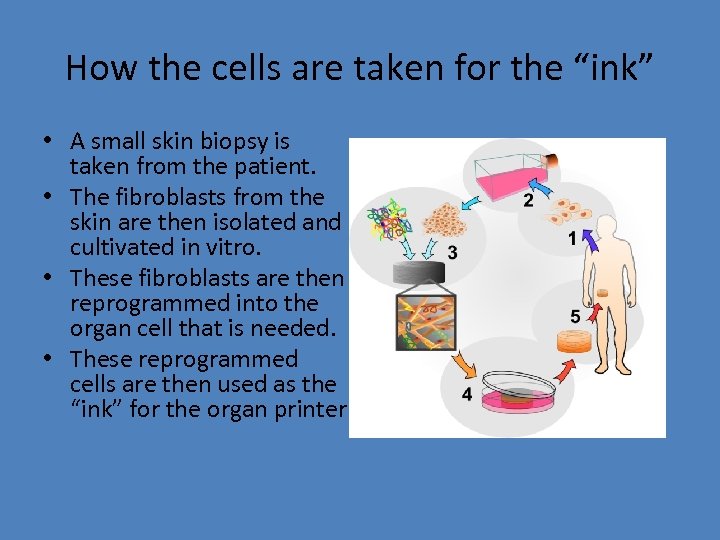
How the cells are taken for the “ink” • A small skin biopsy is taken from the patient. • The fibroblasts from the skin are then isolated and cultivated in vitro. • These fibroblasts are then reprogrammed into the organ cell that is needed. • These reprogrammed cells are then used as the “ink” for the organ printer.

Benefits • Most organs can be made using this method, as long as the fibroblast can be reprogrammed to be that organ cell. • No organ rejection will occur because it will be the patient’s own DNA. • Can by pass the organ donor list. • Can be used to treat anyone since the organ is made for the individual.

Cons • Still very expensive. • The organ that is being made can die if no blood vessels are created within the organ. • Creating these blood vessels requires certain stem cells which are expensive. • Still takes a long time to actually make the organ. • Not being used in practice yet, still trying to work out the kinks.

Future • Minimize the cost of the process so that the machines can be available for everyone. • Get it out of the clinical trials and actually be using by doctors. • Make it more time efficient and be able to create whole organs within hours.

Conclusion • Organ printers are just modified 3 D printers that have been outfitted to make human organs out of living cells. • There are several benefits, a major one being no chance of organ rejection. • In the future this procedure will hopefully be less expensive and more widely available.

Questions?
37ea0d77576e9be564540dd4454c2784.ppt