Oral Ulcerations Azmi Darwazeh BDS., MSc., PhD., FFD


Oral Ulcerations Azmi Darwazeh BDS., MSc., PhD., FFD RCSI. Professor of Oral Medicine & Pathology Faculty of Dentistry Jordan University of Science & Technology
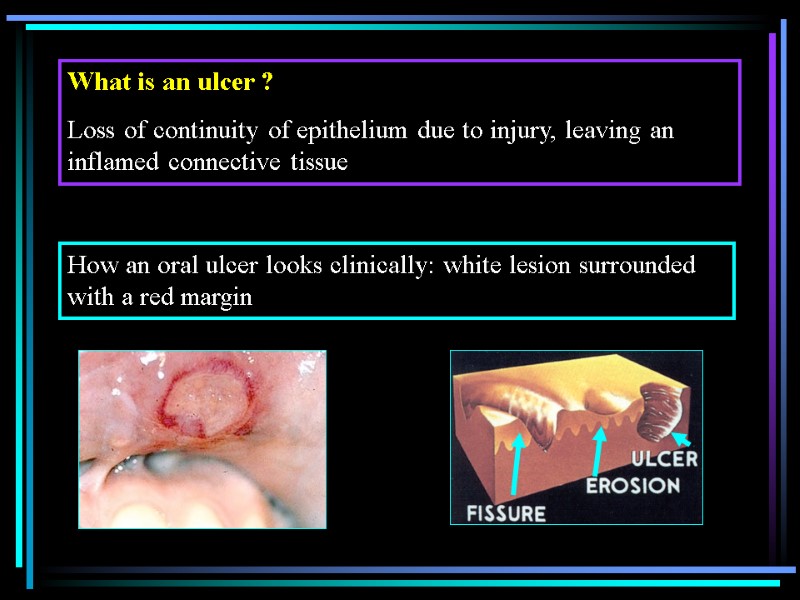
What is an ulcer ? Loss of continuity of epithelium due to injury, leaving an inflamed connective tissue How an oral ulcer looks clinically: white lesion surrounded with a red margin

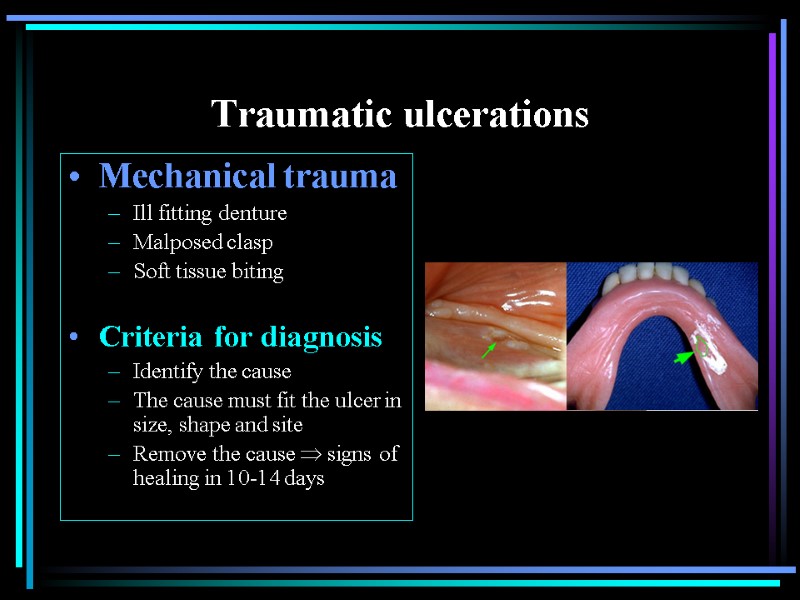
Traumatic ulcerations Mechanical trauma Ill fitting denture Malposed clasp Soft tissue biting Criteria for diagnosis Identify the cause The cause must fit the ulcer in size, shape and site Remove the cause signs of healing in 10-14 days
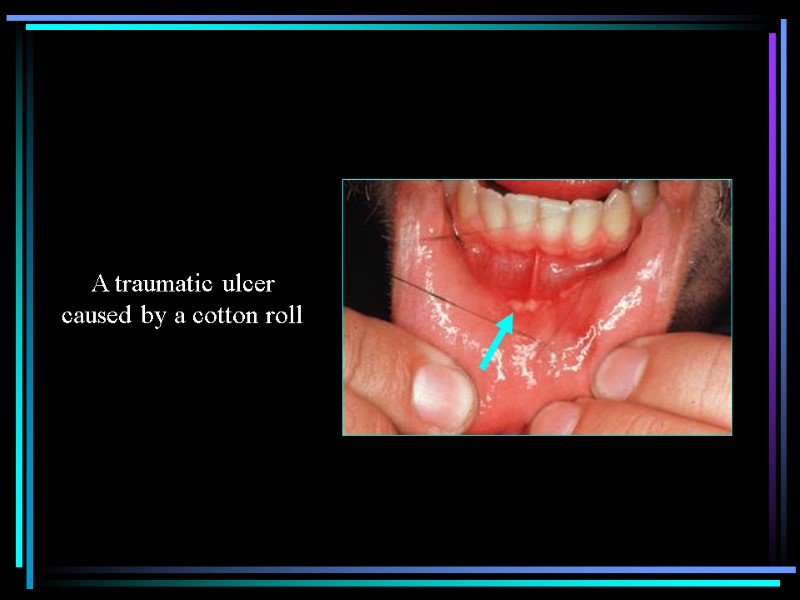
A traumatic ulcer caused by a cotton roll
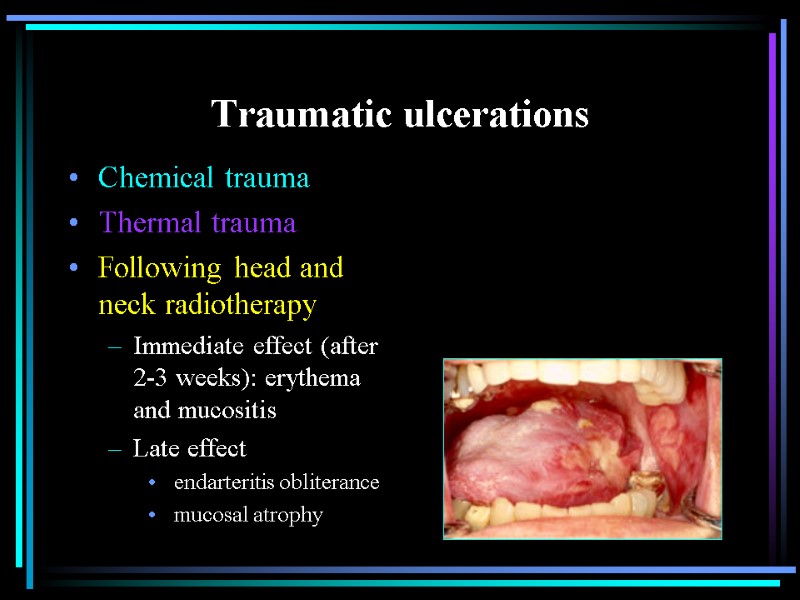
Traumatic ulcerations Chemical trauma Thermal trauma Following head and neck radiotherapy Immediate effect (after 2-3 weeks): erythema and mucositis Late effect endarteritis obliterance mucosal atrophy

Traumatic Ulcer - Management Identify the cause and remove it Prevent secondary infection Review after 10-14 days If the ulcer is not showing signs of healing then biopsy is a must to exclude malignancy
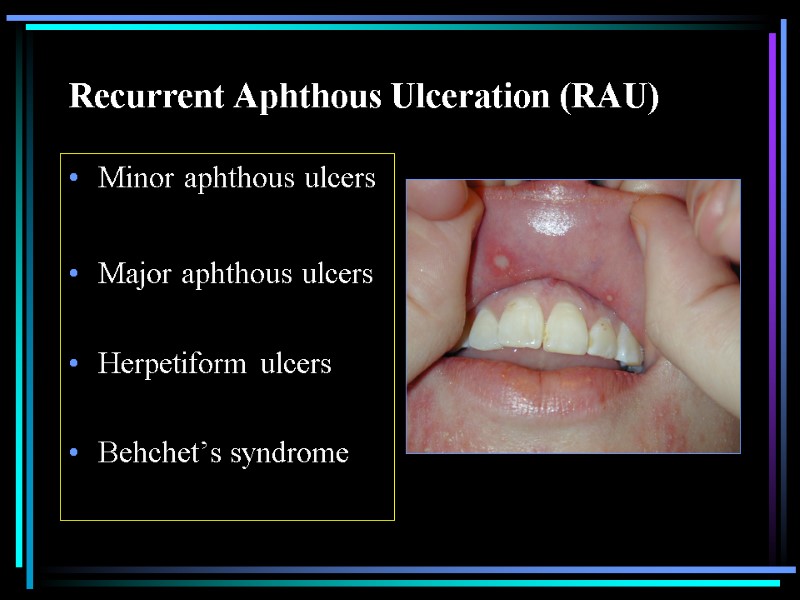
Recurrent Aphthous Ulceration (RAU) Minor aphthous ulcers Major aphthous ulcers Herpetiform ulcers Behchet’s syndrome
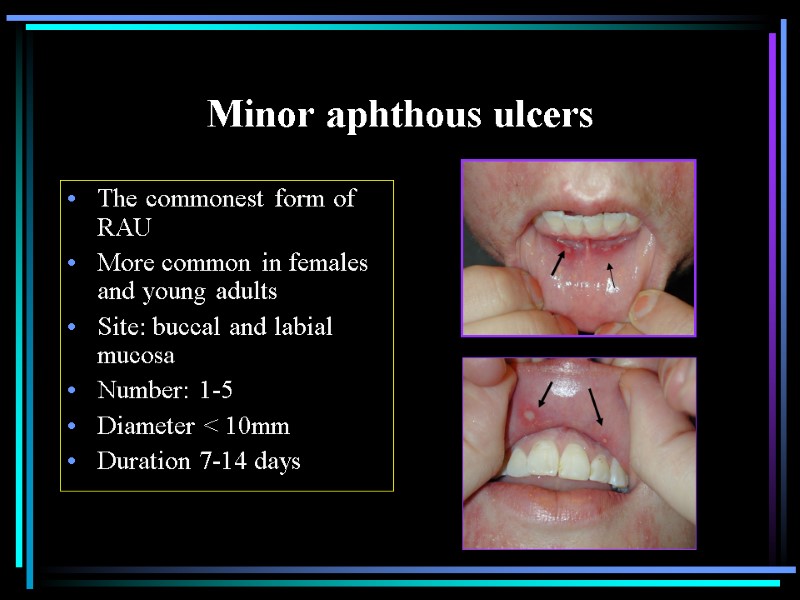
Minor aphthous ulcers The commonest form of RAU More common in females and young adults Site: buccal and labial mucosa Number: 1-5 Diameter < 10mm Duration 7-14 days
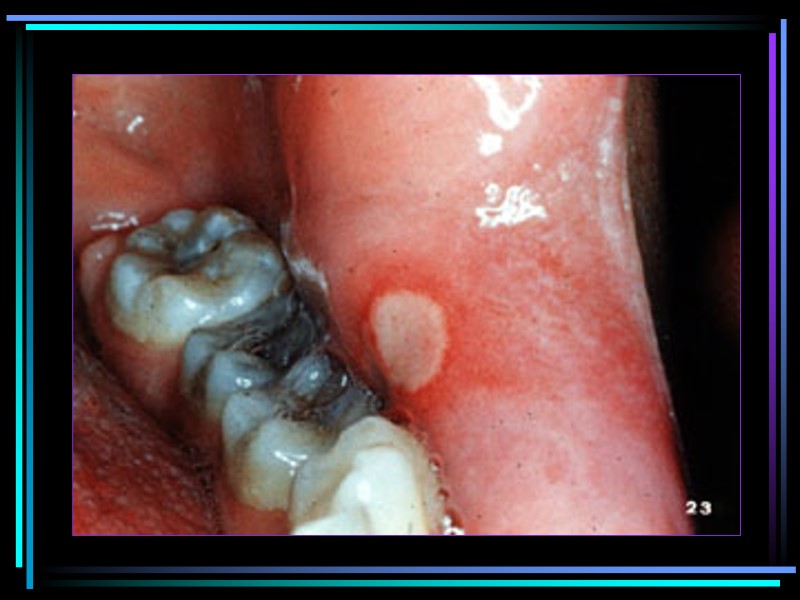
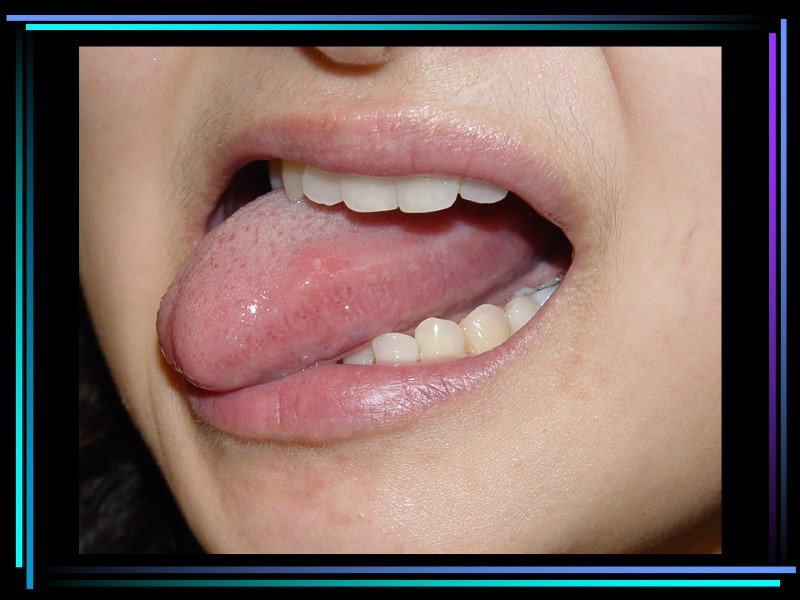
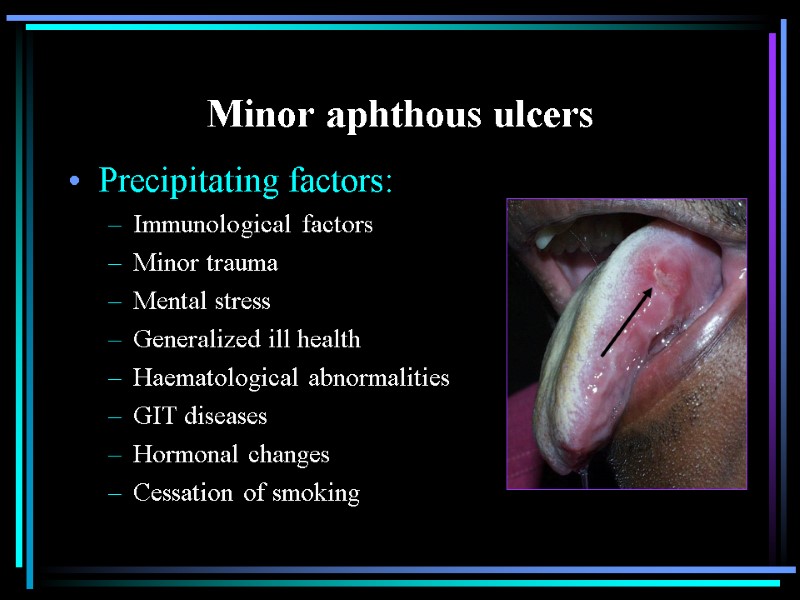
Minor aphthous ulcers Precipitating factors: Immunological factors Minor trauma Mental stress Generalized ill health Haematological abnormalities GIT diseases Hormonal changes Cessation of smoking

Minor aphthous ulcers Diagnosis: clinical picture + history Causes: not determined yet !!! Infection: herpes virus, S. sanguis, hypersensitivity reaction to microbes Abnormalities of the immune system: allergy and autoimmunity.

Minor aphthous ulcers Treatment: Identify and correct predisposing factor(s) Strict oral hygiene Medications: Covering agents Antiseptic mouth washes Topical antibiotics Topical steroids Hormones Topical anesthetics Other drugs: Na cromoglycate, Prostogflandin, Carbenoxolone
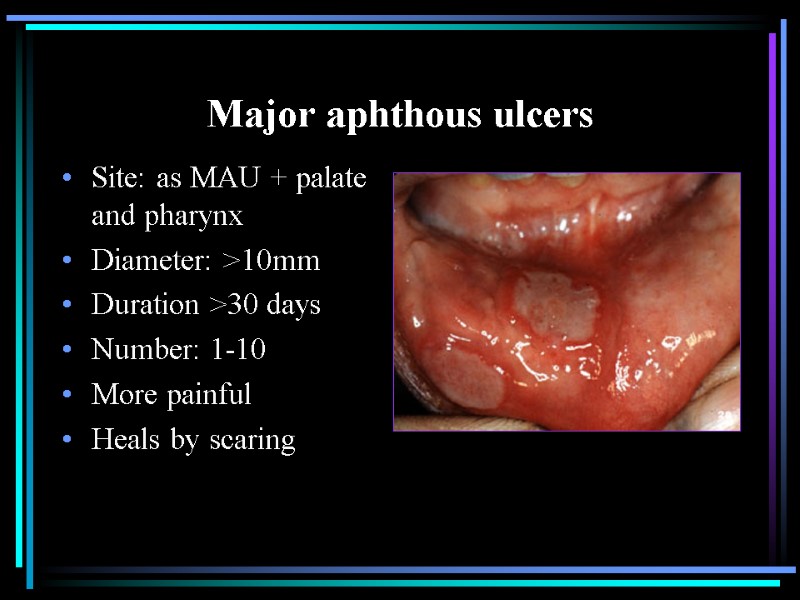
Major aphthous ulcers Site: as MAU + palate and pharynx Diameter: >10mm Duration >30 days Number: 1-10 More painful Heals by scaring
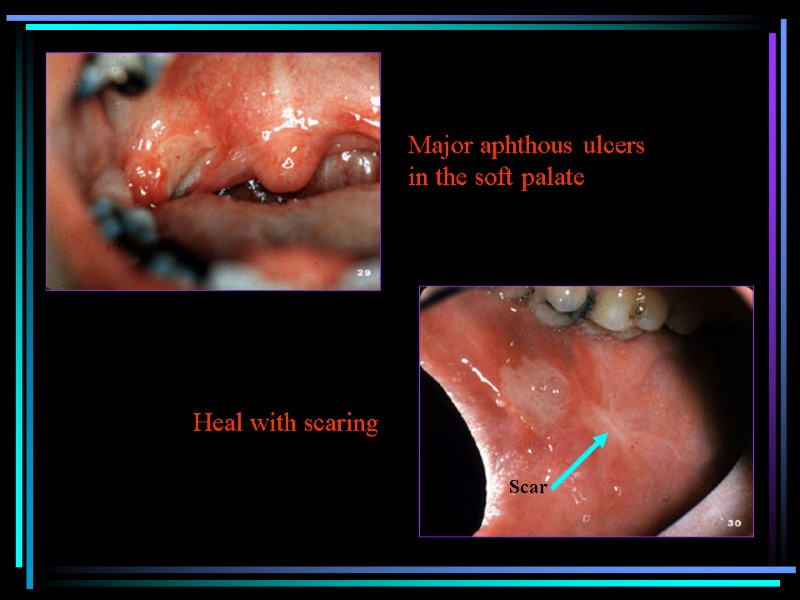
Heal with scaring Major aphthous ulcers in the soft palate Scar

Major aphthous ulcers Treatment: as MAU + Systemic steroids: Rx: Prednisolone 40 mg. For 3 days 30mg. 20mg. 10mg. 0mg. Intra- or sub-lesional injection of steroids Triamcinolone acetonide susp. High concentration steroid mouth wash Steroid sparing drugs: e.g. azathioprine
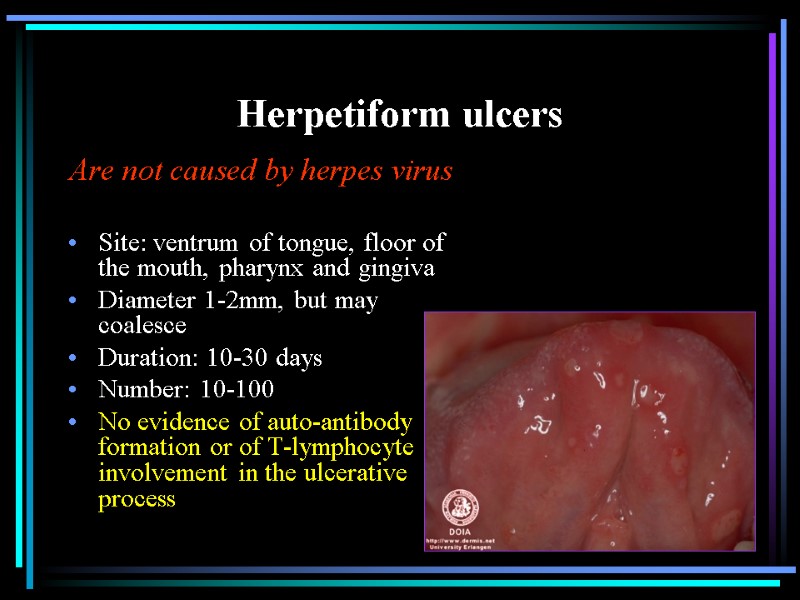
Herpetiform ulcers Are not caused by herpes virus Site: ventrum of tongue, floor of the mouth, pharynx and gingiva Diameter 1-2mm, but may coalesce Duration: 10-30 days Number: 10-100 No evidence of auto-antibody formation or of T-lymphocyte involvement in the ulcerative process
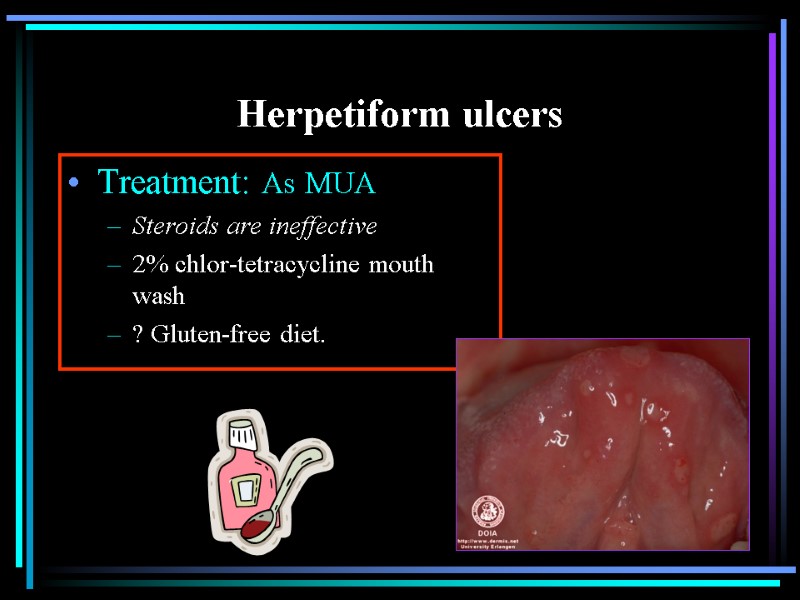
Herpetiform ulcers Treatment: As MUA Steroids are ineffective 2% chlor-tetracycline mouth wash ? Gluten-free diet.
Behchet’s syndrome Oral ulcers Genital ulcers Eye lesions BS

Behchet’s syndrome Immunological cross-reactivity between mucosal epithelia of the : Mouth Pharynx Oesophagus Vagina Conjunctiva Skin
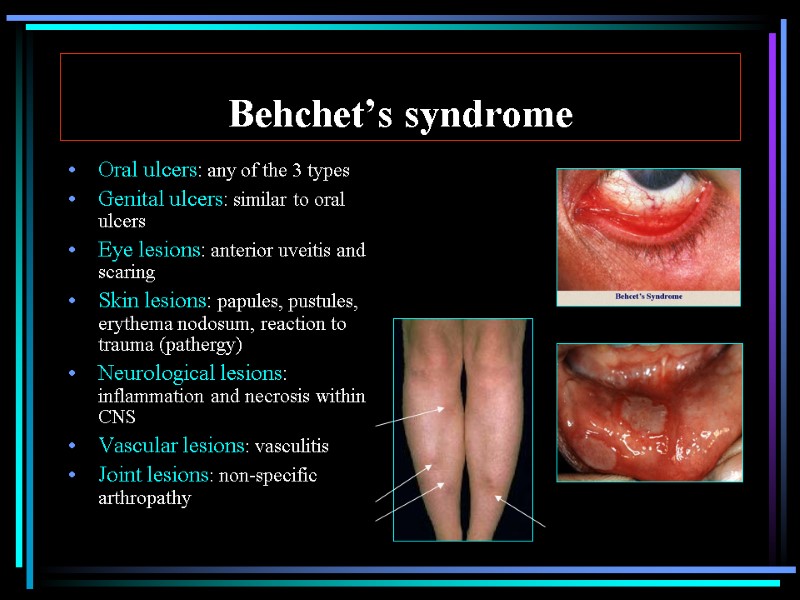
Behchet’s syndrome Oral ulcers: any of the 3 types Genital ulcers: similar to oral ulcers Eye lesions: anterior uveitis and scaring Skin lesions: papules, pustules, erythema nodosum, reaction to trauma (pathergy) Neurological lesions: inflammation and necrosis within CNS Vascular lesions: vasculitis Joint lesions: non-specific arthropathy
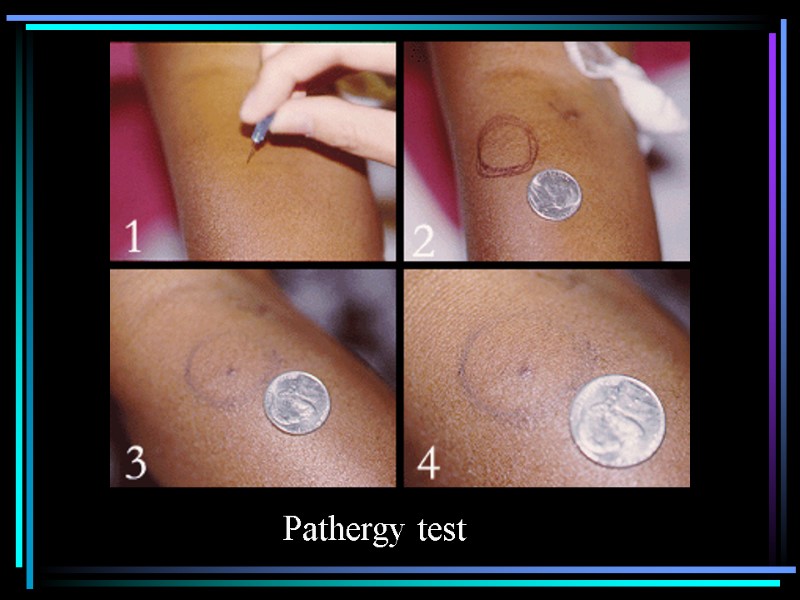
Pathergy test

Behchet’s syndrome - Diagnosis Major criteria: Oral ulcers Genital ulcers Eye lesions Minor criteria: CNS Vascular lesions Joint lesions others

Behchet’s Syndrome - Management Oral lesions: As other forms of RAU Generalized manifestations: Systemic steroids Azathioprine Cyclosporine Thalidomide (teratogenic effect) Penicillamine Colchicine Chlorambucil
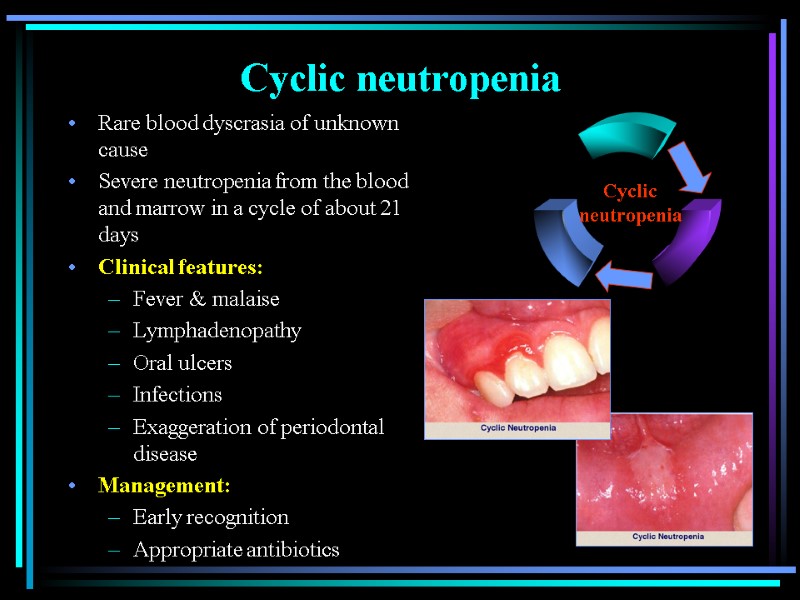
Cyclic neutropenia Rare blood dyscrasia of unknown cause Severe neutropenia from the blood and marrow in a cycle of about 21 days Clinical features: Fever & malaise Lymphadenopathy Oral ulcers Infections Exaggeration of periodontal disease Management: Early recognition Appropriate antibiotics Cyclic neutropenia
16062-oral_ulcerations.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

