Oral anatomy Table of contents. Introduction





















































alfa_gate_initial_presentation_-_english.pptx
- Размер: 57.5 Мб
- Автор: Абдиль Медеуов
- Количество слайдов: 126
Описание презентации Oral anatomy Table of contents. Introduction по слайдам
 Oral anatomy
Oral anatomy
 Table of contents. Introduction Teeth Anatomical Structures Bone Types Clinical Considerations
Table of contents. Introduction Teeth Anatomical Structures Bone Types Clinical Considerations
 Teeth Loss Function Esthetics Phonetics Anatomical changes
Teeth Loss Function Esthetics Phonetics Anatomical changes
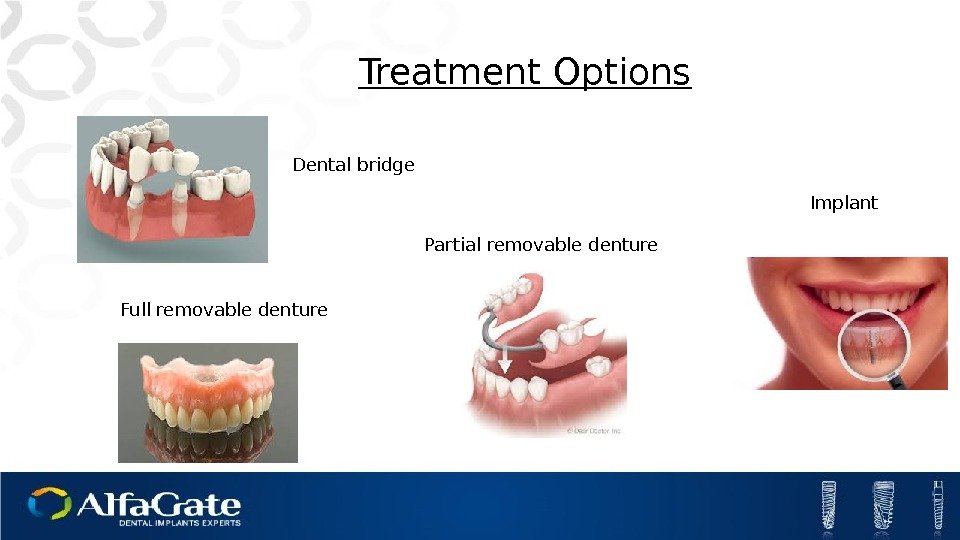
 Dental bridge Treatment Options Partial removable denture Full removable denture Implant
Dental bridge Treatment Options Partial removable denture Full removable denture Implant
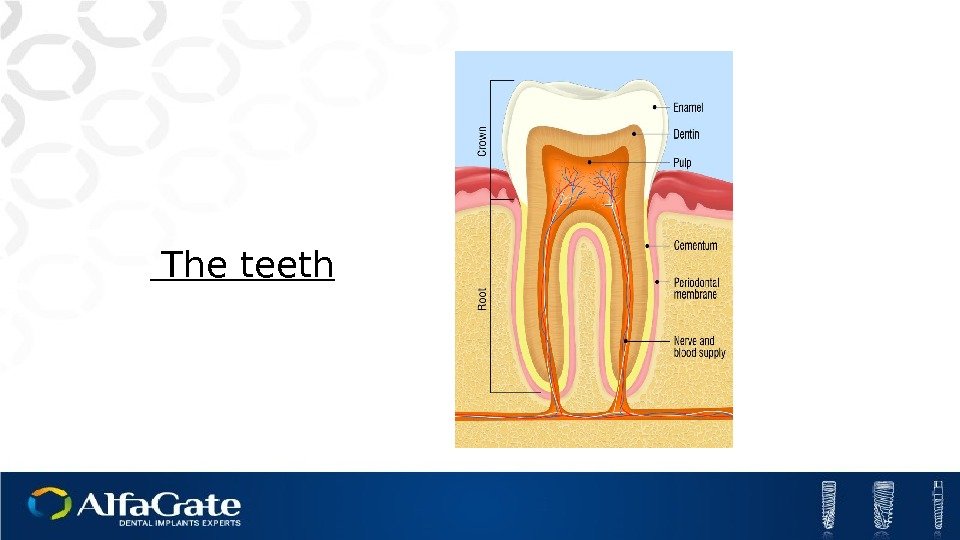
 The teeth
The teeth
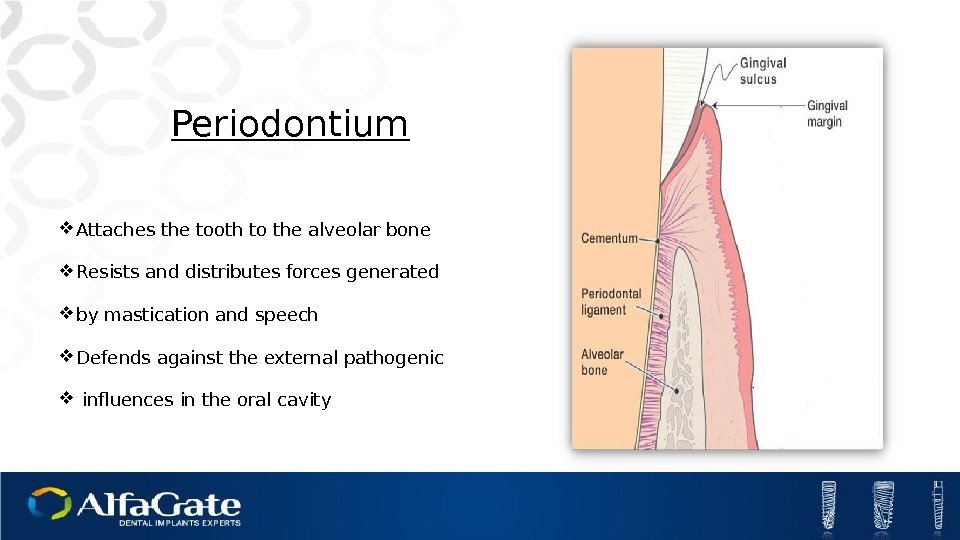
 Periodontium Attaches the tooth to the alveolar bone Resists and distributes forces generated by mastication and speech Defends against the external pathogenic influences in the oral cavity
Periodontium Attaches the tooth to the alveolar bone Resists and distributes forces generated by mastication and speech Defends against the external pathogenic influences in the oral cavity

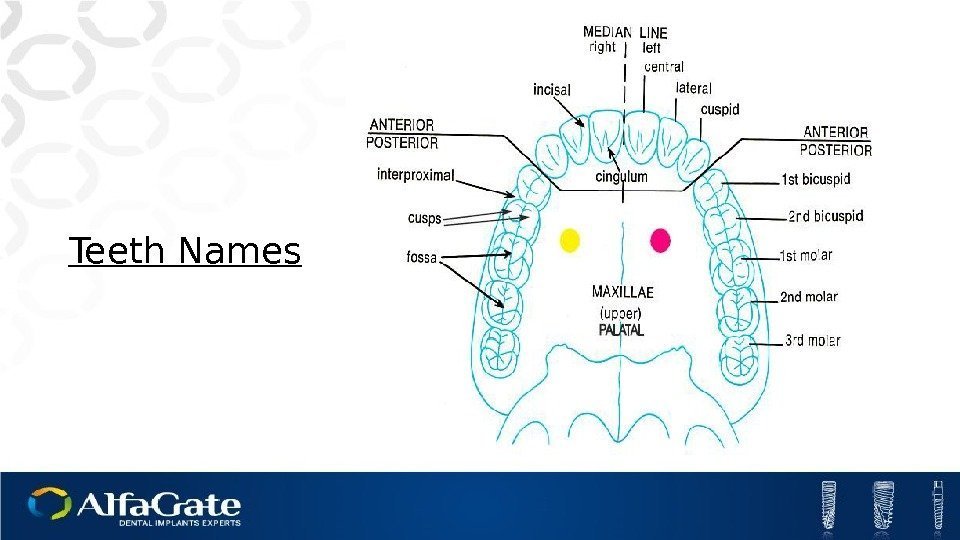
 Teeth Names
Teeth Names
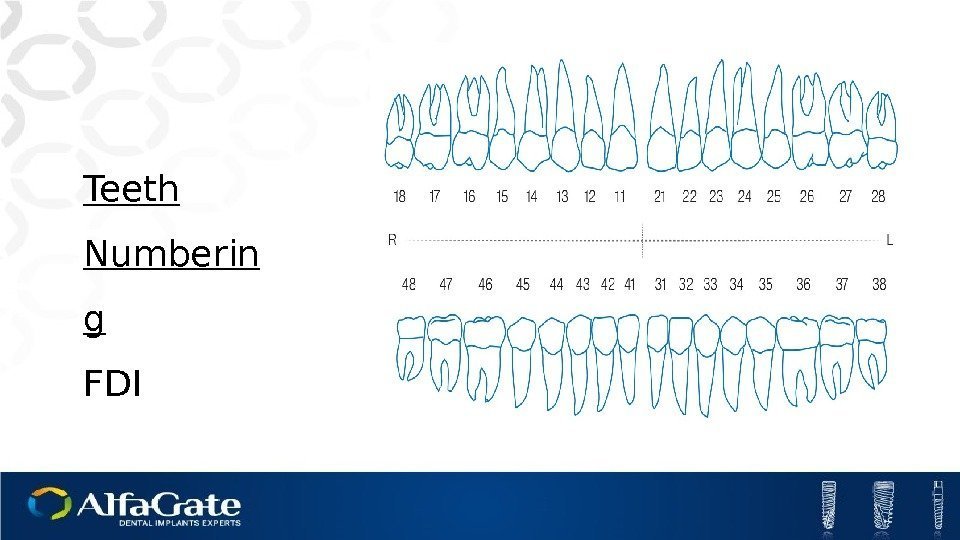
 Teeth Numberin g FDI
Teeth Numberin g FDI
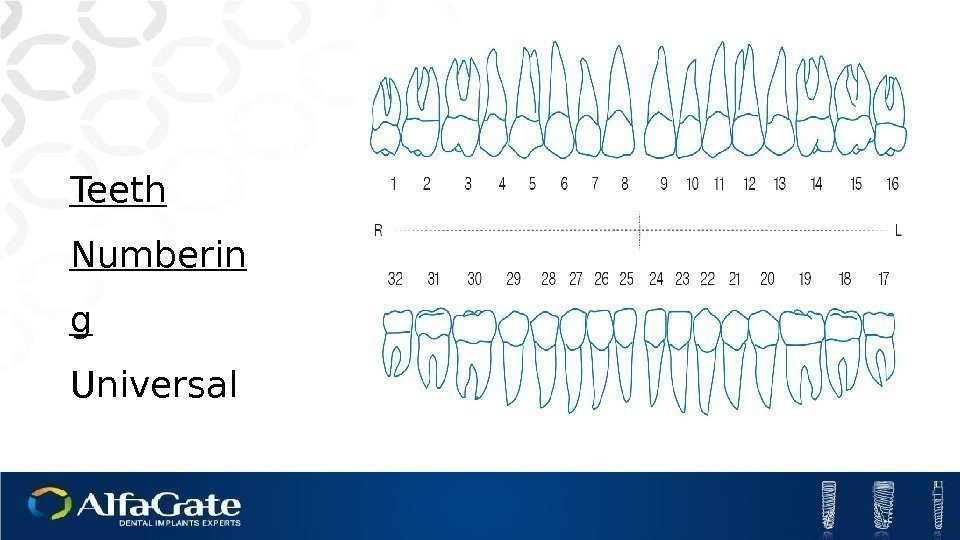
 Teeth Numberin g Universal
Teeth Numberin g Universal
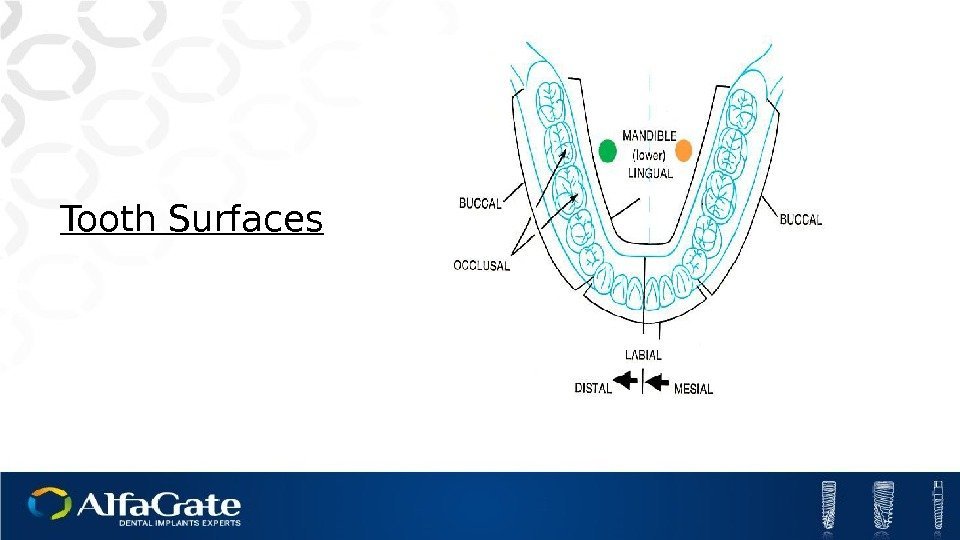
 Tooth Surfaces
Tooth Surfaces
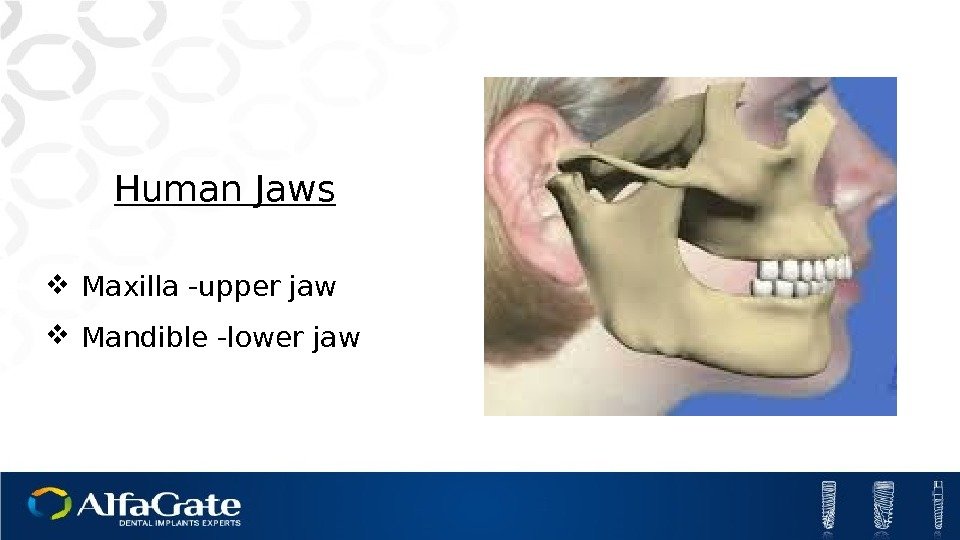
 Human Jaws Maxilla -upper jaw Mandible -lower jaw
Human Jaws Maxilla -upper jaw Mandible -lower jaw
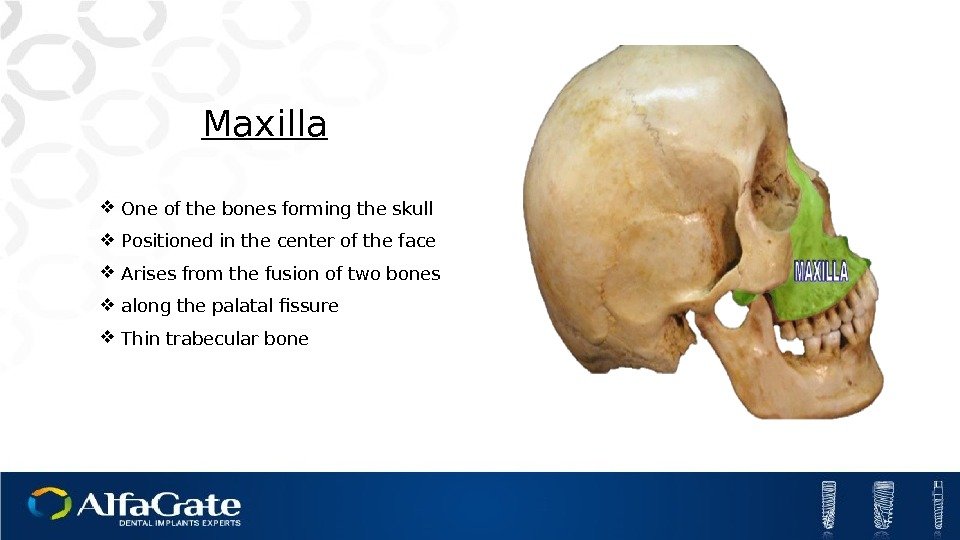
 Maxilla One of the bones forming the skull Positioned in the center of the face Arises from the fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure Thin trabecular bone
Maxilla One of the bones forming the skull Positioned in the center of the face Arises from the fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure Thin trabecular bone
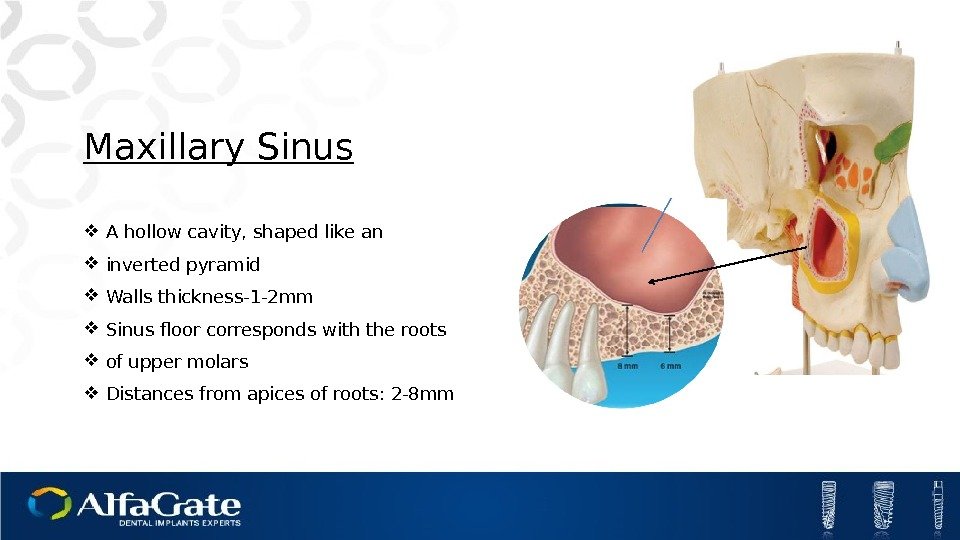
 Maxillary Sinus A hollow cavity, shaped like an inverted pyramid Walls thickness-1 -2 mm Sinus floor corresponds with the roots of upper molars Distances from apices of roots: 2 -8 mm
Maxillary Sinus A hollow cavity, shaped like an inverted pyramid Walls thickness-1 -2 mm Sinus floor corresponds with the roots of upper molars Distances from apices of roots: 2 -8 mm
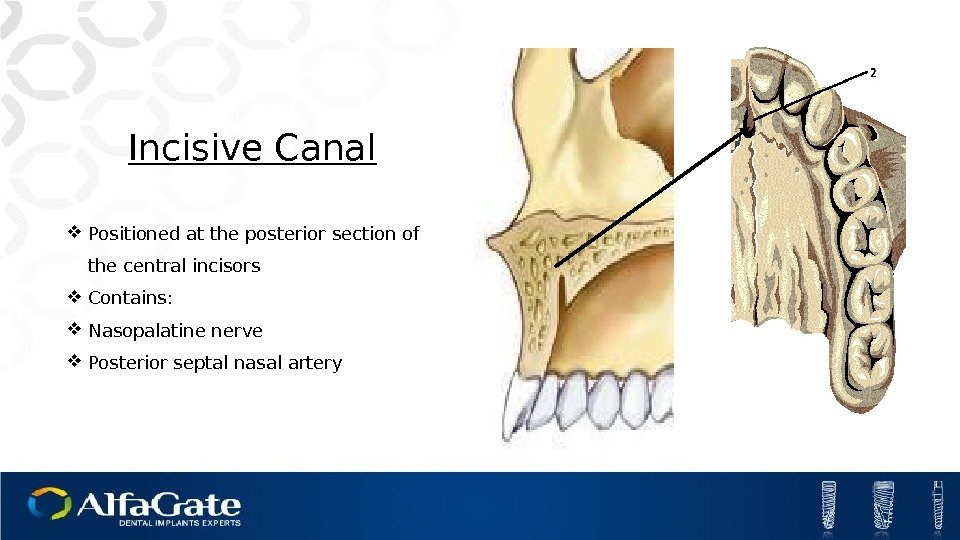
 Incisive Canal Positioned at the posterior section of the central incisors Contains: Nasopalatine nerve Posterior septal nasal artery
Incisive Canal Positioned at the posterior section of the central incisors Contains: Nasopalatine nerve Posterior septal nasal artery
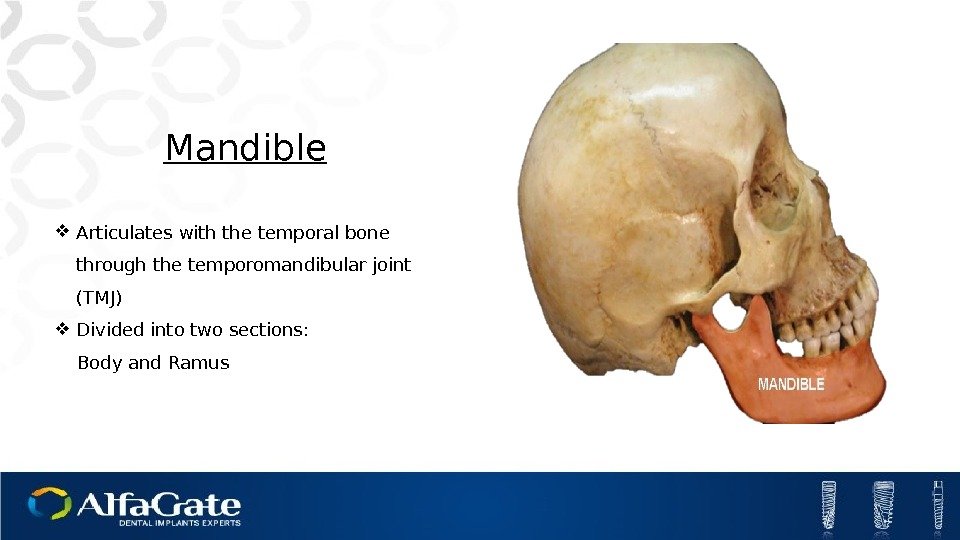
 Mandible Articulates with the temporal bone through the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) Divided into two sections: Body and Ramus
Mandible Articulates with the temporal bone through the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) Divided into two sections: Body and Ramus
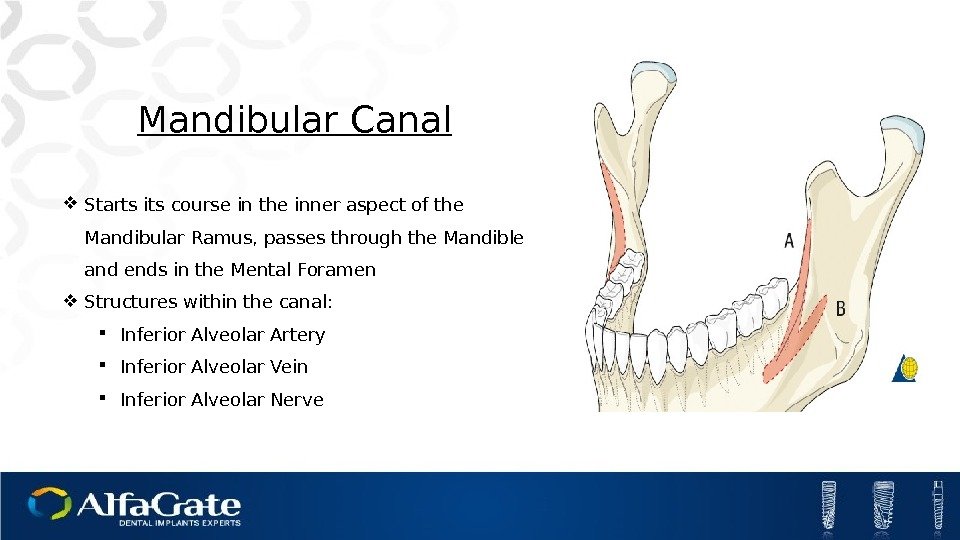
 Mandibular Canal Starts its course in the inner aspect of the Mandibular Ramus, passes through the Mandible and ends in the Mental Foramen Structures within the canal: Inferior Alveolar Artery Inferior Alveolar Vein Inferior Alveolar Nerve
Mandibular Canal Starts its course in the inner aspect of the Mandibular Ramus, passes through the Mandible and ends in the Mental Foramen Structures within the canal: Inferior Alveolar Artery Inferior Alveolar Vein Inferior Alveolar Nerve
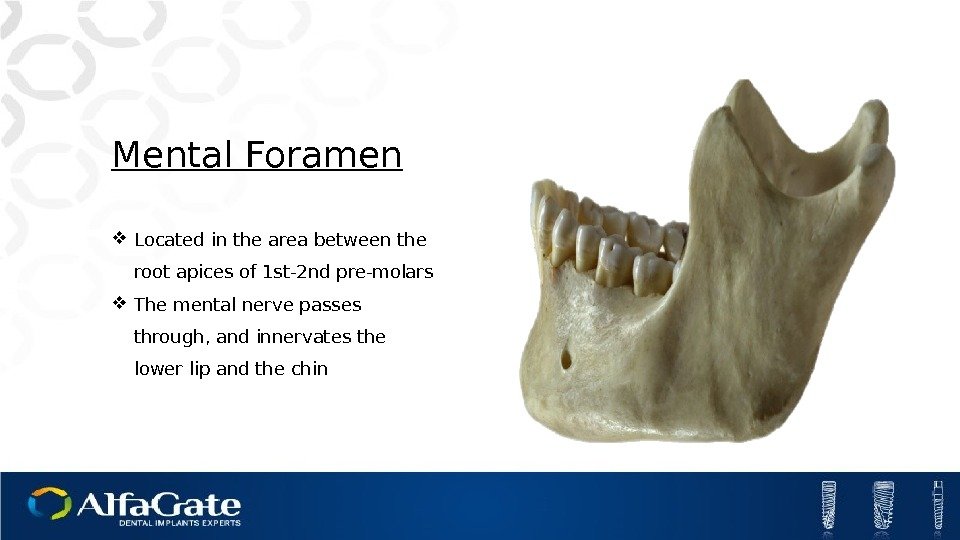
 Mental Foramen Located in the area between the root apices of 1 st-2 nd pre-molars The mental nerve passes through, and innervates the lower lip and the chin
Mental Foramen Located in the area between the root apices of 1 st-2 nd pre-molars The mental nerve passes through, and innervates the lower lip and the chin
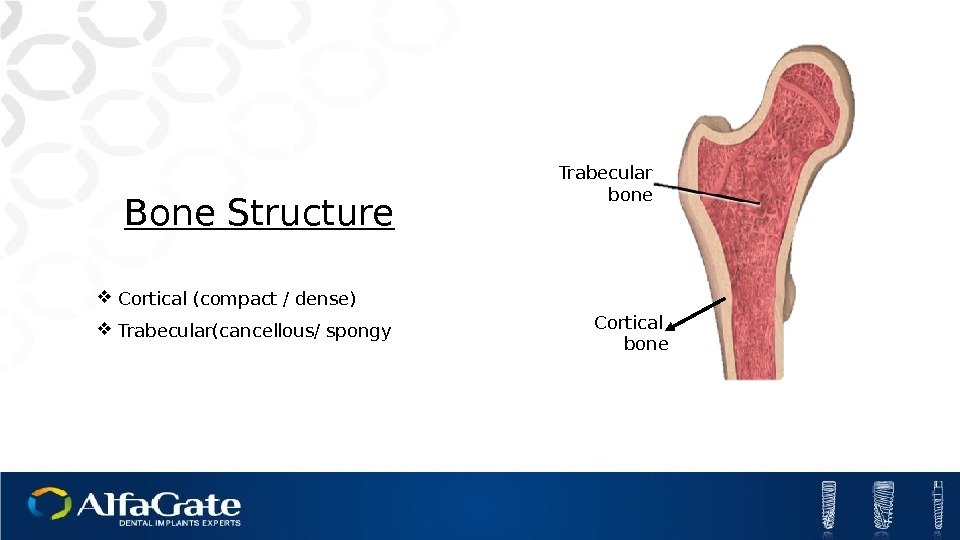
 Bone Structure Cortical (compact / dense) Trabecular(cancellous/ spongy Cortical bone. Trabecular bone
Bone Structure Cortical (compact / dense) Trabecular(cancellous/ spongy Cortical bone. Trabecular bone
 D 1 -Anterior Mandible Composed mainly of cortical bone mass Fewer intrinsic blood vessels Excellent BIC and initial stability “ Safe Zone”
D 1 -Anterior Mandible Composed mainly of cortical bone mass Fewer intrinsic blood vessels Excellent BIC and initial stability “ Safe Zone”
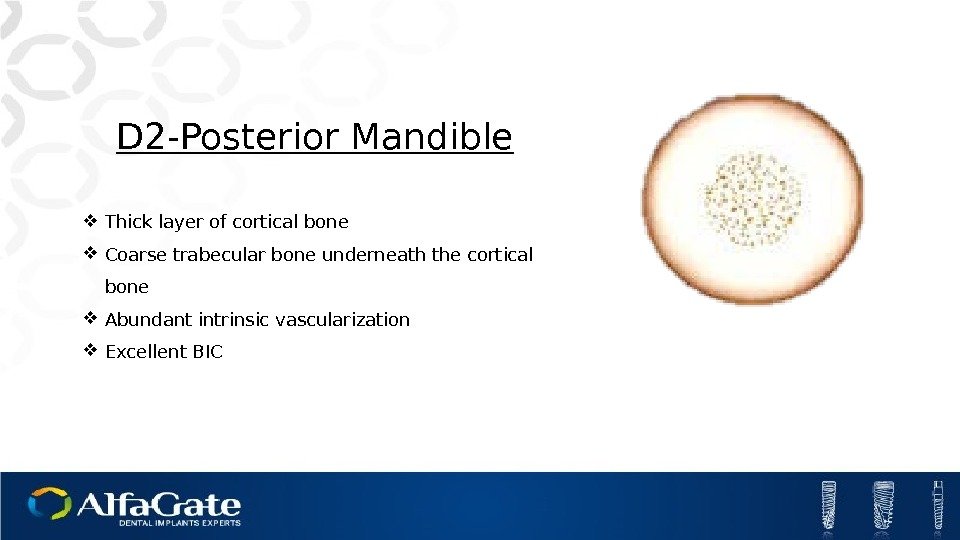
 D 2 -Posterior Mandible Thick layer of cortical bone Coarse trabecular bone underneath the cortical bone Abundant intrinsic vascularization Excellent BI
D 2 -Posterior Mandible Thick layer of cortical bone Coarse trabecular bone underneath the cortical bone Abundant intrinsic vascularization Excellent BI
 D 3 -Anterior Maxilla Porous layer of cortical bone Fine trabecular bone underneath the cortical bone Well vascularized Palatal portion thicker than labial portion Reduced BI
D 3 -Anterior Maxilla Porous layer of cortical bone Fine trabecular bone underneath the cortical bone Well vascularized Palatal portion thicker than labial portion Reduced BI
 D 4 -Posterior Maxilla Fine trabecular bone Often absence of cortical bone Poor BI
D 4 -Posterior Maxilla Fine trabecular bone Often absence of cortical bone Poor BI
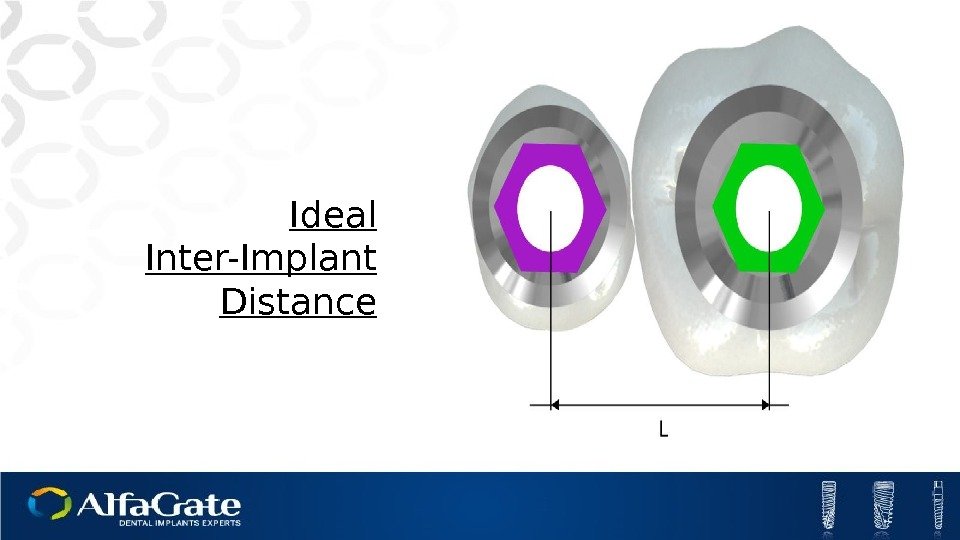
 Ideal Inter-Implant Distance
Ideal Inter-Implant Distance
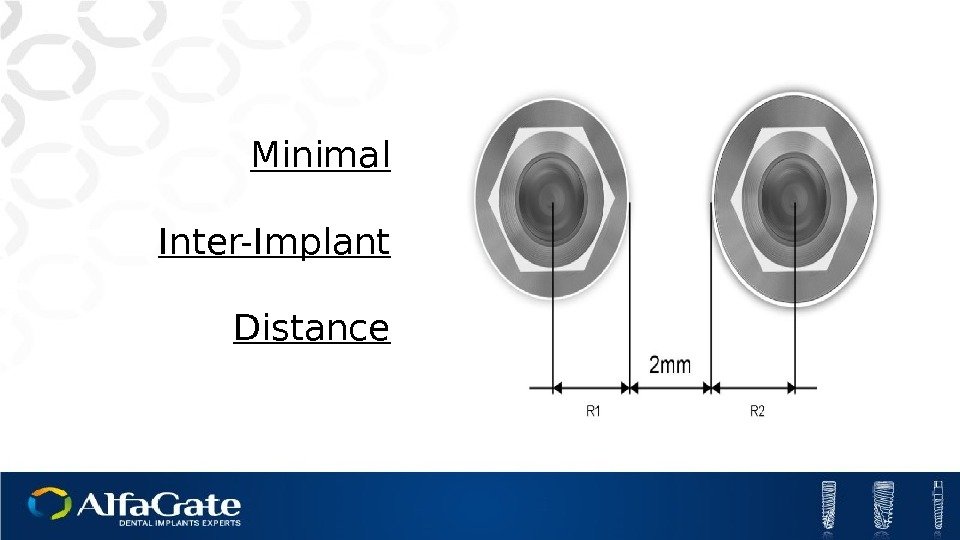
 Minimal Inter-Implant Distance
Minimal Inter-Implant Distance
 Minimal distance of + 2 mm is required Implant to Natural Tooth Distance
Minimal distance of + 2 mm is required Implant to Natural Tooth Distance
 Panoramic X-Ray
Panoramic X-Ray
 Implants -Introduction
Implants -Introduction
 Table of contents. Implant Types Implantation Procedures Surface Treatment
Table of contents. Implant Types Implantation Procedures Surface Treatment
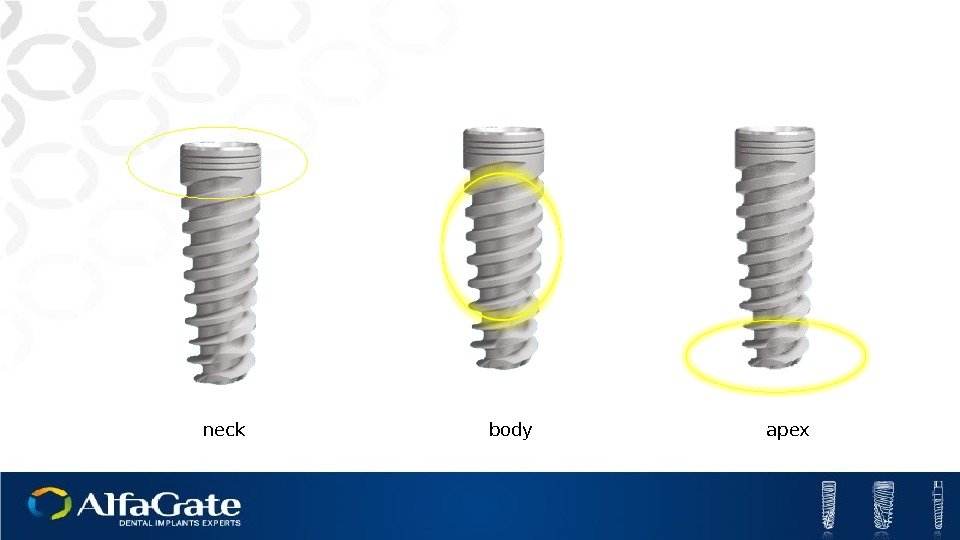
 neck body apex
neck body apex
 Dual Thread Increased BIC (bone implant contact ) Fast insertion (2. 4 mm per revolution) Mild bone condensation primary stability
Dual Thread Increased BIC (bone implant contact ) Fast insertion (2. 4 mm per revolution) Mild bone condensation primary stability
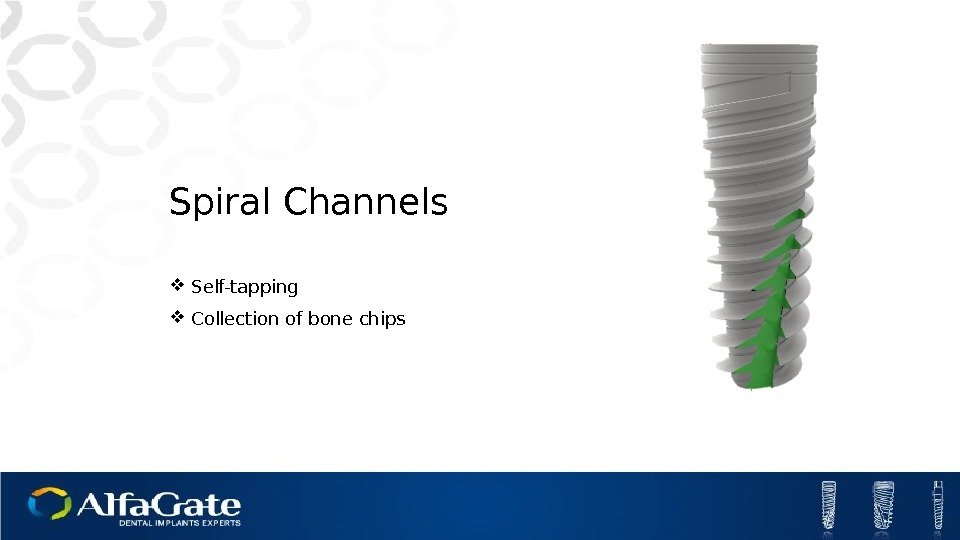
 Spiral Channels Self-tapping Collection of bone chips
Spiral Channels Self-tapping Collection of bone chips
 Micro-rings Increased BIC in Crestal area Distribution of forces
Micro-rings Increased BIC in Crestal area Distribution of forces
 2. 42 mm. Internal Hexagon
2. 42 mm. Internal Hexagon
 Domed Apex Allows a safer procedure when working close to the nerve canal or the sinus floor. Flat Cutting Apex Enables a safe and easy insertion in hard and dense bone, providing excellent primary stability, especially in immediate placement procedures
Domed Apex Allows a safer procedure when working close to the nerve canal or the sinus floor. Flat Cutting Apex Enables a safe and easy insertion in hard and dense bone, providing excellent primary stability, especially in immediate placement procedures
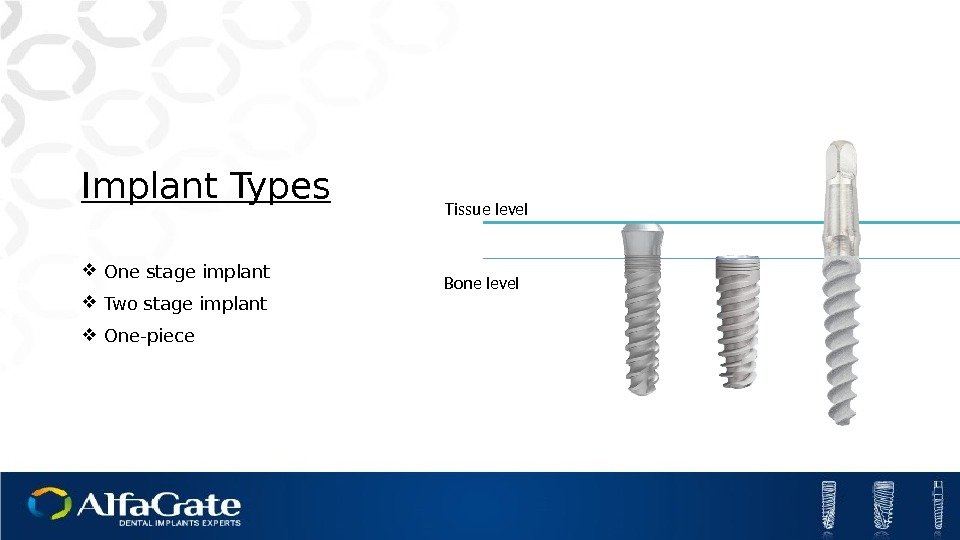
 Implant Types One stage implant Two stage implant One-piece Bone level Tissue level
Implant Types One stage implant Two stage implant One-piece Bone level Tissue level
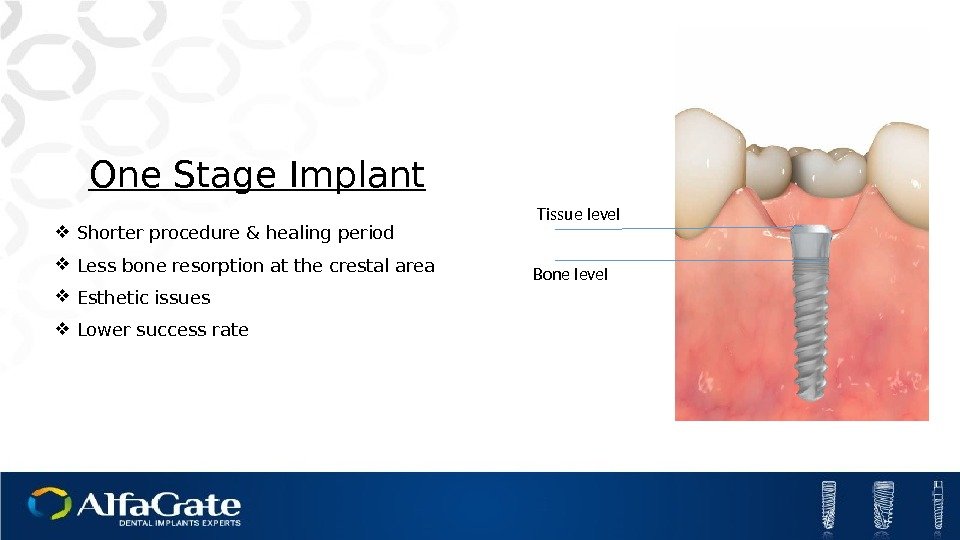
 One Stage Implant Shorter procedure & healing period Less bone resorption at the crestal area Esthetic issues Lower success rate Bone level Tissue level
One Stage Implant Shorter procedure & healing period Less bone resorption at the crestal area Esthetic issues Lower success rate Bone level Tissue level
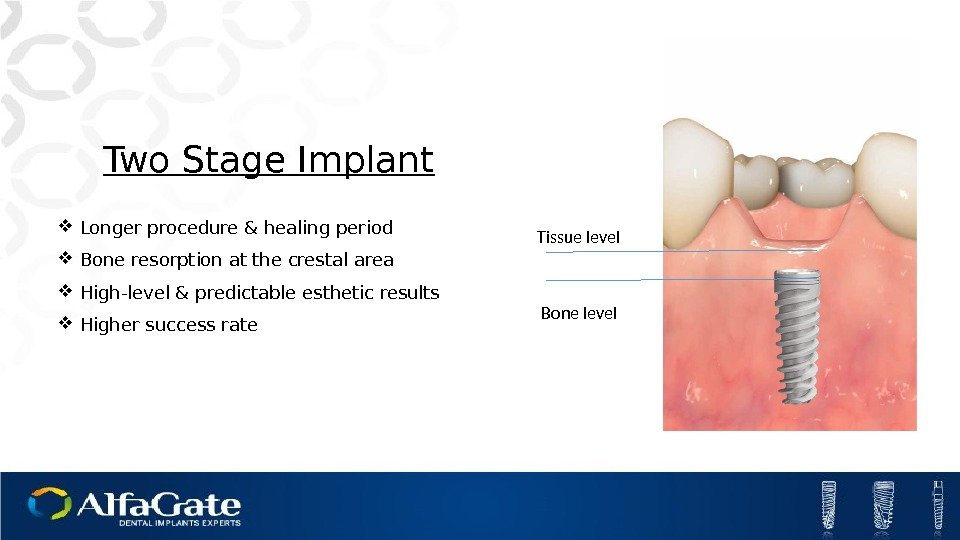
 Two Stage Implant Longer procedure & healing period Bone resorption at the crestal area High-level & predictable esthetic results Higher success rate Bone level Tissue level
Two Stage Implant Longer procedure & healing period Bone resorption at the crestal area High-level & predictable esthetic results Higher success rate Bone level Tissue level

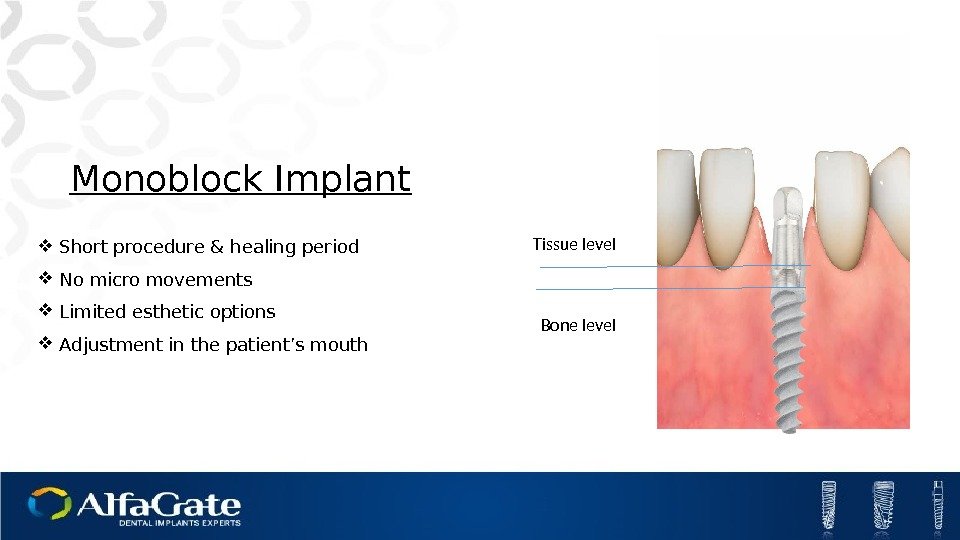
 Monoblock Implant Short procedure & healing period No micro movements Limited esthetic options Adjustment in the patient’s mouth Bone level Tissue level
Monoblock Implant Short procedure & healing period No micro movements Limited esthetic options Adjustment in the patient’s mouth Bone level Tissue level
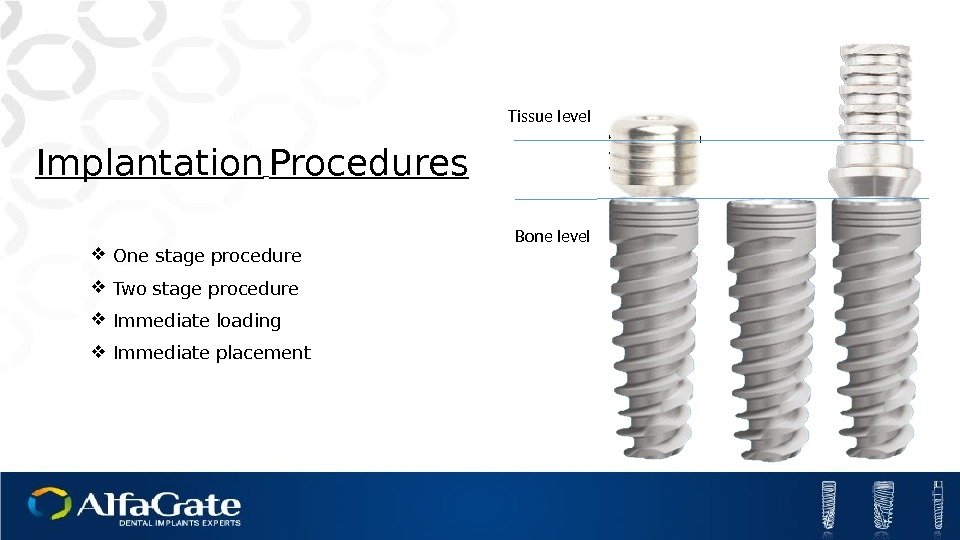
 Implantation Procedures One stage procedure Two stage procedure Immediate loading Immediate placement Bone level Tissue level
Implantation Procedures One stage procedure Two stage procedure Immediate loading Immediate placement Bone level Tissue level
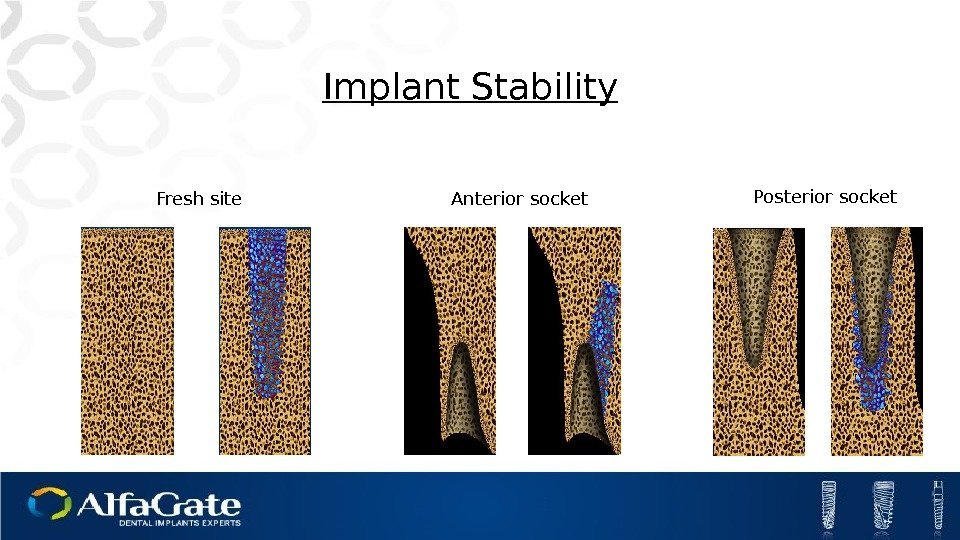
 Implant Stability Fresh site Anterior socket Posterior socket
Implant Stability Fresh site Anterior socket Posterior socket
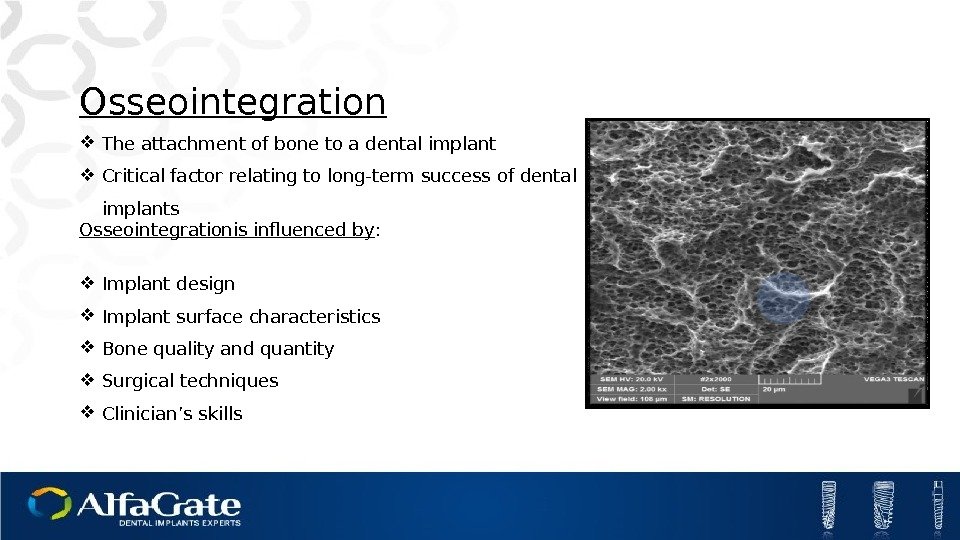
 Osseointegration The attachment of bone to a dental implant Critical factor relating to long-term success of dental implants Osseointegrationis influenced by : Implant design Implant surface characteristics Bone quality and quantity Surgical techniques Clinician’s skills
Osseointegration The attachment of bone to a dental implant Critical factor relating to long-term success of dental implants Osseointegrationis influenced by : Implant design Implant surface characteristics Bone quality and quantity Surgical techniques Clinician’s skills
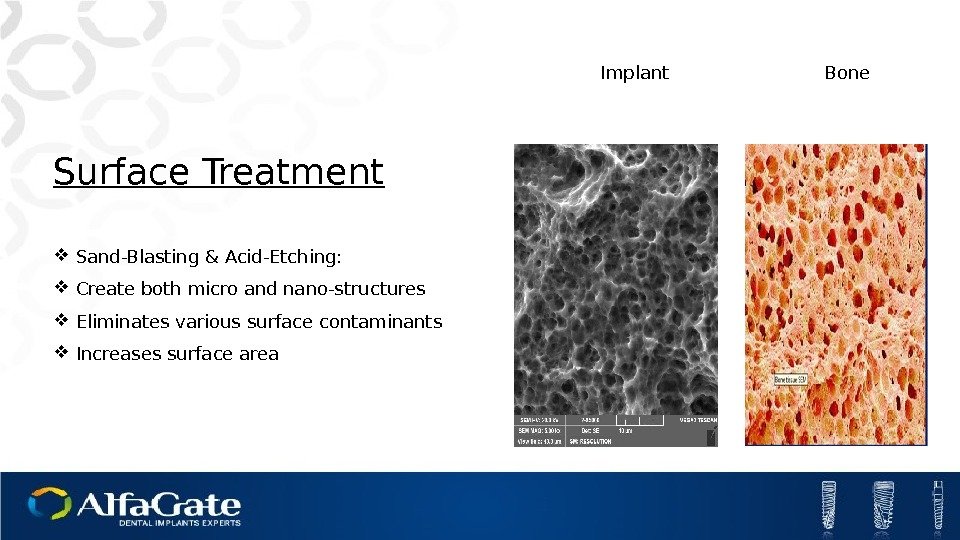
 Surface Treatment Sand-Blasting & Acid-Etching: Create both micro and nano-structures Eliminates various surface contaminants Increases surface area Implant Bone
Surface Treatment Sand-Blasting & Acid-Etching: Create both micro and nano-structures Eliminates various surface contaminants Increases surface area Implant Bone
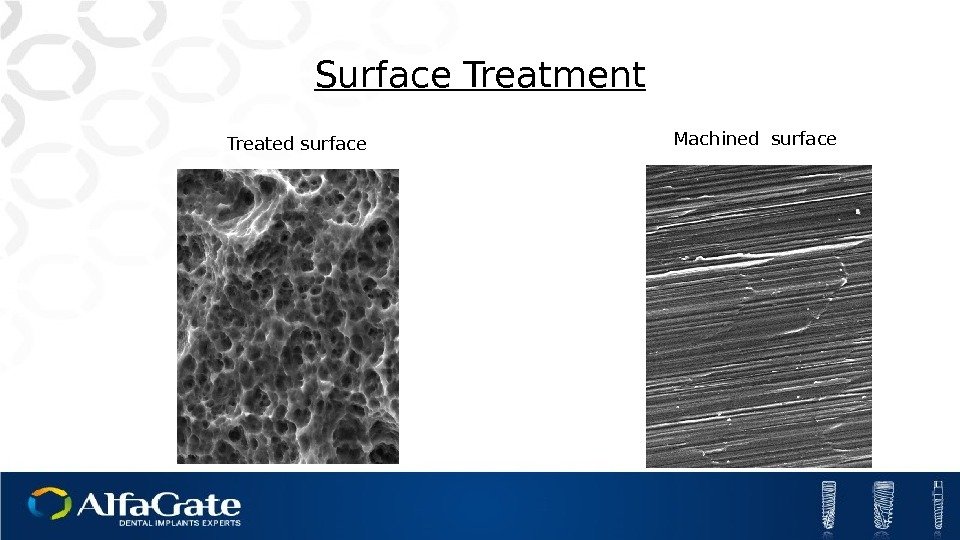
 Surface Treatment Machined surface Treated surface
Surface Treatment Machined surface Treated surface
 Alfa Gate Surface Treatment Benefits Raw material-high mechanical properties of Titanium alloy Process reproducibility is routinely validated using advanced techniques The hydrophilic property of Alfa Gate surface enhances blood with stem cells attachment, resulting in early osseointegration Alfa Gate surface type provides the best nesting site for the cells, resulting in improved osseointegration
Alfa Gate Surface Treatment Benefits Raw material-high mechanical properties of Titanium alloy Process reproducibility is routinely validated using advanced techniques The hydrophilic property of Alfa Gate surface enhances blood with stem cells attachment, resulting in early osseointegration Alfa Gate surface type provides the best nesting site for the cells, resulting in improved osseointegration
 Kits
Kits
 Table of contents. Advanced Surgical Kit Basic Surgical Kit Conical drills Kit Drills Kit with stopper
Table of contents. Advanced Surgical Kit Basic Surgical Kit Conical drills Kit Drills Kit with stopper
 Advanced surgical kit Alfa Gate Advanced Surgical kit includes instruments for Bioactive, Porous, MAX, S-line, Slim and Patro implants
Advanced surgical kit Alfa Gate Advanced Surgical kit includes instruments for Bioactive, Porous, MAX, S-line, Slim and Patro implants
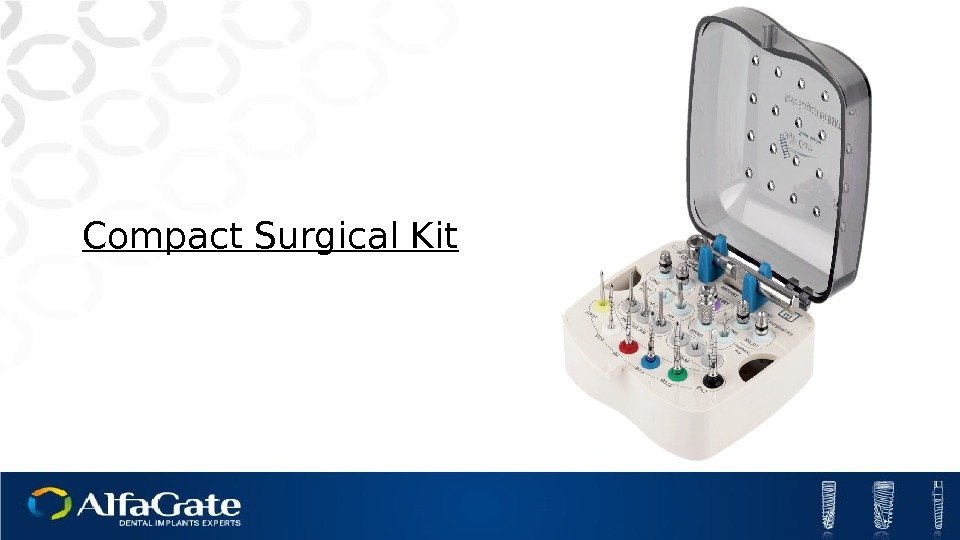
 Compact Surgical Kit
Compact Surgical Kit
 The Conical drills kit is a small kit which contains 6 Conical drills and instruments necessary for Bio-active implants placement Conical Drills Kit
The Conical drills kit is a small kit which contains 6 Conical drills and instruments necessary for Bio-active implants placement Conical Drills Kit
 Drills Kit With Stopper The kit ensure the dental surgeon simple and accurate depth control during the drilling process. 25 external irrigation drills 5 different diameters — 2. 0 mm, 2. 80 mm, 3. 20 mm, 3. 65 mm, 4. 20 mm 5 different lengths — 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 11. 5 mm, 13 mm
Drills Kit With Stopper The kit ensure the dental surgeon simple and accurate depth control during the drilling process. 25 external irrigation drills 5 different diameters — 2. 0 mm, 2. 80 mm, 3. 20 mm, 3. 65 mm, 4. 20 mm 5 different lengths — 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 11. 5 mm, 13 mm
 Implants
Implants
 Table of contents. Implant Types Implantation Procedures Surface Treatment
Table of contents. Implant Types Implantation Procedures Surface Treatment
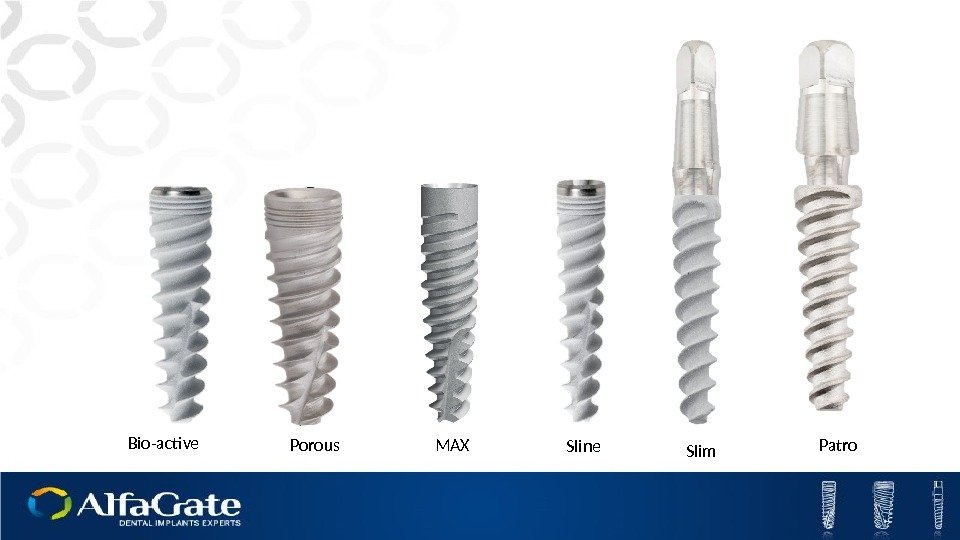
 Bio-active Porous MAX Sline Patro Slim
Bio-active Porous MAX Sline Patro Slim
 Bioactive surface The bioactive coat consists of a thin layer of calcium phosphate Ca. P: osteoconductive and osteoinductive 1. High hydrophilicity 2. Shortens the period of recovery-osteointegration: 6 to 10 weeks 3. Increases implant success rate: 99. 7% 4. Clinical studies showed better results than Premium brands implants
Bioactive surface The bioactive coat consists of a thin layer of calcium phosphate Ca. P: osteoconductive and osteoinductive 1. High hydrophilicity 2. Shortens the period of recovery-osteointegration: 6 to 10 weeks 3. Increases implant success rate: 99. 7% 4. Clinical studies showed better results than Premium brands implants
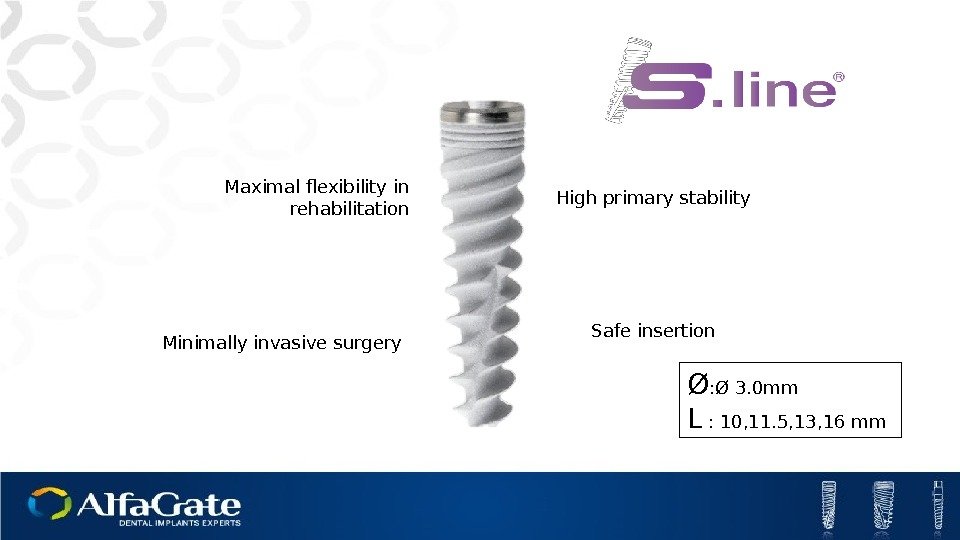
 Maximal flexibility in rehabilitation High primary stability Safe insertion Minimally invasive surgery Ø : Ø 3. 0 mm L : 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm
Maximal flexibility in rehabilitation High primary stability Safe insertion Minimally invasive surgery Ø : Ø 3. 0 mm L : 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm
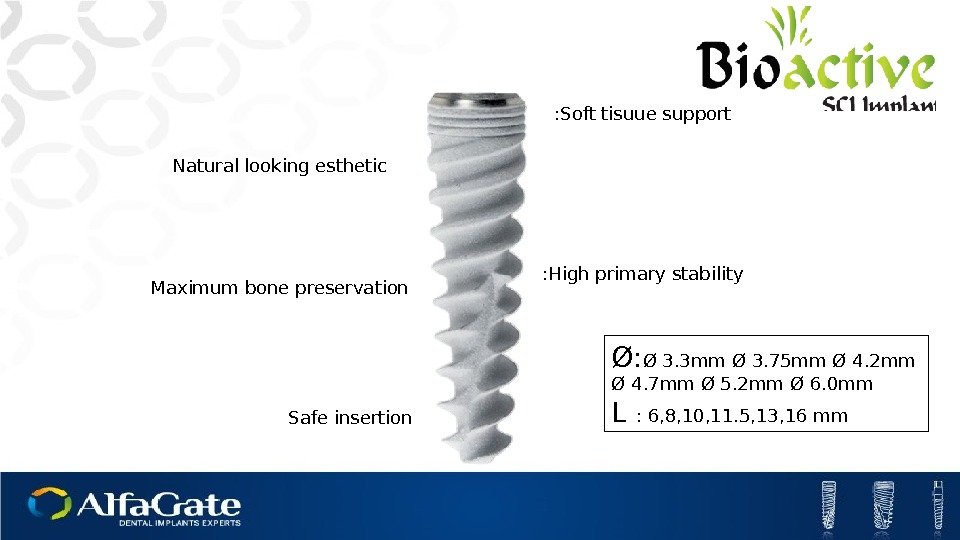
 High primary stability : Soft tisuue support : Safe insertion Maximum bone preservation Natural looking esthetic Ø: Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm Ø 4. 7 mm Ø 5. 2 mm Ø 6. 0 mm L : 6, 8, 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm
High primary stability : Soft tisuue support : Safe insertion Maximum bone preservation Natural looking esthetic Ø: Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm Ø 4. 7 mm Ø 5. 2 mm Ø 6. 0 mm L : 6, 8, 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm
 Dual thread Combined cylindrical and conical body Apically tapered body A flat cutting apex Switching platform Ø : Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm Ø 4. 7 mm Ø 5. 2 mm L : 8, 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm
Dual thread Combined cylindrical and conical body Apically tapered body A flat cutting apex Switching platform Ø : Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm Ø 4. 7 mm Ø 5. 2 mm L : 8, 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm
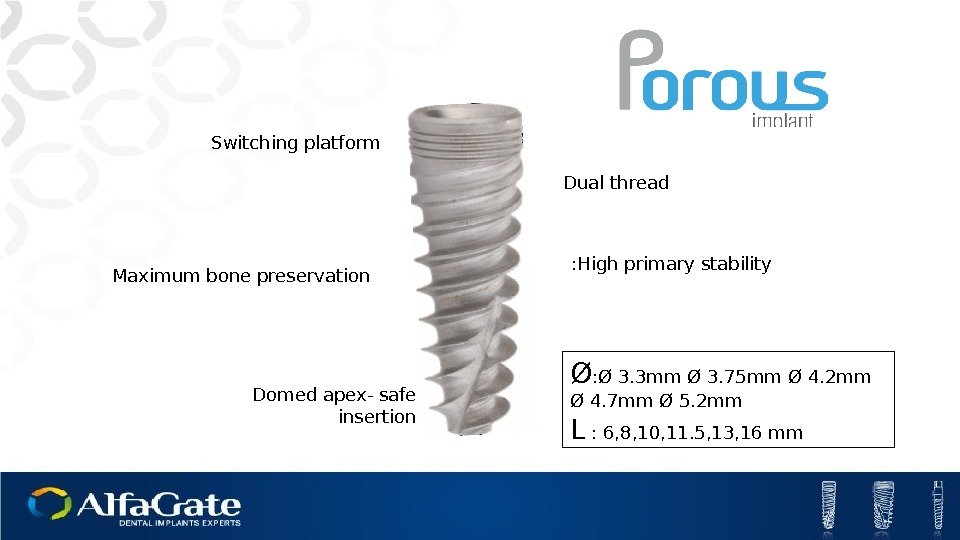
 Switching platform Dual thread Domed apex- safe insertion Ø : Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm Ø 4. 7 mm Ø 5. 2 mm L : 6, 8, 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm. Maximum bone preservation High primary stability :
Switching platform Dual thread Domed apex- safe insertion Ø : Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm Ø 4. 7 mm Ø 5. 2 mm L : 6, 8, 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm. Maximum bone preservation High primary stability :
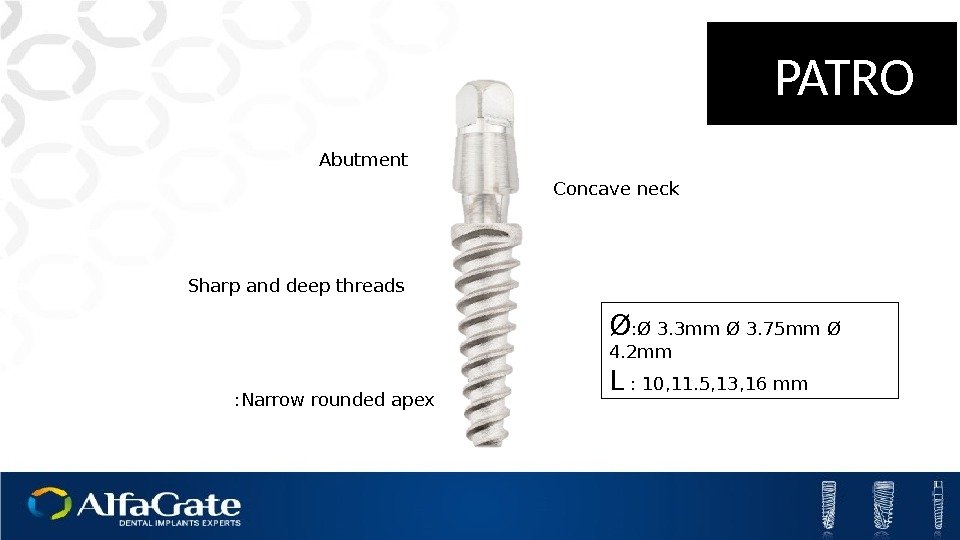
 Abutment Concave neck Sharp and deep threads Narrow rounded apex: Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm L : 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm PATRO
Abutment Concave neck Sharp and deep threads Narrow rounded apex: Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm L : 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm PATRO
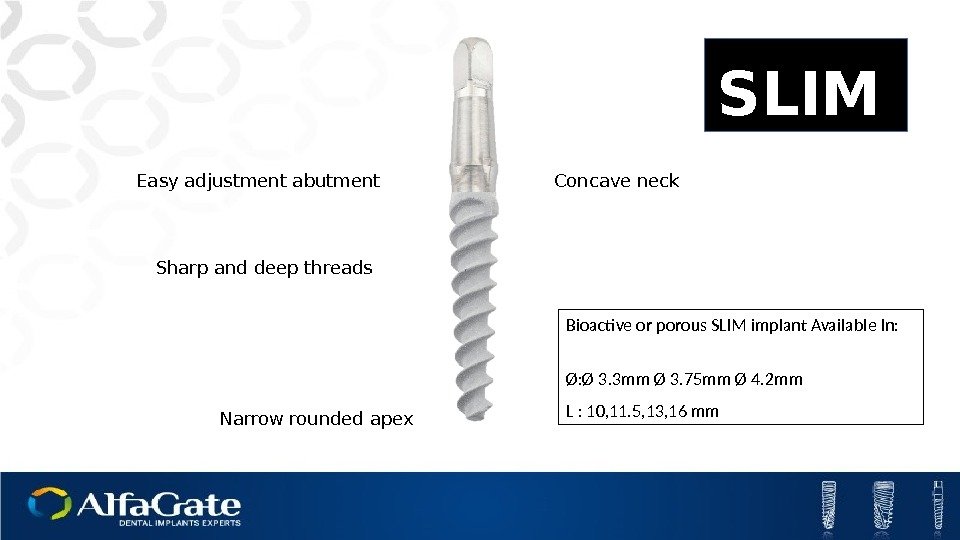
 Concave neck Sharp and deep threads Bioactive or porous SLIM implant Available In: Ø: Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm L : 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm SLIM Narrow rounded apex. Easy adjustment abutment
Concave neck Sharp and deep threads Bioactive or porous SLIM implant Available In: Ø: Ø 3. 3 mm Ø 3. 75 mm Ø 4. 2 mm L : 10, 11. 5, 13, 16 mm SLIM Narrow rounded apex. Easy adjustment abutment
 Prostetic solutions
Prostetic solutions
 Table of contents. Impression Coping Cemented Restoration Screw Retained Restoration Over Dentures
Table of contents. Impression Coping Cemented Restoration Screw Retained Restoration Over Dentures
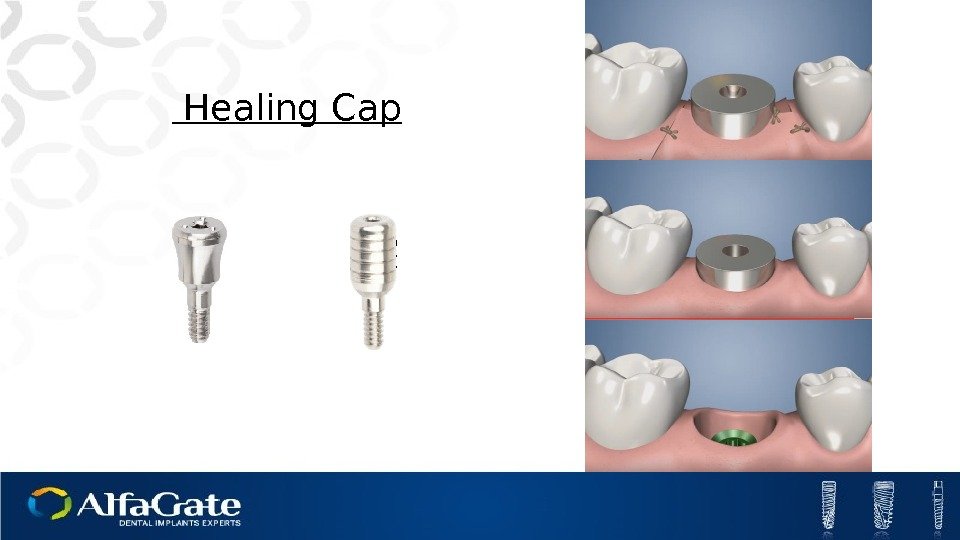
 Healing Cap
Healing Cap
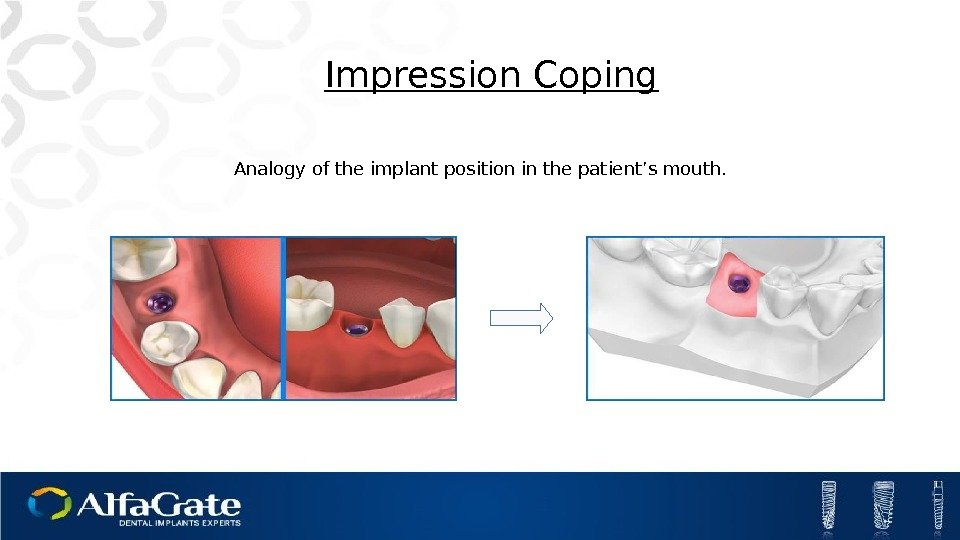
 Impression Coping Analogy of the implant position in the patient’s mouth.
Impression Coping Analogy of the implant position in the patient’s mouth.
 Impression Coping Open Tray Closed Tray
Impression Coping Open Tray Closed Tray
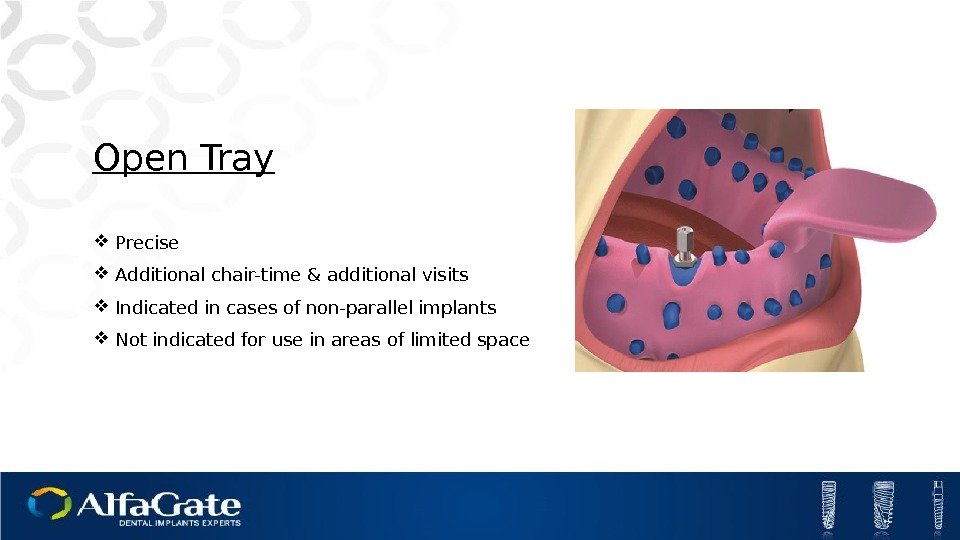
 Open Tray Precise Additional chair-time & additional visits Indicated in cases of non-parallel implants Not indicated for use in areas of limited space
Open Tray Precise Additional chair-time & additional visits Indicated in cases of non-parallel implants Not indicated for use in areas of limited space
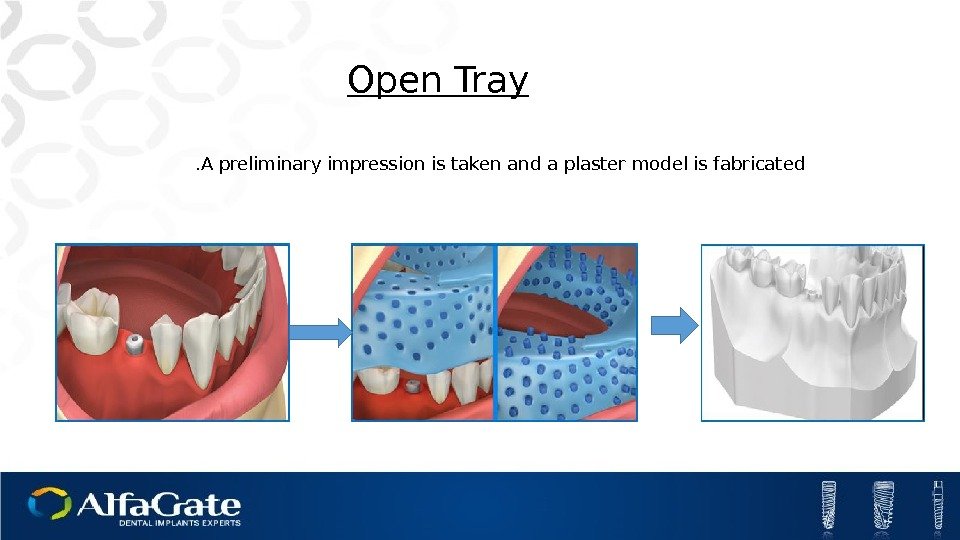
 Open Tray A preliminary impression is taken and a plaster model is fabricated.
Open Tray A preliminary impression is taken and a plaster model is fabricated.
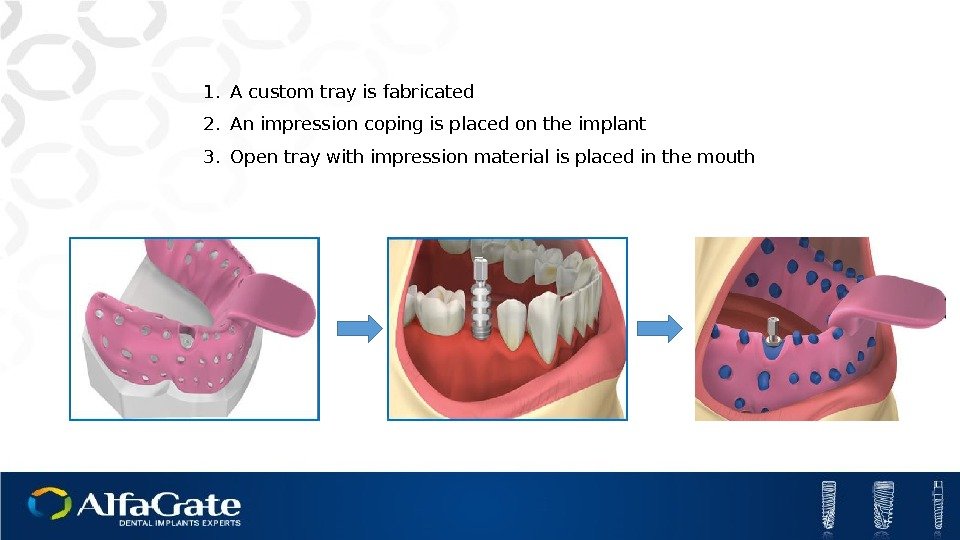
 1. A custom tray is fabricated 2. An impression coping is placed on the implant 3. Open tray with impression material is placed in the mouth
1. A custom tray is fabricated 2. An impression coping is placed on the implant 3. Open tray with impression material is placed in the mouth
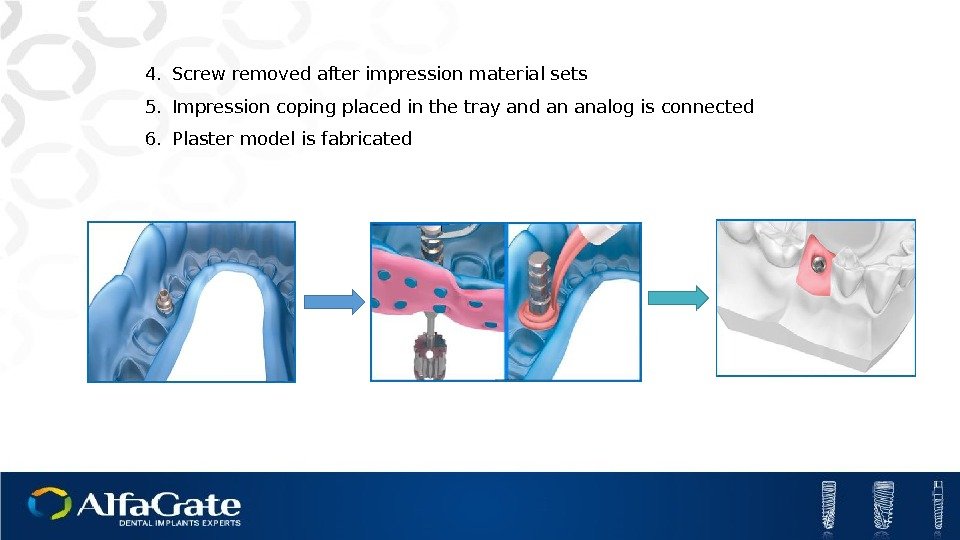
 4. Screw removed after impression material sets 5. Impression coping placed in the tray and an analog is connected 6. Plaster model is fabricated
4. Screw removed after impression material sets 5. Impression coping placed in the tray and an analog is connected 6. Plaster model is fabricated
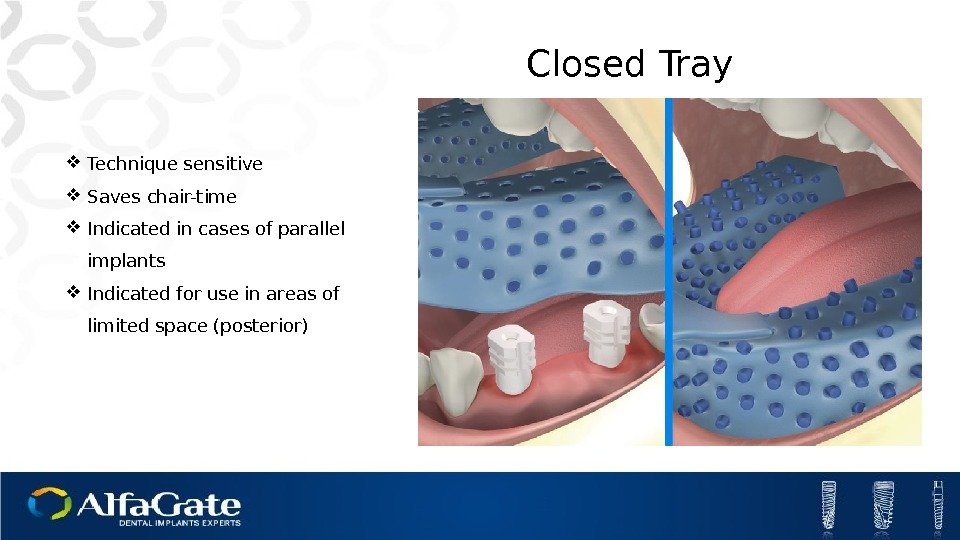
 Closed Tray Technique sensitive Saves chair-time Indicated in cases of parallel implants Indicated for use in areas of limited space (posterior)
Closed Tray Technique sensitive Saves chair-time Indicated in cases of parallel implants Indicated for use in areas of limited space (posterior)
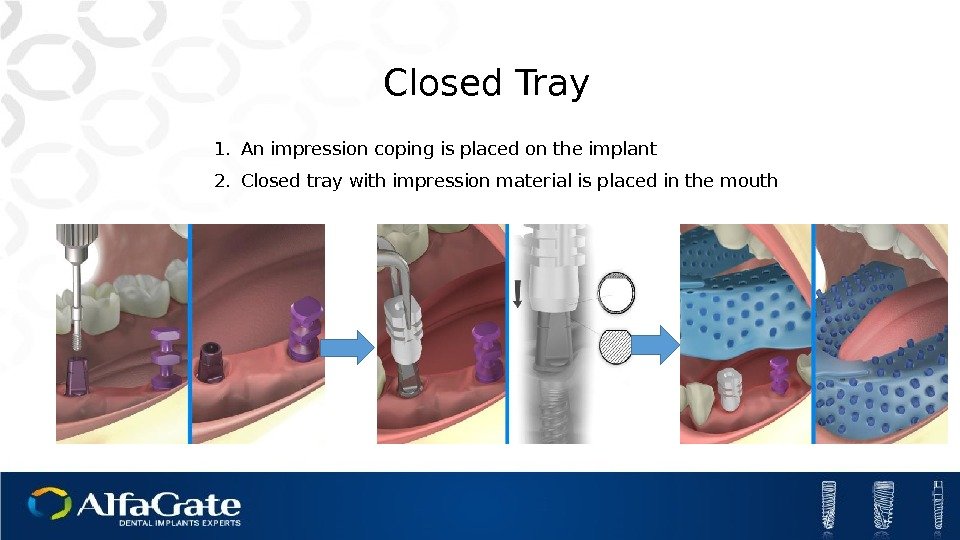
 1. An impression coping is placed on the implant 2. Closed tray with impression material is placed in the mouth Closed Tray
1. An impression coping is placed on the implant 2. Closed tray with impression material is placed in the mouth Closed Tray
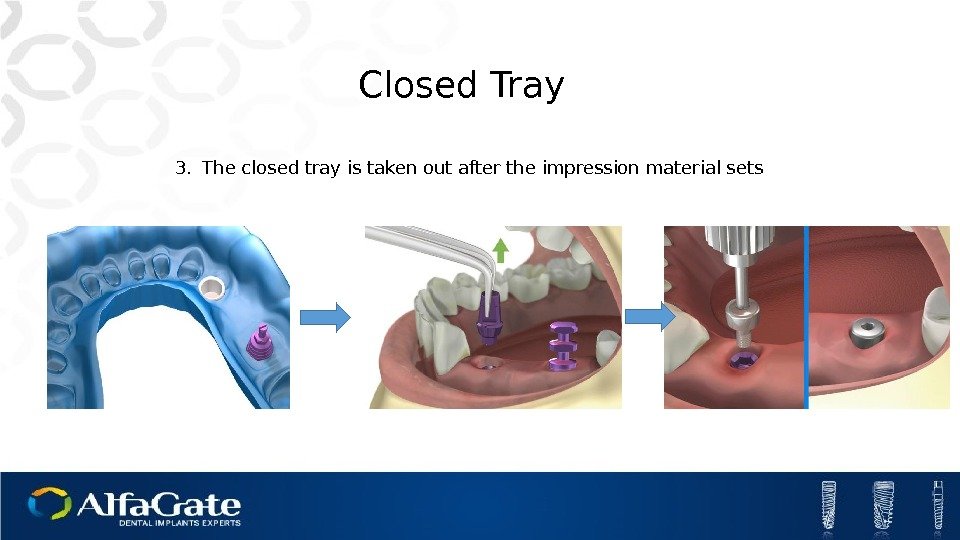
 Closed Tray 3. The closed tray is taken out after the impression material sets
Closed Tray 3. The closed tray is taken out after the impression material sets
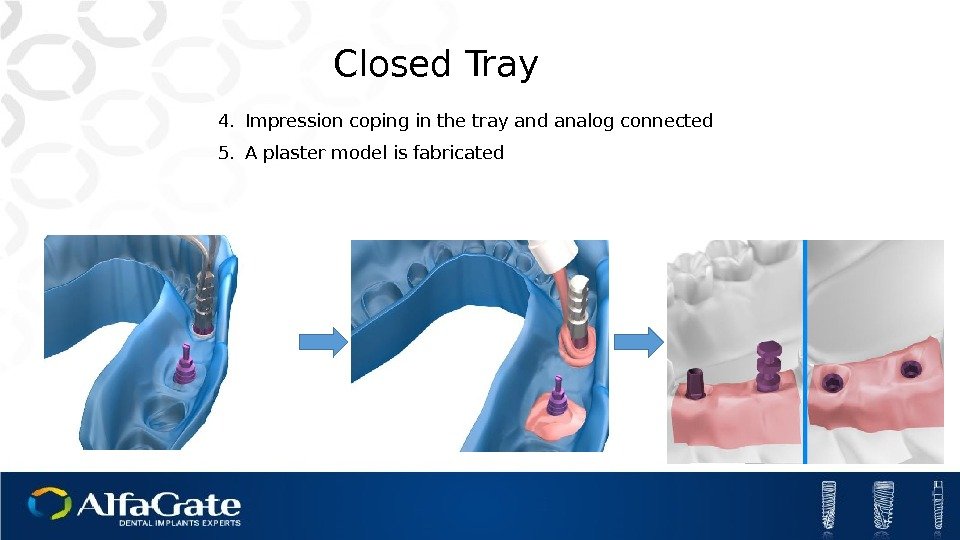
 Closed Tray 4. Impression coping in the tray and analog connected 5. A plaster model is fabricated
Closed Tray 4. Impression coping in the tray and analog connected 5. A plaster model is fabricated
 Hands-On
Hands-On
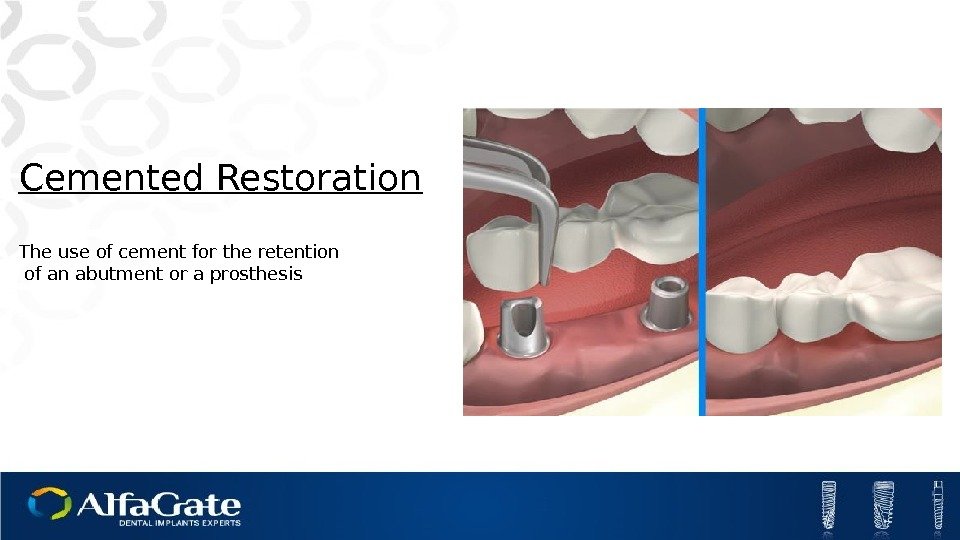
 Cemented Restoration The use of cement for the retention of an abutment or a prosthesis
Cemented Restoration The use of cement for the retention of an abutment or a prosthesis
 Esthetic Standard
Esthetic Standard
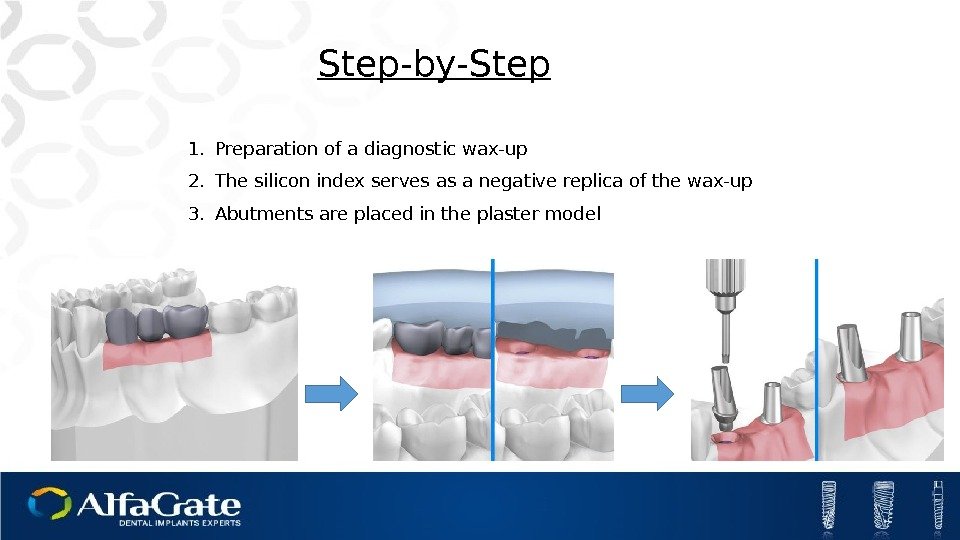
 Step-by-Step 1. Preparation of a diagnostic wax-up 2. The silicon index serves as a negative replica of the wax-up 3. Abutments are placed in the plaster model
Step-by-Step 1. Preparation of a diagnostic wax-up 2. The silicon index serves as a negative replica of the wax-up 3. Abutments are placed in the plaster model
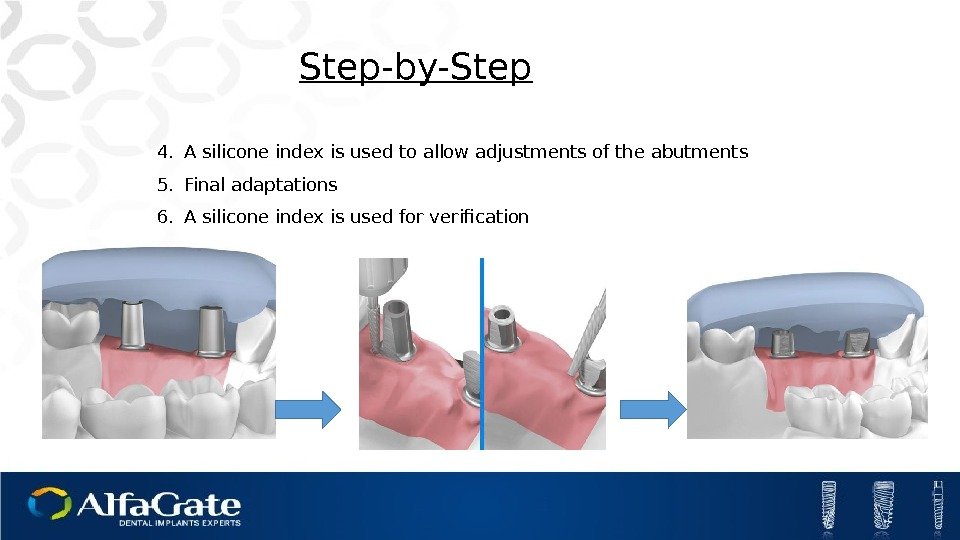
 Step-by-Step 4. A silicone index is used to allow adjustments of the abutments 5. Final adaptations 6. A silicone index is used for verification
Step-by-Step 4. A silicone index is used to allow adjustments of the abutments 5. Final adaptations 6. A silicone index is used for verification
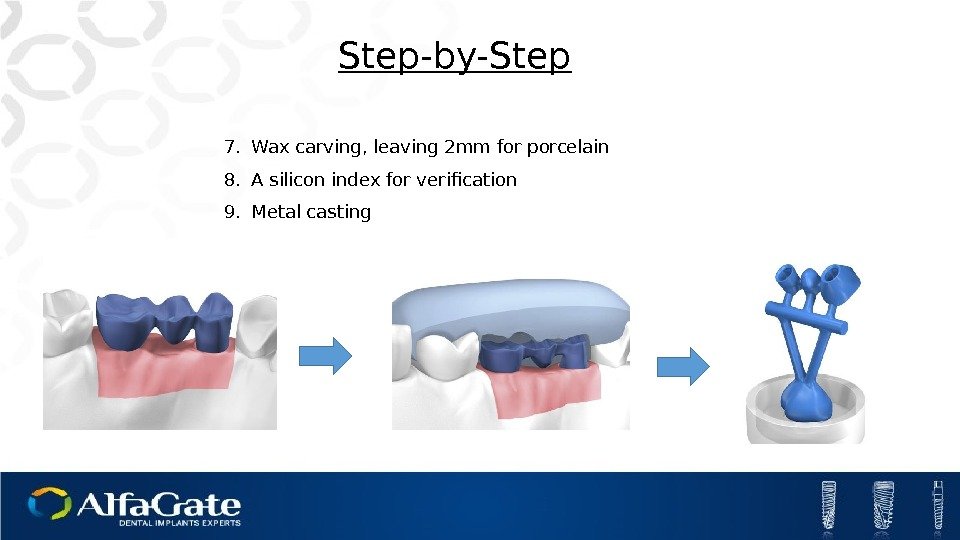
 7. Wax carving, leaving 2 mm for porcelain 8. A silicon index for verification 9. Metal casting Step-by-Step
7. Wax carving, leaving 2 mm for porcelain 8. A silicon index for verification 9. Metal casting Step-by-Step
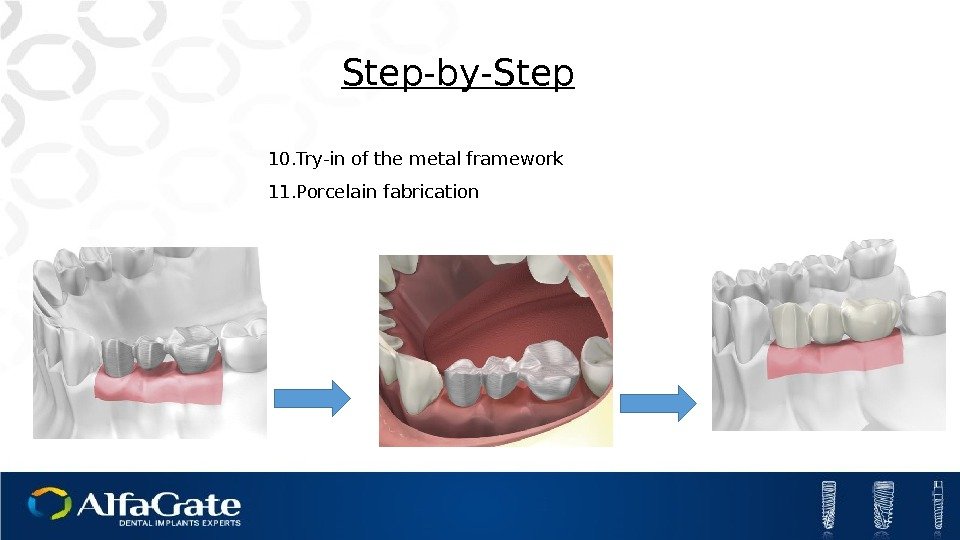
 10. Try-in of the metal framework 11. Porcelain fabrication Step-by-Step
10. Try-in of the metal framework 11. Porcelain fabrication Step-by-Step
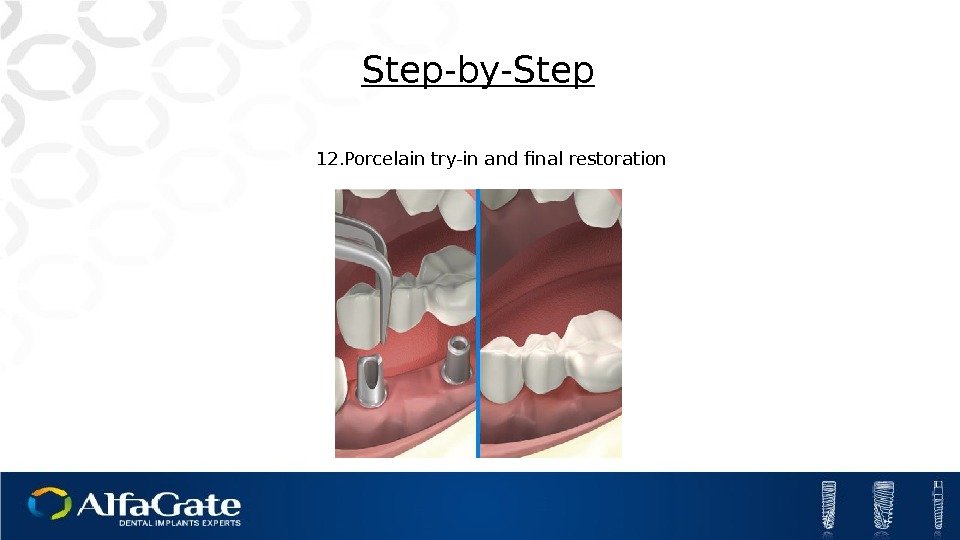
 12. Porcelain try-in and final restoration Step-by-Step
12. Porcelain try-in and final restoration Step-by-Step
 Esthetic Abutments Deep chamfer margin for excellent esthetics Minor adjustments needed Gingival height of 1, 2, 3 mm
Esthetic Abutments Deep chamfer margin for excellent esthetics Minor adjustments needed Gingival height of 1, 2, 3 mm
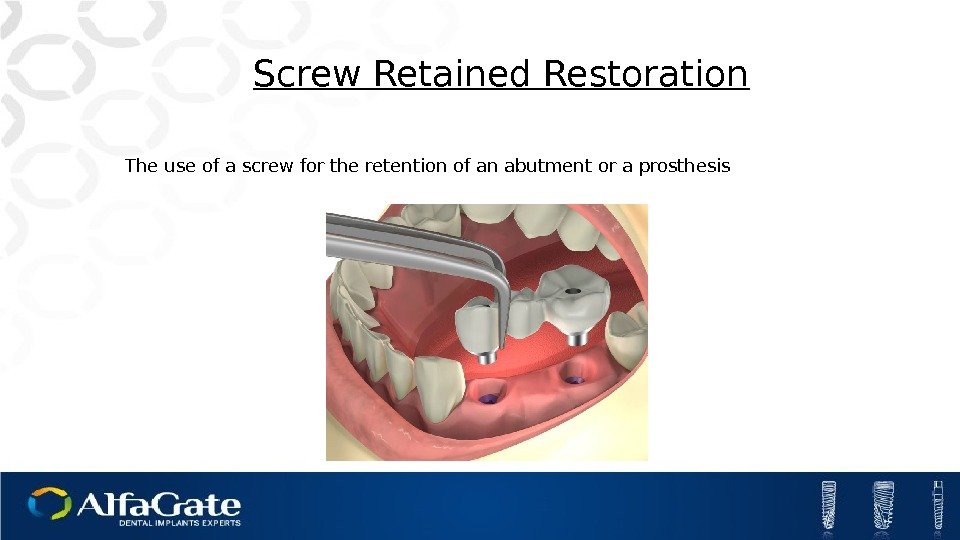
 Screw Retained Restoration The use of a screw for the retention of an abutment or a prosthesis
Screw Retained Restoration The use of a screw for the retention of an abutment or a prosthesis
 Plastic abutment Multi-Unit
Plastic abutment Multi-Unit
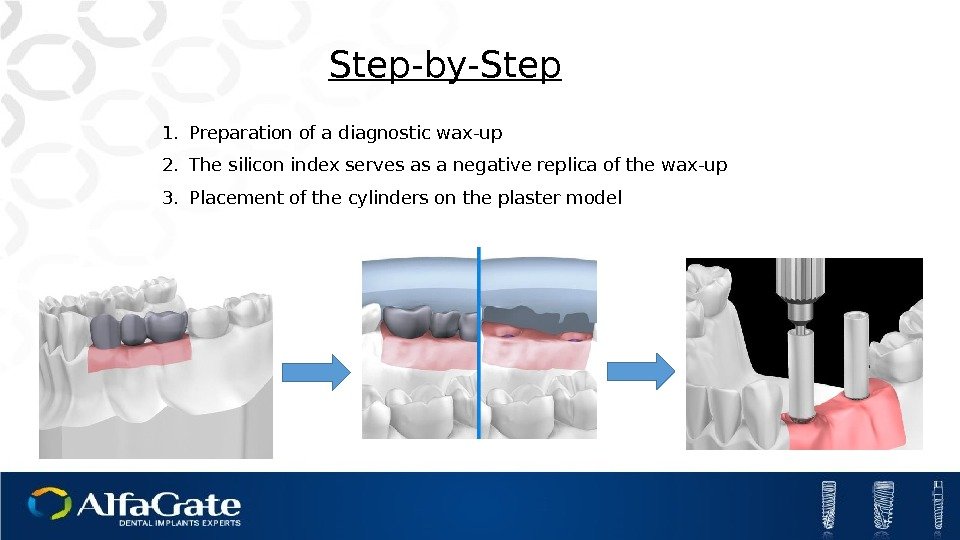
 1. Preparation of a diagnostic wax-up 2. The silicon index serves as a negative replica of the wax-up 3. Placement of the cylinders on the plaster model Step-by-Step
1. Preparation of a diagnostic wax-up 2. The silicon index serves as a negative replica of the wax-up 3. Placement of the cylinders on the plaster model Step-by-Step
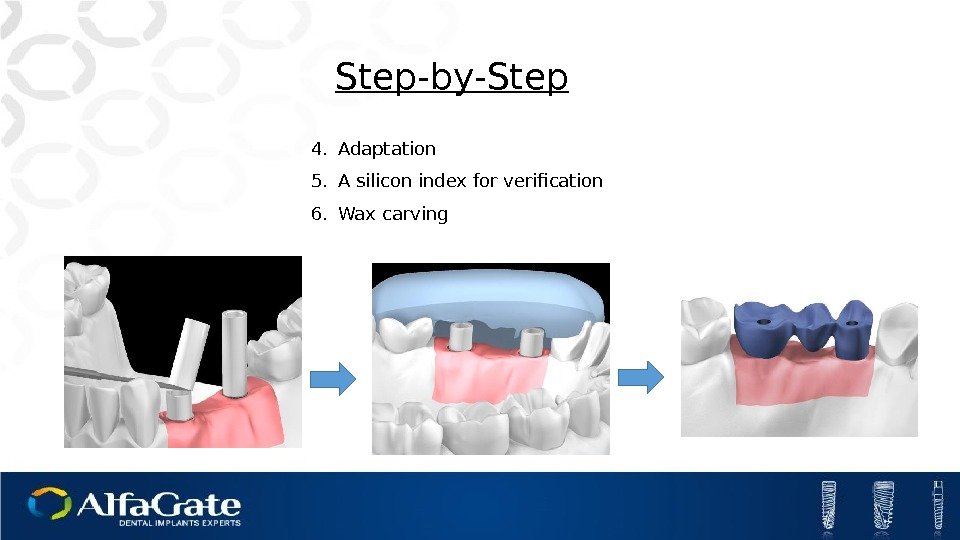
 4. Adaptation 5. A silicon index for verification 6. Wax carving. Step-by-Step
4. Adaptation 5. A silicon index for verification 6. Wax carving. Step-by-Step
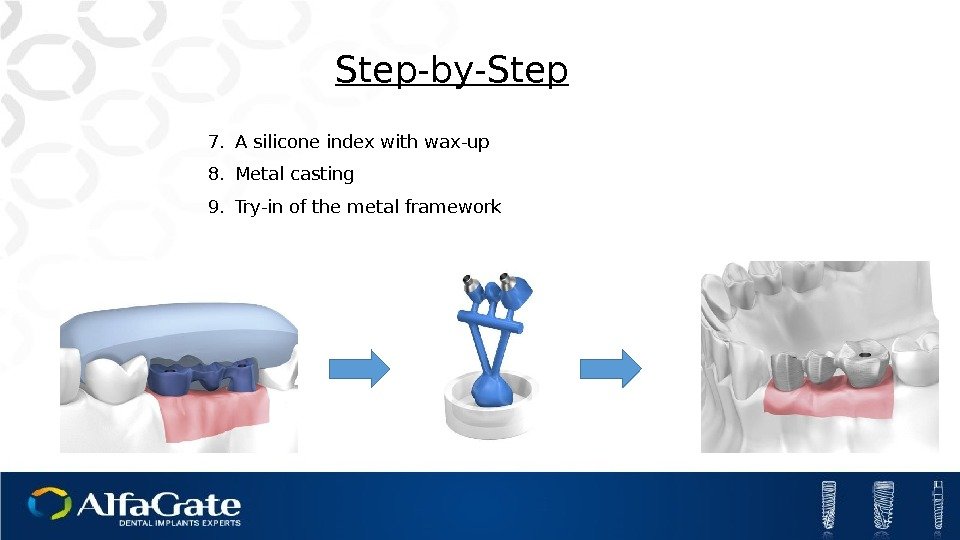
 7. A silicone index with wax-up 8. Metal casting 9. Try-in of the metal framework Step-by-Step
7. A silicone index with wax-up 8. Metal casting 9. Try-in of the metal framework Step-by-Step
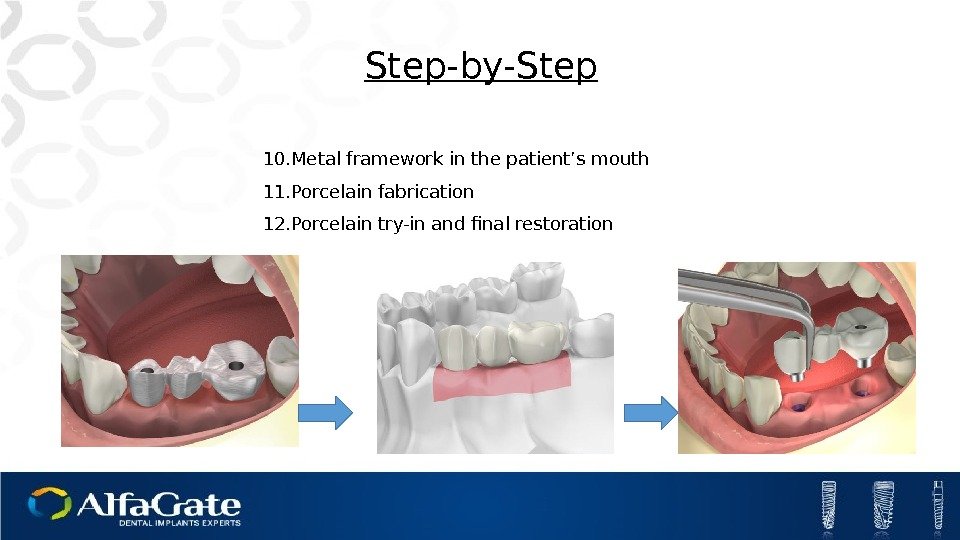
 10. Metal framework in the patient’s mouth 11. Porcelain fabrication 12. Porcelain try-in and final restoration Step-by-Step
10. Metal framework in the patient’s mouth 11. Porcelain fabrication 12. Porcelain try-in and final restoration Step-by-Step
 Plastic Cylinder Fair implant-to-crown connection Metal casting Affordable
Plastic Cylinder Fair implant-to-crown connection Metal casting Affordable
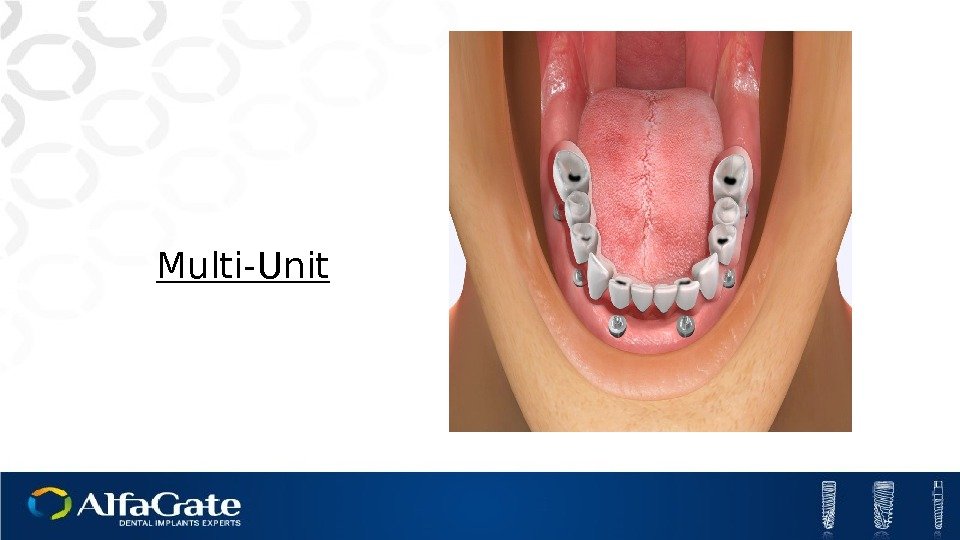
 Multi-Unit Angulation flexibility-17°and 30° Enables working above the soft tissue level Good distribution of forces between implants Dolder bar options Profile height-1, 2, 3, 4 mm and 1, 4 in angulated units
Multi-Unit Angulation flexibility-17°and 30° Enables working above the soft tissue level Good distribution of forces between implants Dolder bar options Profile height-1, 2, 3, 4 mm and 1, 4 in angulated units
 Multi-Unit
Multi-Unit
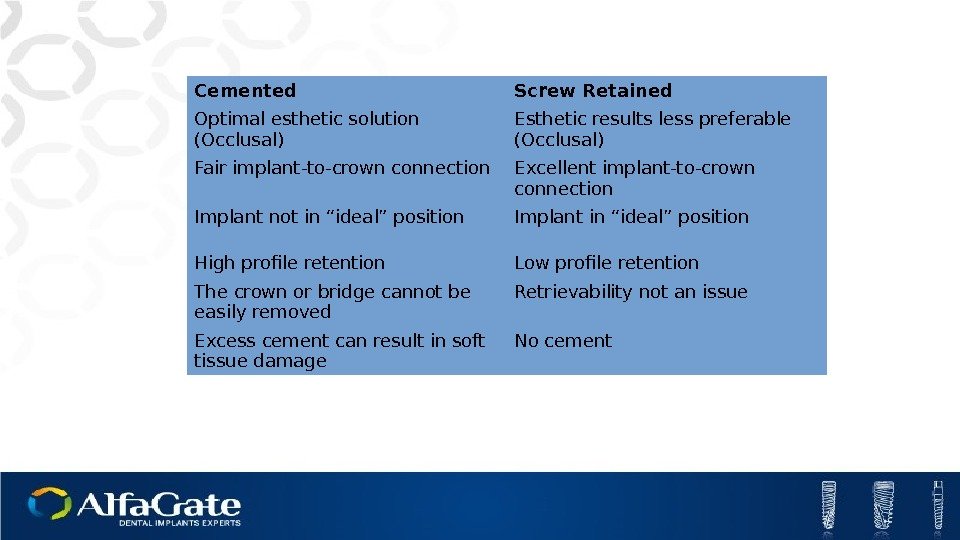
 Cemented Screw Retained Optimal esthetic solution (Occlusal) Esthetic results less preferable (Occlusal) Fair implant-to-crown connection Excellent implant-to-crown connection Implant not in “ideal” position Implant in “ideal” position High profile retention Low profile retention The crown or bridge cannot be easily removed Retrievability not an issue Excess cement can result in soft tissue damage No cement
Cemented Screw Retained Optimal esthetic solution (Occlusal) Esthetic results less preferable (Occlusal) Fair implant-to-crown connection Excellent implant-to-crown connection Implant not in “ideal” position Implant in “ideal” position High profile retention Low profile retention The crown or bridge cannot be easily removed Retrievability not an issue Excess cement can result in soft tissue damage No cement
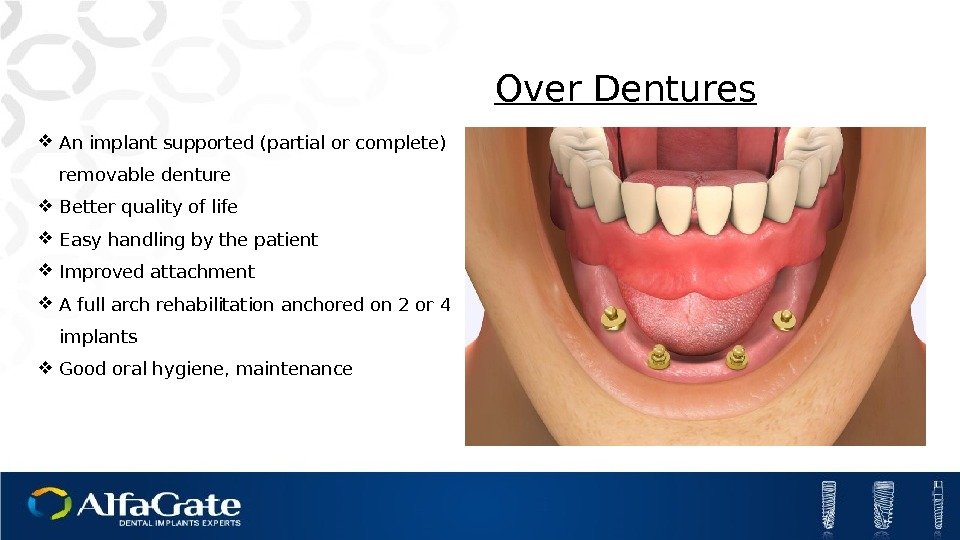
 Over Dentures An implant supported (partial or complete) removable denture Better quality of life Easy handling by the patient Improved attachment A full arch rehabilitation anchored on 2 or 4 implants Good oral hygiene, maintenance
Over Dentures An implant supported (partial or complete) removable denture Better quality of life Easy handling by the patient Improved attachment A full arch rehabilitation anchored on 2 or 4 implants Good oral hygiene, maintenance
 Ball Attachment Alfa Lock
Ball Attachment Alfa Lock
 Regenerative Solutions
Regenerative Solutions
 Table of contents. Introduction to Bone Grafting Types of Bone Grafts Regenerative Products Challenges
Table of contents. Introduction to Bone Grafting Types of Bone Grafts Regenerative Products Challenges
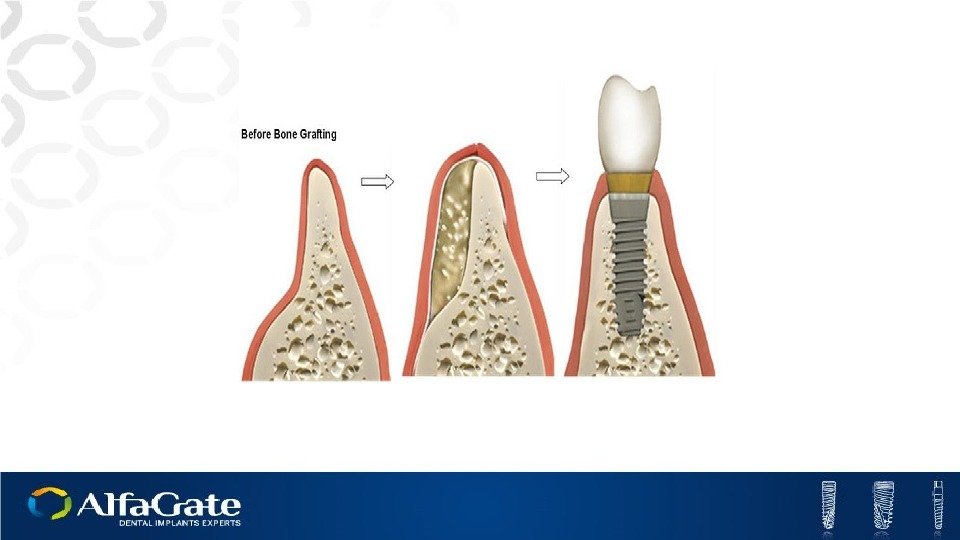
 Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone with a material from the patients own body, an artificial, synthetic, or natural substitute. Bone grafting must provide similar properties to those of natural bone Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone with a material from the patients own body, an artificial, synthetic, or natural substitute. Bone grafting must provide similar properties to those of natural bone Bone Grafting
 Regeneration is the restoration or regrowth of lost, destroyed or injured parts or organs. The regenerated area is not always exactly identical to the original tissue or organ. Regeneration
Regeneration is the restoration or regrowth of lost, destroyed or injured parts or organs. The regenerated area is not always exactly identical to the original tissue or organ. Regeneration
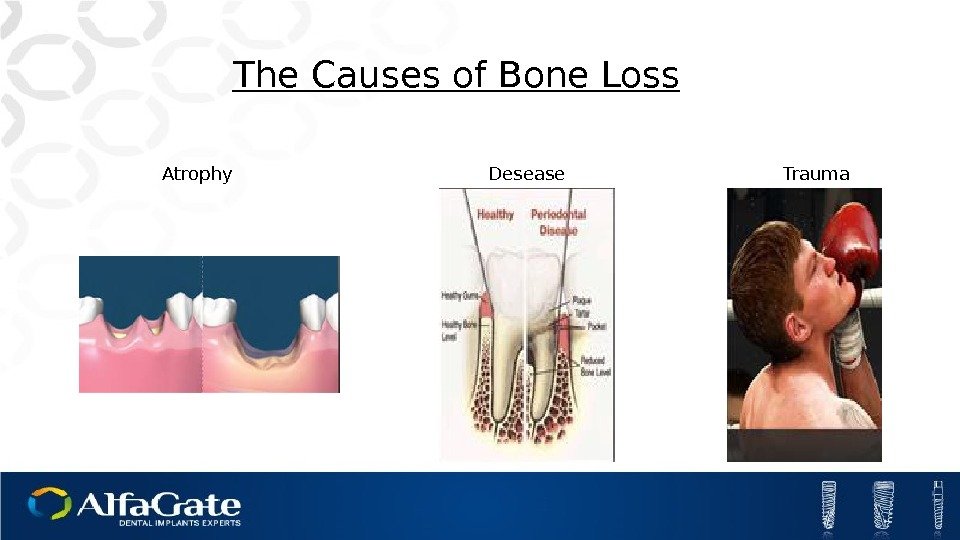
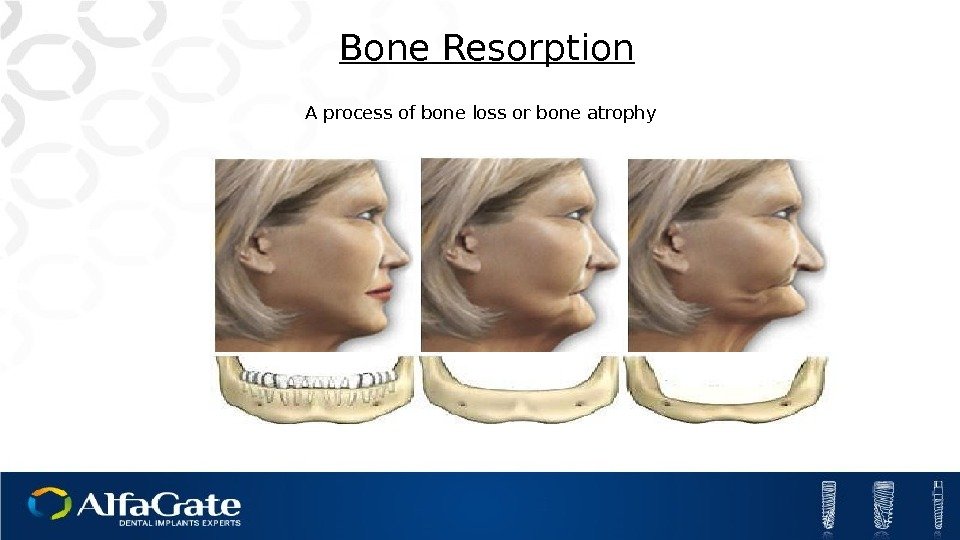
 The Causes of Bone Loss Atrophy Trauma. Desease
The Causes of Bone Loss Atrophy Trauma. Desease
 A process of bone loss or bone atrophy Bone Resorption
A process of bone loss or bone atrophy Bone Resorption
 Numerous studies have shown that implants less than 10 mm in length have diminished survival and success rates compared to implants of 10 mm in length or greater. This “ loss of bone volume width or height” may be the deciding factor for using an implant of less than 10 mm in length.
Numerous studies have shown that implants less than 10 mm in length have diminished survival and success rates compared to implants of 10 mm in length or greater. This “ loss of bone volume width or height” may be the deciding factor for using an implant of less than 10 mm in length.

 BONE GRAFTING
BONE GRAFTING
 Basic Terms
Basic Terms
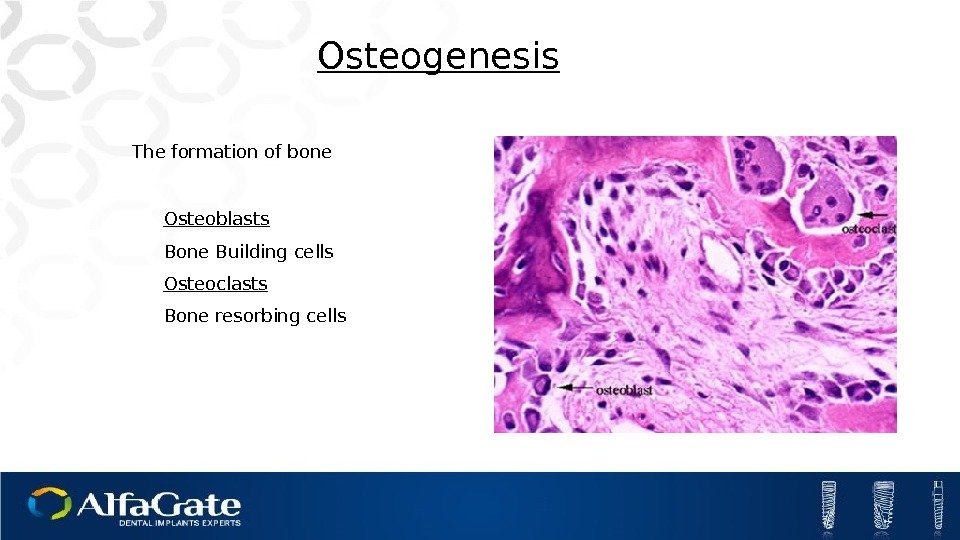
 Osteoblasts Bone Building cells Osteoclasts Bone resorbing cells Osteogenesis The formation of bone
Osteoblasts Bone Building cells Osteoclasts Bone resorbing cells Osteogenesis The formation of bone
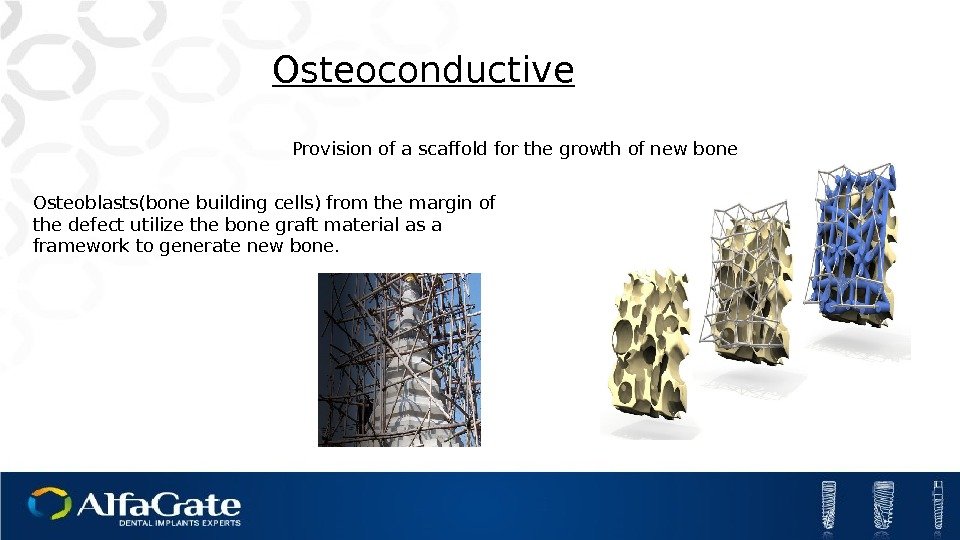
 Provision of a scaffold for the growth of new bone. Osteoconductive Osteoblasts(bone building cells) from the margin of the defect utilize the bone graft material as a framework to generate new bone.
Provision of a scaffold for the growth of new bone. Osteoconductive Osteoblasts(bone building cells) from the margin of the defect utilize the bone graft material as a framework to generate new bone.
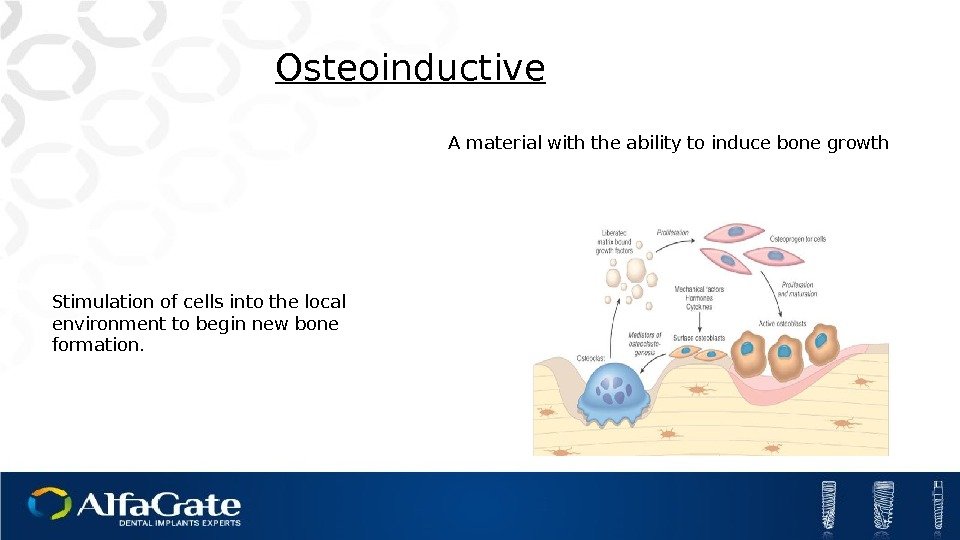
 Stimulation of cells into the local environment to begin new bone formation. Osteoinductive A material with the ability to induce bone growth
Stimulation of cells into the local environment to begin new bone formation. Osteoinductive A material with the ability to induce bone growth
 BONE GRAFT CATEGORIES
BONE GRAFT CATEGORIES
 Autograft Patient Origin Allograft Same Species Origin Xenograft Animal Origin Alloplast Synthetic Origin
Autograft Patient Origin Allograft Same Species Origin Xenograft Animal Origin Alloplast Synthetic Origin
 Bone from the same patient, taken From one site to another site. Patient Origin Autogenous Bone. Autograft
Bone from the same patient, taken From one site to another site. Patient Origin Autogenous Bone. Autograft
 Advantages No risk of transmitting disease Limited risk of graft rejection Osteoconductive Osteoinductive Osteogenic Disadvantages Morbidity-additional surgical site Prolonged operatory time Prolonged healing time Limited quantity that can be harvested Cost
Advantages No risk of transmitting disease Limited risk of graft rejection Osteoconductive Osteoinductive Osteogenic Disadvantages Morbidity-additional surgical site Prolonged operatory time Prolonged healing time Limited quantity that can be harvested Cost
 Tissue graft between individuals of the same species but of non-identical genetics. Allograft Human Cadaver Origin
Tissue graft between individuals of the same species but of non-identical genetics. Allograft Human Cadaver Origin
 Advantages Good mechanical properties Closest product in market to human bone Osteoconductive Osteoinductive? ? ? Disadvantages Risk of viral cross contamination May induce host immune response No repeatability (Differences between samples) Patient reluctance Human cadaver origin
Advantages Good mechanical properties Closest product in market to human bone Osteoconductive Osteoinductive? ? ? Disadvantages Risk of viral cross contamination May induce host immune response No repeatability (Differences between samples) Patient reluctance Human cadaver origin
 Xenograft Tissue graft between individuals of different species. Usually from cows, pigs, horses. • Cows-Bovine • Pigs-Porcine • Horse-Equine Animal Origin
Xenograft Tissue graft between individuals of different species. Usually from cows, pigs, horses. • Cows-Bovine • Pigs-Porcine • Horse-Equine Animal Origin
 Advantages High mechanical properties Large supply Over 20 years of studies Osteoconductive Disadvantages Risk of cross-contamination Difficult to adequately screen Partial resorption Cost
Advantages High mechanical properties Large supply Over 20 years of studies Osteoconductive Disadvantages Risk of cross-contamination Difficult to adequately screen Partial resorption Cost
 Alloplast Graft material from ceramic, coral hydroxyapatite, calcium phosphate, calcium sulfate…. Synthetic origin
Alloplast Graft material from ceramic, coral hydroxyapatite, calcium phosphate, calcium sulfate…. Synthetic origin
 Advantages No risk of disease transmission Unlimited supply Osteoconductive Disadvantages Usually poor mechanical properties Resorption time too fast or too slow Longer healing time and/or lower bone volume obtained
Advantages No risk of disease transmission Unlimited supply Osteoconductive Disadvantages Usually poor mechanical properties Resorption time too fast or too slow Longer healing time and/or lower bone volume obtained
 Bone Grafting Procedure
Bone Grafting Procedure
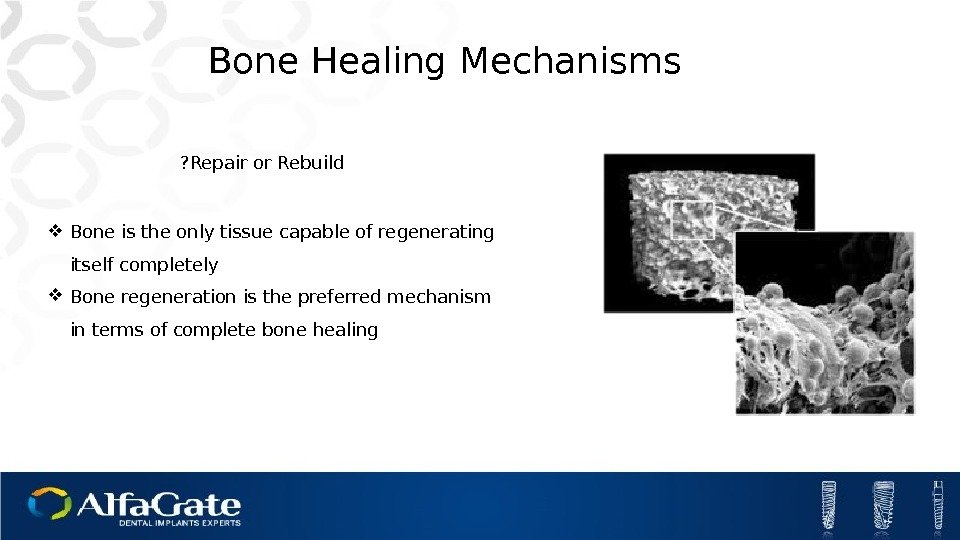
 Bone is the only tissue capable of regenerating itself completely Bone regeneration is the preferred mechanism in terms of complete bone healing Bone Healing Mechanisms Repair or Rebuild?
Bone is the only tissue capable of regenerating itself completely Bone regeneration is the preferred mechanism in terms of complete bone healing Bone Healing Mechanisms Repair or Rebuild?
 Granules Size 5 -1. 0 mm 1. 0 -2. 0 mm Quantity 2 g x 5 catalog No. ALBS ALBL
Granules Size 5 -1. 0 mm 1. 0 -2. 0 mm Quantity 2 g x 5 catalog No. ALBS ALBL
 Bone Grafts: The Ideal Safe and biocompatible Osteoinductive Bioresorbable, enables complete bone regeneration Space maintaining capabilities Easy handling, technique insensitive Shortens procedure time and period to final rehabilitation
Bone Grafts: The Ideal Safe and biocompatible Osteoinductive Bioresorbable, enables complete bone regeneration Space maintaining capabilities Easy handling, technique insensitive Shortens procedure time and period to final rehabilitation
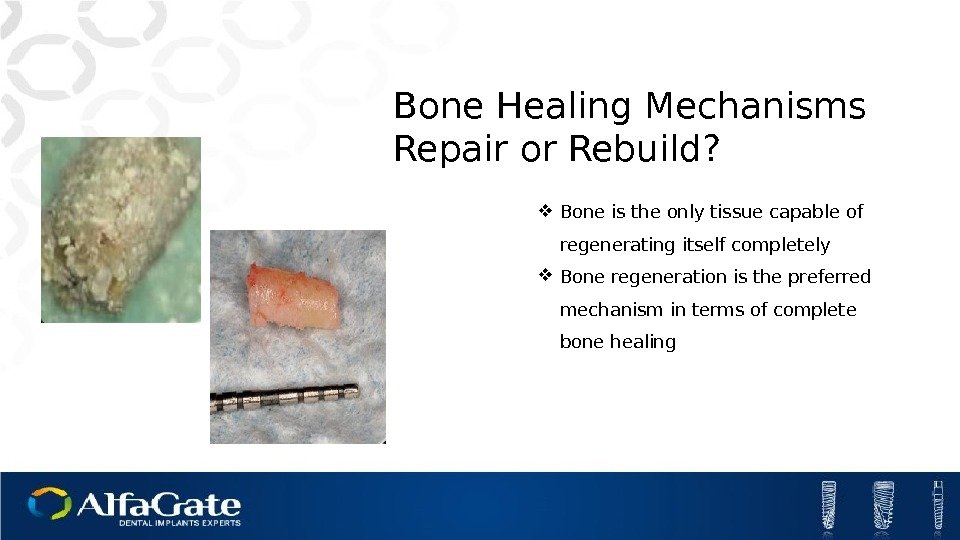
 Bone Healing Mechanisms Repair or Rebuild? Bone is the only tissue capable of regenerating itself completely Bone regeneration is the preferred mechanism in terms of complete bone healing
Bone Healing Mechanisms Repair or Rebuild? Bone is the only tissue capable of regenerating itself completely Bone regeneration is the preferred mechanism in terms of complete bone healing
 Contemporary Augmentations: Products in the market Graft materials do not meet all augmentation requirements Practitioner skills and experience are a major factor for obtaining optimal results of bone grafting procedures
Contemporary Augmentations: Products in the market Graft materials do not meet all augmentation requirements Practitioner skills and experience are a major factor for obtaining optimal results of bone grafting procedures
 Thank you
Thank you

