d4db7614badcf62facc36a918fd42354.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 95
 Oracle Application Server Migrating to OC 4 J Self-Validation Tech Guide 1
Oracle Application Server Migrating to OC 4 J Self-Validation Tech Guide 1
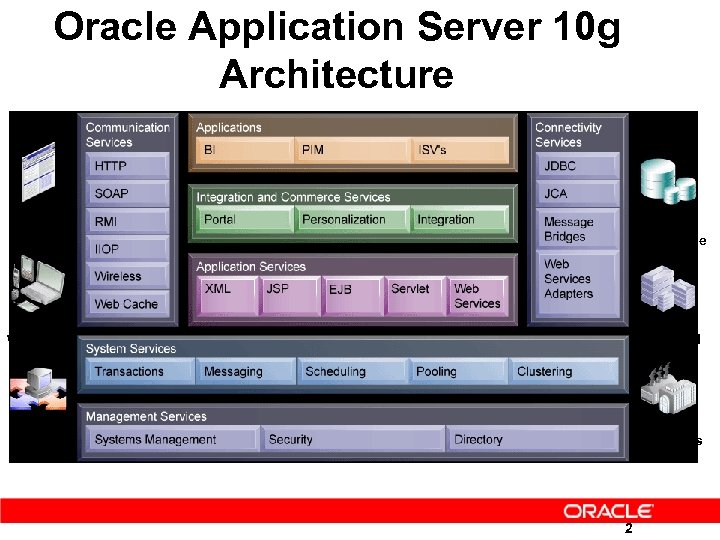 Oracle Application Server 10 g Architecture Browser Oracle DB Non-Oracle Packaged Apps Wireless Web Services B 2 B Apps 2
Oracle Application Server 10 g Architecture Browser Oracle DB Non-Oracle Packaged Apps Wireless Web Services B 2 B Apps 2
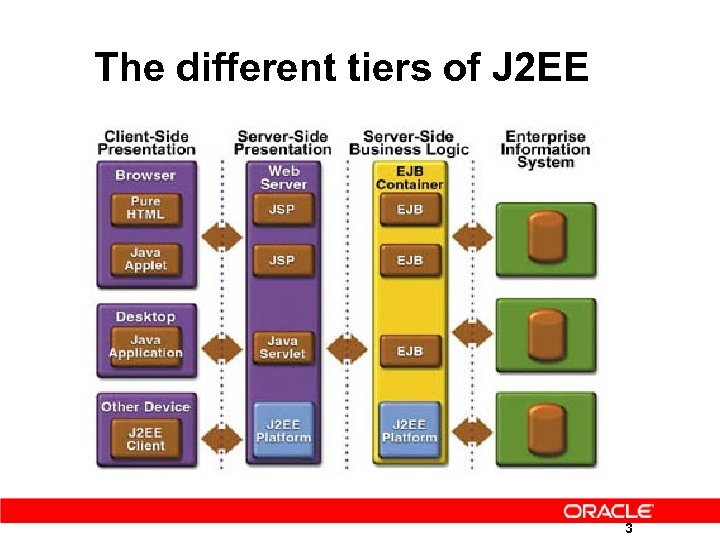 The different tiers of J 2 EE 3
The different tiers of J 2 EE 3
 Four different levels of product support • • OC 4 J Standalone Java Edition Standard Edition Enterprise Edition 4
Four different levels of product support • • OC 4 J Standalone Java Edition Standard Edition Enterprise Edition 4
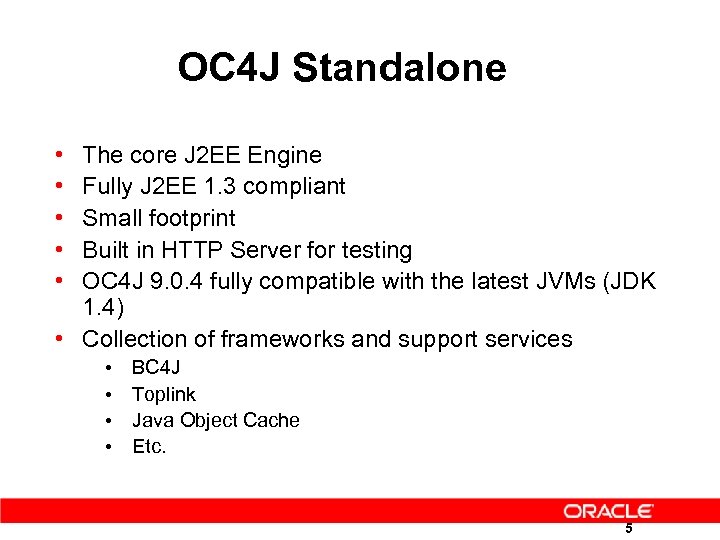 OC 4 J Standalone • • • The core J 2 EE Engine Fully J 2 EE 1. 3 compliant Small footprint Built in HTTP Server for testing OC 4 J 9. 0. 4 fully compatible with the latest JVMs (JDK 1. 4) • Collection of frameworks and support services • • BC 4 J Toplink Java Object Cache Etc. 5
OC 4 J Standalone • • • The core J 2 EE Engine Fully J 2 EE 1. 3 compliant Small footprint Built in HTTP Server for testing OC 4 J 9. 0. 4 fully compatible with the latest JVMs (JDK 1. 4) • Collection of frameworks and support services • • BC 4 J Toplink Java Object Cache Etc. 5
 Java Edition • Adds industry strength to OC 4 J • Secure Apache HTTP Server (1. 3. x) • Oracle Enterprise Manager • File based repository for deploying components across multiple JVMs • File based clustering • Development Tools • JDeveloper • Top. Link 6
Java Edition • Adds industry strength to OC 4 J • Secure Apache HTTP Server (1. 3. x) • Oracle Enterprise Manager • File based repository for deploying components across multiple JVMs • File based clustering • Development Tools • JDeveloper • Top. Link 6
 Standard Edition • Adds manageability • Database Managed Repository for application management • GUI administered clustering and management • Oracle Portal • Includes restricted use of LDAP and webcache • Single Signon 7
Standard Edition • Adds manageability • Database Managed Repository for application management • GUI administered clustering and management • Oracle Portal • Includes restricted use of LDAP and webcache • Single Signon 7
 Enterprise Edition • Adds enterprise features • • HTTP Web Cache Full use of LDAP Oracle Forms and Reports Oracle Business Intelligence tools Wireless (option) Process Connect Identity Management 8
Enterprise Edition • Adds enterprise features • • HTTP Web Cache Full use of LDAP Oracle Forms and Reports Oracle Business Intelligence tools Wireless (option) Process Connect Identity Management 8
 Quick start to Oracle OC 4 J 9
Quick start to Oracle OC 4 J 9
 OC 4 J Overview • • Complete J 2 EE implementation Lightweight & High Performance Small memory footprint XML file based configuration for all aspects of server, web server and applications • Simplified installation, configuration, deployment and administration • Auto deployment and “Hot” deployment of J 2 EE Applications • Clustering, Load balancing and Fail-over of Web & EJB Apps 10
OC 4 J Overview • • Complete J 2 EE implementation Lightweight & High Performance Small memory footprint XML file based configuration for all aspects of server, web server and applications • Simplified installation, configuration, deployment and administration • Auto deployment and “Hot” deployment of J 2 EE Applications • Clustering, Load balancing and Fail-over of Web & EJB Apps 10
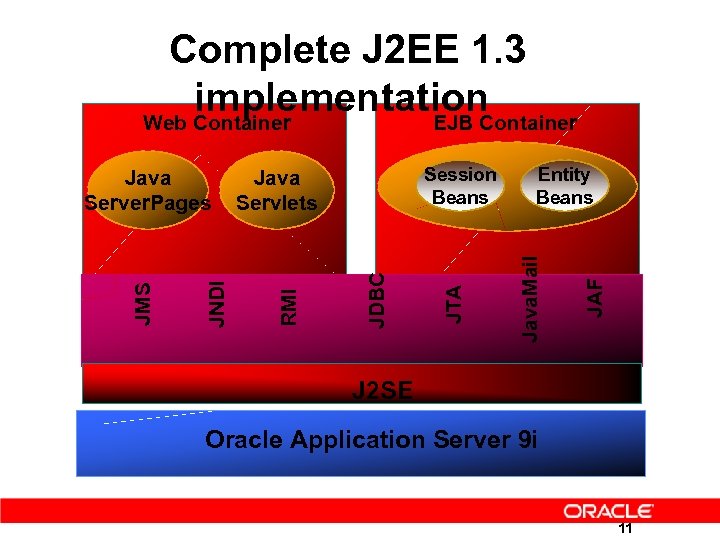 Complete J 2 EE 1. 3 implementation Web Container EJB Container JAF Entity Beans Java. Mail JDBC JTA Session Beans Java Servlets RMI JNDI JMS Java Server. Pages J 2 SE Oracle Application Server 9 i 11
Complete J 2 EE 1. 3 implementation Web Container EJB Container JAF Entity Beans Java. Mail JDBC JTA Session Beans Java Servlets RMI JNDI JMS Java Server. Pages J 2 SE Oracle Application Server 9 i 11
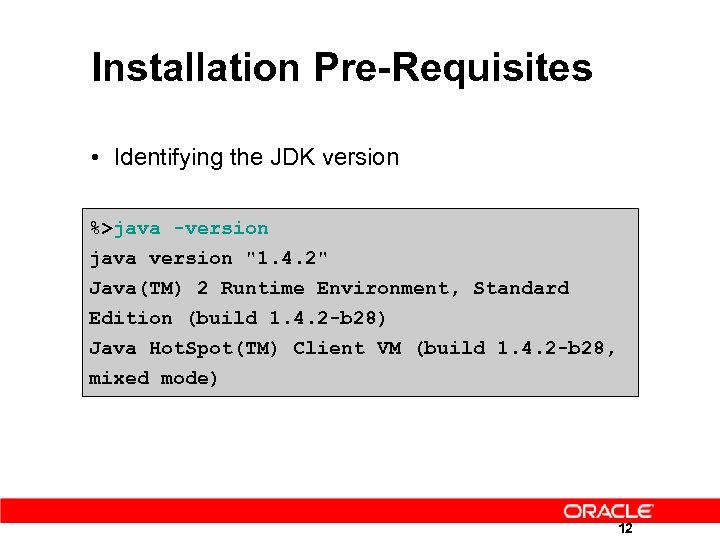 Installation Pre-Requisites • Identifying the JDK version %>java -version java version "1. 4. 2" Java(TM) 2 Runtime Environment, Standard Edition (build 1. 4. 2 -b 28) Java Hot. Spot(TM) Client VM (build 1. 4. 2 -b 28, mixed mode) 12
Installation Pre-Requisites • Identifying the JDK version %>java -version java version "1. 4. 2" Java(TM) 2 Runtime Environment, Standard Edition (build 1. 4. 2 -b 28) Java Hot. Spot(TM) Client VM (build 1. 4. 2 -b 28, mixed mode) 12
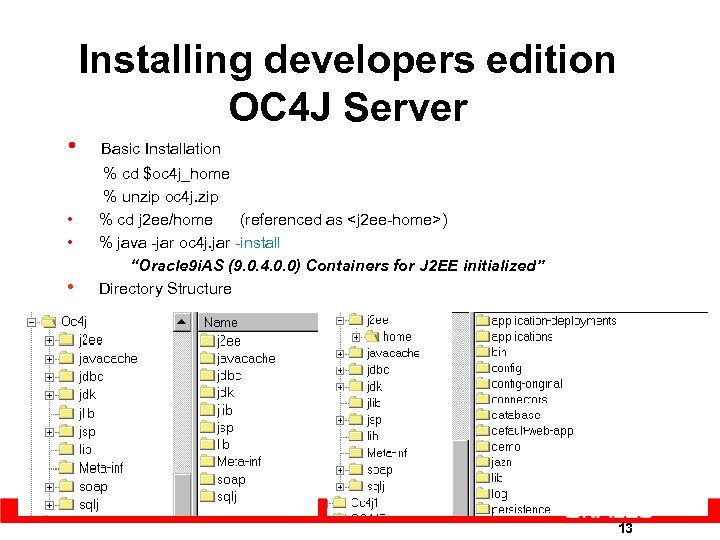 Installing developers edition OC 4 J Server • Basic Installation • • • % cd $oc 4 j_home % unzip oc 4 j. zip % cd j 2 ee/home (referenced as
Installing developers edition OC 4 J Server • Basic Installation • • • % cd $oc 4 j_home % unzip oc 4 j. zip % cd j 2 ee/home (referenced as
 • Starting up OC 4 J Server Startup Commands • % java -jar oc 4 j. jar
• Starting up OC 4 J Server Startup Commands • % java -jar oc 4 j. jar
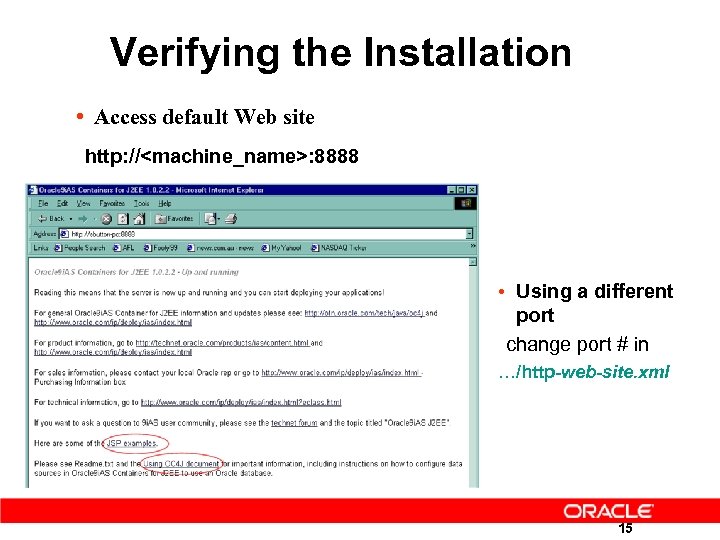 Verifying the Installation • Access default Web site http: //
Verifying the Installation • Access default Web site http: //
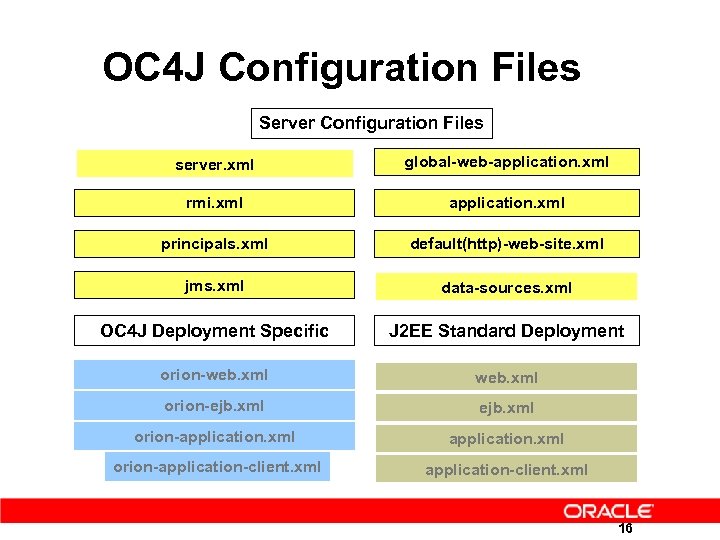 OC 4 J Configuration Files Server Configuration Files server. xml global-web-application. xml rmi. xml application. xml principals. xml default(http)-web-site. xml jms. xml data-sources. xml OC 4 J Deployment Specific J 2 EE Standard Deployment orion-web. xml orion-ejb. xml orion-application-client. xml 16
OC 4 J Configuration Files Server Configuration Files server. xml global-web-application. xml rmi. xml application. xml principals. xml default(http)-web-site. xml jms. xml data-sources. xml OC 4 J Deployment Specific J 2 EE Standard Deployment orion-web. xml orion-ejb. xml orion-application-client. xml 16
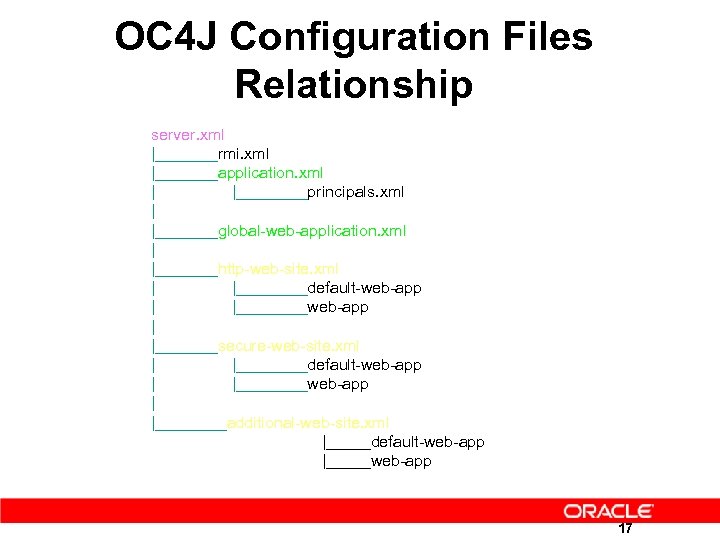 OC 4 J Configuration Files Relationship server. xml |_______rmi. xml |_______application. xml | |____principals. xml | |_______global-web-application. xml | |_______http-web-site. xml | |____default-web-app | |____web-app | |_______secure-web-site. xml | |____default-web-app | |____web-app | |____additional-web-site. xml |_____default-web-app |_____web-app 17
OC 4 J Configuration Files Relationship server. xml |_______rmi. xml |_______application. xml | |____principals. xml | |_______global-web-application. xml | |_______http-web-site. xml | |____default-web-app | |____web-app | |_______secure-web-site. xml | |____default-web-app | |____web-app | |____additional-web-site. xml |_____default-web-app |_____web-app 17
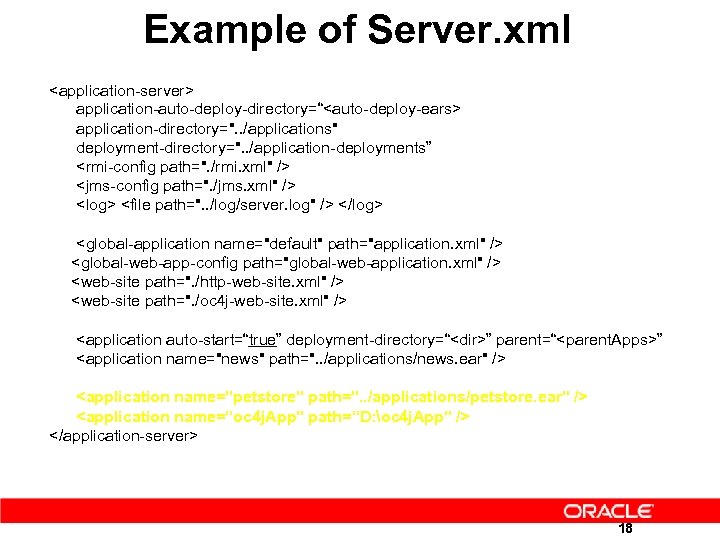 Example of Server. xml
Example of Server. xml
" cluster-island="1" display-name=”
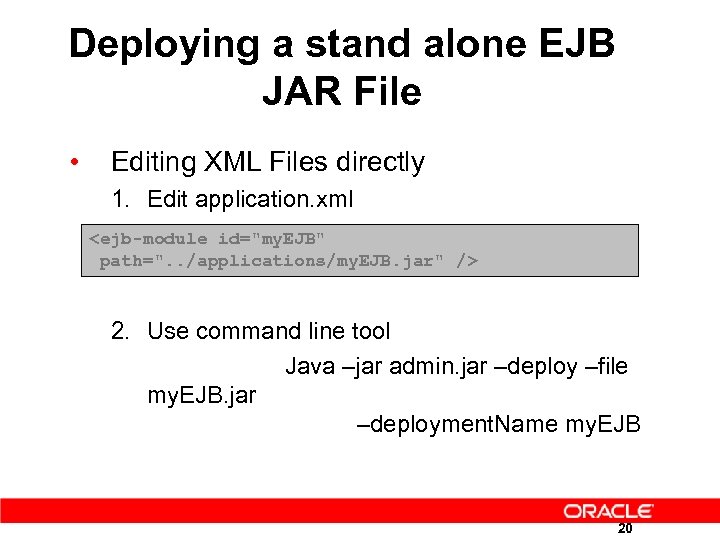 Deploying a stand alone EJB JAR File • Editing XML Files directly 1. Edit application. xml
Deploying a stand alone EJB JAR File • Editing XML Files directly 1. Edit application. xml
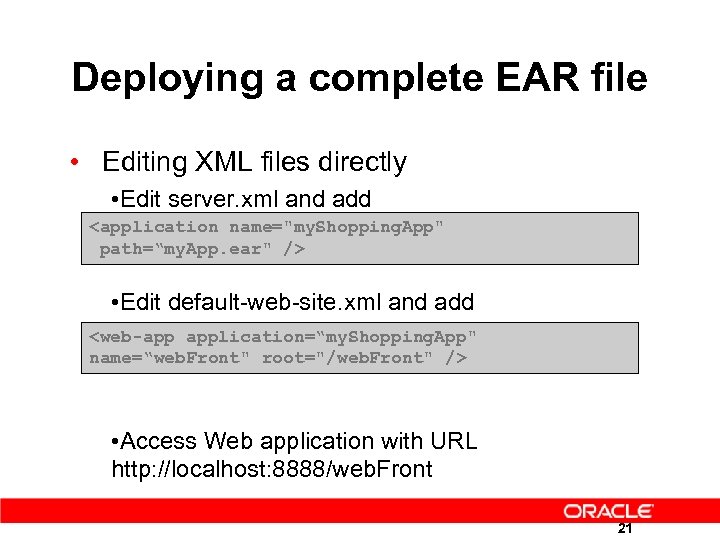 Deploying a complete EAR file • Editing XML files directly • Edit server. xml and add
Deploying a complete EAR file • Editing XML files directly • Edit server. xml and add
 Deploy a complete EAR file • Using admin command line $ java –jar admin. jar -file myapp. ear -deployment. Name my. Shopping. App $ java –jar admin. jar -bind. Web. App my. Shopping. App web. Front /webfront 22
Deploy a complete EAR file • Using admin command line $ java –jar admin. jar -file myapp. ear -deployment. Name my. Shopping. App $ java –jar admin. jar -bind. Web. App my. Shopping. App web. Front /webfront 22
 OC 4 J Java Database Connectivity • Fully implements JDBC 2. 0 specification • Provides Oracle JDBC drivers • Type 2 and Type 4 drivers • Certified with Oracle 8, 8 i, 9 i out of the box • Implements JDBC 2. 0 extensions • Connection pooling, advanced type handling, enhanced result sets, JNDI data sources, X/A support • Certified with Merant Type 4 JDBC drivers • Provides access to non-Oracle data sources such as Informix, Sybase, DB 2, SS 7 23
OC 4 J Java Database Connectivity • Fully implements JDBC 2. 0 specification • Provides Oracle JDBC drivers • Type 2 and Type 4 drivers • Certified with Oracle 8, 8 i, 9 i out of the box • Implements JDBC 2. 0 extensions • Connection pooling, advanced type handling, enhanced result sets, JNDI data sources, X/A support • Certified with Merant Type 4 JDBC drivers • Provides access to non-Oracle data sources such as Informix, Sybase, DB 2, SS 7 23
 Datasources • • Databases & J 2 EE • A persistent store for data • Servlets, JSP, EJB (BMP/CMP) • portable across application servers • No dependency on operational details • Provides logical to physical mappings What is a J 2 EE Datasource • Provide logical definitions of databases • Developer uses logical representation of a database • Deployer maps to physical datasources • Published in JNDI tree • J 2 EE applications use published Data. Source objects • Lookup via JNDI using published name 24
Datasources • • Databases & J 2 EE • A persistent store for data • Servlets, JSP, EJB (BMP/CMP) • portable across application servers • No dependency on operational details • Provides logical to physical mappings What is a J 2 EE Datasource • Provide logical definitions of databases • Developer uses logical representation of a database • Deployer maps to physical datasources • Published in JNDI tree • J 2 EE applications use published Data. Source objects • Lookup via JNDI using published name 24
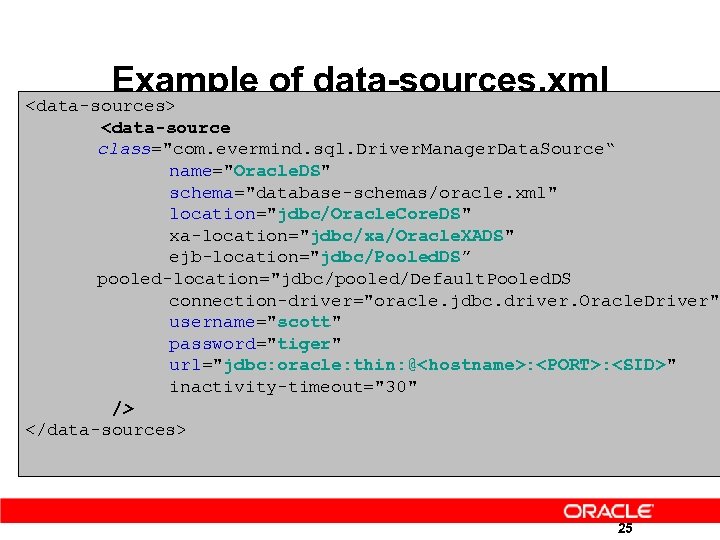 Example of data-sources. xml
Example of data-sources. xml
 orion-ejb-jar. xml • Contains OC 4 J specific application settings for EJBS • Various EJB flags such as copy. By. Value, exclusivewrite-access, isolation-level etc • CMP Entity Bean Persistence to Database mapping • Tables • Fields • Relationships • etc 27
orion-ejb-jar. xml • Contains OC 4 J specific application settings for EJBS • Various EJB flags such as copy. By. Value, exclusivewrite-access, isolation-level etc • CMP Entity Bean Persistence to Database mapping • Tables • Fields • Relationships • etc 27
 orion-web. xml • Contains OC 4 J specific web settings • Must be placed in the same directory as the standard web. xml • Example of settings • • • Clusterable or not development mode (checks for jsp page changes) directory-browsing true/false Local classpath information EJB/Resource reference mappings. . etc. 28
orion-web. xml • Contains OC 4 J specific web settings • Must be placed in the same directory as the standard web. xml • Example of settings • • • Clusterable or not development mode (checks for jsp page changes) directory-browsing true/false Local classpath information EJB/Resource reference mappings. . etc. 28
 jazn-data. xml • Contains security definitions for JAAS/JAZN security provider • Roles • Users • Realms 29
jazn-data. xml • Contains security definitions for JAAS/JAZN security provider • Roles • Users • Realms 29
 The Migration steps 30
The Migration steps 30
 J 2 EE Migration • Can be easy or difficult • Standard J 2 EE App easy • Proprietary difficult • Is a moving target, different versions of the app server from a vendor will have different issues • Web Tier tends to be the easiest to port • EJB tiers can cause issues • Session beans port easily • Entity beans usually require assistance • Transaction boundries may differ • Platform specific code may need to be rewritten • E. g. BEA jolt 31
J 2 EE Migration • Can be easy or difficult • Standard J 2 EE App easy • Proprietary difficult • Is a moving target, different versions of the app server from a vendor will have different issues • Web Tier tends to be the easiest to port • EJB tiers can cause issues • Session beans port easily • Entity beans usually require assistance • Transaction boundries may differ • Platform specific code may need to be rewritten • E. g. BEA jolt 31
 Basic Steps in any migration • Identify differences between the application servers • Remove platform specific proprietary features if possible • E. g. BEA JOLT, IBM Tags etc • Port platform specific deployment descriptors • E. g. weblogic-ejb-jar. xml -> orion-ejb-jar. xml • Port application in tiers starting from data tier (e. g. EJB, webservices) up to client 32
Basic Steps in any migration • Identify differences between the application servers • Remove platform specific proprietary features if possible • E. g. BEA JOLT, IBM Tags etc • Port platform specific deployment descriptors • E. g. weblogic-ejb-jar. xml -> orion-ejb-jar. xml • Port application in tiers starting from data tier (e. g. EJB, webservices) up to client 32
 Step 1 : Convert XML Deployment Descriptor • Standard J 2 EE descriptors need little changes and should port easily • Proprietary J 2 EE descriptors will need rewriting • E. g. weblogic-ejb-jar. xml equivalent in OC 4 J is orion-ejbjar. xml • Definition of whats available in OC 4 J xml files can be obtained online via DTDs or online manuals • http: //xmlns. oracle. com/ias/dtds/orion-ejb-jar. dtd 33
Step 1 : Convert XML Deployment Descriptor • Standard J 2 EE descriptors need little changes and should port easily • Proprietary J 2 EE descriptors will need rewriting • E. g. weblogic-ejb-jar. xml equivalent in OC 4 J is orion-ejbjar. xml • Definition of whats available in OC 4 J xml files can be obtained online via DTDs or online manuals • http: //xmlns. oracle. com/ias/dtds/orion-ejb-jar. dtd 33
 Methods of rewriting XML deployment files • Manual creation of platform specific deployment descriptor files, using vi, emacs, notepad etc • XSLT • We provide sample BEA, JBoss & Borland • Reverse Engineer project into JDeveloper • Let JDeveloper generate deployment descriptors • Use JDeveloper’s deployment descriptor wizards to assist in the authoring of the deployment descriptors 34
Methods of rewriting XML deployment files • Manual creation of platform specific deployment descriptor files, using vi, emacs, notepad etc • XSLT • We provide sample BEA, JBoss & Borland • Reverse Engineer project into JDeveloper • Let JDeveloper generate deployment descriptors • Use JDeveloper’s deployment descriptor wizards to assist in the authoring of the deployment descriptors 34
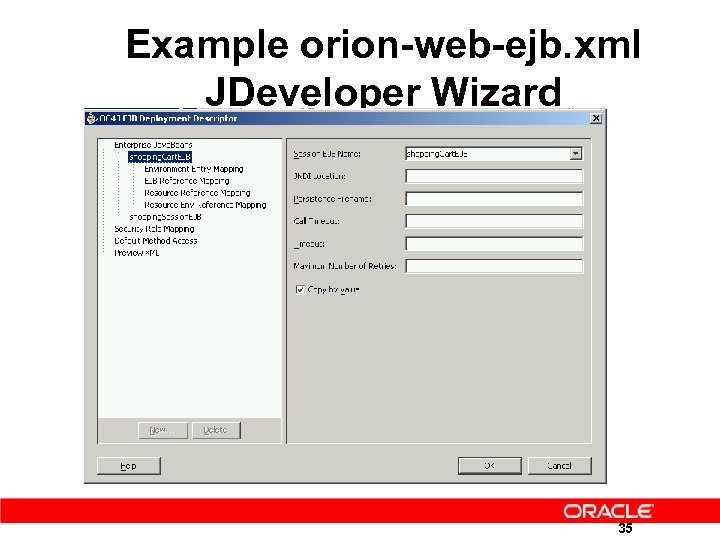 Example orion-web-ejb. xml JDeveloper Wizard 35
Example orion-web-ejb. xml JDeveloper Wizard 35
 Step 2 : Migrate EJB Components • Always migrate data layer first • Usually the most difficult layer to port • Unit Test each EJB as you go along • JDeveloper is able to create test client stubs which may assist in testing EJBS induvidually • EJBQL & Finder queries may be different 36
Step 2 : Migrate EJB Components • Always migrate data layer first • Usually the most difficult layer to port • Unit Test each EJB as you go along • JDeveloper is able to create test client stubs which may assist in testing EJBS induvidually • EJBQL & Finder queries may be different 36
 Step 3 : Migrate Web/Client • Migrate web/client tier • Usually easier than EJB tier • Beware that Oracle OC 4 J doesn’t support client side transactions • JNDI names can be different • Use JDeveloper to browse JNDI tree in OC 4 J • JDEVELOPER IMAGE 37
Step 3 : Migrate Web/Client • Migrate web/client tier • Usually easier than EJB tier • Beware that Oracle OC 4 J doesn’t support client side transactions • JNDI names can be different • Use JDeveloper to browse JNDI tree in OC 4 J • JDEVELOPER IMAGE 37
 Step 4 : Migrate other components • Datasources • JMS Message Queues • JCA Adaptors 38
Step 4 : Migrate other components • Datasources • JMS Message Queues • JCA Adaptors 38
 Step 5 : Implementing Clustering • Options • OC 4 J Standalone does not support clustering • Java Edition supports file based clustering • Oracle Application Server 10 g supports managed Clustering • When deploying an application to a managed cluster you must have the
Step 5 : Implementing Clustering • Options • OC 4 J Standalone does not support clustering • Java Edition supports file based clustering • Oracle Application Server 10 g supports managed Clustering • When deploying an application to a managed cluster you must have the
 Migration in more detail 40
Migration in more detail 40
 Migrating Servlets 41
Migrating Servlets 41
 Migrating Servlets • Migrating servlets to 9 i. AS is usually a smooth & effortless exercise • Typically no modifications are necessary • However if proprietary server extensions have been used then they will almost certainly need to be rewritten. Cont. …. 42
Migrating Servlets • Migrating servlets to 9 i. AS is usually a smooth & effortless exercise • Typically no modifications are necessary • However if proprietary server extensions have been used then they will almost certainly need to be rewritten. Cont. …. 42
 IBM Servlet Migration Issues Websphere has non-standard extensions • Websphere has two mode of deployment • Compatibility Mode: Servlet API 2. 0 and 2. 1 • Compliance Mode : Servlet 2. 2 (partial) • Websphere Studio generated code not portable • Websphere servlet extensions packages • Web Application Deployment • No direct support for war files • custom. servlet file for configuring servlet Cont. …. 43
IBM Servlet Migration Issues Websphere has non-standard extensions • Websphere has two mode of deployment • Compatibility Mode: Servlet API 2. 0 and 2. 1 • Compliance Mode : Servlet 2. 2 (partial) • Websphere Studio generated code not portable • Websphere servlet extensions packages • Web Application Deployment • No direct support for war files • custom. servlet file for configuring servlet Cont. …. 43
 IBM Web. Sphere Extensions to Servlets • Servlet Session Management Package • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. session (replace with J 2 EE javax. servlet. http. Http. Session) • Personalization Package • com. ibm. servlet. personalization (replace with 9 i. AS Personalization ) • Event Manager package • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. event (replace with Servlet 2. 3 API: Servlet. Context. Event, Http. Session. Binding event) • Custom Servlet Filtering package • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. filter (replace with Servlet 2. 3 API: javax. servlet. Filter, Filter. Config) • Servlet Proxy Package • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. request(replace with HTTPServlet Request, use servlet chaining features in Servlet 2. 3 ) • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. response(replace with HTTPServlet Response, use servlet chaining features in Servlet 2. 3 ) Cont…. 44
IBM Web. Sphere Extensions to Servlets • Servlet Session Management Package • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. session (replace with J 2 EE javax. servlet. http. Http. Session) • Personalization Package • com. ibm. servlet. personalization (replace with 9 i. AS Personalization ) • Event Manager package • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. event (replace with Servlet 2. 3 API: Servlet. Context. Event, Http. Session. Binding event) • Custom Servlet Filtering package • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. filter (replace with Servlet 2. 3 API: javax. servlet. Filter, Filter. Config) • Servlet Proxy Package • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. request(replace with HTTPServlet Request, use servlet chaining features in Servlet 2. 3 ) • com. ibm. websphere. servlet. response(replace with HTTPServlet Response, use servlet chaining features in Servlet 2. 3 ) Cont…. 44
 Migrating JSPs 45
Migrating JSPs 45
 Migrating JSPs • Migrating JSPs to 9 i. AS typically is a smooth & effortless exercise • Proprietary tag libraries will need to be ported to either • Oracle proprietory tag libraries • Custom tag library. Tab • Tag Libraries can be migrated with ease • Proprietary extensions may need to be ported • E. g. BEA Weblogic html. Kona 46
Migrating JSPs • Migrating JSPs to 9 i. AS typically is a smooth & effortless exercise • Proprietary tag libraries will need to be ported to either • Oracle proprietory tag libraries • Custom tag library. Tab • Tag Libraries can be migrated with ease • Proprietary extensions may need to be ported • E. g. BEA Weblogic html. Kona 46
 Migrating JSP Custom Tags • Custom tag libraries can be easily deployed on 9 i. AS as part of a Web application • Customer or 3 rd Party Tags can be deployed on 9 i. AS typically with very little changes • Proprietary custom tags to be replaced with equivalent 9 i. AS Custom Tags • E. g. IBM Websphere data tags can partially be replaced by OJSP tags 47
Migrating JSP Custom Tags • Custom tag libraries can be easily deployed on 9 i. AS as part of a Web application • Customer or 3 rd Party Tags can be deployed on 9 i. AS typically with very little changes • Proprietary custom tags to be replaced with equivalent 9 i. AS Custom Tags • E. g. IBM Websphere data tags can partially be replaced by OJSP tags 47
 Using Tag Libraries in OC 4 J • 3 Steps to using tag libraries in OC 4 J • 1. Copy the
Using Tag Libraries in OC 4 J • 3 Steps to using tag libraries in OC 4 J • 1. Copy the
 IBM specific JSP Migration issues • Bean scripting framework(BSF) (Websphere specific ) • Websphere specific Tags and properties • “
IBM specific JSP Migration issues • Bean scripting framework(BSF) (Websphere specific ) • Websphere specific Tags and properties • “
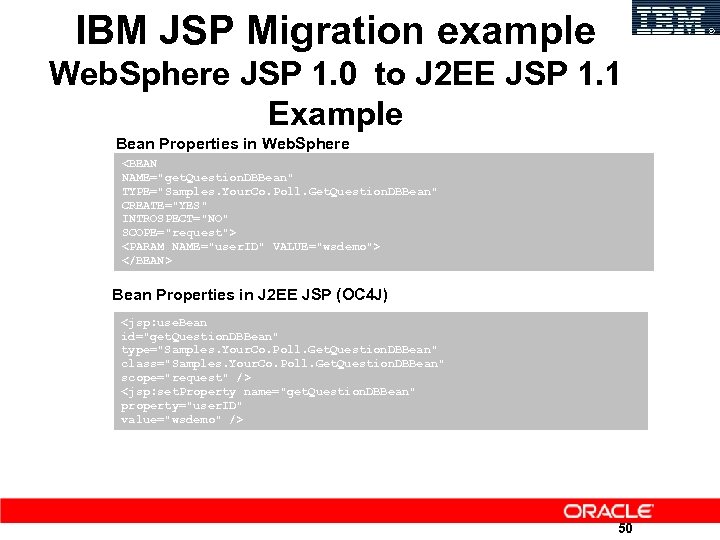 IBM JSP Migration example Web. Sphere JSP 1. 0 to J 2 EE JSP 1. 1 Example Bean Properties in Web. Sphere
IBM JSP Migration example Web. Sphere JSP 1. 0 to J 2 EE JSP 1. 1 Example Bean Properties in Web. Sphere
 Migrating EJBs 51
Migrating EJBs 51
 Migrating EJBs • Migration of EJBs to OC 4 J is typically straightforward • Session Beans migrate easier than Entity beans • Typically little or no code modifications are required • Code modifications often relate to minor JNDI lookup changes • Implementation-specific adaptations for O/R mapping, container class generation, & customization of deployment properties are required 52
Migrating EJBs • Migration of EJBs to OC 4 J is typically straightforward • Session Beans migrate easier than Entity beans • Typically little or no code modifications are required • Code modifications often relate to minor JNDI lookup changes • Implementation-specific adaptations for O/R mapping, container class generation, & customization of deployment properties are required 52
 Migrating EJBs • Standard J 2 EE components and deployment descriptors require almost no modifications • Implementation-specific dependencies require modification • Hard-coded JNDI context access and lookups • Data source JNDI names and lookups • Correct and re-generate the code and EJB archive file as required 53
Migrating EJBs • Standard J 2 EE components and deployment descriptors require almost no modifications • Implementation-specific dependencies require modification • Hard-coded JNDI context access and lookups • Data source JNDI names and lookups • Correct and re-generate the code and EJB archive file as required 53
 Migrating Session Beans • Migration of session beans involves only the generic steps of EJB migration • Session EJBs are much easier to migrate than Entity EJBs since there are no persistencerelated migration issues 54
Migrating Session Beans • Migration of session beans involves only the generic steps of EJB migration • Session EJBs are much easier to migrate than Entity EJBs since there are no persistencerelated migration issues 54
 Migrating Entity Beans • Migration of Entity beans involves the generic steps of EJB migration • Plus • removal of implementation-specific JNDI or Data. Source lookups • Rewriting of specific database deploment descriptors • E. g. weblogic-ejb-jar. xml to orion-ejb-jar. xml • Removal of Proprietary APIs or Flags • Transaction Mgmt, Locking, Caching, … 56
Migrating Entity Beans • Migration of Entity beans involves the generic steps of EJB migration • Plus • removal of implementation-specific JNDI or Data. Source lookups • Rewriting of specific database deploment descriptors • E. g. weblogic-ejb-jar. xml to orion-ejb-jar. xml • Removal of Proprietary APIs or Flags • Transaction Mgmt, Locking, Caching, … 56
 Migrating CMP Entity Beans • O/R mapping definitions are vendor dependent, require re-generation • E. g. weblogic-ejb-jar. xml, weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar*. xml • Use xslt transformers to give you a head start • Check XML DTD & Documentation for options available • Data. Source for persistence to be configured for OC 4 J • BEA Web. Logic-specific container stub & skeleton classes need to be removed • OC 4 J will generate the appropriate equivalent stub & skeleton classes 58
Migrating CMP Entity Beans • O/R mapping definitions are vendor dependent, require re-generation • E. g. weblogic-ejb-jar. xml, weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar*. xml • Use xslt transformers to give you a head start • Check XML DTD & Documentation for options available • Data. Source for persistence to be configured for OC 4 J • BEA Web. Logic-specific container stub & skeleton classes need to be removed • OC 4 J will generate the appropriate equivalent stub & skeleton classes 58
 Transactions • OC 4 J (9. 0. 4) does not support client side transactions • Need to delegate transaction to middle tier, prehaps a façade • BEA & IBM support distributed transactions across multiple JVMs • Presently OC 4 J does not support this • Planned for a release post 10 g 59
Transactions • OC 4 J (9. 0. 4) does not support client side transactions • Need to delegate transaction to middle tier, prehaps a façade • BEA & IBM support distributed transactions across multiple JVMs • Presently OC 4 J does not support this • Planned for a release post 10 g 59
 Migrating CMP Entity Beans • EJB CMP/CMT Transaction management is different • BEA has Read-Commited with versioning • OC 4 J has this only with Toplink as DAO • Some differences in CMR • Compound Keys are dealt with slightly differently • Workarounds including using ejb. Create() and ejb. Post. Create() 60
Migrating CMP Entity Beans • EJB CMP/CMT Transaction management is different • BEA has Read-Commited with versioning • OC 4 J has this only with Toplink as DAO • Some differences in CMR • Compound Keys are dealt with slightly differently • Workarounds including using ejb. Create() and ejb. Post. Create() 60
 EJBs need recompilation in following cases • if EJB uses javax. jts. User. Transaction • replace it with javax. transaction. User. Transaction • If EJB uses get. Caller. Identity() and is. Caller. In. Role(Identity) methods • replace with get. Caller. Principal() and is. Callerin. Role(String role. Name) respectively • CMP-EJBs require recompilation • return value of ejb. Create(. . . )is different in EJB 1. 0 and 1. 1 • interface methods like ejb. Create etc. have different signatures 61
EJBs need recompilation in following cases • if EJB uses javax. jts. User. Transaction • replace it with javax. transaction. User. Transaction • If EJB uses get. Caller. Identity() and is. Caller. In. Role(Identity) methods • replace with get. Caller. Principal() and is. Callerin. Role(String role. Name) respectively • CMP-EJBs require recompilation • return value of ejb. Create(. . . )is different in EJB 1. 0 and 1. 1 • interface methods like ejb. Create etc. have different signatures 61
 Migrating CMP Entity Beans • Standalone OC 4 J can’t yet use Oracle Sequence number generator to generate Primary Keys • Workarounds include : • Using Toplink as the CMP Engine • Coding specific ejb. Create() methods 62
Migrating CMP Entity Beans • Standalone OC 4 J can’t yet use Oracle Sequence number generator to generate Primary Keys • Workarounds include : • Using Toplink as the CMP Engine • Coding specific ejb. Create() methods 62
 Finder Methods • Standard finder methods are automatically generated in OC 4 J, these do not need to be regenerated • Finder methods in WLS 5. 1 use WLQL (Web. Logic Query Language), a proprietary query language for specifying selection criteria • These need to be rewritten • OC 4 J uses standard SQL WHERE clauses for specifying selection criteria or EJB-QL • Some vendors have extended EJB-QL, these changes need to be addressed • E. g. BEA support Order by 63
Finder Methods • Standard finder methods are automatically generated in OC 4 J, these do not need to be regenerated • Finder methods in WLS 5. 1 use WLQL (Web. Logic Query Language), a proprietary query language for specifying selection criteria • These need to be rewritten • OC 4 J uses standard SQL WHERE clauses for specifying selection criteria or EJB-QL • Some vendors have extended EJB-QL, these changes need to be addressed • E. g. BEA support Order by 63
 IBM EJBs need recompilation • Websphere requires every CMP Entity. Bean define
IBM EJBs need recompilation • Websphere requires every CMP Entity. Bean define
 Classloader issues • Can occur at any tier of the application • Common clashes are different versions of XML parsers • Use OC 4 J Parent classloader architecture to overcome this • E. g. adding
Classloader issues • Can occur at any tier of the application • Common clashes are different versions of XML parsers • Use OC 4 J Parent classloader architecture to overcome this • E. g. adding
 JNDI Issues • In OC 4 J JNDI is rooted at the application level not at the Server level • Can be solved in some cases by the use of the
JNDI Issues • In OC 4 J JNDI is rooted at the application level not at the Server level • Can be solved in some cases by the use of the
 Implementing Startup classes • Many application servers support startup classes • OC 4 J 10 g onwards support startup classes • Steps • Create a startup class which implements OC 4 JStartup interface • Modify server. xml • Ensure class is in a jar file and present in the
Implementing Startup classes • Many application servers support startup classes • OC 4 J 10 g onwards support startup classes • Steps • Create a startup class which implements OC 4 JStartup interface • Modify server. xml • Ensure class is in a jar file and present in the
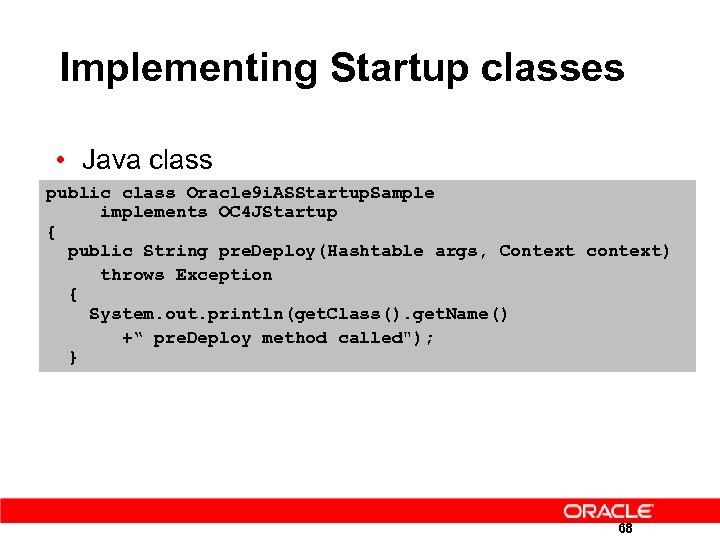 Implementing Startup classes • Java class public class Oracle 9 i. ASStartup. Sample implements OC 4 JStartup { public String pre. Deploy(Hashtable args, Context context) throws Exception { System. out. println(get. Class(). get. Name() +“ pre. Deploy method called"); } 68
Implementing Startup classes • Java class public class Oracle 9 i. ASStartup. Sample implements OC 4 JStartup { public String pre. Deploy(Hashtable args, Context context) throws Exception { System. out. println(get. Class(). get. Name() +“ pre. Deploy method called"); } 68
 JDBC Datasources Migration 70
JDBC Datasources Migration 70
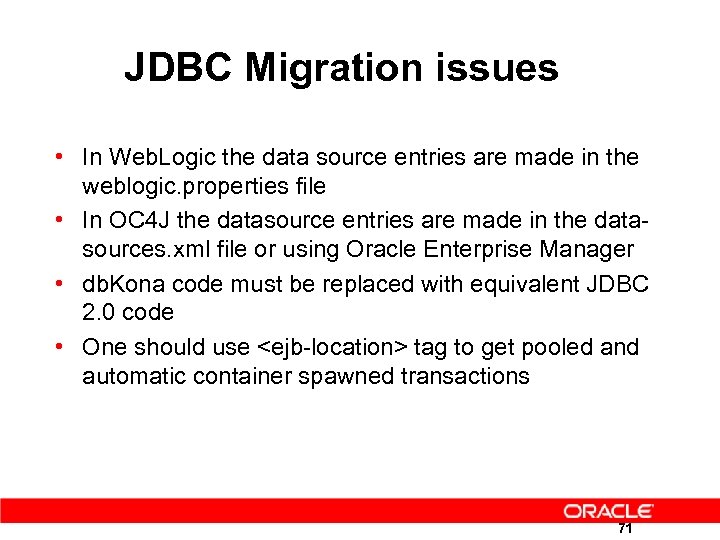 JDBC Migration issues • In Web. Logic the data source entries are made in the weblogic. properties file • In OC 4 J the datasource entries are made in the datasources. xml file or using Oracle Enterprise Manager • db. Kona code must be replaced with equivalent JDBC 2. 0 code • One should use
JDBC Migration issues • In Web. Logic the data source entries are made in the weblogic. properties file • In OC 4 J the datasource entries are made in the datasources. xml file or using Oracle Enterprise Manager • db. Kona code must be replaced with equivalent JDBC 2. 0 code • One should use
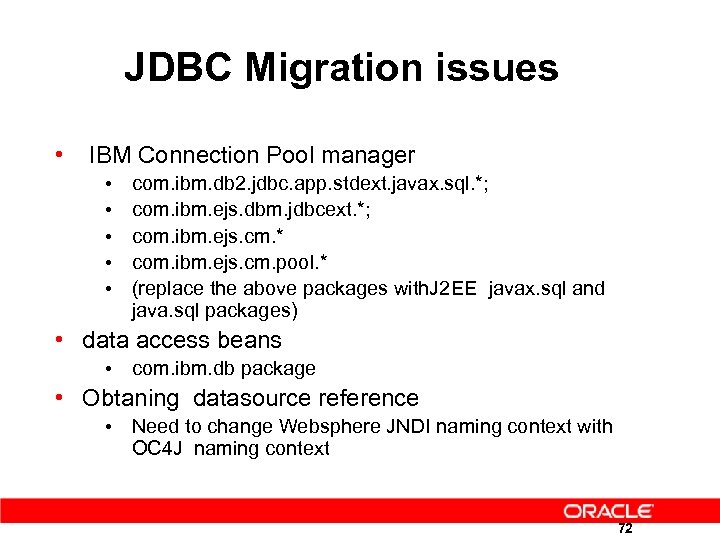 JDBC Migration issues • IBM Connection Pool manager • • • com. ibm. db 2. jdbc. app. stdext. javax. sql. *; com. ibm. ejs. dbm. jdbcext. *; com. ibm. ejs. cm. * com. ibm. ejs. cm. pool. * (replace the above packages with. J 2 EE javax. sql and java. sql packages) • data access beans • com. ibm. db package • Obtaning datasource reference • Need to change Websphere JNDI naming context with OC 4 J naming context 72
JDBC Migration issues • IBM Connection Pool manager • • • com. ibm. db 2. jdbc. app. stdext. javax. sql. *; com. ibm. ejs. dbm. jdbcext. *; com. ibm. ejs. cm. * com. ibm. ejs. cm. pool. * (replace the above packages with. J 2 EE javax. sql and java. sql packages) • data access beans • com. ibm. db package • Obtaning datasource reference • Need to change Websphere JNDI naming context with OC 4 J naming context 72
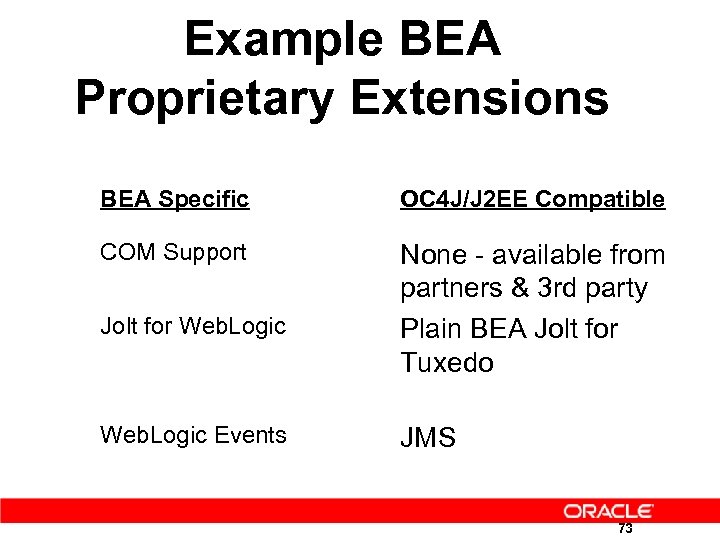 Example BEA Proprietary Extensions BEA Specific OC 4 J/J 2 EE Compatible COM Support None - available from partners & 3 rd party Plain BEA Jolt for Tuxedo Jolt for Web. Logic Events JMS 73
Example BEA Proprietary Extensions BEA Specific OC 4 J/J 2 EE Compatible COM Support None - available from partners & 3 rd party Plain BEA Jolt for Tuxedo Jolt for Web. Logic Events JMS 73
 Proprietary Hints and Tips • Migration hints and tips document • Separate MS-Word documents with hints and tips for popular J 2 EE application servers 74
Proprietary Hints and Tips • Migration hints and tips document • Separate MS-Word documents with hints and tips for popular J 2 EE application servers 74
 Clustering and Deployment 75
Clustering and Deployment 75
 Deployment is easy • Standalone OC 4 J • Edit XML Files directly • Use java –jar admin. jar utility • Using Enterprise Manager • Select OC 4 J Instance • Then select Deploy EAR, or WAR 76
Deployment is easy • Standalone OC 4 J • Edit XML Files directly • Use java –jar admin. jar utility • Using Enterprise Manager • Select OC 4 J Instance • Then select Deploy EAR, or WAR 76
 Clustering Web Applications • For clustered web solutions ensure • web. xml has
Clustering Web Applications • For clustered web solutions ensure • web. xml has
 Clustering EJB applications • OC 4 J can cluster • stateful and Stateless session beans • Three types of replication • • JVM Termination replication End of Call Replication Stateful session context replication Set using replication attribute of the
Clustering EJB applications • OC 4 J can cluster • stateful and Stateless session beans • Three types of replication • • JVM Termination replication End of Call Replication Stateful session context replication Set using replication attribute of the
 CORBA Migration 79
CORBA Migration 79
 CORBA Security & TX Series OC 4 J has no direct support for the following • No support for CORBA in OC 4 J • OC 4 J 9. 0. 3 onwards has support for calling EJBs using IIOP • CORBA model for security is not supported • TX series based code not directly supported • CICS TP Monitor • ENCINA TP Monitor 80
CORBA Security & TX Series OC 4 J has no direct support for the following • No support for CORBA in OC 4 J • OC 4 J 9. 0. 3 onwards has support for calling EJBs using IIOP • CORBA model for security is not supported • TX series based code not directly supported • CICS TP Monitor • ENCINA TP Monitor 80
 JDeveloper 10 g • Since Oracle Jdeveloper 9 i we provides an IDE that facilitates • code changes (refactoring, source control etc) • fine-tuning and rapid-deployment of the applications to OC 4 J • Wizard based generation of generic and specific XML files 81
JDeveloper 10 g • Since Oracle Jdeveloper 9 i we provides an IDE that facilitates • code changes (refactoring, source control etc) • fine-tuning and rapid-deployment of the applications to OC 4 J • Wizard based generation of generic and specific XML files 81
 Example Migration 82
Example Migration 82
 Download Page : BEA Developer Center • Requirement : Weblogic 8. 1 installed • http: //developer. bea. com/code/wls. jsp • Download Post. Card Demo • This application uses CMP EJB and Servlets 83
Download Page : BEA Developer Center • Requirement : Weblogic 8. 1 installed • http: //developer. bea. com/code/wls. jsp • Download Post. Card Demo • This application uses CMP EJB and Servlets 83
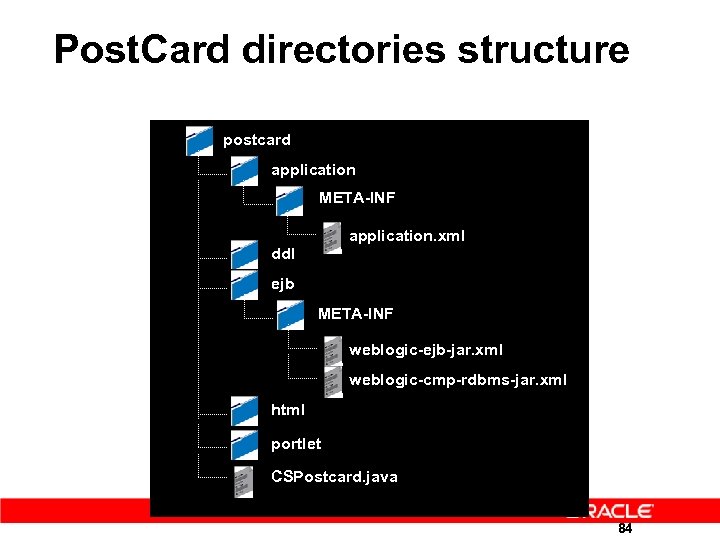 Post. Card directories structure postcard application META-INF application. xml ddl ejb META-INF weblogic-ejb-jar. xml weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar. xml html portlet CSPostcard. java 84
Post. Card directories structure postcard application META-INF application. xml ddl ejb META-INF weblogic-ejb-jar. xml weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar. xml html portlet CSPostcard. java 84
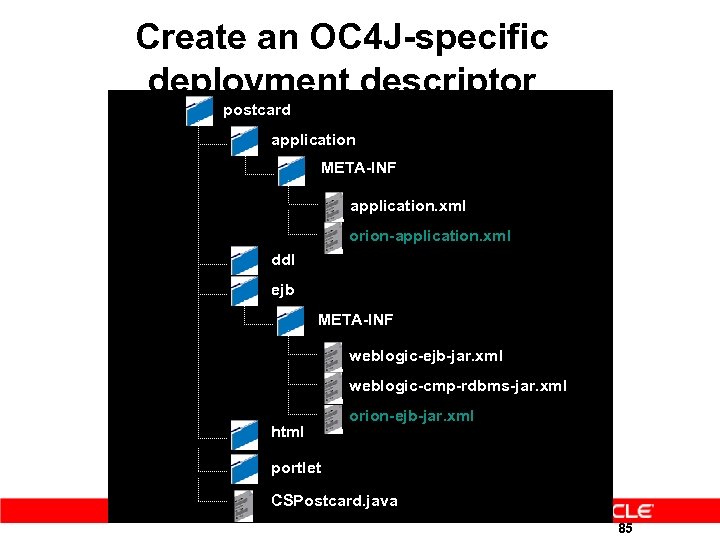 Create an OC 4 J-specific deployment descriptor postcard application META-INF application. xml orion-application. xml ddl ejb META-INF weblogic-ejb-jar. xml weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar. xml html orion-ejb-jar. xml portlet CSPostcard. java 85
Create an OC 4 J-specific deployment descriptor postcard application META-INF application. xml orion-application. xml ddl ejb META-INF weblogic-ejb-jar. xml weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar. xml html orion-ejb-jar. xml portlet CSPostcard. java 85
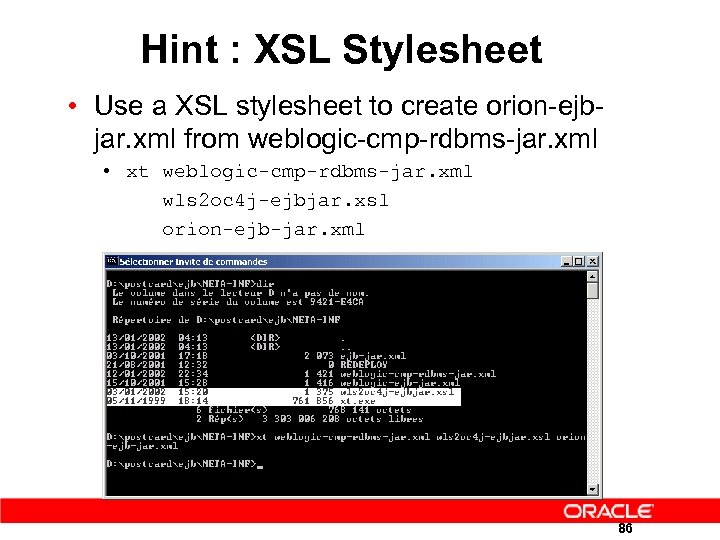 Hint : XSL Stylesheet • Use a XSL stylesheet to create orion-ejbjar. xml from weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar. xml • xt weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar. xml wls 2 oc 4 j-ejbjar. xsl orion-ejb-jar. xml 86
Hint : XSL Stylesheet • Use a XSL stylesheet to create orion-ejbjar. xml from weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar. xml • xt weblogic-cmp-rdbms-jar. xml wls 2 oc 4 j-ejbjar. xsl orion-ejb-jar. xml 86
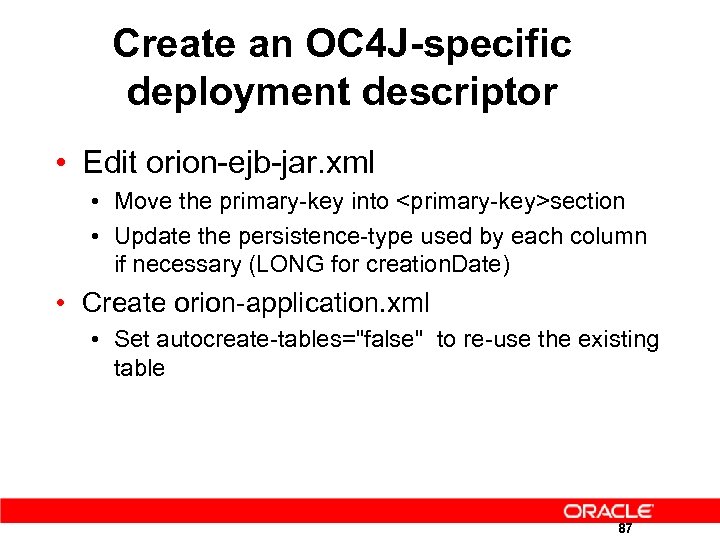 Create an OC 4 J-specific deployment descriptor • Edit orion-ejb-jar. xml • Move the primary-key into
Create an OC 4 J-specific deployment descriptor • Edit orion-ejb-jar. xml • Move the primary-key into
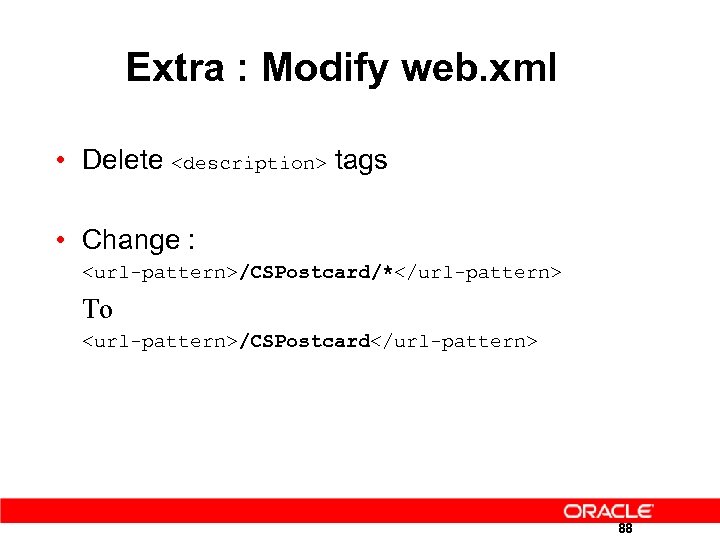 Extra : Modify web. xml • Delete
Extra : Modify web. xml • Delete
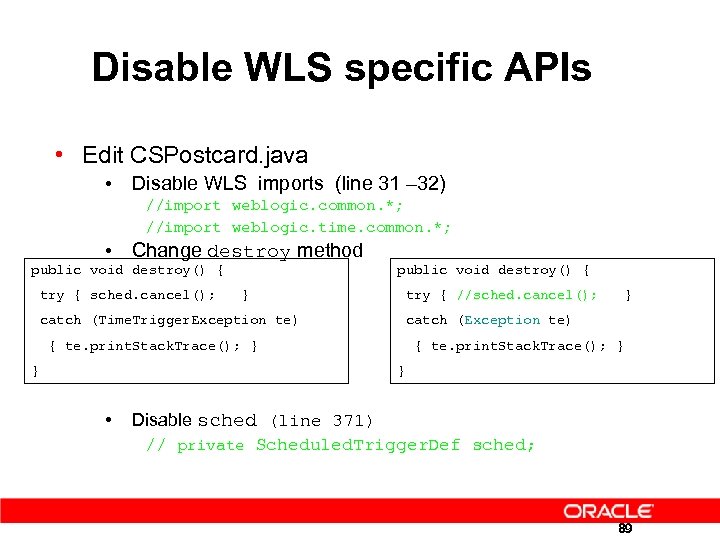 Disable WLS specific APIs • Edit CSPostcard. java • Disable WLS imports (line 31 – 32) //import weblogic. common. *; //import weblogic. time. common. *; • Change destroy method public void destroy() { try { sched. cancel(); } try { //sched. cancel(); } catch (Time. Trigger. Exception te) catch (Exception te) { te. print. Stack. Trace(); } } } • Disable sched (line 371) // private Scheduled. Trigger. Def sched; 89
Disable WLS specific APIs • Edit CSPostcard. java • Disable WLS imports (line 31 – 32) //import weblogic. common. *; //import weblogic. time. common. *; • Change destroy method public void destroy() { try { sched. cancel(); } try { //sched. cancel(); } catch (Time. Trigger. Exception te) catch (Exception te) { te. print. Stack. Trace(); } } } • Disable sched (line 371) // private Scheduled. Trigger. Def sched; 89
 Create datasource
Create datasource
 Create EAR • Edit setup. bat and set the correct environment variables • Run setup. bat • Run install. bat 91
Create EAR • Edit setup. bat and set the correct environment variables • Run setup. bat • Run install. bat 91
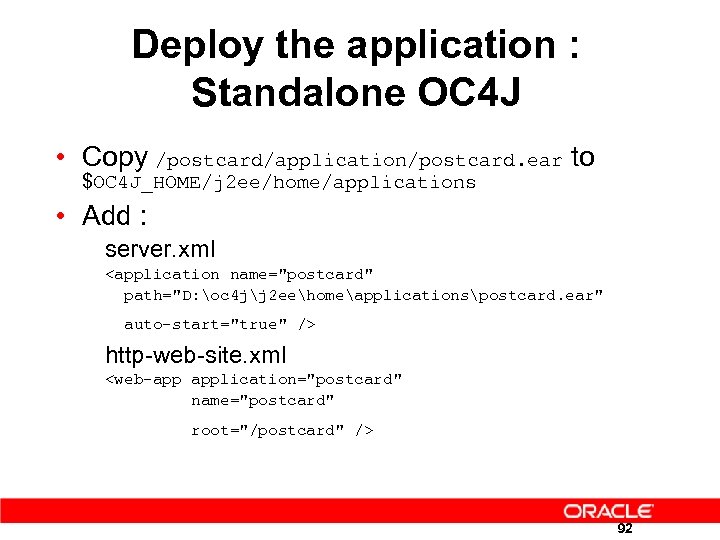 Deploy the application : Standalone OC 4 J • Copy /postcard/application/postcard. ear to $OC 4 J_HOME/j 2 ee/home/applications • Add : server. xml
Deploy the application : Standalone OC 4 J • Copy /postcard/application/postcard. ear to $OC 4 J_HOME/j 2 ee/home/applications • Add : server. xml
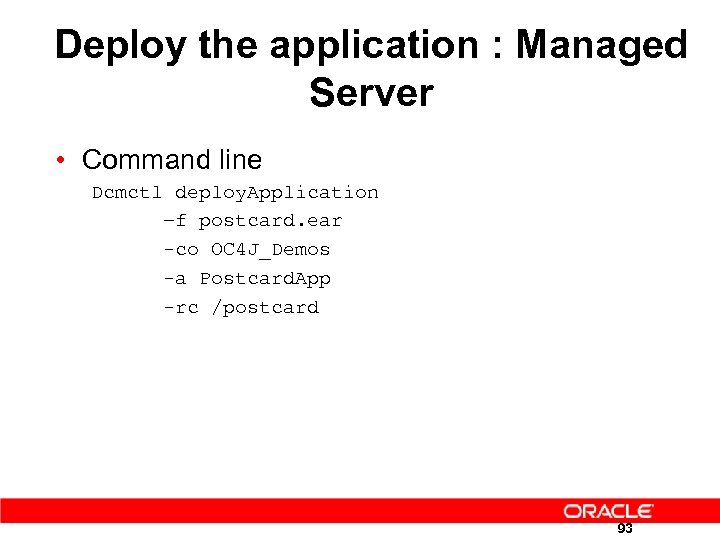 Deploy the application : Managed Server • Command line Dcmctl deploy. Application –f postcard. ear -co OC 4 J_Demos -a Postcard. App -rc /postcard 93
Deploy the application : Managed Server • Command line Dcmctl deploy. Application –f postcard. ear -co OC 4 J_Demos -a Postcard. App -rc /postcard 93
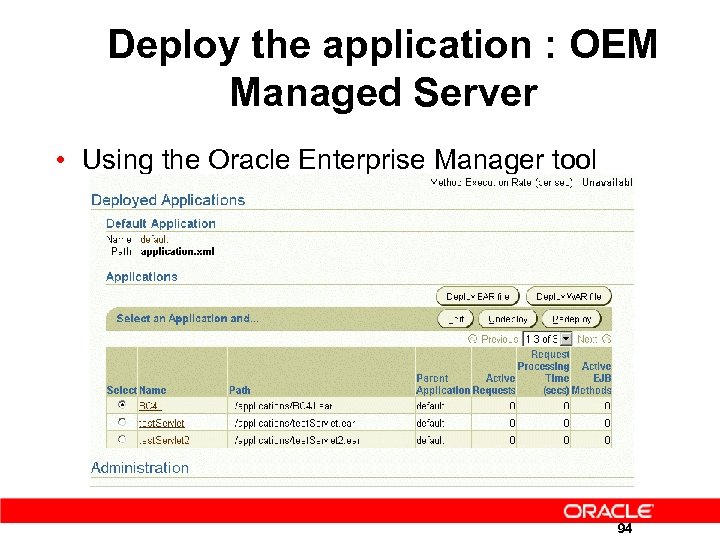 Deploy the application : OEM Managed Server • Using the Oracle Enterprise Manager tool 94
Deploy the application : OEM Managed Server • Using the Oracle Enterprise Manager tool 94
 Deploy the application as usual • Go to http: //localhost: 8888/postcard/CSPostcard_ send. html • Check the file orion-ejb-jar. xml in applicationdeployments/postcard/ejb_postcard. jar directory and make sure that we have :
Deploy the application as usual • Go to http: //localhost: 8888/postcard/CSPostcard_ send. html • Check the file orion-ejb-jar. xml in applicationdeployments/postcard/ejb_postcard. jar directory and make sure that we have :
 Next Steps 1 - Getting Software 2 – Tech Migration 96
Next Steps 1 - Getting Software 2 – Tech Migration 96
 Resources & Contacts • Get Product Info & Downloads • http: //www. oracle. com/technology/tech/java/oc 4 j/index. html • Get Validation Assistance from Oracle • No fees for OPN Partners • Email request to: ptshelp_ww@oracle. com 97
Resources & Contacts • Get Product Info & Downloads • http: //www. oracle. com/technology/tech/java/oc 4 j/index. html • Get Validation Assistance from Oracle • No fees for OPN Partners • Email request to: ptshelp_ww@oracle. com 97
 Q & A 98
Q & A 98


