2f964b8943d9b2ddad2836d3b63fde9b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Option Strategies
Option Strategies
 Definitions • In the money An option is in-the-money when there would be profit in exercising it immediately • Out of the money Out-of-the-money when it would be worthless if exercised immediately.
Definitions • In the money An option is in-the-money when there would be profit in exercising it immediately • Out of the money Out-of-the-money when it would be worthless if exercised immediately.
 Definitions The option price, or premium, can be considered as the sum of two specific elements: intrinsic value and time value The intrinsic value of an option is the amount an option holder can realise by exercising the option immediately. Intrinsic value is always positive or zero. An out-of-the-money option has zero intrinsic value
Definitions The option price, or premium, can be considered as the sum of two specific elements: intrinsic value and time value The intrinsic value of an option is the amount an option holder can realise by exercising the option immediately. Intrinsic value is always positive or zero. An out-of-the-money option has zero intrinsic value
 Definitions Bearish Market: Market in which prices are generally declining and the underlying sentiment reinforces that decline. Bullish Market: Rising market, or a market in which further price increases are expected , due to strong demand. Stagnated Market in which neither increases or decreases are to be expected
Definitions Bearish Market: Market in which prices are generally declining and the underlying sentiment reinforces that decline. Bullish Market: Rising market, or a market in which further price increases are expected , due to strong demand. Stagnated Market in which neither increases or decreases are to be expected
 Definitions • The time value of an option is the value over and above intrinsic value that the market places on the option. It can be considered as the value of the continuing exposure to the movement in the underlying product price that the option provides. The price that the market puts on this time value depends on a number of factors: time to expiry, volatility of the underlying product price, risk free interest rates and expected dividends.
Definitions • The time value of an option is the value over and above intrinsic value that the market places on the option. It can be considered as the value of the continuing exposure to the movement in the underlying product price that the option provides. The price that the market puts on this time value depends on a number of factors: time to expiry, volatility of the underlying product price, risk free interest rates and expected dividends.
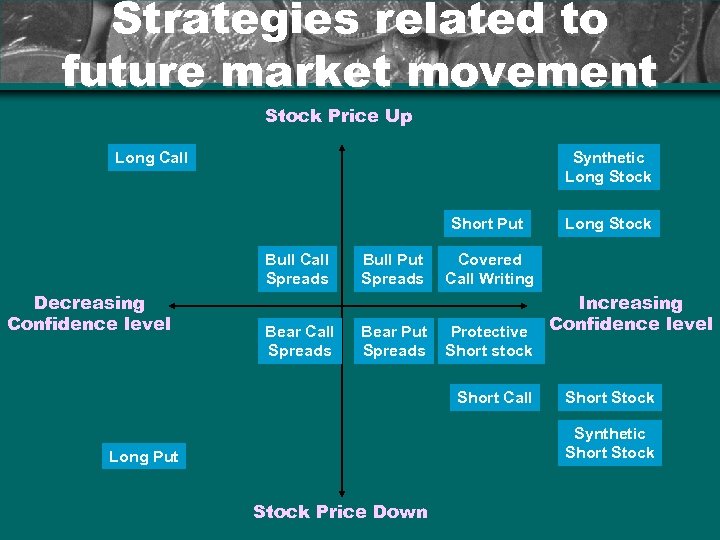 Strategies related to future market movement Stock Price Up Long Call Synthetic Long Stock Short Put Bull Call Spreads Decreasing Confidence level Bear Call Spreads Bull Put Spreads Bear Put Spreads Long Stock Covered Call Writing Protective Short stock Short Call Increasing Confidence level Short Stock Synthetic Short Stock Long Put Stock Price Down
Strategies related to future market movement Stock Price Up Long Call Synthetic Long Stock Short Put Bull Call Spreads Decreasing Confidence level Bear Call Spreads Bull Put Spreads Bear Put Spreads Long Stock Covered Call Writing Protective Short stock Short Call Increasing Confidence level Short Stock Synthetic Short Stock Long Put Stock Price Down
 Strategies related to future market Volatility
Strategies related to future market Volatility
 Option Strategies Single Option Strategy: • Short Call • Short Put • Long Call • Long Put
Option Strategies Single Option Strategy: • Short Call • Short Put • Long Call • Long Put
 Short Call An option strategy whereby a person sells (shorts) a Call option When to Use: If you firmly believe the market is not going up. Sell out-of-the-money (higher strike) options if you are only some what convinced; sell at-the-money options if you are very confident the market will stagnate or fall. If you doubt market will stagnate, sell in-the-money options for maximum profit
Short Call An option strategy whereby a person sells (shorts) a Call option When to Use: If you firmly believe the market is not going up. Sell out-of-the-money (higher strike) options if you are only some what convinced; sell at-the-money options if you are very confident the market will stagnate or fall. If you doubt market will stagnate, sell in-the-money options for maximum profit
 Short Call Profit: Limited to the premium received from selling the call. Loss: Unlimited in a rising market. Break-even: reached when the underlying rises above the strike price, by the same amount as the premium received from selling the call
Short Call Profit: Limited to the premium received from selling the call. Loss: Unlimited in a rising market. Break-even: reached when the underlying rises above the strike price, by the same amount as the premium received from selling the call
 Short Put An option strategy whereby a person sells (shorts) a put option When to use: If you firmly believe the market is not going down. Sell out-of-the-money (lower strike) options if you are only somewhat convinced; sell at-the-money options if you are very confident the market will stagnate or rise. If you doubt market will stagnate, sell in-the-money options for maximum profit.
Short Put An option strategy whereby a person sells (shorts) a put option When to use: If you firmly believe the market is not going down. Sell out-of-the-money (lower strike) options if you are only somewhat convinced; sell at-the-money options if you are very confident the market will stagnate or rise. If you doubt market will stagnate, sell in-the-money options for maximum profit.
 Short Put Profit possibilities: Limited to premium received Loss possibilities: Unlimited in a falling market Break-even: When the price underlying falls below the strike price by the same amount as the premium
Short Put Profit possibilities: Limited to premium received Loss possibilities: Unlimited in a falling market Break-even: When the price underlying falls below the strike price by the same amount as the premium
 Long Call Buy a call with an exercise price of (A). A When to Use: When you are very bullish on the market. The more bullish you are, the more out-of-the-money (higher) should be the option you buy. No other positions gives you as much leverage advantage in a rising market ( with limited downside risk).
Long Call Buy a call with an exercise price of (A). A When to Use: When you are very bullish on the market. The more bullish you are, the more out-of-the-money (higher) should be the option you buy. No other positions gives you as much leverage advantage in a rising market ( with limited downside risk).
 Long Call Profit possibilities: Unlimited in a rising market Loss possibilities Limited to the initial premium. Break-even Reached when the underlying rises above the strike price, by the same amount as the premium paid to establish the position.
Long Call Profit possibilities: Unlimited in a rising market Loss possibilities Limited to the initial premium. Break-even Reached when the underlying rises above the strike price, by the same amount as the premium paid to establish the position.
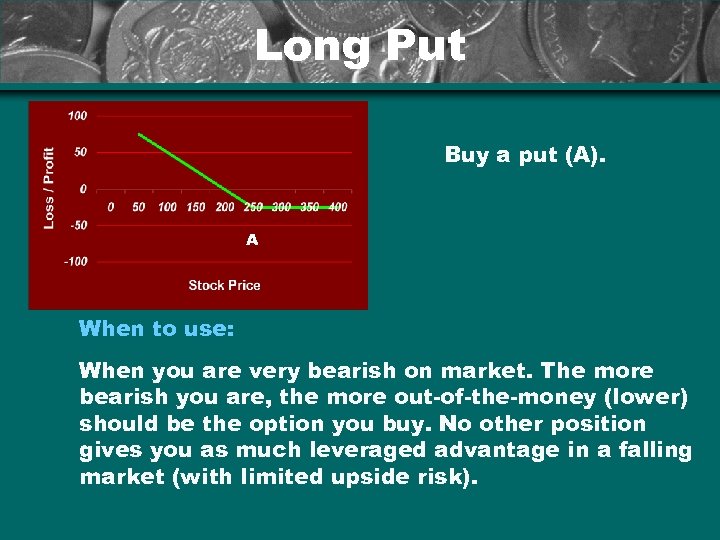 Long Put Buy a put (A). A When to use: When you are very bearish on market. The more bearish you are, the more out-of-the-money (lower) should be the option you buy. No other position gives you as much leveraged advantage in a falling market (with limited upside risk).
Long Put Buy a put (A). A When to use: When you are very bearish on market. The more bearish you are, the more out-of-the-money (lower) should be the option you buy. No other position gives you as much leveraged advantage in a falling market (with limited upside risk).
 Long Put Profit possibilities Unlimited in a falling market Loss possibilities Limited to the initial premium paid Break-even Reached when the underlying falls below the strike price A by the same amount as the premium paid to establish the position
Long Put Profit possibilities Unlimited in a falling market Loss possibilities Limited to the initial premium paid Break-even Reached when the underlying falls below the strike price A by the same amount as the premium paid to establish the position
 Option Strategies General Combination Strategies: – Long Straddle – Short Straddle – Long Strangle – Short Strangle
Option Strategies General Combination Strategies: – Long Straddle – Short Straddle – Long Strangle – Short Strangle
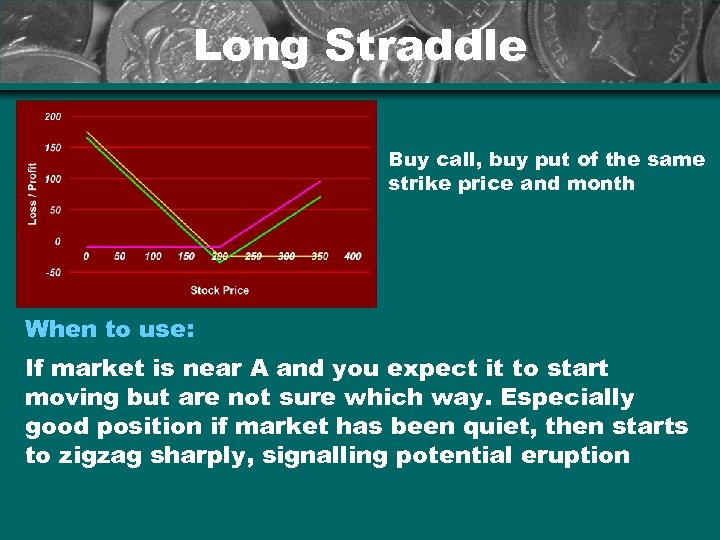 Long Straddle Buy call, buy put of the same strike price and month When to use: If market is near A and you expect it to start moving but are not sure which way. Especially good position if market has been quiet, then starts to zigzag sharply, signalling potential eruption
Long Straddle Buy call, buy put of the same strike price and month When to use: If market is near A and you expect it to start moving but are not sure which way. Especially good position if market has been quiet, then starts to zigzag sharply, signalling potential eruption
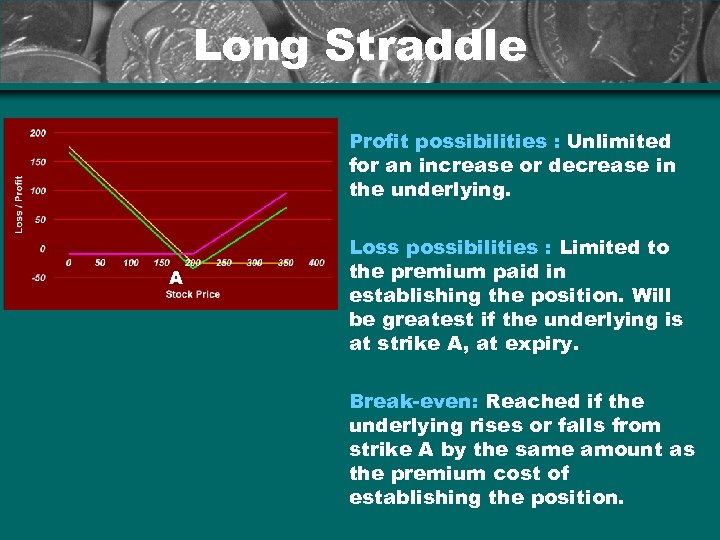 Long Straddle Profit possibilities : Unlimited for an increase or decrease in the underlying. A Loss possibilities : Limited to the premium paid in establishing the position. Will be greatest if the underlying is at strike A, at expiry. Break-even: Reached if the underlying rises or falls from strike A by the same amount as the premium cost of establishing the position.
Long Straddle Profit possibilities : Unlimited for an increase or decrease in the underlying. A Loss possibilities : Limited to the premium paid in establishing the position. Will be greatest if the underlying is at strike A, at expiry. Break-even: Reached if the underlying rises or falls from strike A by the same amount as the premium cost of establishing the position.
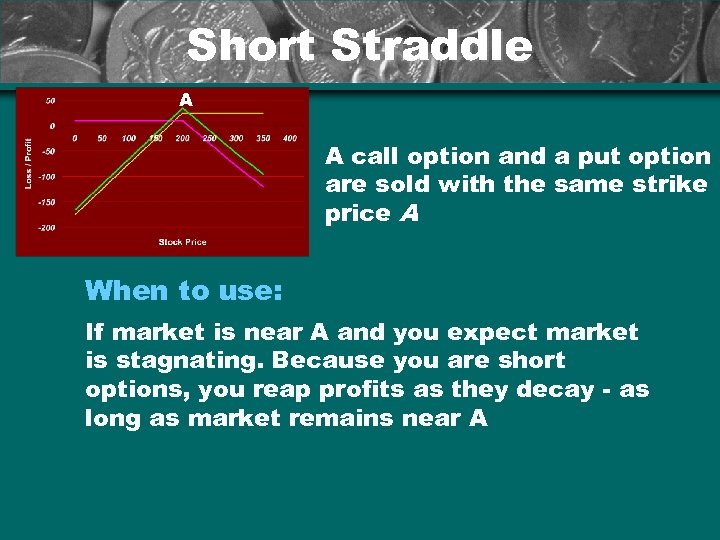 Short Straddle A A call option and a put option are sold with the same strike price A When to use: If market is near A and you expect market is stagnating. Because you are short options, you reap profits as they decay - as long as market remains near A
Short Straddle A A call option and a put option are sold with the same strike price A When to use: If market is near A and you expect market is stagnating. Because you are short options, you reap profits as they decay - as long as market remains near A
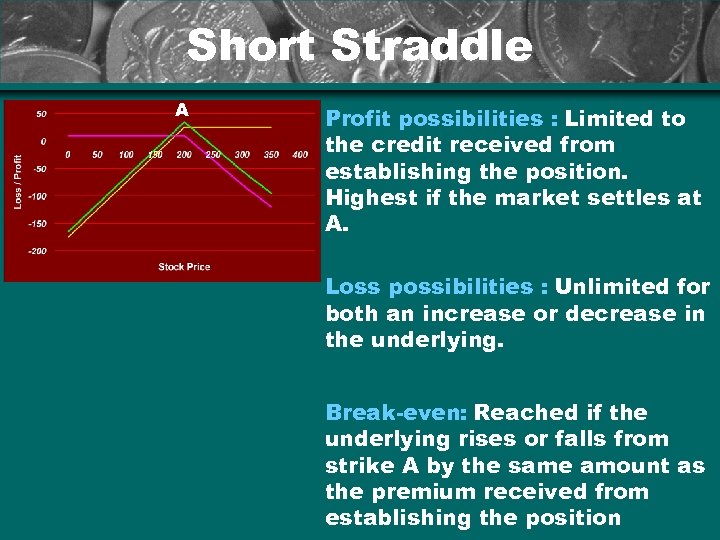 Short Straddle A Profit possibilities : Limited to the credit received from establishing the position. Highest if the market settles at A. Loss possibilities : Unlimited for both an increase or decrease in the underlying. Break-even: Reached if the underlying rises or falls from strike A by the same amount as the premium received from establishing the position
Short Straddle A Profit possibilities : Limited to the credit received from establishing the position. Highest if the market settles at A. Loss possibilities : Unlimited for both an increase or decrease in the underlying. Break-even: Reached if the underlying rises or falls from strike A by the same amount as the premium received from establishing the position
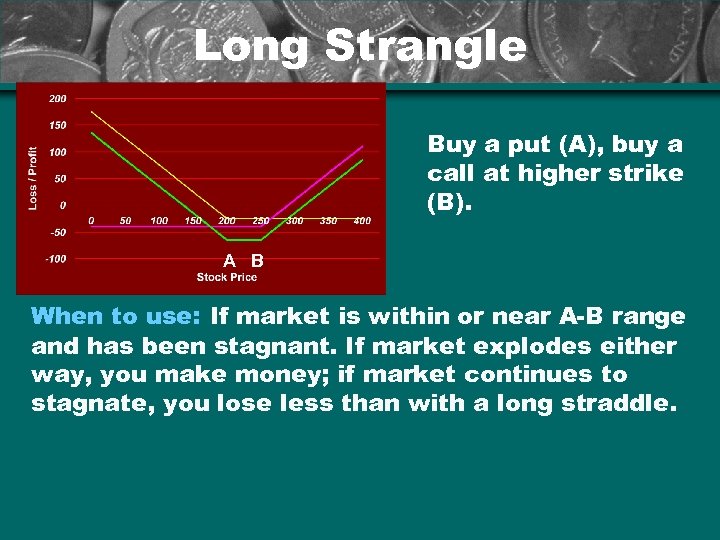 Long Strangle Buy a put (A), buy a call at higher strike (B). A B When to use: If market is within or near A-B range and has been stagnant. If market explodes either way, you make money; if market continues to stagnate, you lose less than with a long straddle.
Long Strangle Buy a put (A), buy a call at higher strike (B). A B When to use: If market is within or near A-B range and has been stagnant. If market explodes either way, you make money; if market continues to stagnate, you lose less than with a long straddle.
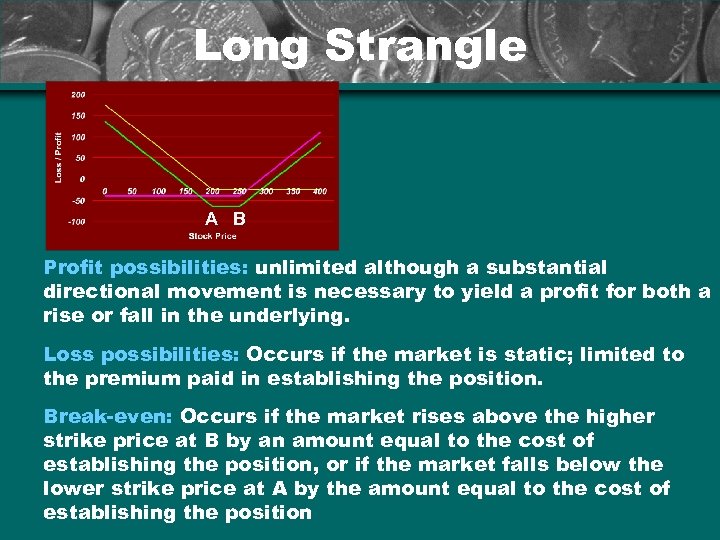 Long Strangle A B Profit possibilities: unlimited although a substantial directional movement is necessary to yield a profit for both a rise or fall in the underlying. Loss possibilities: Occurs if the market is static; limited to the premium paid in establishing the position. Break-even: Occurs if the market rises above the higher strike price at B by an amount equal to the cost of establishing the position, or if the market falls below the lower strike price at A by the amount equal to the cost of establishing the position
Long Strangle A B Profit possibilities: unlimited although a substantial directional movement is necessary to yield a profit for both a rise or fall in the underlying. Loss possibilities: Occurs if the market is static; limited to the premium paid in establishing the position. Break-even: Occurs if the market rises above the higher strike price at B by an amount equal to the cost of establishing the position, or if the market falls below the lower strike price at A by the amount equal to the cost of establishing the position
 Short Strangle A B Sell a put (A), sell call at higher strike (B) When to use: If market is within or near A-B range and, though active, is quieting down. If market goes into stagnation, you make money; if it continues to be active, you have a bit less risk than with a short straddle
Short Strangle A B Sell a put (A), sell call at higher strike (B) When to use: If market is within or near A-B range and, though active, is quieting down. If market goes into stagnation, you make money; if it continues to be active, you have a bit less risk than with a short straddle
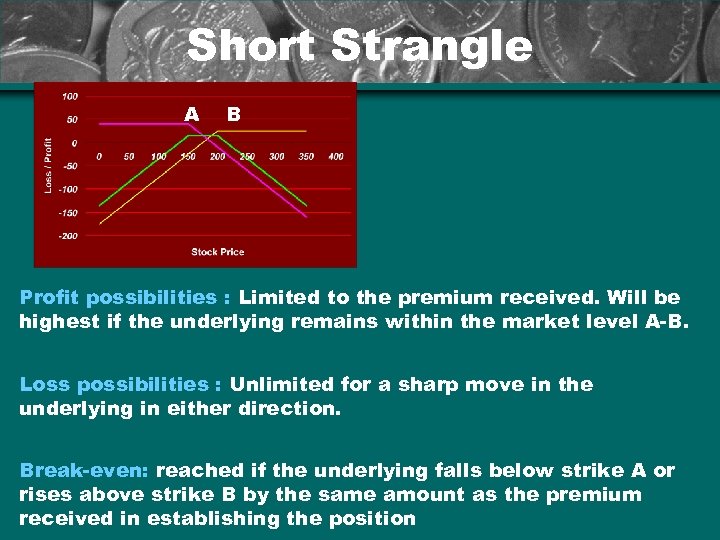 Short Strangle A B Profit possibilities : Limited to the premium received. Will be highest if the underlying remains within the market level A-B. Loss possibilities : Unlimited for a sharp move in the underlying in either direction. Break-even: reached if the underlying falls below strike A or rises above strike B by the same amount as the premium received in establishing the position
Short Strangle A B Profit possibilities : Limited to the premium received. Will be highest if the underlying remains within the market level A-B. Loss possibilities : Unlimited for a sharp move in the underlying in either direction. Break-even: reached if the underlying falls below strike A or rises above strike B by the same amount as the premium received in establishing the position
 Option Strategies Vertical Spread This strategy involves buying and selling option contracts of the same type, same number, same expiry month but different strike prices. If the spread portfolio consists of buying lower strike price options and selling higher strike price options, it is referred to as a Bull Spread. Following the same logic, if the spread portfolio consists of buying higher strike price options and selling lower strike price options, it is referred to as a Bear Spread. – Bull Spread – Bear Spread
Option Strategies Vertical Spread This strategy involves buying and selling option contracts of the same type, same number, same expiry month but different strike prices. If the spread portfolio consists of buying lower strike price options and selling higher strike price options, it is referred to as a Bull Spread. Following the same logic, if the spread portfolio consists of buying higher strike price options and selling lower strike price options, it is referred to as a Bear Spread. – Bull Spread – Bear Spread
 Bull Call Spread B Buy a call (A), sell call at higher strike (B). A When to use: If you think the market will go up somewhat or at least is a bit more likely to rise than fall. Good position if you want to be in the market but are unsure of bullish expectations.
Bull Call Spread B Buy a call (A), sell call at higher strike (B). A When to use: If you think the market will go up somewhat or at least is a bit more likely to rise than fall. Good position if you want to be in the market but are unsure of bullish expectations.
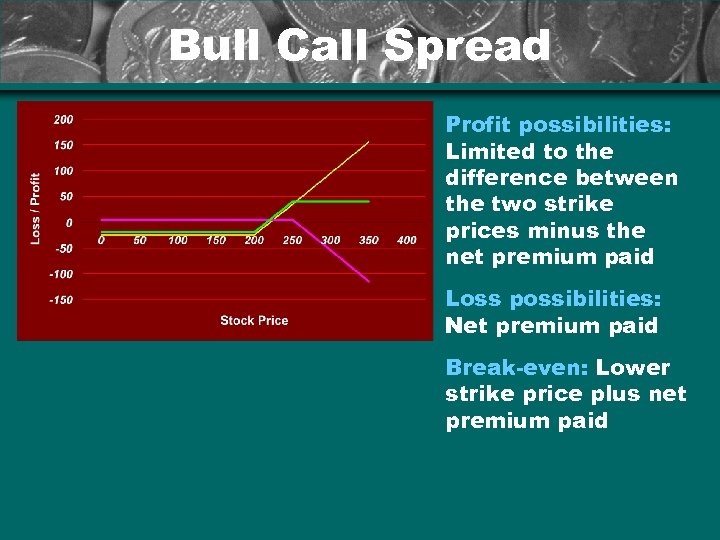 Bull Call Spread Profit possibilities: Limited to the difference between the two strike prices minus the net premium paid Loss possibilities: Net premium paid Break-even: Lower strike price plus net premium paid
Bull Call Spread Profit possibilities: Limited to the difference between the two strike prices minus the net premium paid Loss possibilities: Net premium paid Break-even: Lower strike price plus net premium paid
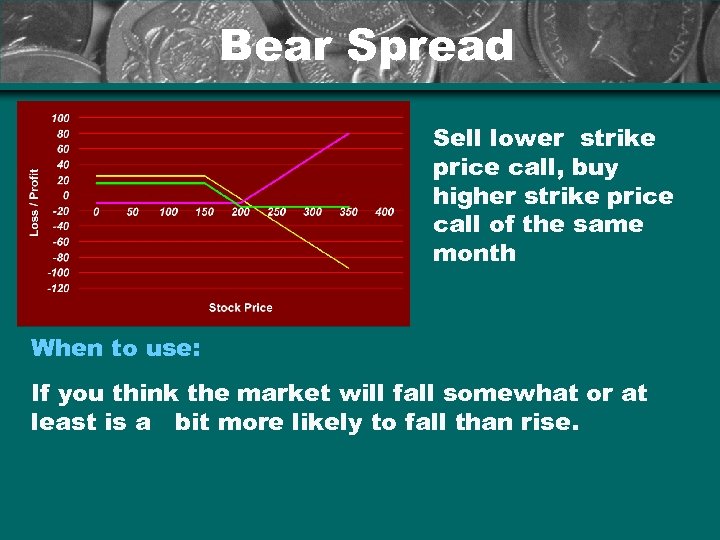 Bear Spread Sell lower strike price call, buy higher strike price call of the same month When to use: If you think the market will fall somewhat or at least is a bit more likely to fall than rise.
Bear Spread Sell lower strike price call, buy higher strike price call of the same month When to use: If you think the market will fall somewhat or at least is a bit more likely to fall than rise.
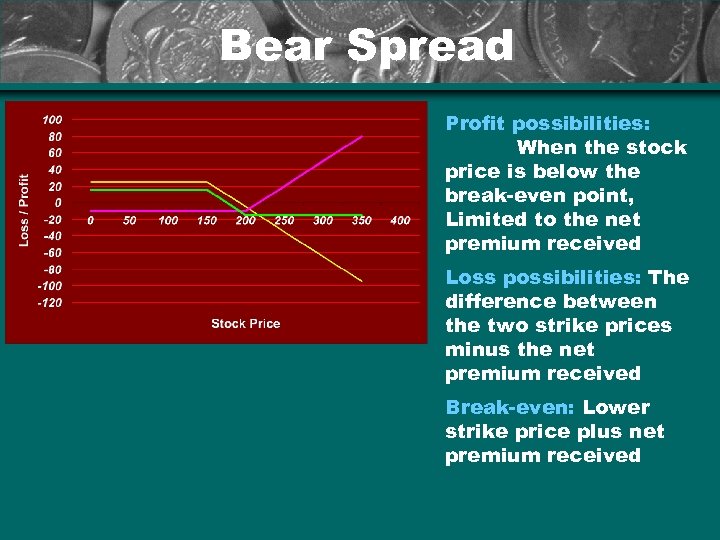 Bear Spread Profit possibilities: When the stock price is below the break-even point, Limited to the net premium received Loss possibilities: The difference between the two strike prices minus the net premium received Break-even: Lower strike price plus net premium received
Bear Spread Profit possibilities: When the stock price is below the break-even point, Limited to the net premium received Loss possibilities: The difference between the two strike prices minus the net premium received Break-even: Lower strike price plus net premium received


