8a7b6d3fc3b6c9a49d248088be5ba3d0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 OPTION PRICING
OPTION PRICING
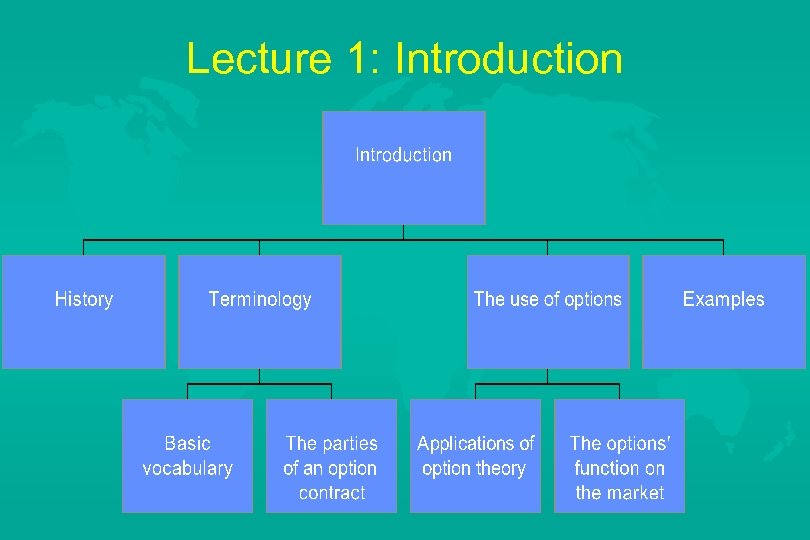 Lecture 1: Introduction
Lecture 1: Introduction
 What is an option ? u A security, which gives the owner the right, but not the obligation, to buy (sell) an asset for a specific price at a future point in time
What is an option ? u A security, which gives the owner the right, but not the obligation, to buy (sell) an asset for a specific price at a future point in time
 History u Options (standardized) based on stocks were for the first time traded in 1973 at Chicago Board of Options Exchange (CBOE). u Standardized options came to Europe (Amsterdam) in 1978. u Suomen Optiomeklarit (SOM) started trading in a larger scale in Finland 2. 5. 1988.
History u Options (standardized) based on stocks were for the first time traded in 1973 at Chicago Board of Options Exchange (CBOE). u Standardized options came to Europe (Amsterdam) in 1978. u Suomen Optiomeklarit (SOM) started trading in a larger scale in Finland 2. 5. 1988.
 u Trading in options has been by far largest in FOX-options (FOX=Finnish Options Index), consisting of the 25 most traded stocks on Helsinki stock exchange, weighted by their share of the turnover. u The FOX-basket is updated every six months.
u Trading in options has been by far largest in FOX-options (FOX=Finnish Options Index), consisting of the 25 most traded stocks on Helsinki stock exchange, weighted by their share of the turnover. u The FOX-basket is updated every six months.
 Terminology u Call option: gives the holder the right, but not the obligation to buy a specific stock in the future. u Put option: gives the holder the right, but not the obligation to sell a specific stock in the future. u American option: can be exercised any time before the day of expiration. u European option: can be exercised only on the day of its expiration.
Terminology u Call option: gives the holder the right, but not the obligation to buy a specific stock in the future. u Put option: gives the holder the right, but not the obligation to sell a specific stock in the future. u American option: can be exercised any time before the day of expiration. u European option: can be exercised only on the day of its expiration.
 u Striking price: the price at which one has the right to buy (sell) the underlying asset. (We will during the course discuss european options)
u Striking price: the price at which one has the right to buy (sell) the underlying asset. (We will during the course discuss european options)
 Applications of Options u Option pricing u Firm valuation (leveraged) u Capital budgeting u Other applications (Insurance valuation etc. )
Applications of Options u Option pricing u Firm valuation (leveraged) u Capital budgeting u Other applications (Insurance valuation etc. )
 Opportunities enabled with options u Better possibilities to make investments according to investors’ risk and return preferences. u The increasing possibilities to choose investment strategies are also increasing the need for better knowledge of the different financial instruments.
Opportunities enabled with options u Better possibilities to make investments according to investors’ risk and return preferences. u The increasing possibilities to choose investment strategies are also increasing the need for better knowledge of the different financial instruments.
 Options have two main functions on the market: 1. Give protection against the risk in stock ownership. With a small capital investment in options You can control the risk of a large position in a stock (or portfolio). 2. Option prices tend to change very much (High volatility). Risk lovers can make huge and quick profits.
Options have two main functions on the market: 1. Give protection against the risk in stock ownership. With a small capital investment in options You can control the risk of a large position in a stock (or portfolio). 2. Option prices tend to change very much (High volatility). Risk lovers can make huge and quick profits.
 An intuitive example: Buy: 100 call options on Kymmene Striking price: 135 mu Current stock price: 132 mu Call option price: 1 mu/share.
An intuitive example: Buy: 100 call options on Kymmene Striking price: 135 mu Current stock price: 132 mu Call option price: 1 mu/share.
 Two possible outcomes: • • If the price of Kymmene on due date is 135 mu or less, the call option is worthless and you lose your investment (1 mu*100 call options=) 100 mu. The option is “out of the money”.
Two possible outcomes: • • If the price of Kymmene on due date is 135 mu or less, the call option is worthless and you lose your investment (1 mu*100 call options=) 100 mu. The option is “out of the money”.
 2. Stock price on due date 140 mu. u Recall that the Striking Price is 135 mu Buy 100 shares 13 500 mu (100 * striking price) Sell 100 shares 14 000 mu Profit + 500 mu Options - 100 mu Net profit + 400 mu u This option is “in the money”.
2. Stock price on due date 140 mu. u Recall that the Striking Price is 135 mu Buy 100 shares 13 500 mu (100 * striking price) Sell 100 shares 14 000 mu Profit + 500 mu Options - 100 mu Net profit + 400 mu u This option is “in the money”.
 u The most important feature of an option is its ability to generate huge profits with a small investment (leverage). u If You had bought a put option in the above example, You would have profited only when the stock price had fallen below the striking price.
u The most important feature of an option is its ability to generate huge profits with a small investment (leverage). u If You had bought a put option in the above example, You would have profited only when the stock price had fallen below the striking price.
 The parties of an option contract: There are two parties in each option contract: u The one who buys the option (Long position) u The one who writes the option (Short position)
The parties of an option contract: There are two parties in each option contract: u The one who buys the option (Long position) u The one who writes the option (Short position)

 Example (cont. on the previous example) The option writer got 100 mu for the call option contracts he wrote. u If the stock price on due date was below 135 mu, the options would have been worthless and the option writer’s net profit had been 100 mu. u If the stock price exceeded 135 mu, the option writer had to pay the option holder the difference, in one way or another.
Example (cont. on the previous example) The option writer got 100 mu for the call option contracts he wrote. u If the stock price on due date was below 135 mu, the options would have been worthless and the option writer’s net profit had been 100 mu. u If the stock price exceeded 135 mu, the option writer had to pay the option holder the difference, in one way or another.
 u The potential loss for the option writer is theoretically unlimited The writer has to prove that he is capable of fullfilling his obligation by giving a collateral to the broker. u This collateral is continuously monitored and adjusted.
u The potential loss for the option writer is theoretically unlimited The writer has to prove that he is capable of fullfilling his obligation by giving a collateral to the broker. u This collateral is continuously monitored and adjusted.
 Interesting addresses on the Internet u The Chicago Mercantile Exchange http: //www. interaccess. com: 80/cme/ u The Chicago Board of Trade http: //www. cbot. com u The London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange http: //www. liffe. com u An Option pricer http: //slag. capmkt. com/cgi-bin/robert/optionpricer
Interesting addresses on the Internet u The Chicago Mercantile Exchange http: //www. interaccess. com: 80/cme/ u The Chicago Board of Trade http: //www. cbot. com u The London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange http: //www. liffe. com u An Option pricer http: //slag. capmkt. com/cgi-bin/robert/optionpricer
 More addresses. . . u Portfolio Challenge (competition) http: //pawws. secapl. com u The Basics of Trading Options http: //www. teleport. com/~futures /options. html u A Link to some other related servers http: //www. yahoo. com/economy/markets_and_investm ents/futures_and_options/ u Goethe Investment Club http: //www. wiwi. uni-frankfurt. de/AG/JWGI/ u US Stock price data: http: //www. ai. mit. edu/stocks/graphs. html
More addresses. . . u Portfolio Challenge (competition) http: //pawws. secapl. com u The Basics of Trading Options http: //www. teleport. com/~futures /options. html u A Link to some other related servers http: //www. yahoo. com/economy/markets_and_investm ents/futures_and_options/ u Goethe Investment Club http: //www. wiwi. uni-frankfurt. de/AG/JWGI/ u US Stock price data: http: //www. ai. mit. edu/stocks/graphs. html


