88cf746d7920c7374c2d84453f4a0ab6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Optimizing Life Course Health Development 3. 0 Strategies for Addressing the Upstream Determinants of Health Development Neal Halfon MD MPH Professor of Pediatrics, Health Policy & Management , Public Policy UCLA Center for Healthier Children Families and Communities Children’s Hospital Grand Rounds Chattanooga, Tennessee July 26, 2016
Optimizing Life Course Health Development 3. 0 Strategies for Addressing the Upstream Determinants of Health Development Neal Halfon MD MPH Professor of Pediatrics, Health Policy & Management , Public Policy UCLA Center for Healthier Children Families and Communities Children’s Hospital Grand Rounds Chattanooga, Tennessee July 26, 2016
 Outline • Pressing need to transform our health system - The opportunity of children leading the way • New Science - Life Course Health Development (LCHD) • 3. 0 Transformation Framework - How it can be used to redesign the system • What do 3. 0 Innovations look like • How Transforming Early Childhood Community Systems (TECCS) and All Children Thrive ( ACT) are taking on the 3. 0 challenge
Outline • Pressing need to transform our health system - The opportunity of children leading the way • New Science - Life Course Health Development (LCHD) • 3. 0 Transformation Framework - How it can be used to redesign the system • What do 3. 0 Innovations look like • How Transforming Early Childhood Community Systems (TECCS) and All Children Thrive ( ACT) are taking on the 3. 0 challenge
 The Health Policy Challenge • Most inefficient, low value, low ROI health system • Triple Aim - Improve population health, quality care at lower cost • Many other challenges - Enormous social &health disparities Rapidly rising rates of chronic disease Unavoidable demographic shifts Relentless cost increases • An Anemic and Tired Health Policy Strategy that does not reflect what we know about producing health • Old Outdated Operating System - Mismatch between 3. 0 apps and 2. 0 goals and 1. 0 payment methodology
The Health Policy Challenge • Most inefficient, low value, low ROI health system • Triple Aim - Improve population health, quality care at lower cost • Many other challenges - Enormous social &health disparities Rapidly rising rates of chronic disease Unavoidable demographic shifts Relentless cost increases • An Anemic and Tired Health Policy Strategy that does not reflect what we know about producing health • Old Outdated Operating System - Mismatch between 3. 0 apps and 2. 0 goals and 1. 0 payment methodology
 Framework to Rationalize different types of Change, Innovation, Improvement Strategies • Fixit – fix broken parts and pieces • Incremental Improvement - Evidence based improvements in services and care - Most of health care improvements fall into this category (new screening tool, new program ) • Transitions - New way of performing; Quantum leap; - Where innovations drives improvement - Requires nudges and jolts - 3. 0 ACOs/HDOs, C 3 N, TECCS • Transformation: Paradigm Shift - New Operating System
Framework to Rationalize different types of Change, Innovation, Improvement Strategies • Fixit – fix broken parts and pieces • Incremental Improvement - Evidence based improvements in services and care - Most of health care improvements fall into this category (new screening tool, new program ) • Transitions - New way of performing; Quantum leap; - Where innovations drives improvement - Requires nudges and jolts - 3. 0 ACOs/HDOs, C 3 N, TECCS • Transformation: Paradigm Shift - New Operating System
 How we allocate resources • Other nations invest in success (education and social care) • We pay for failure (health care and rehab) More Chronic Illness US children are less healthy and carry that burden with them in the form of chronic illness, dependency and disability
How we allocate resources • Other nations invest in success (education and social care) • We pay for failure (health care and rehab) More Chronic Illness US children are less healthy and carry that burden with them in the form of chronic illness, dependency and disability
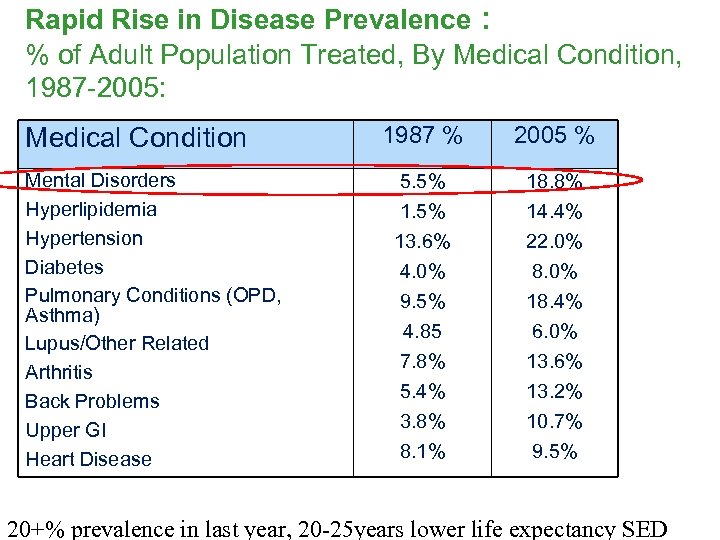 Rapid Rise in Disease Prevalence : % of Adult Population Treated, By Medical Condition, 1987 -2005: Medical Condition Mental Disorders Hyperlipidemia Hypertension Diabetes Pulmonary Conditions (OPD, Asthma) Lupus/Other Related Arthritis Back Problems Upper GI Heart Disease 1987 % 2005 % 5. 5% 13. 6% 4. 0% 18. 8% 14. 4% 22. 0% 8. 0% 9. 5% 18. 4% 4. 85 6. 0% 7. 8% 13. 6% 5. 4% 13. 2% 3. 8% 8. 1% 10. 7% 9. 5% 20+% prevalence in last year, 20 -25 years lower life expectancy SED
Rapid Rise in Disease Prevalence : % of Adult Population Treated, By Medical Condition, 1987 -2005: Medical Condition Mental Disorders Hyperlipidemia Hypertension Diabetes Pulmonary Conditions (OPD, Asthma) Lupus/Other Related Arthritis Back Problems Upper GI Heart Disease 1987 % 2005 % 5. 5% 13. 6% 4. 0% 18. 8% 14. 4% 22. 0% 8. 0% 9. 5% 18. 4% 4. 85 6. 0% 7. 8% 13. 6% 5. 4% 13. 2% 3. 8% 8. 1% 10. 7% 9. 5% 20+% prevalence in last year, 20 -25 years lower life expectancy SED
 April 2013
April 2013
 Changing Pattern of Childhood Morbidity • Increase in chronic health problems (33%) - Not Hemophilia, Cancer, Congenital Heart Disease • Growing prevalence of mental health disorders (22+%) • Greater appreciation of role and impact of neuro-developmental health problems – learning, language (10 -17%) • Growing number of children with multiple conditions (co-morbidities) e. g. asthma, obesity, ADHD
Changing Pattern of Childhood Morbidity • Increase in chronic health problems (33%) - Not Hemophilia, Cancer, Congenital Heart Disease • Growing prevalence of mental health disorders (22+%) • Greater appreciation of role and impact of neuro-developmental health problems – learning, language (10 -17%) • Growing number of children with multiple conditions (co-morbidities) e. g. asthma, obesity, ADHD
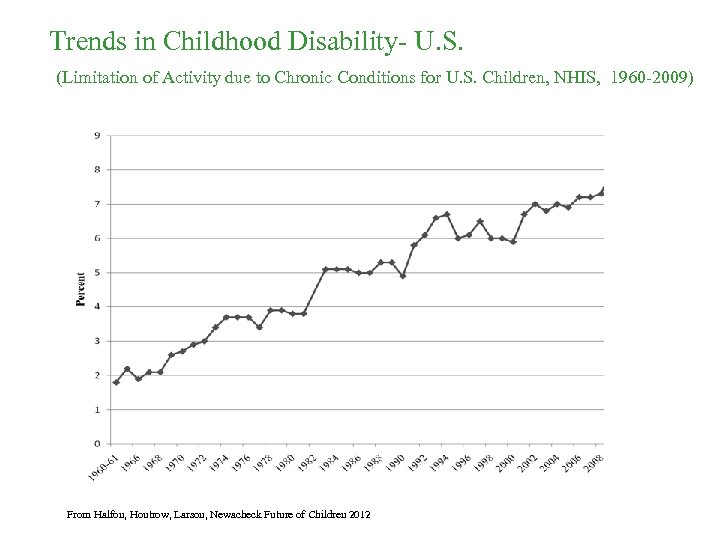 Trends in Childhood Disability- U. S. (Limitation of Activity due to Chronic Conditions for U. S. Children, NHIS, 1960 -2009) From Halfon, Houtrow, Larson, Newacheck Future of Children 2012
Trends in Childhood Disability- U. S. (Limitation of Activity due to Chronic Conditions for U. S. Children, NHIS, 1960 -2009) From Halfon, Houtrow, Larson, Newacheck Future of Children 2012
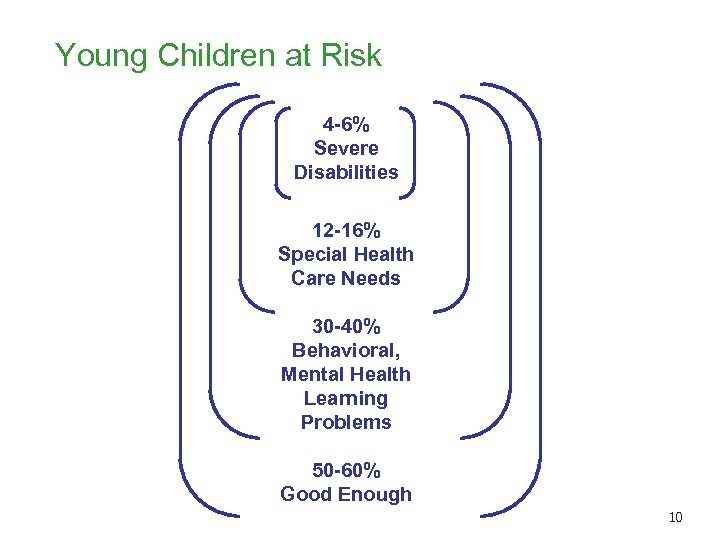 Young Children at Risk 4 -6% Severe Disabilities 12 -16% Special Health Care Needs 30 -40% Behavioral, Mental Health Learning Problems 50 -60% Good Enough 10
Young Children at Risk 4 -6% Severe Disabilities 12 -16% Special Health Care Needs 30 -40% Behavioral, Mental Health Learning Problems 50 -60% Good Enough 10
 Adversity & the Loss of Health Potential • Adversity & Prosperity have a dramatic effects on health development • Adversity comes in many forms; economic, social, environmental, familial, behavioral • ACE’s - 44. 8% of children (0 -17) have one, and 22% have two or more ACEs, • ACE’s have a steep social gradient • Rising rates of mental, behavioral and developmental problems are indications of growing levels of adversity • Over 40% of children live in low income families, and over 40% live in families with one parent • Families don’t have the resources and capacities to support optimal health development
Adversity & the Loss of Health Potential • Adversity & Prosperity have a dramatic effects on health development • Adversity comes in many forms; economic, social, environmental, familial, behavioral • ACE’s - 44. 8% of children (0 -17) have one, and 22% have two or more ACEs, • ACE’s have a steep social gradient • Rising rates of mental, behavioral and developmental problems are indications of growing levels of adversity • Over 40% of children live in low income families, and over 40% live in families with one parent • Families don’t have the resources and capacities to support optimal health development
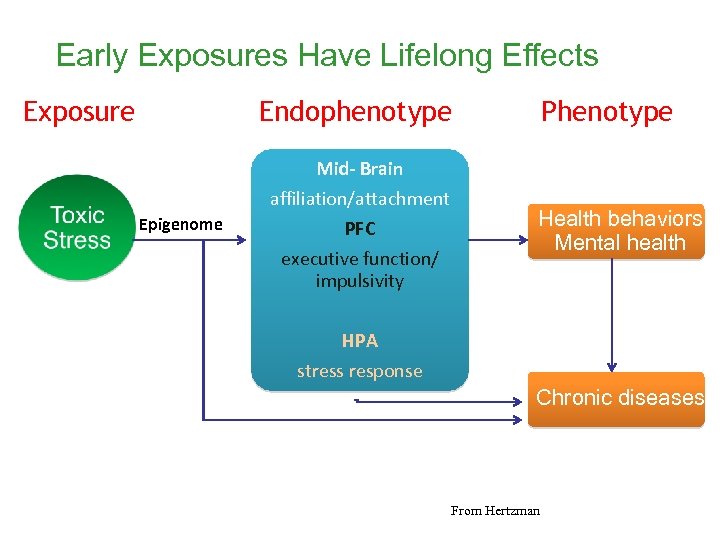 Early Exposures Have Lifelong Effects Exposure Endophenotype Phenotype Mid- Brain Epigenome affiliation/attachment PFC executive function/ impulsivity Health behaviors Mental health HPA stress response Chronic diseases From Hertzman
Early Exposures Have Lifelong Effects Exposure Endophenotype Phenotype Mid- Brain Epigenome affiliation/attachment PFC executive function/ impulsivity Health behaviors Mental health HPA stress response Chronic diseases From Hertzman
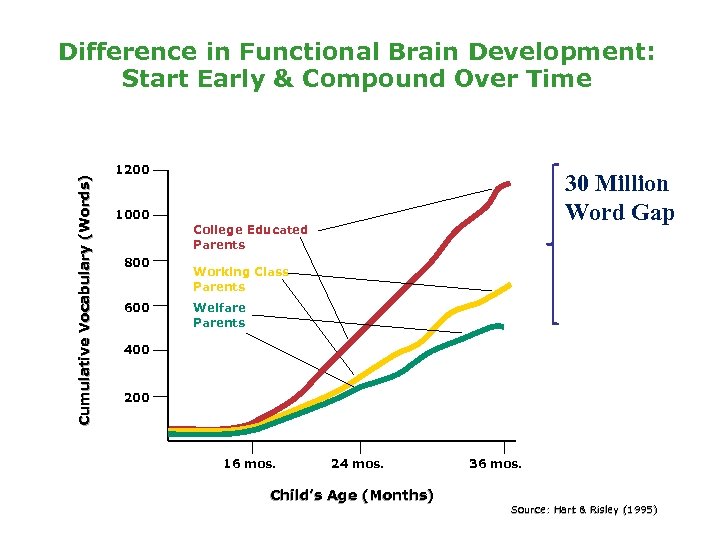 Cumulative Vocabulary (Words) Difference in Functional Brain Development: Start Early & Compound Over Time 1200 30 Million Word Gap 1000 College Educated Parents 800 600 Working Class Parents Welfare Parents 400 200 16 mos. 24 mos. Child’s Age (Months) 36 mos. Source: Hart & Risley (1995)
Cumulative Vocabulary (Words) Difference in Functional Brain Development: Start Early & Compound Over Time 1200 30 Million Word Gap 1000 College Educated Parents 800 600 Working Class Parents Welfare Parents 400 200 16 mos. 24 mos. Child’s Age (Months) 36 mos. Source: Hart & Risley (1995)

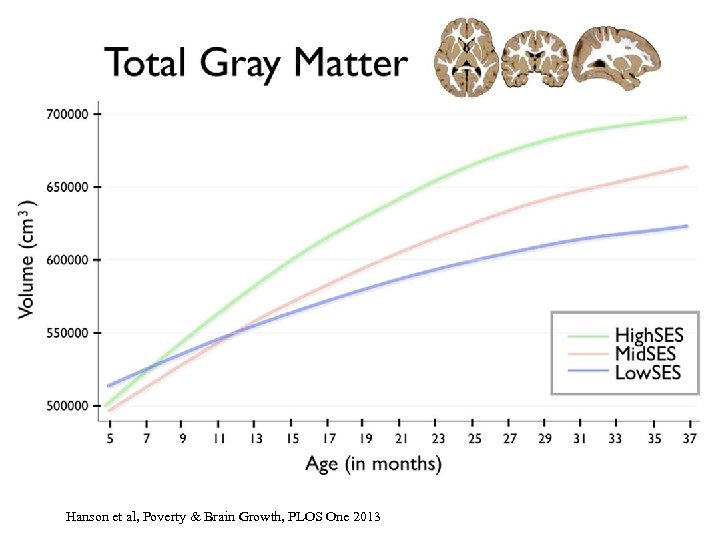 Hanson et al, Poverty & Brain Growth, PLOS One 2013
Hanson et al, Poverty & Brain Growth, PLOS One 2013
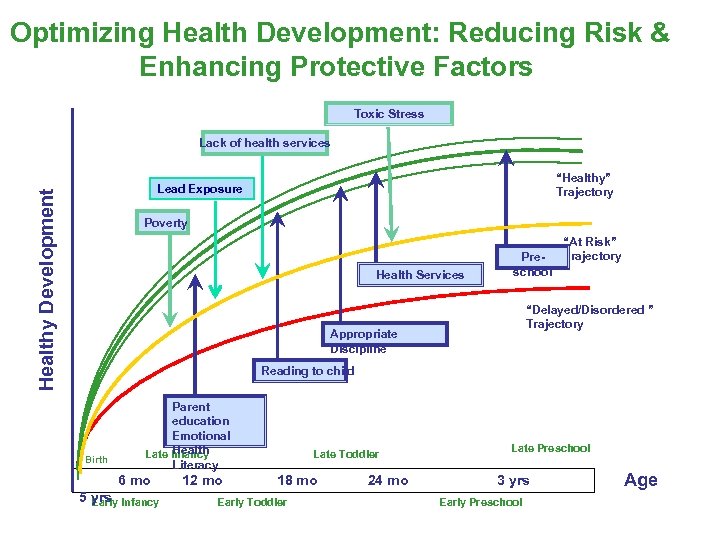 Optimizing Health Development: Reducing Risk & Enhancing Protective Factors Toxic Stress Lack of health services “Healthy” Trajectory Healthy Development Lead Exposure Poverty Health Services Preschool “At Risk” Trajectory “Delayed/Disordered ” Trajectory Appropriate Discipline Reading to child Birth Parent education Emotional Health Late Infancy Literacy 6 mo 5 yrs Infancy Early 12 mo Late Toddler 18 mo Early Toddler 24 mo Late Preschool 3 yrs Early Preschool Age
Optimizing Health Development: Reducing Risk & Enhancing Protective Factors Toxic Stress Lack of health services “Healthy” Trajectory Healthy Development Lead Exposure Poverty Health Services Preschool “At Risk” Trajectory “Delayed/Disordered ” Trajectory Appropriate Discipline Reading to child Birth Parent education Emotional Health Late Infancy Literacy 6 mo 5 yrs Infancy Early 12 mo Late Toddler 18 mo Early Toddler 24 mo Late Preschool 3 yrs Early Preschool Age
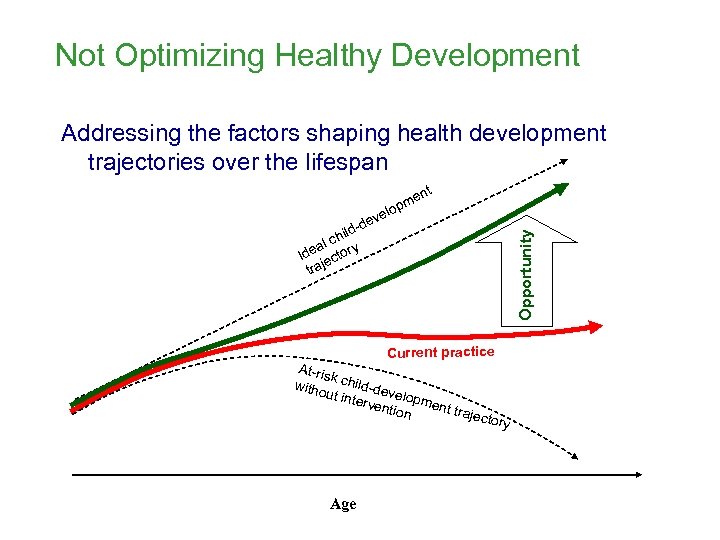 Not Optimizing Healthy Development Addressing the factors shaping health development trajectories over the lifespan nt me op vel e Opportunity -d hild al c de ctory I je tra Current practice At-ris k witho child-de v ut int erve elopmen ntion t traj ector Age y
Not Optimizing Healthy Development Addressing the factors shaping health development trajectories over the lifespan nt me op vel e Opportunity -d hild al c de ctory I je tra Current practice At-ris k witho child-de v ut int erve elopmen ntion t traj ector Age y

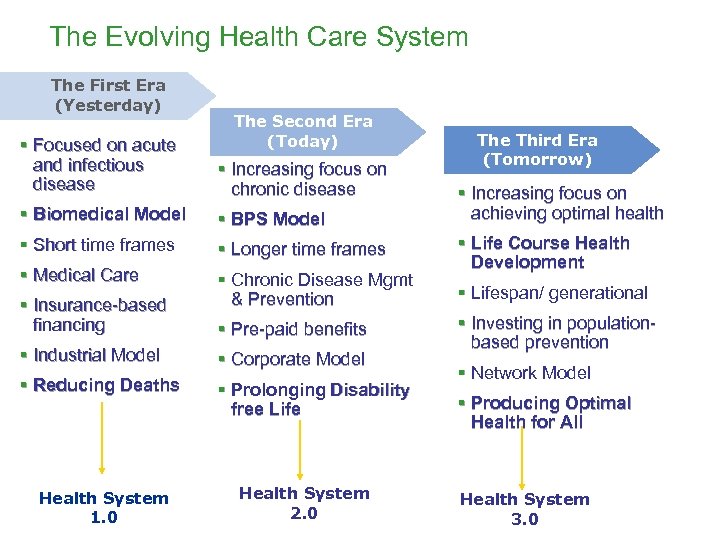 The Evolving Health Care System The First Era (Yesterday) The Second Era (Today) § Focused on acute and infectious disease § Increasing focus on chronic disease § Biomedical Model § BPS Model § Short time frames § Longer time frames § Medical Care § Chronic Disease Mgmt & Prevention § Insurance-based financing § Pre-paid benefits § Industrial Model § Corporate Model § Reducing Deaths § Prolonging Disability free Life Health System 1. 0 Health System 2. 0 The Third Era (Tomorrow) § Increasing focus on achieving optimal health § Life Course Health Development § Lifespan/ generational § Investing in populationbased prevention § Network Model § Producing Optimal Health for All Health System 3. 0
The Evolving Health Care System The First Era (Yesterday) The Second Era (Today) § Focused on acute and infectious disease § Increasing focus on chronic disease § Biomedical Model § BPS Model § Short time frames § Longer time frames § Medical Care § Chronic Disease Mgmt & Prevention § Insurance-based financing § Pre-paid benefits § Industrial Model § Corporate Model § Reducing Deaths § Prolonging Disability free Life Health System 1. 0 Health System 2. 0 The Third Era (Tomorrow) § Increasing focus on achieving optimal health § Life Course Health Development § Lifespan/ generational § Investing in populationbased prevention § Network Model § Producing Optimal Health for All Health System 3. 0
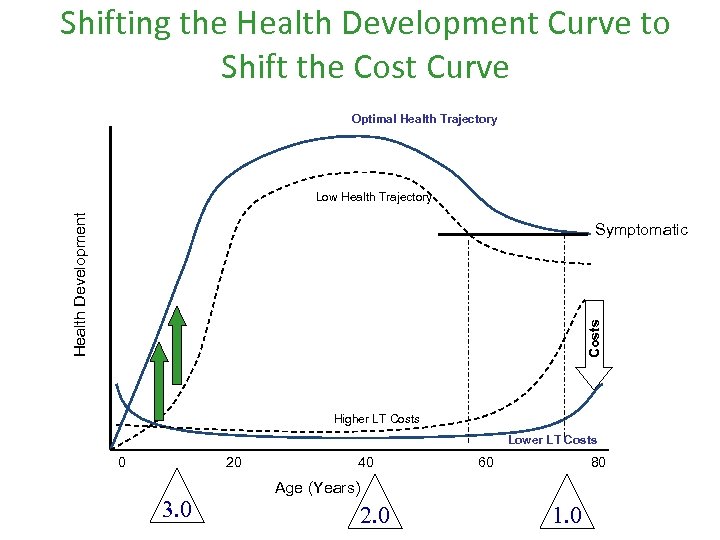 Shifting the Health Development Curve to Shift the Cost Curve Optimal Health Trajectory Health Development Low Health Trajectory Costs Symptomatic Higher LT Costs Lower LT Costs 0 20 3. 0 40 60 80 Age (Years) 2. 0 1. 0
Shifting the Health Development Curve to Shift the Cost Curve Optimal Health Trajectory Health Development Low Health Trajectory Costs Symptomatic Higher LT Costs Lower LT Costs 0 20 3. 0 40 60 80 Age (Years) 2. 0 1. 0
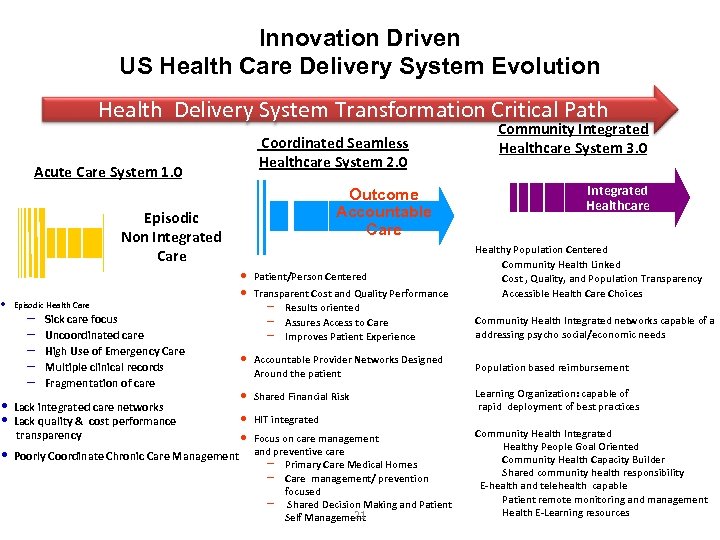 • Innovation Driven US Health Care Delivery System Evolution Health Delivery System Transformation Critical Path Coordinated Seamless Healthcare System 2. 0 Acute Care System 1. 0 Outcome Accountable Care Episodic Non Integrated Care Episodic Health Care – – – Sick care focus Uncoordinated care High Use of Emergency Care Multiple clinical records Fragmentation of care • • Lack integrated care networks Lack quality & cost performance transparency • Poorly Coordinate Chronic Care Management Community Integrated Healthcare System 3. 0 Community Integrated Healthcare v Healthy Population Centered – Community Health Linked – Cost , Quality, and Population Transparency – Accessible Health Care Choices – • Community Health Integrated networks capable of a • addressing psycho social/economic needs • • Patient/Person Centered Transparent Cost and Quality Performance – Results oriented – Assures Access to Care – Improves Patient Experience • Accountable Provider Networks Designed Around the patient • Population based reimbursement • Shared Financial Risk • • HIT integrated • Learning Organization: capable of • rapid deployment of best practices • Community Health Integrated Focus on care management Healthy People Goal Oriented and preventive care – Community Health Capacity Builder – Primary Care Medical Homes – Shared community health responsibility – Care management/ prevention – E-health and telehealth capable focused – Patient remote monitoring and management – Shared Decision Making and Patient – Health E-Learning resources 21 Self Management
• Innovation Driven US Health Care Delivery System Evolution Health Delivery System Transformation Critical Path Coordinated Seamless Healthcare System 2. 0 Acute Care System 1. 0 Outcome Accountable Care Episodic Non Integrated Care Episodic Health Care – – – Sick care focus Uncoordinated care High Use of Emergency Care Multiple clinical records Fragmentation of care • • Lack integrated care networks Lack quality & cost performance transparency • Poorly Coordinate Chronic Care Management Community Integrated Healthcare System 3. 0 Community Integrated Healthcare v Healthy Population Centered – Community Health Linked – Cost , Quality, and Population Transparency – Accessible Health Care Choices – • Community Health Integrated networks capable of a • addressing psycho social/economic needs • • Patient/Person Centered Transparent Cost and Quality Performance – Results oriented – Assures Access to Care – Improves Patient Experience • Accountable Provider Networks Designed Around the patient • Population based reimbursement • Shared Financial Risk • • HIT integrated • Learning Organization: capable of • rapid deployment of best practices • Community Health Integrated Focus on care management Healthy People Goal Oriented and preventive care – Community Health Capacity Builder – Primary Care Medical Homes – Shared community health responsibility – Care management/ prevention – E-health and telehealth capable focused – Patient remote monitoring and management – Shared Decision Making and Patient – Health E-Learning resources 21 Self Management
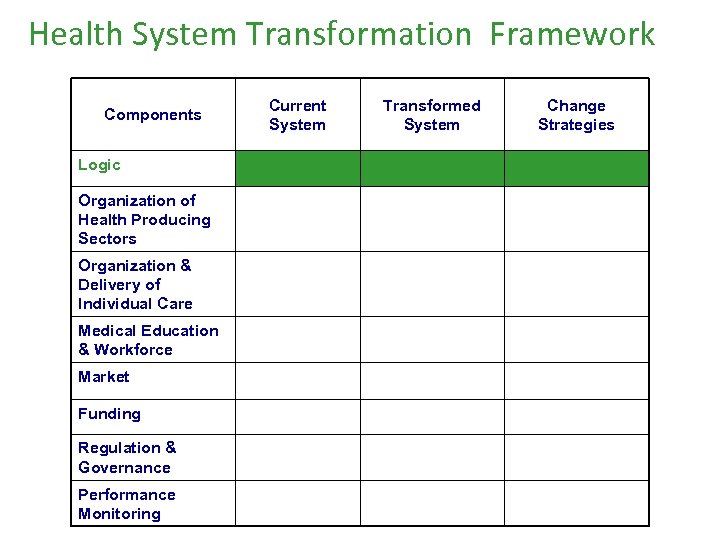 Health System Transformation Framework Components Logic Organization of Health Producing Sectors Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Medical Education & Workforce Market Funding Regulation & Governance Performance Monitoring Current System Transformed System Change Strategies
Health System Transformation Framework Components Logic Organization of Health Producing Sectors Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Medical Education & Workforce Market Funding Regulation & Governance Performance Monitoring Current System Transformed System Change Strategies
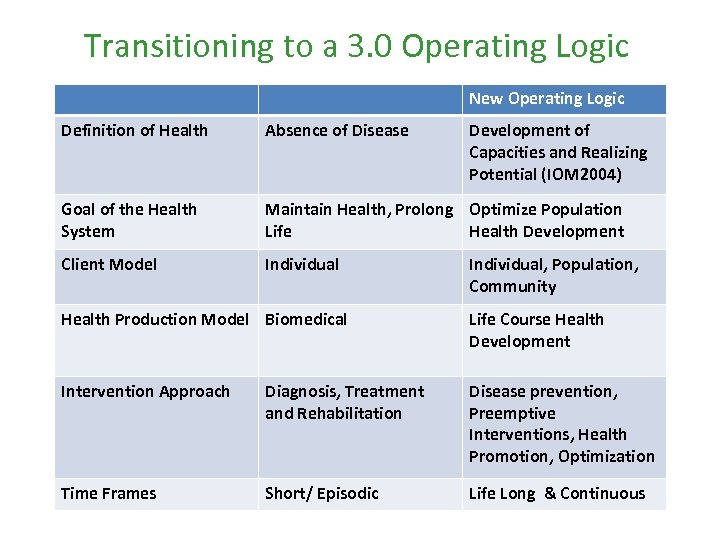 Transitioning to a 3. 0 Operating Logic New Operating Logic Definition of Health Absence of Disease Development of Capacities and Realizing Potential (IOM 2004) Goal of the Health System Maintain Health, Prolong Optimize Population Life Health Development Client Model Individual, Population, Community Health Production Model Biomedical Life Course Health Development Intervention Approach Diagnosis, Treatment and Rehabilitation Disease prevention, Preemptive Interventions, Health Promotion, Optimization Time Frames Short/ Episodic Life Long & Continuous
Transitioning to a 3. 0 Operating Logic New Operating Logic Definition of Health Absence of Disease Development of Capacities and Realizing Potential (IOM 2004) Goal of the Health System Maintain Health, Prolong Optimize Population Life Health Development Client Model Individual, Population, Community Health Production Model Biomedical Life Course Health Development Intervention Approach Diagnosis, Treatment and Rehabilitation Disease prevention, Preemptive Interventions, Health Promotion, Optimization Time Frames Short/ Episodic Life Long & Continuous
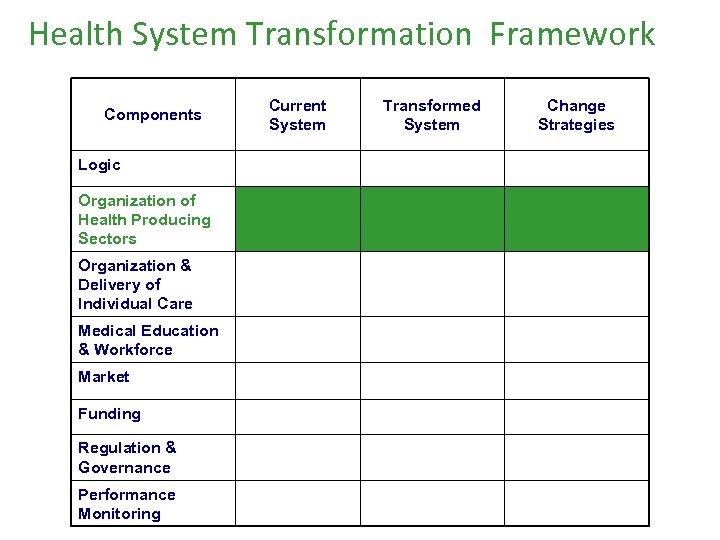 Health System Transformation Framework Components Logic Organization of Health Producing Sectors Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Medical Education & Workforce Market Funding Regulation & Governance Performance Monitoring Current System Transformed System Change Strategies
Health System Transformation Framework Components Logic Organization of Health Producing Sectors Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Medical Education & Workforce Market Funding Regulation & Governance Performance Monitoring Current System Transformed System Change Strategies
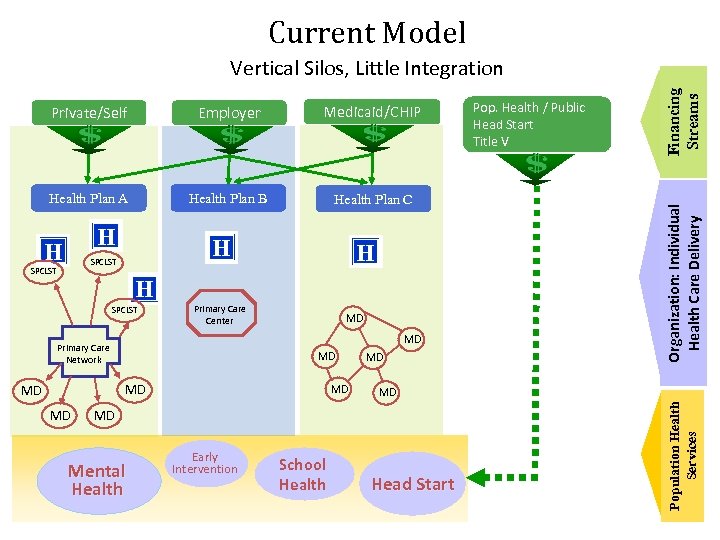 Current Model Employer Medicaid/CHIP Health Plan A Health Plan B Health Plan C H SPCLST H H SPCLST Primary Care Center MD MD Primary Care Network MD MD Mental Health Early Intervention School Health Head Start Population Health Services H H Pop. Health / Public Head Start Title V Organization: Individual Health Care Delivery Private/Self Financing Streams Vertical Silos, Little Integration
Current Model Employer Medicaid/CHIP Health Plan A Health Plan B Health Plan C H SPCLST H H SPCLST Primary Care Center MD MD Primary Care Network MD MD Mental Health Early Intervention School Health Head Start Population Health Services H H Pop. Health / Public Head Start Title V Organization: Individual Health Care Delivery Private/Self Financing Streams Vertical Silos, Little Integration
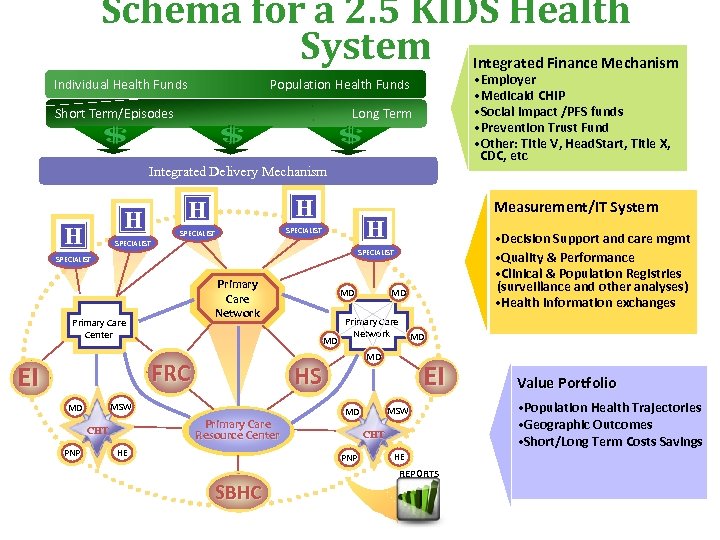 Schema for a 2. 5 KIDS Health System Integrated Finance Mechanism Individual Health Funds • Employer • Medicaid CHIP • Social Impact /PFS funds • Prevention Trust Fund • Other: Title V, Head. Start, Title X, CDC, etc Population Health Funds Short Term/Episodes Long Term Integrated Delivery Mechanism H H SPECIALIST Primary Care Network Primary Care Center Primary Care Resource Center CHT PNP Primary Care Network HE EI MSW MD CHT PNP SBHC MD MD HS MSW MD MD MD FRC MD • Decision Support and care mgmt • Quality & Performance • Clinical & Population Registries (surveillance and other analyses) • Health information exchanges SPECIALIST EI Me a s u r e m e n t / I T S y s t e m HE REPORTS V a l u e Po r t f o l i o • Population Health Trajectories • Geographic Outcomes • Short/Long Term Costs Savings
Schema for a 2. 5 KIDS Health System Integrated Finance Mechanism Individual Health Funds • Employer • Medicaid CHIP • Social Impact /PFS funds • Prevention Trust Fund • Other: Title V, Head. Start, Title X, CDC, etc Population Health Funds Short Term/Episodes Long Term Integrated Delivery Mechanism H H SPECIALIST Primary Care Network Primary Care Center Primary Care Resource Center CHT PNP Primary Care Network HE EI MSW MD CHT PNP SBHC MD MD HS MSW MD MD MD FRC MD • Decision Support and care mgmt • Quality & Performance • Clinical & Population Registries (surveillance and other analyses) • Health information exchanges SPECIALIST EI Me a s u r e m e n t / I T S y s t e m HE REPORTS V a l u e Po r t f o l i o • Population Health Trajectories • Geographic Outcomes • Short/Long Term Costs Savings
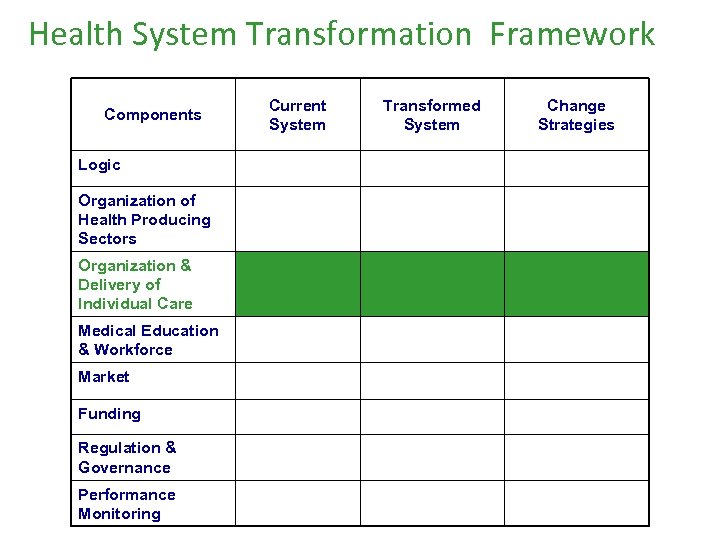 Health System Transformation Framework Components Logic Organization of Health Producing Sectors Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Medical Education & Workforce Market Funding Regulation & Governance Performance Monitoring Current System Transformed System Change Strategies
Health System Transformation Framework Components Logic Organization of Health Producing Sectors Organization & Delivery of Individual Care Medical Education & Workforce Market Funding Regulation & Governance Performance Monitoring Current System Transformed System Change Strategies
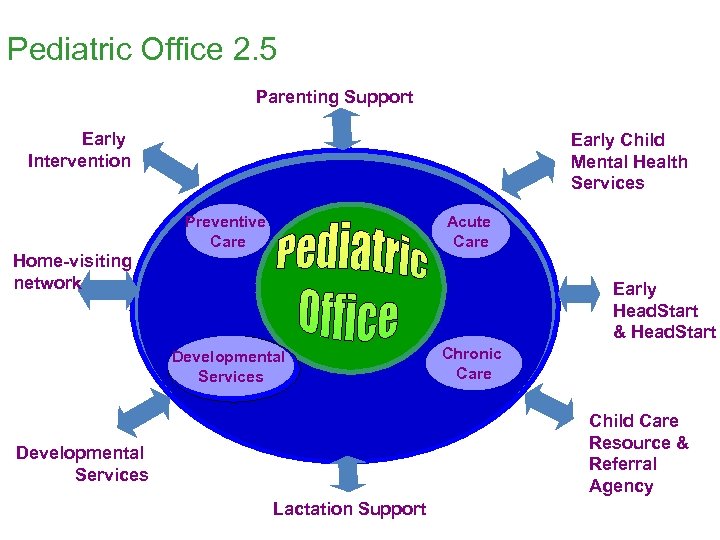 Pediatric Office 2. 5 Parenting Support Early Intervention Early Child Mental Health Services Preventive Care Acute Care Home-visiting network Early Head. Start & Head. Start Developmental Services Chronic Care Child Care Resource & Referral Agency Developmental Services Lactation Support
Pediatric Office 2. 5 Parenting Support Early Intervention Early Child Mental Health Services Preventive Care Acute Care Home-visiting network Early Head. Start & Head. Start Developmental Services Chronic Care Child Care Resource & Referral Agency Developmental Services Lactation Support
 2. 0 vs. 3. 0 >>>18 month visit • Pediatric Care 2. 0 • Pediatric Care 3. 0 - Optimize - C. D – Disability Developmental Health - Screen 4 -6 % w/ - I. D 30 -40% disability developmental risk - Screening tools & Pathway - Pediatric Office connected: connected to • Child care Regional Center • Many other programs • Coordination • Regional center ++
2. 0 vs. 3. 0 >>>18 month visit • Pediatric Care 2. 0 • Pediatric Care 3. 0 - Optimize - C. D – Disability Developmental Health - Screen 4 -6 % w/ - I. D 30 -40% disability developmental risk - Screening tools & Pathway - Pediatric Office connected: connected to • Child care Regional Center • Many other programs • Coordination • Regional center ++
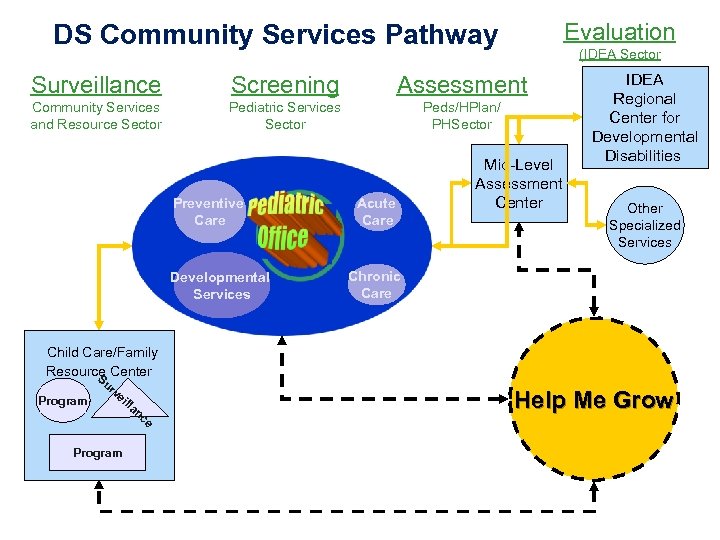 Evaluation DS Community Services Pathway (IDEA Sector Surveillance Screening Assessment Community Services and Resource Sector Pediatric Services Sector Peds/HPlan/ PHSector Preventive Care Developmental Services Acute Care Mid-Level Assessment Center IDEA Regional Center for Developmental Disabilities Other Specialized Services Chronic Care Child Care/Family Resource Center S Program ur ve ill Program an ce Help Me Grow
Evaluation DS Community Services Pathway (IDEA Sector Surveillance Screening Assessment Community Services and Resource Sector Pediatric Services Sector Peds/HPlan/ PHSector Preventive Care Developmental Services Acute Care Mid-Level Assessment Center IDEA Regional Center for Developmental Disabilities Other Specialized Services Chronic Care Child Care/Family Resource Center S Program ur ve ill Program an ce Help Me Grow
 Bridging Sectors to Enhance Health Development A Working Symposium of Community Leaders and Other Experts #teccsbridgingsectors #ECD #investinus
Bridging Sectors to Enhance Health Development A Working Symposium of Community Leaders and Other Experts #teccsbridgingsectors #ECD #investinus
 Creating a 21 st Century Health Development System • Vision, goals, & analytic framework • Leadership and participation of - multiple sectors ( health, Ed, family support, etc) - Multiple levels ( national, state, city, community) • • Cross sector pathways & innovations Evidence-based & informed practices Innovative & integrated finance strategies Shared data & shared learning to catalyzes improvement and innovation • Collaborative Improvement &Transformation Methods (e. g. BTS)
Creating a 21 st Century Health Development System • Vision, goals, & analytic framework • Leadership and participation of - multiple sectors ( health, Ed, family support, etc) - Multiple levels ( national, state, city, community) • • Cross sector pathways & innovations Evidence-based & informed practices Innovative & integrated finance strategies Shared data & shared learning to catalyzes improvement and innovation • Collaborative Improvement &Transformation Methods (e. g. BTS)
 Lessons Learned: Optimizing Health Development in Communities • Not about services & programs but about systems • Embrace Complexity - Communities are complex, growing, developing ecologies • Scale the Change Needed - Big problems in complex system are not going to respond to incremental changes • Complex Systems Learn their way Forward - Need a Learning System to foster adaptive change • Systems perform better (i. e. resilient) when sectors are aligned, production is network, services are integrated and user friendly, and where adaptive innovation and improvements are normative
Lessons Learned: Optimizing Health Development in Communities • Not about services & programs but about systems • Embrace Complexity - Communities are complex, growing, developing ecologies • Scale the Change Needed - Big problems in complex system are not going to respond to incremental changes • Complex Systems Learn their way Forward - Need a Learning System to foster adaptive change • Systems perform better (i. e. resilient) when sectors are aligned, production is network, services are integrated and user friendly, and where adaptive innovation and improvements are normative
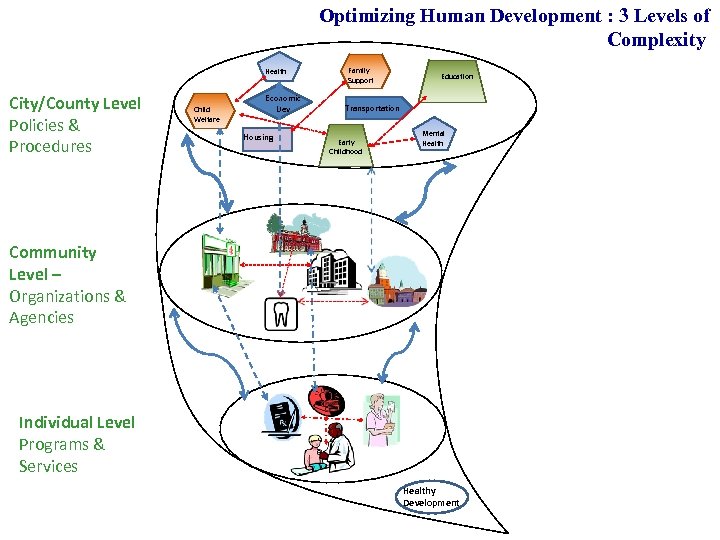 Optimizing Human Development : 3 Levels of Complexity Health City/County Level Policies & Procedures Child Welfare Economic Dev Housing Family Support Education Transportation Early Childhood Mental Health Community Level – Organizations & Agencies Individual Level Programs & Services Healthy Development
Optimizing Human Development : 3 Levels of Complexity Health City/County Level Policies & Procedures Child Welfare Economic Dev Housing Family Support Education Transportation Early Childhood Mental Health Community Level – Organizations & Agencies Individual Level Programs & Services Healthy Development
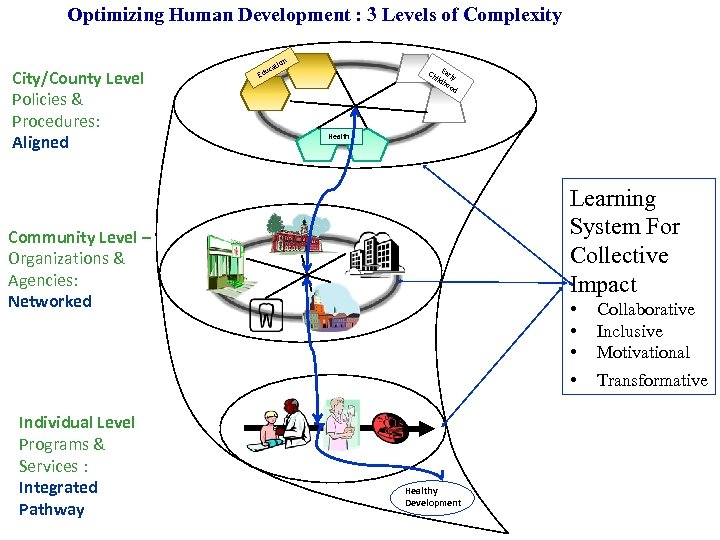 Optimizing Human Development : 3 Levels of Complexity City/County Level Policies & Procedures: Aligned n tio uca Ed Ch Early ild ho od Health Learning System For Collective Impact Community Level – Organizations & Agencies: Networked Individual Level Programs & Services : Integrated Pathway • • Healthy Development Collaborative Inclusive Motivational Transformative
Optimizing Human Development : 3 Levels of Complexity City/County Level Policies & Procedures: Aligned n tio uca Ed Ch Early ild ho od Health Learning System For Collective Impact Community Level – Organizations & Agencies: Networked Individual Level Programs & Services : Integrated Pathway • • Healthy Development Collaborative Inclusive Motivational Transformative
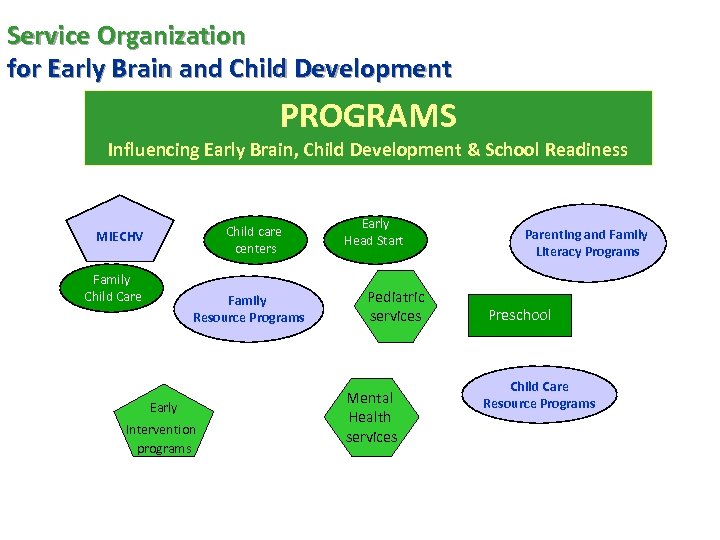 Service Organization for Early Brain and Child Development PROGRAMS Influencing Early Brain, Child Development & School Readiness Child care centers MIECHV Family Child Care Family Resource Programs Early Intervention programs Early Head Start Pediatric services Mental Health services Parenting and Family Literacy Programs Preschool Child Care Resource Programs
Service Organization for Early Brain and Child Development PROGRAMS Influencing Early Brain, Child Development & School Readiness Child care centers MIECHV Family Child Care Family Resource Programs Early Intervention programs Early Head Start Pediatric services Mental Health services Parenting and Family Literacy Programs Preschool Child Care Resource Programs
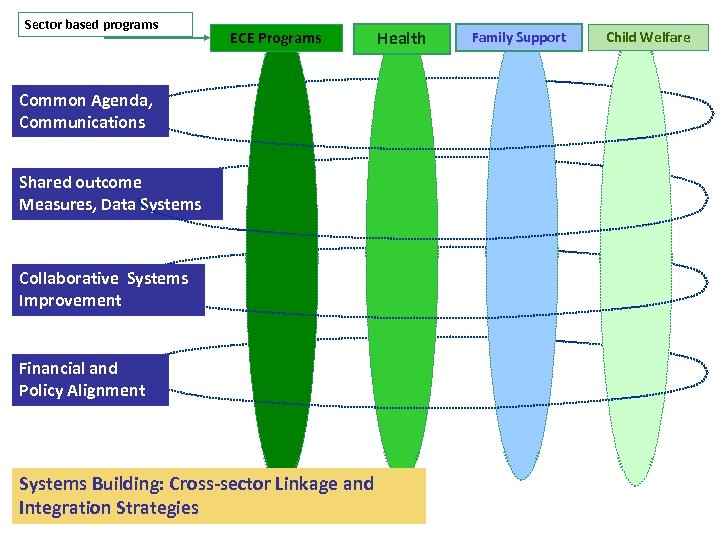 Sector based programs ECE Programs Common Agenda, Communications Shared outcome Measures, Data Systems Collaborative Systems Improvement Financial and Policy Alignment Systems Building: Cross-sector Linkage and Integration Strategies Health Family Support Child Welfare
Sector based programs ECE Programs Common Agenda, Communications Shared outcome Measures, Data Systems Collaborative Systems Improvement Financial and Policy Alignment Systems Building: Cross-sector Linkage and Integration Strategies Health Family Support Child Welfare
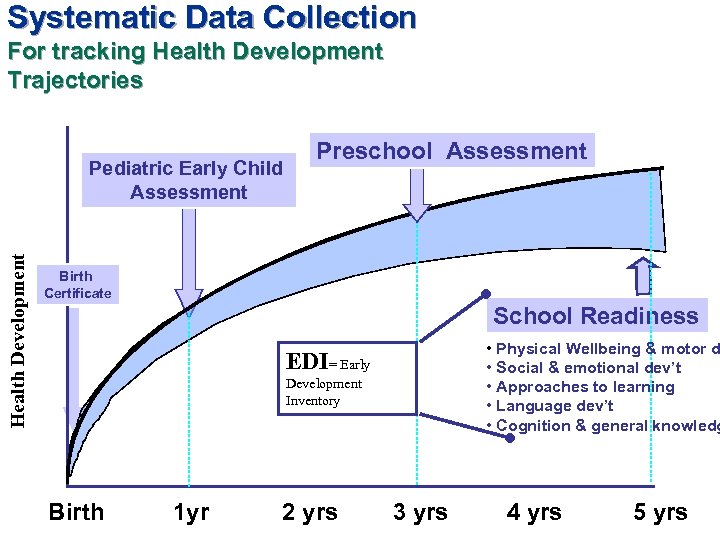 Systematic Data Collection For tracking Health Development Trajectories Health Development Pediatric Early Child Assessment Preschool Assessment Birth Certificate School Readiness • Physical Wellbeing & motor d • Social & emotional dev’t • Approaches to learning • Language dev’t • Cognition & general knowledg EDI= Early Development Inventory Birth 1 yr 2 yrs 3 yrs 4 yrs 5 yrs
Systematic Data Collection For tracking Health Development Trajectories Health Development Pediatric Early Child Assessment Preschool Assessment Birth Certificate School Readiness • Physical Wellbeing & motor d • Social & emotional dev’t • Approaches to learning • Language dev’t • Cognition & general knowledg EDI= Early Development Inventory Birth 1 yr 2 yrs 3 yrs 4 yrs 5 yrs
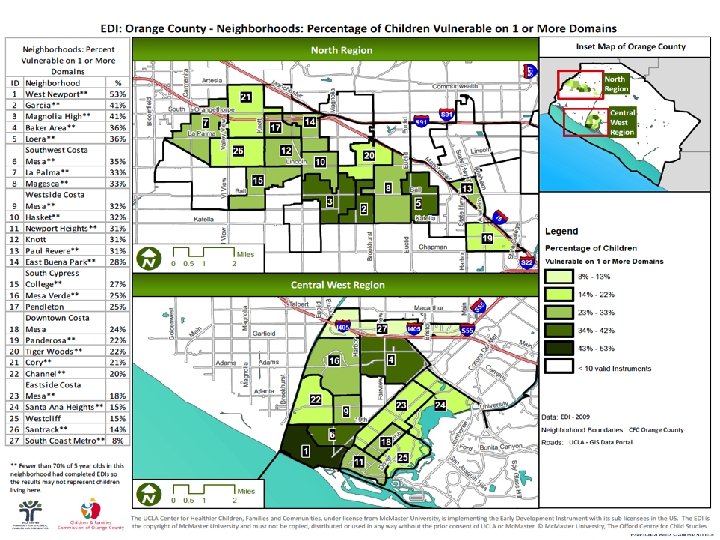
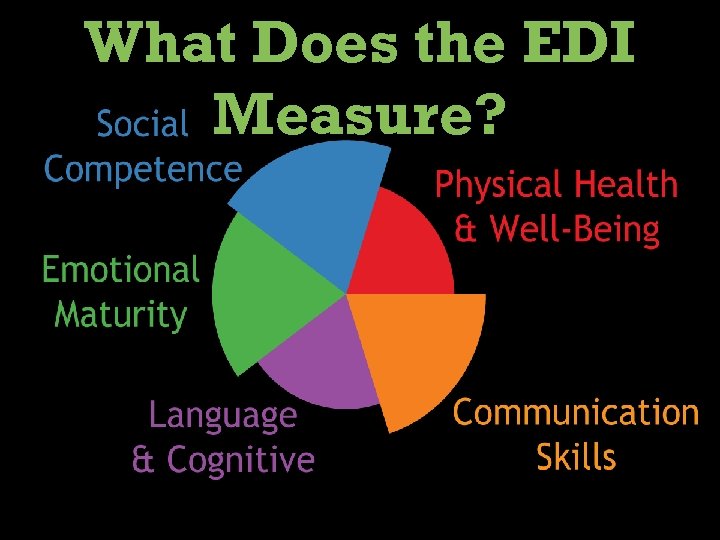 What Does the EDI Measure?
What Does the EDI Measure?
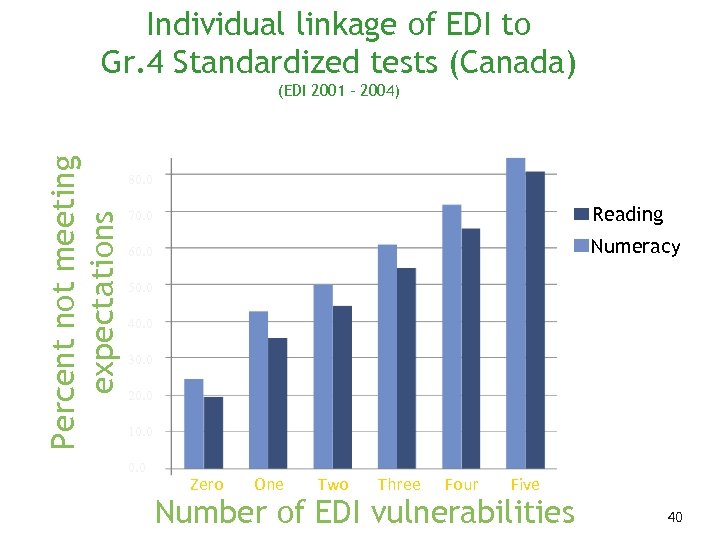 Individual linkage of EDI to Gr. 4 Standardized tests (Canada) Percent not meeting expectations (EDI 2001 – 2004) 80. 0 70. 0 Reading 60. 0 Numeracy 50. 0 40. 0 30. 0 20. 0 10. 0 Zero One Two Three Four Five Number of EDI vulnerabilities 40
Individual linkage of EDI to Gr. 4 Standardized tests (Canada) Percent not meeting expectations (EDI 2001 – 2004) 80. 0 70. 0 Reading 60. 0 Numeracy 50. 0 40. 0 30. 0 20. 0 10. 0 Zero One Two Three Four Five Number of EDI vulnerabilities 40