b9dfe97f4263e61a8784b46a418a587f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

OPTIMA INCO-MPC Third Management Board Meeting, May 18/19 2008 Gumpoldskirchen DDr. Kurt Fedra Environmental Software & Services Gmb. H A-2352 Gumpoldskirchen Austria kurt@ess. co. at http: //www. ess. co. at 1

Baseline targets: • WRM performance targets: – – – Complete and reasonable scenario Total outflow +/- 25% observations Daily flow at least for ONE station close to end node */ 2 – Basic economic assessment • (basis for optimization and comparison ) STREAM performance targets: – DO/BOD within reasonable ranges – any WQ observation data ? – WQ related economics under development 2

Case studies: how to proceed By PM 18 (December 2005): • Baselines ready for each case • Basic economic assessment • Basic water technologies ready to link, on-line data base • Optimization framework agreed: – Criteria, objectives, constraints 3
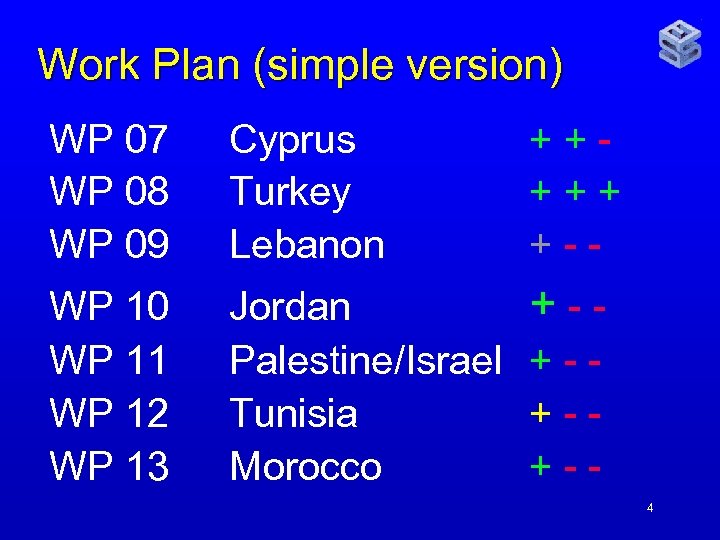
Work Plan (simple version) WP 07 WP 08 WP 09 Cyprus Turkey Lebanon +++++ +-- WP 10 WP 11 WP 12 WP 13 Jordan +-Palestine/Israel + - Tunisia +-Morocco +-4
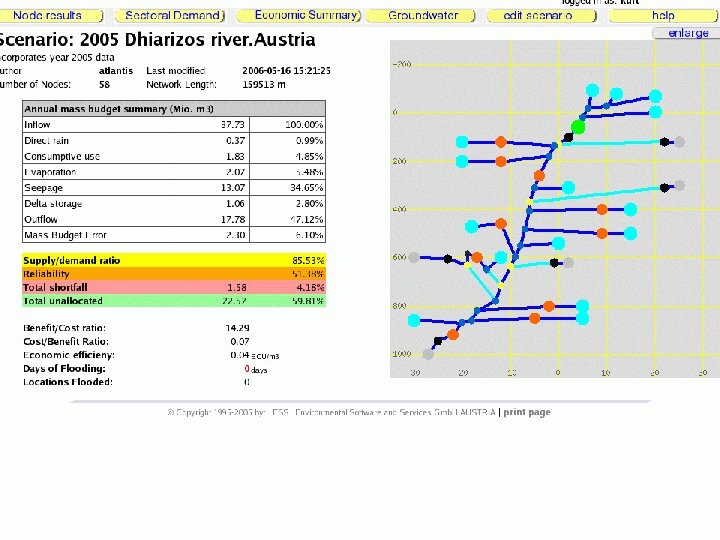
5
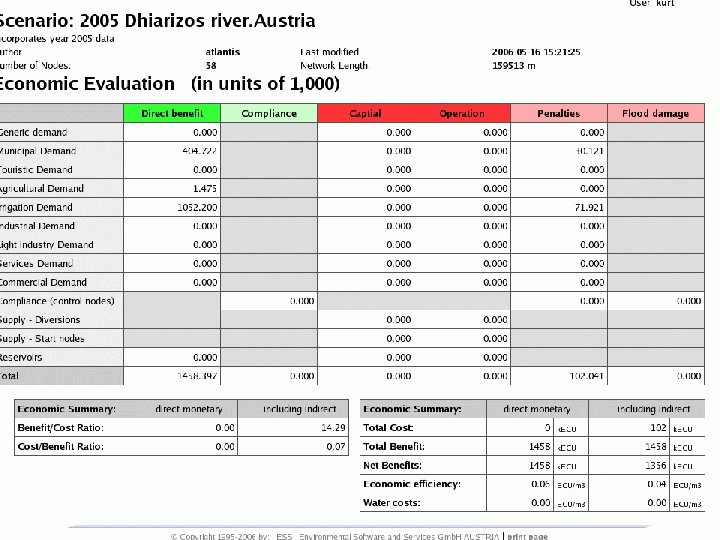
6
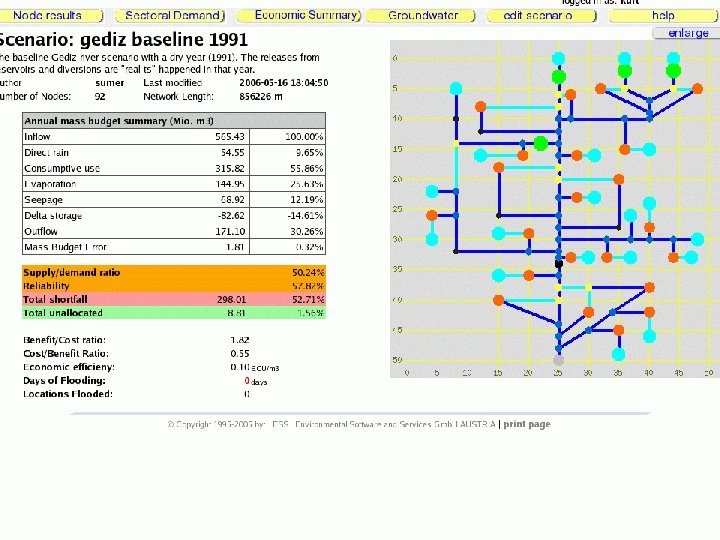
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15

Case studies: how to proceed Optimization framework: • Basic economics – TR, CY, ? • Objectives, constraints: • Instruments, water technologies: New questionnaires ? INSTRUMENTS, CONSTRAINTS 16

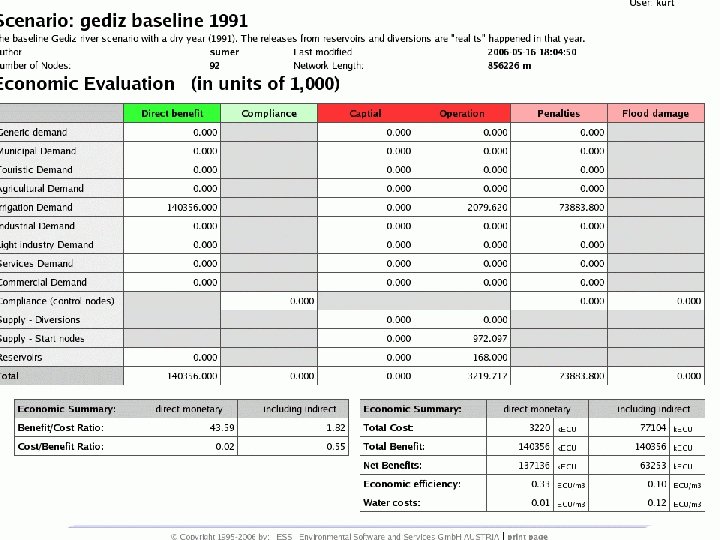
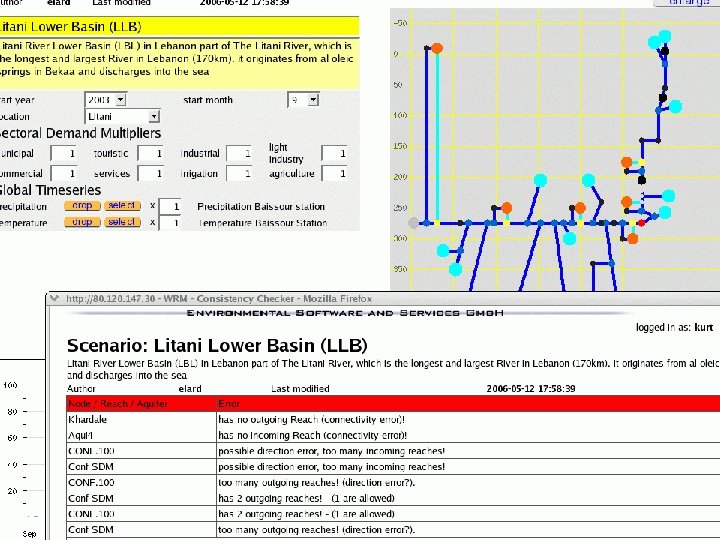
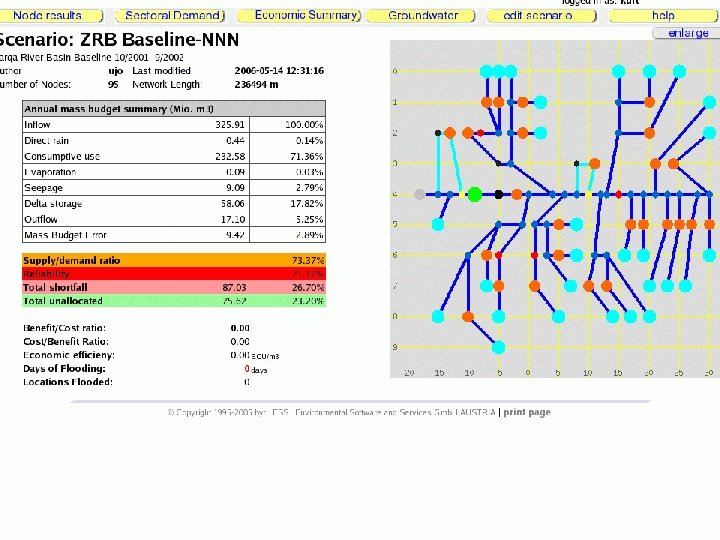
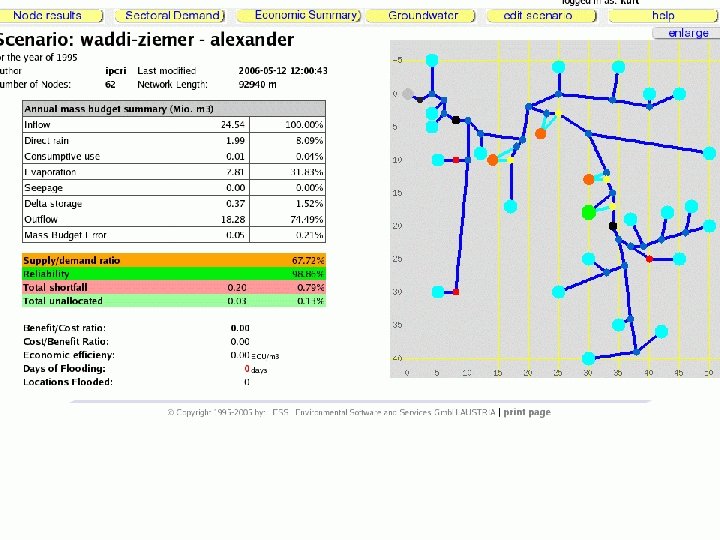
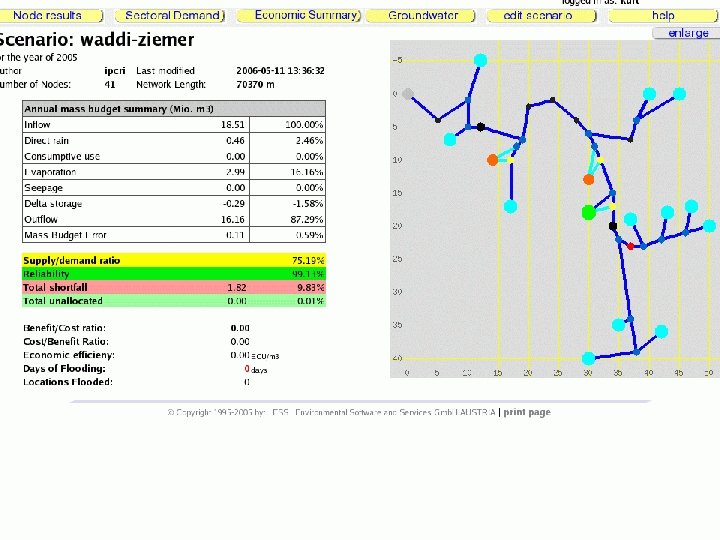
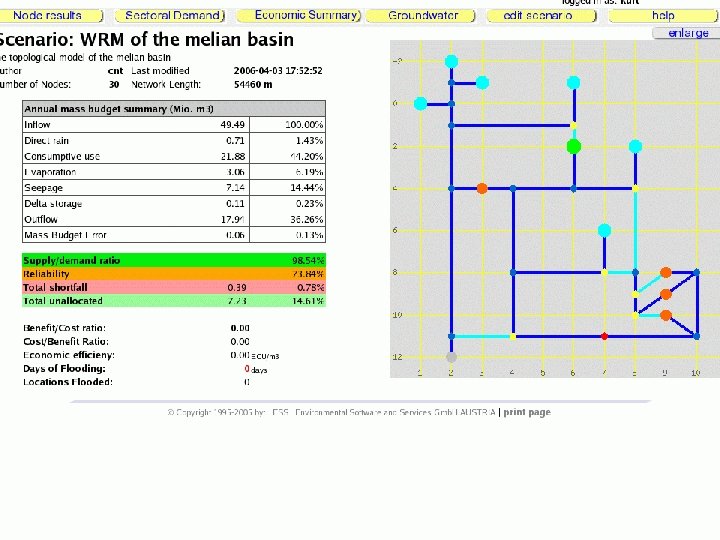
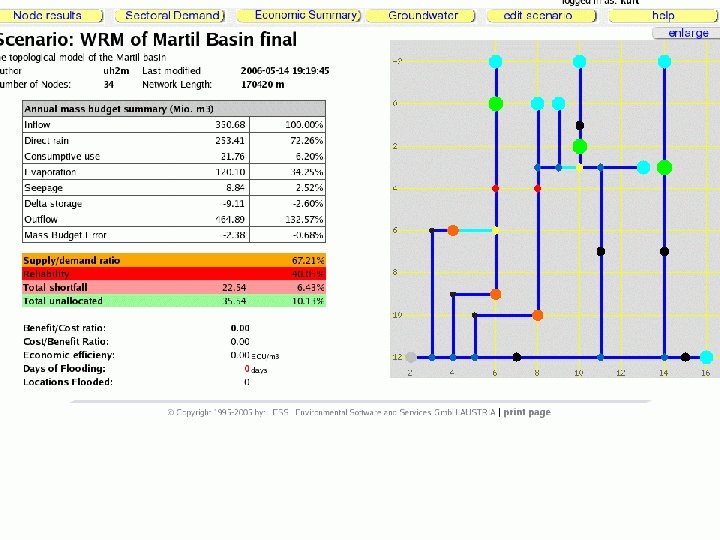
Model use targets: WRM performance targets: • Complete and reasonable scenarios includes groundwater links, realistic reservoir data • Provide observation data for CONTROL NODES, add control nodes for all monitoring stations -> compliance, flood damages • Basic economic assessment 17

ECONOMICS: Direct Costs: • Capital and OMR for start nodes, reservoirs, diversions. Direct Benefits: • demands satisfied for demand nodes 18

ECONOMICS: Indirect Costs: • shortfall at demand nodes • penalties at control nodes • flood damages Indirect benefits: • compliance at control nodes 19

ECONOMICS: Under development for QUALITY: • Cost of treatment (capital, OMR) • Cost of waste water reduction (at demand nodes, capital and OMR) • • Penalties for standard violations (control) Use benefits for clean water (demand) Compliance benefits (control nodes) Use benefits (reaches, e. g. , recreational) 20

OPTIMISATION: CONSTRAINTS: • Global constraints • Node specific constraints • Sectoral (not implemented) directly derived from model results: 21
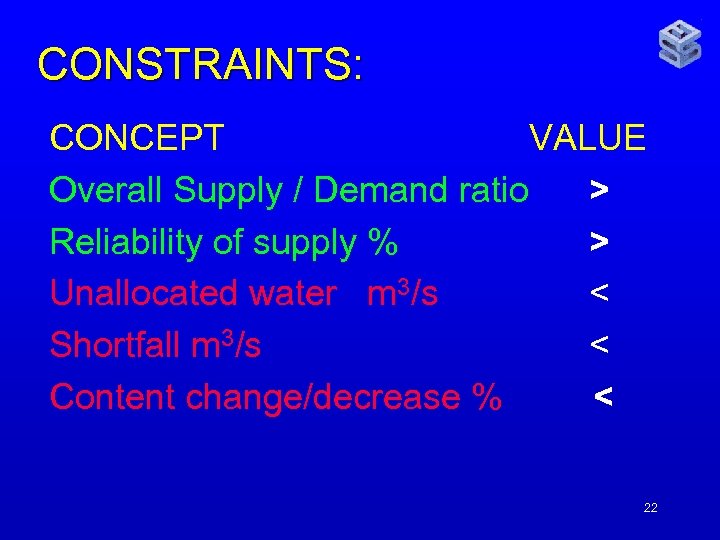
CONSTRAINTS: CONCEPT VALUE Overall Supply / Demand ratio > Reliability of supply % > Unallocated water m 3/s < Shortfall m 3/s < Content change/decrease % < 22

CONSTRAINTS: Total Cost (combined) Total Cost (direct) Cost/Benefit ratio (comb. ) Cost/Benefit ratio (direct) Water Cost (combined) Water Cost (direct) Total Benefit (combined) Total Benefit (direct) Benefit/Cost ratio (comb. ) Benefit/Cost ratio (direct) Economic Efficiency (comb. ) Economic Efficiency (direct) Net Benefit (combined) Net Benefit (direct) And any number of combinations, ratios, node specific, sectoral values, etc. 23
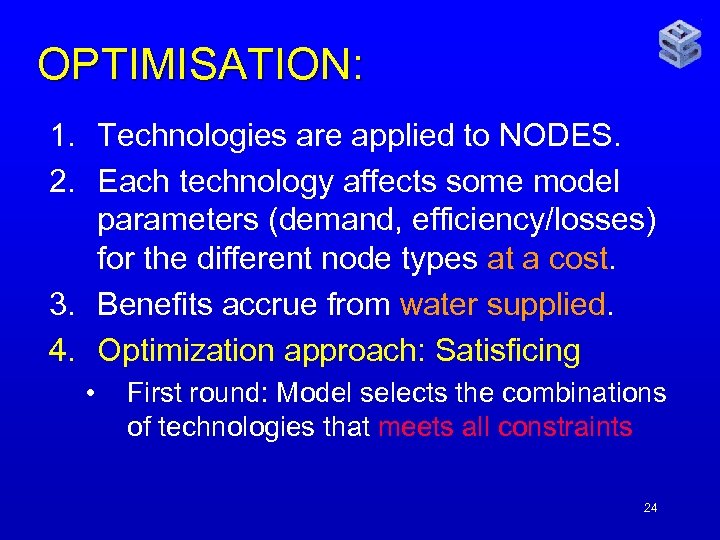
OPTIMISATION: 1. Technologies are applied to NODES. 2. Each technology affects some model parameters (demand, efficiency/losses) for the different node types at a cost. 3. Benefits accrue from water supplied. 4. Optimization approach: Satisficing • First round: Model selects the combinations of technologies that meets all constraints 24

TECHNOLOGIES: Are NOT restricted to technology in a narrow sense, can include policies and institutional change that do affect supply, allocation, demand, efficiency, quality FOR example: – Pricing/subsidies affects demand – Market (privatization) affects allocation – Enforcement (regulatory change) affects quality and efficiency 25
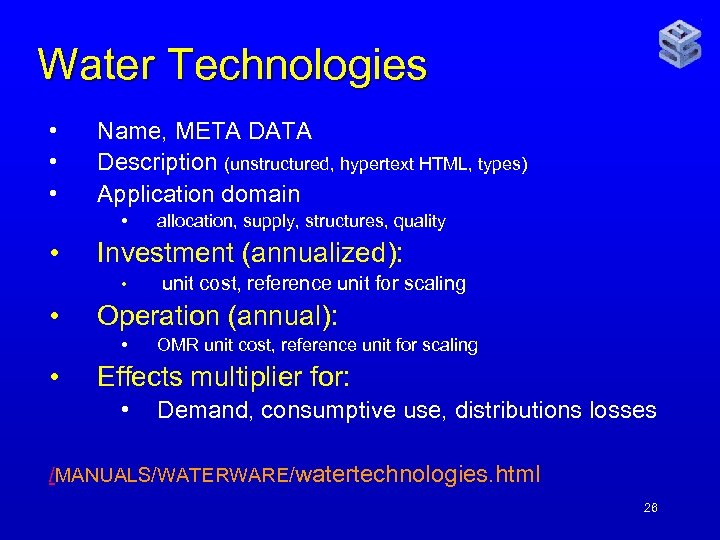
Water Technologies • • • Name, META DATA Description (unstructured, hypertext HTML, types) Application domain • • Investment (annualized): • • unit cost, reference unit for scaling Operation (annual): • • allocation, supply, structures, quality OMR unit cost, reference unit for scaling Effects multiplier for: • Demand, consumptive use, distributions losses /MANUALS/WATERWARE/watertechnologies. html 26
b9dfe97f4263e61a8784b46a418a587f.ppt