151da53235220809ad99cdf64495f308.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Optical telescopes: An oldest eye to the Universe Extremely valuable for Astrophysical studies. As old as human civilization as our Eye acts as optical telescope, detector and analyzer. On 30 Nov 1609, Galileo— 400 years--IYA 09 Recent developments in computers, electronics and in other areas have contributed significantly to the growth of optical telescopes, detectors and image analysis. Ram Sagar 3/18/2018 Optical Telescopes 1
Optical telescopes: An oldest eye to the Universe Extremely valuable for Astrophysical studies. As old as human civilization as our Eye acts as optical telescope, detector and analyzer. On 30 Nov 1609, Galileo— 400 years--IYA 09 Recent developments in computers, electronics and in other areas have contributed significantly to the growth of optical telescopes, detectors and image analysis. Ram Sagar 3/18/2018 Optical Telescopes 1
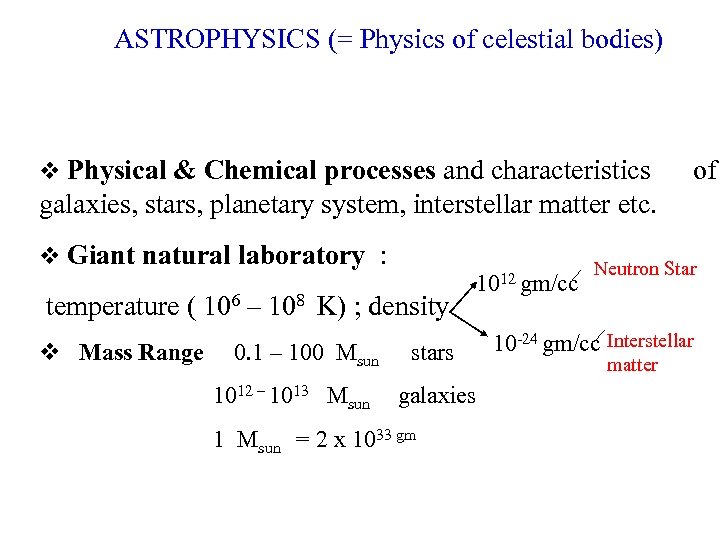 ASTROPHYSICS (= Physics of celestial bodies) Physical & Chemical processes and characteristics of galaxies, stars, planetary system, interstellar matter etc. Giant natural laboratory : temperature ( 106 – 108 K) ; density Mass Range 0. 1 – 100 Msun 1012 – 1013 Msun stars galaxies 1 Msun = 2 x 1033 gm 1012 gm/cc Neutron Star 10 -24 gm/cc Interstellar matter
ASTROPHYSICS (= Physics of celestial bodies) Physical & Chemical processes and characteristics of galaxies, stars, planetary system, interstellar matter etc. Giant natural laboratory : temperature ( 106 – 108 K) ; density Mass Range 0. 1 – 100 Msun 1012 – 1013 Msun stars galaxies 1 Msun = 2 x 1033 gm 1012 gm/cc Neutron Star 10 -24 gm/cc Interstellar matter
 Planetary orbits are elliptical 1605 -1609 Johannes Kepler
Planetary orbits are elliptical 1605 -1609 Johannes Kepler
 Some Contributions to Physics; Pure Science Newton’s interpretations of observations of planetary laws of motions and mechanics; development of calculus General theory of relativity Concept of nuclear fusion Cosmology and high energy particle physics Nobel prize in Physics: - H. A. Bethe in 1967; M. Ryle & A. Hewish in 1974; A. A. Penzias & R. W. Wilson in 1978; S. Chandrasekhar & W. A. Flower in 1983; J. H. Taylor & R. A. Hulse in 1993; R. Davis Jr. , M. Koshiba & R. Giacconi (8 during last 50 yrs); Extremely valuable for knowledge & Society in 2002; J. C. Mather & G. C. Smoot in 2006; Smith group in 2011
Some Contributions to Physics; Pure Science Newton’s interpretations of observations of planetary laws of motions and mechanics; development of calculus General theory of relativity Concept of nuclear fusion Cosmology and high energy particle physics Nobel prize in Physics: - H. A. Bethe in 1967; M. Ryle & A. Hewish in 1974; A. A. Penzias & R. W. Wilson in 1978; S. Chandrasekhar & W. A. Flower in 1983; J. H. Taylor & R. A. Hulse in 1993; R. Davis Jr. , M. Koshiba & R. Giacconi (8 during last 50 yrs); Extremely valuable for knowledge & Society in 2002; J. C. Mather & G. C. Smoot in 2006; Smith group in 2011
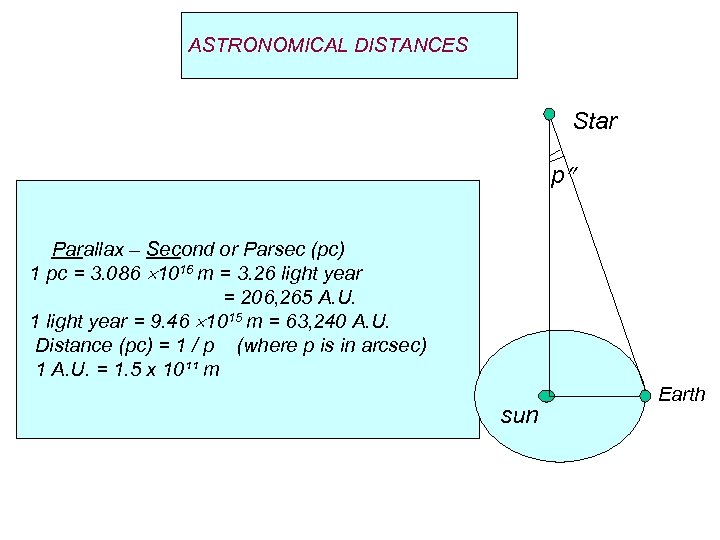 ASTRONOMICAL DISTANCES Star p Parallax – Second or Parsec (pc) 1 pc = 3. 086 1016 m = 3. 26 light year = 206, 265 A. U. 1 light year = 9. 46 1015 m = 63, 240 A. U. Distance (pc) = 1 / p (where p is in arcsec) 1 A. U. = 1. 5 x 10¹¹ m sun Earth
ASTRONOMICAL DISTANCES Star p Parallax – Second or Parsec (pc) 1 pc = 3. 086 1016 m = 3. 26 light year = 206, 265 A. U. 1 light year = 9. 46 1015 m = 63, 240 A. U. Distance (pc) = 1 / p (where p is in arcsec) 1 A. U. = 1. 5 x 10¹¹ m sun Earth
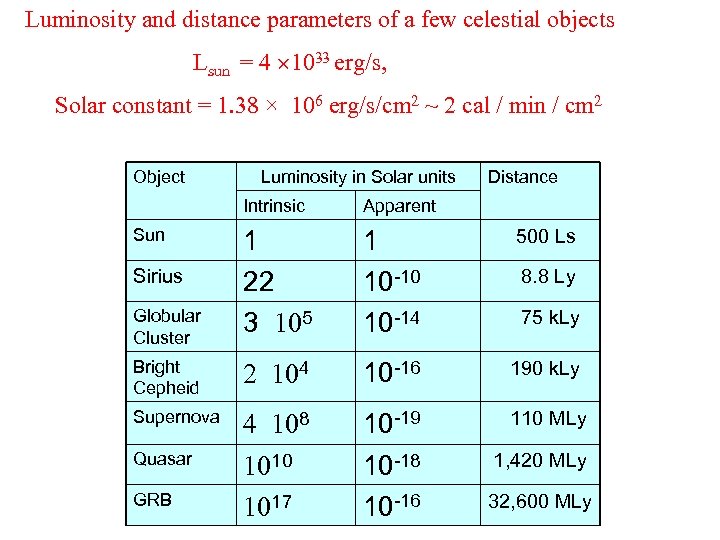 Luminosity and distance parameters of a few celestial objects Lsun = 4 1033 erg/s, Solar constant = 1. 38 × 106 erg/s/cm 2 ~ 2 cal / min / cm 2 Object Luminosity in Solar units Distance Intrinsic Apparent 1 22 3 105 1 10 -10 10 -14 500 Ls Bright Cepheid 2 104 10 -16 190 k. Ly Supernova 4 108 10 -19 110 MLy Quasar 1010 1017 10 -18 10 -16 1, 420 MLy Sun Sirius Globular Cluster GRB 8. 8 Ly 75 k. Ly 32, 600 MLy
Luminosity and distance parameters of a few celestial objects Lsun = 4 1033 erg/s, Solar constant = 1. 38 × 106 erg/s/cm 2 ~ 2 cal / min / cm 2 Object Luminosity in Solar units Distance Intrinsic Apparent 1 22 3 105 1 10 -10 10 -14 500 Ls Bright Cepheid 2 104 10 -16 190 k. Ly Supernova 4 108 10 -19 110 MLy Quasar 1010 1017 10 -18 10 -16 1, 420 MLy Sun Sirius Globular Cluster GRB 8. 8 Ly 75 k. Ly 32, 600 MLy
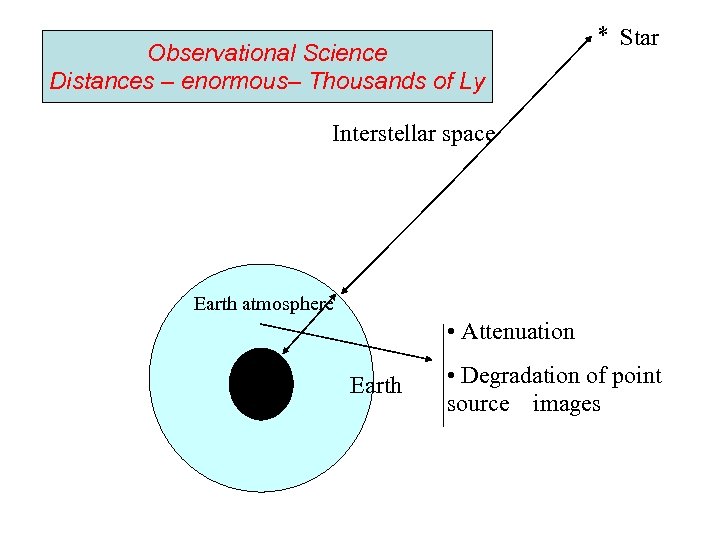 Observational Science Distances – enormous– Thousands of Ly Star Interstellar space Earth atmosphere • Attenuation Earth • Degradation of point source images
Observational Science Distances – enormous– Thousands of Ly Star Interstellar space Earth atmosphere • Attenuation Earth • Degradation of point source images
 Purpose of an optical telescope 1. Angular resolution or Resolving Power - indicates ability to see fine details - limited by two factors. Diffraction Resolving Power (RP) = 1. 22 D = 14 / D (in cm) At 5500 Å OPTICAL (can be improved by using a larger size objective). Environment (telescope images are degraded by the blurring effect of Earth’s atmosphere and light pollution (can be improved by placing the telescope on top a mountain hill with very smooth air or in space)
Purpose of an optical telescope 1. Angular resolution or Resolving Power - indicates ability to see fine details - limited by two factors. Diffraction Resolving Power (RP) = 1. 22 D = 14 / D (in cm) At 5500 Å OPTICAL (can be improved by using a larger size objective). Environment (telescope images are degraded by the blurring effect of Earth’s atmosphere and light pollution (can be improved by placing the telescope on top a mountain hill with very smooth air or in space)
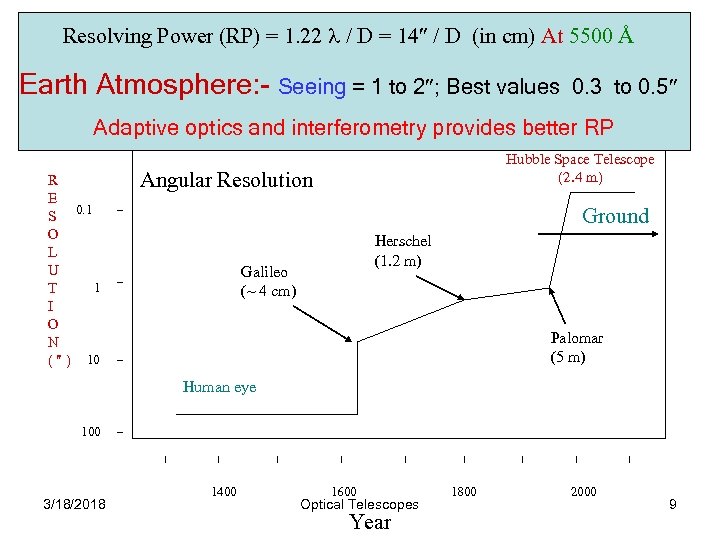 Resolving Power (RP) = 1. 22 l / D = 14² / D (in cm) At 5500 Å Resolving Power : Cont’d Earth Atmosphere: - Seeing = 1 to 2²; Best values 0. 3 to 0. 5² Adaptive optics and interferometry provides better RP R E S 0. 1 O L U 1 T I O N ( ² ) 10 Hubble Space Telescope (2. 4 m) Angular Resolution Ground Herschel (1. 2 m) Galileo (~ 4 cm) Palomar (5 m) Human eye 100 3/18/2018 1400 1600 Optical Telescopes Year 1800 2000 9
Resolving Power (RP) = 1. 22 l / D = 14² / D (in cm) At 5500 Å Resolving Power : Cont’d Earth Atmosphere: - Seeing = 1 to 2²; Best values 0. 3 to 0. 5² Adaptive optics and interferometry provides better RP R E S 0. 1 O L U 1 T I O N ( ² ) 10 Hubble Space Telescope (2. 4 m) Angular Resolution Ground Herschel (1. 2 m) Galileo (~ 4 cm) Palomar (5 m) Human eye 100 3/18/2018 1400 1600 Optical Telescopes Year 1800 2000 9
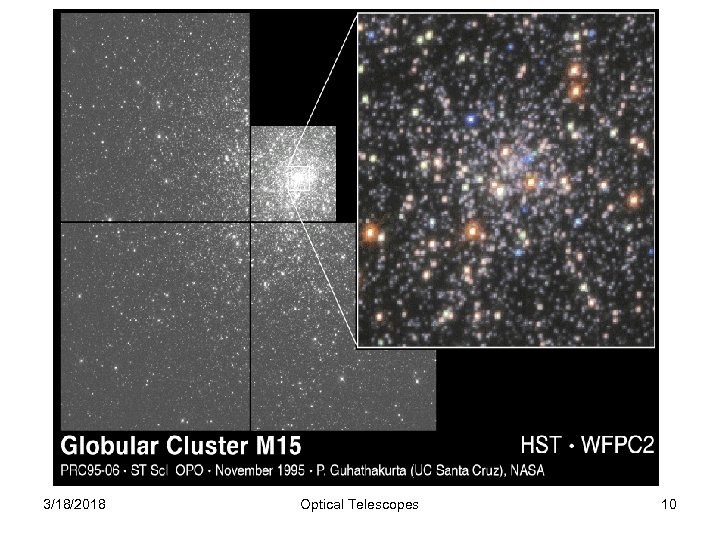 3/18/2018 Optical Telescopes 10
3/18/2018 Optical Telescopes 10
 Star Forming Regions
Star Forming Regions
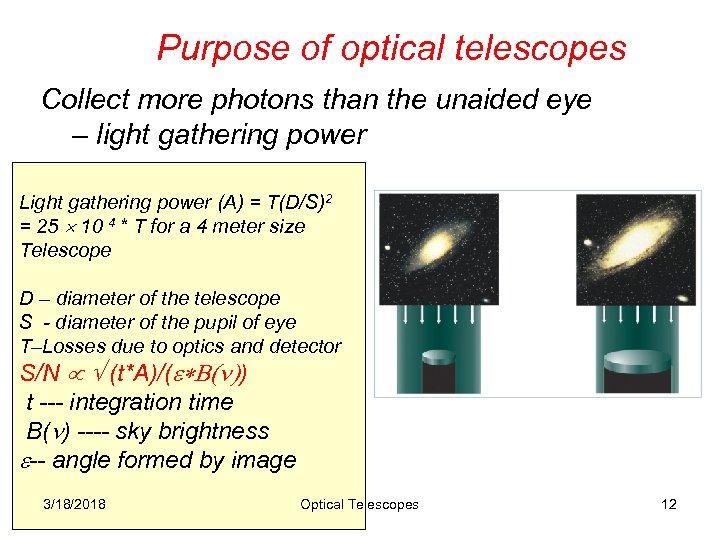 Purpose of optical telescopes Collect more photons than the unaided eye – light gathering power Light gathering power (A) = T(D/S)2 = 25 10 4 * T for a 4 meter size Telescope D – diameter of the telescope S - diameter of the pupil of eye T–Losses due to optics and detector S/N (t*A)/( ) t --- integration time B( ) ---- sky brightness -- angle formed by image 3/18/2018 Optical Telescopes 12
Purpose of optical telescopes Collect more photons than the unaided eye – light gathering power Light gathering power (A) = T(D/S)2 = 25 10 4 * T for a 4 meter size Telescope D – diameter of the telescope S - diameter of the pupil of eye T–Losses due to optics and detector S/N (t*A)/( ) t --- integration time B( ) ---- sky brightness -- angle formed by image 3/18/2018 Optical Telescopes 12
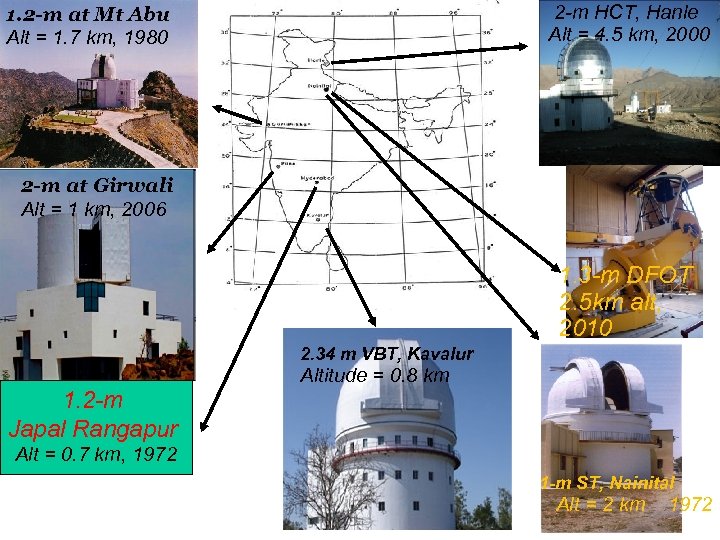 2 -m HCT, Hanle Alt = 4. 5 km, 2000 1. 2 -m at Mt Abu Alt = 1. 7 km, 1980 2 -m at Girwali Alt = 1 km, 2006 1. 3 -m DFOT 2. 5 km alt, 2010 2. 34 m VBT, Kavalur Altitude = 0. 8 km 1. 2 -m Japal Rangapur Alt = 0. 7 km, 1972 1 -m ST, Nainital Alt = 2 km 1972
2 -m HCT, Hanle Alt = 4. 5 km, 2000 1. 2 -m at Mt Abu Alt = 1. 7 km, 1980 2 -m at Girwali Alt = 1 km, 2006 1. 3 -m DFOT 2. 5 km alt, 2010 2. 34 m VBT, Kavalur Altitude = 0. 8 km 1. 2 -m Japal Rangapur Alt = 0. 7 km, 1972 1 -m ST, Nainital Alt = 2 km 1972
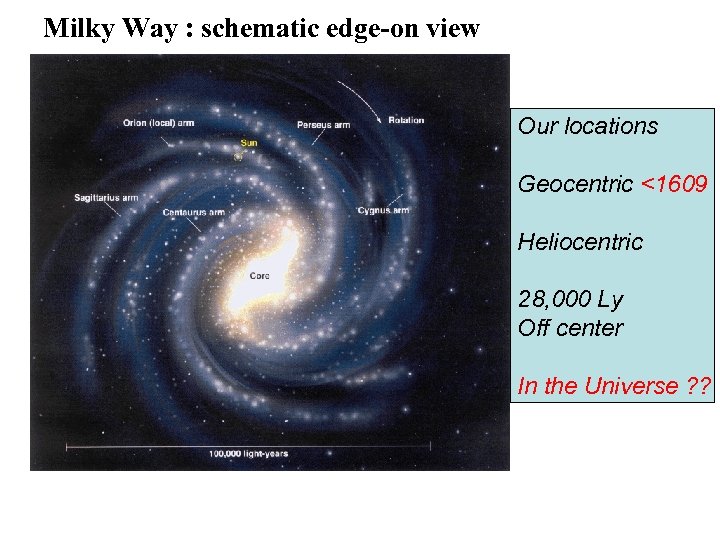 Milky Way : schematic edge-on view Our locations Geocentric <1609 Heliocentric 28, 000 Ly Off center In the Universe ? ?
Milky Way : schematic edge-on view Our locations Geocentric <1609 Heliocentric 28, 000 Ly Off center In the Universe ? ?
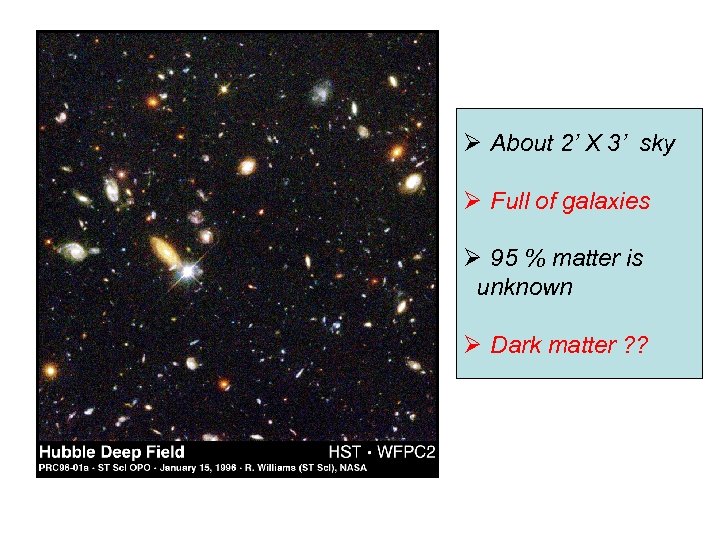 Ø About 2’ X 3’ sky Ø Full of galaxies Ø 95 % matter is unknown Ø Dark matter ? ?
Ø About 2’ X 3’ sky Ø Full of galaxies Ø 95 % matter is unknown Ø Dark matter ? ?
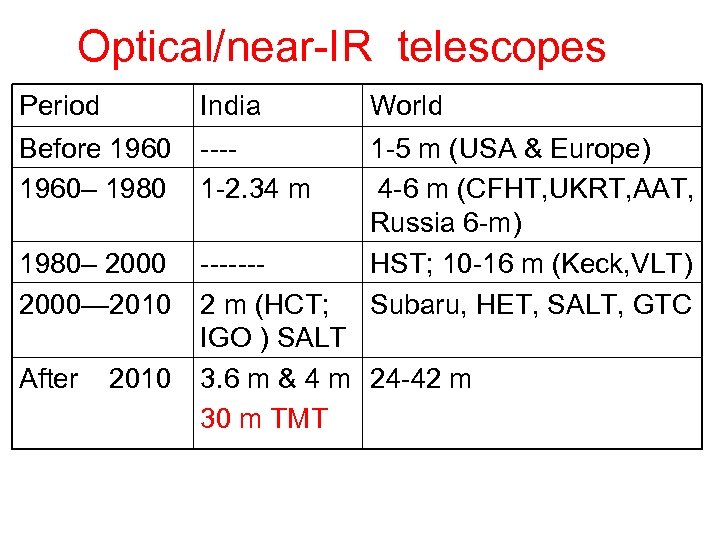 Optical/near-IR telescopes Period India World Before 1960– 1980 ---1 -2. 34 m 1980– 2000— 2010 1 -5 m (USA & Europe) 4 -6 m (CFHT, UKRT, AAT, Russia 6 -m) HST; 10 -16 m (Keck, VLT) Subaru, HET, SALT, GTC ------2 m (HCT; IGO ) SALT 3. 6 m & 4 m 24 -42 m 30 m TMT After 2010
Optical/near-IR telescopes Period India World Before 1960– 1980 ---1 -2. 34 m 1980– 2000— 2010 1 -5 m (USA & Europe) 4 -6 m (CFHT, UKRT, AAT, Russia 6 -m) HST; 10 -16 m (Keck, VLT) Subaru, HET, SALT, GTC ------2 m (HCT; IGO ) SALT 3. 6 m & 4 m 24 -42 m 30 m TMT After 2010
 Latest Major Indian Initiatives in Astrophysics ASTROSAT – Visible, UV and X-ray astronomy The first Indian multi-wavelength astronomy satellite launched on Sep 28, 2015 with 5 instruments and a life time of ~5 years. LARGE OPTICAL TELESCOPES 4 -meter ILMT by 2016 with Belgium, Poland & Canada 3. 6 -meter Indian optical telescope installed in May 2015 at Devasthal, Nainital (Jointly with Belgium) Participate in 30 -meter size telescope (10%) and built 8 -10 meter class optical telescope in India by 2030 Square KM Array Radio Telescope by 2025 (10%) LIGO; Indian Neutrino Observatory; NLST etc.
Latest Major Indian Initiatives in Astrophysics ASTROSAT – Visible, UV and X-ray astronomy The first Indian multi-wavelength astronomy satellite launched on Sep 28, 2015 with 5 instruments and a life time of ~5 years. LARGE OPTICAL TELESCOPES 4 -meter ILMT by 2016 with Belgium, Poland & Canada 3. 6 -meter Indian optical telescope installed in May 2015 at Devasthal, Nainital (Jointly with Belgium) Participate in 30 -meter size telescope (10%) and built 8 -10 meter class optical telescope in India by 2030 Square KM Array Radio Telescope by 2025 (10%) LIGO; Indian Neutrino Observatory; NLST etc.
 ASTROSAT Mission – UV & X-Ray Space Observatory (Cost ~ Rs. 500 Crore) The First Indian Multi-wavelength Astronomical Satellite
ASTROSAT Mission – UV & X-Ray Space Observatory (Cost ~ Rs. 500 Crore) The First Indian Multi-wavelength Astronomical Satellite
 3. 6 m Project Schedule (2007 -2015) Project Cost ~ Rs. 150 Crore (BELGIUM Contribution is ~ 10 % => 7 % observing time) Key players • The telescope is manufactured by Advanced Mechanical & Optical System (AMOS), Liege in Belgium. Observatory Control system and data archiving are being developed by ARIES. • The mirror blank was purchased from SCHOTT, Germany. • It is 3. 7 meter in diameter & 165 mm in thickness. It was figured and polished by Lytkarino Optical Glass Factory (LZOS), Moscow, Russia. • The dome/enclosure is being completed by Pedvak & PPS, India. • The aluminizing unit was delivered by HHV, India.
3. 6 m Project Schedule (2007 -2015) Project Cost ~ Rs. 150 Crore (BELGIUM Contribution is ~ 10 % => 7 % observing time) Key players • The telescope is manufactured by Advanced Mechanical & Optical System (AMOS), Liege in Belgium. Observatory Control system and data archiving are being developed by ARIES. • The mirror blank was purchased from SCHOTT, Germany. • It is 3. 7 meter in diameter & 165 mm in thickness. It was figured and polished by Lytkarino Optical Glass Factory (LZOS), Moscow, Russia. • The dome/enclosure is being completed by Pedvak & PPS, India. • The aluminizing unit was delivered by HHV, India.
 As-built Telescope Height : 13 m Width : 7 m Weight : 150 ton AMOS workshop, Feb 2012
As-built Telescope Height : 13 m Width : 7 m Weight : 150 ton AMOS workshop, Feb 2012
 Telescope installed and first image taken in May 2015
Telescope installed and first image taken in May 2015
 URANUS and its Rings (Discovered on 13 March 1781 by William Herschel) • • • Diameter : 52640 Km (4. 1 times Earth) Mass : 14. 5 times Earth Density : 1. 1 gm/cc Surface Gravity : 0. 9 times Earth Distance from Sun : 19. 2 AU Distance from Earth : 17 to 21 AU Orbital Period : 84 years Rotation Period : 17 h 14 m Known Moons : 26 Rings : Present Atmosphere : >1000 times Earth (82% H 2, 15% He, 2% CH 4)
URANUS and its Rings (Discovered on 13 March 1781 by William Herschel) • • • Diameter : 52640 Km (4. 1 times Earth) Mass : 14. 5 times Earth Density : 1. 1 gm/cc Surface Gravity : 0. 9 times Earth Distance from Sun : 19. 2 AU Distance from Earth : 17 to 21 AU Orbital Period : 84 years Rotation Period : 17 h 14 m Known Moons : 26 Rings : Present Atmosphere : >1000 times Earth (82% H 2, 15% He, 2% CH 4)
 Hale-Bopp Comet (Dust and Ion Tails are Visible)
Hale-Bopp Comet (Dust and Ion Tails are Visible)
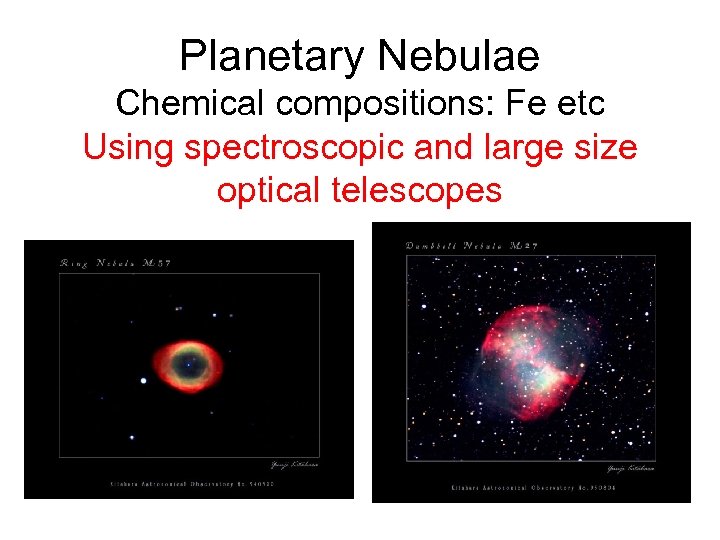 Planetary Nebulae Chemical compositions: Fe etc Using spectroscopic and large size optical telescopes
Planetary Nebulae Chemical compositions: Fe etc Using spectroscopic and large size optical telescopes
 Where life can exist? • Human life can not exist on the surface of stars as its temperature ranges from few to 50 thousands deg C and surfaces are gaseous • Places like MOON are not conducive for human life as there is no atmosphere (escape velocity) • Knowledge of Solar system indicates that planetary systems around other stars should exist so that some form of life can exist on the planets • Theory of Solar system formation indicates that other stars should also have Planetary systems
Where life can exist? • Human life can not exist on the surface of stars as its temperature ranges from few to 50 thousands deg C and surfaces are gaseous • Places like MOON are not conducive for human life as there is no atmosphere (escape velocity) • Knowledge of Solar system indicates that planetary systems around other stars should exist so that some form of life can exist on the planets • Theory of Solar system formation indicates that other stars should also have Planetary systems
 Evidence for planetary system around stars located within 1000 ly • More than 3000 Planets around ~400 stars are observed • This is one of the major discovery in the area of Astrophysics during last decade • Life (may be human also) can exist beyond Earth. How to communicate with them? • Efforts are on but problems are enormous. It could be due to language, culture etc
Evidence for planetary system around stars located within 1000 ly • More than 3000 Planets around ~400 stars are observed • This is one of the major discovery in the area of Astrophysics during last decade • Life (may be human also) can exist beyond Earth. How to communicate with them? • Efforts are on but problems are enormous. It could be due to language, culture etc
 Giant Segmented Mirror Telescopes (GSMTs) 24. 5 -m GMT 30 -m TMT 39 -m E-ELT • In 1997, Indian Astronomers led by ARIES, IIA & IUCAA started thinking about participation. DST also took initiative. • In June 2010, DST approved India’s participation and also provided seed money for capability demonstration. • In March 2012, DST and DAE decided to set up India TMT coordination centre (ITCC) at IIA, Bengaluru. • In Oct 2014, India signed agreement (~Rs 15, 000 Crores) 27/25
Giant Segmented Mirror Telescopes (GSMTs) 24. 5 -m GMT 30 -m TMT 39 -m E-ELT • In 1997, Indian Astronomers led by ARIES, IIA & IUCAA started thinking about participation. DST also took initiative. • In June 2010, DST approved India’s participation and also provided seed money for capability demonstration. • In March 2012, DST and DAE decided to set up India TMT coordination centre (ITCC) at IIA, Bengaluru. • In Oct 2014, India signed agreement (~Rs 15, 000 Crores) 27/25
 Thanks 28
Thanks 28
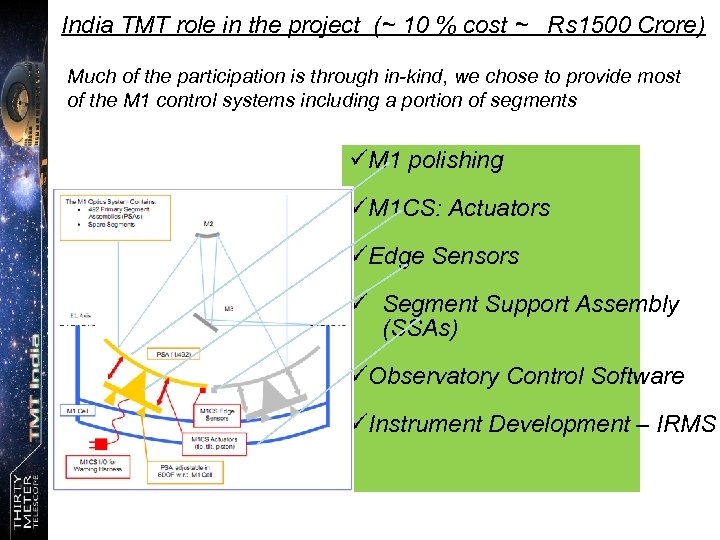 India TMT role in the project (~ 10 % cost ~ Rs 1500 Crore) Much of the participation is through in-kind, we chose to provide most of the M 1 control systems including a portion of segments üM 1 polishing üM 1 CS: Actuators üEdge Sensors ü Segment Support Assembly (SSAs) üObservatory Control Software üInstrument Development – IRMS
India TMT role in the project (~ 10 % cost ~ Rs 1500 Crore) Much of the participation is through in-kind, we chose to provide most of the M 1 control systems including a portion of segments üM 1 polishing üM 1 CS: Actuators üEdge Sensors ü Segment Support Assembly (SSAs) üObservatory Control Software üInstrument Development – IRMS
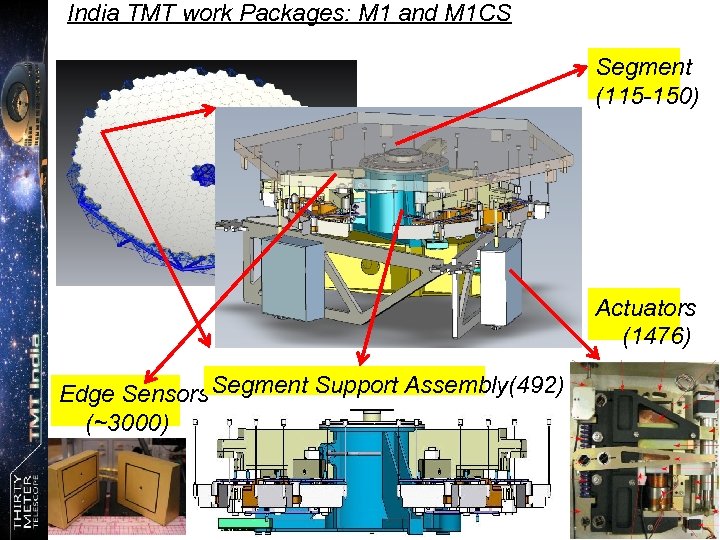 India TMT work Packages: M 1 and M 1 CS Segment (115 -150) Actuators (1476) Edge Sensors Segment Support Assembly(492) (~3000) 30
India TMT work Packages: M 1 and M 1 CS Segment (115 -150) Actuators (1476) Edge Sensors Segment Support Assembly(492) (~3000) 30
 Summary and conclusions • Modern GB techniques and space HST have provided us with unprecedented angular resolution and has brought the Universe 10 times closure. • CCDs have virtually become an optical detector - capable of detecting a billionth times fainter than naked eye stars. • With innovative technologies like thin & segmented mirrors techniques and advancements in computers and electronics, the telescopes have become cheaper than they were 30 -40 years back. • As a result Ground based optical telescopes as big as ~ 40 meter are being designed and ~ 100 meter are under planning. Hence it always require cutting edge of the latest technology. • Enormous potential for discovery due to vastness of the Universe. It could be more than 1 everyday.
Summary and conclusions • Modern GB techniques and space HST have provided us with unprecedented angular resolution and has brought the Universe 10 times closure. • CCDs have virtually become an optical detector - capable of detecting a billionth times fainter than naked eye stars. • With innovative technologies like thin & segmented mirrors techniques and advancements in computers and electronics, the telescopes have become cheaper than they were 30 -40 years back. • As a result Ground based optical telescopes as big as ~ 40 meter are being designed and ~ 100 meter are under planning. Hence it always require cutting edge of the latest technology. • Enormous potential for discovery due to vastness of the Universe. It could be more than 1 everyday.
 Thanks for your attention
Thanks for your attention


