bfed648934832e8c6dde9edbd3fe3b20.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Optical synchronization overview Holger Schlarb on behave of Lb. Syn
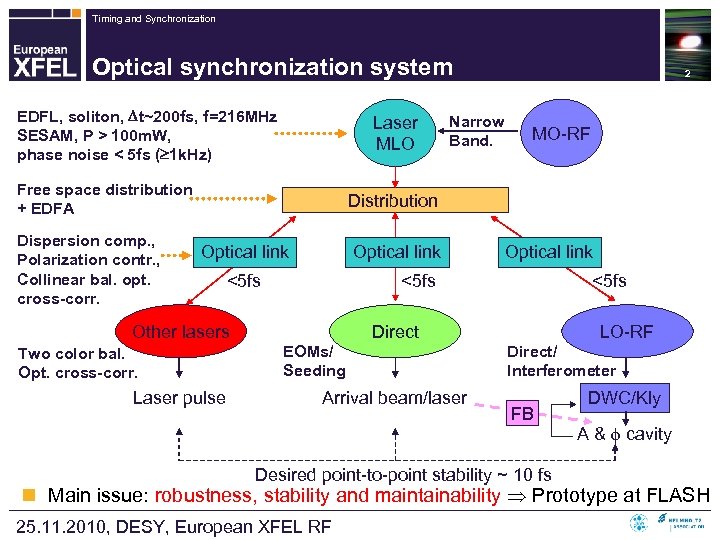
Timing and Synchronization Optical synchronization system EDFL, soliton, t~200 fs, f=216 MHz SESAM, P > 100 m. W, phase noise < 5 fs ( 1 k. Hz) Laser MLO Free space distribution + EDFA Dispersion comp. , Polarization contr. , Collinear bal. opt. cross-corr. Narrow Band. 2 MO-RF Distribution Optical link <5 fs Other lasers Two color bal. Opt. cross-corr. Laser pulse Optical link <5 fs End-station Direct EOMs/ Seeding Arrival beam/laser LO-RF Direct/ Interferometer FB Desired point-to-point stability ~ 10 fs DWC/Kly A & cavity n Main issue: robustness, stability and maintainability Prototype at FLASH 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF
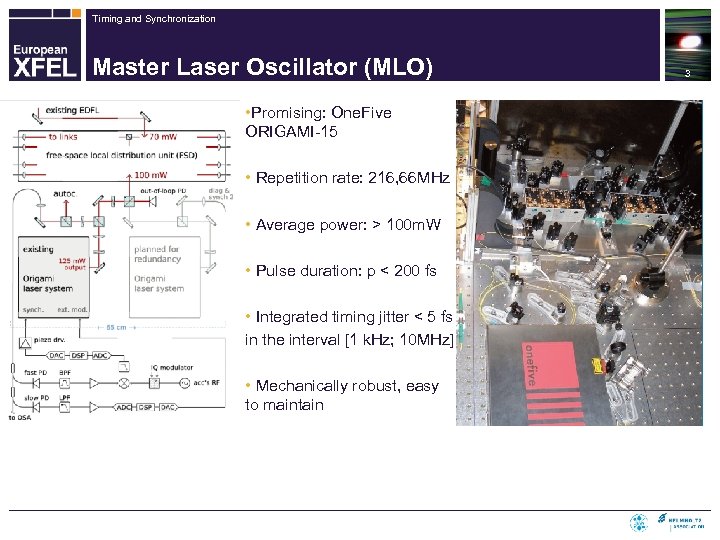
Timing and Synchronization Master Laser Oscillator (MLO) • Promising: One. Five ORIGAMI-15 • Repetition rate: 216, 66 MHz • Average power: > 100 m. W • Pulse duration: p < 200 fs • Integrated timing jitter < 5 fs in the interval [1 k. Hz; 10 MHz] • Mechanically robust, easy to maintain 3
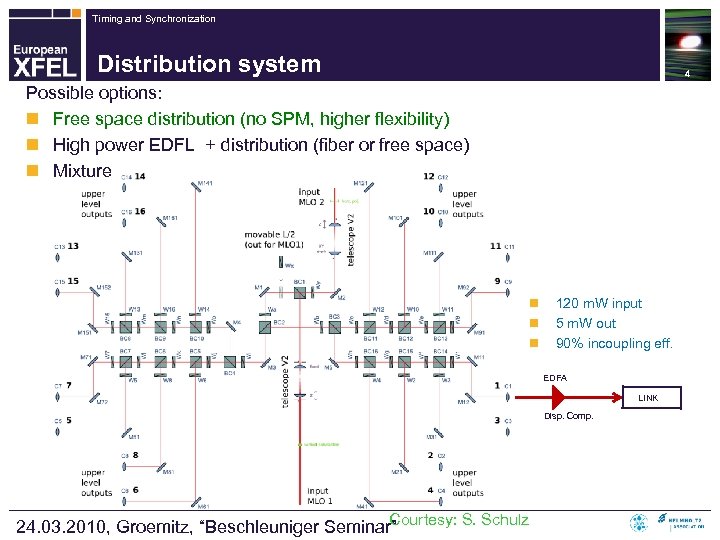
Timing and Synchronization Distribution system 4 Possible options: n Free space distribution (no SPM, higher flexibility) n High power EDFL + distribution (fiber or free space) n Mixture n n n 120 m. W input 5 m. W out 90% incoupling eff. EDFA LINK Disp. Comp. Courtesy: S. Schulz 24. 03. 2010, Groemitz, “Beschleuniger Seminar”
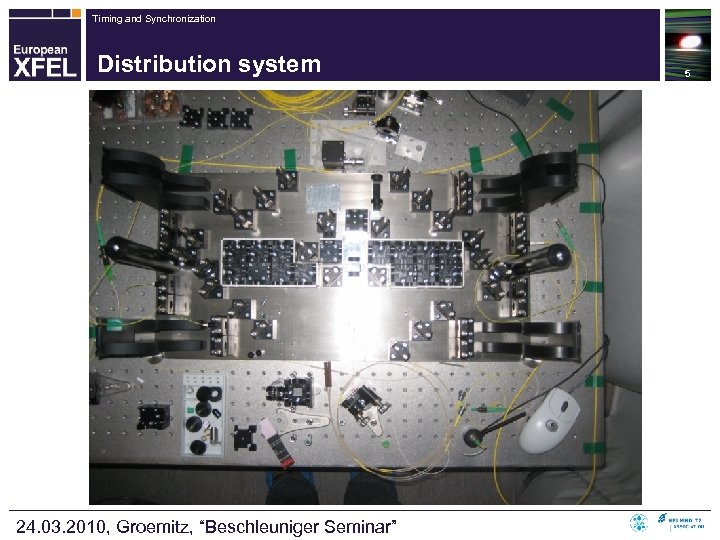
Timing and Synchronization Distribution system 24. 03. 2010, Groemitz, “Beschleuniger Seminar” 5
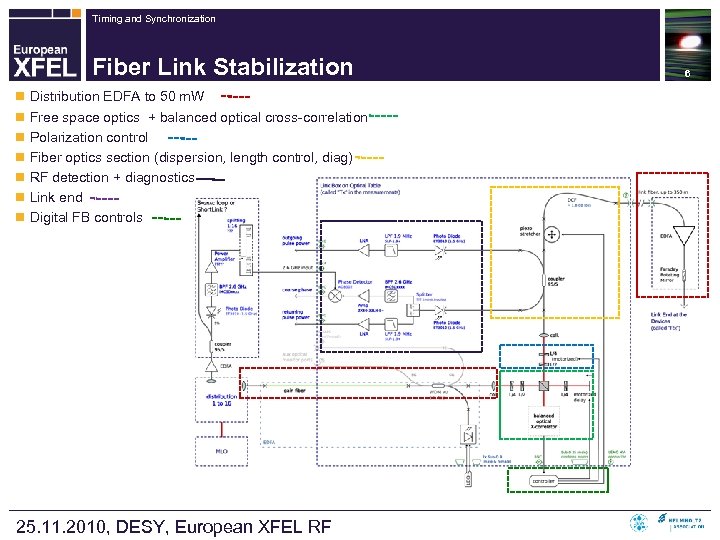
Timing and Synchronization Fiber Link Stabilization n Distribution EDFA to 50 m. W n Free space optics + balanced optical cross-correlation n Polarization control n Fiber optics section (dispersion, length control, diag) n RF detection + diagnostics n Link end n Digital FB controls 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF 6
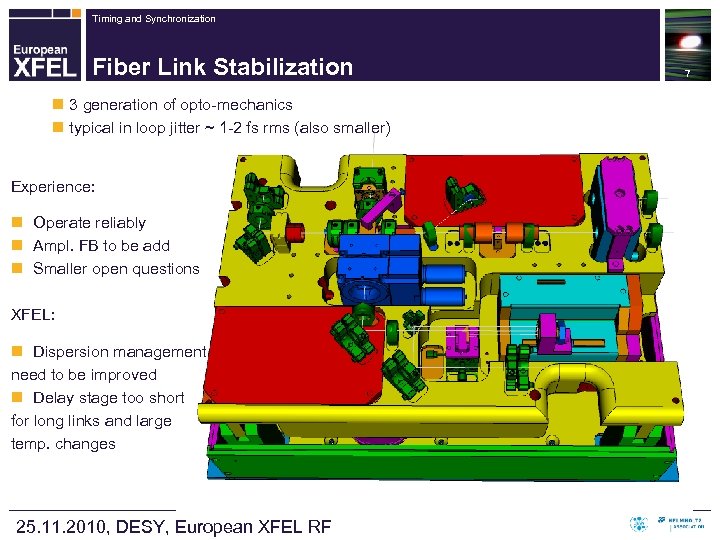
Timing and Synchronization Fiber Link Stabilization n 3 generation of opto-mechanics n typical in loop jitter ~ 1 -2 fs rms (also smaller) Experience: n Operate reliably n Ampl. FB to be add n Smaller open questions XFEL: n Dispersion management need to be improved n Delay stage too short for long links and large temp. changes 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF 7
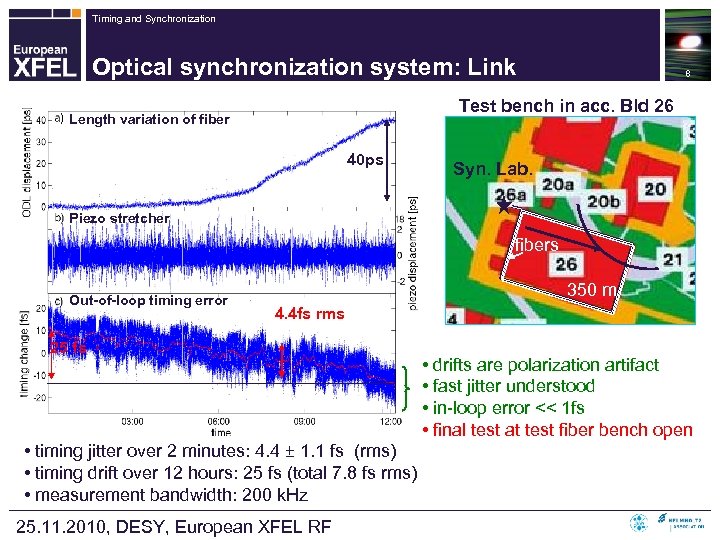
Timing and Synchronization Optical synchronization system: Link 8 Test bench in acc. Bld 26 Length variation of fiber 40 ps Syn. Lab. Piezo stretcher fibers Out-of-loop timing error 350 m 4. 4 fs rms 25 fs • timing jitter over 2 minutes: 4. 4 ± 1. 1 fs (rms) • timing drift over 12 hours: 25 fs (total 7. 8 fs rms) • measurement bandwidth: 200 k. Hz 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF • drifts are polarization artifact • fast jitter understood • in-loop error << 1 fs • final test at test fiber bench open
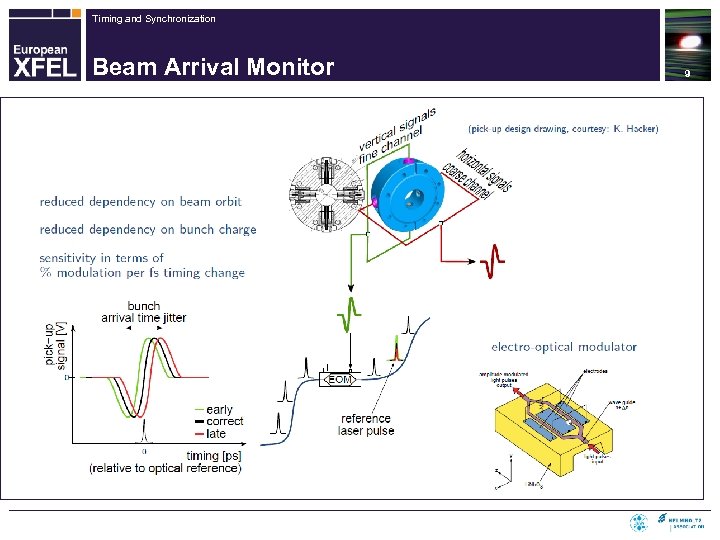
Timing and Synchronization Beam Arrival Monitor 9
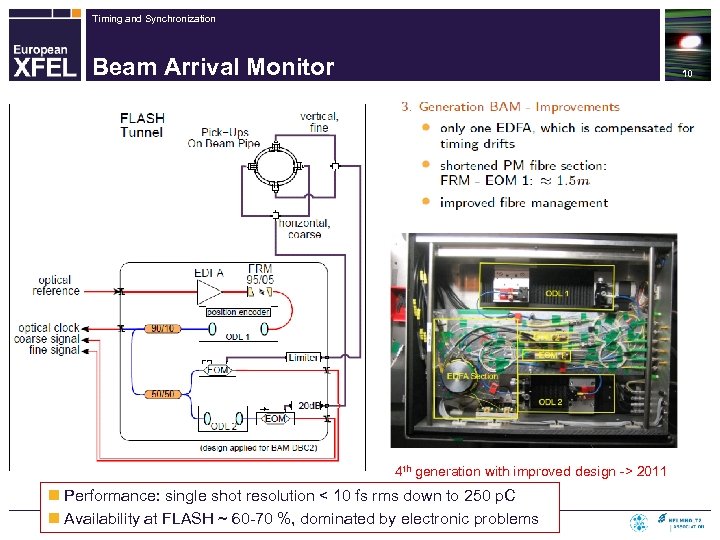
Timing and Synchronization Beam Arrival Monitor 10 4 th generation with improved design -> 2011 n Performance: single shot resolution < 10 fs rms down to 250 p. C n Availability at FLASH ~ 60 -70 %, dominated by electronic problems
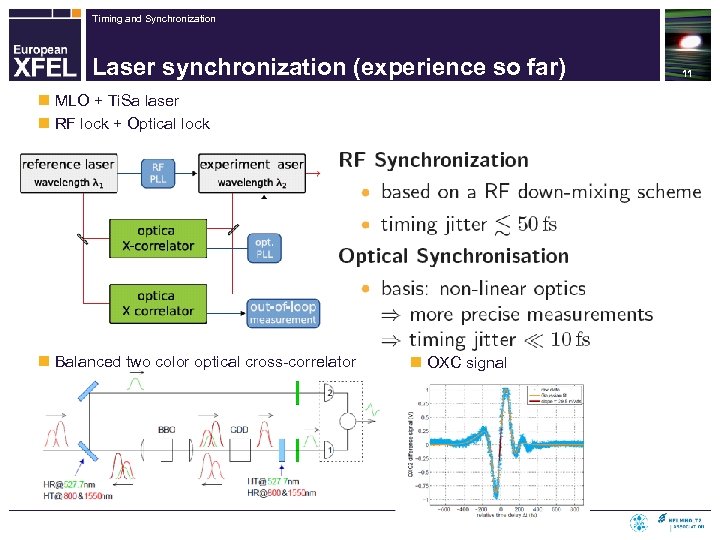
Timing and Synchronization Laser synchronization (experience so far) n MLO + Ti. Sa laser n RF lock + Optical lock n Balanced two color optical cross-correlator n OXC signal 11
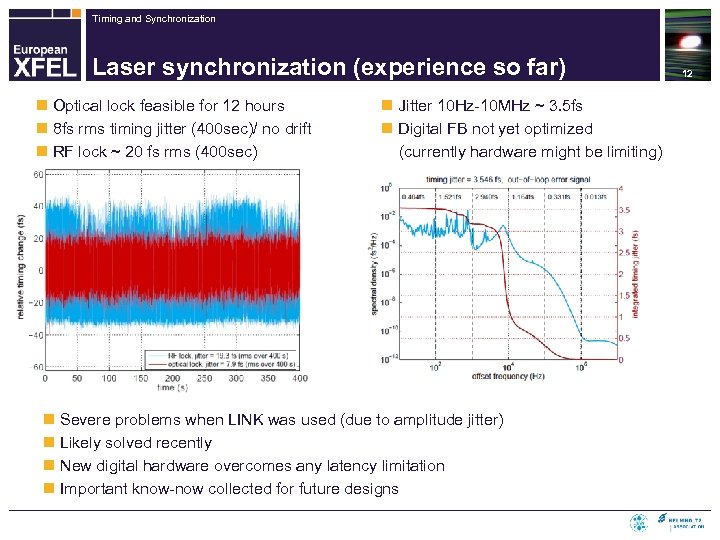
Timing and Synchronization Laser synchronization (experience so far) n Optical lock feasible for 12 hours n 8 fs rms timing jitter (400 sec)/ no drift n RF lock ~ 20 fs rms (400 sec) n Jitter 10 Hz-10 MHz ~ 3. 5 fs n Digital FB not yet optimized (currently hardware might be limiting) n Severe problems when LINK was used (due to amplitude jitter) n Likely solved recently n New digital hardware overcomes any latency limitation n Important know-now collected for future designs 12
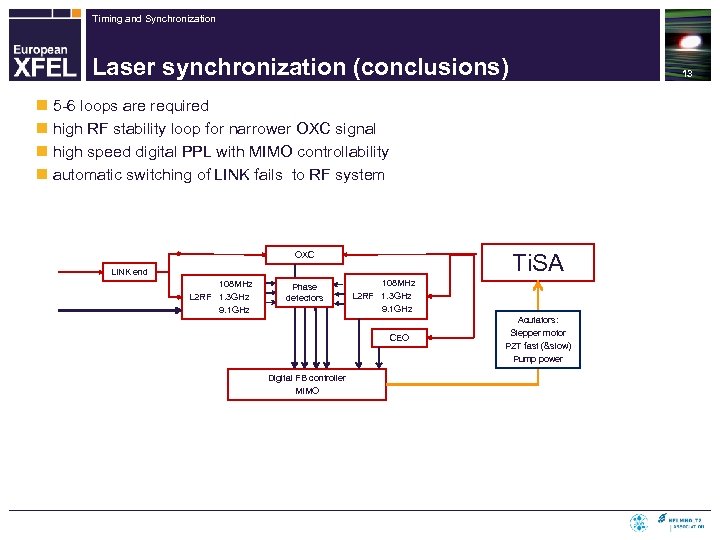
Timing and Synchronization Laser synchronization (conclusions) 13 n 5 -6 loops are required n high RF stability loop for narrower OXC signal n high speed digital PPL with MIMO controllability n automatic switching of LINK fails to RF system Ti. SA OXC LINK end 108 MHz L 2 RF 1. 3 GHz 9. 1 GHz Phase detectors 108 MHz L 2 RF 1. 3 GHz 9. 1 GHz CEO Digital FB controller MIMO Acutators: Stepper motor PZT fast (&slow) Pump power
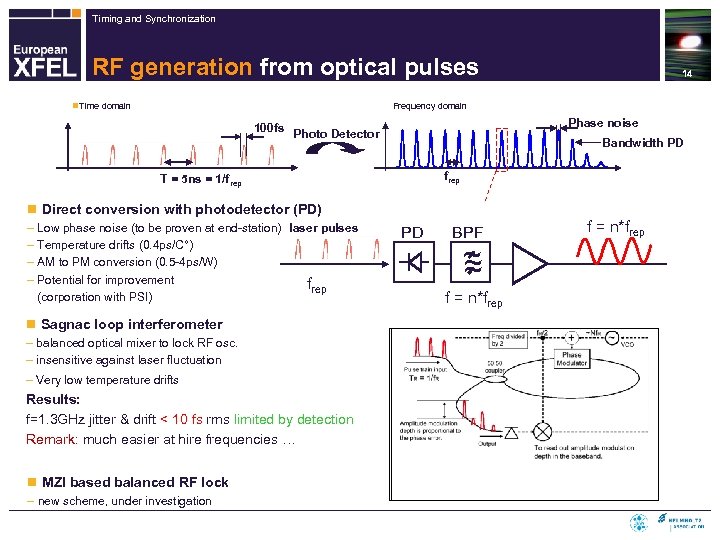
Timing and Synchronization RF generation from optical pulses 14 Frequency domain n. Time domain Phase noise 100 fs Photo Detector Bandwidth PD frep T = 5 ns = 1/frep n Direct conversion with photodetector (PD) – Low phase noise (to be proven at end-station) laser pulses – Temperature drifts (0. 4 ps/C°) – AM to PM conversion (0. 5 -4 ps/W) – Potential for improvement frep (corporation with PSI) n Sagnac loop interferometer – balanced optical mixer to lock RF osc. – insensitive against laser fluctuation – Very low temperature drifts Results: f=1. 3 GHz jitter & drift < 10 fs rms limited by detection Remark: much easier at hire frequencies … n MZI based balanced RF lock – new scheme, under investigation PD BPF ~ ~ ~ f = n*frep
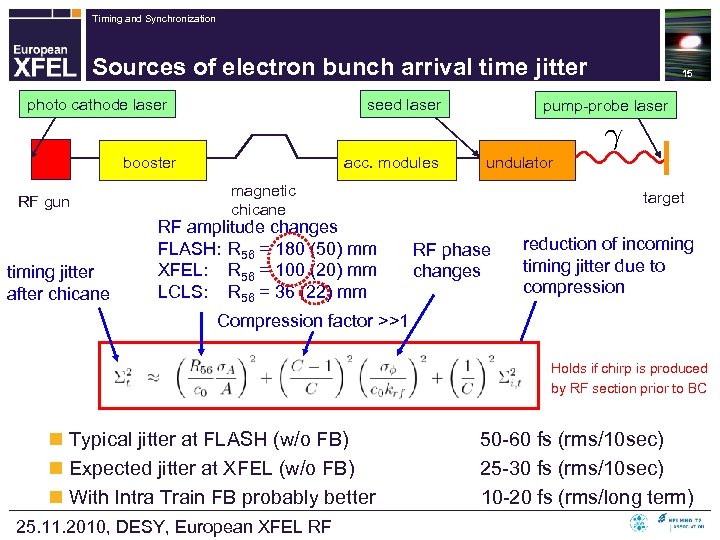
Timing and Synchronization Sources of electron bunch arrival time jitter photo cathode laser seed laser booster RF gun timing jitter after chicane acc. modules pump-probe laser undulator magnetic chicane RF amplitude changes FLASH: R 56 = 180 (50) mm XFEL: R 56 = 100 (20) mm LCLS: R 56 = 36 (22) mm 15 target RF phase changes reduction of incoming timing jitter due to compression Compression factor >>1 Holds if chirp is produced by RF section prior to BC n Typical jitter at FLASH (w/o FB) n Expected jitter at XFEL (w/o FB) n With Intra Train FB probably better 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF 50 -60 fs (rms/10 sec) 25 -30 fs (rms/10 sec) 10 -20 fs (rms/long term)
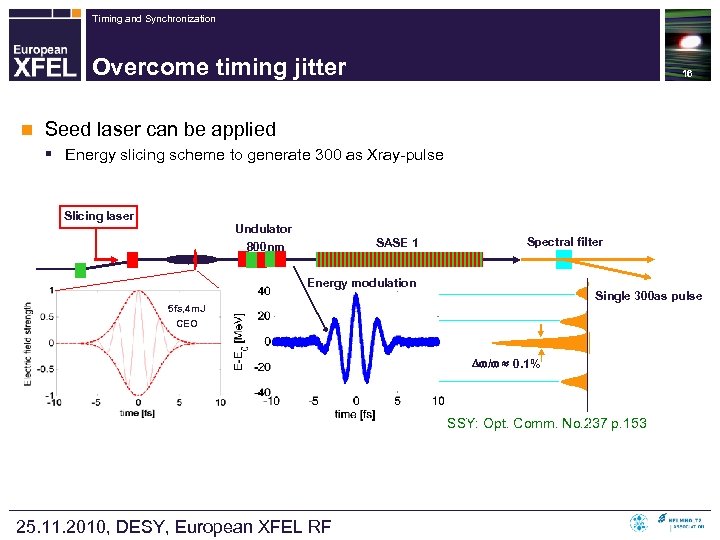
Timing and Synchronization Overcome timing jitter n 16 Seed laser can be applied § Energy slicing scheme to generate 300 as Xray-pulse Slicing laser Undulator 800 nm SASE 1 Spectral filter Energy modulation Single 300 as pulse 5 fs, 4 m. J CEO / 0. 1% SSY: Opt. Comm. No. 237 p. 153 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF
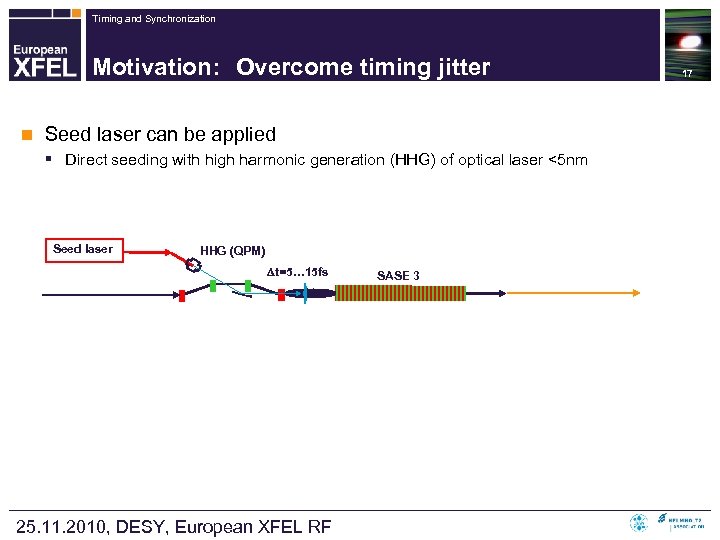
Timing and Synchronization Motivation: Overcome timing jitter n Seed laser can be applied § Direct seeding with high harmonic generation (HHG) of optical laser <5 nm Seed laser HHG (QPM) t=5… 15 fs 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF SASE 3 17
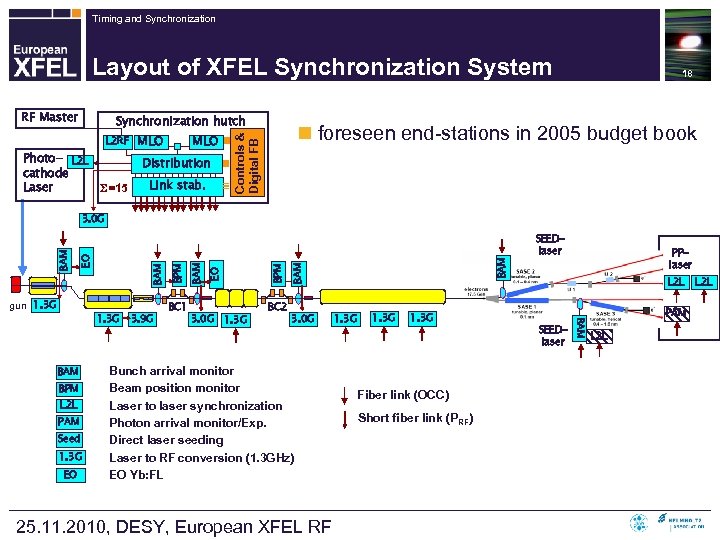
Timing and Synchronization Layout of XFEL Synchronization System RF Master Synchronization hutch Photo- L 2 L cathode Laser =15 MLO Distribution Link stab. n foreseen end-stations in 2005 budget book Controls & Digital FB L 2 RF 18 gun 1. 3 G BAM BPM L 2 L PAM Seed 1. 3 G EO 3. 9 G BC 1 1. 3 G BC 2 BAM BPM EO BAM 3. 0 G Bunch arrival monitor Beam position monitor Laser to laser synchronization Photon arrival monitor/Exp. Direct laser seeding Laser to RF conversion (1. 3 GHz) EO Yb: FL 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF 1. 3 G Fiber link (OCC) Short fiber link (P RF) SEEDlaser PPlaser L 2 L SEEDlaser BAM 1. 3 G BPM BAM EO BAM 3. 0 G PAM L 2 L
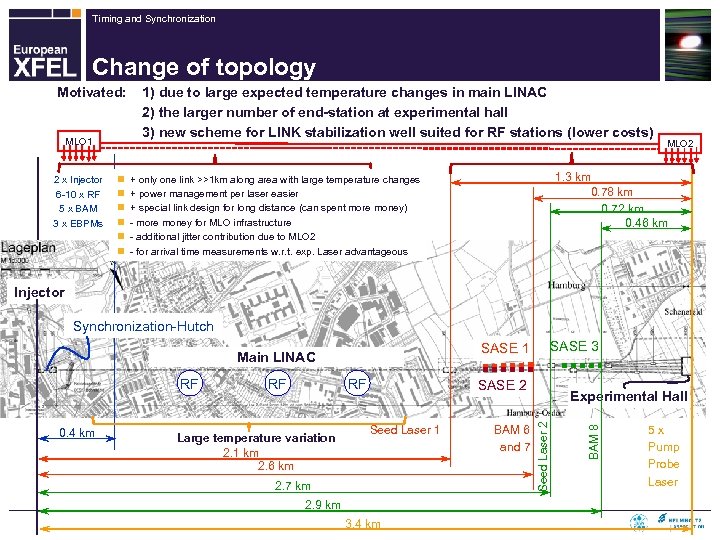
Timing and Synchronization Change of topology Motivated: MLO 1 2 x Injector 6 -10 x RF 5 x BAM 3 x EBPMs n n n 1) due to large expected temperature changes in main LINAC 2) the larger number of end-station at experimental hall 3) new scheme for LINK stabilization well suited for RF stations (lower costs) MLO 2 1. 3 km 0. 78 km 0. 72 km 0. 46 km + only one link >>1 km along area with large temperature changes + power management per laser easier + special link design for long distance (can spent more money) - more money for MLO infrastructure - additional jitter contribution due to MLO 2 - for arrival time measurements w. r. t. exp. Laser advantageous Injector Synchronization-Hutch RF Large temperature variation 2. 1 km 2. 6 km SASE 2 Seed Laser 1 2. 7 km 2. 9 km 3. 4 km BAM 6 and 7 Experimental Hall BAM 8 0. 4 km RF Seed Laser 2 RF SASE 3 SASE 1 Main LINAC 5 x Pump Probe Laser

Timing and Synchronization 20 Thanks for your attention 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF

Timing and Synchronization Infrastructure for FLASH optical synchronization n 300 cables to optical table (including 120 signal cables) n 58 motors n 20. . . 24 laser diodes for MLOs and EDFAs n 16. . . 20 piezo stretchers n 4 VME crates (change to u. TCA in planning) n optical fibers to all critical end-stations n 42 temperature sensors, 2 active temperature regulations n air conditioning and option for water cooling. . . and almost everything assembled in-house! Status: ~ 85% done In house electronics developments: n VME laser diode driver (FPGA) n VME ADCs 130 MHz, 16 bit n LN Piezo driver 300 V n DSP regulation (old) n ADC (9 MHz, 14 bit) n DAC (9 MHz, 16 bit) n Vector modulator Status: exist or in productions 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF 21
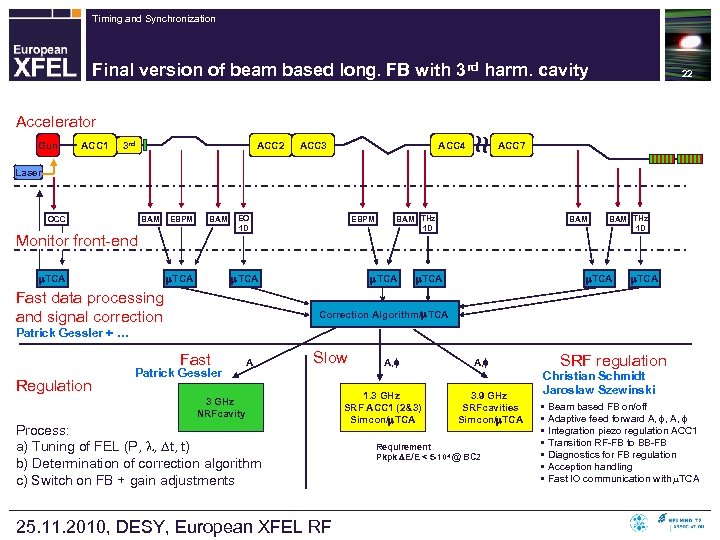
Timing and Synchronization Final version of beam based long. FB with 3 rd harm. cavity 22 Accelerator ACC 1 ACC 2 3 rd ~ ~ Gun ACC 3 ACC 4 ACC 7 Laser OCC BAM EBPM BAM Monitor front-end TCA EO 1 D EBPM TCA Fast data processing and signal correction BAM THz 1 D TCA Correction Algorithm/ TCA Patrick Gessler + … Fast Regulation Patrick Gessler A Slow 3 GHz NRFcavity Process: a) Tuning of FEL (P, , t, t) b) Determination of correction algorithm c) Switch on FB + gain adjustments 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF A, 1. 3 GHz SRF ACC 1 (2&3) Simcon/ TCA A, 3. 9 GHz SRFcavities Simcon/ TCA Requirement Pkpk E/E < 5 104 @ BC 2 SRF regulation Christian Schmidt Jaroslaw Szewinski • Beam based FB on/off • Adaptive feed forward A, , A, • Integration piezo regulation ACC 1 • Transition RF-FB to BB-FB • Diagnostics for FB regulation • Acception handling • Fast IO communication with TCA
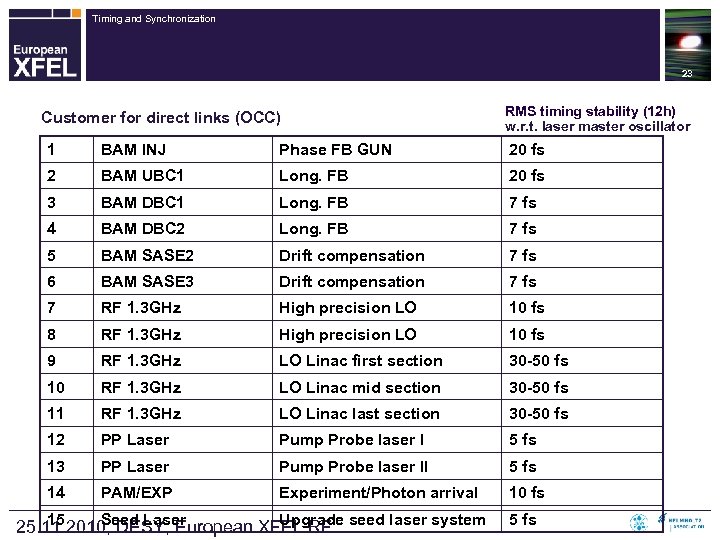
Timing and Synchronization 23 Layout of XFEL Synchronization System Customer for direct links (OCC) RMS timing stability (12 h) w. r. t. laser master oscillator 1 BAM INJ Phase FB GUN 20 fs 2 BAM UBC 1 Long. FB 20 fs 3 BAM DBC 1 Long. FB 7 fs 4 BAM DBC 2 Long. FB 7 fs 5 BAM SASE 2 Drift compensation 7 fs 6 BAM SASE 3 Drift compensation 7 fs 7 RF 1. 3 GHz High precision LO 10 fs 8 RF 1. 3 GHz High precision LO 10 fs 9 RF 1. 3 GHz LO Linac first section 30 -50 fs 10 RF 1. 3 GHz LO Linac mid section 30 -50 fs 11 RF 1. 3 GHz LO Linac last section 30 -50 fs 12 PP Laser Pump Probe laser I 5 fs 13 PP Laser Pump Probe laser II 5 fs 14 PAM/EXP Experiment/Photon arrival 10 fs 15 Seed Laser Upgrade 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF seed laser system 5 fs
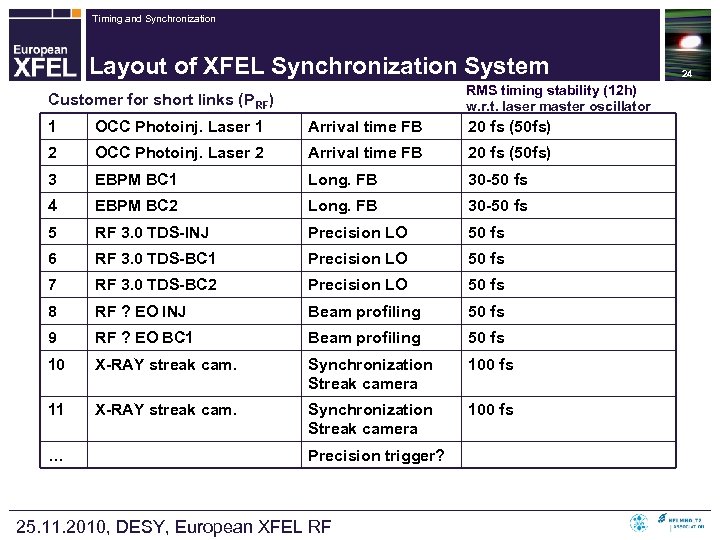
Timing and Synchronization Layout of XFEL Synchronization System RMS timing stability (12 h) w. r. t. laser master oscillator Customer for short links (PRF) 1 OCC Photoinj. Laser 1 Arrival time FB 20 fs (50 fs) 2 OCC Photoinj. Laser 2 Arrival time FB 20 fs (50 fs) 3 EBPM BC 1 Long. FB 30 -50 fs 4 EBPM BC 2 Long. FB 30 -50 fs 5 RF 3. 0 TDS-INJ Precision LO 50 fs 6 RF 3. 0 TDS-BC 1 Precision LO 50 fs 7 RF 3. 0 TDS-BC 2 Precision LO 50 fs 8 RF ? EO INJ Beam profiling 50 fs 9 RF ? EO BC 1 Beam profiling 50 fs 10 X-RAY streak cam. Synchronization Streak camera 100 fs 11 X-RAY streak cam. Synchronization Streak camera 100 fs … Precision trigger? 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF 24
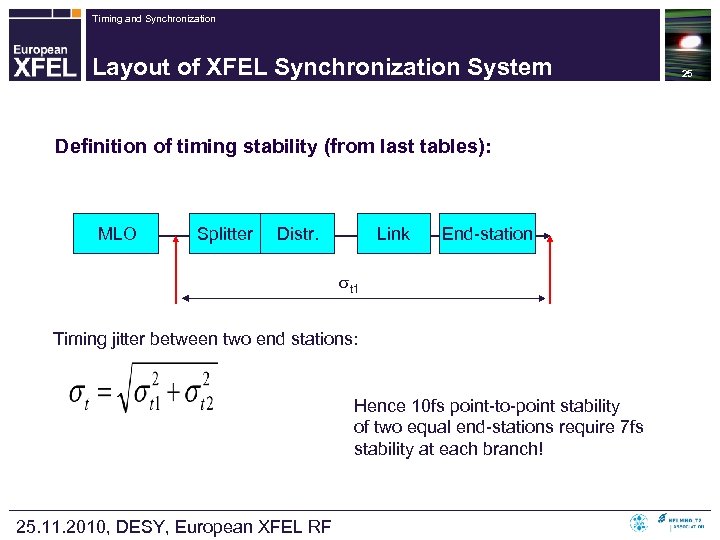
Timing and Synchronization Layout of XFEL Synchronization System Definition of timing stability (from last tables): MLO Splitter Distr. Link End-station t 1 Timing jitter between two end stations: Hence 10 fs point-to-point stability of two equal end-stations require 7 fs stability at each branch! 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF 25
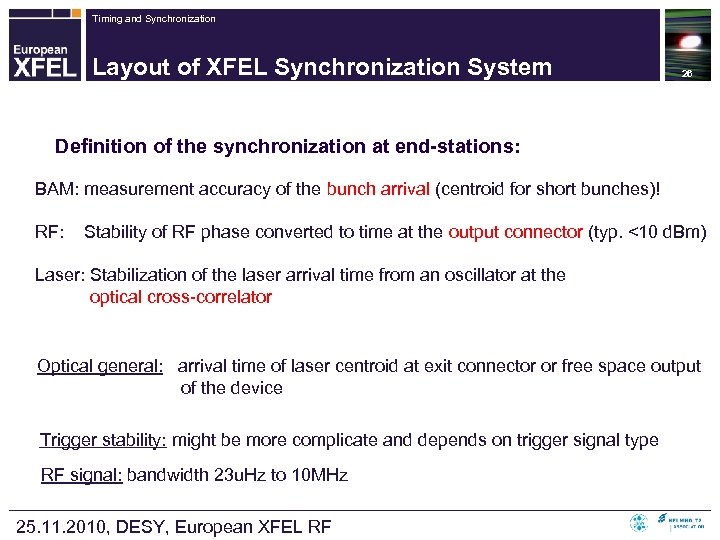
Timing and Synchronization Layout of XFEL Synchronization System 26 Definition of the synchronization at end-stations: BAM: measurement accuracy of the bunch arrival (centroid for short bunches)! RF: Stability of RF phase converted to time at the output connector (typ. <10 d. Bm) Laser: Stabilization of the laser arrival time from an oscillator at the optical cross-correlator Optical general: arrival time of laser centroid at exit connector or free space output of the device Trigger stability: might be more complicate and depends on trigger signal type RF signal: bandwidth 23 u. Hz to 10 MHz 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF
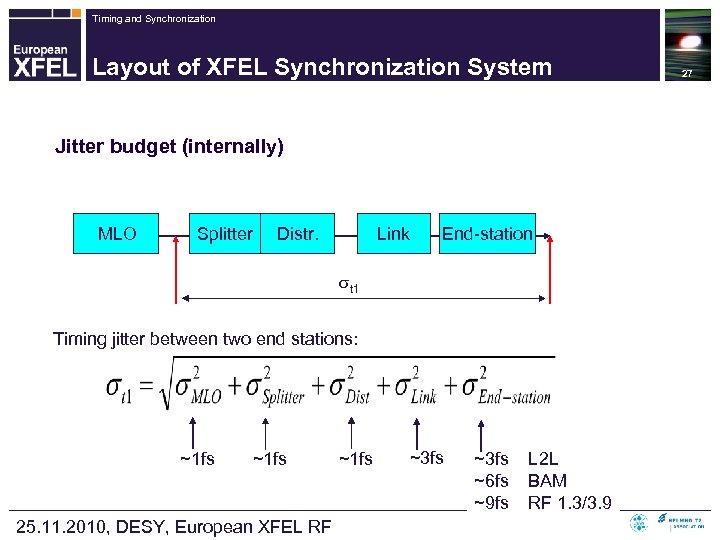
Timing and Synchronization Layout of XFEL Synchronization System Jitter budget (internally) MLO Splitter Distr. Link End-station t 1 Timing jitter between two end stations: ~1 fs 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF ~1 fs ~3 fs ~6 fs ~9 fs L 2 L BAM RF 1. 3/3. 9 27
Timing and Synchronization Layout of XFEL Synchronization System Achievements so far: Link MLO BAM RF 10. 2 GHz 7 fs rms (12 hours) DESY Lab environment 3. 3 fs (35 u. Hz-100 k. Hz) 1 fs rms (100 k. Hz) 7 fs (minutes, drifts to be checked) 6. 8 fs (27 u. Hz-1 MHz) RF 1. 3 GHz RF Link L 2 L reliable version to be demonstrated, 10 fs rms achieved has been demonstrated <<10 fs @20 m, check for 400 m! to be demonstrated with LINK 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF 28
Timing and Synchronization Layout of XFEL Synchronization System Options Links: • long distance with fs precision: but expensive cross-correlator required with length FB • short distance 2 -50 m ~ 5 -20 fs achievable -> without length compensation (suited for RF -> with length compensation (suited for OCC) RF generation: • direct conversion N*frep ~ 100 fs (eventually smaller needs design) • Sagnac loop: demanding N*frep ~ sub 10 fs expected • trigger via direct conversion 25. 11. 2010, DESY, European XFEL RF 29
bfed648934832e8c6dde9edbd3fe3b20.ppt