11ce272e408ea086b93f873cc93cc446.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

Optical Fiber Access Network OFAN& ZXA 10 Presented By: Ammara Khan Baloch
Table of Contents • • • Why AN? Definition of AN Structure of AN Definition of OLT Structure of OLT Definition of ONU Structure of ONU Modules of ONU Build-in SDH

Why we need Access Network? 1)The reason of technology Mostly, it is because of digital transfer system, especially, the optical transfer system. 2)The reason of Market requirement For the Operation and Maintenance. 3) The reason of competition The telecom company want to get cheaper system.
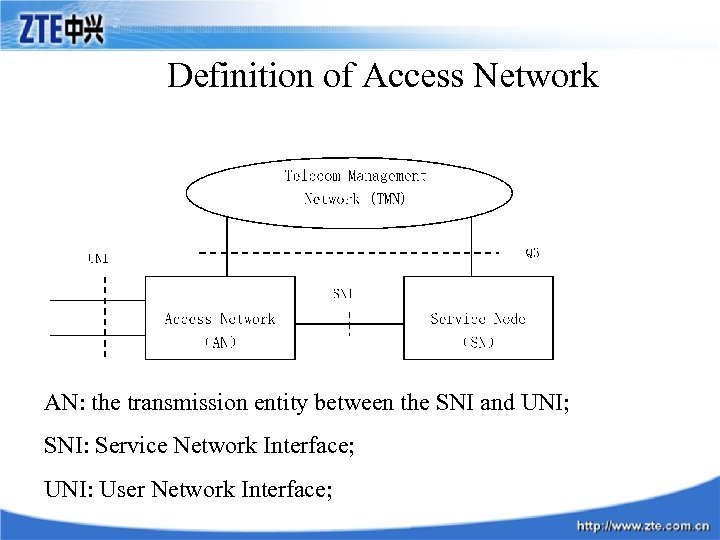
Definition of Access Network AN: the transmission entity between the SNI and UNI; SNI: Service Network Interface; UNI: User Network Interface;
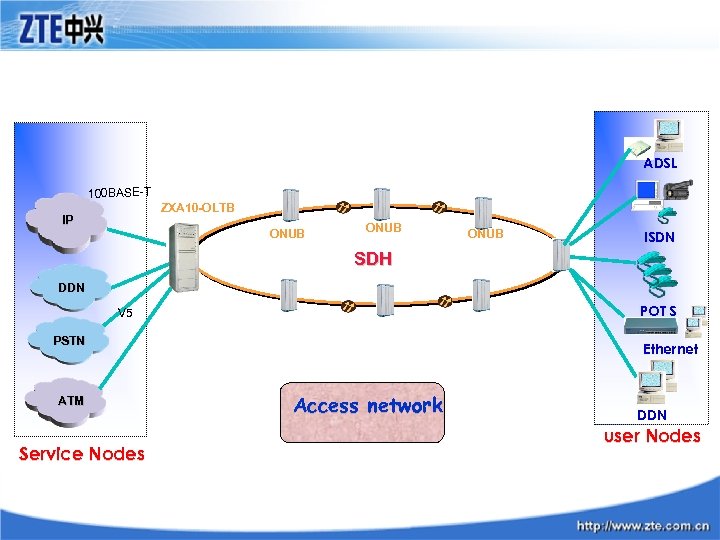
ADSL 100 BASE-T ZXA 10 -OLTB IP ONUB ISDN SDH DDN POT S V 5 PSTN ATM Service Nodes Ethernet Access network DDN user Nodes
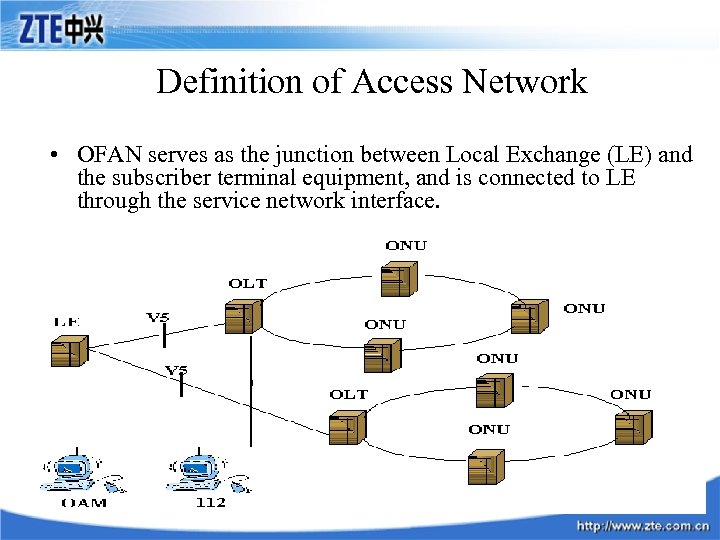
Definition of Access Network • OFAN serves as the junction between Local Exchange (LE) and the subscriber terminal equipment, and is connected to LE through the service network interface.
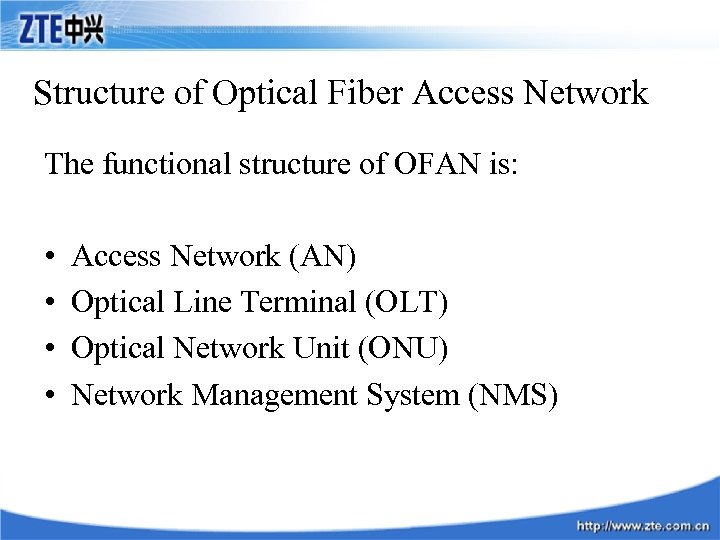
Structure of Optical Fiber Access Network The functional structure of OFAN is: • • Access Network (AN) Optical Line Terminal (OLT) Optical Network Unit (ONU) Network Management System (NMS)

Definition of OLT • OLT function is to provide OFAN with the interface between the network side and the LE, and to communicate with ONU of the subscriber. • “Interface b/w an optical line and the network”. • OLT can completely isolate the switching function of LE from the subscriber access. • OLT is placed at the exchange end together with LE. • OLT is connected to multiple ONU’s that can be used in networking of point-to-point, chain, and ring network. • Large capacity OLT equipment with 19’ rack structure; • High integration density ODT board, with 8 E 1 per card and 120 E 1 per module. All these E 1 can be assigned to connect V 5 or ONU as per actual requirements;

ZXA 10 -OLTB ØConcentration ratio can be adjusted freely to meet different traffic model; ØHigh performance multi cpu system, can meet the high traffic requirements; ØSingle module provides 10240 lines and for single rack 3 modules can be mounted together to provide more lines; ØMain boards, such as MP, SSU, are working in master/slave mode, to provide high reliability. ØFeatures are: • Hubbing • Multiplexing • Cross-Connection.
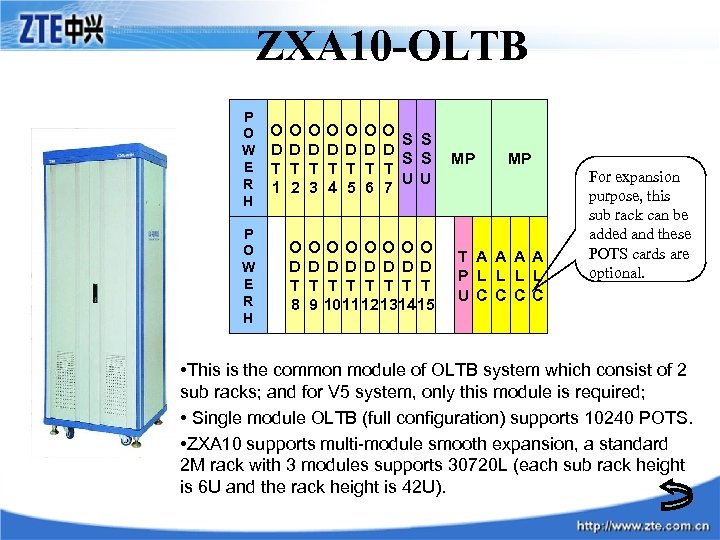
ZXA 10 -OLTB P O W E R H O D T 1 O D T 2 O D T 3 O D T 4 O D T 5 O D T 6 O S S D S S T U U 7 O D T 8 OOOOOOO D D D D T T T T 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 MP MP T A A P L L U C C For expansion purpose, this sub rack can be added and these POTS cards are optional. • This is the common module of OLTB system which consist of 2 sub racks; and for V 5 system, only this module is required; • Single module OLTB (full configuration) supports 10240 POTS. • ZXA 10 supports multi-module smooth expansion, a standard 2 M rack with 3 modules supports 30720 L (each sub rack height is 6 U and the rack height is 42 U).
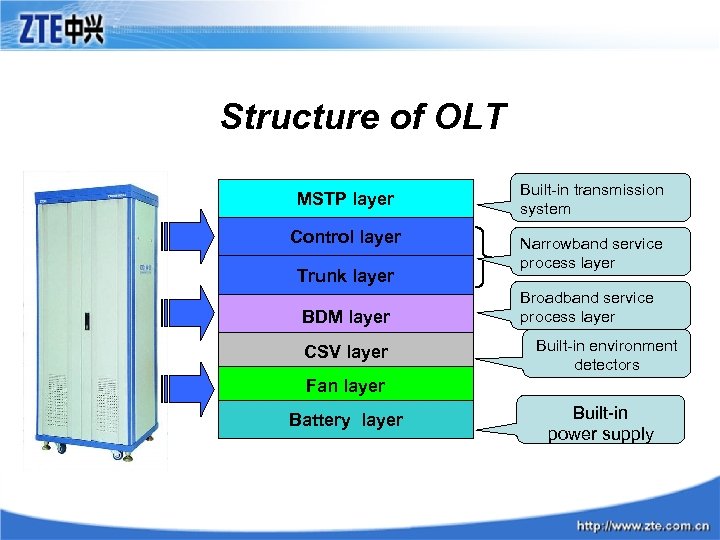
Structure of OLT MSTP layer Control layer Trunk layer BDM layer CSV layer Built-in transmission system Narrowband service process layer Broadband service process layer Built-in environment detectors Fan layer Battery layer Built-in power supply

Hardware Structure of OLT On OLTB, there are three layers: • Control layer (MCTLB ) • ODT layer( MODT) • Subscriber layer (MALC).
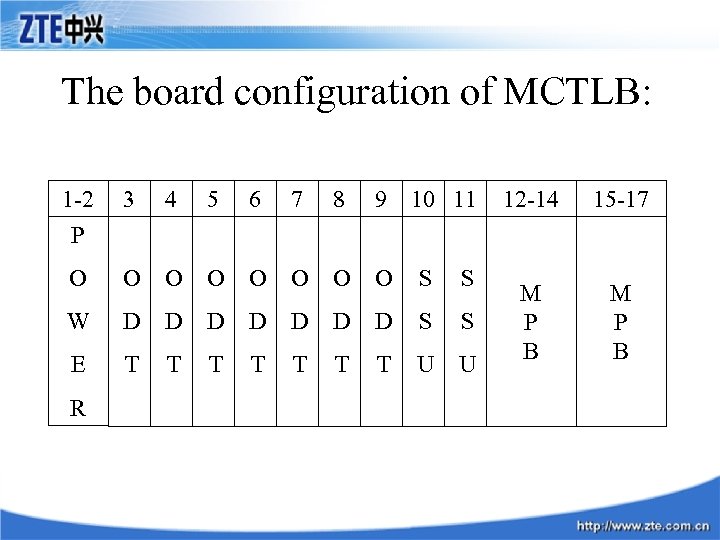
The board configuration of MCTLB: 1 -2 P 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 O O O O S S W D D D D S S E T T T T U U R 12 -14 15 -17 M P B
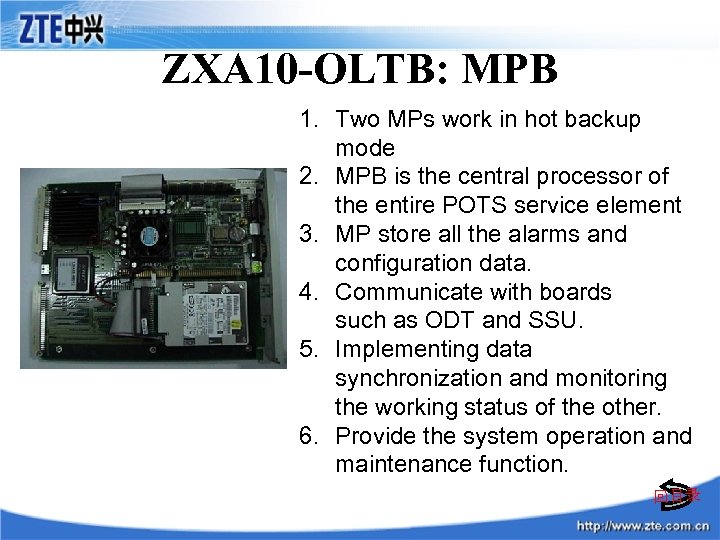
ZXA 10 -OLTB: MPB 1. Two MPs work in hot backup mode 2. MPB is the central processor of the entire POTS service element 3. MP store all the alarms and configuration data. 4. Communicate with boards such as ODT and SSU. 5. Implementing data synchronization and monitoring the working status of the other. 6. Provide the system operation and maintenance function. 回目录
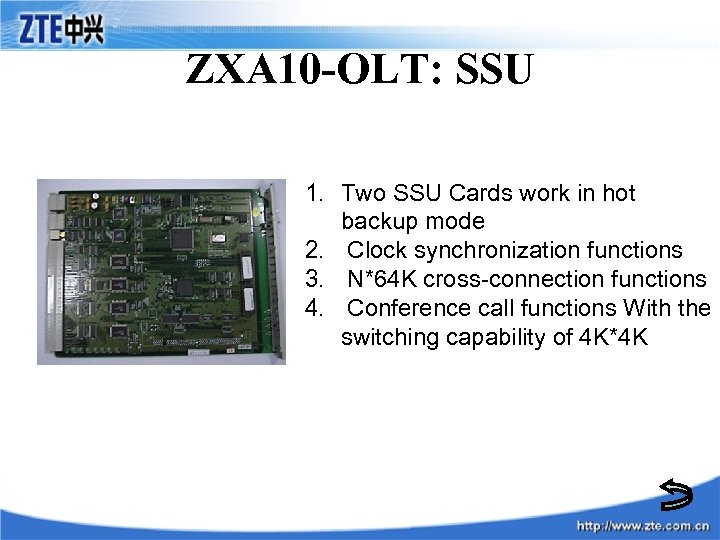
ZXA 10 -OLT: SSU 1. Two SSU Cards work in hot backup mode 2. Clock synchronization functions 3. N*64 K cross-connection functions 4. Conference call functions With the switching capability of 4 K*4 K
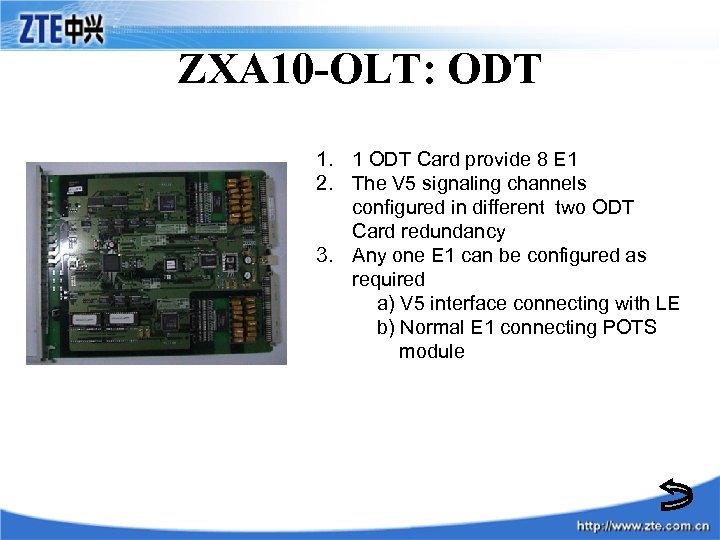
ZXA 10 -OLT: ODT 1. 1 ODT Card provide 8 E 1 2. The V 5 signaling channels configured in different two ODT Card redundancy 3. Any one E 1 can be configured as required a) V 5 interface connecting with LE b) Normal E 1 connecting POTS module
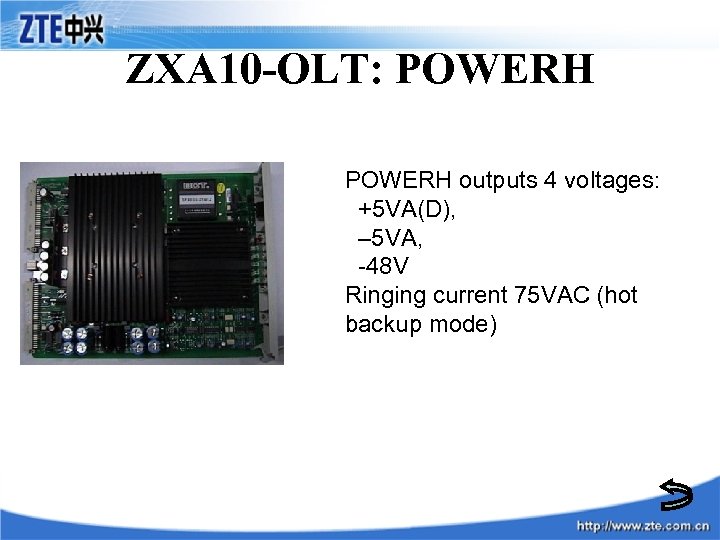
ZXA 10 -OLT: POWERH outputs 4 voltages: +5 VA(D), – 5 VA, -48 V Ringing current 75 VAC (hot backup mode)
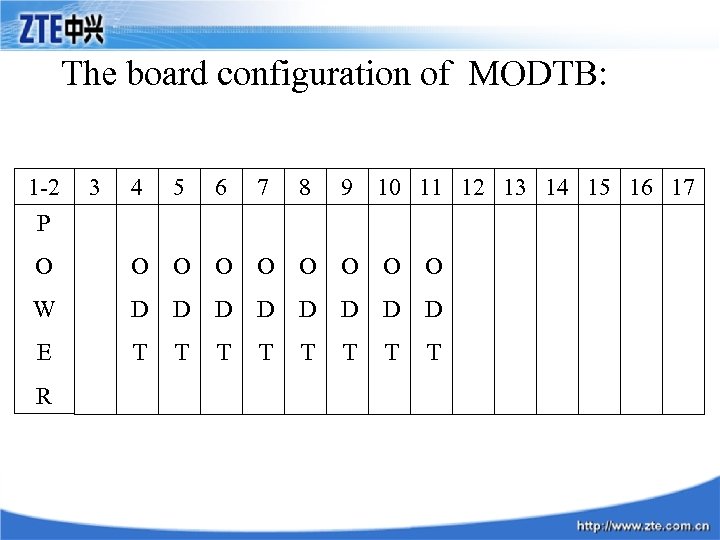
The board configuration of MODTB: 1 -2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 O O O O O W D D D D E T T T T P R
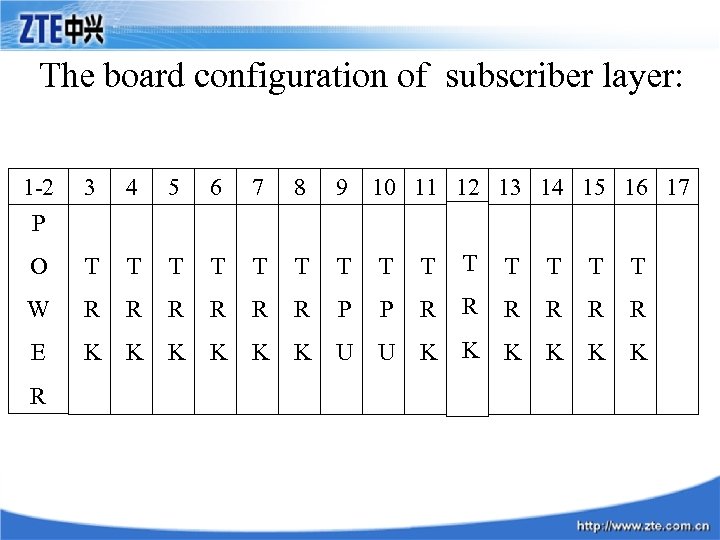
The board configuration of subscriber layer: 1 -2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 O T T T T W R R R P P R R R E K K K U U K K K P R

TRK: • At OLT side, TRK is used in ZXA 10 to connect to switch. • At ONU side ALC is used to connect to ordinary subscriber telephone set, expanding Z interface. • There are 16 L in one TRK board. TPU • • TPU is the main processor board of ZXA 10 SU 2 user unit. At maximum one TPU can control 12 subscriber boards. TPU can provide at most four 4 E 1 interface. Two TPU serves as backup for each other. 2 TPU work in load sharing mode to manage subscriber boards.

Definition of ONU • ONU is used to provide OFAN with interface at the subscriber side. • ONU is connected to number of subscriber terminals. • ONU is capable of optical-electrical conversion. • Maintenance and monitoring functions. • ONU is placed in the vicinity of subscriber.
• ONU is the equipment used to implement FTTB, FTTC and FTTZ. • ONU provide various interface to connect to the subscribe, support various subscriber terminal such as POTS, ISDN and leased line. Structure of ONU: • ONU is composed of – Processing Nodes – Transmission Nodes
ONU Transmission node consist of following type: • Built-in 155 M/622 M SDH optical transmission equipment • ATM broadband transmission equipment ZXA 10 OFAN provide build-in SDH optical transmission systems: – – ZXA 10 -AS 1 ZXA 10 -AS 2 ZXA 10 -S 200 ZXA 10 -S 300

• ONU consist of following cards: – – – SU (Subscriber Unit) ALC (Analog Subscriber Card) DLCA (Digital Subscriber Card) TPU ( Main processor board) POWERH (Power board) TSLC (Subscriber line test board) AUDB (2/4 Audio board) DLC HLC (Hotline board) HSB DIB (64 K G. 703)

Analog Subscriber Board (ALC): • • • ALC is used to provide the analog subscriber Z interface. Implements POTS service. Providing 32 subscriber lines Most popular card in ZXA 10. 1 SU can be inserted with up to 12 ALC’s. Basic functions are: B_Battery feeding function O_Over Voltage Protection R_Ringing function S_Supervision Function C_Codec function H_Hybrid function T_Test function

2 B+D Digital Subscriber Board (DLCA): • • Provide 2 B+D interface 1 DLCA = 8 ISDN sub 2/4 wire conversion Over voltage protection Offer test interface Self –loop testing Remote power supply. 2/4 Wire Audio Board (AUDB) • • • It is used to convert analog signal into digital signal. Convert audio and data into digital form Provide 8 voice ports. Output/input levels are adjustable through software. Provide two transmission modes – 2 line – 4 line

Hotline board (HLC): • • • Resembles semi-permanent leased line service. One HLC provide hotline interface , plugged with ALC in SU unit. 1 HLC = 8 hotlines FLC card: • • FLC is used to support the public payphone subscribers. Each board can support 16 sub lines. ADSL subscriber board • • • ADLG board is used for providing ADSL service. Each ADLG board support 16 ADSL subscriber. Each ADLG support 4 uplink E 1 interface.

Subscriber line test board (TSLC): • There are mainly two test boards used in ZXA 10 -SU. – TSLCB – TSLCC • TSLCB is used for analog subscriber lines and terminals • TSLCC is used for digital tests on ISDN in addition to tests on ordinary analog subscribers. • Test boards has the following functions: – Test of external line – Test of internal line – Test of subscriber telephone
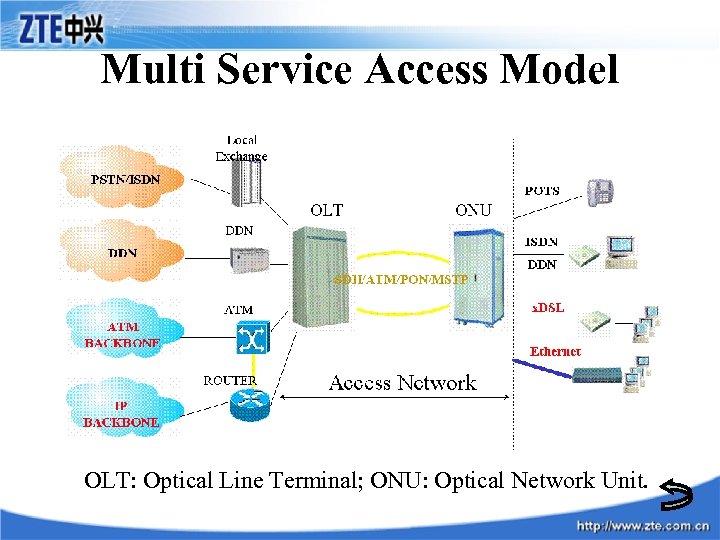
Multi Service Access Model OLT: Optical Line Terminal; ONU: Optical Network Unit.

ZXA 10 ONU Module OUT 40 OUT 30 IN/1500 ONU 200 OUT 50
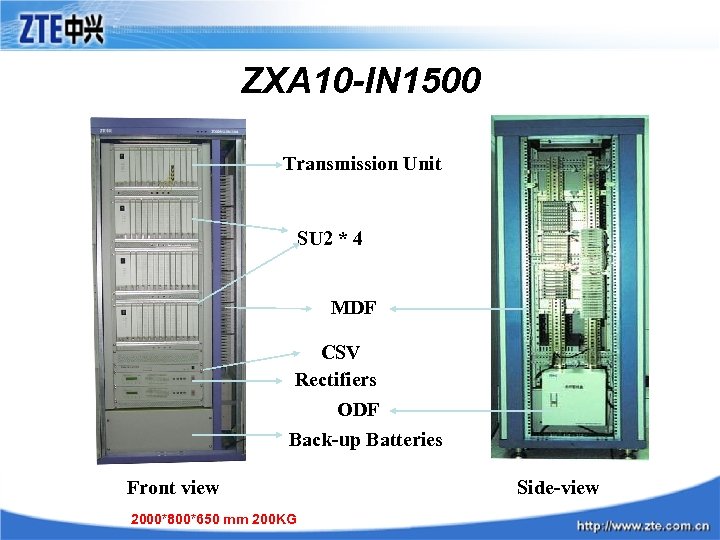
ZXA 10 -IN 1500 Transmission Unit SU 2 * 4 MDF CSV Rectifiers ODF Back-up Batteries Front view 2000*800*650 mm 200 KG Side-view
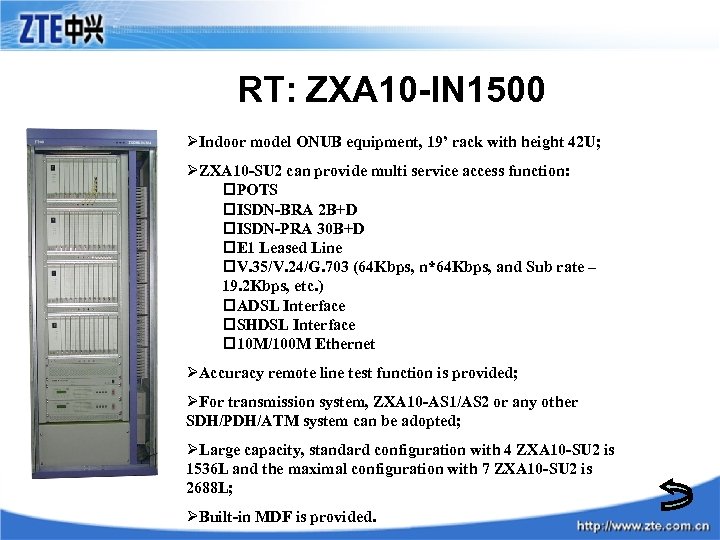
RT: ZXA 10 -IN 1500 ØIndoor model ONUB equipment, 19’ rack with height 42 U; ØZXA 10 -SU 2 can provide multi service access function: p. POTS p. ISDN-BRA 2 B+D p. ISDN-PRA 30 B+D p. E 1 Leased Line p. V. 35/V. 24/G. 703 (64 Kbps, n*64 Kbps, and Sub rate – 19. 2 Kbps, etc. ) p. ADSL Interface p. SHDSL Interface p 10 M/100 M Ethernet ØAccuracy remote line test function is provided; ØFor transmission system, ZXA 10 -AS 1/AS 2 or any other SDH/PDH/ATM system can be adopted; ØLarge capacity, standard configuration with 4 ZXA 10 -SU 2 is 1536 L and the maximal configuration with 7 ZXA 10 -SU 2 is 2688 L; ØBuilt-in MDF is provided.
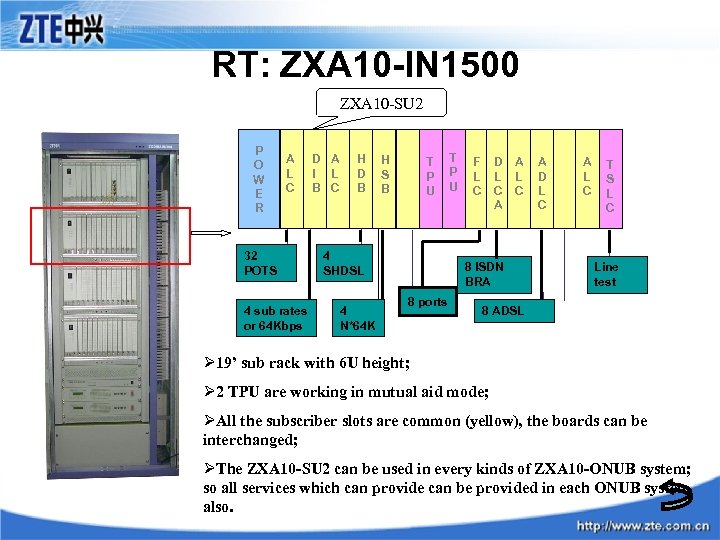
RT: ZXA 10 -IN 1500 ZXA 10 -SU 2 P O W E R A L C 32 POTS 4 sub rates or 64 Kbps D A I L B C H D B H S B T P U 4 SHDSL 4 N*64 K T P U F L C D L C A A L C 8 ISDN BRA 8 ports A D L C A L C T S L C Line test 8 ADSL Ø 19’ sub rack with 6 U height; Ø 2 TPU are working in mutual aid mode; ØAll the subscriber slots are common (yellow), the boards can be interchanged; ØThe ZXA 10 -SU 2 can be used in every kinds of ZXA 10 -ONUB system; so all services which can provide can be provided in each ONUB system also.
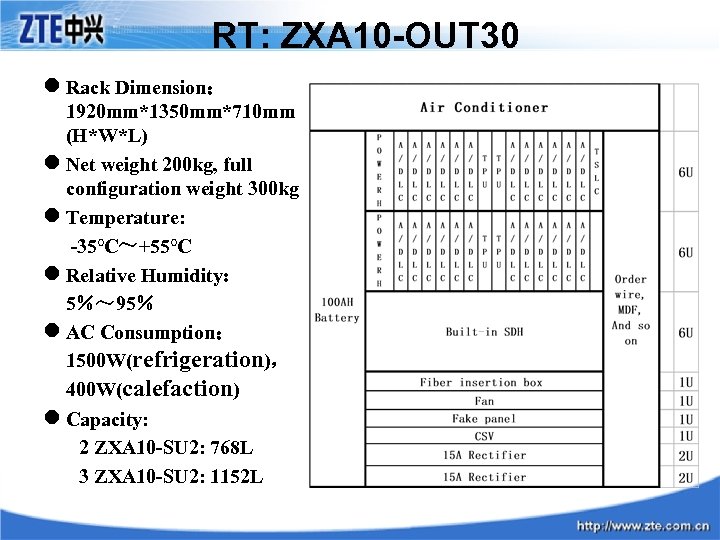
RT: ZXA 10 -OUT 30 l Rack Dimension: 1920 mm*1350 mm*710 mm (H*W*L) l Net weight 200 kg, full configuration weight 300 kg l Temperature: -35℃~+55℃ l Relative Humidity: 5%~ 95% l AC Consumption: 1500 W(refrigeration), 400 W(calefaction) l Capacity: 2 ZXA 10 -SU 2: 768 L 3 ZXA 10 -SU 2: 1152 L
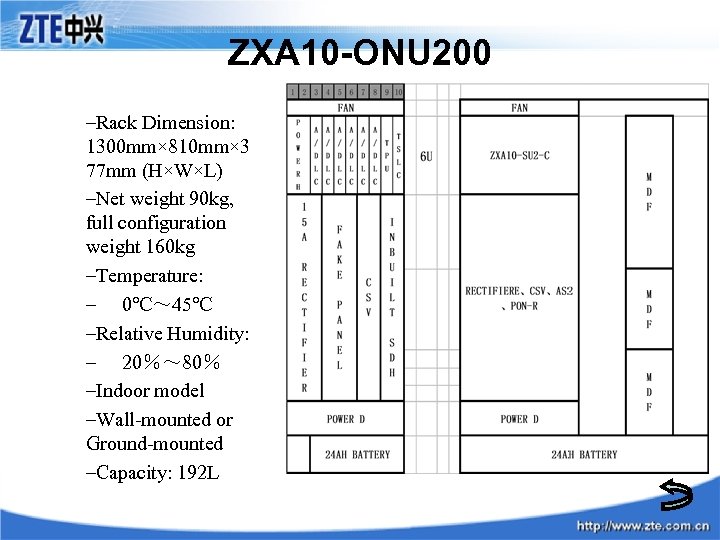
ZXA 10 -ONU 200 –Rack Dimension: 1300 mm× 810 mm× 3 77 mm (H×W×L) –Net weight 90 kg, full configuration weight 160 kg –Temperature: – 0℃~ 45℃ –Relative Humidity: – 20%~ 80% –Indoor model –Wall-mounted or Ground-mounted –Capacity: 192 L

ZXA 10 -OUT 40 • • • Rack Dimension: 1450 mm× 1500 mm× 500 mm (H×W×L) Full configuration weight: 250 kg Temperature: -35℃~ 55℃ Relative Humidity: 5%~ 95% Outdoor model and Ground-mounted or pole-mounted Capacity: 1 ZXA 10 -SU 2 384 L (ZXA 10 -AS 1); 2 ZXA 10 -SU 2 768 L (ZXA 10 -AS 2)
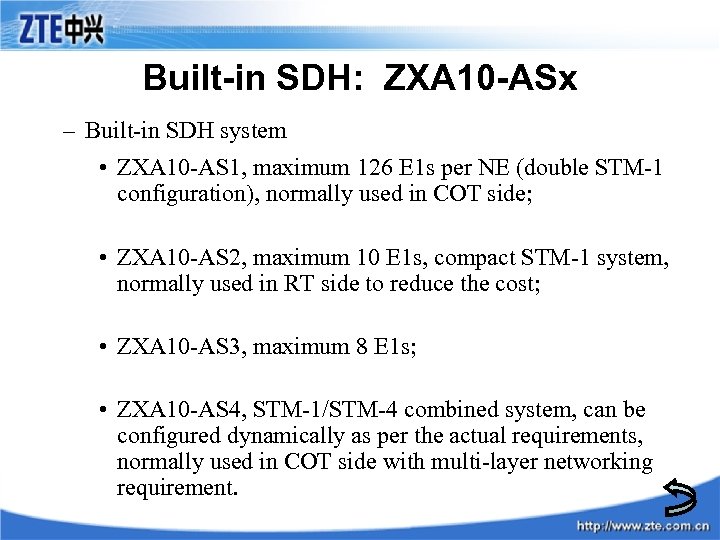
Built-in SDH: ZXA 10 -ASx – Built-in SDH system • ZXA 10 -AS 1, maximum 126 E 1 s per NE (double STM-1 configuration), normally used in COT side; • ZXA 10 -AS 2, maximum 10 E 1 s, compact STM-1 system, normally used in RT side to reduce the cost; • ZXA 10 -AS 3, maximum 8 E 1 s; • ZXA 10 -AS 4, STM-1/STM-4 combined system, can be configured dynamically as per the actual requirements, normally used in COT side with multi-layer networking requirement.
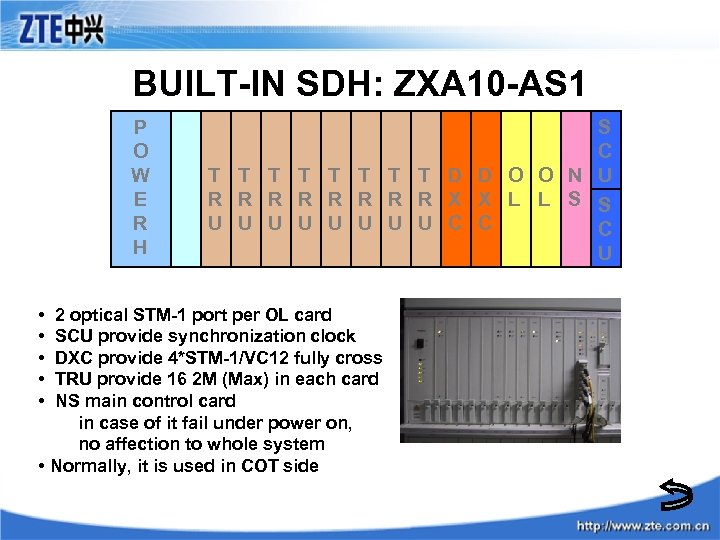
BUILT-IN SDH: ZXA 10 -AS 1 P O W E R H • • • S C T T T T D D O O N U R R R R X X L L S S U U U U C C C 2 optical STM-1 port per OL card SCU provide synchronization clock DXC provide 4*STM-1/VC 12 fully cross TRU provide 16 2 M (Max) in each card NS main control card in case of it fail under power on, no affection to whole system • Normally, it is used in COT side U

BUILT-IN SDH: ZXA 10 -AS 2 Ø 19 Inch, 1 U, Compact STM-1 system Ø 2 Optical Interface (west and east), 10 E 1

BUILT-IN SDH: ZXA 10 -AS 3 Ø 19’ and 2 U box, compact design; Ø 2 optical direction and 8 E 1; ØIt can be used in the system which capacity is not so big and does not need more than 2 optical directions; ØNormally, in AN system we propose the ZXA 10 -AS 2 instead of this one.

BUILT-IN SDH: ZXA 10 -AS 4 ØZXA 10 -AS 4 is STM-4/STM-1 combined compact SDH system, which adopts the ZXSM-600 (V 2) technology; Ø 19’ and 4 U chassis; ØSupporting many kinds of service, E 1/E 3 or T 1/T 3 or STM-1 can be configured as per the actual requirement; ØNormally, it is used in COT side where the requirements are very high, for example, more E 1 s, more optical directions or both STM-1 and STM-4.
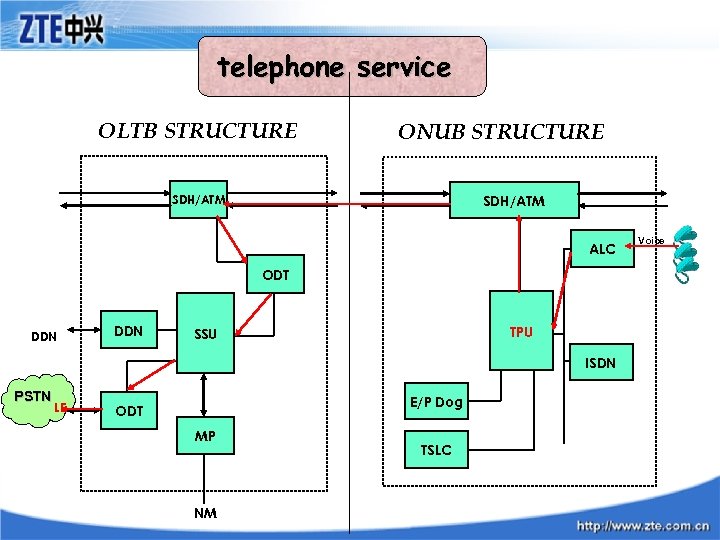
telephone service OLTB STRUCTURE ONUB STRUCTURE SDH/ATM ALC ODT DDN TPU SSU ISDN PSTN LE E/P Dog ODT MP NM TSLC Voice
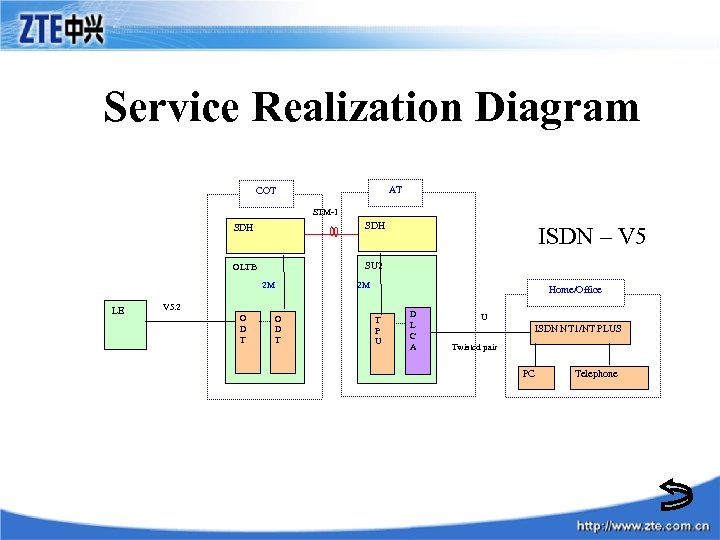
Service Realization Diagram AT COT STM-1 SDH OLTB SU 2 2 M LE 2 M Home/Office V 5. 2 O D T ISDN – V 5 O D T T P U D L C A U ISDN NT 1/NT PLUS Twisted pair PC Telephone

THANK YOU!
11ce272e408ea086b93f873cc93cc446.ppt