8c5155b8a116bc3ee0135555456bc7e3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Opportunities in India’s Infrastructure Sector Presentation by Abhaya K Agarwal Vice President INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION LIMITED
Presentation Structure Section 1 Country Focus Section 2 FDI caps in infrastructure sector Section 3 Opportunities in infrastructure sector Section 4 Role of IL&FS and Public Private Partnerships

SECTION 1 COUNTRY FOCUS

Country Focus n n n Adequacy in Infrastructure facilities is vital for acceleration of economic development Increasing need of the country to compete in global market Provision of efficient infrastructure services Government's priority Infrastructure Sectors: n Railways n Telecommunication n Sanitation n Roads n n n Power Water Supply Sewerage n Ports n Airports
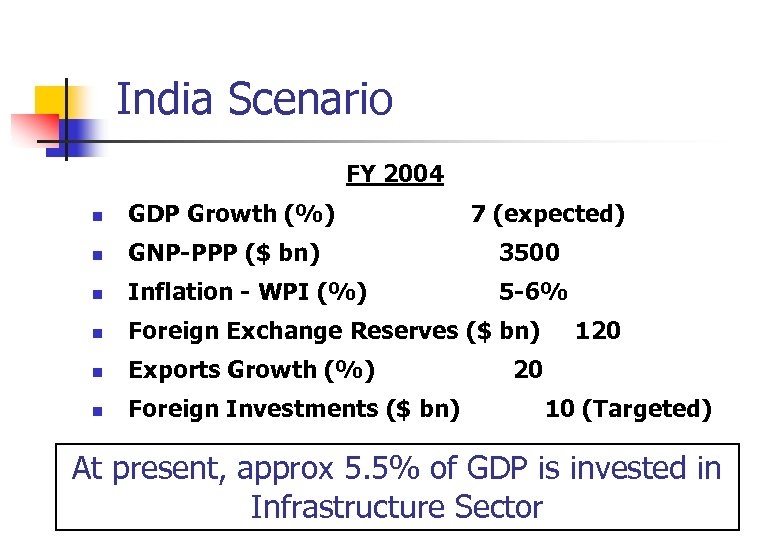
India Scenario FY 2004 n GDP Growth (%) 7 (expected) n GNP-PPP ($ bn) 3500 n Inflation - WPI (%) 5 -6% n Foreign Exchange Reserves ($ bn) n Exports Growth (%) n Foreign Investments ($ bn) 120 20 10 (Targeted) At present, approx 5. 5% of GDP is invested in Infrastructure Sector

India Scenario (Contd. ) n n n Indian Economy is projected to grow at 8 per cent by 2005 -06 Total expected investment requirement in infrastructure in next 5 years: Rs. 4, 000 -4, 500 billion (US $ 115 -120 billion) Investment requirement to be provided by various collective sources, FDI prime source: n n n Government funds, schemes and programs Lending institution such as World Bank, ADB etc. Private sector participation including Foreign Investment Donor and multilateral agencies Innovative financing measures such as User fees charges etc. Estimated investment through FDI- US$ 15 -16 billion /year by 200506, expecting 40% investments in infrastructure sector

SECTION 2 FDI CAPS IN INFRASTRUCTURE SECTOR
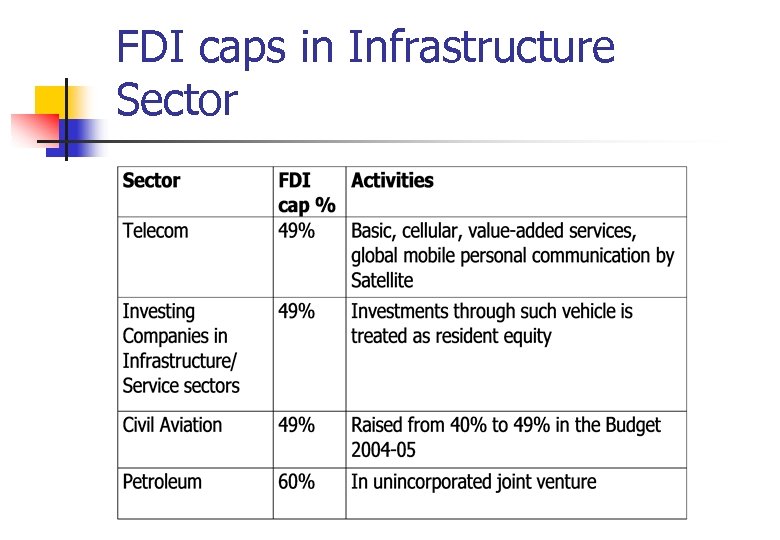
FDI caps in Infrastructure Sector
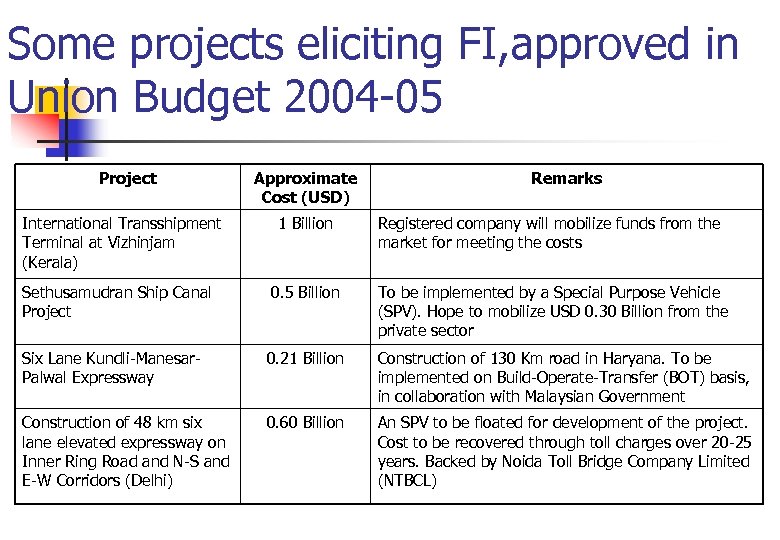
Some projects eliciting FI, approved in Union Budget 2004 -05 Project International Transshipment Terminal at Vizhinjam (Kerala) Approximate Cost (USD) Remarks 1 Billion Registered company will mobilize funds from the market for meeting the costs Sethusamudran Ship Canal Project 0. 5 Billion To be implemented by a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). Hope to mobilize USD 0. 30 Billion from the private sector Six Lane Kundli-Manesar. Palwal Expressway 0. 21 Billion Construction of 130 Km road in Haryana. To be implemented on Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) basis, in collaboration with Malaysian Government Construction of 48 km six lane elevated expressway on Inner Ring Road and N-S and E-W Corridors (Delhi) 0. 60 Billion An SPV to be floated for development of the project. Cost to be recovered through toll charges over 20 -25 years. Backed by Noida Toll Bridge Company Limited (NTBCL)

SECTION 3 OPPORTUNITIES IN INFRASTRUCTURE SECTOR

Opportunities in Urban Infrastructure sector Urban Infrastructure n Tenth Plan fund allocation to Mo. UD & Poverty Alleviation= USD 6. 46 billion n Investments required for provision of core urban infrastructure services like water supply, sanitation and roads

Opportunities in Rail Infrastructure sector n n Annual Plan of Rail budget 2004 -05: USD 3. 15 Billion. Target Projects: n Removal of bottlenecks in critical railway network sections requires investment of USD 3. 15 Billion, projects include:

Infrastructure Development n Strengthening of Golden Quadrilaterals and its diagonals to enable railways to run more long distance & freight mails at a higher speed of 100 Kmph: Investment of USD 1. 74 billion n Strengthening of rail connectivity to ports and development of multi modal corridors: Investment of USD 0. 65 billion

Infrastructure Development n Construction of 4 Mega bridges over Rivers-Ganga (2), Brahmaputra, Kosi: Investment of USD 0. 76 billion n Accelerated Completion of last mile & other important projects, at a cost of USD 0. 17 billion

Expected Infrastructure Development through Plan Funds n Special Railway Safety Fund of USD 3. 7 billion, to be utilized till 2007: n n For renewal and replacement of overaged railway assets, bridges, rolling stock etc. Total arrears in track renewal (km) = 34, 990 km Broad Guage renewal BG, yard & sides Metre Gauge Narrow gauge n n = 20000 km = 6030 km = 7820 km = 1140 km New Lines for 1310 km expected to be completed Gauge conversion of 2365 km planned- till 2007

Infrastructure Development in Road Sector Plan outlay for Central Sector Roads is USD 12. 93 billion. n Target projects: n n n National highway development project (NHDP) envisages development of 5, 846 km of Golden Quadrilateral & 7300 km NS-EW corridors, required investment = USD 11. 74 billion. National Highway network two laning within next 7 years for 4000 km and 4 laning 800 km of non NHDP stretches to be taken up.

Infrastructure Development n n n Improving riding quality of 10, 000 km and rehabilitation of 200 bridges. Plan expressways for high density corridors and conduct feasibility studies of about 1000 km of expressways. State highways road surface to be black topped for 6800 km and 40, 000 km on Major District Roads Development of roads in North-Eastern Region State Highways links carrying very heavy traffic to be 4 laned for about 1000 km. Providing rural connectivity through all weather roads
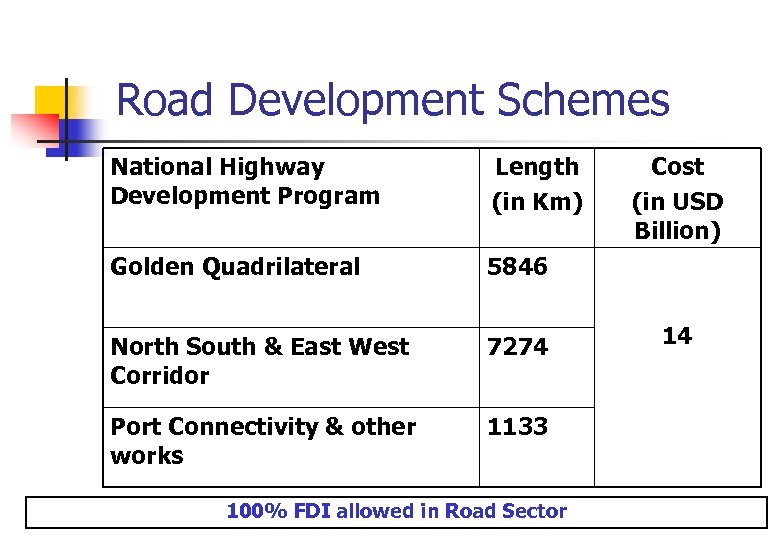
Road Development Schemes National Highway Development Program Length (in Km) Golden Quadrilateral 5846 North South & East West Corridor 7274 Port Connectivity & other works 1133 100% FDI allowed in Road Sector Cost (in USD Billion) 14

Other Road Initiatives n Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojna (PMGSY) n n Upgradation of 500, 000 Km of existing Rural Roads Estimated total outlay on project is USD 29 billion

Other Road Initiatives n Pradhan Mantri Bharat Jodo Pariyojna (PMBJP) n n The 10, 000 Km project envisages linking all State Capitals and important commercial centres not covered under NHDP with 4/6 lanes highways by 2009. Estimated total outlay on project is USD 9 billion

Infrastructure Development in Power Sector n Investment requirement of Rs. 6, 244 billion (US $ 111. 6 billion) from 1996 -2006. n n Tenth plan working group reports estimates energy requirement of 7, 19, 097 MKWh Target 80 Projects such as: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Electrification of 62, 000 villages through grid supply Accelerated Power Development Program envisages metering of 11 KV feeders Schemes in Hydro Sector=14, 393 MW capacity Schemes in Nuclear Sector=1, 300 MW capacity Schemes in Thermal Sector=25, 417 MW capacity

Infrastructure Development in Ports Sector n Ports capacity to be increased till 2007: n n n Plan outlay of USD 11. 8 billion for port sector Traffic expected to increase - 565 million tonnes in major and minor ports. Target Projects: Ø Ø Leasing out of assets of the ports Construction and operation of container terminals, multiple cargo berths and specialized berths, warehousing, storage facilities, captive power plant etc Leasing of equipment for cargo handling Automation by vessel traffic management system for navigation, for cargo & document handling operations

Infrastructure Development Options n Major Ports : Go. I has identified 26 projects for PSP: n Container berths at Mumbai port in Maharashtra n POL handling facilities at JNPT in Maharashtra n 2 Coal berths at Mormugao port in Goa n 2 oil jetties at Kandla in Gujarat n LPG Terminal at Vizag in Andhra Pradesh

Infrastructure Development in Civil Aviation Sector n n Plan outlay in Central sector in 10 th Plan is USD 2. 81 billion Target Projects: n n Public private partnerships in major ports at Delhi, Chennai, Mumbai and Kolkatta Air India considering phasing aircrafts, comprising small capacity long range small capacity short range aircrafts.

Large projects carried out in past n n Krishna Water Supply Project in Andhra Pradesh, Rs. 8 billion water privatization project, project would bring 410 million lts/ day of treated water. HUDCO financed water supply scheme in Jeypore, Orrisa, Project cost of Rs. 112. 9 million, Rs. 79 million via HUDCO and rest State grant, cost recovery through hike in user charge & one time connection charge.

Large projects carried out with Private Sector Participation n n Development & Implementation of Toll Bridge across the River Yamuna at NOIDA Development & Implementation of Gujarat Toll Roads Tirupur Industrial Water Supply Project Visakhapatnam Industrial Water Supply Project Development of International Convention Centre in Hydrebad, Andhra Pradesh

Investing in India – Foreign Direct Investments n n Through financial collaborations Through Joint Ventures and technical collaborations Through capital markets via Euro issues (Global Depository Receipt – GDR) Through private placement or preferential allotments
SECTION 4 ROLE OF IL&FS AND PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP
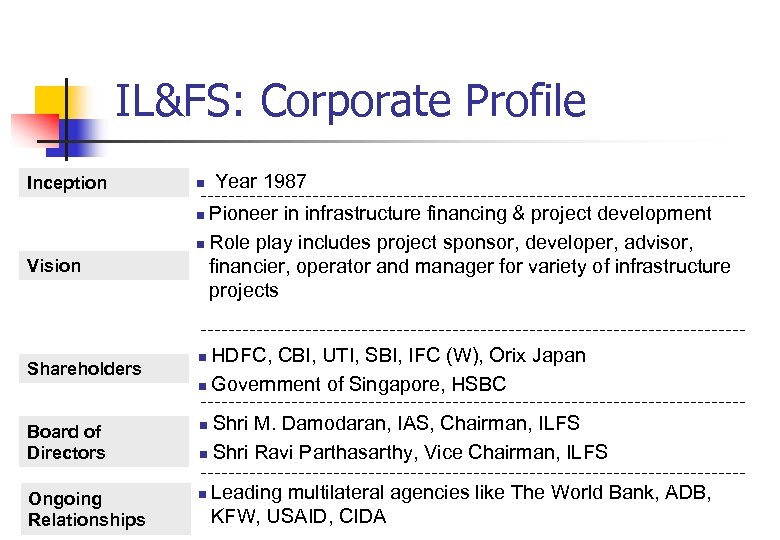
IL&FS: Corporate Profile Inception n Year 1987 Pioneer in infrastructure financing & project development n Role play includes project sponsor, developer, advisor, financier, operator and manager for variety of infrastructure projects n Vision Shareholders HDFC, CBI, UTI, SBI, IFC (W), Orix Japan n Government of Singapore, HSBC n Shri M. Damodaran, IAS, Chairman, ILFS n Shri Ravi Parthasarthy, Vice Chairman, ILFS Board of Directors n Ongoing Relationships n Leading multilateral agencies like The World Bank, ADB, KFW, USAID, CIDA
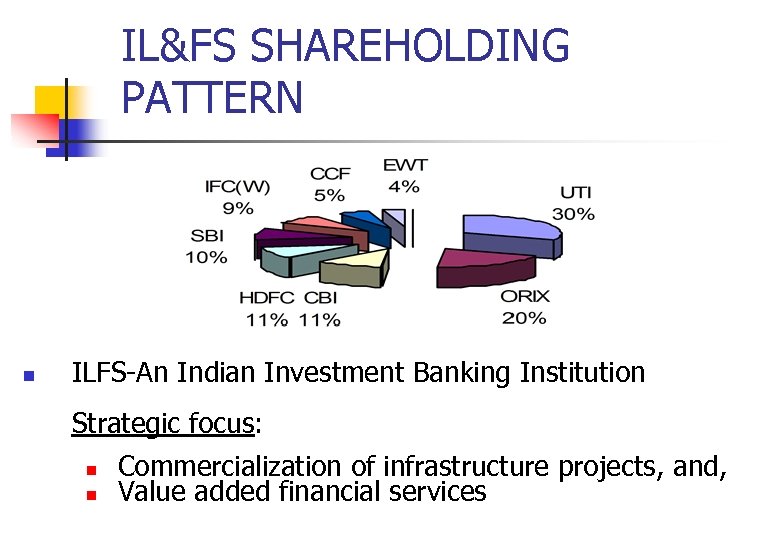
IL&FS SHAREHOLDING PATTERN n ILFS-An Indian Investment Banking Institution Strategic focus: n n Commercialization of infrastructure projects, and, Value added financial services

Public Private Partnership (PPP): Characteristics A partnership between the public and private sectors n Delivers projects/services traditionally provided by the public sector n Leverages scarce public sector resources to attract private capital n Combines Capabilities & Social Focus of Government with Management Efficiency, Technical Capabilities and Commercial Focus of private sector n Combines the strengths of the public and private sectors with an emphasis on: n Private Capital n. Value for money n. Delivering quality public services n
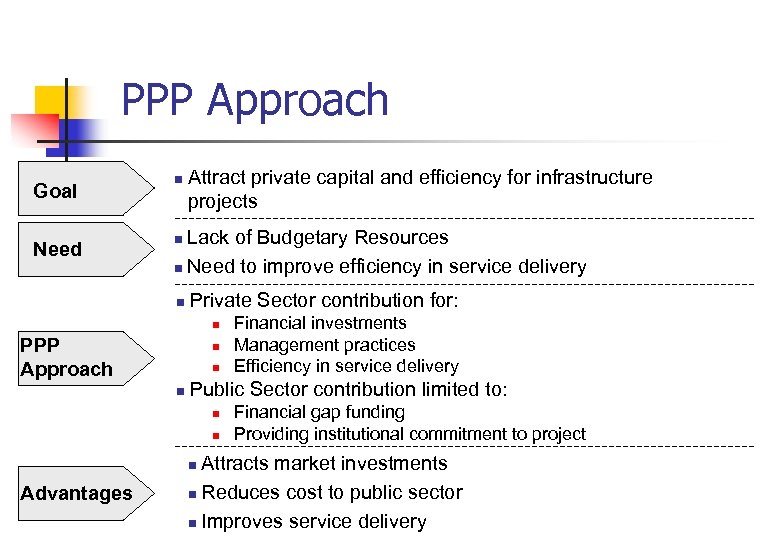
PPP Approach Goal Need n Attract private capital and efficiency for infrastructure projects Lack of Budgetary Resources n Need to improve efficiency in service delivery n n Private Sector contribution for: n PPP Approach n n n Public Sector contribution limited to: n n Financial gap funding Providing institutional commitment to project Attracts market investments n Reduces cost to public sector n Improves service delivery n Advantages Financial investments Management practices Efficiency in service delivery

IL&FS Projects n IL&FS has played a catalytic role as sponsor-developer • Delhi Noida Bridge : 8 -lane bridge linking Delhi to Noida • Vadodara-Halol Road : 32 kms road widening project • Ahmedabad-Mahesana Road: 62 kms road widening project • Tirupur Water Supply : 250 mld water supply project • Tamil Nadu Roads : 250 kms strengthening of roads • Mahindra Industrial Park : 1200 acres industrial estate with state-of-the-art facilities

Thank you Infrastructure Leasing & Financial Services Infrastructure Development Corporation
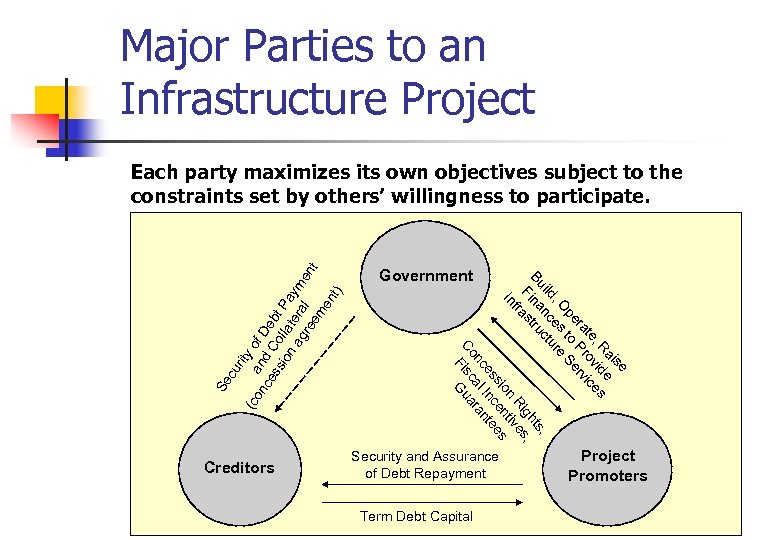
Major Parties to an Infrastructure Project Se c Creditors Government se ai e , R id s te ov ice ra Pr rv pe to Se , O es re ild nc ctu , ts Bu na ru gh , Fi st Ri es fra n tiv In sio en es es Inc te nc al ran Co Fisc ua G ur ity (c on an of D ce d C e ss o bt ion lla Pa ag tera ym en re l t em en t) Each party maximizes its own objectives subject to the constraints set by others’ willingness to participate. Security and Assurance of Debt Repayment Term Debt Capital Project Promoters
8c5155b8a116bc3ee0135555456bc7e3.ppt