Rus_IS250_220D (Engine[GR Series]).ppt
- Количество слайдов: 87

Описание двигателя l Общие сведения – V-образный 6 -ти цилиндровый, угол развала блока 600, рабочий объём 2. 5 л, 24 -клапана, система газораспределения DOHC с механизмом VVT-i, на впуске и выпуске, система ACIS электронный дроссель (система ETCS-i) 4 GR-FSE Система D-4 [Непосредственное впрыскивание] 1

Описание двигателя l Характеристики 4 GR-FSE Датчик VVT с MRE 3 Цепи газораспределения Масляный фильтр со сменным элементом 2 Свечи зажигания с длинной юбкой

Описание двигателя l Характеристики 4 GR-FSE Клапан управления впуском воздуха Топливный насос высоко давления Плита распредвалов Гидрокомпенсатор клапанного зазора Проставка рубашки охлаждения 3 Поворотный электромагнитный клапан системы ACIS Два механизма VVT-i Непосредственное впрыскивание (D-4) Форсунка с щелевым соплом

Описание двигателя l Основные характеристики 4 GR-FSE Число и расположение цилиндров Механизм газораспределения Тип камеры сгорания Раб. Объём, cm 3 Диаметр цилиндра x ход поршня mm Степень сжатия Макс. мощность к. Вт @ обор. (л. с. @ обор. ) Макс. кр. момент N·m @ обор. 4 6, V-образно 24 -клапана, DOHC, цепной привод, два VVT-i Шатровая 2499 83. 0 x 77. 0 12. 0 152 @ 6, 400 (204 @ 6, 400) 250 @ 4, 800

Engine Proper l Cylinder Head – Camshaft housing to simply the cylinder head structure – Camshaft bearing cap for IN and EX is one piece Cylinder Head Cover Gasket Camshaft Bearing Cap Camshaft Housing Cylinder Head Gasket 5 For IN and EX is one piece

Service Point (Engine Proper) l Cylinder Head – Camshaft and camshaft housing installation Step 1 : Temporary tighten (Torque: 10 N·m [102 kgf·cm]) X : Tightening order 1 5 2 6 LH Bank 6 3 4 7 8

Service Point (Engine Proper) l Cylinder Head – Camshaft and camshaft housing installation Step 2 : Tighten (Torque: 28 N·m [286 kgf·cm]) X : Tightening order 9 7 8 3 6 1 4 10 2 5 11 LH Bank 7 12

Service Point (Engine Proper) l Cylinder Head – Camshaft and camshaft housing installation Step 3 : Tighten (Torque: 16 N·m [163 kgf·cm]) X : Tightening order 1 5 2 6 LH Bank 8 3 4 7 8

Engine Proper l Cylinder Block – Water jacket spacer optimizes the cylinder bore temp. to reduce friction Water Jacket Spacer (RH) Water Jacket Spacer (LH) Without Water jacket spacer reduces coolant flow Overcool 9 Low Oil Viscosity Low Friction High Oil Viscosity High Friction

Engine Proper l Cylinder Block – Spiny liner is used to increase cooling performance Approx. 1. 0 mm (0. 039 in. ) Outside Cylinder Block Cylinder Liner Cross Section 10

Engine Proper l Piston – Optimal piston head shape to promote the mixture of fuel and air Injector 11

Engine Proper l Bearing – Bearing without bearing claw is used for crankshaft bearings and connecting rod bearings Without bearing claw 12

Service Point (Engine Proper) l Installation of Crankshaft Upper Bearing – Bearing position should be centered to the cylinder block journal to align the oil hole Upper Bearing Lubricatio n Holes [OK] Center [NG] Oil Hole 13

Service Point (Engine Proper) l Installation of Crankshaft Lower Bearing, Connecting Rod Upper and Lower Bearings – Bearing should be positioned in center and measure the position Difference Between “B” and “C”: 0. 7 mm (0. 028 in. ) or less B C 14 Vernier Caliper

Service Point (Engine Proper) l Crankshaft Bearing (upper and lower) – Combination of different width of the Bearings 21. 0 mm (0. 827 in. ) No. 1 and No. 4 Journals 15 18. 0 mm (0. 709 in. ) No. 2 and No. 3 Journals

Valve Mechanism l General – Three timing chains to drive intake and exhaust camshafts of each bank VVT-i Controller (for Exhaust) VVT-i Controller (for Intake) Primary Chain Tensioner Primary Chain 16 Secondary Chain Tensioner Secondary Chain (RH) Intake Camshaft Exhaust Camshaft Hydraulic Lash Adjuster

Valve Mechanism l Camshaft – VVT-i system is used for intake & exhaust camshafts Intake (Dual VVT-i) Camshaft Timing Rotor VVT-i Controller Assist Spring VVT-i Controller 17 Exhaust

Valve Mechanism l Camshaft – RH bank exhaust camshaft is provided with the cam to drive the high-pressure fuel pump High-Pressure Fuel Pump Exhaust Camshaft Intake Camshaft RH Bank 18

Valve Mechanism l Timing Chain – Three timing chains to drive intake and exhaust camshafts of each bank Automatic Tensioner for Secondary Chain (RH) Primary Chain Automatic Tensioner for Secondary Chain (LH) Secondary Chain (RH) Automatic Tensioner for Primary Chain Secondary Chain (LH) Idler Sprocket Crankshaft 19

Valve Mechanism l Chain Tensioner – Primary chain tensioner • Ratchet type non-return mechanism Service hall for remove and replace 20

Valve Mechanism l Chain Tensioner – 2 secondary chain tensioners are used for left and right bank Pin (Stopper) Chain Tensioner Ball Spring Left Bank 21 Oil Pressure (from cylinder head)

Reference (Valve Mechanism) l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster – Maintaining a constant zero valve clearance through use of oil pressure and spring force Plunger Low Pressure Chamber Zero Valve Clearance Oil Passage Check Ball Spring High Pressure Chamber Plunger Spring Oil Passage 22

Reference (Valve Mechanism) l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster – Start cam lift, plunger is pressed and oil in high pressure chamber is kept Plunger High Pressure Chamber 23

Reference (Valve Mechanism) l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster – Then the rocker arm pushes the valve by using hydraulic lash adjuster as a fulcrum Fixed Fulcrum Plunger High Pressure Chamber 24

Reference (Valve Mechanism) l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster – Plunger pushes back, check valve is opened and fills up oil Body Plunger Check Ball High Pressure Chamber 25

Reference (Valve Mechanism) l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster – Plunger is pushed up, then, valve clearance is maintained at zero Zero Valve Clearance Plunger Spring 26

Reference (Valve Mechanism) l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster – Operation 27

Service Point (Valve l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Mechanism) – Engine oil changing procedure • 1. Pushing check ball down by using SST SST: 09276 -75010 Hydraulic Lash Adjuster 28 Correct Incorrect

Service Point (Valve l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Mechanism) – Engine oil changing procedure • 2. Immerse hydraulic lash adjuster in clean engine oil, then compress and return the plunger with SST 5 to 6 times Clean Engine Oil 29

Service Point (Valve l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Mechanism) – Engine oil changing procedure • 3. Press the plunger by finger and check the blockage of plunger 30

Service Point (Valve l Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Mechanism) – Engine oil changing procedure • If plunger is compressed after 3 times trial, replace to new one 31

Lubrication System l Oil Delivery Pipe – Oil delivery pipe is used to lubricate cam and rocker arm Oil Delivery Pipe Cylinder Head Cover 32

Lubrication System l Oil Filter (2 WD) – Element replacing type oil filter is used Oil Filter Cap Oil Filter Element Cap Rib Portion Cut Out Portion Oil Pan No. 1 Front 33

Service Point (Lubrication l Oil Filter (2 WD) System) – Oil filter replacement • Removal Remove filter element Rib SST: 09228 -06501 Loosen the filter cap for approx. 4 rev. 34 Align the cap rib vertically and drain oil

Service Point (Lubrication l Oil Filter (2 WD) System) – Oil filter replacement • Removal O-ring Remove oil filter cap and filter element 35 Remove filter element and O-ring from filter cap

Service Point (Lubrication l Oil Filter (2 WD) System) – Oil filter replacement • Installation Install filter element New Set new filter element and Oring 36 SST: 09228 -06501 Install filter cap using SST

Service Point (Lubrication l Oil Filter (2 WD) System) – Oil filter replacement • Installation No Leakage Refill engine oil 37 Run the engine and check oil leakage

Intake and Exhaust System l ACIS Valve – Rotary solenoid type ACIS valve is used – ACIS valve is unified by laser-welding Plastic Rotary Solenoid Type ACIS Valve Laser-welding 38

Reference (Intake & Exhaust l ACIS Valve System) – Rotary solenoid type ACIS valve is used Stator Valve Shaft Magnet Rotary Solenoid Type Motor ACIS Valve 39

Intake and Exhaust System l Intake Air Control Valve – Intake air control valve is operated by DC motor Intake Manifold DC Motor Position Sensor Linkage 40 Intake Air Control Valve

Intake and Exhaust System l Intake Air Control Valve – Operation Intake Air Valve Position DC Motor Open / Close Valve is closed at low engine speed, or cold engine start 41 Engine ECU (ECM) Water Temp. Engine Speed Accelerator Pedal Opening

D-4 System l General – 4 GR-FSE engine uses D-4 System D-4 (Direct injection 4 -stroke gasoline engine) 42

D-4 System l System Diagram Injector : 400 k. Pa EDU : 4 – 13 MPa Fuel Pressure Sensor Engine ECU (ECM) Delivery Pipe Pulsation Damper Relief Valve SCV Fuel Tank Fuel Pump Jet Pump Pressure Regulator 43 High-Pressure Fuel Pump

D-4 System l Difference from usual gasoline EFI Injector • Slit-nozzle type • Injection pressure is 4 – 13 MPa • Installed on the combustion chamber EDU for high speed injector operation Fuel pressure sensor is provided to delivery pipe High Pressure Fuel Pump 44

Reference l Features of D-4 System Improved volumetric efficiency Direct Injection Slit-nozzle Injector Expanded knocking limit High Pressure Injection Fuel does not adhere to the intake port Piston head shape is changed for D-4 system High Performance 45 Higher atomization of fuel Clean Emission Better Fuel Economy

D-4 System l Location High-Pressure Fuel Pump Delivery Pipe EDU 46 Pulsation Damper Fuel Pressure Sensor Injector

D-4 System l High-Pressure Fuel Pump – Supplies the high pressure fuel to the delivery pipe SCV (Spill Control Valve) Pulsation Damper to Delivery Pipe (4 -13 MPa) from Fuel Tank (0. 4 MPa) Lifter 47 Return to fuel tank

D-4 System l High-Pressure Fuel Pump – Fuel control operation (SCV close timing is late) Plunger Lift SCV Open Close [Suction] SCV from Fuel Tank [Inactive] Open (OFF) [Pumping] Close ON Check Valve to Delivery Pipe 48

D-4 System l High-Pressure Fuel Pump – Fuel control operation (SCV close timing is early) Plunger Lift SCV Open Close [Suction] SCV from Fuel Tank [Inactive] Open (OFF) [Pumping] Close (ON) Check Valve to Delivery Pipe 49

D-4 System l High-Pressure Fuel Pump – The SCV close timing regulates the pumping volume to control fuel pressure [Fuel Pressure Control] Fuel Pressure Sensor SCV Controls SCV close timing Fuel pressure (Feedback) Crankshaft Position Sensor Calculation of target pressure Engine ECU (ECM) 50

D-4 System l Delivery Pipe – Stores high-pressure fuel (4 – 13 MPa) produced by highpressure fuel pump From Fuel Pump (High Pressure) Delivery Pipe Fuel Pressure Sensor Return to Fuel Tank Injector Relief Valve 51

D-4 System l Delivery Pipe – Fuel pressure sensor Sensor Portion Output Voltage (V) Output characteristic 4. 5 2. 5 0 9. 8 19. 6 Delivery Pipe Pressure (MPa) Fuel Pressure 52

D-4 System l Injector – High pressure, slit-nozzle type injector Slit-nozzle 53

D-4 System l Injector – Slit-nozzle makes sector formed injection 0. 71 mm (0. 028 in. ) Sector Formed Injection A Slit-nozzle 54 0. 15 mm (0. 006 in. ) A Cross Section
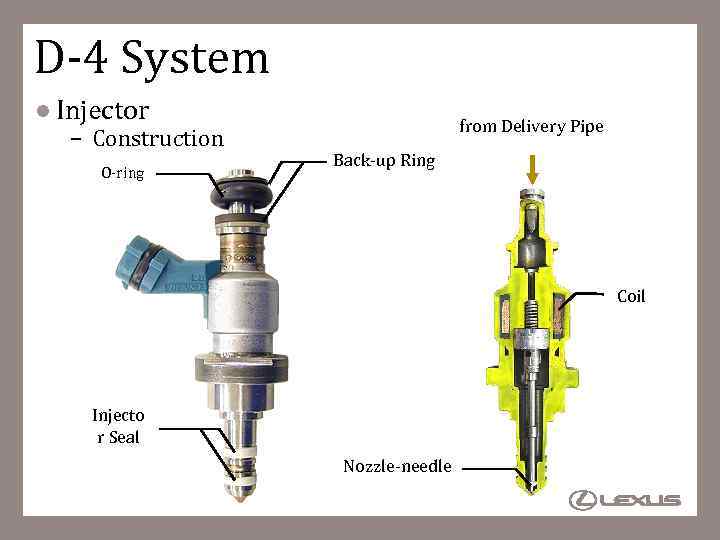
D-4 System l Injector – Construction O-ring from Delivery Pipe Back-up Ring Coil Injecto r Seal Nozzle-needle 55

Service Point (D-4 System) l Injector – When remove the injector from cylinder head, replace the injector seal using new SST Injector Seal Guide (09268 -03020) Injector Seal Holder (09268 -03010) SST 09260 -39015 56

Service Point (D-4 System) l Injector – Replacement of injector seals (using SST) Needle-nosed Pliers 1. Remove injector seals 57 Taper Shape 2. Attach the guide (SST)

Service Point (D-4 System) l Injector – Replacement of injector seals (using SST) 3. Install a new injector 58 4. Slide the injector seal into the injector groove

Service Point (D-4 System) l Injector – Replacement of injector seals (using SST) Gently press 5. Settle the injector seal 59 6. Install a new injector seal

Service Point (D-4 System) l Injector – Replacement of injector seals (using SST) 7. Slide the injector seal into the injector groove 60 8. Fully align the injector seal

Service Point (D-4 System) l Injector – Replacement of injector seals (using SST) Gently press 9. Settle the injector seal 61 10. Fully align the injector seal

Service Point (D-4 System) l Injector – Replacement of injector seals (using SST) Replace 11. Check the injector seals 62

D-4 System l EDU (Electronic Driver Unit) – Drives the injectors at high speed EDU Battery DC / DC Converter High Voltage Command Pulse IJT #16 Control Circuit High-speed operation IJF Engine ECU (ECM) 63 Confirmation Pulse Injectors

Ignition System l Spark Plug – Long-reach type spark plug to improve cooling performance on cylinder head Long-reach Type Iridium Platinum 64 Normal Type Extended Water Jacket

Charging System l Alternator Pulley – One-way clutch is used in the pulley to absorb engine fluctuation One-way Clutch Alternator Shaft Bearing Spring Alternator Pulley 65 Alternator

Service Point (Charging l Alternator Pulley System) – Using a SST, when remove or install the alternator pulley SST 09820 -63020 (2 parts) Remove Shaft Pulley SST 66

Service Point (Charging l Alternator Pulley System) – Alternator pulley cap is non-reusable part Alternator Pulley Cap (Non-reusable Part) 67

Engine Control System l D-4 EFI Control (for 4 GR-FSE) – D-4 EFI conducts the injection volume control and injection timing control simultaneously Stoichiometric Airfuel Ratio Intake (Injection) Compression Rich 68 Sparking Lean Combustion

Engine Control System l D-4 EFI Control (for 4 GR-FSE) – At cold start, weak stratification combustion to improve TWC worm-up performance Lean Intake Compression (Injection) Rich 69 Rich Sparking Lean Combustion

Reference (Engine Control l D-4 EFI Control System) (for 4 GR-FSE) – Weak stratification combustion • Creates rich and lean portions of air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber Lean Rich Injector Plug Piston 70

Engine Control System l VVT Sensor – 4 MRE type VVT sensors are used for intake and exhaust camshaft of each bank MRE Type VVT Sensor (Exhaust) MRE Type VVT Sensor (Intake) RH Bank Timing Rotor LH Bank 71 MRE Type VVT Sensor (Exhaust)

Reference (Engine Control l VVT Sensor System) – Output signal is digital waveform Timing Rotor MRE Magnet 0 V MRE Type Coil Magnet 0 V Pickup Coil Type 72

Reference (Engine Control l VVT Sensor System) – The resistance of MRE is changed by the magnetic flux direction Timing Magnetic Rotor Flux Sensor Output ”High” 73 Sensor Output ”Low”

Reference (Engine Control l VVT Sensor System) – Signal output at extremely low speed rotation can be ensured MRE Type Pickup Coil Type Engine Speed Sensor Output Engine Speed No Detecting Time 74 Time

Reference (Engine Control System) l VVT Sensor – By the adoption of MRE type VVT sensor, ECM can detects the sensor low input or high input malfunction V Sensor high input malfunction 4. 7 High VVT Sensor Output Voltage Low 0. 3 Sensor low input malfunction 75
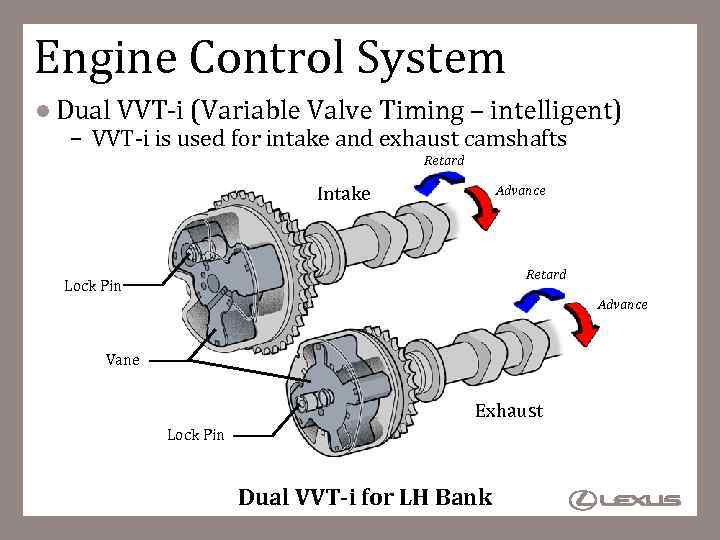
Engine Control System l Dual VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing – intelligent) – VVT-i is used for intake and exhaust camshafts Retard Intake Advance Retard Lock Pin Advance Vane Exhaust Lock Pin Dual VVT-i for LH Bank 76

Reference (Engine Control l Dual VVT-i System) – Operation At Idle, Light Load, Low Temp. and Starting TDC Engine Load Operation Range Reduce blow back to the intake side BDC Engine Speed 77 - Effect • Stable combustion for fuel economy

Reference (Engine Control l Dual VVT-i System) – Operation Increase internal EGR, Eliminate pumping loss At Medium Load TDC Engine Load Operation Range BDC Engine Speed 78 - Effect • Improved emission control • Better fuel economy

Reference (Engine Control l Dual VVT-i System) At Low/Middle speed Heavy Load – Operation TDC Engine Load Operation Range Using the combustion pressure completely Volumetric efficiency improvement BDC Engine Speed 79 - Effect • Improved torque/output

Reference (Engine Control l Dual VVT-i System) At High speed Heavy Load – Operation TDC Operation Range Engine Load volumetric efficiency improvement Reduce pumping loss BDC Engine Speed 80 - Effect • Improved output

Service Point (Engine Control System) l Dual VVT-i – Following 14 DTCs are added by adoption of exhaust VVT DTC -i Detection Item DTC No. Detection Item No. P 0013 Camshaft Position "B" Actuator Circuit (Bank 1) Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Over. P 0014 Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) Position P 0015 Camshaft (Bank 1) "B" - Timing Over. Retarded Crankshaft Position - Camshaft P 0017 Position Correlation (Bank 1 Sensor B) Crankshaft Position - Camshaft P 0019 Position Correlation (Bank 2 Sensor B) P 0023 Camshaft Position "B" Actuator Circuit (Bank 2) Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Over. P 0024 Advanced or System Performance (Bank 2) 81 P 0025 Camshaft Position "B" - Timing Over-Retarded (Bank 2) P 0365 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit (Bank 1) P 0367 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Low Input (Bank 1) P 0368 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit High Input (Bank 1) P 0390 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit (Bank 2) P 0392 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Low Input (Bank 2) P 0393 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit High Input (Bank 2)

Engine Control System l Cranking Hold Function – Once the power mode is turned to “Engine Starting”, starter operates until engine starting Engine Switch 1, Start signal Power Source Control ECU Stop Light Switch (AT) or Clutch Switch (MT) ACC Relay IG 1, 2 Relay Starter 82 STSW 2, ACC power cut ACCR 3, Operates starter STAR Starter Cut Relay Park Neutral Position Switch (AT) or Clutch Switch (MT) Starter Relay Engine ECU (ECM) STA Stop Light Switch Crankshaft Position Sensor Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor

Reference (Engine Control l Cranking Hold System) Function – Operation Start Signal : With this system : Without this system ON OFF ACC ON Relay OFF Automatically Controlled Starter ON Relay OFF Judgment NE Signal Time 83

Reference (Engine Control l Cranking Hold System) Function Judgment Level (rpm) Max. Cranking Time (sec. ) – Judgment of the engine firing – Maximum cranking time Engine Coolant Temp. ( C) Judgment of the engine firing Engine Coolant Temp. ( C) Maximum cranking time (When engine does not start by some abnormalities) 84

Reference (Engine Control l Cranking Hold System) Function – Protection during engine starting If the engine speed becomes 1200 rpm or more while cranking, engine ECU (ECM) stops starter to prevent starter overrun Start Signal ON Driver pushes the engine switch intentionally OFF Starter Relay OFF 1200 rpm NE Signal Time 85

Reference (Engine Control l Cranking Hold System) Function – Protection during engine starting Starter overheating protection operates starter max. 30 sec. with intentional starter operation Start Signal ON Driver pushes the engine switch intentionally OFF Starter Relay NE Signal 30 sec. OFF Engine does not start (Problem) Time 86

Engine Control System l Communication – CAN (Controller Area Network) communication for DLC 3 and other ECUs Engine ECU (ECM) Gate Way ECU J/C DLC 3 CAN Other Bus 87 Intelligent Tester II Diagnosis Communication
Rus_IS250_220D (Engine[GR Series]).ppt