48067625d76e79a82524d433c6791a7e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Operations Management § Operations Management is: The management of systems or processes that create goods and/or provide services § Operations Management affects: § Companies’ ability to compete § Nation’s ability to compete internationally 1 -1
Operations Management § Operations Management is: The management of systems or processes that create goods and/or provide services § Operations Management affects: § Companies’ ability to compete § Nation’s ability to compete internationally 1 -1
 Value-Added Process The operations function involves the conversion of inputs into outputs Value added Inputs Land Labor Capital Transformation/ Conversion process Outputs Goods Services Feedback Control Feedback 1 -2
Value-Added Process The operations function involves the conversion of inputs into outputs Value added Inputs Land Labor Capital Transformation/ Conversion process Outputs Goods Services Feedback Control Feedback 1 -2
 Value-Added & Product Packages § Value-added is the difference between the cost of inputs and the value or price of outputs. § Product packages are a combination of goods and services. § Product packages can make a company more competitive. 1 -3
Value-Added & Product Packages § Value-added is the difference between the cost of inputs and the value or price of outputs. § Product packages are a combination of goods and services. § Product packages can make a company more competitive. 1 -3
 Production of Goods vs. Delivery of Services § Production of goods – tangible output § Delivery of services – an act § Service job categories § § § § Government Wholesale/retail Financial services Healthcare Personal services Business services Education 1 -4
Production of Goods vs. Delivery of Services § Production of goods – tangible output § Delivery of services – an act § Service job categories § § § § Government Wholesale/retail Financial services Healthcare Personal services Business services Education 1 -4
 Key Differences 1. Customer contact 2. Uniformity of input 3. Labor content of jobs 4. Uniformity of output 5. Measurement of productivity 1 -5
Key Differences 1. Customer contact 2. Uniformity of input 3. Labor content of jobs 4. Uniformity of output 5. Measurement of productivity 1 -5
 Key Differences 6. Production and delivery 7. Quality assurance 8. Amount of inventory 9. Evaluation of work 1 -6
Key Differences 6. Production and delivery 7. Quality assurance 8. Amount of inventory 9. Evaluation of work 1 -6
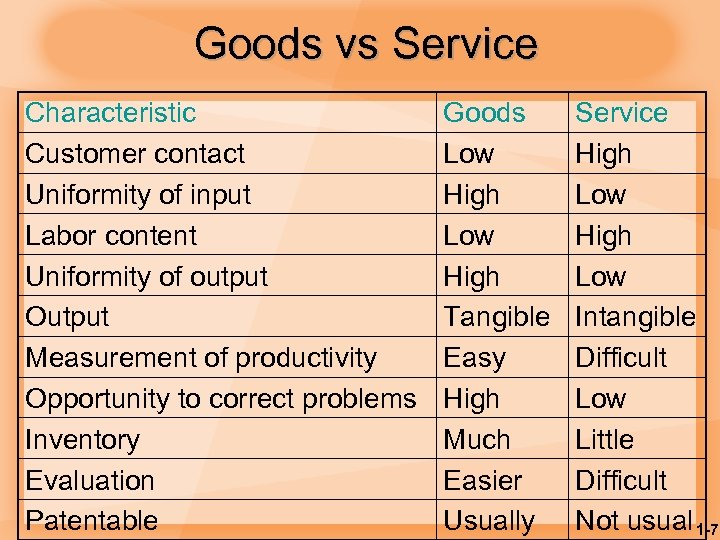 Goods vs Service Characteristic Customer contact Uniformity of input Labor content Uniformity of output Output Measurement of productivity Opportunity to correct problems Inventory Evaluation Patentable Goods Low High Tangible Easy High Much Easier Usually Service High Low Intangible Difficult Low Little Difficult Not usual 1 -7
Goods vs Service Characteristic Customer contact Uniformity of input Labor content Uniformity of output Output Measurement of productivity Opportunity to correct problems Inventory Evaluation Patentable Goods Low High Tangible Easy High Much Easier Usually Service High Low Intangible Difficult Low Little Difficult Not usual 1 -7
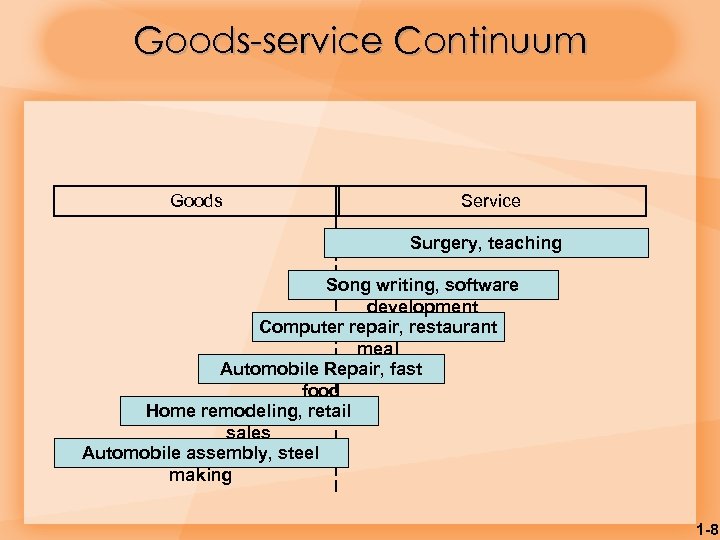 Goods-service Continuum Goods Service Surgery, teaching Song writing, software development Computer repair, restaurant meal Automobile Repair, fast food Home remodeling, retail sales Automobile assembly, steel making 1 -8
Goods-service Continuum Goods Service Surgery, teaching Song writing, software development Computer repair, restaurant meal Automobile Repair, fast food Home remodeling, retail sales Automobile assembly, steel making 1 -8
 Manufacturing or Service? Tangible Act 1 -9
Manufacturing or Service? Tangible Act 1 -9
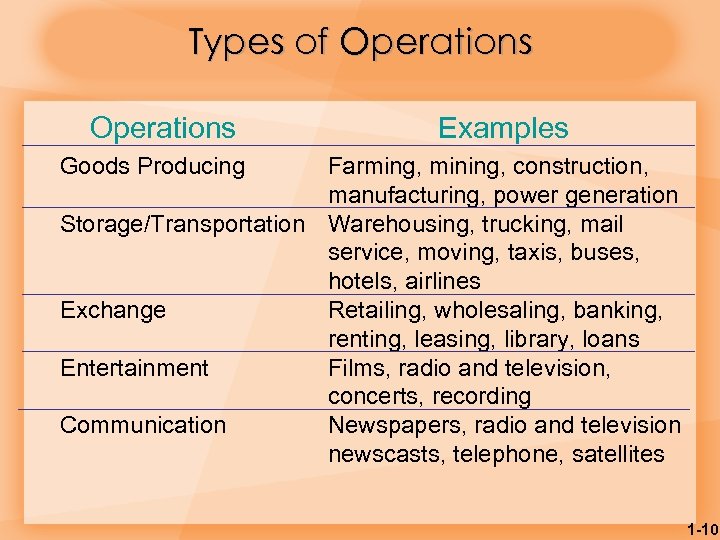 Types of Operations Examples Goods Producing Farming, mining, construction, manufacturing, power generation Storage/Transportation Warehousing, trucking, mail service, moving, taxis, buses, hotels, airlines Exchange Retailing, wholesaling, banking, renting, leasing, library, loans Entertainment Films, radio and television, concerts, recording Communication Newspapers, radio and television newscasts, telephone, satellites 1 -10
Types of Operations Examples Goods Producing Farming, mining, construction, manufacturing, power generation Storage/Transportation Warehousing, trucking, mail service, moving, taxis, buses, hotels, airlines Exchange Retailing, wholesaling, banking, renting, leasing, library, loans Entertainment Films, radio and television, concerts, recording Communication Newspapers, radio and television newscasts, telephone, satellites 1 -10
 Challenges of Managing Services § Service jobs are often less structured than manufacturing jobs § Customer contact is higher § Worker skill levels are lower § Services hire many low-skill, entry-level workers § Employee turnover is higher § Input variability is higher § Service performance can be affected by worker’s personal factors 1 -11
Challenges of Managing Services § Service jobs are often less structured than manufacturing jobs § Customer contact is higher § Worker skill levels are lower § Services hire many low-skill, entry-level workers § Employee turnover is higher § Input variability is higher § Service performance can be affected by worker’s personal factors 1 -11
 Key Decisions of Operations Managers § What resources/what amounts § When Needed/scheduled/ordered § Where Work to be done § How Designed § Who To do the work 1 -12
Key Decisions of Operations Managers § What resources/what amounts § When Needed/scheduled/ordered § Where Work to be done § How Designed § Who To do the work 1 -12
 Decision Making System Design – – – capacity location arrangement of departments product and service planning acquisition and placement of equipment 1 -13
Decision Making System Design – – – capacity location arrangement of departments product and service planning acquisition and placement of equipment 1 -13
 Decision Making System operation personnel inventory scheduling project management – quality assurance – – 1 -14
Decision Making System operation personnel inventory scheduling project management – quality assurance – – 1 -14
 Scope of Operations Management § Operations Management includes: § § § § § Forecasting Capacity planning Scheduling Managing inventories Assuring quality Motivating employees Deciding where to locate facilities Supply chain management And more. . . 1 -15
Scope of Operations Management § Operations Management includes: § § § § § Forecasting Capacity planning Scheduling Managing inventories Assuring quality Motivating employees Deciding where to locate facilities Supply chain management And more. . . 1 -15
 The Organization The Three Basic Functions Organization Finance Operations Marketing 1 -16
The Organization The Three Basic Functions Organization Finance Operations Marketing 1 -16
 Business Operations Overlap Operations Marketing Finance 1 -17
Business Operations Overlap Operations Marketing Finance 1 -17
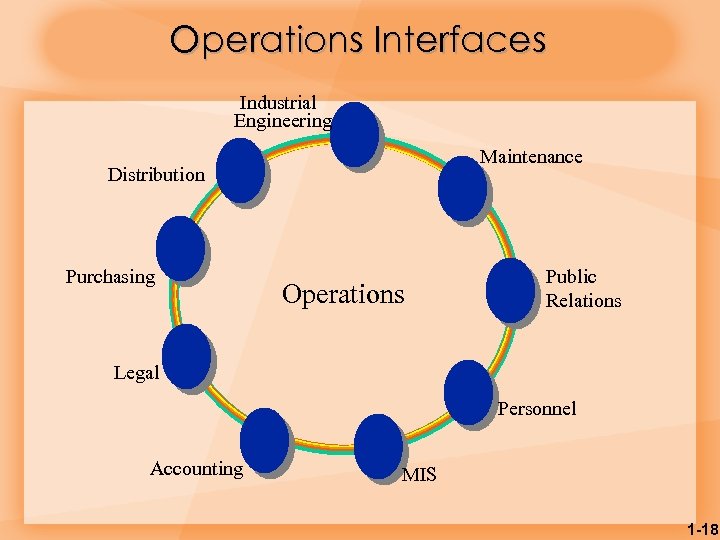 Operations Interfaces Industrial Engineering Maintenance Distribution Purchasing Operations Public Relations Legal Personnel Accounting MIS 1 -18
Operations Interfaces Industrial Engineering Maintenance Distribution Purchasing Operations Public Relations Legal Personnel Accounting MIS 1 -18
 Historical Evolution of Operations Management § Industrial revolution (1770’s) § Scientific management (1911) § Mass production § Interchangeable parts § Division of labor § Human relations movement (1920 -60) § Decision models (1915, 1960 -70’s) § Influence of Japanese manufacturers 1 -19
Historical Evolution of Operations Management § Industrial revolution (1770’s) § Scientific management (1911) § Mass production § Interchangeable parts § Division of labor § Human relations movement (1920 -60) § Decision models (1915, 1960 -70’s) § Influence of Japanese manufacturers 1 -19
 Trends in Business § Major trends § § § § The Internet, e-commerce, e-business Management technology Globalization Management of supply chains Outsourcing Agility Ethical behavior 1 -20
Trends in Business § Major trends § § § § The Internet, e-commerce, e-business Management technology Globalization Management of supply chains Outsourcing Agility Ethical behavior 1 -20
 Management Technology § Technology: The application of scientific discoveries to the development and improvement of goods and services § Product and service technology § Process technology § Information technology 1 -21
Management Technology § Technology: The application of scientific discoveries to the development and improvement of goods and services § Product and service technology § Process technology § Information technology 1 -21
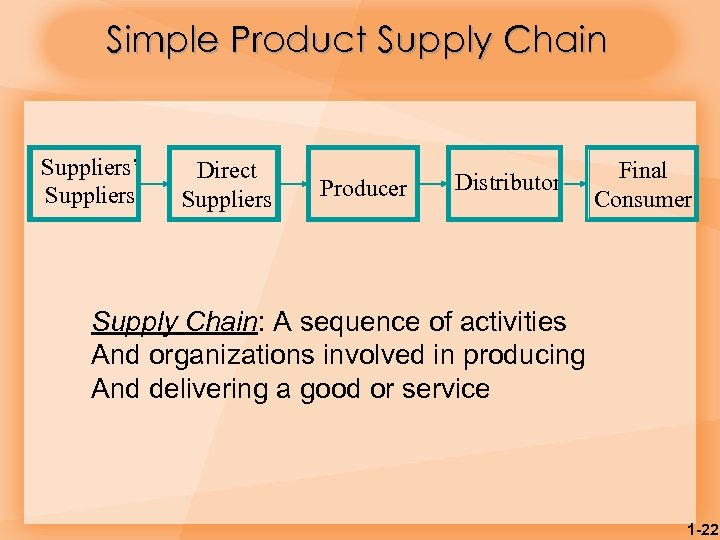 Simple Product Supply Chain Suppliers’ Suppliers Direct Suppliers Producer Distributor Final Consumer Supply Chain: A sequence of activities And organizations involved in producing And delivering a good or service 1 -22
Simple Product Supply Chain Suppliers’ Suppliers Direct Suppliers Producer Distributor Final Consumer Supply Chain: A sequence of activities And organizations involved in producing And delivering a good or service 1 -22
 Other Important Trends § § § Working with fewer resources Revenue management Process analysis and improvement Increased regulation and product liability Lean production 1 -23
Other Important Trends § § § Working with fewer resources Revenue management Process analysis and improvement Increased regulation and product liability Lean production 1 -23


