010588e256f0a55198e20b166a0db30e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Operations Management OM 306. 001 Lecture 5 – PM Tools, Methods and Cases Al Baharmast, Ph. D.
Operations Management OM 306. 001 Lecture 5 – PM Tools, Methods and Cases Al Baharmast, Ph. D.
 Project 2 Expectations Team Project I – Staging an Event Project Your team is vying to win a contract to support the preparations for and management of a major local event. The event is to raise money to a national charity. The event financiers would like to hire a firm to plan, organize and run this event. Their only guidelines are as follows – The event must accommodate a minimum of 10, 000 attendees. Food and drink must be provided (whether by concession or made available as part of the entry fee). The event project team must plan the venue, promotions, security, music/entertainment, food/drinks services and the cleaning services during and after the event. They must also make this event profitable! Assignment – Prepare a presentation to sell the event project team’s services. The team must have a project manager and its members must each be assigned at least one area of responsibility among the team’s assigned tasks. Artifacts that must be included the presentation include – • Event & Project overview • Description of project team qualifications/capabilities • Proposed venue, promotions, security, entertainment, food/drink and cleaning plan • Project financial proposal (realistic assumptions for revenues, costs & net income) • Project risks overview • Project plan (WBS and GANTT Chart to be provided as hand-outs) • Assessment of the critical path and critical tasks Assessing Project Financial Analyses 1. Looking to make sure you have adequately captured ALL (both categories of and individual contributors to) revenues and expenses 2. Looking to make sure you have realistically reflected revenues and expenses 3. Looking to make sure you can add and subtract : ) Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
Project 2 Expectations Team Project I – Staging an Event Project Your team is vying to win a contract to support the preparations for and management of a major local event. The event is to raise money to a national charity. The event financiers would like to hire a firm to plan, organize and run this event. Their only guidelines are as follows – The event must accommodate a minimum of 10, 000 attendees. Food and drink must be provided (whether by concession or made available as part of the entry fee). The event project team must plan the venue, promotions, security, music/entertainment, food/drinks services and the cleaning services during and after the event. They must also make this event profitable! Assignment – Prepare a presentation to sell the event project team’s services. The team must have a project manager and its members must each be assigned at least one area of responsibility among the team’s assigned tasks. Artifacts that must be included the presentation include – • Event & Project overview • Description of project team qualifications/capabilities • Proposed venue, promotions, security, entertainment, food/drink and cleaning plan • Project financial proposal (realistic assumptions for revenues, costs & net income) • Project risks overview • Project plan (WBS and GANTT Chart to be provided as hand-outs) • Assessment of the critical path and critical tasks Assessing Project Financial Analyses 1. Looking to make sure you have adequately captured ALL (both categories of and individual contributors to) revenues and expenses 2. Looking to make sure you have realistically reflected revenues and expenses 3. Looking to make sure you can add and subtract : ) Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
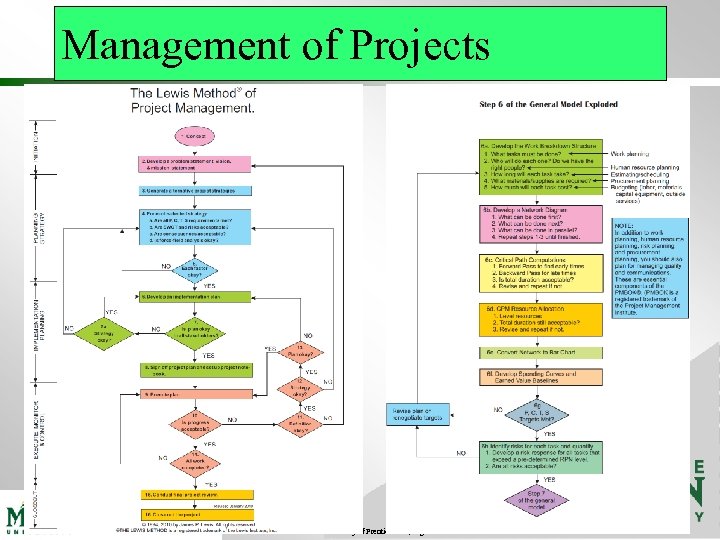 Management of Projects Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
Management of Projects Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
 Considerations in Developing a WBS • Manage WBS depth (levels) carefully; four to eight levels is reasonable/manageable. Lewis says more than 20 is overkill… chances are any approaching that is overkill (best determined by what you need to manage and what you can reasonably manage) • All WBS tasks do NOT have to go the same level • WBS tasks are logical decompositions of tasks, not a sequenced occurrence of tasks • WBS development should precede scheduling and resource planning • WBS development requires some knowledge of the tasks to be performed Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
Considerations in Developing a WBS • Manage WBS depth (levels) carefully; four to eight levels is reasonable/manageable. Lewis says more than 20 is overkill… chances are any approaching that is overkill (best determined by what you need to manage and what you can reasonably manage) • All WBS tasks do NOT have to go the same level • WBS tasks are logical decompositions of tasks, not a sequenced occurrence of tasks • WBS development should precede scheduling and resource planning • WBS development requires some knowledge of the tasks to be performed Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
 Considerations in Project Scheduling • Identify direct task dependencies (task dependencies become apparent when one task cannot start until another is completed… though there are different types of dependencies and some interdependent tasks can coincide in their schedule) • Three types of dependencies - logical dependency, management decision dependency, resource availability (personnel, funding, equipment) dependency • Be realistic in time estimation; a bit of management reserve is reasonable, but don’t overdo it • No resources can be 100% utilized • Be cognizant of opportunities for overlapping working; even where overlap is possible, some tasks may need to lag others • Brook’s Law – Adding resources to a project that is already delayed may serve to only delay the project further Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
Considerations in Project Scheduling • Identify direct task dependencies (task dependencies become apparent when one task cannot start until another is completed… though there are different types of dependencies and some interdependent tasks can coincide in their schedule) • Three types of dependencies - logical dependency, management decision dependency, resource availability (personnel, funding, equipment) dependency • Be realistic in time estimation; a bit of management reserve is reasonable, but don’t overdo it • No resources can be 100% utilized • Be cognizant of opportunities for overlapping working; even where overlap is possible, some tasks may need to lag others • Brook’s Law – Adding resources to a project that is already delayed may serve to only delay the project further Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
 Build a WBS & Estimate Task Durations Class Exercise (15 minutes) – - Work with your project team - Open up MS Project, MS Excel or work on paper - Create a WBS and begin to outline task dependencies - Start estimating durations (does the critical path become intuitively apparent? ) Buying a House • Agents • House location/budget • Loans • House selection • Negotiation • Inspection • Closing Building a Boat Dock • Design concept • Budget • Contractors • Detailed design • Permits • Build • Inspection Other Options – Find and move into new housing Plan and go on a family vacation Plan and run a block-party Plan and manage a renovation project (bath/kitchen) Plan and run your office holiday party Plan for admission into graduate school Plan your next job search courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved Some lecture content
Build a WBS & Estimate Task Durations Class Exercise (15 minutes) – - Work with your project team - Open up MS Project, MS Excel or work on paper - Create a WBS and begin to outline task dependencies - Start estimating durations (does the critical path become intuitively apparent? ) Buying a House • Agents • House location/budget • Loans • House selection • Negotiation • Inspection • Closing Building a Boat Dock • Design concept • Budget • Contractors • Detailed design • Permits • Build • Inspection Other Options – Find and move into new housing Plan and go on a family vacation Plan and run a block-party Plan and manage a renovation project (bath/kitchen) Plan and run your office holiday party Plan for admission into graduate school Plan your next job search courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved Some lecture content
 PM Terms þ Project Plan – A formal, approved document(s) that includes (but is not limited to) the project scope, schedule. Supports the PM in managing execution and control over Cost, Schedule and Performance. þ Project Schedule – Outlines dates for performing project activities and realizing milestones. Schedule should highlight the critical path and execution should be reported against all scheduled activities/milestones. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
PM Terms þ Project Plan – A formal, approved document(s) that includes (but is not limited to) the project scope, schedule. Supports the PM in managing execution and control over Cost, Schedule and Performance. þ Project Schedule – Outlines dates for performing project activities and realizing milestones. Schedule should highlight the critical path and execution should be reported against all scheduled activities/milestones. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
 PM Terms þ Project Resources – Assets applied to supporting project activities – budgets, personnel, equipment, services (contractors), material, supplies, etc. . þ Milestones – Significant events or points of a project. Usually associated with a set of project activities (work packages). þ Deliverables – Controlled (often contractually enforced) outputs of project activities. Objects/artifacts that demonstrate achievement of project objectives. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
PM Terms þ Project Resources – Assets applied to supporting project activities – budgets, personnel, equipment, services (contractors), material, supplies, etc. . þ Milestones – Significant events or points of a project. Usually associated with a set of project activities (work packages). þ Deliverables – Controlled (often contractually enforced) outputs of project activities. Objects/artifacts that demonstrate achievement of project objectives. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
 PM Terms þ Project Scope – Identifies the sum of all objectives, activities, products, services, and results to which constrained project resources will be allocated. Project schedules and resources are allocated to supporting this specified scope. þ Change Control – Formal methods of managing change from the project baseline (that outlines cost, schedule and performance parameters). Provides for methods of identifying, approving/rejecting, and assessing impact of change. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
PM Terms þ Project Scope – Identifies the sum of all objectives, activities, products, services, and results to which constrained project resources will be allocated. Project schedules and resources are allocated to supporting this specified scope. þ Change Control – Formal methods of managing change from the project baseline (that outlines cost, schedule and performance parameters). Provides for methods of identifying, approving/rejecting, and assessing impact of change. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
 PM Terms þ Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) – Hierarchical decomposition of work (tasks) required to achieve project objectives. Tasks are broken down into work packages used to develop project schedule and allocate resources. Includes activities & milestones; details project activities’ scope. þ Critical Path – Most inflexible (not necessarily most important) series of tasks in a project. Isolates the longest pathway through the project (shortest period in which project could be completed). May change if durations of other tasks change. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
PM Terms þ Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) – Hierarchical decomposition of work (tasks) required to achieve project objectives. Tasks are broken down into work packages used to develop project schedule and allocate resources. Includes activities & milestones; details project activities’ scope. þ Critical Path – Most inflexible (not necessarily most important) series of tasks in a project. Isolates the longest pathway through the project (shortest period in which project could be completed). May change if durations of other tasks change. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
 PM Terms þ Project Risks and Issues – A risk is an uncertain event that could have a negative or positive (less likely) impact on the project, its objectives, activities or milestones. Risks are measured in terms of probability of occurrence and severity of impact. Issues are risks that have already been realized. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
PM Terms þ Project Risks and Issues – A risk is an uncertain event that could have a negative or positive (less likely) impact on the project, its objectives, activities or milestones. Risks are measured in terms of probability of occurrence and severity of impact. Issues are risks that have already been realized. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
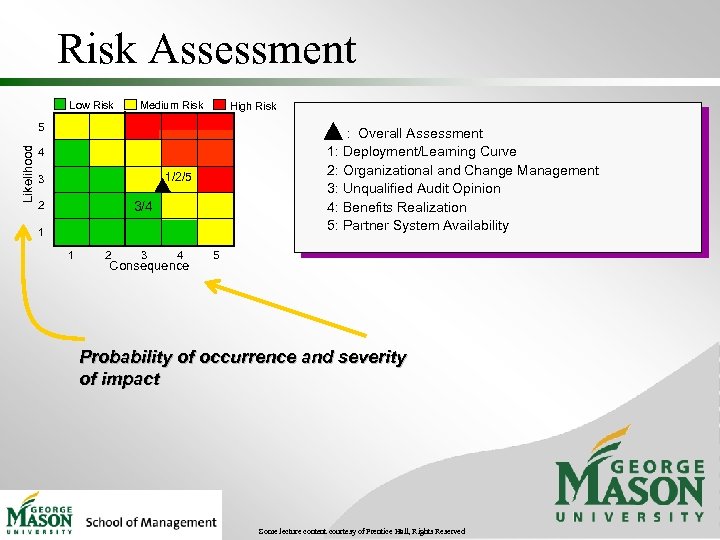 Risk Assessment Low Risk Medium Risk High Risk Likelihood 5 : Overall Assessment 1: Deployment/Learning Curve 2: Organizational and Change Management 3: Unqualified Audit Opinion 4: Benefits Realization 5: Partner System Availability 4 1/2/5 3 3/4 2 1 1 2 3 4 Consequence 5 Probability of occurrence and severity of impact Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
Risk Assessment Low Risk Medium Risk High Risk Likelihood 5 : Overall Assessment 1: Deployment/Learning Curve 2: Organizational and Change Management 3: Unqualified Audit Opinion 4: Benefits Realization 5: Partner System Availability 4 1/2/5 3 3/4 2 1 1 2 3 4 Consequence 5 Probability of occurrence and severity of impact Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
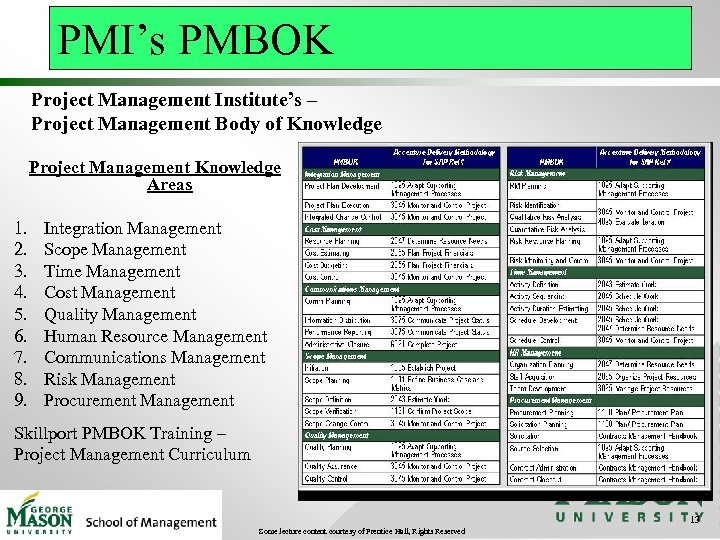 PMI’s PMBOK Project Management Institute’s – Project Management Body of Knowledge Project Management Knowledge Areas 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Integration Management Scope Management Time Management Cost Management Quality Management Human Resource Management Communications Management Risk Management Procurement Management Skillport PMBOK Training – Project Management Curriculum 13 Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
PMI’s PMBOK Project Management Institute’s – Project Management Body of Knowledge Project Management Knowledge Areas 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Integration Management Scope Management Time Management Cost Management Quality Management Human Resource Management Communications Management Risk Management Procurement Management Skillport PMBOK Training – Project Management Curriculum 13 Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
 PM Cases þ Jordan Petroleum Refinery Co. (Amman, Jordan) – ERP implementation project supported by institutionalizing standard PM methods. þ TDS Group (Neckarsulm, Germany) – Implemented simple PM systems and standardized methods to support IT, HR and other consulting services. þ Meridian Energy Ltd. (New Zealand) – Managed project to build a Te Apiti wind farm as part of an overall alternative energies initiative. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved
PM Cases þ Jordan Petroleum Refinery Co. (Amman, Jordan) – ERP implementation project supported by institutionalizing standard PM methods. þ TDS Group (Neckarsulm, Germany) – Implemented simple PM systems and standardized methods to support IT, HR and other consulting services. þ Meridian Energy Ltd. (New Zealand) – Managed project to build a Te Apiti wind farm as part of an overall alternative energies initiative. Some lecture content courtesy of Prentice Hall, Rights Reserved


