83a1ad94415d0403a89753a449f47507.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Operations Management and Technology Ross L. Fink
Operations Management and Technology Ross L. Fink
 Design Technology Computer-Aided Design (CAD) o Refers to the use of computers to interactively design products and prepare engineering documentation http: //www. swissspecialties. com/product 2. htm
Design Technology Computer-Aided Design (CAD) o Refers to the use of computers to interactively design products and prepare engineering documentation http: //www. swissspecialties. com/product 2. htm
 Design Technology Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) q Refers to the use of specialized computer programs to direct and control manufacturing equipment
Design Technology Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) q Refers to the use of specialized computer programs to direct and control manufacturing equipment
 Design Technology Benefits of CAD and CAM q q q Product quality Shorter design time Production cost reductions Database availability New range of capabilities Reduces need for “similar” parts
Design Technology Benefits of CAD and CAM q q q Product quality Shorter design time Production cost reductions Database availability New range of capabilities Reduces need for “similar” parts
 Production Technology q Numerically controlled machines q q q q q Numerical control Computer numerical control Direct numerical control Process control Vision systems Robots Automated storage and retrieval systems Automated guided vehicles Flexible manufacturing systems Computer integrated manufacturing
Production Technology q Numerically controlled machines q q q q q Numerical control Computer numerical control Direct numerical control Process control Vision systems Robots Automated storage and retrieval systems Automated guided vehicles Flexible manufacturing systems Computer integrated manufacturing
 Production Technology Process Control - Operation q q q Sensors, often analog devices, collect data Analog devices read data on some periodic basis, perhaps once a minute or once a second Measurements are translated into digital signals, and transmitted to a digital computer Computer programs read the file (the digital data) and analyze the data Output may be a: message on printer or console, signal to a motor to change a value setting, warning light or horn, process control chart, etc.
Production Technology Process Control - Operation q q q Sensors, often analog devices, collect data Analog devices read data on some periodic basis, perhaps once a minute or once a second Measurements are translated into digital signals, and transmitted to a digital computer Computer programs read the file (the digital data) and analyze the data Output may be a: message on printer or console, signal to a motor to change a value setting, warning light or horn, process control chart, etc.
 Photo S 7. 7
Photo S 7. 7
 Production Technology Robots q q q Machines that hold, move, or grasp items Perform monotonous or dangerous tasks Used when speed, accuracy, or strength are needed © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co.
Production Technology Robots q q q Machines that hold, move, or grasp items Perform monotonous or dangerous tasks Used when speed, accuracy, or strength are needed © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co.
 Automated Storage and Retrieval System (ASRS) q Provide for automatic placement and withdrawal of parts and products into and from designated places in a warehouse.
Automated Storage and Retrieval System (ASRS) q Provide for automatic placement and withdrawal of parts and products into and from designated places in a warehouse.
 Production Technology Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGV) q q q Material handling machines Used to move parts & equipment in manufacturing May be used to deliver mail & meals in service facilities © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co.
Production Technology Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGV) q q q Material handling machines Used to move parts & equipment in manufacturing May be used to deliver mail & meals in service facilities © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co.
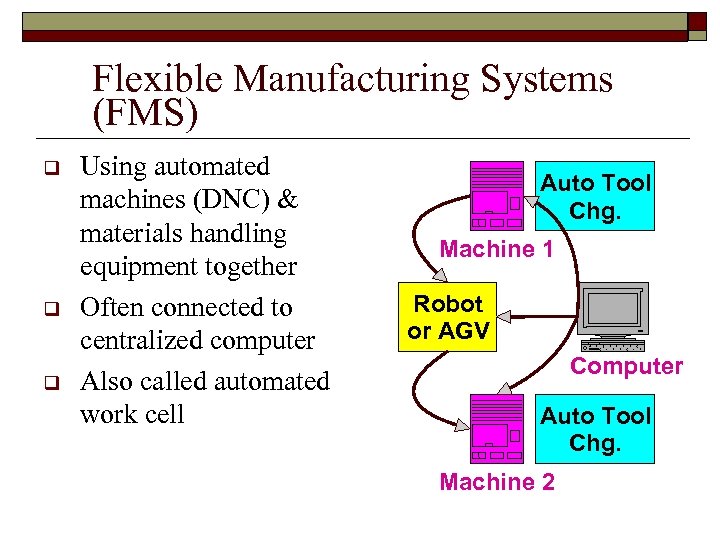 Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) q q q Using automated machines (DNC) & materials handling equipment together Often connected to centralized computer Also called automated work cell Auto Tool Chg. Machine 1 Robot or AGV Computer Auto Tool Chg. Machine 2
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS) q q q Using automated machines (DNC) & materials handling equipment together Often connected to centralized computer Also called automated work cell Auto Tool Chg. Machine 1 Robot or AGV Computer Auto Tool Chg. Machine 2
 Production Technology FMS - Pros & Cons q q Advantages q Faster, lower-cost changes from one part to another q Lower direct labor costs q Reduced inventory q Consistent, and perhaps better quality Disadvantages q Limited ability to adapt to product or product mix changes q Requires substantial preplanning and capital expenditures q Technological problems of exact component positioning and precise timing q Tooling and fixture requirements
Production Technology FMS - Pros & Cons q q Advantages q Faster, lower-cost changes from one part to another q Lower direct labor costs q Reduced inventory q Consistent, and perhaps better quality Disadvantages q Limited ability to adapt to product or product mix changes q Requires substantial preplanning and capital expenditures q Technological problems of exact component positioning and precise timing q Tooling and fixture requirements
 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) q Packaged business software systems that allow companies to: q q q Automate and integrate the majority of their business processes Share common data and practices across the entire enterprise Produce and access information in a real-time environment
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) q Packaged business software systems that allow companies to: q q q Automate and integrate the majority of their business processes Share common data and practices across the entire enterprise Produce and access information in a real-time environment
 Advantages of ERP q q q q Provides integration of supply-chain, production and administrative processes Creates commonality of databases Can incorporate improved, redesigned, “best processes: Increases communication and collaboration worldwide Helps integrate multiple sites and business units Is packaged with a software core that is off-the-shelf coding Can provide a strategic advantage over competitors
Advantages of ERP q q q q Provides integration of supply-chain, production and administrative processes Creates commonality of databases Can incorporate improved, redesigned, “best processes: Increases communication and collaboration worldwide Helps integrate multiple sites and business units Is packaged with a software core that is off-the-shelf coding Can provide a strategic advantage over competitors
 Disadvantages of ERP q q q Is very expensive to purchase, and even more costly to customize Requires major changes in the company and its processes to implement Is such a complex program that many companies cannot adjust to it Involves an ongoing process for implementation, which is often never completed Expertise in ERP is limited, with staffing an ongoing problem
Disadvantages of ERP q q q Is very expensive to purchase, and even more costly to customize Requires major changes in the company and its processes to implement Is such a complex program that many companies cannot adjust to it Involves an ongoing process for implementation, which is often never completed Expertise in ERP is limited, with staffing an ongoing problem
 Internet Uses q Supply Chain Management -- Business Networking q q Exchange of information Purchasing q q q Transactions Identifying vendors Qualifying vendors Order tracking Price negotiation Feedback
Internet Uses q Supply Chain Management -- Business Networking q q Exchange of information Purchasing q q q Transactions Identifying vendors Qualifying vendors Order tracking Price negotiation Feedback
 Internet Uses q q q q Interface with legacy systems Design Order fulfillment Scheduling (Production or Personnel) Project management Quality control Inventory management Capacity
Internet Uses q q q q Interface with legacy systems Design Order fulfillment Scheduling (Production or Personnel) Project management Quality control Inventory management Capacity


