55f8047847eb3f1b33d73fce064b53f5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

Open Source Software for Digital Libraries Jon Dunn Associate Director for Technology John A. Walsh Manager of Electronic Text Technologies Indiana University Digital Library Program IU Digital Library Brown Bag Series Bloomington, IN 09 April 2004

Outline Ø Open Source Introduction Ø Categories of Open Source Software for Libraries Ø Open Source Digital Library Systems Ø Open Source XML Tools and Systems

What is open source software? Ø In the phrase open source, source refers to source code, the human-readable computer code which is the origin, or source, of the computer application. Open refers to the terms of access to that computer source code. So open source software is software for which the source code is freely available. But this is a very general and incomplete definition. Ø A detailed definition of open source software is maintained by the Open Source Initiative

Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages Ø Access to source code and ability and right to modify it Ø Right to redistribute modifications to benefit wider community Ø Free Ø Excellent support networks Ø Large and enthusiastic user base Disadvantages Ø Limited or no accountability Ø Informal and unaccountable support channels

Categories of Open Source Software Ø Operating Systems l Linux Ø Programming Languages l Perl, PHP, Python Ø Applications l Apache, Tomcat, emacs, grep, My. SQL, sendmail, ssh

Different Open Source Licenses Ø GNU GPL ("General Public License") Ø GNU Lesser GPL Ø BSD License Ø Mozilla Public License Ø IU Open Source License Ø And more. . .

Open Source Software in the DLP Ø Linux, Apache, Tomcat, PHP, Perl, DLXS, Image. Magick, e. Prints, My. SQL, Darwin Streaming Server, emacs, CVS, Webalizer, Lib. XML, Lib. XSLT, Saxon, and more!

Open Source Resources Ø Open Source Initiative Ø GNU Ø Source. Forge

Some categories of open source library software Ø Library-oriented search engines l Cheshire, Pears Ø Z 39. 50 toolkits l Zeta. Perl (Perl), JAFER (Java), YAZ (C/C++) Ø MARC parsers l MARC. pm (Perl), MARC 4 J (Java) Ø Image processing l Image. Magick, tiffinfo/tiffdump

Some categories of open source library software Ø Portals l Ø OAI service providers and data providers l l Ø PHP OAI Data Provider Lots! See www. openarchives. org METS tools l Ø My. Library Page turners, toolkits, more: see www. loc. gov/mets/ Digital object repositories l Fedora

A Good Starting Point Ø oss 4 lib: Open Source Systems for Libraries l www. oss 4 lib. org

Complete DL Systems Ø DSpace Ø Eprints Ø Greenstone

DSpace “DSpace is a groundbreaking digital institutional repository that captures, stores, indexes, preserves, and redistributes the intellectual output of a university’s research faculty in digital formats. ” Ø Developed jointly by MIT Libraries and Hewlett. Packard Ø Licensed under BSD distribution license Ø www. dspace. org Ø

DSpace Ø Supports submission of, management of, and access to digital content l Formats: text, images, audio, video Ø Organized based on organizational needs of a large university l Communities and collections
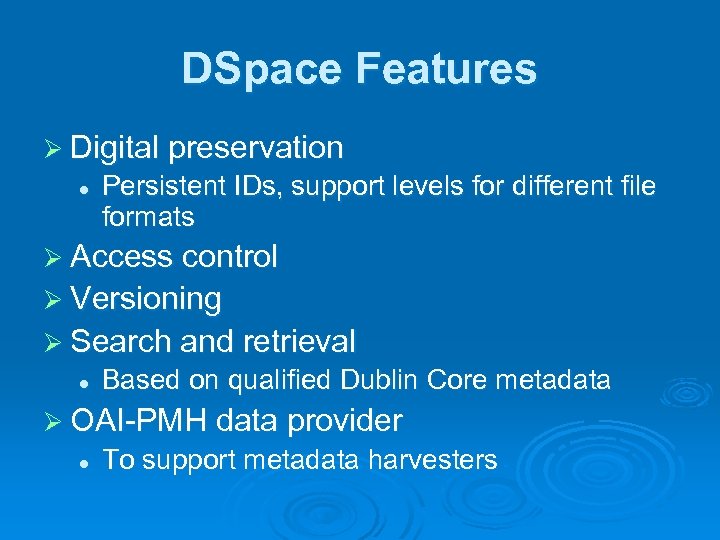
DSpace Features Ø Digital preservation l Persistent IDs, support levels for different file formats Ø Access control Ø Versioning Ø Search and retrieval l Based on qualified Dublin Core metadata Ø OAI-PMH data provider l To support metadata harvesters

DSpace Technology Ø OS: Unix or Linux Ø Written in Java Ø Postgre. SQL relational database Ø Provides complete Web user interface, but Java APIs available
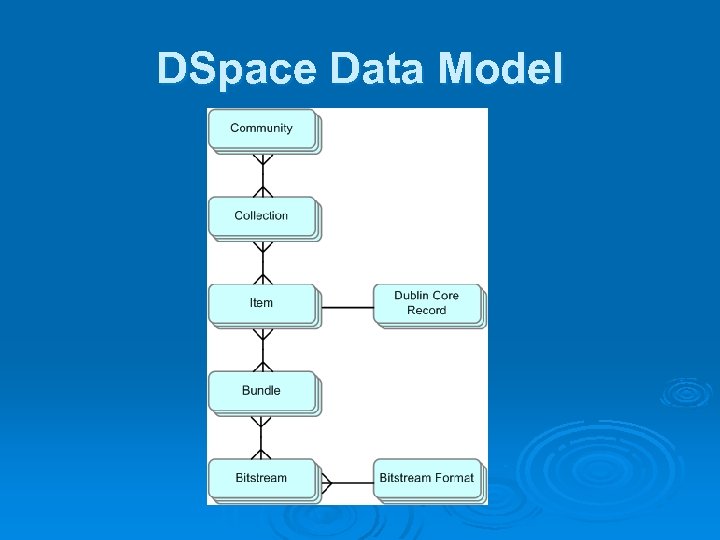
DSpace Data Model
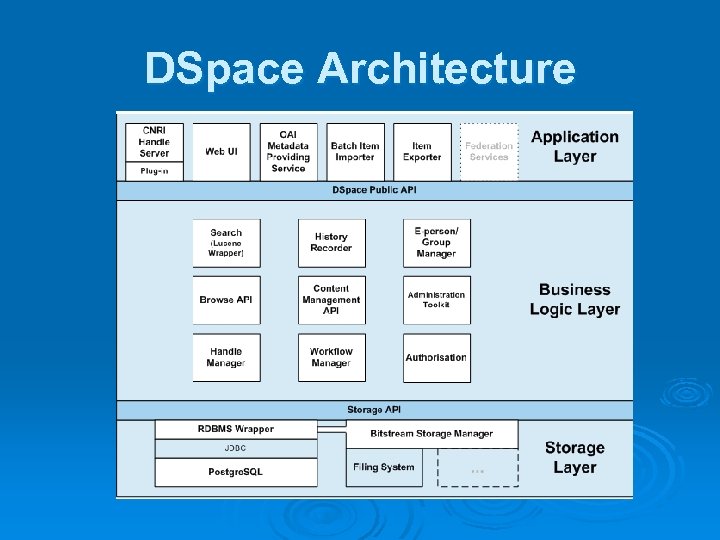
DSpace Architecture

DSpace Demonstration Ø MIT DSpace l dspace. mit. edu

EPrints “free software which creates online archives” Ø Developed by University of Southampton, UK Ø Supports self-archiving of e-prints Ø Can be configured as institutional repository or otherwise, e. g. repository focused on particular research area or discipline Ø Licensed under GNU General Public License Ø software. eprints. org Ø

EPrints Supports submission, management of, and access to digital content Ø Can support multiple archives on one server Ø Moderated or unmoderated archives Ø Search and retrieval Ø l l Based on metadata Metadata can be customized for different archives and document types No access control Ø OAI-PMH data provider Ø

EPrints Technology Ø OS: Unix or Linux Ø Written in Perl Ø Requirements: l l Apache web server My. SQL relational database

EPrints Demonstration Ø Digital Library of the Commons l dlc. dlib. indiana. edu

Greenstone Ø “Suite of software for building and distributing digital library collections” Ø Developed by University of Waikato, New Zealand l Developed in cooperation with UNESCO and the Human Info NGO Ø Licensed under GNU General Public License Ø www. greenstone. org

Greenstone Features Supports creation and management of collections by administrator(s) Ø Web interface for search and retrieval Ø l l Ø Extensive document filters l l Ø Customizable metadata Supports full text search of content Word, Excel, Power. Point, PDF, . . . Can extract metadata from documents Many ways to build a collection, including: l l l Local files Retrieve web sites Retrieve objects via OAI-PMH

Greenstone Features Ø Focus on: l l l Ease of installation Ease of use Internationalization • Full support for English, French, Spanish, Russian, and Kazakh • Support for many other languages l Low barriers to use • Minimal system requirements • Creation of CD-ROMs

Greenstone Technology Runs on Windows (back to 3. 1), Linux, Mac OS X, Unix Ø Written in C++, Perl, and Java Ø Uses MG/MG++ search engine Ø Several different Web and Java/Swing user interfaces for various functions Ø Web interface for user access Ø

Greenstone Demonstration Ø Examples at www. greenstone. org

Open Source XML Tools and Systems Ø Utilities l Ø Editors l Ø Xalan, Xerces, libxml, libxslt, saxon emacs / nxml-mode Database / Search Engines • • • Ø Apache Xindice Berkeley DB XML e. Xist Publishing/Web. Application Frameworks • Ax. Kit • Cocoon

XML Databases & Search Engines Ø Apache Xindice Ø Berkeley DB XML Ø e. Xist

Apache Xindice Ø http: //xml. apache. org/xindice/ Ø Technology: Java Ø Optimized for large numbers of small XML files. Does not work well on large files.

Berkeley DB XML Ø http: //www. sleepycat. com/products/xml. shtml Ø Technology: C Ø C++ and Java APIs

e. Xist Ø http: //exist. sourceforge. net/ Ø Technology: Java

XML Publishing / Web Application Frameworks Ø XML Publishing, or Web Application, Frameworks provide systems for publishing XML data in a variety of formats, such as HTML, WAP/WML, PDF, etc. Both Ax. Kit and Cocoon use a "pipeline" paradigm to route incoming requests through different processing routines. Apache Ax. Kit Ø Apache Cocoon Ø

Apache Ax. Kit http: //axkit. org/ Ø Technology: Perl Ø Ax. Kit is an XML Application Server for Apache. It provides on-the-fly conversion from XML to any format, such as HTML, WAP or text using either W 3 C standard techniques, or flexible custom code. Ax. Kit also uses a built-in Perl interpreter to provide some amazingly powerful techniques for XML transformation. Ø

Apache Cocoon Ø http: //cocoon. apache. org/ Ø Technology: Java Ø "Apache Cocoon is a web development framework built around the concepts of separation of concerns and componentbased web development. "

Cocoon: Key Concepts publishing framework Ø XML and XSLT Ø "pipelined SAX processing" Ø separation of: Ø l l l content logic style centralized configuration Ø sophisticated caching Ø
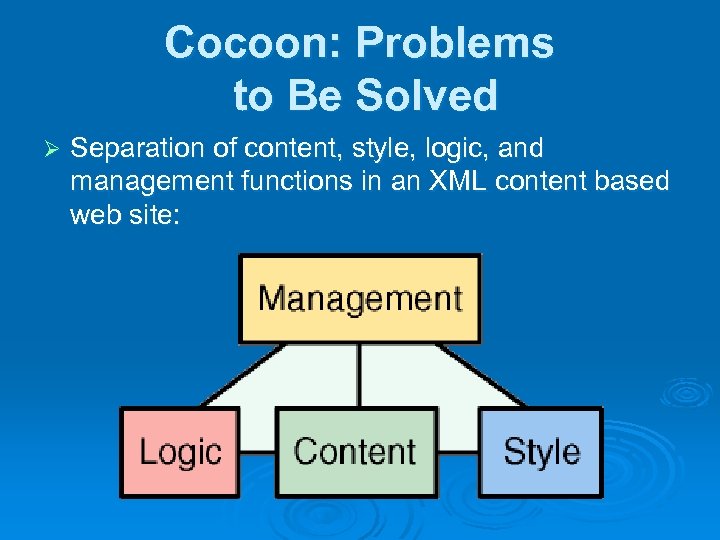
Cocoon: Problems to Be Solved Ø Separation of content, style, logic, and management functions in an XML content based web site:
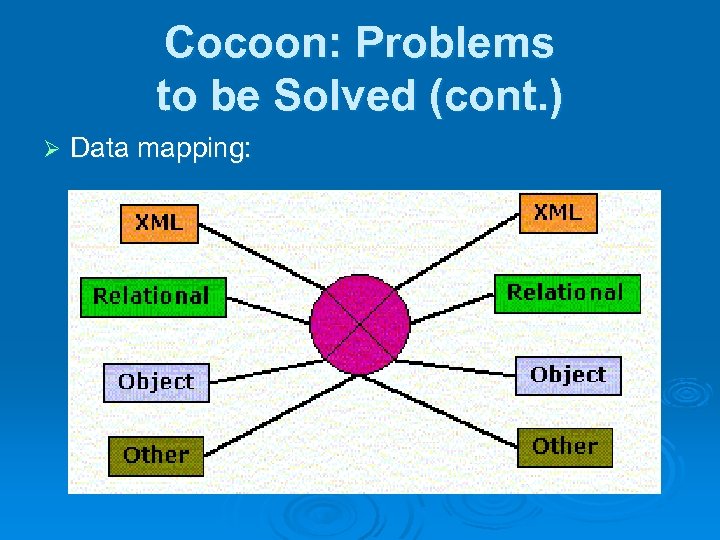
Cocoon: Problems to be Solved (cont. ) Ø Data mapping:

Cocoon: Basic mechanisms for processing XML documents Dispatching based on Matchers. Ø Generation of XML documents (from content, logic, Relation DB, objects or any combination) through Generators Ø Transformation (to another XML, objects or any combination) of XML documents through Transformers Ø Aggregation of XML documents through Aggregators Ø Rendering XML through Serializers Ø
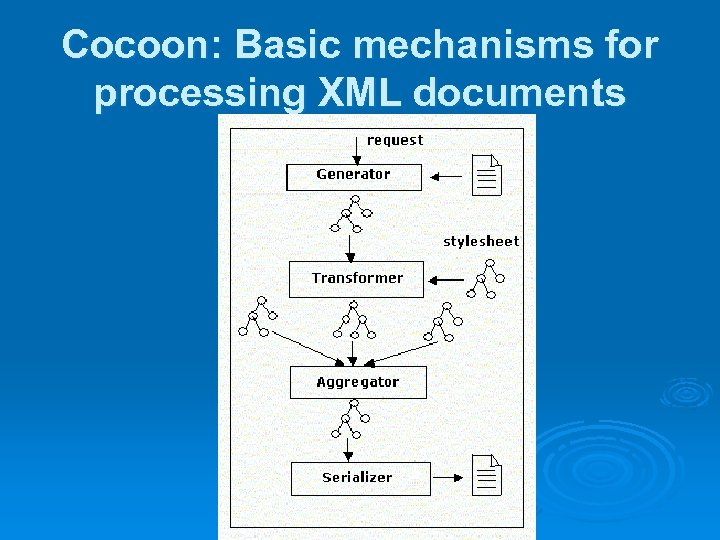
Cocoon: Basic mechanisms for processing XML documents
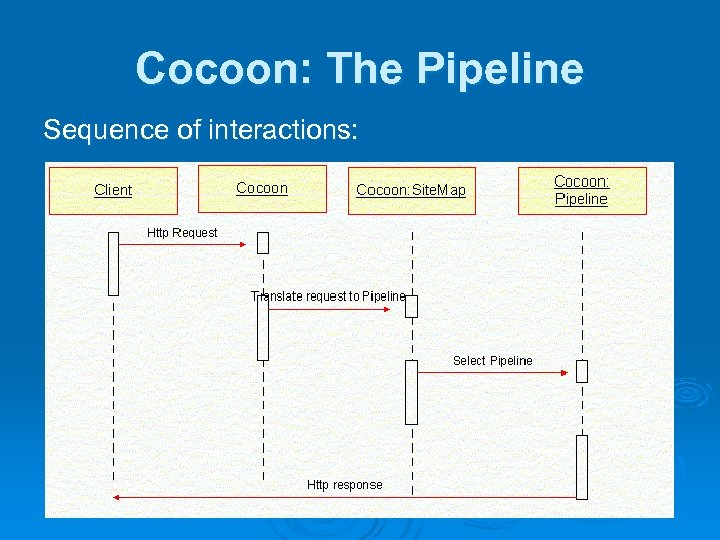
Cocoon: The Pipeline Sequence of interactions:
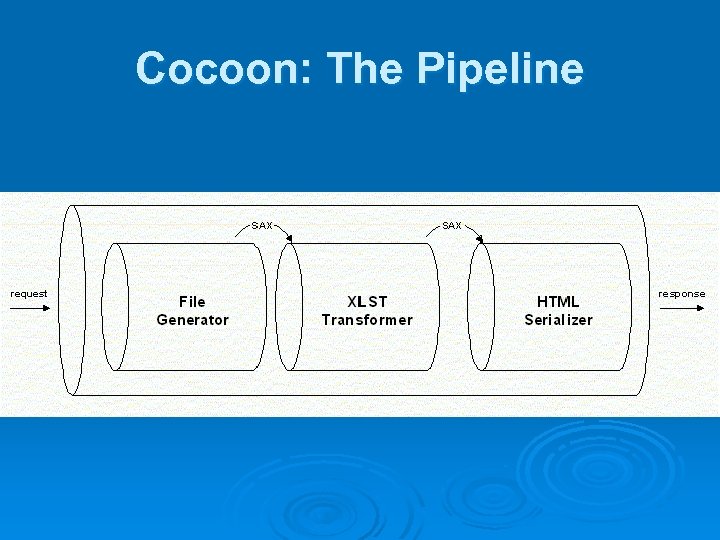
Cocoon: The Pipeline

Generators, Transformers, & Serializers Ø Generators Ø Transformers Ø Serializers

Cocoon: Configuration: The Sitemap <? xml version="1. 0"? > <map: sitemap xmlns: map="http: //apache. org/cocoon/sitemap/1. 0"> <map: components>. . . </map: components> <map: views>. . . </map: views> <map: pipeline> <map: match>. . . </map: pipeline>. . . </map: pipelines>. . . </map: sitemap>

Cocoon: Configuration: A Pipeline <map: pipelines> <map: pipeline> <map: match pattern="technochat/"> <map: generate src="technochat/index. xhtml"/> <map: serialize/> </map: match> <map: match pattern="technochat/*. xml"> <map: read mime-type="text/xml" src="technochat/{1}. xml"/> </map: match> <map: match pattern="technochat/*. html"> <map: generate src="technochat/{1}. xml"/> <map: transform src="technochat/tei 2 html. xsl"/> <map: serialize/> </map: match> <map: match pattern="technochat/*. css"> <map: read mime-type="text/css" src="technochat/resources/styles/{1}. css“ /> </map: match> </ <map: match pattern="technochat/*. svg. jpg"> <map: generate src="technochat/{1}. xml"/> <map: transform src="technochat/tei 2 svg. xsl"/> <map: serialize type="svg 2 jpeg"/> </map: match> <map: match pattern="technochat/*. svg"> <map: generate src="technochat/{1}. xml"/> <map: transform src="technochat/tei 2 svg. xsl"/> <map: serialize type="svgxml"/> </map: match> <map: match pattern="technochat/*. pdf"> <map: generate src="technochat/{1}. xml"/> <map: transform src="technochat/tei 2 fo. xsl"/> <map: serialize type="fo 2 pdf"/> </map: match> </map: pipeline>
55f8047847eb3f1b33d73fce064b53f5.ppt