9f96e121ca8e7deccbb75100d38e8197.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

Open only for Humans; Droids and Robots should go for CSE 462 next door ; -)

General Information • Instructor: Subbarao Kambhampati (Rao) – Office hours: after class, T/Th 11: 45— 12: 45 pm • TA: Yunsong Meng – Took this course in Fall 2006 and did very well… – Office hours: TBD – Additional help from CSE 471 tutors. . • Course Homepage: http: //rakaposhi. eas. asu. edu/cse 471
) nor mi to ( ject s Sub nge Cha Grading etc. – Projects/Homeworks/Participation (~55%) • Projects – Approximately 4 » First project already up! Due in 2 weeks – Expected background » Competence in Lisp programming » Why lisp? (Because!) • Homeworks – Homeworks will be assigned piecemeal. . (Socket system) • Participation – Attendance to and attentiveness in classes is mandatory – Participation on class blog is highly encouraged. – Do ask questions – Midterm & final (~45%)

Lisp Programming • Use Lisp-in-a-box (link from the class page) – Easy to install and use. Take the clisp version • There is a link to a lisp review book • There is also a link to Lisp vs. Scheme differences • You are allowed to use other languages such as Java/Python/C etc. —but the partial code snippets will only be provided for Lisp – If you plan to take this option, please do talk to the instructor

It has not been the path for the faint-hearted, for those who prefer leisure over work, or seek only the pleasures of riches and fame. -Obama inadvertently talking about CSE 471 in his inaugural address Course demands. . • . . your undivided attention – Attendance mandatory; if you have to miss a class, you should let me know before hand • Has been repeatedly seen as a 4 -5 credit course – (while the instructor just thinks your other courses are 1 -2 credit ones ) – No apologies made for setting highexpectations

Grade Anxiety • All letter grades will be awarded – A+, A, B+, B, B-, C+, C, D etc. • No pre-set grade thresholds • CSE 471 and CSE 598 students will have the same assignments/tests etc. During letter grade assignment however, they will be compared to their own group. – The class is currently ~33 CSE 471 and ~10 CSE 598 (grad) students

Honor Code • Unless explicitly stated otherwise, all assignments are: – Strictly individual effort – You are forbidden from trawling the web for answers/code etc • Any infraction will be dealt with in severest terms allowed.

Life with a homepage. . • I will not be giving any handouts – All class related material will be accessible from the web-page • Home works may be specified incrementally – (one problem at a time) – The slides used in the lecture will be available on the class page (along with Audio of the lecture) • I reserve the right to modify slides right up to the time of the class • When printing slides avoid printing the hidden slides


About the only thing Microsoft & Google can agree on these days… • “If you invent a breakthrough in artificial intelligence, so machines can learn, " Mr. Gates responded, "that is worth 10 Microsofts. " (Quoted in NY Times, Monday March 3, 2004) • No. 1: AI at human level in 10 -20 year time frame – Sergey Brin & – Larry Page – (independently, when asked to name the top 5 areas needing research. Google Faculty Summit, July 2007)

Course Overview • • What is AI – Intelligent Agents Search (Problem Solving Agents) – Single agent search [Project 1] • Markov Decision Processes • • • Constraint Satisfaction Problems – Adversarial (multi-agent) search Logical Reasoning [Project 2] Reasoning with uncertainity Planning [Project 3] Learning [Project 4]

Although we will see that all four views have motivations. .

Do we want a machine that beats humans in chess or a machine that thinks like humans while beating humans in chess? Deep. Blue supposedly DOESN’T think like humans. . (But what if the machine is trying to “tutor” humans about how to do things? ) (Bi-directional flow between thinking humanly and thinking rationally)

What if we are writing intelligent agents that interact with humans? The COG project The Robotic care givers Mechanical flight became possible only when people decided to stop emulating birds…
What AI can do is as important as what it can’t yet do. . • Captcha project

Arms race to defeat Captchas… (using unwitting masses) • Start opening an email account at Yahoo. . • Clip the captcha test • Show it to a human trying to get into another site – Usually a site that has pretty pictures of the persons of apposite* sex • Transfer their answer to the Yahoo Note: Apposite—not opposite. This course is nothing if not open minded

It can be argued that all the faculties needed to pass turing test are also needed to act rationally to improve success ratio…

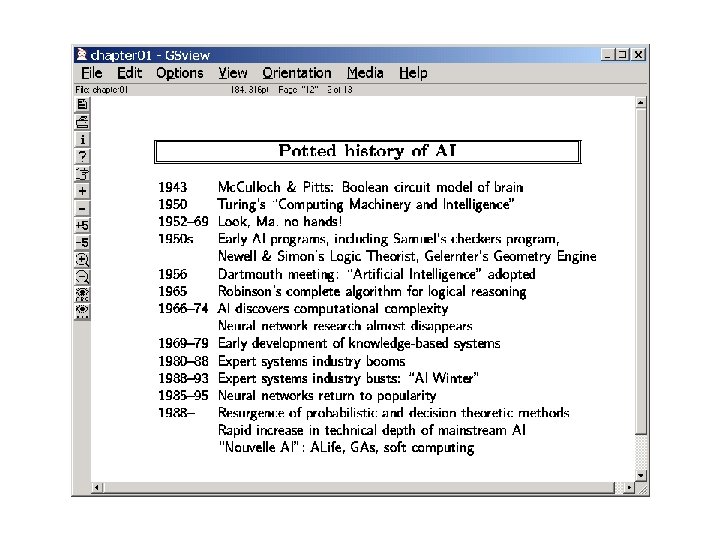

Discuss on Class Blog Playing an (entertaining) game of Soccer Solving NYT crossword puzzles at close to expert level Navigating in deep space Learning patterns in databases (datamining…) Supporting supply-chain management decisions at fortune-500 companies Learning common sense from the web Navigating desert roads Navigating urban roads Bluffing humans in Poker. .

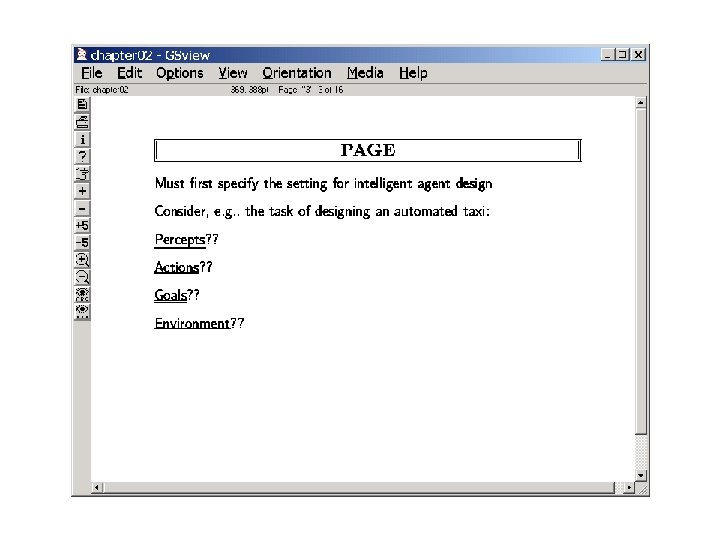
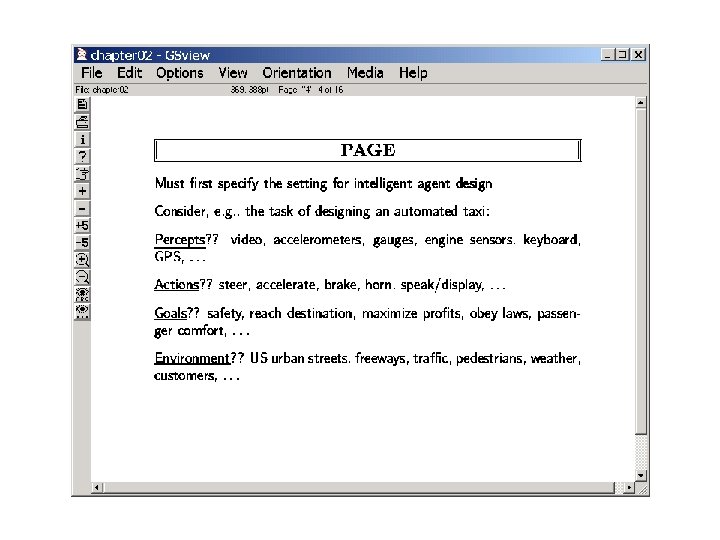
1/22 Architectures for Intelligent Agents Wherein we discuss why do we need representation, reasoning and learning
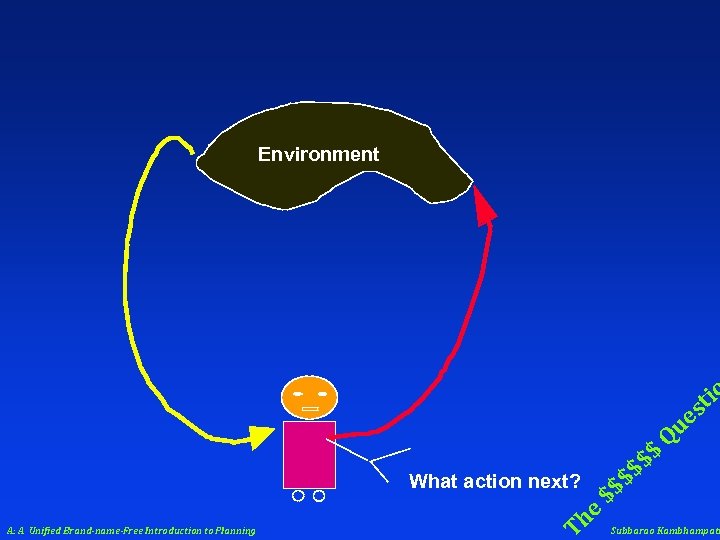
Environment tio s What action next? A: A Unified Brand-name-Free Introduction to Planning T he $$ $$ $ ue Q $ Subbarao Kambhampati
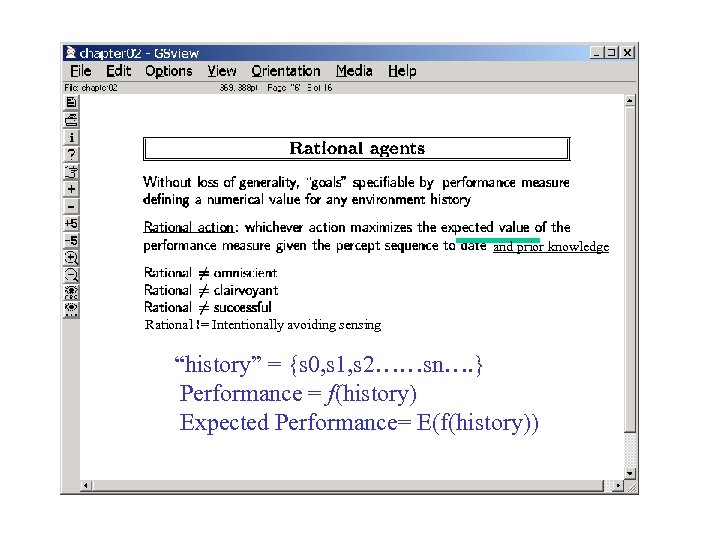
and prior knowledge Rational != Intentionally avoiding sensing “history” = {s 0, s 1, s 2……sn…. } Performance = f(history) Expected Performance= E(f(history))
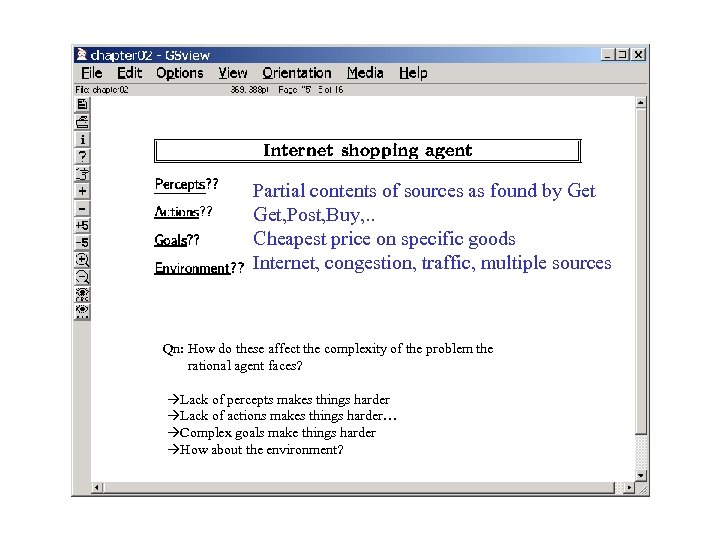
Partial contents of sources as found by Get, Post, Buy, . . Cheapest price on specific goods Internet, congestion, traffic, multiple sources Qn: How do these affect the complexity of the problem the rational agent faces? Lack of percepts makes things harder Lack of actions makes things harder… Complex goals make things harder How about the environment?
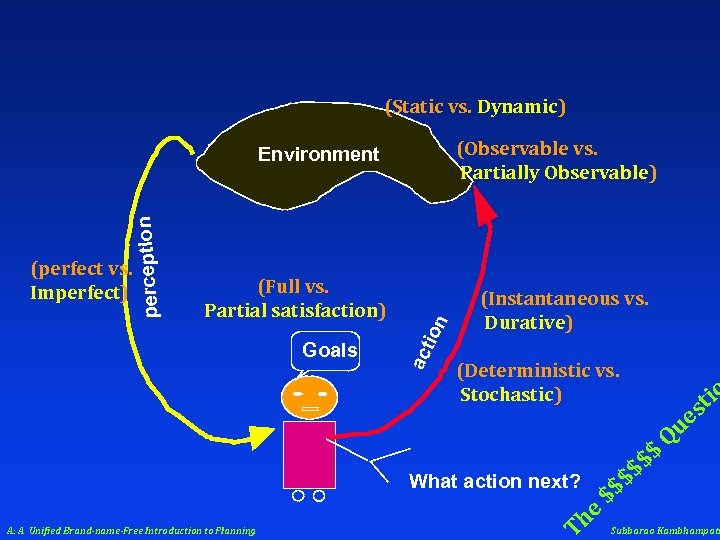
(Static vs. Dynamic) (Observable vs. Partially Observable) Goals on (Full vs. Partial satisfaction) ac ti (perfect vs. Imperfect) perception Environment (Instantaneous vs. Durative) (Deterministic vs. Stochastic) What action next? A: A Unified Brand-name-Free Introduction to Planning T he $$ $$ $ tio s ue Q $ Subbarao Kambhampati
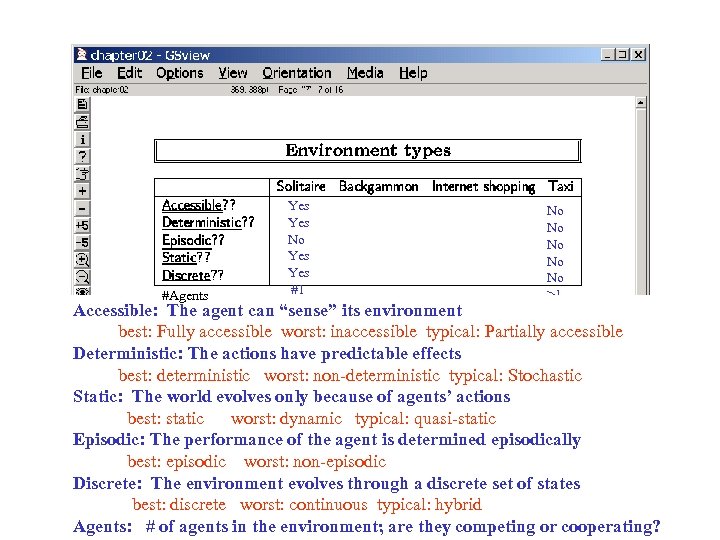
#Agents Yes No Yes #1 No No No >1 Accessible: The agent can “sense” its environment best: Fully accessible worst: inaccessible typical: Partially accessible Deterministic: The actions have predictable effects best: deterministic worst: non-deterministic typical: Stochastic Static: The world evolves only because of agents’ actions best: static worst: dynamic typical: quasi-static Episodic: The performance of the agent is determined episodically best: episodic worst: non-episodic Discrete: The environment evolves through a discrete set of states best: discrete worst: continuous typical: hybrid Agents: # of agents in the environment; are they competing or cooperating?
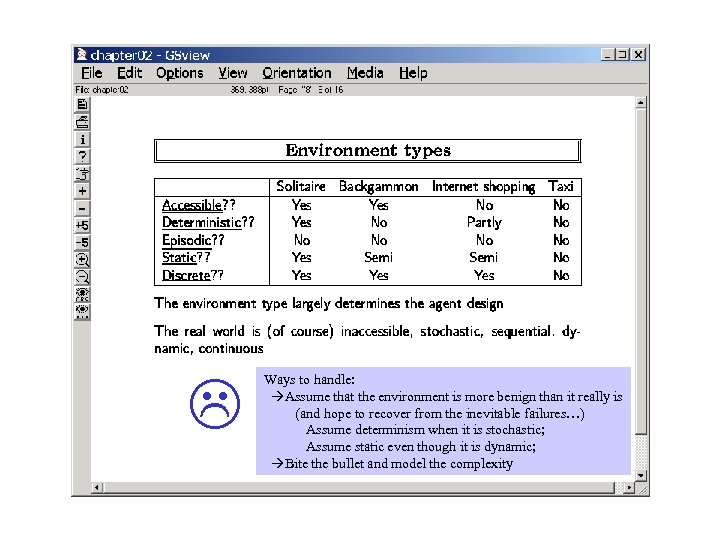
Ways to handle: Assume that the environment is more benign than it really is (and hope to recover from the inevitable failures…) Assume determinism when it is stochastic; Assume static even though it is dynamic; Bite the bullet and model the complexity
(Model-based reflex agents) How do we write agent programs for these?
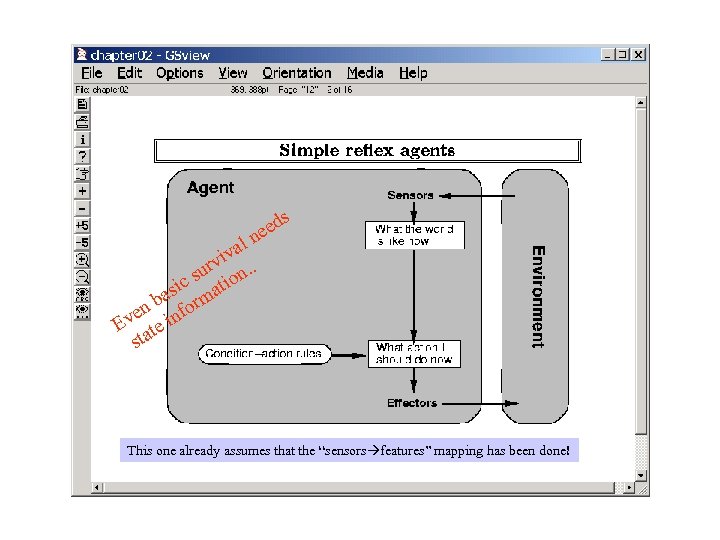
s eed n al v rvi n. . u c s atio si ba orm n ve e inf E t sta This one already assumes that the “sensors features” mapping has been done!
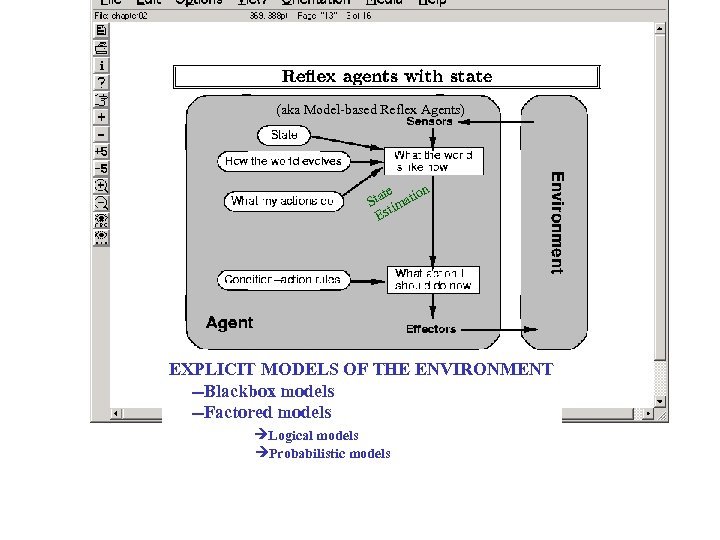
(aka Model-based Reflex Agents) te on Sta imati Est EXPLICIT MODELS OF THE ENVIRONMENT --Blackbox models --Factored models Logical models Probabilistic models
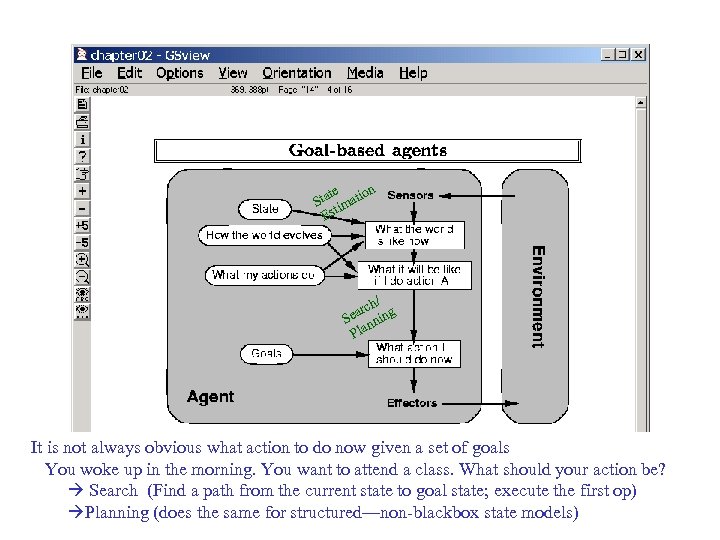
te on Sta imati Est h/ arc ing Se nn Pla It is not always obvious what action to do now given a set of goals You woke up in the morning. You want to attend a class. What should your action be? Search (Find a path from the current state to goal state; execute the first op) Planning (does the same for structured—non-blackbox state models)
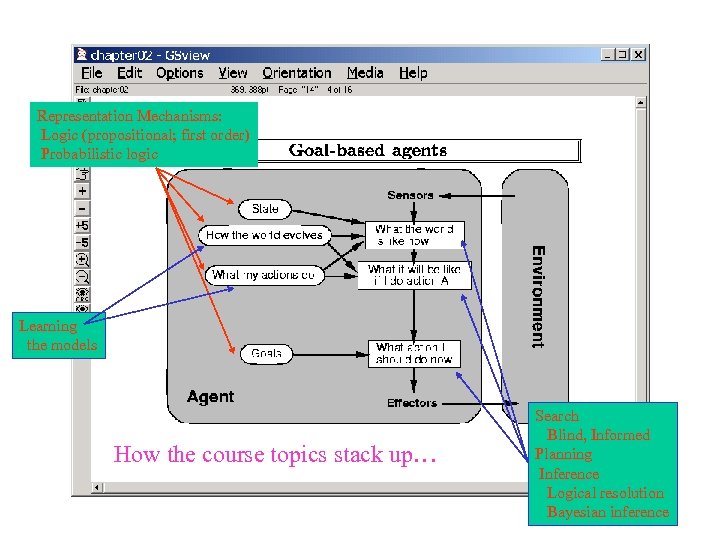
Representation Mechanisms: Logic (propositional; first order) Probabilistic logic Learning the models How the course topics stack up… Search Blind, Informed Planning Inference Logical resolution Bayesian inference
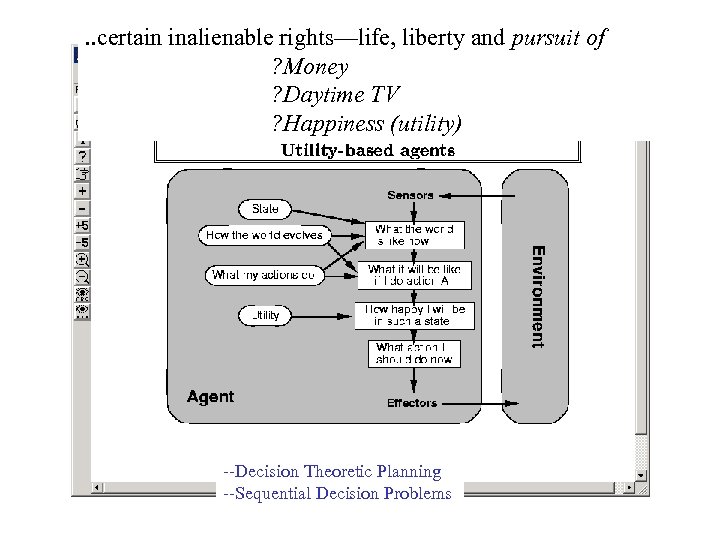
. . certain inalienable rights—life, liberty and pursuit of ? Money ? Daytime TV ? Happiness (utility) --Decision Theoretic Planning --Sequential Decision Problems
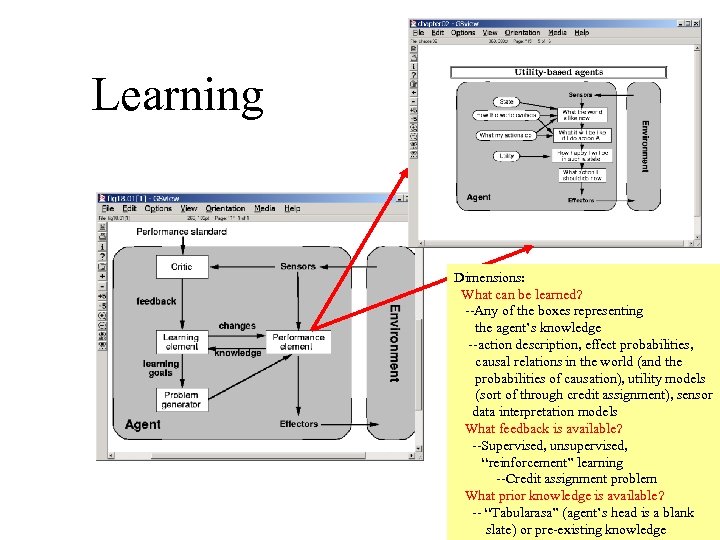
Learning Dimensions: What can be learned? --Any of the boxes representing the agent’s knowledge --action description, effect probabilities, causal relations in the world (and the probabilities of causation), utility models (sort of through credit assignment), sensor data interpretation models What feedback is available? --Supervised, unsupervised, “reinforcement” learning --Credit assignment problem What prior knowledge is available? -- “Tabularasa” (agent’s head is a blank slate) or pre-existing knowledge
9f96e121ca8e7deccbb75100d38e8197.ppt