9046cab2ac7fd301df573361c1475753.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Open Innovation: A New Paradigm for Industrial R&D Presentation to Queen’s University Henry Chesbrough Center for Open Innovation UC Berkeley November 10, 2009
Open Innovation: A New Paradigm for Industrial R&D Presentation to Queen’s University Henry Chesbrough Center for Open Innovation UC Berkeley November 10, 2009
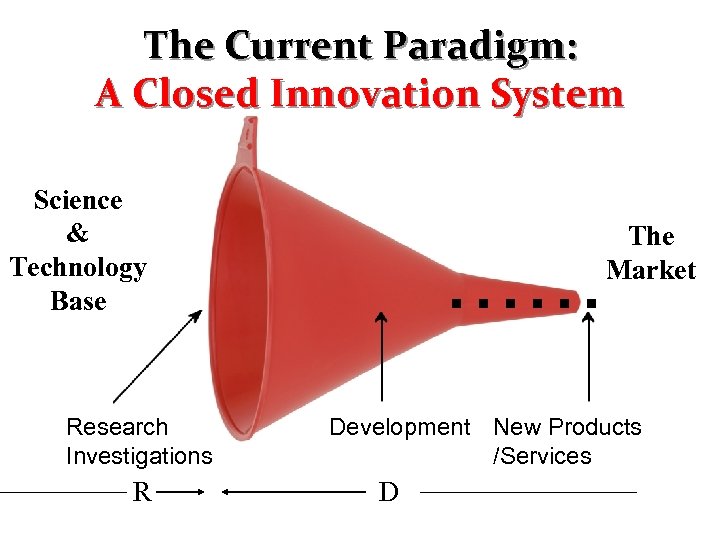 The Current Paradigm: A Closed Innovation System Science & Technology Base Research Investigations R The Market Development New Products /Services D 2
The Current Paradigm: A Closed Innovation System Science & Technology Base Research Investigations R The Market Development New Products /Services D 2
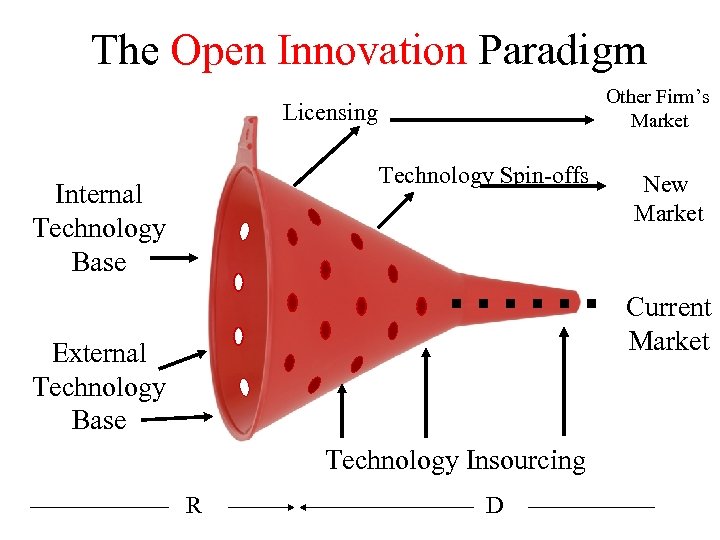 The Open Innovation Paradigm Other Firm’s Market Licensing Technology Spin-offs Internal Technology Base New Market Current Market External Technology Base Technology Insourcing R D 3
The Open Innovation Paradigm Other Firm’s Market Licensing Technology Spin-offs Internal Technology Base New Market Current Market External Technology Base Technology Insourcing R D 3
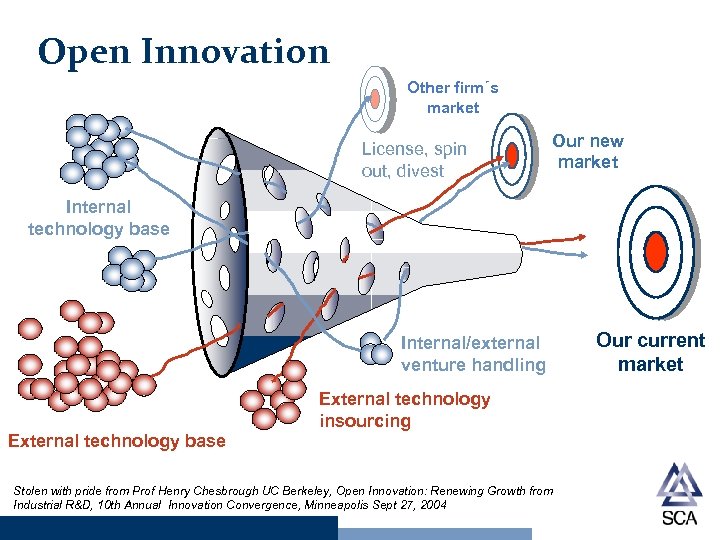 Open Innovation Other firm´s market License, spin out, divest Our new market Internal technology base Internal/external venture handling External technology insourcing External technology base Stolen with pride from Prof Henry Chesbrough UC Berkeley, Open Innovation: Renewing Growth from Industrial R&D, 10 th Annual Innovation Convergence, Minneapolis Sept 27, 2004 Our current market
Open Innovation Other firm´s market License, spin out, divest Our new market Internal technology base Internal/external venture handling External technology insourcing External technology base Stolen with pride from Prof Henry Chesbrough UC Berkeley, Open Innovation: Renewing Growth from Industrial R&D, 10 th Annual Innovation Convergence, Minneapolis Sept 27, 2004 Our current market
 2003: We broke up the fortress … Philips Research, Ronald Wolf, 10/08
2003: We broke up the fortress … Philips Research, Ronald Wolf, 10/08
 Bringing in the right partners – Open innovation > 75 companies and > 7000 people at High Tech Campus Eindhoven Corporate innovators Research institutes Consultancy & services Economic development companies Philips Research, Ronald Wolf, 10/08 6
Bringing in the right partners – Open innovation > 75 companies and > 7000 people at High Tech Campus Eindhoven Corporate innovators Research institutes Consultancy & services Economic development companies Philips Research, Ronald Wolf, 10/08 6
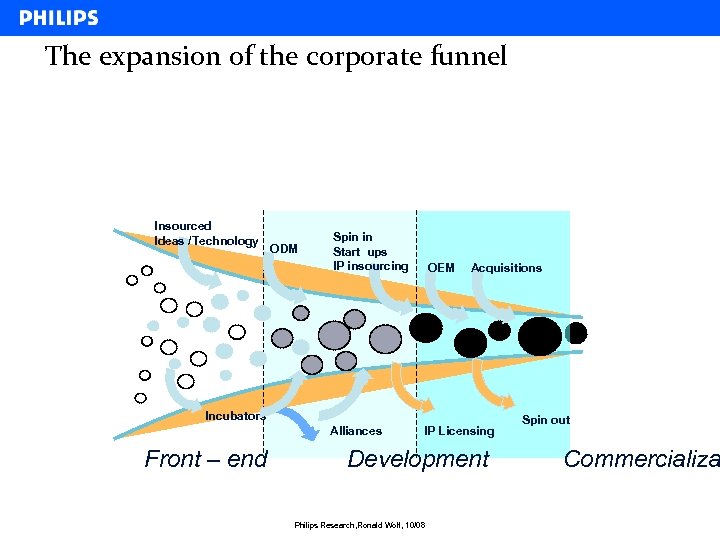 The expansion of the corporate funnel Insourced Ideas /Technology ODM Spin in Start ups IP insourcing OEM Acquisitions Incubators Alliances Front – end IP Licensing Development Philips Research, Ronald Wolf, 10/08 Spin out Commercializa
The expansion of the corporate funnel Insourced Ideas /Technology ODM Spin in Start ups IP insourcing OEM Acquisitions Incubators Alliances Front – end IP Licensing Development Philips Research, Ronald Wolf, 10/08 Spin out Commercializa
 BP’s challenge in February 2006 • Energy Bioscience looked promising (Senior Executive buy-in) • How do we meld commercial/technology strength with biology/biotech? − The company had no bio-expertise • How to reach out to biology/biotech communities − Not a corporate lab! − Corporate labs too insular – can’t tap broader expertise in a rapidly moving field − Where was the Energy/Bio talent pool anyway? − Not the usual university research programme − BP does many of these and knows strengths/weaknesses − Need to facilitate the development, demonstration, and commercialization of research results 8
BP’s challenge in February 2006 • Energy Bioscience looked promising (Senior Executive buy-in) • How do we meld commercial/technology strength with biology/biotech? − The company had no bio-expertise • How to reach out to biology/biotech communities − Not a corporate lab! − Corporate labs too insular – can’t tap broader expertise in a rapidly moving field − Where was the Energy/Bio talent pool anyway? − Not the usual university research programme − BP does many of these and knows strengths/weaknesses − Need to facilitate the development, demonstration, and commercialization of research results 8
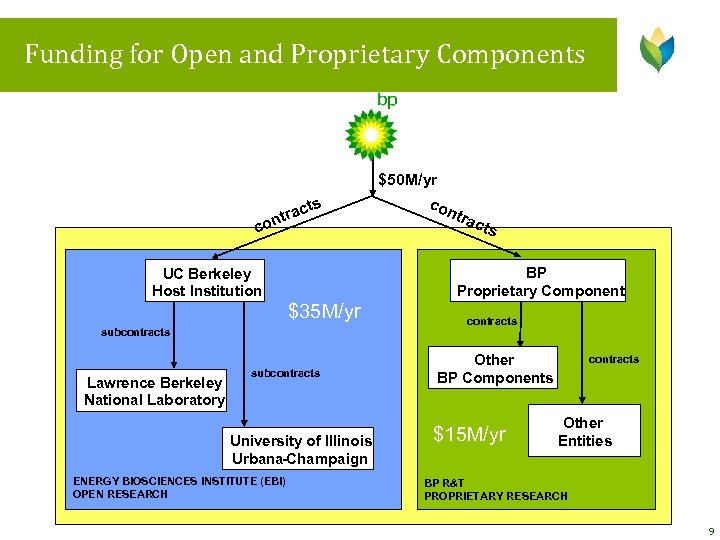 Funding for Open and Proprietary Components ts trac on c $35 M/yr subcontracts University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign ENERGY BIOSCIENCES INSTITUTE (EBI) OPEN RESEARCH cts BP Proprietary Component UC Berkeley Host Institution Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory $50 M/yr con tra contracts Other BP Components $15 M/yr contracts Other Entities BP R&T PROPRIETARY RESEARCH 9
Funding for Open and Proprietary Components ts trac on c $35 M/yr subcontracts University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign ENERGY BIOSCIENCES INSTITUTE (EBI) OPEN RESEARCH cts BP Proprietary Component UC Berkeley Host Institution Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory $50 M/yr con tra contracts Other BP Components $15 M/yr contracts Other Entities BP R&T PROPRIETARY RESEARCH 9
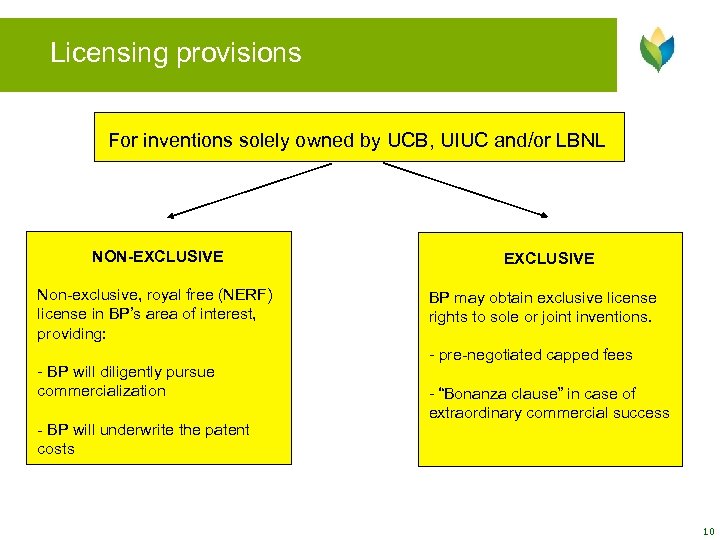 Licensing provisions For inventions solely owned by UCB, UIUC and/or LBNL NON-EXCLUSIVE Non-exclusive, royal free (NERF) license in BP’s area of interest, providing: - BP will diligently pursue commercialization - BP will underwrite the patent costs EXCLUSIVE BP may obtain exclusive license rights to sole or joint inventions. - pre-negotiated capped fees - “Bonanza clause” in case of extraordinary commercial success 10
Licensing provisions For inventions solely owned by UCB, UIUC and/or LBNL NON-EXCLUSIVE Non-exclusive, royal free (NERF) license in BP’s area of interest, providing: - BP will diligently pursue commercialization - BP will underwrite the patent costs EXCLUSIVE BP may obtain exclusive license rights to sole or joint inventions. - pre-negotiated capped fees - “Bonanza clause” in case of extraordinary commercial success 10
 Procter & Gamble • P&G used to be a VERY closed organization – “We invented Not Invented Here” – J. Weedman • P&G financial crisis, in 2000 – Missed a series of quarterly financial estimates – Stock market lost confidence in the company – Stock price fell by more than half in 4 months! – CEO (Jagr) was fired © 2008 Henry Chesbrough 11
Procter & Gamble • P&G used to be a VERY closed organization – “We invented Not Invented Here” – J. Weedman • P&G financial crisis, in 2000 – Missed a series of quarterly financial estimates – Stock market lost confidence in the company – Stock price fell by more than half in 4 months! – CEO (Jagr) was fired © 2008 Henry Chesbrough 11
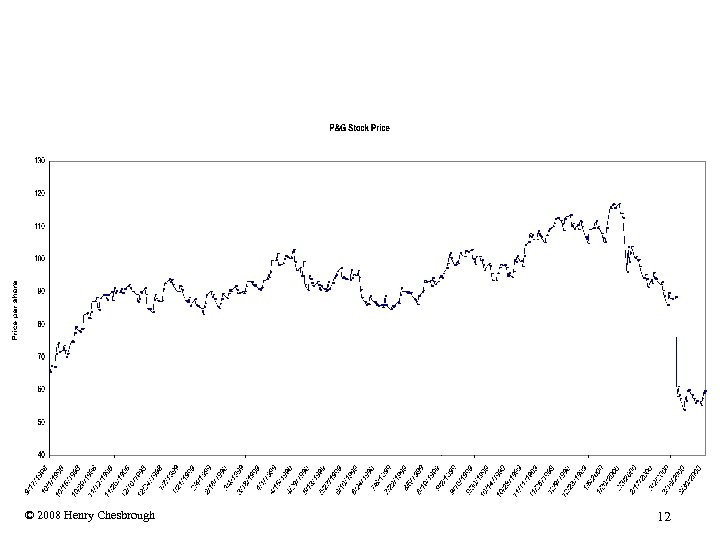 P&G’s Stock Price: 8/1998 -3/2000 © 2008 Henry Chesbrough 12
P&G’s Stock Price: 8/1998 -3/2000 © 2008 Henry Chesbrough 12
 Searching for the Root Cause • “We fundamentally had a growth problem. Our current brands were performing well. But we weren’t developing many new brands. ” – C. Wynett • To get new brands, P&G needed to open up. • Connect and Develop – Spin. Brush, Swiffer, Regenerist © 2008 Henry Chesbrough 13
Searching for the Root Cause • “We fundamentally had a growth problem. Our current brands were performing well. But we weren’t developing many new brands. ” – C. Wynett • To get new brands, P&G needed to open up. • Connect and Develop – Spin. Brush, Swiffer, Regenerist © 2008 Henry Chesbrough 13
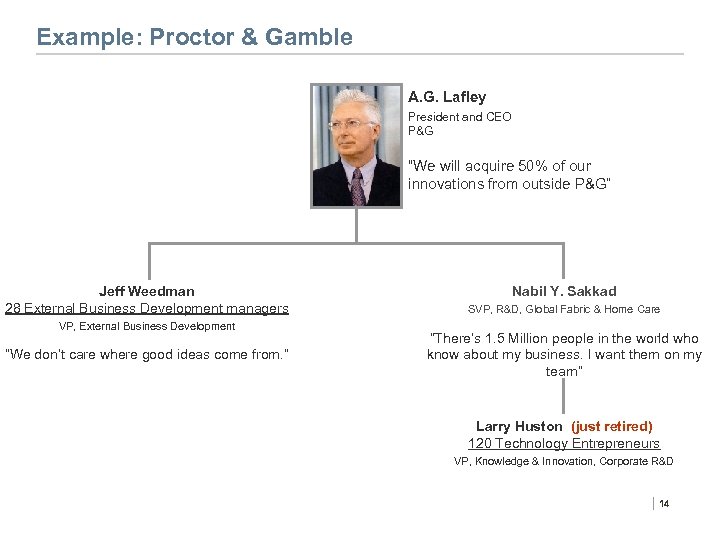 Example: Proctor & Gamble A. G. Lafley President and CEO P&G “We will acquire 50% of our innovations from outside P&G” Jeff Weedman 28 External Business Development managers VP, External Business Development “We don’t care where good ideas come from. ” Nabil Y. Sakkad SVP, R&D, Global Fabric & Home Care “There’s 1. 5 Million people in the world who know about my business. I want them on my team” Larry Huston (just retired) 120 Technology Entrepreneurs VP, Knowledge & Innovation, Corporate R&D | 14
Example: Proctor & Gamble A. G. Lafley President and CEO P&G “We will acquire 50% of our innovations from outside P&G” Jeff Weedman 28 External Business Development managers VP, External Business Development “We don’t care where good ideas come from. ” Nabil Y. Sakkad SVP, R&D, Global Fabric & Home Care “There’s 1. 5 Million people in the world who know about my business. I want them on my team” Larry Huston (just retired) 120 Technology Entrepreneurs VP, Knowledge & Innovation, Corporate R&D | 14
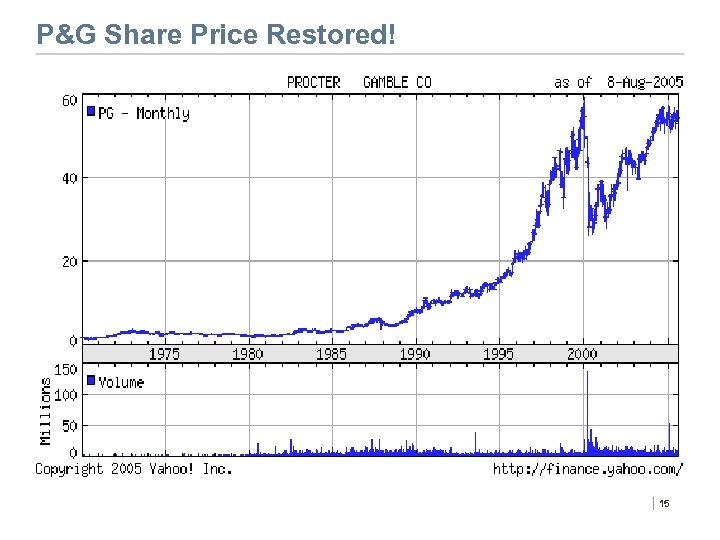 P&G Share Price Restored! | 15
P&G Share Price Restored! | 15
 The New P&G • Many processes to enable open innovation – Technology scouts – Legal templates for IP, partnering – Investments in Innovation Intermediaries • The Goal Now: Become the open innovation partner of choice © 2008 Henry Chesbrough 16
The New P&G • Many processes to enable open innovation – Technology scouts – Legal templates for IP, partnering – Investments in Innovation Intermediaries • The Goal Now: Become the open innovation partner of choice © 2008 Henry Chesbrough 16
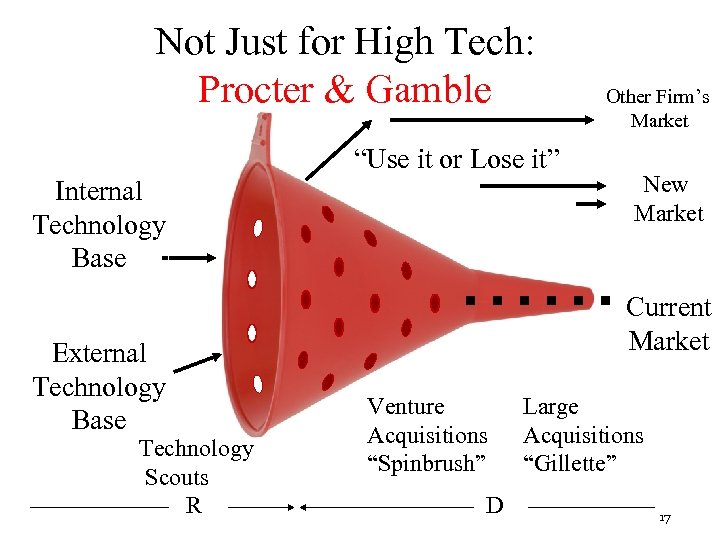 Not Just for High Tech: Procter & Gamble “Use it or Lose it” Internal Technology Base External Technology Base Technology Scouts R Other Firm’s Market New Market Current Market Venture Acquisitions “Spinbrush” D Large Acquisitions “Gillette” 17
Not Just for High Tech: Procter & Gamble “Use it or Lose it” Internal Technology Base External Technology Base Technology Scouts R Other Firm’s Market New Market Current Market Venture Acquisitions “Spinbrush” D Large Acquisitions “Gillette” 17
 An Iberian Example: El Bulli • Ferran Adria studies molecular gastronomy, working with Herve This, a French physical chemist • Adria brings this to El Bulli, restaurant is the Lab • Adria launches many business experiments • Borges: oils, snacks • Lavassa: coffee • N H Hoteles: Fast. Good, Nhube • Iberian Airlines (with Fast. Good) • Careful not to dilute the El Bulli brand 18
An Iberian Example: El Bulli • Ferran Adria studies molecular gastronomy, working with Herve This, a French physical chemist • Adria brings this to El Bulli, restaurant is the Lab • Adria launches many business experiments • Borges: oils, snacks • Lavassa: coffee • N H Hoteles: Fast. Good, Nhube • Iberian Airlines (with Fast. Good) • Careful not to dilute the El Bulli brand 18
 Is the internal R&D department an antiquated concept? • • No – open innovation can leverage internal R&D But…. . New focus: must look outside as well as inside New role: connecting to and collaborating with the outside • New skill: integrating internal and external together 19
Is the internal R&D department an antiquated concept? • • No – open innovation can leverage internal R&D But…. . New focus: must look outside as well as inside New role: connecting to and collaborating with the outside • New skill: integrating internal and external together 19
 The Crisis in Copenhagen • Successor to Kyoto protocol • Disputes over emissions targets…. • …. and over access to the IP and technology to achieve them! • Proposals of $100 billion + are ill-suited to the times • Can Open Innovation help?
The Crisis in Copenhagen • Successor to Kyoto protocol • Disputes over emissions targets…. • …. and over access to the IP and technology to achieve them! • Proposals of $100 billion + are ill-suited to the times • Can Open Innovation help?

 Founding Partner resources: - brand development (Nike) - legal architecture (Science Commons) - technical implementation (Force. com) - technical implementation (n. Genera) - technical implementation (2 degrees) - messaging and story (IDEO) - academic outreach (U Washington) - business rationale for sharing (UC Berkeley)
Founding Partner resources: - brand development (Nike) - legal architecture (Science Commons) - technical implementation (Force. com) - technical implementation (n. Genera) - technical implementation (2 degrees) - messaging and story (IDEO) - academic outreach (U Washington) - business rationale for sharing (UC Berkeley)
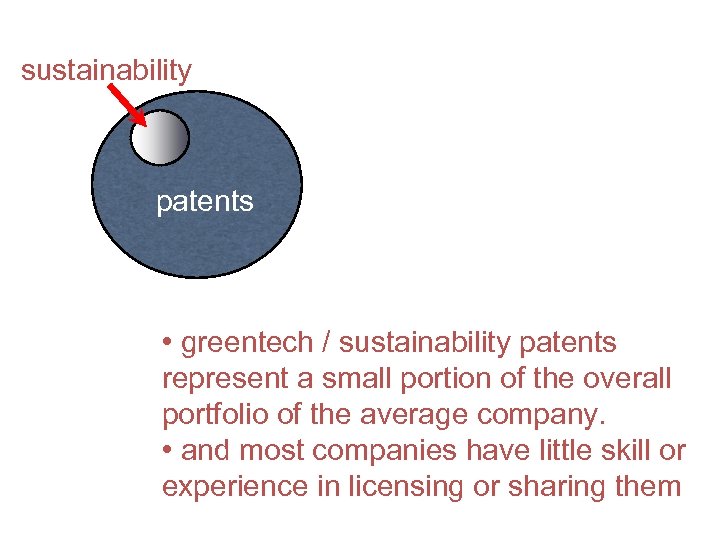 sustainability patents • greentech / sustainability patents represent a small portion of the overall portfolio of the average company. • and most companies have little skill or experience in licensing or sharing them
sustainability patents • greentech / sustainability patents represent a small portion of the overall portfolio of the average company. • and most companies have little skill or experience in licensing or sharing them
 Businesses Control the Use of Their Green IP • retain the essential rights inside the core business • use a standard offer to license the rights via automated transactions • determine exceptions to licensing requirements – research – geography – field of use – etc….
Businesses Control the Use of Their Green IP • retain the essential rights inside the core business • use a standard offer to license the rights via automated transactions • determine exceptions to licensing requirements – research – geography – field of use – etc….
 The Business Benefits of Sharing or Exchanging Green IP Publicity, yes, but there’s much more … Greater usage of technology to lower costs Commoditize an input to lower costs Establish a technical standard to influence the future development path • Incremental revenues from licensing outside of your business • Stimulate greater research activity in areas of value to your business • •
The Business Benefits of Sharing or Exchanging Green IP Publicity, yes, but there’s much more … Greater usage of technology to lower costs Commoditize an input to lower costs Establish a technical standard to influence the future development path • Incremental revenues from licensing outside of your business • Stimulate greater research activity in areas of value to your business • •
 Open Innovation in Copenhagen? • Private reasons to share or exchange Green IP – Good business, not just good publicity • No government action required – Though policy can help stimulate the process… • Developing nations need not pay for all IP rights – Exchange, share, or license just those they need • Developing nations innovate too – And these can be shared with other developing countries
Open Innovation in Copenhagen? • Private reasons to share or exchange Green IP – Good business, not just good publicity • No government action required – Though policy can help stimulate the process… • Developing nations need not pay for all IP rights – Exchange, share, or license just those they need • Developing nations innovate too – And these can be shared with other developing countries
 Policy Can Help! • Provide greater information on available green technologies, whether private or publicly held • Offer financial assistance for licensing useful Green IP to developing countries – Also technical assistance • Award prizes for most useful Green IP • Provide tax incentives to stimulate sharing or exchange of Green IP
Policy Can Help! • Provide greater information on available green technologies, whether private or publicly held • Offer financial assistance for licensing useful Green IP to developing countries – Also technical assistance • Award prizes for most useful Green IP • Provide tax incentives to stimulate sharing or exchange of Green IP
 29
29
 Photo Credits Flickr: Chess/Fox, Tuesday Night Poker/Rambis, Ryan Air/ezreenphotography, Ryan Air New Boeing 787 Colours/macrodebs, 332/265/Digg Pirate, The bus shelter at the edge of the ocean/goddess_spiral, Flickr treo ad/Steve Rhodes, Technology - "Future Vision“/$ydney i. Stockphoto: 000003004014, 000003062424, 000004293861, 000007135639, 000005589058, 000000718722 i. Pod photo: http: //www. apple. com/ipodclassic/ 30
Photo Credits Flickr: Chess/Fox, Tuesday Night Poker/Rambis, Ryan Air/ezreenphotography, Ryan Air New Boeing 787 Colours/macrodebs, 332/265/Digg Pirate, The bus shelter at the edge of the ocean/goddess_spiral, Flickr treo ad/Steve Rhodes, Technology - "Future Vision“/$ydney i. Stockphoto: 000003004014, 000003062424, 000004293861, 000007135639, 000005589058, 000000718722 i. Pod photo: http: //www. apple. com/ipodclassic/ 30


