fe12c312d14a129c55bdb2218b1bd054.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Open GIS: Helping the World Communicate Geographically April 16, 2003 Louis Hecht Chair, Open GIS Consortium (Europe) Limited © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc.
Open GIS: Helping the World Communicate Geographically April 16, 2003 Louis Hecht Chair, Open GIS Consortium (Europe) Limited © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc.
 The Open. GIS Consortium Vision A world in which everyone benefits from geographic information and services made available across any network, application, or platform. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 2
The Open. GIS Consortium Vision A world in which everyone benefits from geographic information and services made available across any network, application, or platform. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 2
 What is OGC? • The Open GIS Consortium (OGC) – Not-for-profit, international consortium – 250+ industry, government, & university members • Specification Development Program - Committee process similar to other industry consortia and SDO’s (W 3 C, OMG, ISO, CEN). • Interoperability Program - Testbeds, pilot projects etc. to develop and test Open. GIS Specifications and help bring conformant products to market. • Outreach and Community Adoption Program – Education, training and outreach to encourage the use of products with Open. GIS interfaces. Includes business development services for our members. OGC Mission Our core mission is to deliver interface specifications that are openly available for global use. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 3
What is OGC? • The Open GIS Consortium (OGC) – Not-for-profit, international consortium – 250+ industry, government, & university members • Specification Development Program - Committee process similar to other industry consortia and SDO’s (W 3 C, OMG, ISO, CEN). • Interoperability Program - Testbeds, pilot projects etc. to develop and test Open. GIS Specifications and help bring conformant products to market. • Outreach and Community Adoption Program – Education, training and outreach to encourage the use of products with Open. GIS interfaces. Includes business development services for our members. OGC Mission Our core mission is to deliver interface specifications that are openly available for global use. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 3
 Our goal is … …improve public and private sector organizations ability to author, publish, share, and use geospatial information in… Neighborhoods, Communities, Localities, Provinces, Nations, Regions, … the World Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 4
Our goal is … …improve public and private sector organizations ability to author, publish, share, and use geospatial information in… Neighborhoods, Communities, Localities, Provinces, Nations, Regions, … the World Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 4
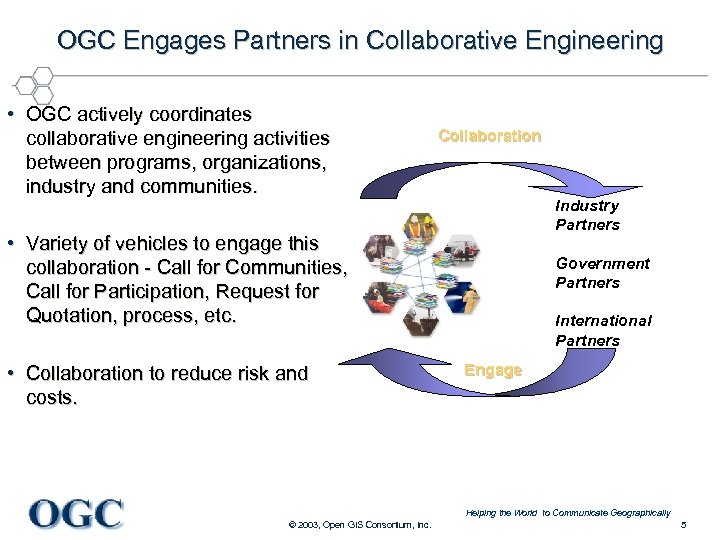 OGC Engages Partners in Collaborative Engineering • OGC actively coordinates collaborative engineering activities between programs, organizations, industry and communities. Collaboration Industry Partners • Variety of vehicles to engage this collaboration - Call for Communities, Call for Participation, Request for Quotation, process, etc. • Collaboration to reduce risk and costs. Government Partners International Partners Engage Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 5
OGC Engages Partners in Collaborative Engineering • OGC actively coordinates collaborative engineering activities between programs, organizations, industry and communities. Collaboration Industry Partners • Variety of vehicles to engage this collaboration - Call for Communities, Call for Participation, Request for Quotation, process, etc. • Collaboration to reduce risk and costs. Government Partners International Partners Engage Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 5
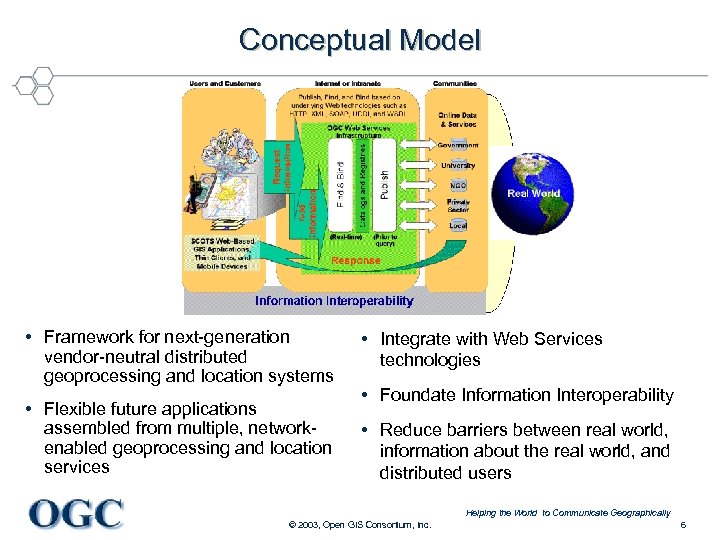 Conceptual Model • Framework for next-generation vendor-neutral distributed geoprocessing and location systems • Flexible future applications assembled from multiple, networkenabled geoprocessing and location services • Integrate with Web Services technologies • Foundate Information Interoperability • Reduce barriers between real world, information about the real world, and distributed users Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 6
Conceptual Model • Framework for next-generation vendor-neutral distributed geoprocessing and location systems • Flexible future applications assembled from multiple, networkenabled geoprocessing and location services • Integrate with Web Services technologies • Foundate Information Interoperability • Reduce barriers between real world, information about the real world, and distributed users Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 6
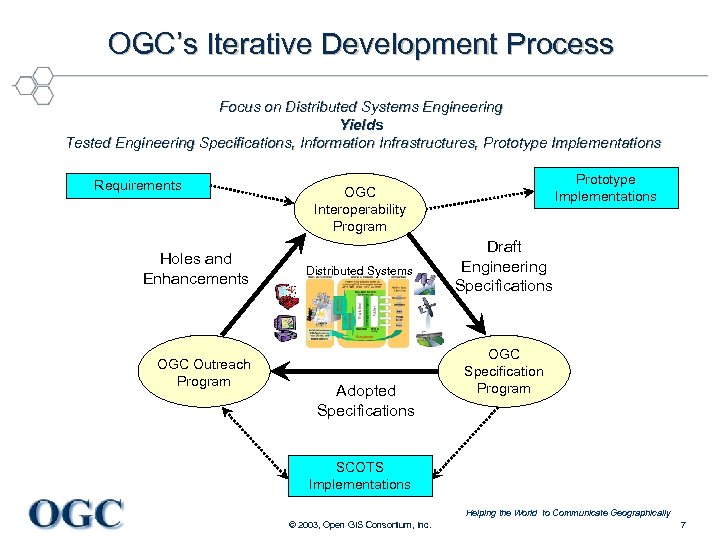 OGC’s Iterative Development Process Focus on Distributed Systems Engineering Yields Tested Engineering Specifications, Information Infrastructures, Prototype Implementations Requirements Holes and Enhancements OGC Outreach Program Prototype Implementations OGC Interoperability Program Distributed Systems Adopted Specifications Draft Engineering Specifications OGC Specification Program SCOTS Implementations Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 7
OGC’s Iterative Development Process Focus on Distributed Systems Engineering Yields Tested Engineering Specifications, Information Infrastructures, Prototype Implementations Requirements Holes and Enhancements OGC Outreach Program Prototype Implementations OGC Interoperability Program Distributed Systems Adopted Specifications Draft Engineering Specifications OGC Specification Program SCOTS Implementations Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 7
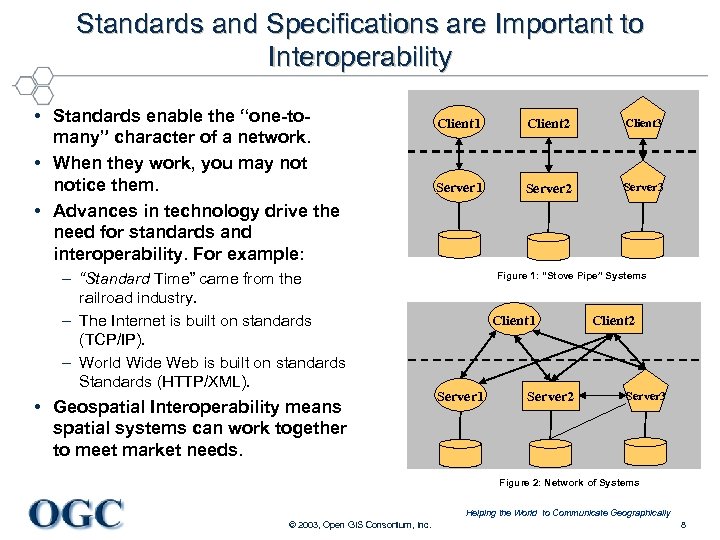 Standards and Specifications are Important to Interoperability • Standards enable the “one-tomany” character of a network. • When they work, you may notice them. • Advances in technology drive the need for standards and interoperability. For example: – “Standard Time” came from the railroad industry. – The Internet is built on standards (TCP/IP). – World Wide Web is built on standards Standards (HTTP/XML). • Geospatial Interoperability means spatial systems can work together to meet market needs. Client 1 Client 2 Client 3 Server 1 Server 2 Server 3 Figure 1: “Stove Pipe” Systems Client 1 Server 2 Client 2 Server 3 Figure 2: Network of Systems Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 8
Standards and Specifications are Important to Interoperability • Standards enable the “one-tomany” character of a network. • When they work, you may notice them. • Advances in technology drive the need for standards and interoperability. For example: – “Standard Time” came from the railroad industry. – The Internet is built on standards (TCP/IP). – World Wide Web is built on standards Standards (HTTP/XML). • Geospatial Interoperability means spatial systems can work together to meet market needs. Client 1 Client 2 Client 3 Server 1 Server 2 Server 3 Figure 1: “Stove Pipe” Systems Client 1 Server 2 Client 2 Server 3 Figure 2: Network of Systems Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 8
 Market Signals • Diminishing use of the term “Geographic Information System” • Increasing use of “spatially enabled enterprise services”, “location services” and “location-based services”. • Geographic processing is no longer isolated. • Geographic information services support business processes throughout an enterprise - decision support, route planning, analysis tools, geocoding, gazetteer services, geoparsing, proximity determination, locating points of customer service… Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 9
Market Signals • Diminishing use of the term “Geographic Information System” • Increasing use of “spatially enabled enterprise services”, “location services” and “location-based services”. • Geographic processing is no longer isolated. • Geographic information services support business processes throughout an enterprise - decision support, route planning, analysis tools, geocoding, gazetteer services, geoparsing, proximity determination, locating points of customer service… Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 9
 Addressing Market Requirements Users want to blend spatial technology with classic information technology (IT) topics like • • security, authentication real-time requirements process chaining accuracy, time and timeliness multi-use information persistence, revision and versioning business objects and their rules upward compatibility…. . Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 10
Addressing Market Requirements Users want to blend spatial technology with classic information technology (IT) topics like • • security, authentication real-time requirements process chaining accuracy, time and timeliness multi-use information persistence, revision and versioning business objects and their rules upward compatibility…. . Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 10
 Domains are Changing Requirements • Traditional map makers, photo interpreters, surveyors, and GIS analysts benefit from automated tools, better access to data, more data, improved means of distribution, etc. • Judgment and training remain essential in creating spatial information products. • Expanding Spatial Data Infrastructures put spatial information products – and raw data and tools – into the hands of – More people in traditional user domains: planning, resource management, utilities, agriculture etc. – People in new user domains: risk management, e-Gov, first responders, customer support, logistics, insurance, etc. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 11
Domains are Changing Requirements • Traditional map makers, photo interpreters, surveyors, and GIS analysts benefit from automated tools, better access to data, more data, improved means of distribution, etc. • Judgment and training remain essential in creating spatial information products. • Expanding Spatial Data Infrastructures put spatial information products – and raw data and tools – into the hands of – More people in traditional user domains: planning, resource management, utilities, agriculture etc. – People in new user domains: risk management, e-Gov, first responders, customer support, logistics, insurance, etc. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 11
 Why is Interoperability Important to Spatial Data Infrastructure? • People care about SDI because they need information. – Networks supply more information than “islands of automation. ” • Resources are limited. – Both data and software tend to become less expensive through interoperability. • Finding useful data has been difficult. – Digital catalogs support much faster discovery, assessment and access by individuals. • Geoprocessing software has been expensive. – The component paradigm and Web Services paradigm save society time and money. • Sharing data reduces redundant efforts, but sharing has been difficult. – Technical interoperability gives users Web-direct views into online data sets, and Web-direct access to the real data, usually eliminating the need for batch transfers and batch conversions. – XML will be helpful in overcoming semantic non-interoperability at the human and machine levels. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 12
Why is Interoperability Important to Spatial Data Infrastructure? • People care about SDI because they need information. – Networks supply more information than “islands of automation. ” • Resources are limited. – Both data and software tend to become less expensive through interoperability. • Finding useful data has been difficult. – Digital catalogs support much faster discovery, assessment and access by individuals. • Geoprocessing software has been expensive. – The component paradigm and Web Services paradigm save society time and money. • Sharing data reduces redundant efforts, but sharing has been difficult. – Technical interoperability gives users Web-direct views into online data sets, and Web-direct access to the real data, usually eliminating the need for batch transfers and batch conversions. – XML will be helpful in overcoming semantic non-interoperability at the human and machine levels. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 12
 Quick Reference of Open. GIS® Specifications – Accomplishments To Date © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc.
Quick Reference of Open. GIS® Specifications – Accomplishments To Date © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc.
 Categories of Open. GIS® Specifications 2003 • Encodings / Common Architecture – Encodings and interfaces that underpin the entire framework of OGC Implementation Specifications – GML • Open. GIS Web Services – Catalog Services – Publish, Discover and access geospatial data, services – Web Mapping Services – Dynamic access, integration and visualization of geospatial information – Geospatial Fusion Services – Discover, geocode and apply spatial information from text and other non mapping sources – Sensor Web Services – access and integrate data from sensor and sensor networks – Web Exploitation Services – dynamic application of geospatial information between collaborating organizations – Open Location Services – Core framework of specifications to enable applications on mobile, location aware networks Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 14
Categories of Open. GIS® Specifications 2003 • Encodings / Common Architecture – Encodings and interfaces that underpin the entire framework of OGC Implementation Specifications – GML • Open. GIS Web Services – Catalog Services – Publish, Discover and access geospatial data, services – Web Mapping Services – Dynamic access, integration and visualization of geospatial information – Geospatial Fusion Services – Discover, geocode and apply spatial information from text and other non mapping sources – Sensor Web Services – access and integrate data from sensor and sensor networks – Web Exploitation Services – dynamic application of geospatial information between collaborating organizations – Open Location Services – Core framework of specifications to enable applications on mobile, location aware networks Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 14
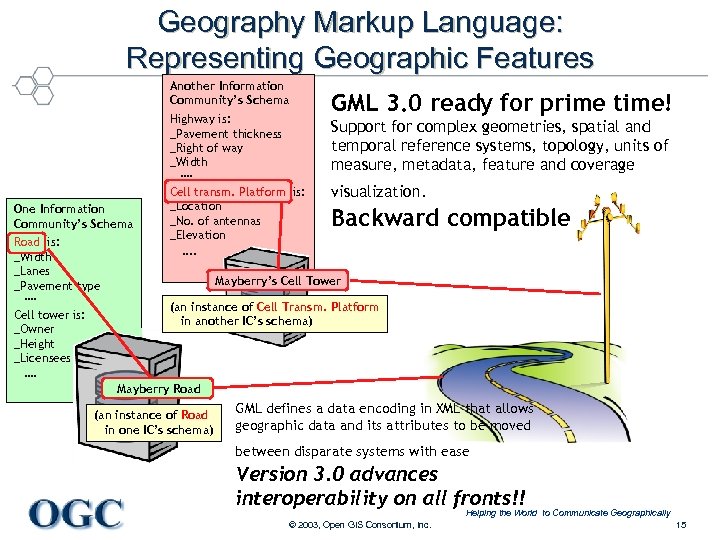 Geography Markup Language: Representing Geographic Features Another Information Community’s Schema Highway is: _Pavement thickness _Right of way _Width …. One Information Community’s Schema Road is: _Width _Lanes _Pavement type …. Cell tower is: _Owner _Height _Licensees …. GML 3. 0 ready for prime time! Support for complex geometries, spatial and temporal reference systems, topology, units of measure, metadata, feature and coverage Cell transm. Platform is: _Location _No. of antennas _Elevation visualization. Backward compatible …. Mayberry’s Cell Tower (an instance of Cell Transm. Platform in another IC’s schema) Mayberry Road (an instance of Road in one IC’s schema) GML defines a data encoding in XML that allows geographic data and its attributes to be moved between disparate systems with ease Version 3. 0 advances interoperability on all fronts!! Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 15
Geography Markup Language: Representing Geographic Features Another Information Community’s Schema Highway is: _Pavement thickness _Right of way _Width …. One Information Community’s Schema Road is: _Width _Lanes _Pavement type …. Cell tower is: _Owner _Height _Licensees …. GML 3. 0 ready for prime time! Support for complex geometries, spatial and temporal reference systems, topology, units of measure, metadata, feature and coverage Cell transm. Platform is: _Location _No. of antennas _Elevation visualization. Backward compatible …. Mayberry’s Cell Tower (an instance of Cell Transm. Platform in another IC’s schema) Mayberry Road (an instance of Road in one IC’s schema) GML defines a data encoding in XML that allows geographic data and its attributes to be moved between disparate systems with ease Version 3. 0 advances interoperability on all fronts!! Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 15
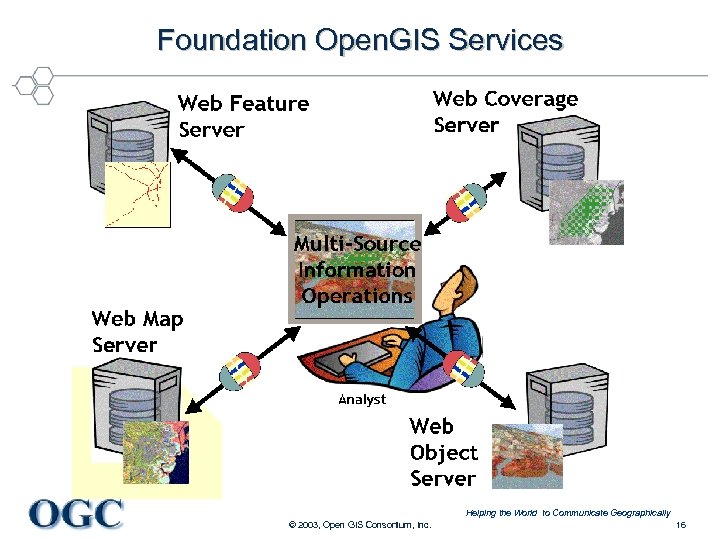 Foundation Open. GIS Services Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 16
Foundation Open. GIS Services Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 16
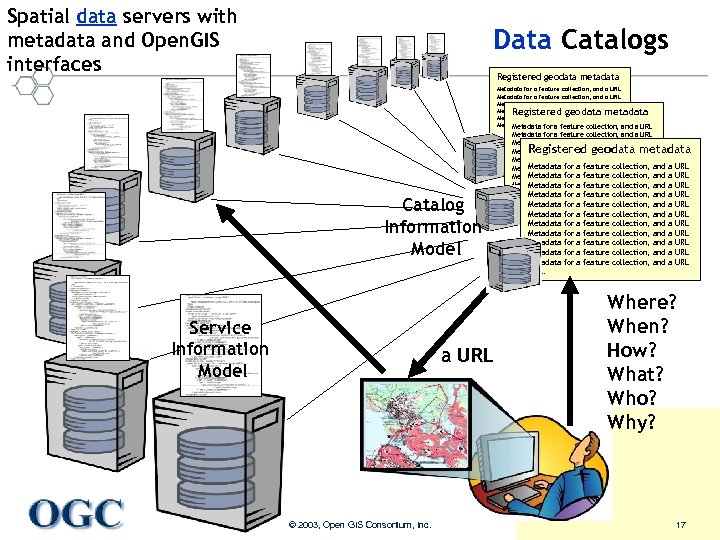 Spatial data servers with metadata and Open. GIS interfaces Data Catalogs Registered geodata metadata Metadata for a feature collection, and a URL Metadata for a feature collection, and a URL Metadata for a collection, and a URL Registered geodata metadata Metadata for a feature collection, and a URL Metadata for a collection, and a URL Metadata for a featurefeature collection, and a URL Metadata for a collection, and a Registered geodata metadata Catalog Information Model Service Information Model a URL Metadata Metadata ……… for for a a a a feature feature collection, collection, and and a a a a URL URL Where? When? How? What? Who? Why? Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 17
Spatial data servers with metadata and Open. GIS interfaces Data Catalogs Registered geodata metadata Metadata for a feature collection, and a URL Metadata for a feature collection, and a URL Metadata for a collection, and a URL Registered geodata metadata Metadata for a feature collection, and a URL Metadata for a collection, and a URL Metadata for a featurefeature collection, and a URL Metadata for a collection, and a Registered geodata metadata Catalog Information Model Service Information Model a URL Metadata Metadata ……… for for a a a a feature feature collection, collection, and and a a a a URL URL Where? When? How? What? Who? Why? Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 17
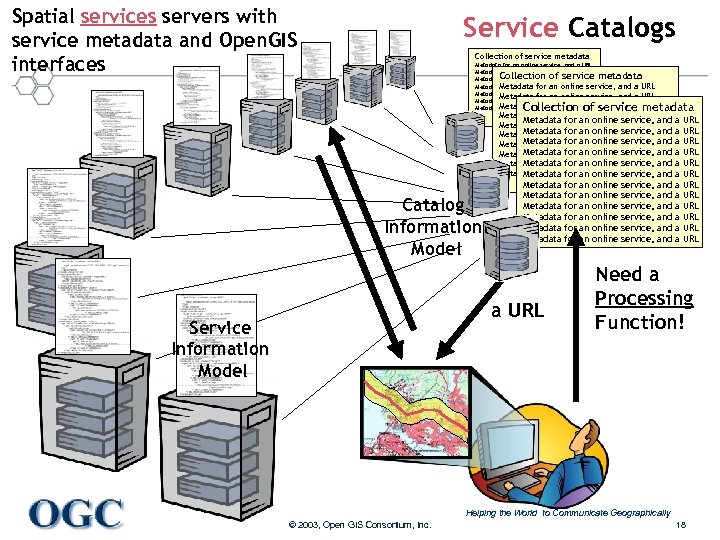 Spatial services servers with service metadata and Open. GIS interfaces Service Catalogs Collection of service metadata Metadata for an online service, and a URL Metadata for an online service, and a URL Metadata for an online service, and a service, Collection of service metadata and a URL and a metadata Collection of service URL Metadata for an online service, and a URL Metadata for an online service, Metadata for an online service, and a URL and a URL Metadata for an online service, and a URL Metadata for an online service, Catalog Information Model Metadata Metadata a URL Service Information Model for for for an an an online online service, service, and and and a a a URL URL URL Need a Processing Function! Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 18
Spatial services servers with service metadata and Open. GIS interfaces Service Catalogs Collection of service metadata Metadata for an online service, and a URL Metadata for an online service, and a URL Metadata for an online service, and a service, Collection of service metadata and a URL and a metadata Collection of service URL Metadata for an online service, and a URL Metadata for an online service, Metadata for an online service, and a URL and a URL Metadata for an online service, and a URL Metadata for an online service, Catalog Information Model Metadata Metadata a URL Service Information Model for for for an an an online online service, service, and and and a a a URL URL URL Need a Processing Function! Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 18
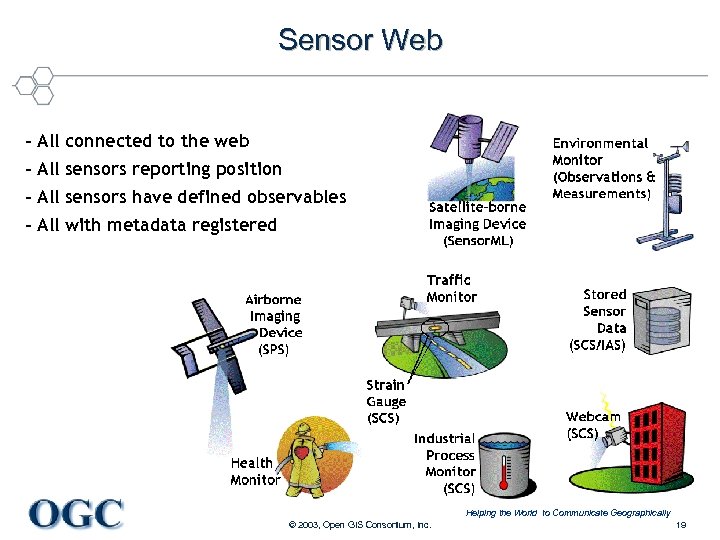 Sensor Web – All connected to the web – All sensors reporting position – All sensors have defined observables – All with metadata registered Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 19
Sensor Web – All connected to the web – All sensors reporting position – All sensors have defined observables – All with metadata registered Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 19
 One set of geospatial information… …many different styles! Style Management Services Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 20
One set of geospatial information… …many different styles! Style Management Services Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 20
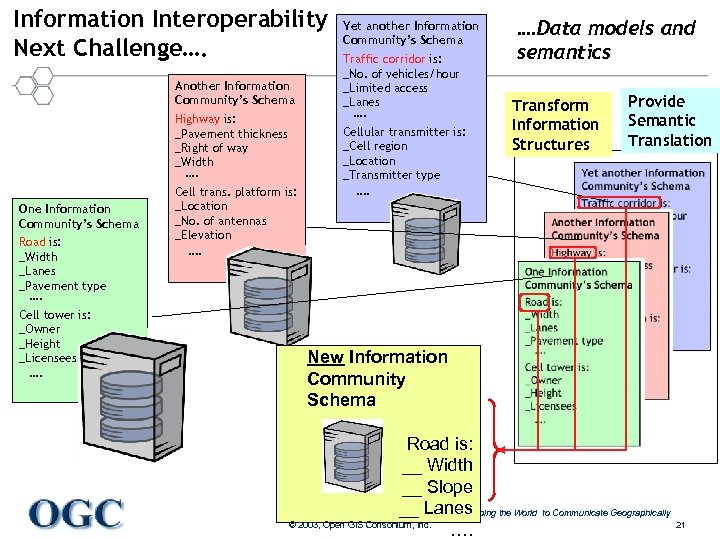 Information Interoperability Next Challenge…. Another Information Community’s Schema Highway is: _Pavement thickness _Right of way _Width …. One Information Community’s Schema Road is: _Width _Lanes _Pavement type …. Cell tower is: _Owner _Height _Licensees …. Yet another Information Community’s Schema Traffic corridor is: _No. of vehicles/hour _Limited access _Lanes …. Cellular transmitter is: _Cell region _Location _Transmitter type Cell trans. platform is: _Location _No. of antennas _Elevation …. Data models and semantics Transform Information Structures Provide Semantic Translation …. New Information Community Schema Road is: __ Width __ Slope __ Lanes the World to Communicate Geographically Helping © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 21 ….
Information Interoperability Next Challenge…. Another Information Community’s Schema Highway is: _Pavement thickness _Right of way _Width …. One Information Community’s Schema Road is: _Width _Lanes _Pavement type …. Cell tower is: _Owner _Height _Licensees …. Yet another Information Community’s Schema Traffic corridor is: _No. of vehicles/hour _Limited access _Lanes …. Cellular transmitter is: _Cell region _Location _Transmitter type Cell trans. platform is: _Location _No. of antennas _Elevation …. Data models and semantics Transform Information Structures Provide Semantic Translation …. New Information Community Schema Road is: __ Width __ Slope __ Lanes the World to Communicate Geographically Helping © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 21 ….
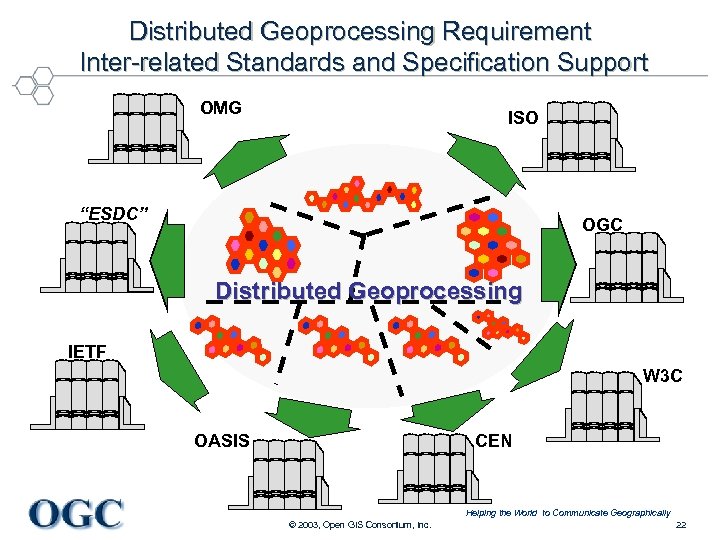 Distributed Geoprocessing Requirement Inter-related Standards and Specification Support OMG ISO “ESDC” OGC Distributed Geoprocessing IETF W 3 C OASIS CEN Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 22
Distributed Geoprocessing Requirement Inter-related Standards and Specification Support OMG ISO “ESDC” OGC Distributed Geoprocessing IETF W 3 C OASIS CEN Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 22
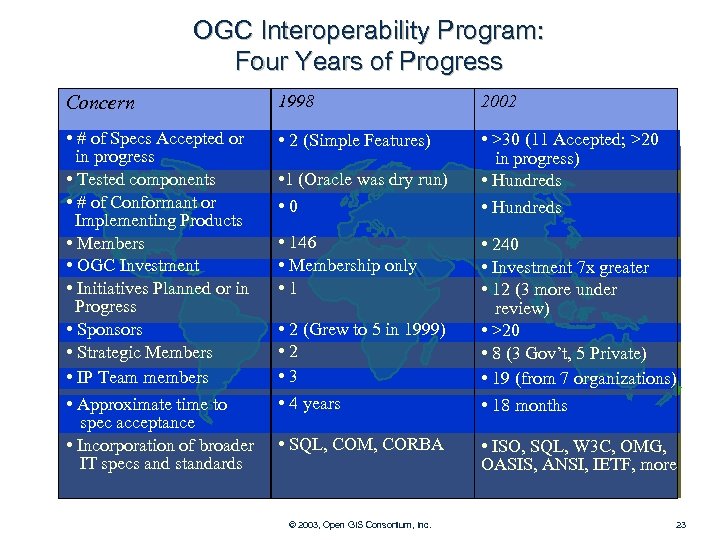 OGC Interoperability Program: Four Years of Progress Concern 1998 2002 • # of Specs Accepted or in progress • Tested components • # of Conformant or Implementing Products • Members • OGC Investment • Initiatives Planned or in Progress • Sponsors • Strategic Members • IP Team members • Approximate time to spec acceptance • Incorporation of broader IT specs and standards • 2 (Simple Features) • >30 (11 Accepted; >20 in progress) • Hundreds • 1 (Oracle was dry run) • 0 • 146 • Membership only • 1 • 2 (Grew to 5 in 1999) • 2 • 3 • 4 years • SQL, COM, CORBA © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. • 240 • Investment 7 x greater • 12 (3 more under review) • >20 • 8 (3 Gov’t, 5 Private) • 19 (from 7 organizations) • 18 months • ISO, SQL, W 3 C, OMG, OASIS, ANSI, IETF, more 23
OGC Interoperability Program: Four Years of Progress Concern 1998 2002 • # of Specs Accepted or in progress • Tested components • # of Conformant or Implementing Products • Members • OGC Investment • Initiatives Planned or in Progress • Sponsors • Strategic Members • IP Team members • Approximate time to spec acceptance • Incorporation of broader IT specs and standards • 2 (Simple Features) • >30 (11 Accepted; >20 in progress) • Hundreds • 1 (Oracle was dry run) • 0 • 146 • Membership only • 1 • 2 (Grew to 5 in 1999) • 2 • 3 • 4 years • SQL, COM, CORBA © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. • 240 • Investment 7 x greater • 12 (3 more under review) • >20 • 8 (3 Gov’t, 5 Private) • 19 (from 7 organizations) • 18 months • ISO, SQL, W 3 C, OMG, OASIS, ANSI, IETF, more 23
 Where to Find OGC Specifications - www. opengis. org - Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 24
Where to Find OGC Specifications - www. opengis. org - Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 24
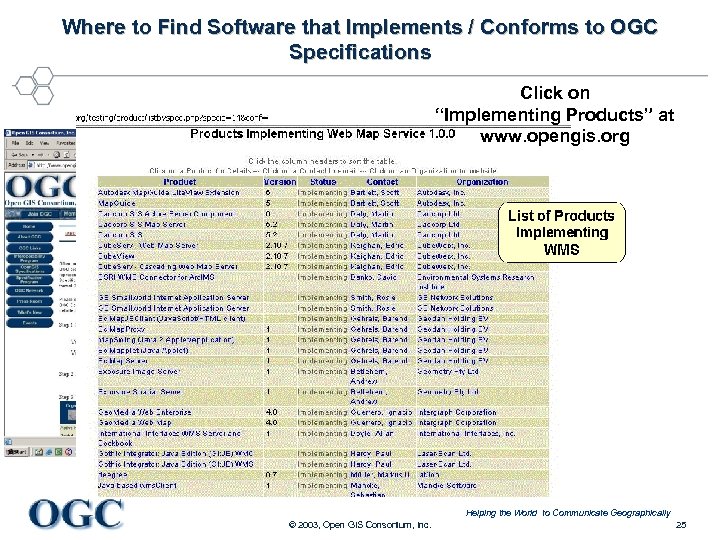 Where to Find Software that Implements / Conforms to OGC Specifications Click on “Implementing Products” at www. opengis. org Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 25
Where to Find Software that Implements / Conforms to OGC Specifications Click on “Implementing Products” at www. opengis. org Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 25
 A Snapshot of 2003 and Forward © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc.
A Snapshot of 2003 and Forward © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc.
 Open. GIS Reference Model (ORM) • The ORM is based on the Reference Model for Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP, ISO/IEC 10746), a widely used methodology for architecting open, distributed processing systems. • The ORM helps you develop a clear and detailed idea about what you want to do, then helps you design an architecture and implementation strategy. • The ORM documents the OGC technology baseline in terms of enterprise, information, and technology view points. • INSPIRE and GOS and their component enterprise systems will have multiple users, developers, operators, and reviewers, each viewing the system from their own viewpoint. The ORM helps ensure that each view will be consistent with the overall requirements and with the other views. • The ORM provides examples. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 27
Open. GIS Reference Model (ORM) • The ORM is based on the Reference Model for Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP, ISO/IEC 10746), a widely used methodology for architecting open, distributed processing systems. • The ORM helps you develop a clear and detailed idea about what you want to do, then helps you design an architecture and implementation strategy. • The ORM documents the OGC technology baseline in terms of enterprise, information, and technology view points. • INSPIRE and GOS and their component enterprise systems will have multiple users, developers, operators, and reviewers, each viewing the system from their own viewpoint. The ORM helps ensure that each view will be consistent with the overall requirements and with the other views. • The ORM provides examples. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 27
 2003 Priority – Stabilize and Enhance OGC Spec Utility Mid-Long Technical Plan: Term TB Goals Concept Technical Baseline Integration Design T Testbeds Prototyp e Annual TB Goals Open. GIS Spec • Initiatives • Maturation Technical Baseline Maturation • Utility OGC Technology Maturity Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 28
2003 Priority – Stabilize and Enhance OGC Spec Utility Mid-Long Technical Plan: Term TB Goals Concept Technical Baseline Integration Design T Testbeds Prototyp e Annual TB Goals Open. GIS Spec • Initiatives • Maturation Technical Baseline Maturation • Utility OGC Technology Maturity Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 28
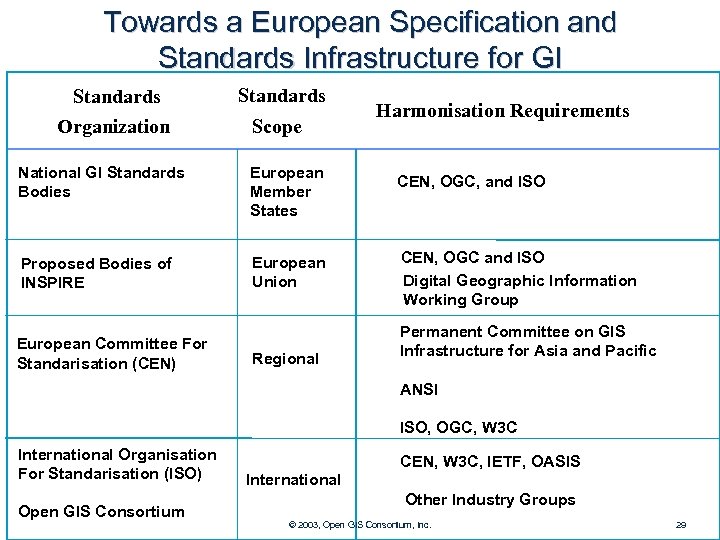 Towards a European Specification and Standards Infrastructure for GI Standards Organization Standards Scope National GI Standards Bodies European Member States Proposed Bodies of INSPIRE European Union European Committee For Standarisation (CEN) Regional Harmonisation Requirements CEN, OGC, and ISO CEN, OGC and ISO Digital Geographic Information Working Group Permanent Committee on GIS Infrastructure for Asia and Pacific ANSI ISO, OGC, W 3 C International Organisation For Standarisation (ISO) Open GIS Consortium CEN, W 3 C, IETF, OASIS International Other Industry Groups © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 29
Towards a European Specification and Standards Infrastructure for GI Standards Organization Standards Scope National GI Standards Bodies European Member States Proposed Bodies of INSPIRE European Union European Committee For Standarisation (CEN) Regional Harmonisation Requirements CEN, OGC, and ISO CEN, OGC and ISO Digital Geographic Information Working Group Permanent Committee on GIS Infrastructure for Asia and Pacific ANSI ISO, OGC, W 3 C International Organisation For Standarisation (ISO) Open GIS Consortium CEN, W 3 C, IETF, OASIS International Other Industry Groups © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 29
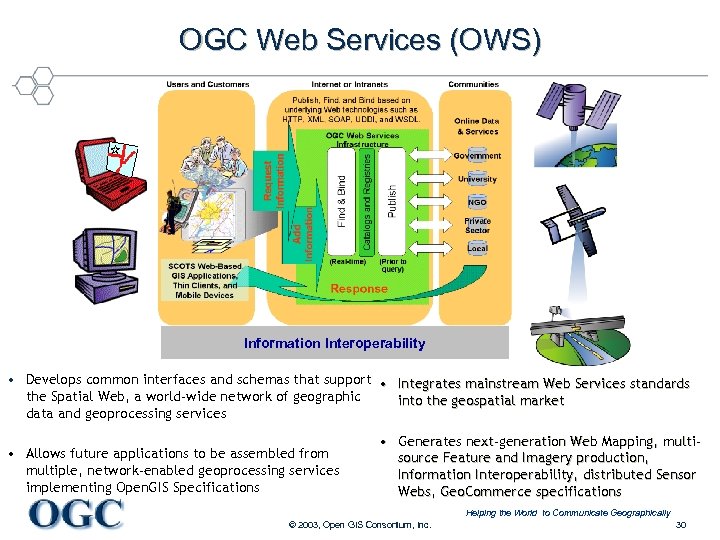 OGC Web Services (OWS) Information Interoperability • Develops common interfaces and schemas that support • Integrates mainstream Web Services standards the Spatial Web, a world-wide network of geographic into the geospatial market data and geoprocessing services • Allows future applications to be assembled from multiple, network-enabled geoprocessing services implementing Open. GIS Specifications • Generates next-generation Web Mapping, multisource Feature and Imagery production, Information Interoperability, distributed Sensor Webs, Geo. Commerce specifications Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 30
OGC Web Services (OWS) Information Interoperability • Develops common interfaces and schemas that support • Integrates mainstream Web Services standards the Spatial Web, a world-wide network of geographic into the geospatial market data and geoprocessing services • Allows future applications to be assembled from multiple, network-enabled geoprocessing services implementing Open. GIS Specifications • Generates next-generation Web Mapping, multisource Feature and Imagery production, Information Interoperability, distributed Sensor Webs, Geo. Commerce specifications Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 30
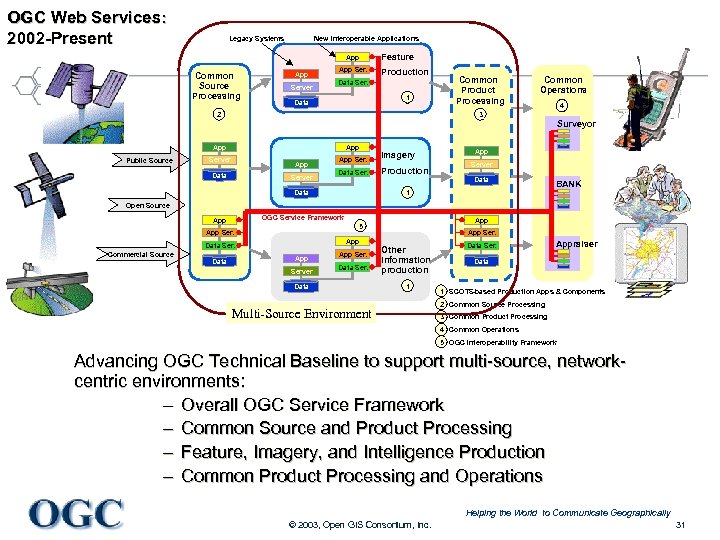 OGC Web Services: 2002 -Present Legacy Systems New Interoperable Applications App Common Source Processing App Server App Ser. Feature Production Data Ser. 1 Data 2 Common Product Processing Common Operations 4 3 Surveyor Pres App Public Source App Server App Ser. App Data Server Data Ser. Data Imagery Production App Server Data 1 BANK CINC Open Source OGC Service Framework App Data Ser. Commercial Source Data App 5 App Server App Ser. Data Ser. Data App Ser. Other information production 1 Multi-Source Environment Data Ser. Analyst Appraiser Data 1 SCOTS-based Production Apps & Components 2 Common Source Processing 3 Common Product Processing 4 Common Operations 5 OGC Interoperability Framework Advancing OGC Technical Baseline to support multi-source, networkcentric environments: – Overall OGC Service Framework – Common Source and Product Processing – Feature, Imagery, and Intelligence Production – Common Product Processing and Operations Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 31
OGC Web Services: 2002 -Present Legacy Systems New Interoperable Applications App Common Source Processing App Server App Ser. Feature Production Data Ser. 1 Data 2 Common Product Processing Common Operations 4 3 Surveyor Pres App Public Source App Server App Ser. App Data Server Data Ser. Data Imagery Production App Server Data 1 BANK CINC Open Source OGC Service Framework App Data Ser. Commercial Source Data App 5 App Server App Ser. Data Ser. Data App Ser. Other information production 1 Multi-Source Environment Data Ser. Analyst Appraiser Data 1 SCOTS-based Production Apps & Components 2 Common Source Processing 3 Common Product Processing 4 Common Operations 5 OGC Interoperability Framework Advancing OGC Technical Baseline to support multi-source, networkcentric environments: – Overall OGC Service Framework – Common Source and Product Processing – Feature, Imagery, and Intelligence Production – Common Product Processing and Operations Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 31
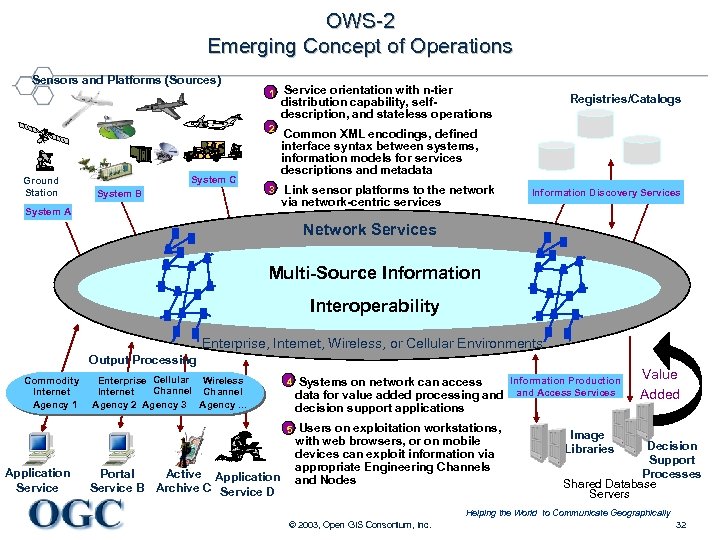 OWS-2 Emerging Concept of Operations Sensors and Platforms (Sources) 1 Service orientation with n-tier distribution capability, selfdescription, and stateless operations 2 Ground Station System C System B Common XML encodings, defined interface syntax between systems, information models for services descriptions and metadata 3 Link sensor platforms to the network via network-centric services Registries/Catalogs System A Information Discovery Services Network Services Multi-Source Information Interoperability Enterprise, Internet, Wireless, or Cellular Environments Output Processing Enterprise Cellular Wireless Channel Internet Agency 2 Agency 3 Agency. . . Application Service Portal Active Application Service B Archive C Service D 4 Information Production Systems on network can access data for value added processing and Access Services decision support applications 5 Commodity Internet Agency 1 Users on exploitation workstations, with web browsers, or on mobile devices can exploit information via appropriate Engineering Channels and Nodes Value Added Image Libraries Decision Support Processes Shared Database Servers Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 32
OWS-2 Emerging Concept of Operations Sensors and Platforms (Sources) 1 Service orientation with n-tier distribution capability, selfdescription, and stateless operations 2 Ground Station System C System B Common XML encodings, defined interface syntax between systems, information models for services descriptions and metadata 3 Link sensor platforms to the network via network-centric services Registries/Catalogs System A Information Discovery Services Network Services Multi-Source Information Interoperability Enterprise, Internet, Wireless, or Cellular Environments Output Processing Enterprise Cellular Wireless Channel Internet Agency 2 Agency 3 Agency. . . Application Service Portal Active Application Service B Archive C Service D 4 Information Production Systems on network can access data for value added processing and Access Services decision support applications 5 Commodity Internet Agency 1 Users on exploitation workstations, with web browsers, or on mobile devices can exploit information via appropriate Engineering Channels and Nodes Value Added Image Libraries Decision Support Processes Shared Database Servers Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 32
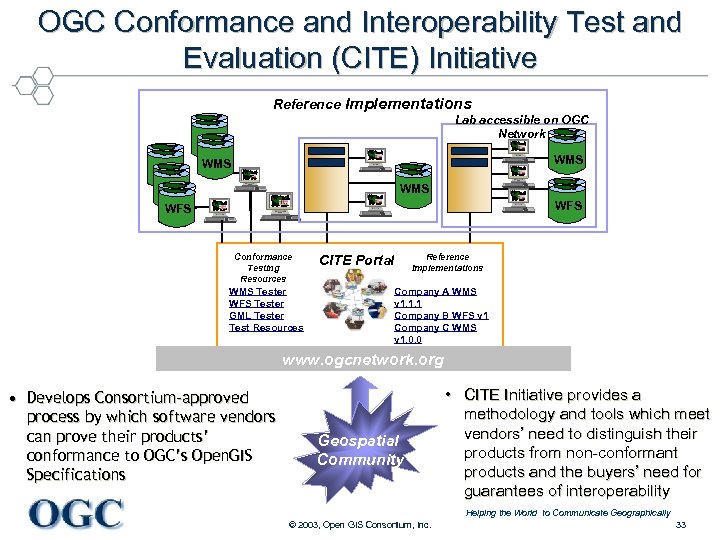 OGC Conformance and Interoperability Test and Evaluation (CITE) Initiative Reference Implementations Lab accessible on OGC Network WMS s WMS WFS Conformance Testing Resources WMS Tester WFS Tester GML Tester Test Resources CITE Portal Reference Implementations Company A WMS v 1. 1. 1 Company B WFS v 1 Company C WMS v 1. 0. 0 www. ogcnetwork. org • Develops Consortium-approved process by which software vendors can prove their products’ conformance to OGC’s Open. GIS Specifications Geospatial Community • CITE Initiative provides a methodology and tools which meet vendors’ need to distinguish their products from non-conformant products and the buyers’ need for guarantees of interoperability Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 33
OGC Conformance and Interoperability Test and Evaluation (CITE) Initiative Reference Implementations Lab accessible on OGC Network WMS s WMS WFS Conformance Testing Resources WMS Tester WFS Tester GML Tester Test Resources CITE Portal Reference Implementations Company A WMS v 1. 1. 1 Company B WFS v 1 Company C WMS v 1. 0. 0 www. ogcnetwork. org • Develops Consortium-approved process by which software vendors can prove their products’ conformance to OGC’s Open. GIS Specifications Geospatial Community • CITE Initiative provides a methodology and tools which meet vendors’ need to distinguish their products from non-conformant products and the buyers’ need for guarantees of interoperability Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 33
 CITE Status • Study completed • Conformance Test Engine: – Notation stabilized (v 1. 2) – Engine in Beta testing • Scripts – WMS and WFS assertions are near stable – GML validator works for GML 2. 1, moving to 3. 0 • Reference Implementations – Underway • Portal – Design and content-free prototype built • Upcoming milestones by September – Conformance Test Engine – Full Operating Capability – GML Validator - Full Operating Capability – WMS Test Script - Full Operating Capability – WFS Test Script - Full Operating Capability – CITE Portal – Initial Operating Capability – WMS Reference Implementation – Initial Operating Capability – WFS Reference Implementation Initial Operating Capability Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 34
CITE Status • Study completed • Conformance Test Engine: – Notation stabilized (v 1. 2) – Engine in Beta testing • Scripts – WMS and WFS assertions are near stable – GML validator works for GML 2. 1, moving to 3. 0 • Reference Implementations – Underway • Portal – Design and content-free prototype built • Upcoming milestones by September – Conformance Test Engine – Full Operating Capability – GML Validator - Full Operating Capability – WMS Test Script - Full Operating Capability – WFS Test Script - Full Operating Capability – CITE Portal – Initial Operating Capability – WMS Reference Implementation – Initial Operating Capability – WFS Reference Implementation Initial Operating Capability Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 34
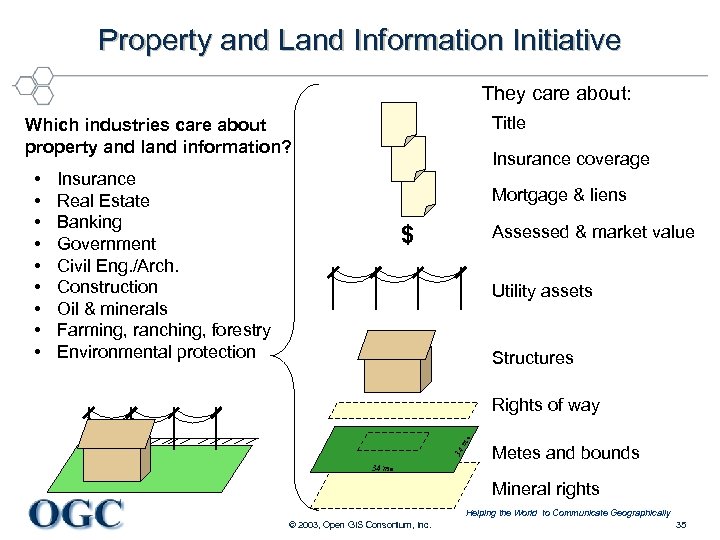 Property and Land Information Initiative They care about: Title Which industries care about property and land information? Insurance Real Estate Banking Government Civil Eng. /Arch. Construction Oil & minerals Farming, ranching, forestry Environmental protection Mortgage & liens $ Assessed & market value Utility assets Structures m . Rights of way 34 m . 34 • • • Insurance coverage Metes and bounds Mineral rights Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 35
Property and Land Information Initiative They care about: Title Which industries care about property and land information? Insurance Real Estate Banking Government Civil Eng. /Arch. Construction Oil & minerals Farming, ranching, forestry Environmental protection Mortgage & liens $ Assessed & market value Utility assets Structures m . Rights of way 34 m . 34 • • • Insurance coverage Metes and bounds Mineral rights Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 35
 Property and Land Information Initiative Planning Activity - Call for Sponsors • Call for Sponsors for a Planning Activity that may support future development of an OGC Property and Land Information (PLI) Initiative. • This planning activity will seek interested Sponsors to provide input on – technology requirements and concepts to foster development of next-generation interoperable networked architectures – capabilities to enable broader sharing and application of property data and land information between collaborating organizations. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 36
Property and Land Information Initiative Planning Activity - Call for Sponsors • Call for Sponsors for a Planning Activity that may support future development of an OGC Property and Land Information (PLI) Initiative. • This planning activity will seek interested Sponsors to provide input on – technology requirements and concepts to foster development of next-generation interoperable networked architectures – capabilities to enable broader sharing and application of property data and land information between collaborating organizations. Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 36
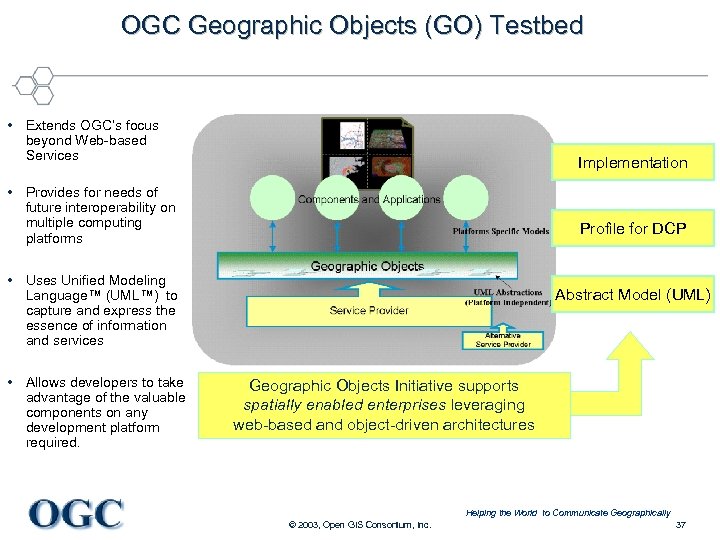 OGC Geographic Objects (GO) Testbed • Extends OGC’s focus beyond Web-based Services Implementation • Provides for needs of future interoperability on multiple computing platforms Profile for DCP • Uses Unified Modeling Language™ (UML™) to capture and express the essence of information and services • Allows developers to take advantage of the valuable components on any development platform required. Abstract Model (UML) Geographic Objects Initiative supports spatially enabled enterprises leveraging web-based and object-driven architectures Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 37
OGC Geographic Objects (GO) Testbed • Extends OGC’s focus beyond Web-based Services Implementation • Provides for needs of future interoperability on multiple computing platforms Profile for DCP • Uses Unified Modeling Language™ (UML™) to capture and express the essence of information and services • Allows developers to take advantage of the valuable components on any development platform required. Abstract Model (UML) Geographic Objects Initiative supports spatially enabled enterprises leveraging web-based and object-driven architectures Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 37
 With OGC Interfaces Seconds to Minutes, instead of days Vendor neutral Up to date data Format neutral Get exactly what you want, not an entire continent Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 38
With OGC Interfaces Seconds to Minutes, instead of days Vendor neutral Up to date data Format neutral Get exactly what you want, not an entire continent Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 38
 Contacts Mr. Louis Hecht Chair, Open GIS Consortium (Europe) Limited lhecht@opengis. org +1 301 792 1365 Mr. Guenther Pichler Managing Director, Open GIS Consortium (Europe) Limited gpichler@opengis. org +49 (89) 43692 -159 Mr. Mark Reichardt, Executive Director, Outreach and Community Adoption Program mreichardt@opengis. org +1 301 840 -1361 Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 39
Contacts Mr. Louis Hecht Chair, Open GIS Consortium (Europe) Limited lhecht@opengis. org +1 301 792 1365 Mr. Guenther Pichler Managing Director, Open GIS Consortium (Europe) Limited gpichler@opengis. org +49 (89) 43692 -159 Mr. Mark Reichardt, Executive Director, Outreach and Community Adoption Program mreichardt@opengis. org +1 301 840 -1361 Helping the World to Communicate Geographically © 2003, Open GIS Consortium, Inc. 39


