 Oogenesis
Oogenesis
 What is Oogenesis: • Oogenesis is the female version of spermatogenesis; meiotic divisions with an end result of haploid daughter cells • It produces 4 end product cells just like spermatogenesis but in females, 3 out of the 4 cells are not used as gametes b/c they are too small (named polar bodies) • The 1 viable product is called the ovum
What is Oogenesis: • Oogenesis is the female version of spermatogenesis; meiotic divisions with an end result of haploid daughter cells • It produces 4 end product cells just like spermatogenesis but in females, 3 out of the 4 cells are not used as gametes b/c they are too small (named polar bodies) • The 1 viable product is called the ovum
 Steps during Oogenesis Phase I: Events before birth 1. oogonia in ovaries (formed from germinal epithelium) undergo mitosis repeatedly in order to build up large numbers (diploid) 2. oogonia grow into larger cells called primary oocytes that begin meiosis I but the process stops at prophase I (diploid) 3. follicle cells undergo mitosis repeatedly and then a single layer of these cells surrounds each primary oocyte; entire structure called primary follicle
Steps during Oogenesis Phase I: Events before birth 1. oogonia in ovaries (formed from germinal epithelium) undergo mitosis repeatedly in order to build up large numbers (diploid) 2. oogonia grow into larger cells called primary oocytes that begin meiosis I but the process stops at prophase I (diploid) 3. follicle cells undergo mitosis repeatedly and then a single layer of these cells surrounds each primary oocyte; entire structure called primary follicle
 Interesting Info • A female is born with ~ 1 million primary follicles, but by the time she reaches puberty only ~400, 000 remain • On average, a woman ovulates 400 times • By menopause (ages ~48 -55) a woman has few primary follicles remaining and what does remain is unlikely to be ovulated due to hormonal changes
Interesting Info • A female is born with ~ 1 million primary follicles, but by the time she reaches puberty only ~400, 000 remain • On average, a woman ovulates 400 times • By menopause (ages ~48 -55) a woman has few primary follicles remaining and what does remain is unlikely to be ovulated due to hormonal changes
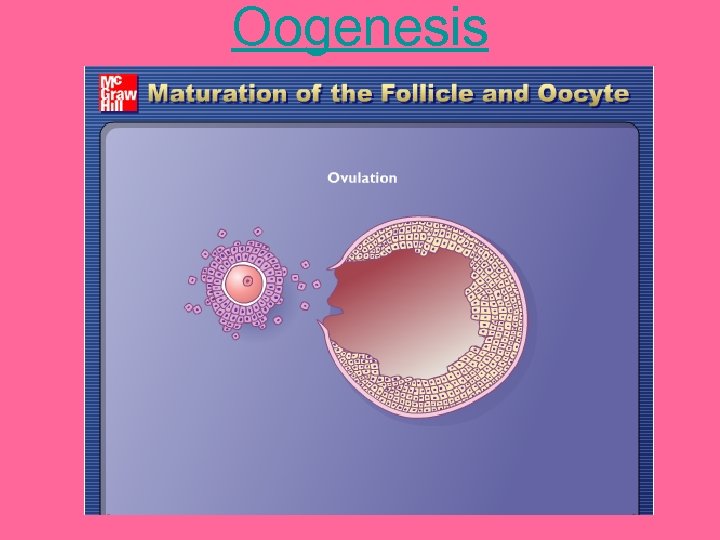
 Phase II: Events occurring from pubertymenopause 1. FSH cues the ovary to begin maturing follicles 2. Primary oocytes finish meiosis I resulting in unequally sized haploid cells Note: the function of the polar body is to house the unneeded chromosomes; the polar body will later degenerate - the large resulting haploid cell is called the secondary oocyte
Phase II: Events occurring from pubertymenopause 1. FSH cues the ovary to begin maturing follicles 2. Primary oocytes finish meiosis I resulting in unequally sized haploid cells Note: the function of the polar body is to house the unneeded chromosomes; the polar body will later degenerate - the large resulting haploid cell is called the secondary oocyte
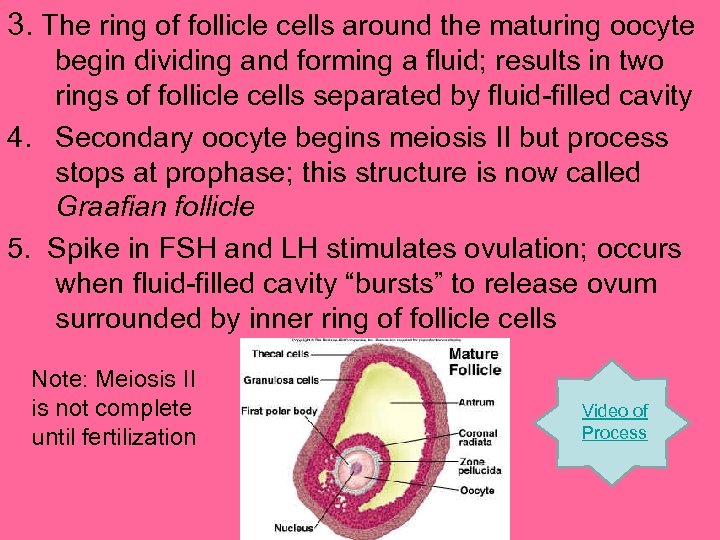 3. The ring of follicle cells around the maturing oocyte begin dividing and forming a fluid; results in two rings of follicle cells separated by fluid-filled cavity 4. Secondary oocyte begins meiosis II but process stops at prophase; this structure is now called Graafian follicle 5. Spike in FSH and LH stimulates ovulation; occurs when fluid-filled cavity “bursts” to release ovum surrounded by inner ring of follicle cells Note: Meiosis II is not complete until fertilization Video of Process
3. The ring of follicle cells around the maturing oocyte begin dividing and forming a fluid; results in two rings of follicle cells separated by fluid-filled cavity 4. Secondary oocyte begins meiosis II but process stops at prophase; this structure is now called Graafian follicle 5. Spike in FSH and LH stimulates ovulation; occurs when fluid-filled cavity “bursts” to release ovum surrounded by inner ring of follicle cells Note: Meiosis II is not complete until fertilization Video of Process
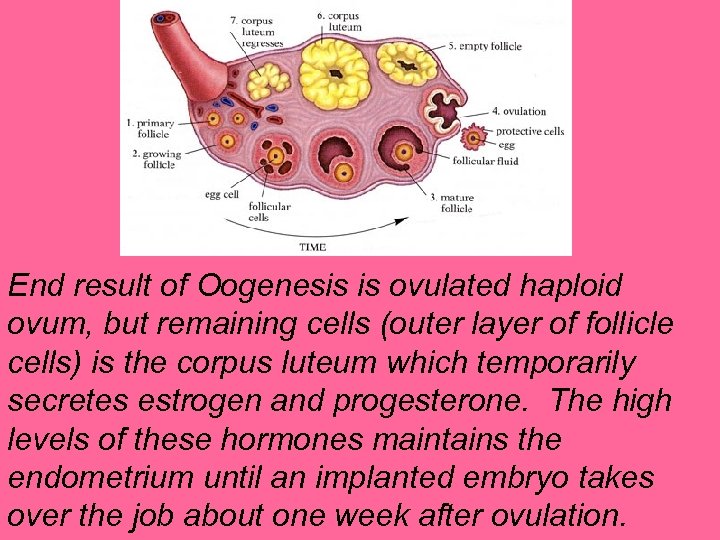 End result of Oogenesis is ovulated haploid ovum, but remaining cells (outer layer of follicle cells) is the corpus luteum which temporarily secretes estrogen and progesterone. The high levels of these hormones maintains the endometrium until an implanted embryo takes over the job about one week after ovulation.
End result of Oogenesis is ovulated haploid ovum, but remaining cells (outer layer of follicle cells) is the corpus luteum which temporarily secretes estrogen and progesterone. The high levels of these hormones maintains the endometrium until an implanted embryo takes over the job about one week after ovulation.
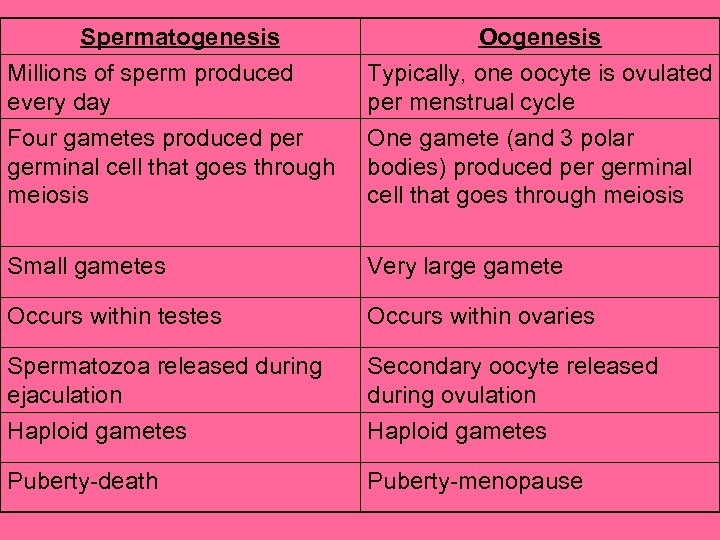 Spermatogenesis Millions of sperm produced every day Four gametes produced per germinal cell that goes through meiosis Oogenesis Typically, one oocyte is ovulated per menstrual cycle One gamete (and 3 polar bodies) produced per germinal cell that goes through meiosis Small gametes Very large gamete Occurs within testes Occurs within ovaries Spermatozoa released during ejaculation Secondary oocyte released during ovulation Haploid gametes Puberty-death Puberty-menopause
Spermatogenesis Millions of sperm produced every day Four gametes produced per germinal cell that goes through meiosis Oogenesis Typically, one oocyte is ovulated per menstrual cycle One gamete (and 3 polar bodies) produced per germinal cell that goes through meiosis Small gametes Very large gamete Occurs within testes Occurs within ovaries Spermatozoa released during ejaculation Secondary oocyte released during ovulation Haploid gametes Puberty-death Puberty-menopause
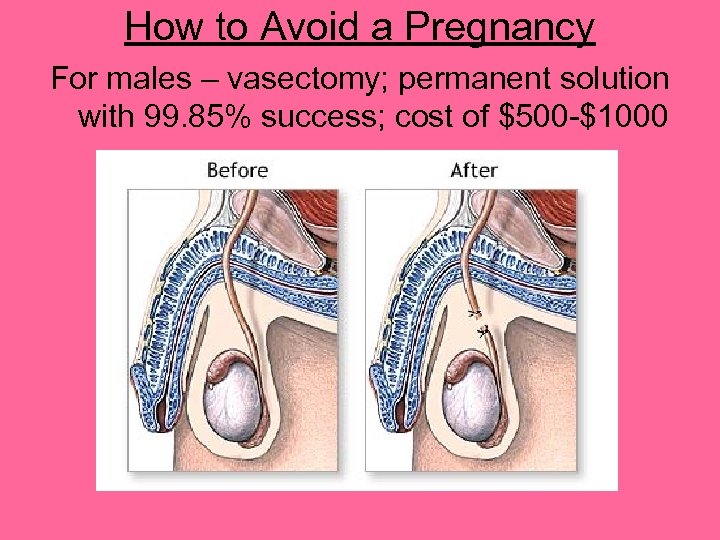 How to Avoid a Pregnancy For males – vasectomy; permanent solution with 99. 85% success; cost of $500 -$1000
How to Avoid a Pregnancy For males – vasectomy; permanent solution with 99. 85% success; cost of $500 -$1000
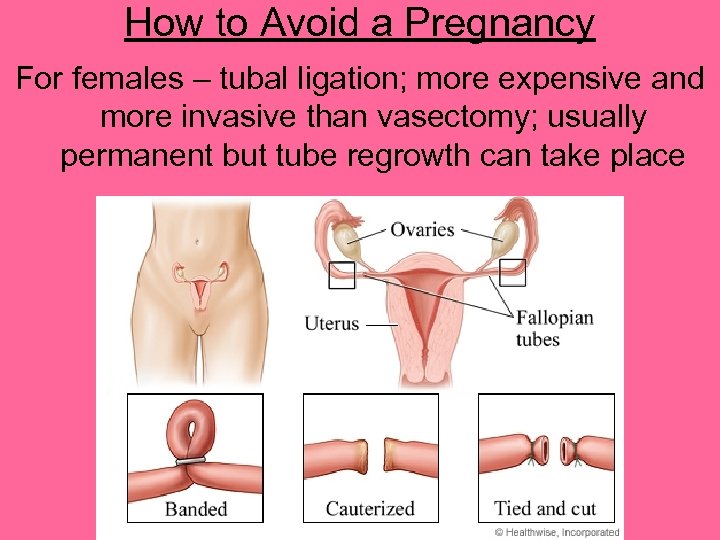 How to Avoid a Pregnancy For females – tubal ligation; more expensive and more invasive than vasectomy; usually permanent but tube regrowth can take place
How to Avoid a Pregnancy For females – tubal ligation; more expensive and more invasive than vasectomy; usually permanent but tube regrowth can take place