5112d7da35fbbabfc04efbbe1774edbb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

Onto. Grid: Paving the way for Knowledgeable Grid Services and Systems www. ontogrid. net FP 6 -511513 WS-DAIOnt-RDF(S) Hands-on session Miguel Esteban Gutiérrez (U. P. M. ) Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial Manchester, Feb 2007 Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 1

Outline of the tutorial § Part I: Theoretical introduction § Part II: Hands-on exercises Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 2

Part I: Theoretical introduction Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 3
Outline of the tutorial Theoretical introduction § An introductory scenario q Ontology share/reuse problem q Possible solutions q Our approach § The specification q Foundations q Operational model § The implementation q Architecture q RDF(S) Storage support Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 4
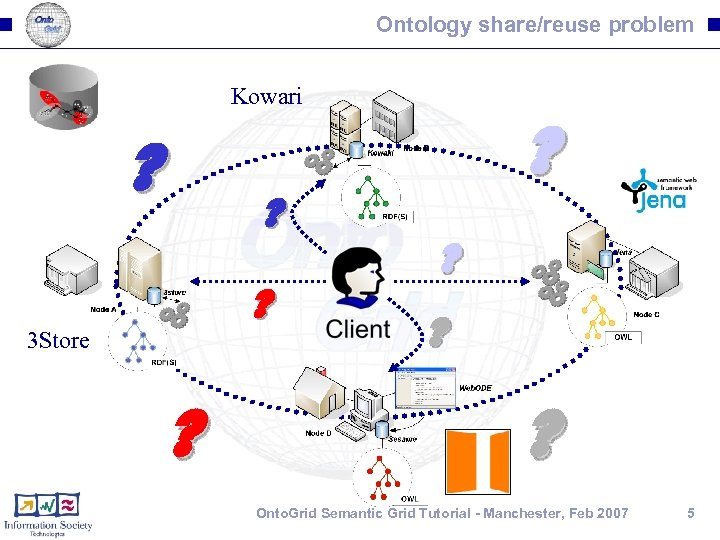
Ontology share/reuse problem Kowari ? ? ? 3 Store ? ? ? ? ? Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 5
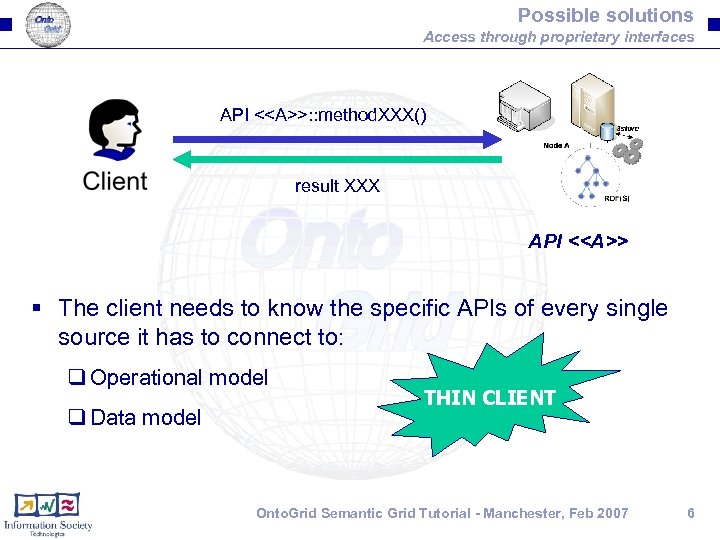
Possible solutions Access through proprietary interfaces API <<A>>: : method. XXX() result XXX API <<A>> § The client needs to know the specific APIs of every single source it has to connect to: q Operational model q Data model THIN CLIENT Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 6
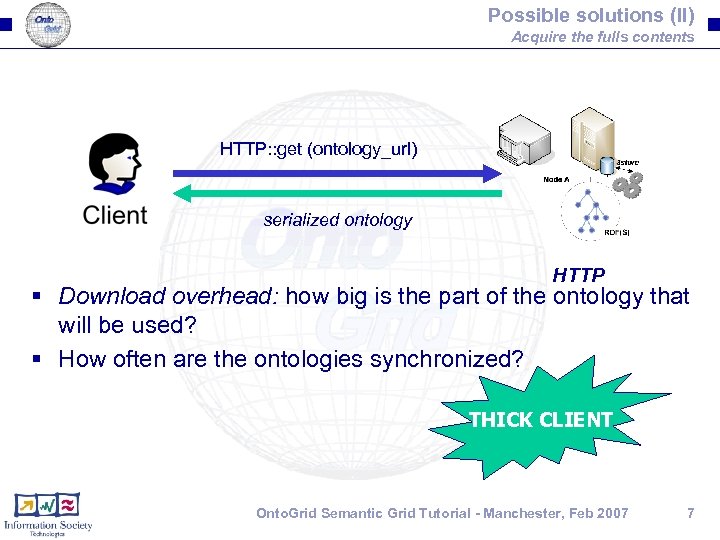
Possible solutions (II) Acquire the fulls contents HTTP: : get (ontology_url) serialized ontology HTTP § Download overhead: how big is the part of the ontology that will be used? § How often are the ontologies synchronized? THICK CLIENT Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 7

Our approach § Standardise an RDF(S) ontology access mechanism that: q Provides an homogeneus access interface q Defines an operational model based on the model itself q Full CRUD (beyond SPARQL protocol) § Prevents the user from dealing directly with the physical resources (resource virtualization) Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 8
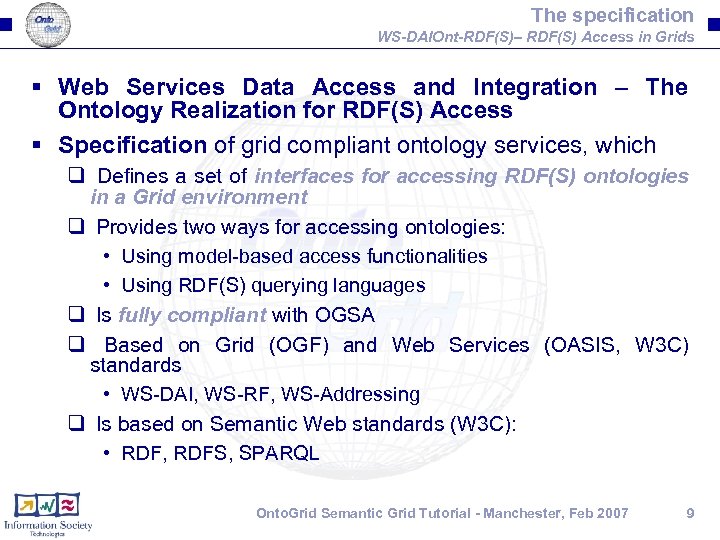
The specification WS-DAIOnt-RDF(S)– RDF(S) Access in Grids § Web Services Data Access and Integration – The Ontology Realization for RDF(S) Access § Specification of grid compliant ontology services, which q Defines a set of interfaces for accessing RDF(S) ontologies in a Grid environment q Provides two ways for accessing ontologies: • Using model-based access functionalities • Using RDF(S) querying languages q Is fully compliant with OGSA q Based on Grid (OGF) and Web Services (OASIS, W 3 C) standards • WS-DAI, WS-RF, WS-Addressing q Is based on Semantic Web standards (W 3 C): • RDF, RDFS, SPARQL Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 9
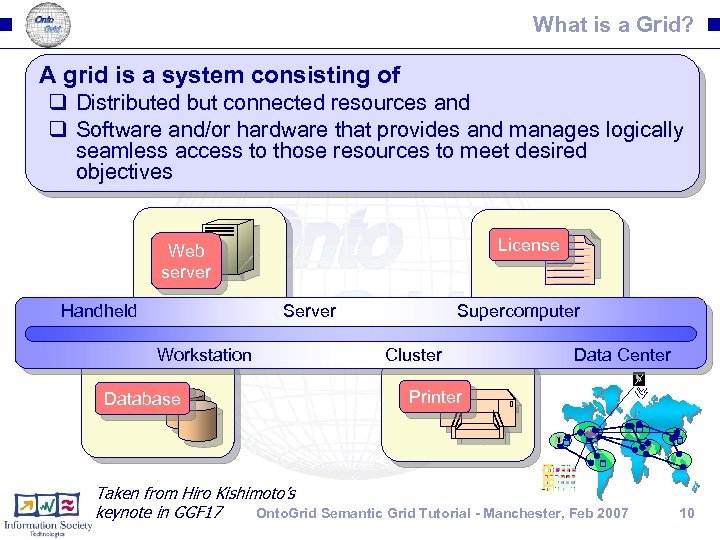
What is a Grid? A grid is a system consisting of q Distributed but connected resources and q Software and/or hardware that provides and manages logically seamless access to those resources to meet desired objectives License Web server Handheld Server Workstation Database Supercomputer Cluster Data Center Printer R 2 AD Taken from Hiro Kishimoto’s Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 keynote in GGF 17 10

The specification (II) The Grid as an ontology deployment playground § EGA Reference Model De-facto standard grid architecture § Open Grid Services Architecture (OGSA) So. A and web services based instantiation of EGA Reference Model q Infrastructure Services (i. e. transactions) q Execution Management Services(i. e. job management) q Data Services q q • Security • Data Description • Data Access • Storage Resource Management • Cache Services • Data Replication • Data Federation • Metadata Catalogue & Registries Resource Management Services Security Services (i. e. AAA) Self-management Services Information Services (i. e. provenance) WS-DAI Specification Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 11
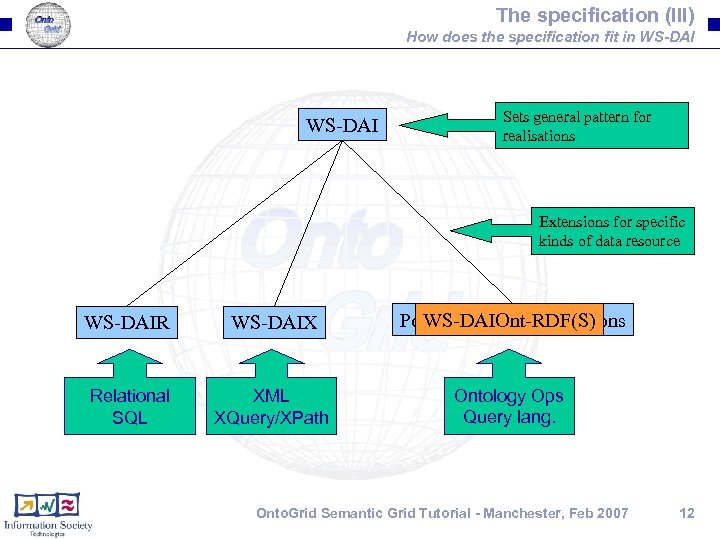
The specification (III) How does the specification fit in WS-DAI Sets general pattern for realisations Extensions for specific kinds of data resource WS-DAIR WS-DAIX Possible Future Realisations WS-DAIOnt-RDF(S) Relational SQL XML XQuery/XPath Ontology Ops Query lang. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 12
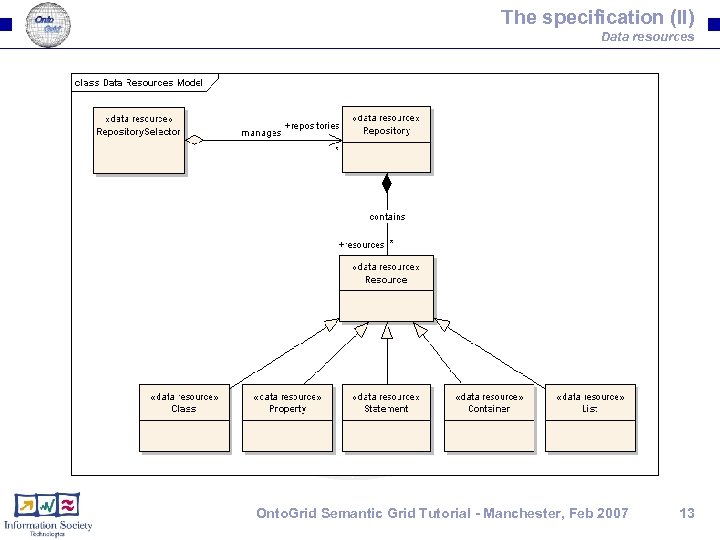
The specification (II) Data resources Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 13
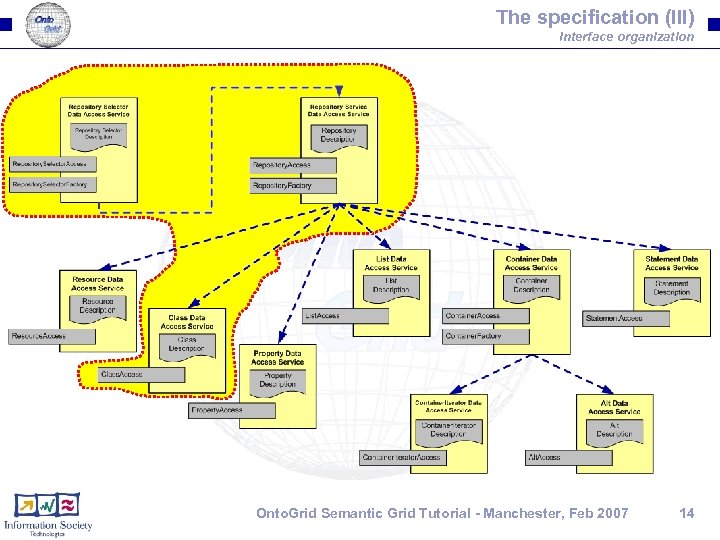
The specification (III) Interface organization Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 14
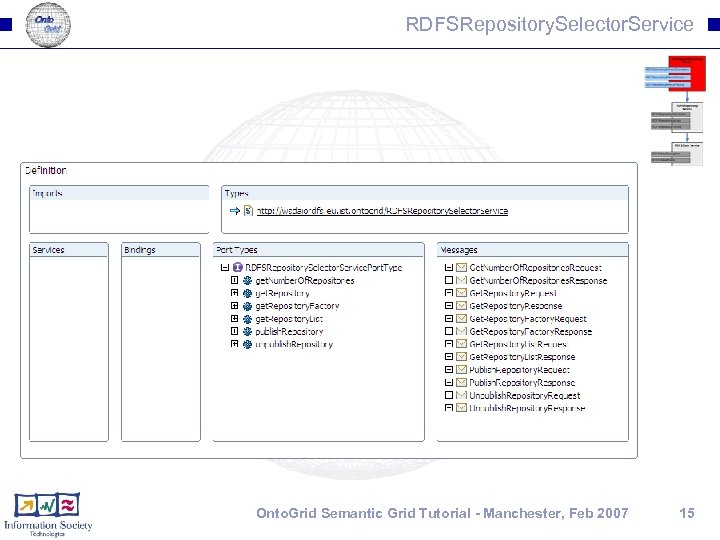
RDFSRepository. Selector. Service Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 15
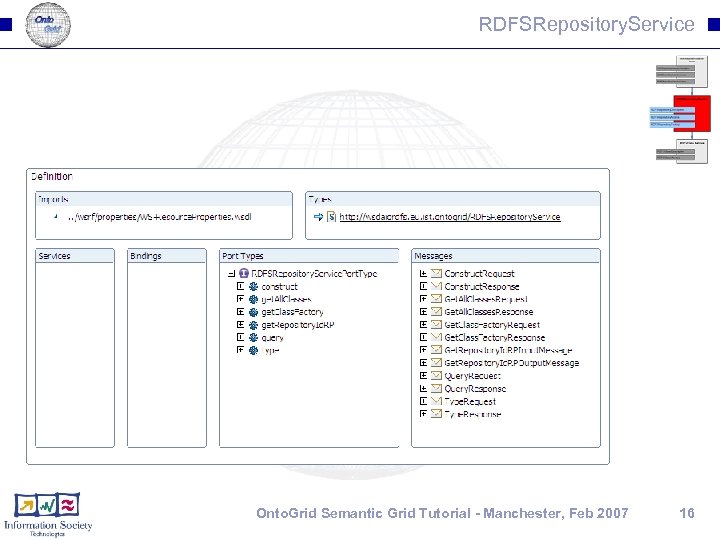
RDFSRepository. Service Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 16
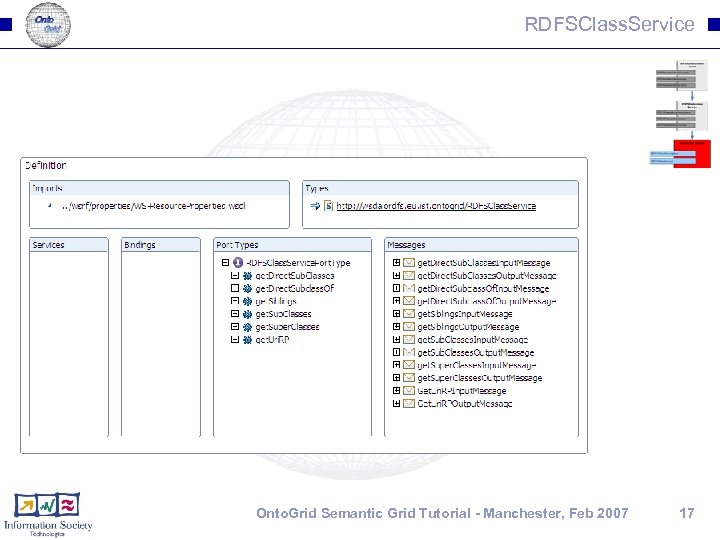
RDFSClass. Service Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 17
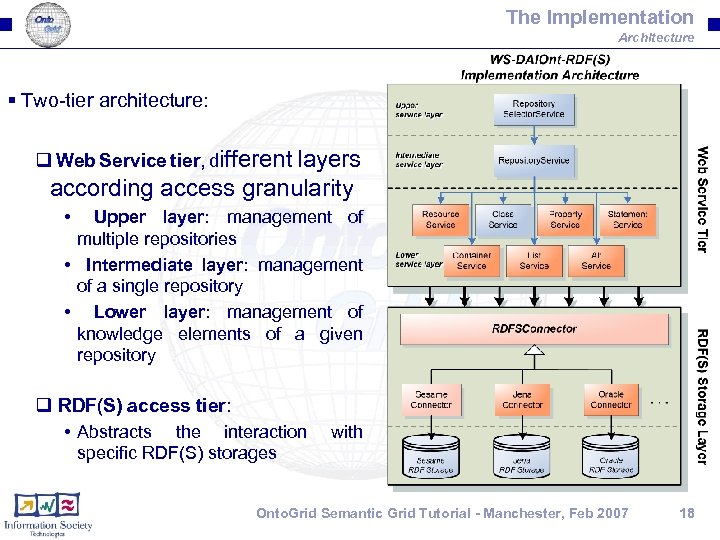
The Implementation Architecture § Two-tier architecture: q Web Service tier, different layers according access granularity • Upper layer: management of multiple repositories • Intermediate layer: management of a single repository • Lower layer: management of knowledge elements of a given repository q RDF(S) access tier: • Abstracts the interaction specific RDF(S) storages with Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 18

Part II: Hands-on exercises Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 19

Outline of the tutorial Hands-on exercises § Methodology § Introducing the players q The software distribution q The sample ontologies § Hands-on work lifecycle overview § Setting up the work environment q Pre-deployment configuration q Prototype services deployment q Post-deployment configuration § Using the services q The repository selector service q The repository service q The class service § Advanced use of the services § Cleaning up Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 20

Methodology § The software will be used in two ways: q Command line clients q Ad-hoc Java clients § The clients will be tested in a controlled scenario: q The scenario will be prepared as part of the practical • The resources will be configured • The services will be deployed in the container q When the practical ends, the alumni will clean up their computer • The services will be undeployed from the container § Two console windows will be necessary: q Client window q Container window Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 21

Setting up the work environment (I) Preparing the resources § Download the resources: q Software: already downloaded yesterday q Ontologies: http: //www. cs. man. ac. uk/~ocorcho/Onto. Grid/SGtutorial/software/backoffice. zip § Unpack the resources: q The directory where the software was unpacked to will be referred to as %DIST% q The directory where the ontologies will be unpacked to will be referred to as %BACKOFFICE% Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 22
Introducing the players (I) The software distribution § Software: § Structure: ws-daio-rdfs. v 0. 5. zip(sg-tutorial-install. zip) Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 23
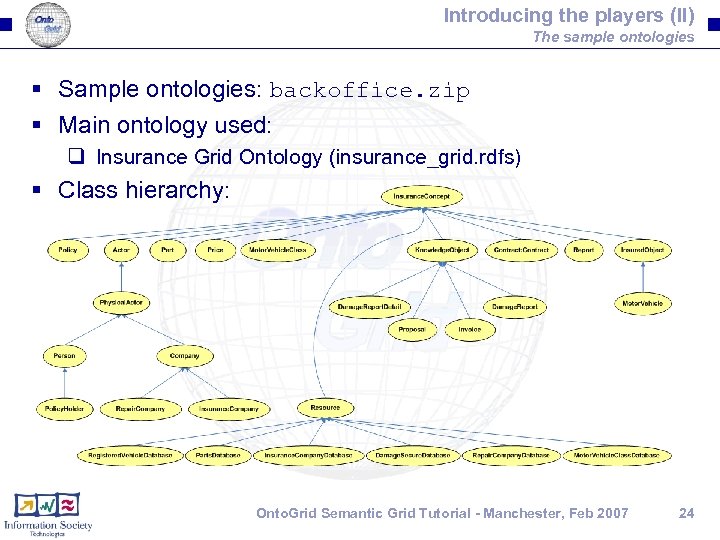
Introducing the players (II) The sample ontologies § Sample ontologies: backoffice. zip § Main ontology used: q Insurance Grid Ontology (insurance_grid. rdfs) § Class hierarchy: Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 24
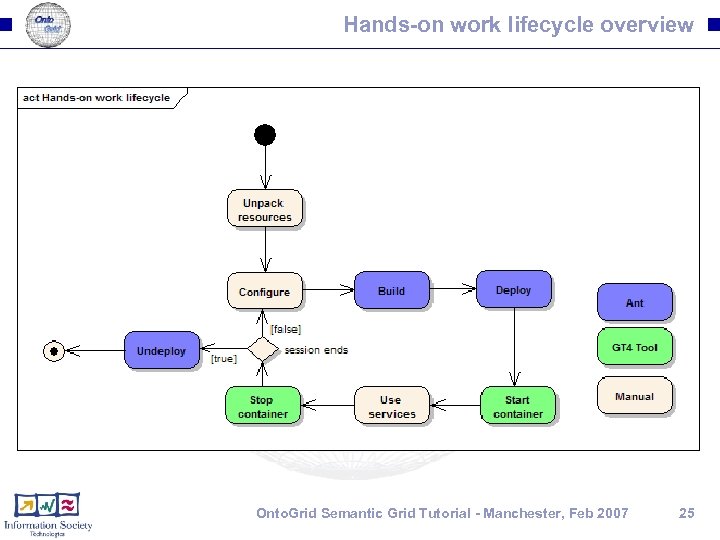
Hands-on work lifecycle overview Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 25
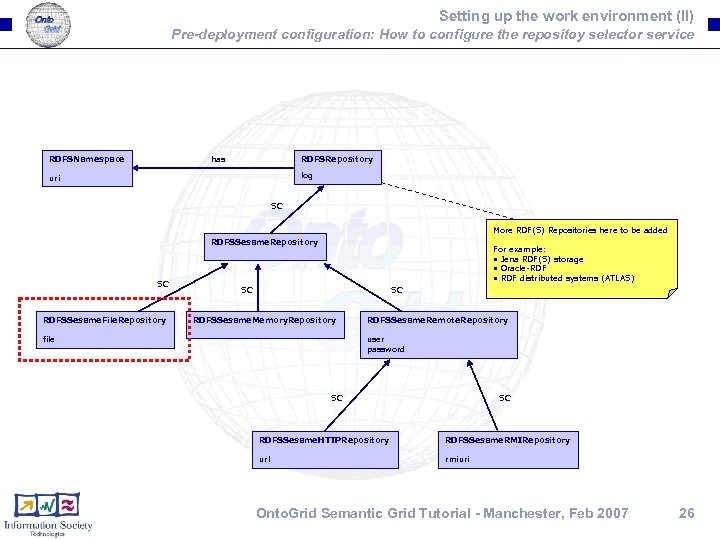
Setting up the work environment (II) Pre-deployment configuration: How to configure the repositoy selector service RDFSNamespace has RDFSRepository log uri SC More RDF(S) Repositories here to be added RDFSSesame. Repository SC RDFSSesame. File. Repository For example: • Jena RDF(S) storage • Oracle-RDF • RDF distributed systems (ATLAS) SC SC RDFSSesame. Memory. Repository file RDFSSesame. Remote. Repository user password SC SC RDFSSesame. HTTPRepository RDFSSesame. RMIRepository url rmiuri Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 26

Setting up the work environment (III) Pre-deployment configuration: How to configure the repositoy selector service(II) <? xml version="1. 0" encoding="WINDOWS-1252"? > <rdf: RDF xmlns: rdfs_repos="http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/RDFSRepository# " xmlns: rdf="http: //www. w 3. org/1999/02/22 -rdf-syntax-ns# " xmlns: rdfs="http: //www. w 3. org/2000/01/rdf-schema# "> <rdf: Description "http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/RDFSRepository#insurance_grid" rdf: about="http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/RDFSRepository#insurance_grid "> <rdfs: comment>The Insurance Grid Ontology </rdfs: comment> <rdfs: label>insurance_grid</rdfs: label> <rdfs_repos: has "http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/RDFSRepository#ig_ns" rdf: resource ="http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/RDFSRepository#ig_ns "/> D: /2 ndreview/backoffice/insurance_grid. rdfs <rdfs_repos: file>D: /2 ndreview/backoffice/insurance_grid. rdfs</ rdfs_repos: file> "http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/ <rdf: type rdf: resource="http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/ RDFSRepository#RDFSSesame. File. Repository "/> RDFSRepository#RDFSSesame. File. Repository" </rdf: Description> "http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/RDFSRepository#ig_ns" <rdf: Description rdf: about="http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/RDFSRepository#ig_ns "> <rdfs: comment>The Insurance Grid Ontology Namespace </rdfs: comment> <rdfs: label>ig_ns</rdfs: label> http: //www. insurancegrid. org/vocabulary# <rdfs_repos: uri>http: //www. insurancegrid. org/vocabulary# </rdfs_repos: uri> <rdf: type "http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/RDFSRepository#RDFSNamespace" rdf: resource ="http: //wsdaiordfs. eu. ist. ontogrid/RDFSRepository#RDFSNamespace "/> </rdf: Description> </rdf: RDF> Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 27

Setting up the work environment (III) Pre-deployment configuration: Configuring the repositories that are to be used (II) § Configure the repositories that will be managed by the selector service: (at least insurance_grid. rdfs) q Create a file named RDFSRepository. rdf in %DIST%/etc q Create a repository description for the default ontology that we will use: • • Name: insurance_grid File: insurance_grid. rdfs Log: <<any you want>> Namespace uri: http: //www. insurancegrid. org/vocabulary# q Include other repository descriptions for any extra repository that you want to use. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 28
Setting up the work environment (IV) Build § Build the prototype: > ant all Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 29
Setting up the work environment (V) Deploy § Deploy the services: > ant deploy Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 30

Setting up the work environment (VI) Running the container & further configuration § Starting the container (Container window) > globus-start-container -nosec § Post-deployment configuration (Client window) q Set up some helpful environment variables > set %SELECTOR%= http: //localhost: 8080/wsrf/services/WS-DAIO-RDFS/RDFSRepository. Selector. Service > set %REPOSITORY%= http: //localhost: 8080/wsrf/services/WS-DAIO-RDFS/RDFSRepository. Service > set %CLASS%= http: //localhost: 8080/wsrf/services/WS-DAIO-RDFS/RDFSClass. Service > set %NS%=http: //www. insurancegrid. org/vocabulary# q Set up GT 4 environment > globus-devel-env Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 31

Using the services (I) – The Repository Selector Service § Check out how many repositories are available > get-number-of-repositories -s %SELECTOR% There are n repositories available in the backoffice directory managed by the selector. § List the names of the available repositories > list-repositories -s %SELECTOR% The name of each of the repositories managed by the selector will be returned. § Retrieve an available repository > get-repository -s %SELECTOR% insurance_grid repository. rdfs The repository is retrieved and stored in the specified file in RDF/XML. § Load an available repository > load-repository -s %SELECTOR% insurance_grid The service returns the EPR of the repository service to which we have to contact in order to access to the specified repository. The EPR is serialized to a file that will be used in the following examples. It will be referred to as <EPR_REPOSITORY>. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 32
Using the services (II) – The Repository Service § List the available classes in the repository: > list-classes -e <EPR_REPOSITORY> The service returns all the available classes defined in the repository, plus those predefined by RDFS. § Load an available class from the repository: > load-class -e <EPR_REPOSITORY> %NS%#Company > load-class -e <EPR_REPOSITORY> %NS%#Physical. Actor The service returns the EPR of the class service to which we have to contact in order to access to the specified classes. The EPR to access to the Company class will be referred to as <EPR_CLASS_1>, and the EPR to access the Physical. Actor class will be referred to as <EPR_CLASS_2>. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 33
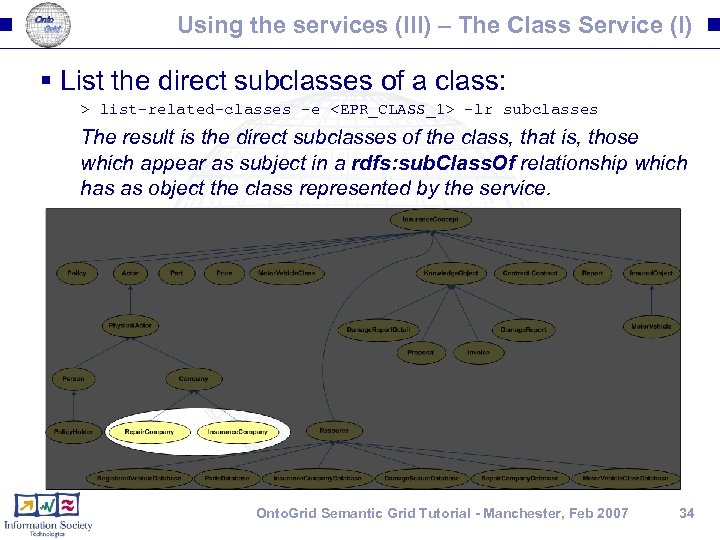
Using the services (III) – The Class Service (I) § List the direct subclasses of a class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_1> -lr subclasses The result is the direct subclasses of the class, that is, those which appear as subject in a rdfs: sub. Class. Of relationship which has as object the class represented by the service. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 34
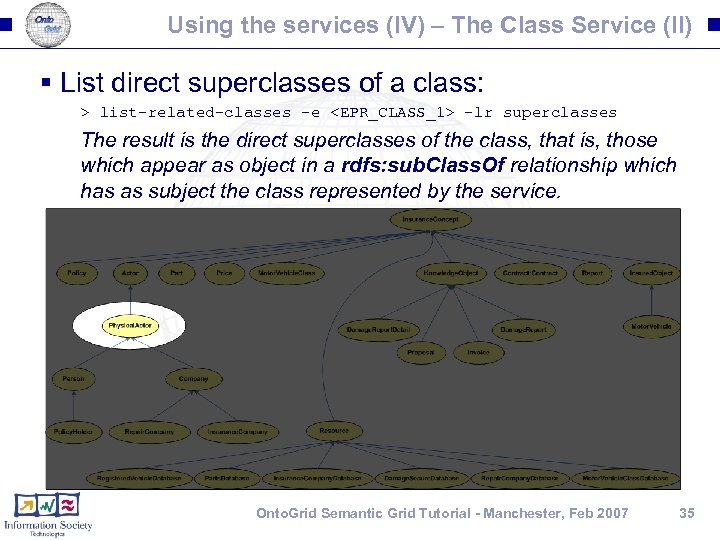
Using the services (IV) – The Class Service (II) § List direct superclasses of a class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_1> -lr superclasses The result is the direct superclasses of the class, that is, those which appear as object in a rdfs: sub. Class. Of relationship which has as subject the class represented by the service. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 35
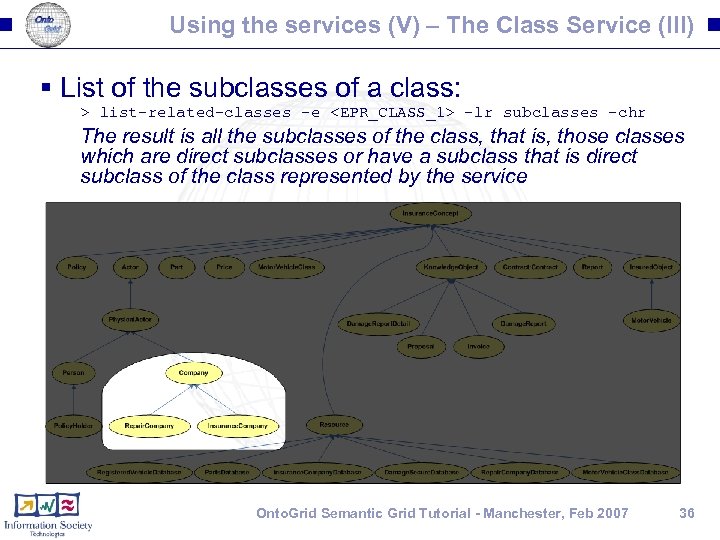
Using the services (V) – The Class Service (III) § List of the subclasses of a class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_1> -lr subclasses -chr The result is all the subclasses of the class, that is, those classes which are direct subclasses or have a subclass that is direct subclass of the class represented by the service Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 36
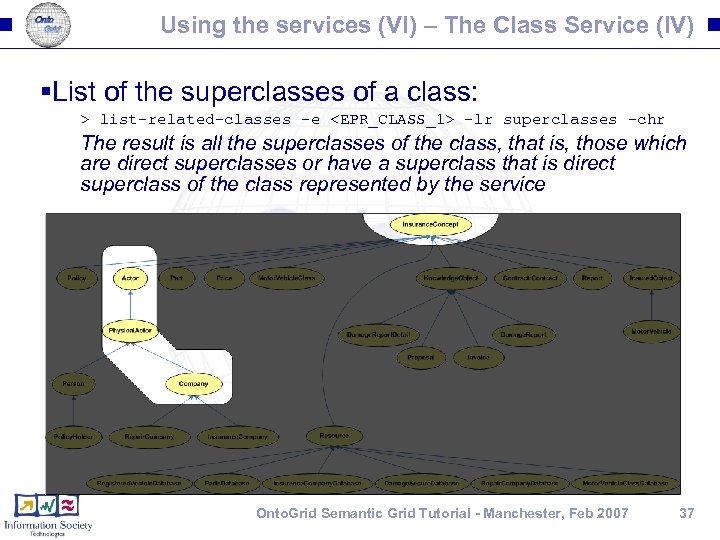
Using the services (VI) – The Class Service (IV) §List of the superclasses of a class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_1> -lr superclasses -chr The result is all the superclasses of the class, that is, those which are direct superclasses or have a superclass that is direct superclass of the class represented by the service Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 37
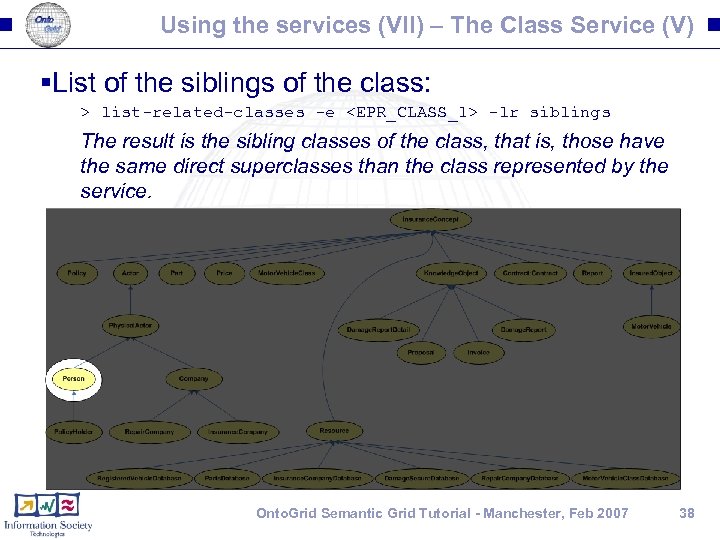
Using the services (VII) – The Class Service (V) §List of the siblings of the class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_1> -lr siblings The result is the sibling classes of the class, that is, those have the same direct superclasses than the class represented by the service. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 38
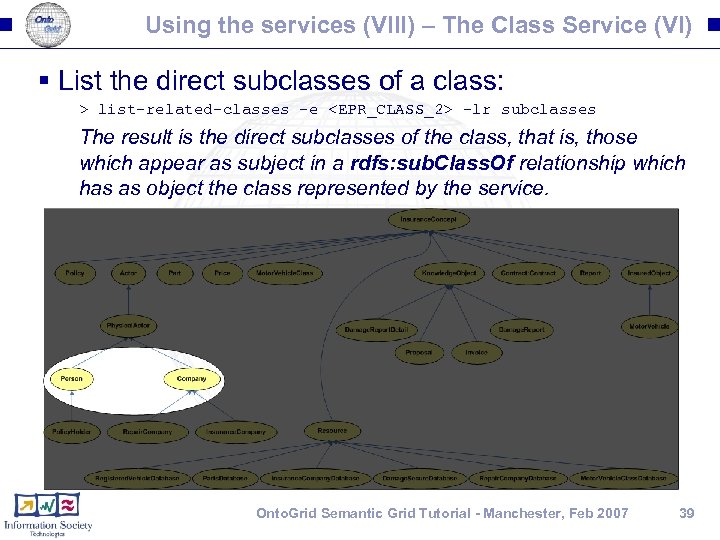
Using the services (VIII) – The Class Service (VI) § List the direct subclasses of a class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_2> -lr subclasses The result is the direct subclasses of the class, that is, those which appear as subject in a rdfs: sub. Class. Of relationship which has as object the class represented by the service. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 39
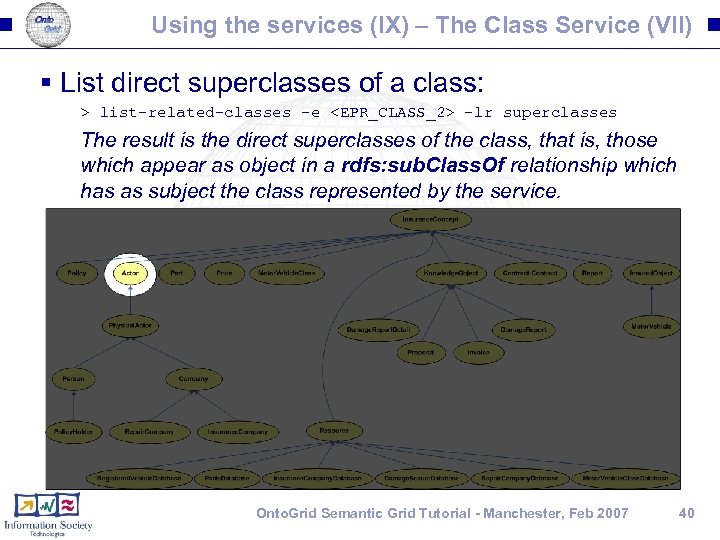
Using the services (IX) – The Class Service (VII) § List direct superclasses of a class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_2> -lr superclasses The result is the direct superclasses of the class, that is, those which appear as object in a rdfs: sub. Class. Of relationship which has as subject the class represented by the service. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 40
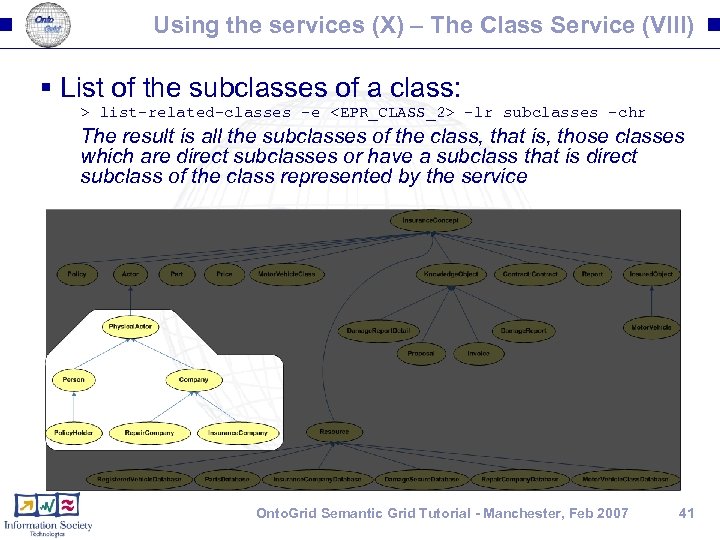
Using the services (X) – The Class Service (VIII) § List of the subclasses of a class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_2> -lr subclasses -chr The result is all the subclasses of the class, that is, those classes which are direct subclasses or have a subclass that is direct subclass of the class represented by the service Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 41
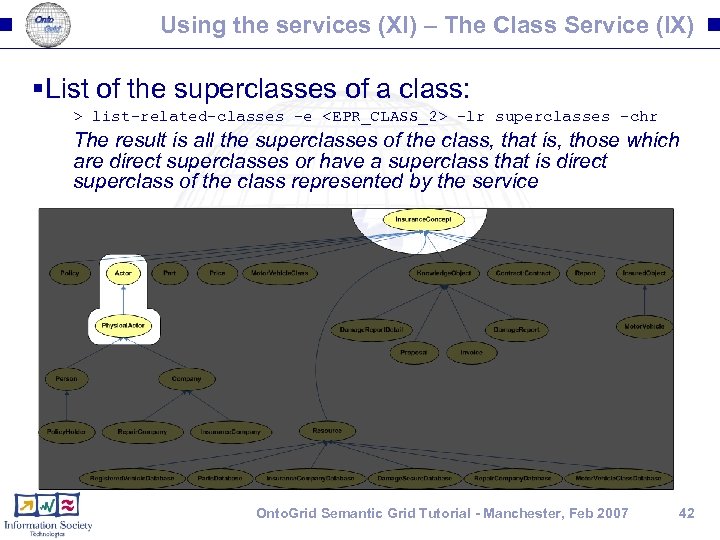
Using the services (XI) – The Class Service (IX) §List of the superclasses of a class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_2> -lr superclasses -chr The result is all the superclasses of the class, that is, those which are direct superclasses or have a superclass that is direct superclass of the class represented by the service Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 42
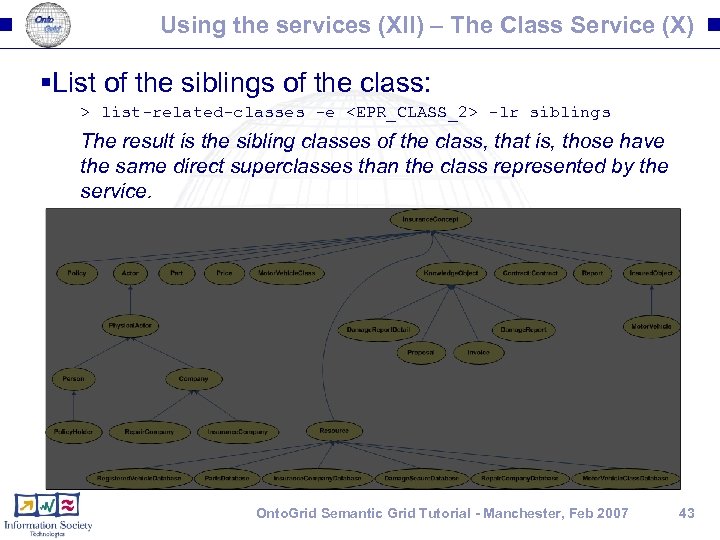
Using the services (XII) – The Class Service (X) §List of the siblings of the class: > list-related-classes -e <EPR_CLASS_2> -lr siblings The result is the sibling classes of the class, that is, those have the same direct superclasses than the class represented by the service. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 43
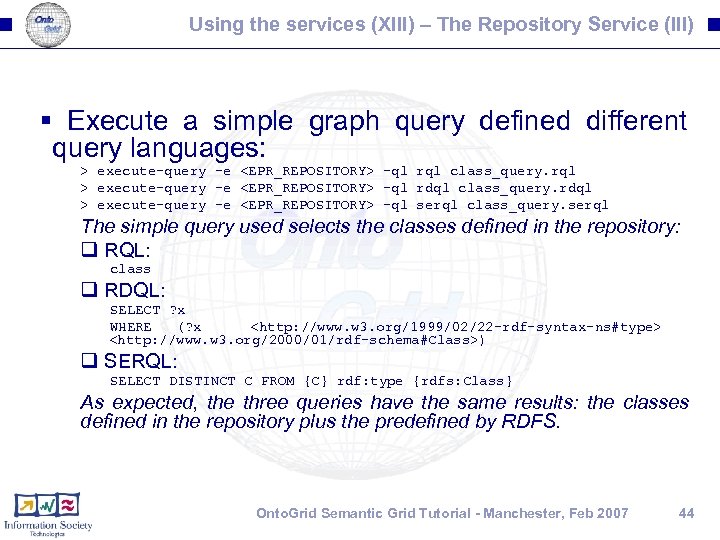
Using the services (XIII) – The Repository Service (III) § Execute a simple graph query defined different query languages: > execute-query -e <EPR_REPOSITORY> -ql rql class_query. rql > execute-query -e <EPR_REPOSITORY> -ql rdql class_query. rdql > execute-query -e <EPR_REPOSITORY> -ql serql class_query. serql The simple query used selects the classes defined in the repository: q RQL: class q RDQL: SELECT ? x WHERE (? x <http: //www. w 3. org/1999/02/22 -rdf-syntax-ns#type> <http: //www. w 3. org/2000/01/rdf-schema#Class>) q SERQL: SELECT DISTINCT C FROM {C} rdf: type {rdfs: Class} As expected, the three queries have the same results: the classes defined in the repository plus the predefined by RDFS. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 44
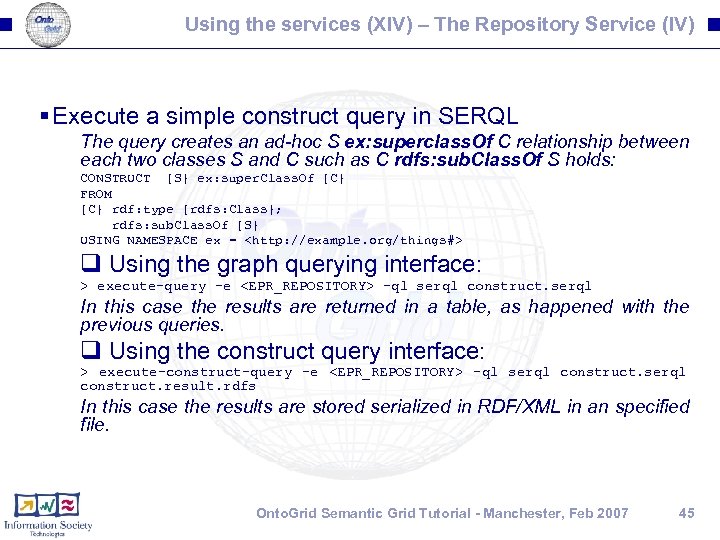
Using the services (XIV) – The Repository Service (IV) § Execute a simple construct query in SERQL The query creates an ad-hoc S ex: superclass. Of C relationship between each two classes S and C such as C rdfs: sub. Class. Of S holds: CONSTRUCT {S} ex: super. Class. Of {C} FROM {C} rdf: type {rdfs: Class}; rdfs: sub. Class. Of {S} USING NAMESPACE ex = <http: //example. org/things#> q Using the graph querying interface: > execute-query -e <EPR_REPOSITORY> -ql serql construct. serql In this case the results are returned in a table, as happened with the previous queries. q Using the construct query interface: > execute-construct-query -e <EPR_REPOSITORY> -ql serql construct. result. rdfs In this case the results are stored serialized in RDF/XML in an specified file. Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 45

Cleaning up § Before moving to the next session, clean the container : -D > cd %DIST% > ant undeploy Onto. Grid Semantic Grid Tutorial - Manchester, Feb 2007 46
5112d7da35fbbabfc04efbbe1774edbb.ppt