dd4209ac8a99018b3c82970d00a5dd2d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 + © Oncology Management Services, 2015
+ © Oncology Management Services, 2015
 + Part I. Oncology Patient-Centered Medical Home Overview
+ Part I. Oncology Patient-Centered Medical Home Overview
 + What is OPCMH©? • The Oncology Patient-Centered Medical Home is a model of healthcare delivery that empowers the physician-led care team and enables them to practice to the best of their abilities. • The goal of OPCMH is to standardize the science of medicine, so that care teams can practice the art of medicine—and thereby provide better healthcare to our patients. • The OPCMH model offers a significant value proposition to a wide-range of healthcare constituents and to society…
+ What is OPCMH©? • The Oncology Patient-Centered Medical Home is a model of healthcare delivery that empowers the physician-led care team and enables them to practice to the best of their abilities. • The goal of OPCMH is to standardize the science of medicine, so that care teams can practice the art of medicine—and thereby provide better healthcare to our patients. • The OPCMH model offers a significant value proposition to a wide-range of healthcare constituents and to society…
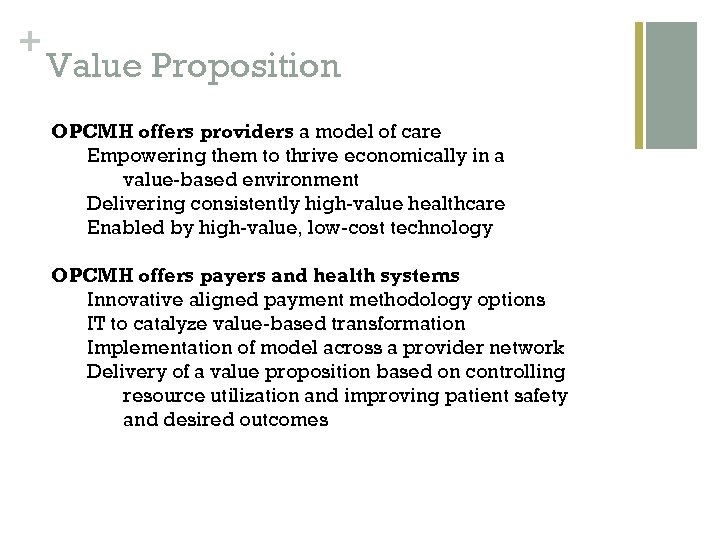 + Value Proposition OPCMH offers providers a model of care Empowering them to thrive economically in a value-based environment Delivering consistently high-value healthcare Enabled by high-value, low-cost technology OPCMH offers payers and health systems Innovative aligned payment methodology options IT to catalyze value-based transformation Implementation of model across a provider network Delivery of a value proposition based on controlling resource utilization and improving patient safety and desired outcomes
+ Value Proposition OPCMH offers providers a model of care Empowering them to thrive economically in a value-based environment Delivering consistently high-value healthcare Enabled by high-value, low-cost technology OPCMH offers payers and health systems Innovative aligned payment methodology options IT to catalyze value-based transformation Implementation of model across a provider network Delivery of a value proposition based on controlling resource utilization and improving patient safety and desired outcomes
 + Highlights of the Model n Reorganizes roles and responsibilities of the existing team n No need to recruit additional staff in most cases n n May not require extended hours n n OPCMH may require fewer staff members per physician OPCMH engages patients to report symptoms early and often— and it works Streamlines administrative & technical barriers in the care team work environment (authorization process, EMR functionality, documentation burdens, transcriptions costs, etc. )
+ Highlights of the Model n Reorganizes roles and responsibilities of the existing team n No need to recruit additional staff in most cases n n May not require extended hours n n OPCMH may require fewer staff members per physician OPCMH engages patients to report symptoms early and often— and it works Streamlines administrative & technical barriers in the care team work environment (authorization process, EMR functionality, documentation burdens, transcriptions costs, etc. )
 + Highlights of the Model n Patient and physician-centered n High-value patient care cannot be consistently delivered if the model of delivery does not seek to optimize the physician and care team workenvironment n Minimize clinically irrelevant physician activity n Top down value solutions (e. g. pathways programs, EMRs) often do not understand the physician and care-team work environment
+ Highlights of the Model n Patient and physician-centered n High-value patient care cannot be consistently delivered if the model of delivery does not seek to optimize the physician and care team workenvironment n Minimize clinically irrelevant physician activity n Top down value solutions (e. g. pathways programs, EMRs) often do not understand the physician and care-team work environment
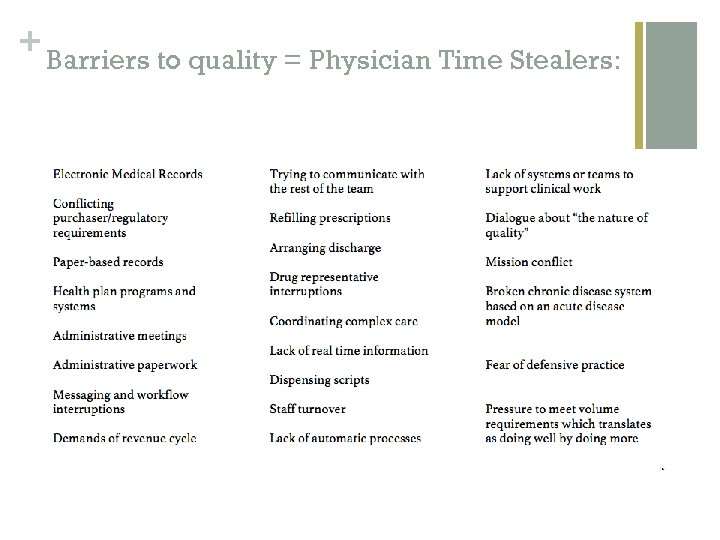 + Barriers to quality = Physician Time Stealers:
+ Barriers to quality = Physician Time Stealers:
 + Barriers to Cost Control n Drivers of cost = unnecessary resource utilization (waste) n Waste is driven by failures in: n Delivery n Coordination n Over-utilization n Pricing n Administrative Burden n Fraud Clinical Domain Administrative Domain
+ Barriers to Cost Control n Drivers of cost = unnecessary resource utilization (waste) n Waste is driven by failures in: n Delivery n Coordination n Over-utilization n Pricing n Administrative Burden n Fraud Clinical Domain Administrative Domain
 + OPCMH focuses first and foremost on standardizing the care team work environment.
+ OPCMH focuses first and foremost on standardizing the care team work environment.
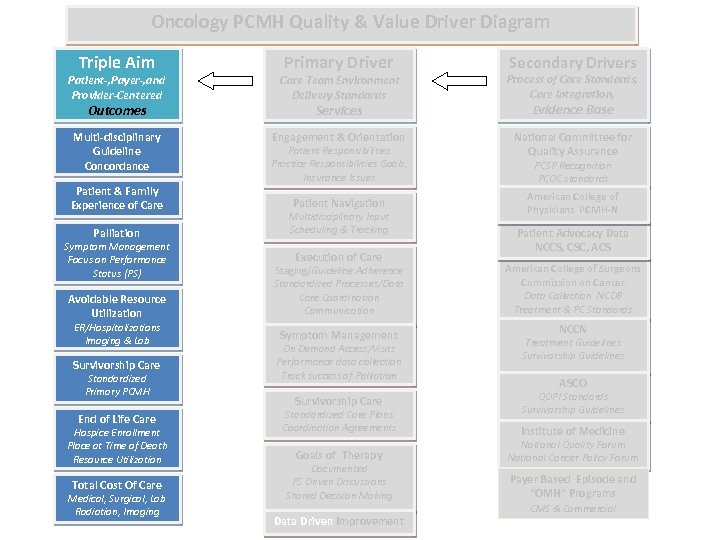
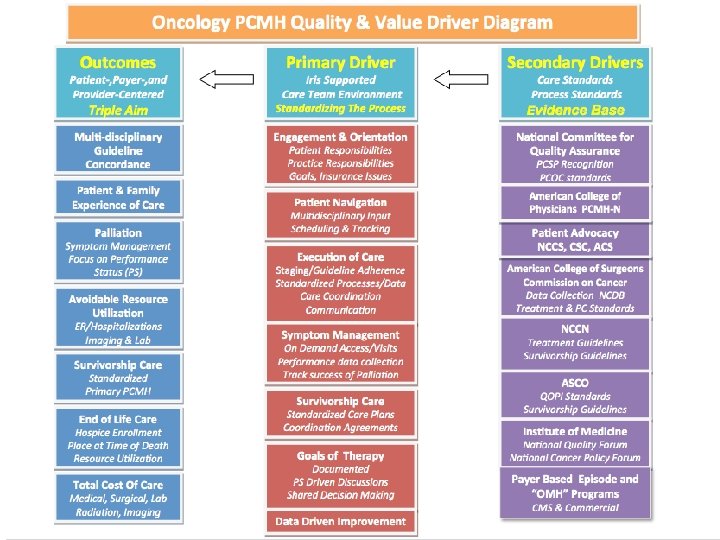
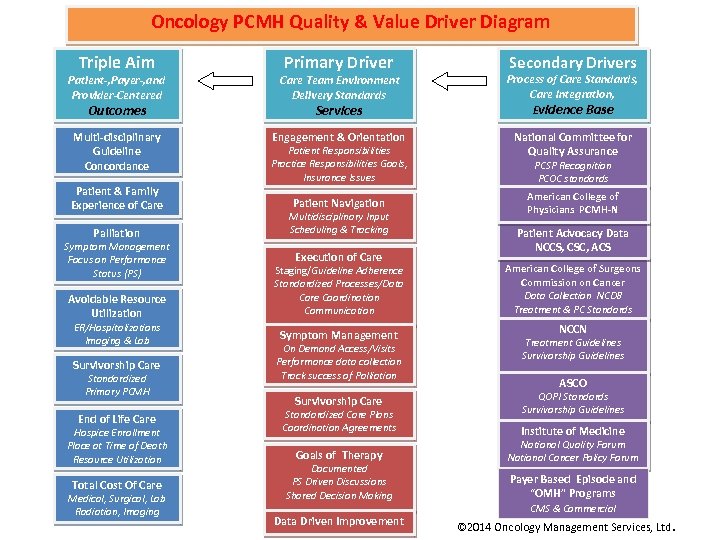 Oncology PCMH Quality & Value Driver Diagram Triple Aim Primary Driver Secondary Drivers Patient-, Payer-, and Provider-Centered Care Team Environment Delivery Standards Process of Care Standards, Care Integration, Evidence Base Multi-disciplinary Guideline Concordance Engagement & Orientation National Committee for Quality Assurance Outcomes Patient & Family Experience of Care Services Patient Responsibilities Practice Responsibilities Goals, Insurance Issues Patient Navigation Palliation Multidisciplinary Input Scheduling & Tracking Avoidable Resource Utilization Staging/Guideline Adherence Standardized Processes/Data Care Coordination Communication Symptom Management Focus on Performance Status (PS) ER/Hospitalizations Imaging & Lab Survivorship Care Standardized Primary PCMH End of Life Care Hospice Enrollment Place at Time of Death Resource Utilization Total Cost Of Care Medical, Surgical, Lab Radiation, Imaging Execution of Care Symptom Management On Demand Access/Visits Performance data collection Track success of Palliation Survivorship Care Standardized Care Plans Coordination Agreements Goals of Therapy Documented PS Driven Discussions Shared Decision Making Data Driven Improvement PCSP Recognition PCOC standards American College of Physicians PCMH-N Patient Advocacy Data NCCS, CSC, ACS American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Data Collection NCDB Treatment & PC Standards NCCN Treatment Guidelines Survivorship Guidelines ASCO QOPI Standards Survivorship Guidelines Institute of Medicine National Quality Forum National Cancer Policy Forum Payer Based Episode and “OMH” Programs CMS & Commercial © 2014 Oncology Management Services, Ltd.
Oncology PCMH Quality & Value Driver Diagram Triple Aim Primary Driver Secondary Drivers Patient-, Payer-, and Provider-Centered Care Team Environment Delivery Standards Process of Care Standards, Care Integration, Evidence Base Multi-disciplinary Guideline Concordance Engagement & Orientation National Committee for Quality Assurance Outcomes Patient & Family Experience of Care Services Patient Responsibilities Practice Responsibilities Goals, Insurance Issues Patient Navigation Palliation Multidisciplinary Input Scheduling & Tracking Avoidable Resource Utilization Staging/Guideline Adherence Standardized Processes/Data Care Coordination Communication Symptom Management Focus on Performance Status (PS) ER/Hospitalizations Imaging & Lab Survivorship Care Standardized Primary PCMH End of Life Care Hospice Enrollment Place at Time of Death Resource Utilization Total Cost Of Care Medical, Surgical, Lab Radiation, Imaging Execution of Care Symptom Management On Demand Access/Visits Performance data collection Track success of Palliation Survivorship Care Standardized Care Plans Coordination Agreements Goals of Therapy Documented PS Driven Discussions Shared Decision Making Data Driven Improvement PCSP Recognition PCOC standards American College of Physicians PCMH-N Patient Advocacy Data NCCS, CSC, ACS American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Data Collection NCDB Treatment & PC Standards NCCN Treatment Guidelines Survivorship Guidelines ASCO QOPI Standards Survivorship Guidelines Institute of Medicine National Quality Forum National Cancer Policy Forum Payer Based Episode and “OMH” Programs CMS & Commercial © 2014 Oncology Management Services, Ltd.
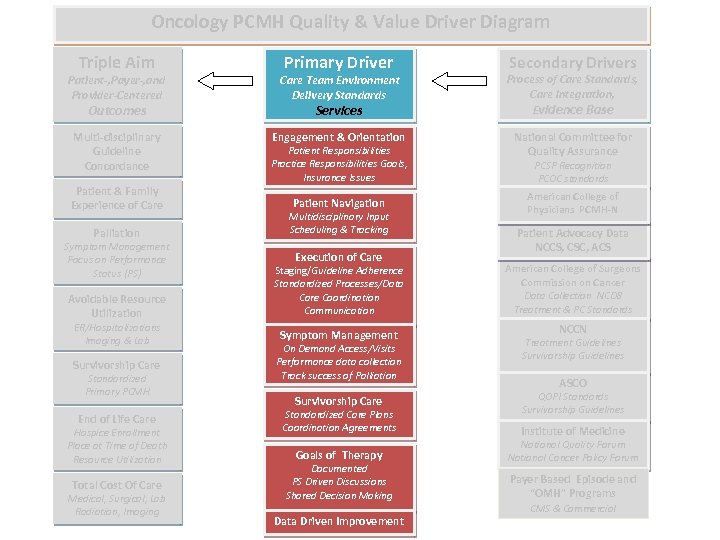 Oncology PCMH Quality & Value Driver Diagram Triple Aim Primary Driver Secondary Drivers Patient-, Payer-, and Provider-Centered Care Team Environment Delivery Standards Process of Care Standards, Care Integration, Evidence Base Multi-disciplinary Guideline Concordance Engagement & Orientation National Committee for Quality Assurance Outcomes Patient & Family Experience of Care Services Patient Responsibilities Practice Responsibilities Goals, Insurance Issues Patient Navigation Palliation Multidisciplinary Input Scheduling & Tracking Avoidable Resource Utilization Staging/Guideline Adherence Standardized Processes/Data Care Coordination Communication Symptom Management Focus on Performance Status (PS) ER/Hospitalizations Imaging & Lab Survivorship Care Standardized Primary PCMH End of Life Care Hospice Enrollment Place at Time of Death Resource Utilization Total Cost Of Care Medical, Surgical, Lab Radiation, Imaging Execution of Care Symptom Management On Demand Access/Visits Performance data collection Track success of Palliation Survivorship Care Standardized Care Plans Coordination Agreements Goals of Therapy Documented PS Driven Discussions Shared Decision Making Data Driven Improvement PCSP Recognition PCOC standards American College of Physicians PCMH-N Patient Advocacy Data NCCS, CSC, ACS American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Data Collection NCDB Treatment & PC Standards NCCN Treatment Guidelines Survivorship Guidelines ASCO QOPI Standards Survivorship Guidelines Institute of Medicine National Quality Forum National Cancer Policy Forum Payer Based Episode and “OMH” Programs CMS & Commercial
Oncology PCMH Quality & Value Driver Diagram Triple Aim Primary Driver Secondary Drivers Patient-, Payer-, and Provider-Centered Care Team Environment Delivery Standards Process of Care Standards, Care Integration, Evidence Base Multi-disciplinary Guideline Concordance Engagement & Orientation National Committee for Quality Assurance Outcomes Patient & Family Experience of Care Services Patient Responsibilities Practice Responsibilities Goals, Insurance Issues Patient Navigation Palliation Multidisciplinary Input Scheduling & Tracking Avoidable Resource Utilization Staging/Guideline Adherence Standardized Processes/Data Care Coordination Communication Symptom Management Focus on Performance Status (PS) ER/Hospitalizations Imaging & Lab Survivorship Care Standardized Primary PCMH End of Life Care Hospice Enrollment Place at Time of Death Resource Utilization Total Cost Of Care Medical, Surgical, Lab Radiation, Imaging Execution of Care Symptom Management On Demand Access/Visits Performance data collection Track success of Palliation Survivorship Care Standardized Care Plans Coordination Agreements Goals of Therapy Documented PS Driven Discussions Shared Decision Making Data Driven Improvement PCSP Recognition PCOC standards American College of Physicians PCMH-N Patient Advocacy Data NCCS, CSC, ACS American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Data Collection NCDB Treatment & PC Standards NCCN Treatment Guidelines Survivorship Guidelines ASCO QOPI Standards Survivorship Guidelines Institute of Medicine National Quality Forum National Cancer Policy Forum Payer Based Episode and “OMH” Programs CMS & Commercial
 Oncology PCMH Quality & Value Driver Diagram Triple Aim Primary Driver Secondary Drivers Patient-, Payer-, and Provider-Centered Care Team Environment Delivery Standards Process of Care Standards, Care Integration, Evidence Base Multi-disciplinary Guideline Concordance Engagement & Orientation National Committee for Quality Assurance Outcomes Patient & Family Experience of Care Services Patient Responsibilities Practice Responsibilities Goals, Insurance Issues Patient Navigation Palliation Multidisciplinary Input Scheduling & Tracking Avoidable Resource Utilization Staging/Guideline Adherence Standardized Processes/Data Care Coordination Communication Symptom Management Focus on Performance Status (PS) ER/Hospitalizations Imaging & Lab Survivorship Care Standardized Primary PCMH End of Life Care Hospice Enrollment Place at Time of Death Resource Utilization Total Cost Of Care Medical, Surgical, Lab Radiation, Imaging Execution of Care Symptom Management On Demand Access/Visits Performance data collection Track success of Palliation Survivorship Care Standardized Care Plans Coordination Agreements Goals of Therapy Documented PS Driven Discussions Shared Decision Making Data Driven Improvement PCSP Recognition PCOC standards American College of Physicians PCMH-N Patient Advocacy Data NCCS, CSC, ACS American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Data Collection NCDB Treatment & PC Standards NCCN Treatment Guidelines Survivorship Guidelines ASCO QOPI Standards Survivorship Guidelines Institute of Medicine National Quality Forum National Cancer Policy Forum Payer Based Episode and “OMH” Programs CMS & Commercial
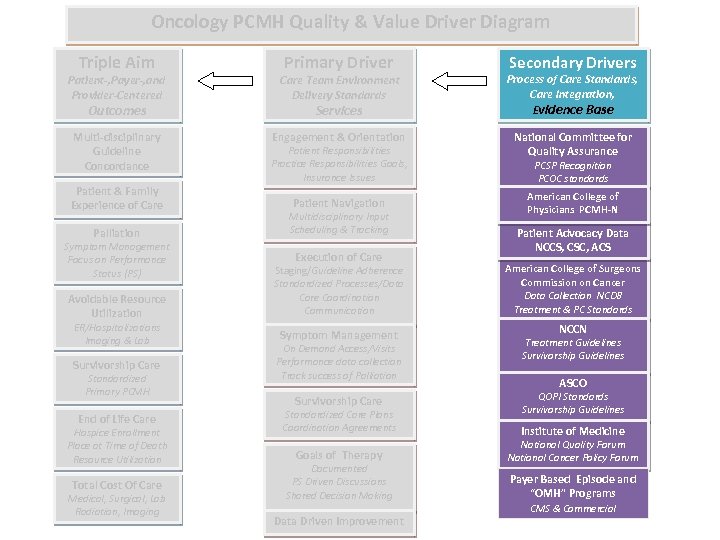
Oncology PCMH Quality & Value Driver Diagram Triple Aim Primary Driver Secondary Drivers Patient-, Payer-, and Provider-Centered Care Team Environment Delivery Standards Process of Care Standards, Care Integration, Evidence Base Multi-disciplinary Guideline Concordance Engagement & Orientation National Committee for Quality Assurance Outcomes Patient & Family Experience of Care Services Patient Responsibilities Practice Responsibilities Goals, Insurance Issues Patient Navigation Palliation Multidisciplinary Input Scheduling & Tracking Avoidable Resource Utilization Staging/Guideline Adherence Standardized Processes/Data Care Coordination Communication Symptom Management Focus on Performance Status (PS) ER/Hospitalizations Imaging & Lab Survivorship Care Standardized Primary PCMH End of Life Care Hospice Enrollment Place at Time of Death Resource Utilization Total Cost Of Care Medical, Surgical, Lab Radiation, Imaging Execution of Care Symptom Management On Demand Access/Visits Performance data collection Track success of Palliation Survivorship Care Standardized Care Plans Coordination Agreements Goals of Therapy Documented PS Driven Discussions Shared Decision Making Data Driven Improvement PCSP Recognition PCOC standards American College of Physicians PCMH-N Patient Advocacy Data NCCS, CSC, ACS American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Data Collection NCDB Treatment & PC Standards NCCN Treatment Guidelines Survivorship Guidelines ASCO QOPI Standards Survivorship Guidelines Institute of Medicine National Quality Forum National Cancer Policy Forum Payer Based Episode and “OMH” Programs CMS & Commercial
 Oncology PCMH Quality & Value Driver Diagram Triple Aim Primary Driver Secondary Drivers Patient-, Payer-, and Provider-Centered Care Team Environment Delivery Standards Process of Care Standards, Care Integration, Evidence Base Multi-disciplinary Guideline Concordance Engagement & Orientation National Committee for Quality Assurance Outcomes Patient & Family Experience of Care Services Patient Responsibilities Practice Responsibilities Goals, Insurance Issues Patient Navigation Palliation Multidisciplinary Input Scheduling & Tracking Avoidable Resource Utilization Staging/Guideline Adherence Standardized Processes/Data Care Coordination Communication Symptom Management Focus on Performance Status (PS) ER/Hospitalizations Imaging & Lab Survivorship Care Standardized Primary PCMH End of Life Care Hospice Enrollment Place at Time of Death Resource Utilization Total Cost Of Care Medical, Surgical, Lab Radiation, Imaging Execution of Care Symptom Management On Demand Access/Visits Performance data collection Track success of Palliation Survivorship Care Standardized Care Plans Coordination Agreements Goals of Therapy Documented PS Driven Discussions Shared Decision Making Data Driven Improvement PCSP Recognition PCOC standards American College of Physicians PCMH-N Patient Advocacy Data NCCS, CSC, ACS American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Data Collection NCDB Treatment & PC Standards NCCN Treatment Guidelines Survivorship Guidelines ASCO QOPI Standards Survivorship Guidelines Institute of Medicine National Quality Forum National Cancer Policy Forum Payer Based Episode and “OMH” Programs CMS & Commercial
Oncology PCMH Quality & Value Driver Diagram Triple Aim Primary Driver Secondary Drivers Patient-, Payer-, and Provider-Centered Care Team Environment Delivery Standards Process of Care Standards, Care Integration, Evidence Base Multi-disciplinary Guideline Concordance Engagement & Orientation National Committee for Quality Assurance Outcomes Patient & Family Experience of Care Services Patient Responsibilities Practice Responsibilities Goals, Insurance Issues Patient Navigation Palliation Multidisciplinary Input Scheduling & Tracking Avoidable Resource Utilization Staging/Guideline Adherence Standardized Processes/Data Care Coordination Communication Symptom Management Focus on Performance Status (PS) ER/Hospitalizations Imaging & Lab Survivorship Care Standardized Primary PCMH End of Life Care Hospice Enrollment Place at Time of Death Resource Utilization Total Cost Of Care Medical, Surgical, Lab Radiation, Imaging Execution of Care Symptom Management On Demand Access/Visits Performance data collection Track success of Palliation Survivorship Care Standardized Care Plans Coordination Agreements Goals of Therapy Documented PS Driven Discussions Shared Decision Making Data Driven Improvement PCSP Recognition PCOC standards American College of Physicians PCMH-N Patient Advocacy Data NCCS, CSC, ACS American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Data Collection NCDB Treatment & PC Standards NCCN Treatment Guidelines Survivorship Guidelines ASCO QOPI Standards Survivorship Guidelines Institute of Medicine National Quality Forum National Cancer Policy Forum Payer Based Episode and “OMH” Programs CMS & Commercial
 + Part II: The Prototype OPCMH Consultants in Medical Oncology & Hematology (CMOH)
+ Part II: The Prototype OPCMH Consultants in Medical Oncology & Hematology (CMOH)
 + Increased Productivity & Decreased Overhead: 2013: 8. 8 physicians, 3 service locations Support staff to fulltime physician ratio 5. 6 (2007 baseline 8. 3) Business Enhancement: Enhanced FFS, PMPM, shared savings, precertification relief Improved documentation, coding, coordination Improved physician efficiency, productivity, QOL New referral patterns Development of Alternate Payment Models: APM contracts (IBC, Keystone First) Covering 48% of practice patient base Performance benchmarked against the market
+ Increased Productivity & Decreased Overhead: 2013: 8. 8 physicians, 3 service locations Support staff to fulltime physician ratio 5. 6 (2007 baseline 8. 3) Business Enhancement: Enhanced FFS, PMPM, shared savings, precertification relief Improved documentation, coding, coordination Improved physician efficiency, productivity, QOL New referral patterns Development of Alternate Payment Models: APM contracts (IBC, Keystone First) Covering 48% of practice patient base Performance benchmarked against the market
 + Projected % Reduction in Cancer Care Cost 1 -3 4 -6. 3 0. 6 -1. 1 0. 1 -. 4 0. 9 -1. 9 Chemotherapy pathways program Inpatient hospitalizations (5 -25% reduction) ER evaluations (20 -40%) Diagnostics End-of-life care coordination Total 6. 6 – 12. 7 % reduction Annual cancer “spend” $125 B = $8 -16 B savings Adapted from international consultants evaluation of OPCMHTM application to cancer care
+ Projected % Reduction in Cancer Care Cost 1 -3 4 -6. 3 0. 6 -1. 1 0. 1 -. 4 0. 9 -1. 9 Chemotherapy pathways program Inpatient hospitalizations (5 -25% reduction) ER evaluations (20 -40%) Diagnostics End-of-life care coordination Total 6. 6 – 12. 7 % reduction Annual cancer “spend” $125 B = $8 -16 B savings Adapted from international consultants evaluation of OPCMHTM application to cancer care
 Traction PCORI funded Oncology Project (SEPA) NCQA, OMS, ASCO, RAND, NCCS, IBC CMS Oncology Payment Reform TEP MITRE, Brookings, RAND, CMS, CMMI Oncology Bundled Payment Consortium CAP, CMS, CMMI, multiple payers ASCO Payment Reform Initiative OMS CMOH Alternate Payment Methods SEPA IBC, Keystone First, (48% of patients)
Traction PCORI funded Oncology Project (SEPA) NCQA, OMS, ASCO, RAND, NCCS, IBC CMS Oncology Payment Reform TEP MITRE, Brookings, RAND, CMS, CMMI Oncology Bundled Payment Consortium CAP, CMS, CMMI, multiple payers ASCO Payment Reform Initiative OMS CMOH Alternate Payment Methods SEPA IBC, Keystone First, (48% of patients)
 Not for redistribution. © 2014 Oncology Management Services, Consultants in Medical Oncology &
Not for redistribution. © 2014 Oncology Management Services, Consultants in Medical Oncology &
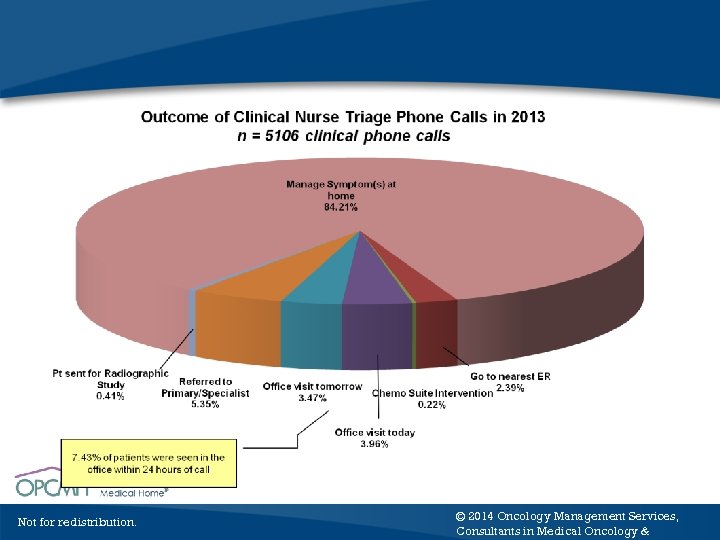
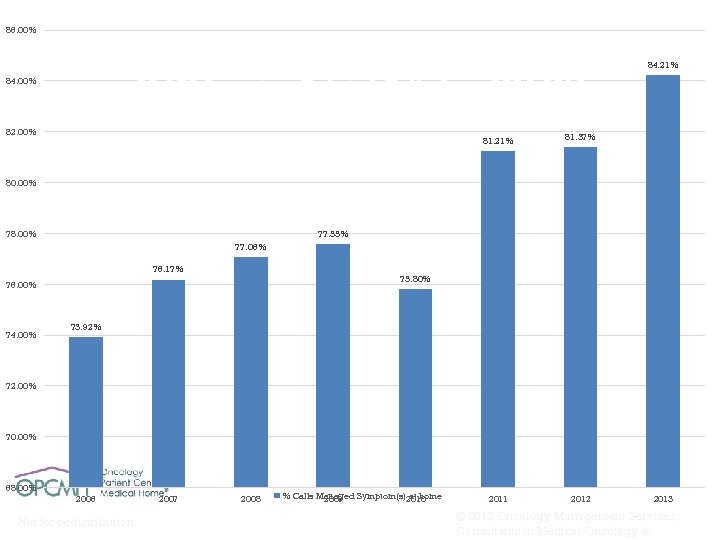 86. 00% % of Clinical Calls to Nurse Triage Line That Were Managed at Home 28, 179 Symptom Related Calls from 2006 -2013 84. 00% 82. 00% 81. 21% 81. 37% 2011 2012 84. 21% 80. 00% 78. 00% 77. 55% 77. 06% 76. 17% 75. 80% 76. 00% 74. 00% 73. 92% 72. 00% 70. 00% 68. 00% 2006 Not for redistribution. 2007 2008 % Calls Managed Symptom(s)2010 at home 2009 2013 © 2013 Oncology Management Services, Consultants in Medical Oncology &
86. 00% % of Clinical Calls to Nurse Triage Line That Were Managed at Home 28, 179 Symptom Related Calls from 2006 -2013 84. 00% 82. 00% 81. 21% 81. 37% 2011 2012 84. 21% 80. 00% 78. 00% 77. 55% 77. 06% 76. 17% 75. 80% 76. 00% 74. 00% 73. 92% 72. 00% 70. 00% 68. 00% 2006 Not for redistribution. 2007 2008 % Calls Managed Symptom(s)2010 at home 2009 2013 © 2013 Oncology Management Services, Consultants in Medical Oncology &
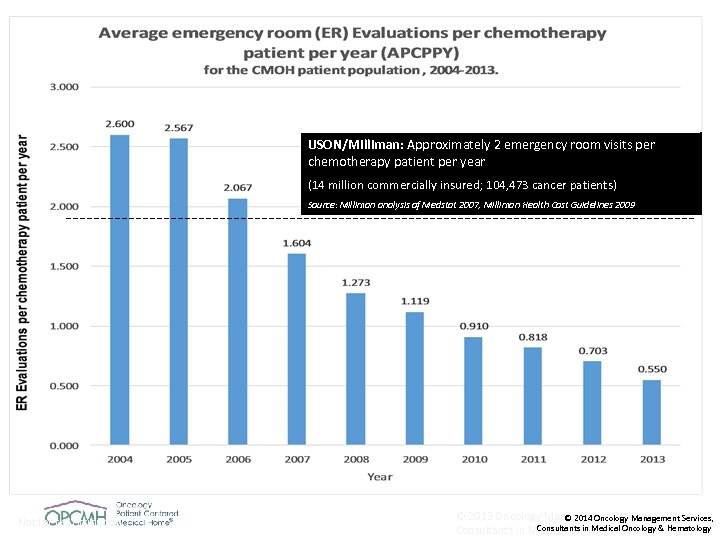 USON/Milliman: Approximately 2 emergency room visits per chemotherapy patient per year (14 million commercially insured; 104, 473 cancer patients) Source: Milliman analysis of Medstat 2007, Milliman Health Cost Guidelines 2009 Not for redistribution. © 2013 Oncology Management Services, © 2014 Oncology Management Services, Consultants in Medical Oncology & Hematology
USON/Milliman: Approximately 2 emergency room visits per chemotherapy patient per year (14 million commercially insured; 104, 473 cancer patients) Source: Milliman analysis of Medstat 2007, Milliman Health Cost Guidelines 2009 Not for redistribution. © 2013 Oncology Management Services, © 2014 Oncology Management Services, Consultants in Medical Oncology & Hematology
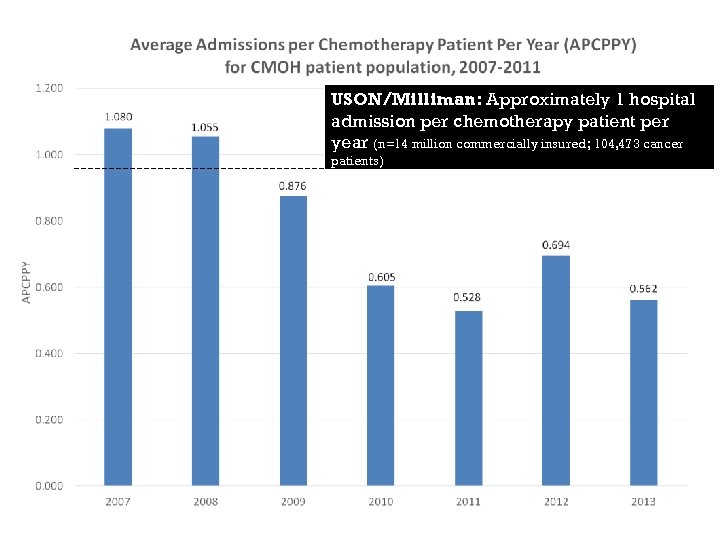 USON/Milliman: Approximately 1 hospital admission per chemotherapy patient per year (n=14 million commercially insured; 104, 473 cancer patients) Source: Milliman analysis of Medstat 2007, Milliman Health Cost Guidelines 2009
USON/Milliman: Approximately 1 hospital admission per chemotherapy patient per year (n=14 million commercially insured; 104, 473 cancer patients) Source: Milliman analysis of Medstat 2007, Milliman Health Cost Guidelines 2009
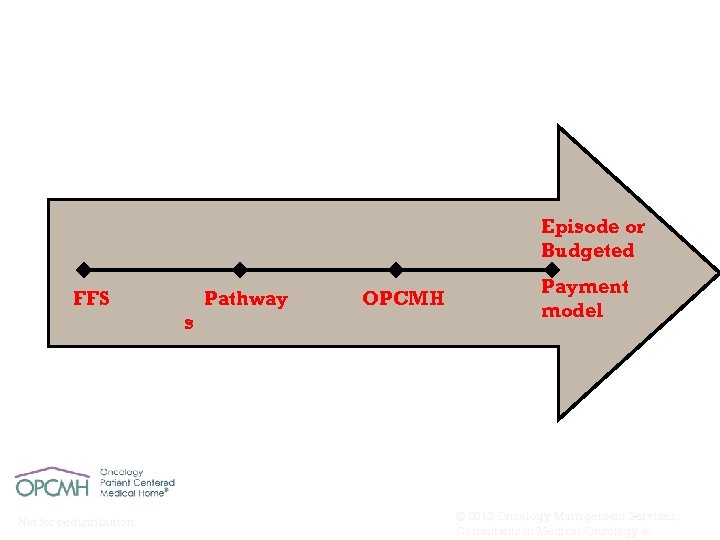 Provider Ability & Accountability Payment Reform for cancer care Episode or Budgeted FFS Pathway s Not for redistribution. OPCMH Payment model © 2013 Oncology Management Services, Consultants in Medical Oncology &
Provider Ability & Accountability Payment Reform for cancer care Episode or Budgeted FFS Pathway s Not for redistribution. OPCMH Payment model © 2013 Oncology Management Services, Consultants in Medical Oncology &
 Part III. Scaling the Model Oncology Management Services
Part III. Scaling the Model Oncology Management Services
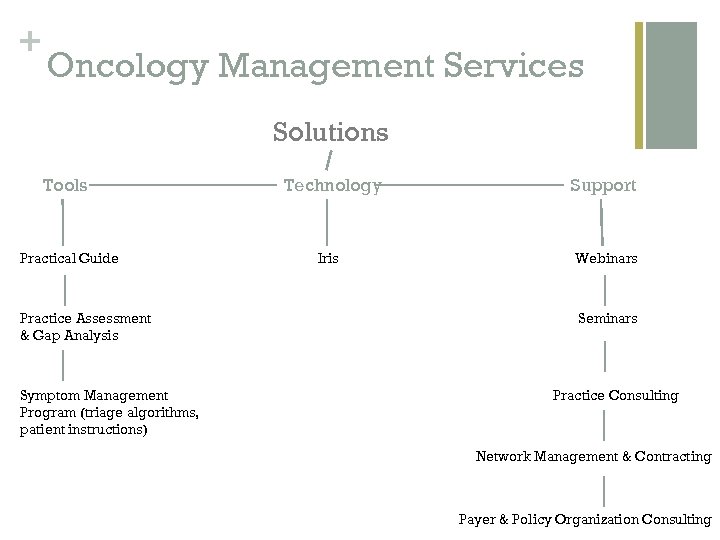 + Oncology Management Services Solutions Tools Practical Guide Practice Assessment & Gap Analysis Symptom Management Program (triage algorithms, patient instructions) Technology Iris Support Webinars Seminars Practice Consulting Network Management & Contracting Payer & Policy Organization Consulting
+ Oncology Management Services Solutions Tools Practical Guide Practice Assessment & Gap Analysis Symptom Management Program (triage algorithms, patient instructions) Technology Iris Support Webinars Seminars Practice Consulting Network Management & Contracting Payer & Policy Organization Consulting
 + Iris™: The OPCMH Enabling Technology n Point-of-care, physician-centric software that minimizes the barriers physicians and care teams face in providing value-based healthcare. Iris is the tool that enables successful OPCMH transformation. n Iris enhances the OPCMH model of care by guiding and facilitating workflow, minimizing clinically irrelevant activities, while collecting and reporting clinically actionable data in real-time at the point of care. n Iris compliments EMR functionality. EMRs commonly provide a detailed roadmap of how to impede value-based healthcare delivery. Iris minimizes each of these barriers and enables seamless transformation.
+ Iris™: The OPCMH Enabling Technology n Point-of-care, physician-centric software that minimizes the barriers physicians and care teams face in providing value-based healthcare. Iris is the tool that enables successful OPCMH transformation. n Iris enhances the OPCMH model of care by guiding and facilitating workflow, minimizing clinically irrelevant activities, while collecting and reporting clinically actionable data in real-time at the point of care. n Iris compliments EMR functionality. EMRs commonly provide a detailed roadmap of how to impede value-based healthcare delivery. Iris minimizes each of these barriers and enables seamless transformation.
 + Iris™ The Iris effect:
+ Iris™ The Iris effect:
 + Iris TM The Barriers to Cost Control n Iris. TM addresses these cost drivers: ü Delivery ü Coordination ü Over-utilization n Pricing ü Administrative Burden n Fraud
+ Iris TM The Barriers to Cost Control n Iris. TM addresses these cost drivers: ü Delivery ü Coordination ü Over-utilization n Pricing ü Administrative Burden n Fraud
 + Iris Consumers TM Referring Physicians Associated Treating Physicians Consulted Specialists Patients Nurse Manager Triage Nurse Billing staff Patient Navigators Emergency Department Hospital Admission Team Home Care Team Hospice Team Survivorship Care Team Tumor Registry State Department of Health Plan Medical Directors Plan Auditors
+ Iris Consumers TM Referring Physicians Associated Treating Physicians Consulted Specialists Patients Nurse Manager Triage Nurse Billing staff Patient Navigators Emergency Department Hospital Admission Team Home Care Team Hospice Team Survivorship Care Team Tumor Registry State Department of Health Plan Medical Directors Plan Auditors
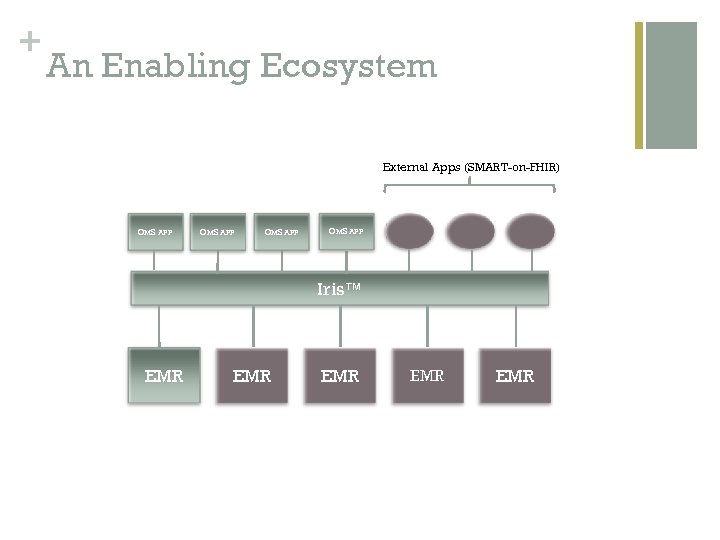 + An Enabling Ecosystem External Apps (SMART-on-FHIR) OMS APP Iris™ EMR EMR EMR
+ An Enabling Ecosystem External Apps (SMART-on-FHIR) OMS APP Iris™ EMR EMR EMR
 + Thank you! Contact Information John D. Sprandio jsprandio@cmoh. org Visit us at www. opcmh. com to register for OMS’ Healthcare Delivery Seminar
+ Thank you! Contact Information John D. Sprandio jsprandio@cmoh. org Visit us at www. opcmh. com to register for OMS’ Healthcare Delivery Seminar


