55a3287db02be2f80a2f098540e06755.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 76
 On the use of Java 3 D
On the use of Java 3 D
 What is Java 3 d? • A wrapper around – Opengl or – Direct 3 d • An OOD for doing 3 d graphics
What is Java 3 d? • A wrapper around – Opengl or – Direct 3 d • An OOD for doing 3 d graphics
 Why use Java 3 D? • • High speed Portable graphic card support Writing games Scientific visualization
Why use Java 3 D? • • High speed Portable graphic card support Writing games Scientific visualization
 Where do I get Java 3 D? • 1. Go to the Java 3 D homepage: http: //java. sun. com/products/java-media/3 D/ • 2. Click on: Java 3 DTM API 1. 3. 1: Now Available for Download • If you want the Linux version of Java 3 D go to: • http: //www. blackdown. org/java-linux/java 2 status/index. html
Where do I get Java 3 D? • 1. Go to the Java 3 D homepage: http: //java. sun. com/products/java-media/3 D/ • 2. Click on: Java 3 DTM API 1. 3. 1: Now Available for Download • If you want the Linux version of Java 3 D go to: • http: //www. blackdown. org/java-linux/java 2 status/index. html
 What classes do I need? • public class Virtual. Universe - A virtual universe consists of a set of Locale objects • Simple. Universe is a sub-class of this.
What classes do I need? • public class Virtual. Universe - A virtual universe consists of a set of Locale objects • Simple. Universe is a sub-class of this.
 How do I set up geometries? • Use a tree-like data structure called a group. • A Branch. Group extends Group
How do I set up geometries? • Use a tree-like data structure called a group. • A Branch. Group extends Group
 The Locale class • public class Locale - A Locale instance defines a high-resolution grid within a Virtual. Universe. It is a container for a collection of Branch. Groups
The Locale class • public class Locale - A Locale instance defines a high-resolution grid within a Virtual. Universe. It is a container for a collection of Branch. Groups
 Bg processing • A Branch. Group may be compiled by calling its compile method. This causes the entire subgraph to be compiled. • A Branch. Group may be inserted into a virtual universe by attaching it to a Locale. The entire subgraph is then said to be live.
Bg processing • A Branch. Group may be compiled by calling its compile method. This causes the entire subgraph to be compiled. • A Branch. Group may be inserted into a virtual universe by attaching it to a Locale. The entire subgraph is then said to be live.
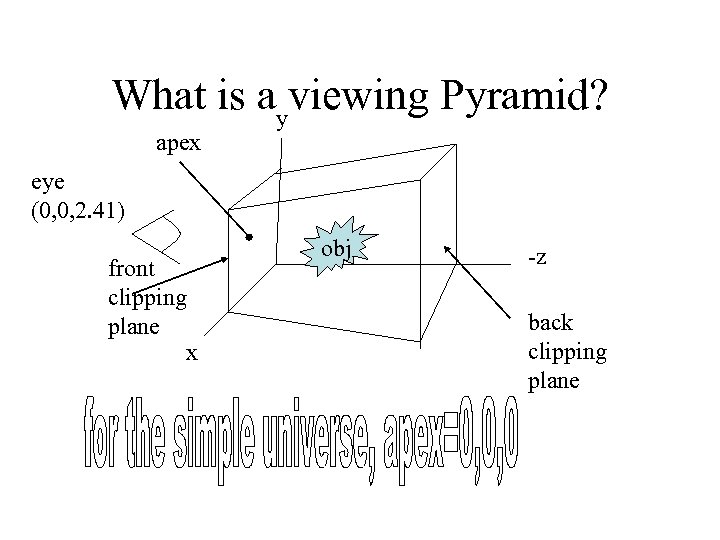 What is ayviewing Pyramid? apex eye (0, 0, 2. 41) front clipping plane x obj -z back clipping plane
What is ayviewing Pyramid? apex eye (0, 0, 2. 41) front clipping plane x obj -z back clipping plane
 Viewing the origin • Viewing. Platform class has the method set. Nominal. Viewing. Transform which sets the eye position to be centered at (0, 0, 2. 41) looking in the negative z direction toward the origin.
Viewing the origin • Viewing. Platform class has the method set. Nominal. Viewing. Transform which sets the eye position to be centered at (0, 0, 2. 41) looking in the negative z direction toward the origin.
 What is a view? • public class View – Has a reference to a Physical. Body and to a Physical. Environment. • Default front clip is 0. 1 meters. Default back clip is 10. 0 meters. • Default FOV is 1 radian (57. 3 degrees) x. 75 radians (43 degrees)
What is a view? • public class View – Has a reference to a Physical. Body and to a Physical. Environment. • Default front clip is 0. 1 meters. Default back clip is 10. 0 meters. • Default FOV is 1 radian (57. 3 degrees) x. 75 radians (43 degrees)
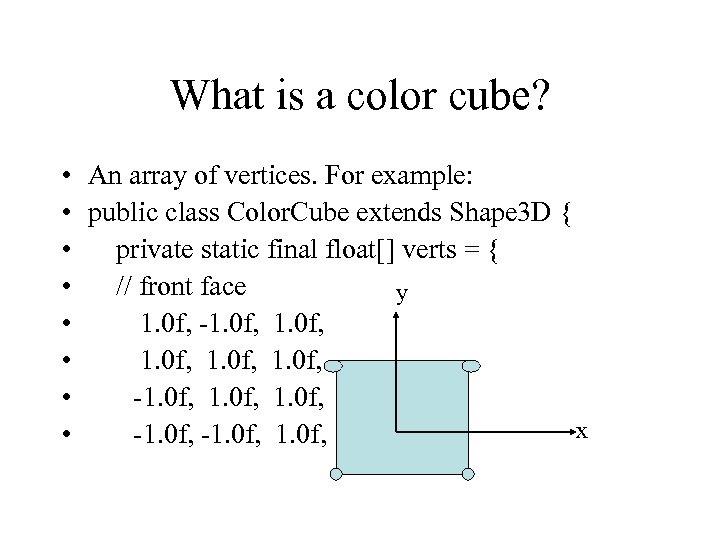 What is a color cube? • An array of vertices. For example: • public class Color. Cube extends Shape 3 D { • private static final float[] verts = { • // front face y • 1. 0 f, -1. 0 f, • 1. 0 f, • -1. 0 f, x • -1. 0 f,
What is a color cube? • An array of vertices. For example: • public class Color. Cube extends Shape 3 D { • private static final float[] verts = { • // front face y • 1. 0 f, -1. 0 f, • 1. 0 f, • -1. 0 f, x • -1. 0 f,
![How do I assign color? • private static final float[] colors = { • How do I assign color? • private static final float[] colors = { •](https://present5.com/presentation/55a3287db02be2f80a2f098540e06755/image-13.jpg) How do I assign color? • private static final float[] colors = { • // front face (red) • 1. 0 f, 0. 0 f,
How do I assign color? • private static final float[] colors = { • // front face (red) • 1. 0 f, 0. 0 f,
 How do I construct a color cube? • public Color. Cube() { • Quad. Array cube = new Quad. Array(24, Quad. Array. COORDINATES | • Quad. Array. COLOR_3); • cube. set. Coordinates(0, verts); //brep • cube. set. Colors(0, colors); • this. set. Geometry(cube); • }
How do I construct a color cube? • public Color. Cube() { • Quad. Array cube = new Quad. Array(24, Quad. Array. COORDINATES | • Quad. Array. COLOR_3); • cube. set. Coordinates(0, verts); //brep • cube. set. Colors(0, colors); • this. set. Geometry(cube); • }
 How do I build a house • 1. Draw the 2 D house! • 2. Use the verticies for the front and The back. This is called extrusion.
How do I build a house • 1. Draw the 2 D house! • 2. Use the verticies for the front and The back. This is called extrusion.
 What is a Quad. Array? • An array of quadrilaterals – Points are stored in a 1 D float array. – There must be 4 at a time – Each point forms a triplet: • • X 1, y 1, z 1, X 2, y 2, z 2, X 3, y 3, z 3 X 4, y 4, z 4
What is a Quad. Array? • An array of quadrilaterals – Points are stored in a 1 D float array. – There must be 4 at a time – Each point forms a triplet: • • X 1, y 1, z 1, X 2, y 2, z 2, X 3, y 3, z 3 X 4, y 4, z 4
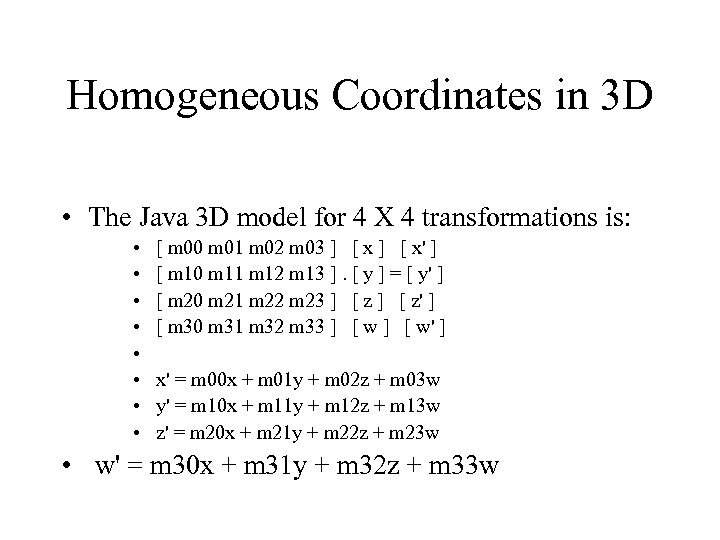 Homogeneous Coordinates in 3 D • The Java 3 D model for 4 X 4 transformations is: • • [ m 00 m 01 m 02 m 03 ] [ x' ] [ m 10 m 11 m 12 m 13 ]. [ y ] = [ y' ] [ m 20 m 21 m 22 m 23 ] [ z' ] [ m 30 m 31 m 32 m 33 ] [ w' ] x' = m 00 x + m 01 y + m 02 z + m 03 w y' = m 10 x + m 11 y + m 12 z + m 13 w z' = m 20 x + m 21 y + m 22 z + m 23 w • w' = m 30 x + m 31 y + m 32 z + m 33 w
Homogeneous Coordinates in 3 D • The Java 3 D model for 4 X 4 transformations is: • • [ m 00 m 01 m 02 m 03 ] [ x' ] [ m 10 m 11 m 12 m 13 ]. [ y ] = [ y' ] [ m 20 m 21 m 22 m 23 ] [ z' ] [ m 30 m 31 m 32 m 33 ] [ w' ] x' = m 00 x + m 01 y + m 02 z + m 03 w y' = m 10 x + m 11 y + m 12 z + m 13 w z' = m 20 x + m 21 y + m 22 z + m 23 w • w' = m 30 x + m 31 y + m 32 z + m 33 w
 You may concatenate xforms • By using the setup and multiply – Speed the transform – Rotate – Translate – Shear – Scale
You may concatenate xforms • By using the setup and multiply – Speed the transform – Rotate – Translate – Shear – Scale
 What is a Transform. Group? • Transform. Group extends Group • specifies a single spatial transformation, via a Transform 3 D object, this is applied to the children.
What is a Transform. Group? • Transform. Group extends Group • specifies a single spatial transformation, via a Transform 3 D object, this is applied to the children.
 How do I use HCTs? • • • Branch. Group bg = new Branch. Group(); Transform 3 D rotate = new Transform 3 D(); Transform 3 D temp. Rotate = new Transform 3 D(); rotate. rot. X(Math. PI / 4. 0 d); temp. Rotate. rot. Y(Math. PI / 5. 0 d); rotate. mul(temp. Rotate); Transform. Group obj. Rotate = new Transform. Group(rotate); bg. add. Child(obj. Rotate); obj. Rotate. add. Child(new Color. Cube(0. 4)); bg. compile(); return bg;
How do I use HCTs? • • • Branch. Group bg = new Branch. Group(); Transform 3 D rotate = new Transform 3 D(); Transform 3 D temp. Rotate = new Transform 3 D(); rotate. rot. X(Math. PI / 4. 0 d); temp. Rotate. rot. Y(Math. PI / 5. 0 d); rotate. mul(temp. Rotate); Transform. Group obj. Rotate = new Transform. Group(rotate); bg. add. Child(obj. Rotate); obj. Rotate. add. Child(new Color. Cube(0. 4)); bg. compile(); return bg;
 Hw • Convert the Hello. Java 3 Db Applet into a JFrame
Hw • Convert the Hello. Java 3 Db Applet into a JFrame
 J 3 d Xplained • 1. Create a Canvas 3 D object • 2. Create a Virtual. Universe object • 3. Create a Locale object, attaching it to the Virtual. Universe object • 4. Construct a view branch graph • 5. Construct content branch graph(s) • 6. Compile branch graph(s) • 7. Insert subgraphs into the Locale
J 3 d Xplained • 1. Create a Canvas 3 D object • 2. Create a Virtual. Universe object • 3. Create a Locale object, attaching it to the Virtual. Universe object • 4. Construct a view branch graph • 5. Construct content branch graph(s) • 6. Compile branch graph(s) • 7. Insert subgraphs into the Locale
 Construct a view branch graph • • • a. Create a View object b. Create a View. Platform object c. Create a Physical. Body object d. Create a Physical. Environment object e. Attach View. Platform, Physical. Body, Physical. Environment, and Canvas 3 D objects to View object
Construct a view branch graph • • • a. Create a View object b. Create a View. Platform object c. Create a Physical. Body object d. Create a Physical. Environment object e. Attach View. Platform, Physical. Body, Physical. Environment, and Canvas 3 D objects to View object
 What is a live bg? • Inserting a branch graph into a Locale makes it live, • each of the objects in that branch graph become live. • Live objects are subject to being rendered. • Parameters cannot be altered unless a capability was set before insertion.
What is a live bg? • Inserting a branch graph into a Locale makes it live, • each of the objects in that branch graph become live. • Live objects are subject to being rendered. • Parameters cannot be altered unless a capability was set before insertion.
 The Render Loop • while(true) { – Process input – If (request to exit) break – Perform Behaviors – Traverse the scene graph – and render visual objects } • Cleanup and exit
The Render Loop • while(true) { – Process input – If (request to exit) break – Perform Behaviors – Traverse the scene graph – and render visual objects } • Cleanup and exit
 Behavior • Behavior is a class for specifying animations of or interaction with visual objects • scheduling region=confining it to a region • Activation volume intersects a scheduling region to activate behavior
Behavior • Behavior is a class for specifying animations of or interaction with visual objects • scheduling region=confining it to a region • Activation volume intersects a scheduling region to activate behavior
 Interpolators • An instance of the Interpolator class is a kind of behavior.
Interpolators • An instance of the Interpolator class is a kind of behavior.
 Adding behavior • Set the Transform. Group’s ALLOW_TRANSFORM_WRITE • 2. Instance Alpha set the time parameters • 3. Instance interpolator reference Alpha and Transform. Group set behavior parameters • 4. Specify a scheduling region Set the scheduling region for the behavior • 5. Make the behavior a child of the Transform. Group
Adding behavior • Set the Transform. Group’s ALLOW_TRANSFORM_WRITE • 2. Instance Alpha set the time parameters • 3. Instance interpolator reference Alpha and Transform. Group set behavior parameters • 4. Specify a scheduling region Set the scheduling region for the behavior • 5. Make the behavior a child of the Transform. Group
 Interpolators • • • Position. Interpolator Rotation. Interpolator Scale. Interpolator Color. Interpolator Transparency. Interpolator
Interpolators • • • Position. Interpolator Rotation. Interpolator Scale. Interpolator Color. Interpolator Transparency. Interpolator
 Alpha • • • Dilation parameter Ranges from 0 to 1 Alpha(int loop. Count, long t) loop. Count=-1 = infinite loop t is in ms
Alpha • • • Dilation parameter Ranges from 0 to 1 Alpha(int loop. Count, long t) loop. Count=-1 = infinite loop t is in ms
 How do I set the bound region? • set. Scheduling. Bounds(Bounds region) Set the Behavior's scheduling region to the specified bounds. • Bounding. Sphere(Point 3 d center, double radius)
How do I set the bound region? • set. Scheduling. Bounds(Bounds region) Set the Behavior's scheduling region to the specified bounds. • Bounding. Sphere(Point 3 d center, double radius)
 Setting up an Animation • Alpha a = new Alpha(-1, 4000); • Rotation. Interpolator ri = • new Rotation. Interpolator(a, tg); • Bounding. Sphere bs = new Bounding. Sphere(); • ri. set. Scheduling. Bounds(bs); • tg. add. Child(ri);
Setting up an Animation • Alpha a = new Alpha(-1, 4000); • Rotation. Interpolator ri = • new Rotation. Interpolator(a, tg); • Bounding. Sphere bs = new Bounding. Sphere(); • ri. set. Scheduling. Bounds(bs); • tg. add. Child(ri);
 Combine transforms and animation • Create the transform group node and initialize it to the identity. Enable the TRANSFORM_WRITE capability so that our behavior code can modify it at runtime. Add it to the root of the subgraph. Transform. Group obj. Spin = new Transform. Group(); obj. Spin. set. Capability(Transform. Group. ALLOW_ TRANSFORM_WRITE); obj. Root. add. Child(obj. Rotate); obj. Rotate. add. Child(obj. Spin);
Combine transforms and animation • Create the transform group node and initialize it to the identity. Enable the TRANSFORM_WRITE capability so that our behavior code can modify it at runtime. Add it to the root of the subgraph. Transform. Group obj. Spin = new Transform. Group(); obj. Spin. set. Capability(Transform. Group. ALLOW_ TRANSFORM_WRITE); obj. Root. add. Child(obj. Rotate); obj. Rotate. add. Child(obj. Spin);
 hw • Convert Hello. Java 3 Dd to Swing • Add a keylistener that controls the speed of the rotation + = faster - = slower
hw • Convert Hello. Java 3 Dd to Swing • Add a keylistener that controls the speed of the rotation + = faster - = slower
 Objectives 4 Geometry in J 3 d • • Use geometric primitive utility classes Write classes to define visual objects Specify geometry using core classes Specify appearance and alternative appearance attributes for visual objects • Use geometry by reference
Objectives 4 Geometry in J 3 d • • Use geometric primitive utility classes Write classes to define visual objects Specify geometry using core classes Specify appearance and alternative appearance attributes for visual objects • Use geometry by reference
 Shape 3 D • Shape 3 D is a class • Shape 3 D(Geometry geometry, Appearance appearance) - constructor – set. Geometry(Geometry geometry) – set. Appearance(Appearance appearance)
Shape 3 D • Shape 3 D is a class • Shape 3 D(Geometry geometry, Appearance appearance) - constructor – set. Geometry(Geometry geometry) – set. Appearance(Appearance appearance)
 Node Components • A Node Component has an attribute for the geometry
Node Components • A Node Component has an attribute for the geometry
 Geometry. Info • • Geometry. Info(int primitive) POLYGON_ARRAY QUAD_ARRAY TRIANGLE_ARRAY
Geometry. Info • • Geometry. Info(int primitive) POLYGON_ARRAY QUAD_ARRAY TRIANGLE_ARRAY
 Adding 2 d text • public class Text 2 DApp extends Applet { • public Branch. Group create. Scene. Graph() { • Branch. Group branch. Group. Root • = new Branch. Group(); • Transform. Group tg • = new Transform. Group(); tg. set. Capability(Transform. Group. ALLOW_TRANSFORM_WRITE); • branch. Group. Root. add. Child(tg); • Text 2 D text 2 d • = new Text 2 D("2 D text in Java 3 D", • new Color 3 f(0. 9 f, 1. 0 f), • "Helvetica", 24, Font. ITALIC); • tg. add. Child(text 2 d);
Adding 2 d text • public class Text 2 DApp extends Applet { • public Branch. Group create. Scene. Graph() { • Branch. Group branch. Group. Root • = new Branch. Group(); • Transform. Group tg • = new Transform. Group(); tg. set. Capability(Transform. Group. ALLOW_TRANSFORM_WRITE); • branch. Group. Root. add. Child(tg); • Text 2 D text 2 d • = new Text 2 D("2 D text in Java 3 D", • new Color 3 f(0. 9 f, 1. 0 f), • "Helvetica", 24, Font. ITALIC); • tg. add. Child(text 2 d);
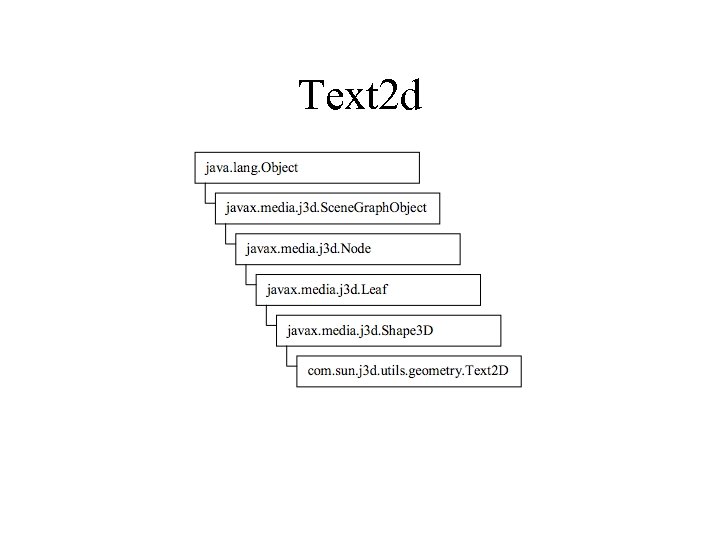 Text 2 d
Text 2 d
 How do I create 3 d text? • Create a Font 3 D object from an AWT Font • Create Text 3 D for a string using the Font 3 D object, optionally specifying a reference point • Reference the object from a Shape 3 D object added to the scene graph
How do I create 3 d text? • Create a Font 3 D object from an AWT Font • Create Text 3 D for a string using the Font 3 D object, optionally specifying a reference point • Reference the object from a Shape 3 D object added to the scene graph
 How do I add 3 d text? • • • • private void add. Text(Appearance text. Appear, Transform. Group obj. Spin) { Font 3 D font 3 D = new Font 3 D(new Font("Helvetica", Font. PLAIN, 1), new Font. Extrusion()); Text 3 D text. Geom = new Text 3 D(font 3 D, new String("3 DText")); text. Geom. set. Alignment(Text 3 D. ALIGN_CENTER); Shape 3 D text. Shape = new Shape 3 D(); text. Shape. set. Geometry(text. Geom); text. Shape. set. Appearance(text. Appear); obj. Spin. add. Child(text. Shape); }
How do I add 3 d text? • • • • private void add. Text(Appearance text. Appear, Transform. Group obj. Spin) { Font 3 D font 3 D = new Font 3 D(new Font("Helvetica", Font. PLAIN, 1), new Font. Extrusion()); Text 3 D text. Geom = new Text 3 D(font 3 D, new String("3 DText")); text. Geom. set. Alignment(Text 3 D. ALIGN_CENTER); Shape 3 D text. Shape = new Shape 3 D(); text. Shape. set. Geometry(text. Geom); text. Shape. set. Appearance(text. Appear); obj. Spin. add. Child(text. Shape); }
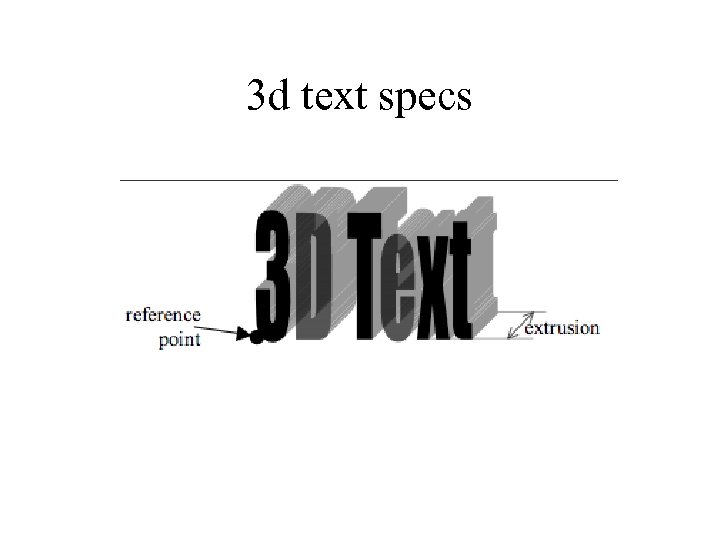 3 d text specs
3 d text specs
 Sample 3 D Text
Sample 3 D Text
 How should we control attributes? • • Rotation. Interpolator controls interpolation Alpha control the Rotation. Interpolator Should RI be observable? How would you do that? – perhaps you want to update(Object o – RI? )
How should we control attributes? • • Rotation. Interpolator controls interpolation Alpha control the Rotation. Interpolator Should RI be observable? How would you do that? – perhaps you want to update(Object o – RI? )
 You will need a mediator • Observable. Rotation. Interpolator ori = new • Observable. Rotation. Interpolator(); • ori. add. Observer(cp); • public void update(Observable obs, Object arg){ • if (arg instanceof Rotation. Interpolator) • ri = (Rotation. Interpolator)arg; • }
You will need a mediator • Observable. Rotation. Interpolator ori = new • Observable. Rotation. Interpolator(); • ori. add. Observer(cp); • public void update(Observable obs, Object arg){ • if (arg instanceof Rotation. Interpolator) • ri = (Rotation. Interpolator)arg; • }
 You will need an observable • class Observable. Rotation. Interpolator extends Observable { • private Rotation. Interpolator ri; • public void set. Rotation. Interpolator(Rotation. Interpolator ri){ • this. ri = ri; • set. Changed(); • notify. Observers(); • } • public Rotation. Interpolator get. Rotation. Interpolator() { • return ri; • }
You will need an observable • class Observable. Rotation. Interpolator extends Observable { • private Rotation. Interpolator ri; • public void set. Rotation. Interpolator(Rotation. Interpolator ri){ • this. ri = ri; • set. Changed(); • notify. Observers(); • } • public Rotation. Interpolator get. Rotation. Interpolator() { • return ri; • }
 How do I make a TFA? • TFA= Triangle Fan Array • Array of triangles • Eg – Tree. Scene
How do I make a TFA? • TFA= Triangle Fan Array • Array of triangles • Eg – Tree. Scene
 To get the triangles, you need to allocate the points • private Triangle. Fan. Array get. Tree. Geometry() { • int counts[] = {19}; • Triangle. Fan. Array tfa = new Triangle. Fan. Array(19, • Geometry. Array. COORDINATES • | Geometry. Array. COLOR_3, • counts);
To get the triangles, you need to allocate the points • private Triangle. Fan. Array get. Tree. Geometry() { • int counts[] = {19}; • Triangle. Fan. Array tfa = new Triangle. Fan. Array(19, • Geometry. Array. COORDINATES • | Geometry. Array. COLOR_3, • counts);
 How do I build a background? • 1. Create a parent BG for the bckgrnd • public Branch. Group create. Background() { – Branch. Group background. Group = new Branch. Group(); • 2. Create a background node – Background back = new Background()
How do I build a background? • 1. Create a parent BG for the bckgrnd • public Branch. Group create. Background() { – Branch. Group background. Group = new Branch. Group(); • 2. Create a background node – Background back = new Background()
 creating a background • Simple. Universe su = new Simple. Universe(canvas 3 D); • su. add. Branch. Graph(create. Background()); • • Branch. Group bg = get. Scene. Branch. Group(su); su. add. Branch. Graph(bg);
creating a background • Simple. Universe su = new Simple. Universe(canvas 3 D); • su. add. Branch. Graph(create. Background()); • • Branch. Group bg = get. Scene. Branch. Group(su); su. add. Branch. Graph(bg);
 Behavior • Appreciate the Behavior Class as the foundation for interaction and animation • Create custom behavior classes • Incorporate behavior objects into virtual worlds to provide interaction • Use utility classes for keyboard navigation • Use utility classes for mouse interaction • Use utility picking classes
Behavior • Appreciate the Behavior Class as the foundation for interaction and animation • Create custom behavior classes • Incorporate behavior objects into virtual worlds to provide interaction • Use utility classes for keyboard navigation • Use utility classes for mouse interaction • Use utility picking classes
 How do I write a custom behavior? • • 1. write (at least one) constructor store a reference to the object of change 2. override public void initialization() specify initial wakeup criteria (trigger) 3. override public void process. Stimulus() decode the trigger condition 4. act according to the trigger condition 5. reset trigger as appropriate
How do I write a custom behavior? • • 1. write (at least one) constructor store a reference to the object of change 2. override public void initialization() specify initial wakeup criteria (trigger) 3. override public void process. Stimulus() decode the trigger condition 4. act according to the trigger condition 5. reset trigger as appropriate
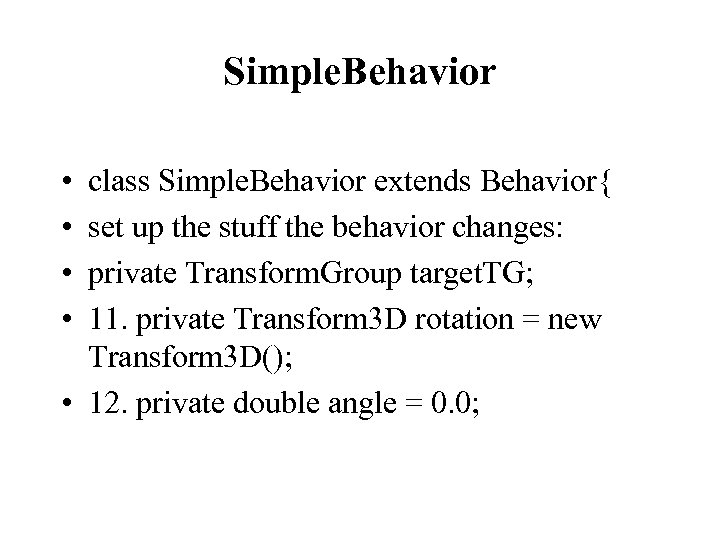 Simple. Behavior • • class Simple. Behavior extends Behavior{ set up the stuff the behavior changes: private Transform. Group target. TG; 11. private Transform 3 D rotation = new Transform 3 D(); • 12. private double angle = 0. 0;
Simple. Behavior • • class Simple. Behavior extends Behavior{ set up the stuff the behavior changes: private Transform. Group target. TG; 11. private Transform 3 D rotation = new Transform 3 D(); • 12. private double angle = 0. 0;
 Review • public class Virtual. Universe - A virtual universe consists of a set of Locale objects. • public class Locale - A Locale object defines a high-resolution grid within a Virtual. Universe. It is a container for a collection of Branch. Groups.
Review • public class Virtual. Universe - A virtual universe consists of a set of Locale objects. • public class Locale - A Locale object defines a high-resolution grid within a Virtual. Universe. It is a container for a collection of Branch. Groups.
 class Branch. Group extends Group • The Branch. Group reference to the root of a scene graph • Branch. Groups are the only objects that can be inserted into a Locale's set of objects. • A subgraph, rooted by a Branch. Group node can be thought of as a compile unit. • A Branch. Group may be compiled by calling its compile method. The entire subgraph is compiled. • A Branch. Group may be inserted into a virtual universe by attaching it to a Locale. • The entire subgraph is then said to be live.
class Branch. Group extends Group • The Branch. Group reference to the root of a scene graph • Branch. Groups are the only objects that can be inserted into a Locale's set of objects. • A subgraph, rooted by a Branch. Group node can be thought of as a compile unit. • A Branch. Group may be compiled by calling its compile method. The entire subgraph is compiled. • A Branch. Group may be inserted into a virtual universe by attaching it to a Locale. • The entire subgraph is then said to be live.
 public class View – • Has a reference to a Physical. Body and to a Physical. Environment. • Default front clip is 0. 1 meters. Default back clip is 10. 0 meters.
public class View – • Has a reference to a Physical. Body and to a Physical. Environment. • Default front clip is 0. 1 meters. Default back clip is 10. 0 meters.
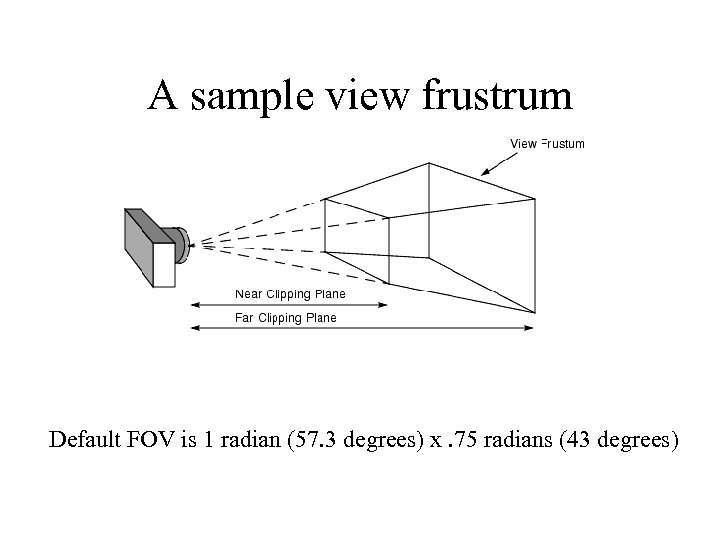 A sample view frustrum Default FOV is 1 radian (57. 3 degrees) x. 75 radians (43 degrees)
A sample view frustrum Default FOV is 1 radian (57. 3 degrees) x. 75 radians (43 degrees)
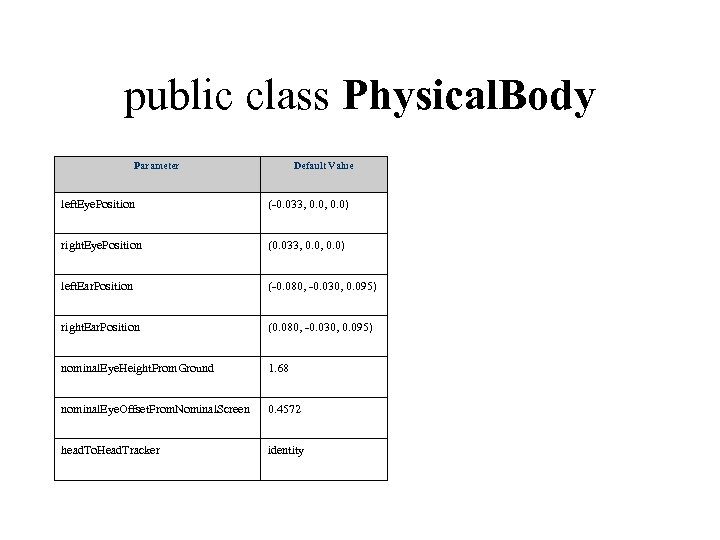 public class Physical. Body Parameter Default Value left. Eye. Position (-0. 033, 0. 0) right. Eye. Position (0. 033, 0. 0) left. Ear. Position (-0. 080, -0. 030, 0. 095) right. Ear. Position (0. 080, -0. 030, 0. 095) nominal. Eye. Height. From. Ground 1. 68 nominal. Eye. Offset. From. Nominal. Screen 0. 4572 head. To. Head. Tracker identity
public class Physical. Body Parameter Default Value left. Eye. Position (-0. 033, 0. 0) right. Eye. Position (0. 033, 0. 0) left. Ear. Position (-0. 080, -0. 030, 0. 095) right. Ear. Position (0. 080, -0. 030, 0. 095) nominal. Eye. Height. From. Ground 1. 68 nominal. Eye. Offset. From. Nominal. Screen 0. 4572 head. To. Head. Tracker identity
 public class Physical. Environment • It is used to set up input devices (sensors) for head-tracking and other uses, and the audio output device.
public class Physical. Environment • It is used to set up input devices (sensors) for head-tracking and other uses, and the audio output device.
 public class Viewing. Platform extends Branch. Group • This class is used to set up the "view" side of a Java 3 D scene graph. • The Viewing. Platform contains a Multi. Transform. Group node to allow for a series of transforms to be linked together. • To this structure the View. Platform is added as well as any geometry to associate with this view platform.
public class Viewing. Platform extends Branch. Group • This class is used to set up the "view" side of a Java 3 D scene graph. • The Viewing. Platform contains a Multi. Transform. Group node to allow for a series of transforms to be linked together. • To this structure the View. Platform is added as well as any geometry to associate with this view platform.
 Example • Branch. Group view. BG = new Branch. Group(); • View view = new View(); • Physical. Body body = new Physical. Body(); • Physical. Environment environment = new Physical. Environment(); • view. add. Canvas 3 D(canvas 3 D); • view. set. Physical. Body(body); • view. set. Physical. Environment(environment); • view. set. Front. Clip. Distance(0. 05); • view. set. Back. Clip. Distance(20000); • view. set. Field. Of. View(1. 0); • View. Platform vp = new View. Platform(); • view. attach. View. Platform(vp);
Example • Branch. Group view. BG = new Branch. Group(); • View view = new View(); • Physical. Body body = new Physical. Body(); • Physical. Environment environment = new Physical. Environment(); • view. add. Canvas 3 D(canvas 3 D); • view. set. Physical. Body(body); • view. set. Physical. Environment(environment); • view. set. Front. Clip. Distance(0. 05); • view. set. Back. Clip. Distance(20000); • view. set. Field. Of. View(1. 0); • View. Platform vp = new View. Platform(); • view. attach. View. Platform(vp);
 example… • // transform the viewer • Transform 3 D t = new Transform 3 D(); • t. set(new Vector 3 f(0. 0 f, 1. 40 f, 10000. 0 f)); • Transform. Group vp. Trans = new Transform. Group(t); • vp. Trans. add. Child(vp); • view. BG. add. Child(vp. Trans); • locale. add. Branch. Graph(view. BG);
example… • // transform the viewer • Transform 3 D t = new Transform 3 D(); • t. set(new Vector 3 f(0. 0 f, 1. 40 f, 10000. 0 f)); • Transform. Group vp. Trans = new Transform. Group(t); • vp. Trans. add. Child(vp); • view. BG. add. Child(vp. Trans); • locale. add. Branch. Graph(view. BG);
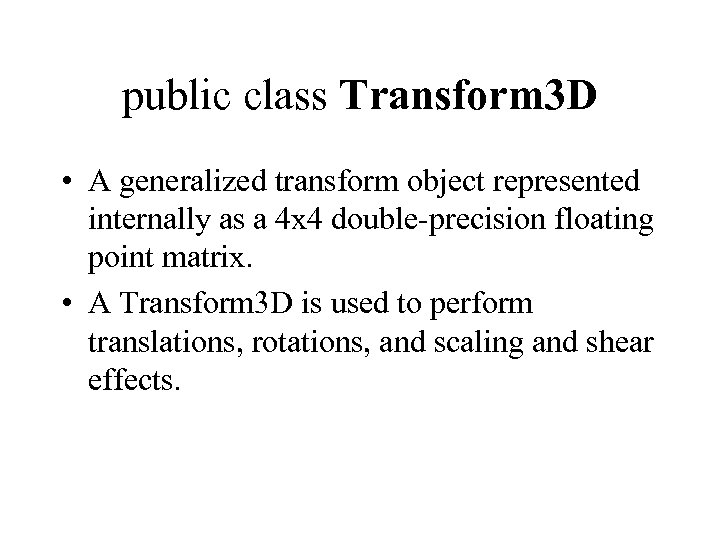 public class Transform 3 D • A generalized transform object represented internally as a 4 x 4 double-precision floating point matrix. • A Transform 3 D is used to perform translations, rotations, and scaling and shear effects.
public class Transform 3 D • A generalized transform object represented internally as a 4 x 4 double-precision floating point matrix. • A Transform 3 D is used to perform translations, rotations, and scaling and shear effects.
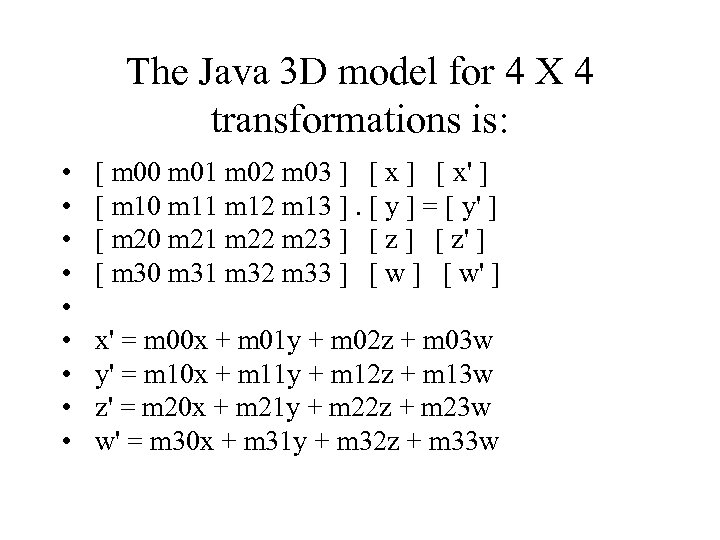 The Java 3 D model for 4 X 4 transformations is: • • • [ m 00 m 01 m 02 m 03 ] [ x' ] [ m 10 m 11 m 12 m 13 ]. [ y ] = [ y' ] [ m 20 m 21 m 22 m 23 ] [ z' ] [ m 30 m 31 m 32 m 33 ] [ w' ] x' = m 00 x + m 01 y + m 02 z + m 03 w y' = m 10 x + m 11 y + m 12 z + m 13 w z' = m 20 x + m 21 y + m 22 z + m 23 w w' = m 30 x + m 31 y + m 32 z + m 33 w
The Java 3 D model for 4 X 4 transformations is: • • • [ m 00 m 01 m 02 m 03 ] [ x' ] [ m 10 m 11 m 12 m 13 ]. [ y ] = [ y' ] [ m 20 m 21 m 22 m 23 ] [ z' ] [ m 30 m 31 m 32 m 33 ] [ w' ] x' = m 00 x + m 01 y + m 02 z + m 03 w y' = m 10 x + m 11 y + m 12 z + m 13 w z' = m 20 x + m 21 y + m 22 z + m 23 w w' = m 30 x + m 31 y + m 32 z + m 33 w
 public static final int AFFINE • An affine matrix can translate, rotate, reflect, scale anisotropically, and shear. Lines remain straight, and parallel lines remain parallel, but the angle between intersecting lines can change. In order for a transform to be classified as affine, the 4 th row must be: [0, 0, 0, 1].
public static final int AFFINE • An affine matrix can translate, rotate, reflect, scale anisotropically, and shear. Lines remain straight, and parallel lines remain parallel, but the angle between intersecting lines can change. In order for a transform to be classified as affine, the 4 th row must be: [0, 0, 0, 1].
 public class Transform. Group extends Group • The Transform. Group node specifies a single spatial transformation, via a Transform 3 D object, that can position, orient, and scale all of its children. • The specified transformation must be affine.
public class Transform. Group extends Group • The Transform. Group node specifies a single spatial transformation, via a Transform 3 D object, that can position, orient, and scale all of its children. • The specified transformation must be affine.
 Here is the way an item can be positioned in your 3 D world. • Transform 3 D tcube = new Transform 3 D(); • tcube. set(new Vector 3 f(0. 0 f, 1. 0 f, -10. 0 f)); • Transform. Group tg. Cube = new Transform. Group(tcube); • tg. Cube. add. Child(new Color. Cube(1. 0)); • scene. BG. add. Child(tg. Cube);
Here is the way an item can be positioned in your 3 D world. • Transform 3 D tcube = new Transform 3 D(); • tcube. set(new Vector 3 f(0. 0 f, 1. 0 f, -10. 0 f)); • Transform. Group tg. Cube = new Transform. Group(tcube); • tg. Cube. add. Child(new Color. Cube(1. 0)); • scene. BG. add. Child(tg. Cube);
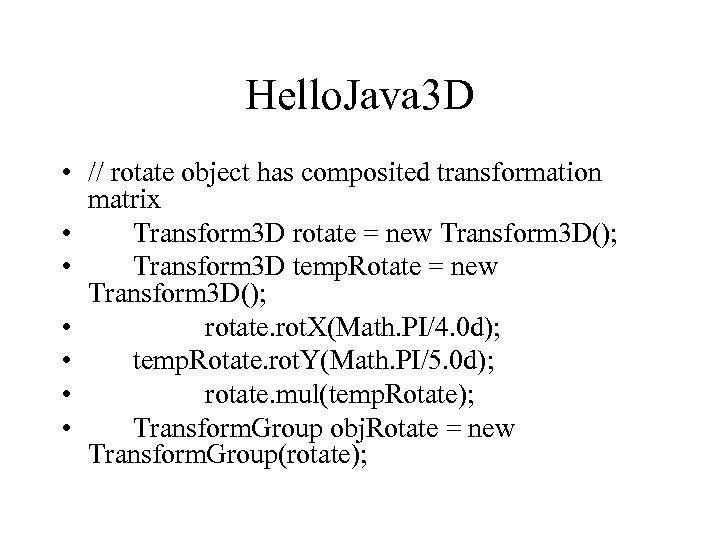 Hello. Java 3 D • // rotate object has composited transformation matrix • Transform 3 D rotate = new Transform 3 D(); • Transform 3 D temp. Rotate = new Transform 3 D(); • rotate. rot. X(Math. PI/4. 0 d); • temp. Rotate. rot. Y(Math. PI/5. 0 d); • rotate. mul(temp. Rotate); • Transform. Group obj. Rotate = new Transform. Group(rotate);
Hello. Java 3 D • // rotate object has composited transformation matrix • Transform 3 D rotate = new Transform 3 D(); • Transform 3 D temp. Rotate = new Transform 3 D(); • rotate. rot. X(Math. PI/4. 0 d); • temp. Rotate. rot. Y(Math. PI/5. 0 d); • rotate. mul(temp. Rotate); • Transform. Group obj. Rotate = new Transform. Group(rotate);
 Enable the TRANSFORM_WRITE • so that behavior can modify it at runtime. • Add it to the root of the subgraph. • Transform. Group obj. Spin = new Transform. Group(); • obj. Spin. set. Capability(Transform. Group. ALLOW_TRANSFORM_WRITE); • obj. Root. add. Child(obj. Rotate); • obj. Rotate. add. Child(obj. Spin);
Enable the TRANSFORM_WRITE • so that behavior can modify it at runtime. • Add it to the root of the subgraph. • Transform. Group obj. Spin = new Transform. Group(); • obj. Spin. set. Capability(Transform. Group. ALLOW_TRANSFORM_WRITE); • obj. Root. add. Child(obj. Rotate); • obj. Rotate. add. Child(obj. Spin);
 Create a simple shape leaf node • add it to the scene graph. • Color. Cube is a Convenience Utility class • obj. Spin. add. Child(new Color. Cube(0. 4)); //Create a new Behavior object that will perform the desired operation on the specified transform object and add it into the scene graph. • Transform 3 D y. Axis = new Transform 3 D(); • Alpha rotation. Alpha = new Alpha(-1, 4000);
Create a simple shape leaf node • add it to the scene graph. • Color. Cube is a Convenience Utility class • obj. Spin. add. Child(new Color. Cube(0. 4)); //Create a new Behavior object that will perform the desired operation on the specified transform object and add it into the scene graph. • Transform 3 D y. Axis = new Transform 3 D(); • Alpha rotation. Alpha = new Alpha(-1, 4000);
 Rotation. Interpolator • • Rotation. Interpolator rotator = new Rotation. Interpolator(rotation. Alpha, obj. Spin, y. Axis, 0. 0 f, (float) Math. PI*2. 0 f); // a bounding sphere specifies a region a behavior is active // create a sphere centered at the origin with radius of 1 Bounding. Sphere bounds = new Bounding. Sphere(); rotator. set. Scheduling. Bounds(bounds); obj. Spin. add. Child(rotator);
Rotation. Interpolator • • Rotation. Interpolator rotator = new Rotation. Interpolator(rotation. Alpha, obj. Spin, y. Axis, 0. 0 f, (float) Math. PI*2. 0 f); // a bounding sphere specifies a region a behavior is active // create a sphere centered at the origin with radius of 1 Bounding. Sphere bounds = new Bounding. Sphere(); rotator. set. Scheduling. Bounds(bounds); obj. Spin. add. Child(rotator);
 Final • Write a 3 D game that is a first-person shooter game. The game has: – a gun – a moving texture mapped target – a view that can be steered – a gun attached to the view. You can see the gun. you can use an image. – bullets that leave the gun and hit or miss the target.
Final • Write a 3 D game that is a first-person shooter game. The game has: – a gun – a moving texture mapped target – a view that can be steered – a gun attached to the view. You can see the gun. you can use an image. – bullets that leave the gun and hit or miss the target.
 The Stage of the Final • to set the stage for the game – houses – trees – The land is needed. – The sky has a texture mapped image on it • When the bullet hits the target there is a visual change in the target.
The Stage of the Final • to set the stage for the game – houses – trees – The land is needed. – The sky has a texture mapped image on it • When the bullet hits the target there is a visual change in the target.
 Due date • By May 4 th, at 2: 00 PM we will meet for the last time to DEMO the final for the class. The final must reside in a package with your last name as a self-contained compilable Java source program. • .
Due date • By May 4 th, at 2: 00 PM we will meet for the last time to DEMO the final for the class. The final must reside in a package with your last name as a self-contained compilable Java source program. • .
 Format for submission • A Main class exists so that the program can be run. Eg. javac metz/*. java will compile the code and java metz. Main will run it • All dependent source code is contained in the package for distribution. • Zip the whole thing up and e-mail to me (or hand me a floppy).
Format for submission • A Main class exists so that the program can be run. Eg. javac metz/*. java will compile the code and java metz. Main will run it • All dependent source code is contained in the package for distribution. • Zip the whole thing up and e-mail to me (or hand me a floppy).


