 On the role of gravity in Holography • Current work: A Minkowski observer restricted to part of space will observe: • Radiation. • Area scaling of thermodynamic quantities • Bulk boundary correspondence*. • Future directions: • Kruskal observer • Ad. S observer • Entanglement of a single string • Experimental verification
On the role of gravity in Holography • Current work: A Minkowski observer restricted to part of space will observe: • Radiation. • Area scaling of thermodynamic quantities • Bulk boundary correspondence*. • Future directions: • Kruskal observer • Ad. S observer • Entanglement of a single string • Experimental verification
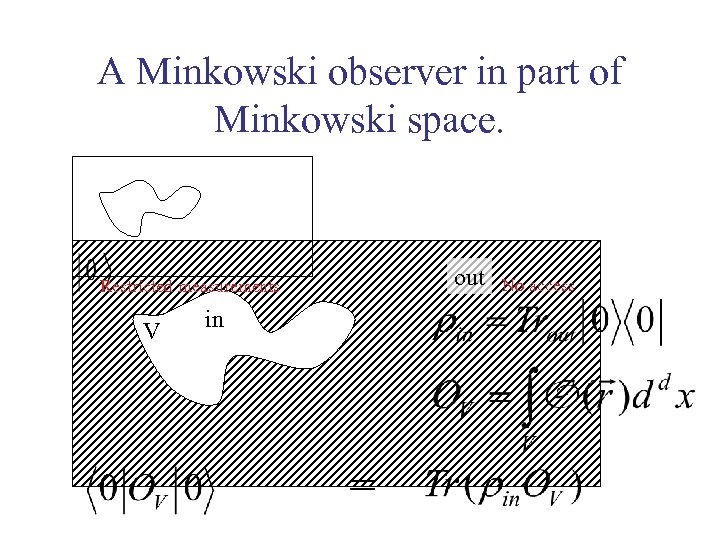 A Minkowski observer in part of Minkowski space. out Restricted measurements V in = No access
A Minkowski observer in part of Minkowski space. out Restricted measurements V in = No access
![Radiation in( ’in, ’’in) = Trout ( ’ ’’ Exp[-SE] Df D out +)= Radiation in( ’in, ’’in) = Trout ( ’ ’’ Exp[-SE] Df D out +)=](https://present5.com/presentation/f06a498c35d6a8f618240c3d161f90b8/image-3.jpg) Radiation in( ’in, ’’in) = Trout ( ’ ’’ Exp[-SE] Df D out +)= ’(x) f(x, 0)= (x) t f(x, 0 -)= ’’(x) f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) out(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) out(x) ’in(x) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’(x) ’’(x) x ’’in(x) f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x)
Radiation in( ’in, ’’in) = Trout ( ’ ’’ Exp[-SE] Df D out +)= ’(x) f(x, 0)= (x) t f(x, 0 -)= ’’(x) f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) out(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) out(x) ’in(x) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’(x) ’’(x) x ’’in(x) f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x)
![Explicit example Kabbat & Strassler (1994) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’| e-b. HR| ’’ Explicit example Kabbat & Strassler (1994) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’| e-b. HR| ’’](https://present5.com/presentation/f06a498c35d6a8f618240c3d161f90b8/image-4.jpg) Explicit example Kabbat & Strassler (1994) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’| e-b. HR| ’’ f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) t ’in(x) x ’’in(x)
Explicit example Kabbat & Strassler (1994) in ’’in Exp[-SE] Df ’| e-b. HR| ’’ f(x, 0+) = ’in(x) f(x, 0 -) = ’’in(x) t ’in(x) x ’’in(x)
 Thermodynamics out V in
Thermodynamics out V in
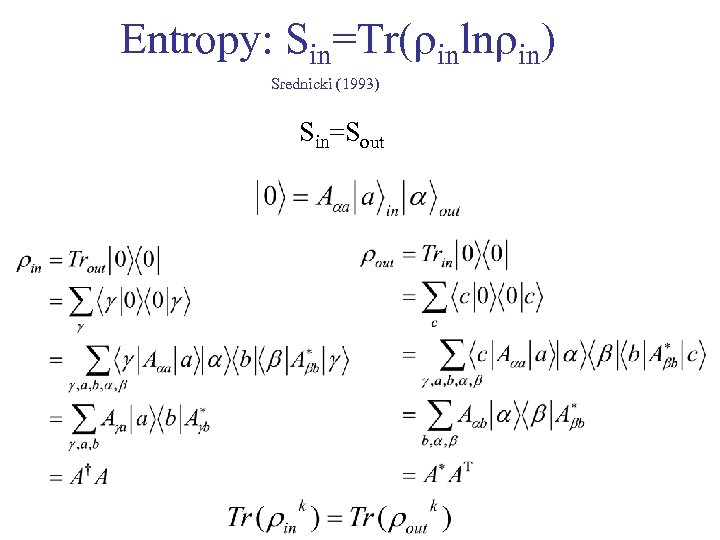 Entropy: Sin=Tr( inln in) Srednicki (1993) Sin=Sout
Entropy: Sin=Tr( inln in) Srednicki (1993) Sin=Sout
 Other quantities R. Brustein and A. Y. (2003) Heat capacity: Generally, we consider:
Other quantities R. Brustein and A. Y. (2003) Heat capacity: Generally, we consider:
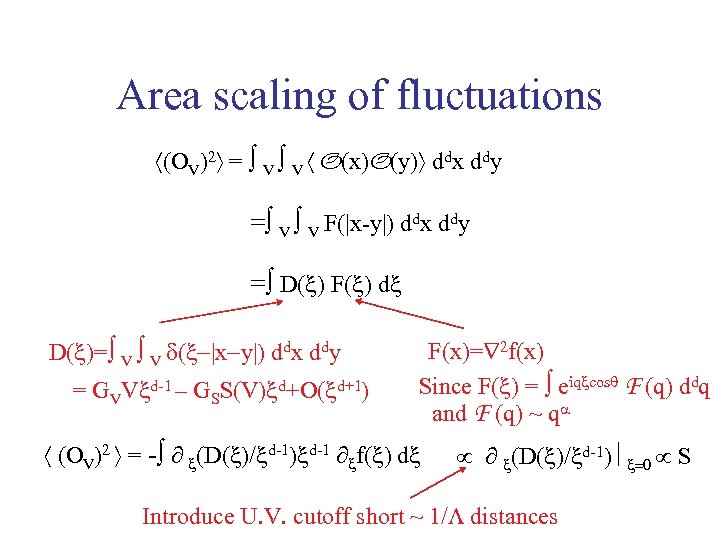 Area scaling of fluctuations (OV)2 = V V O(x)O(y) ddx ddy = V V F(|x-y|) ddx ddy = D( ) F( ) d D( )= V V d( x y ) ddx ddy = GVV d-1 – GSS(V) d+O( d+1) F(x)= 2 f(x) Since F( ) = eiq cosq F (q) ddq and F (q) ~ qa (OV)2 = - ∂ (D( )/ d-1) d-1 ∂ f( ) d ∂ (D( )/ d-1) S Introduce U. V. cutoff short ~ 1/L distances
Area scaling of fluctuations (OV)2 = V V O(x)O(y) ddx ddy = V V F(|x-y|) ddx ddy = D( ) F( ) d D( )= V V d( x y ) ddx ddy = GVV d-1 – GSS(V) d+O( d+1) F(x)= 2 f(x) Since F( ) = eiq cosq F (q) ddq and F (q) ~ qa (OV)2 = - ∂ (D( )/ d-1) d-1 ∂ f( ) d ∂ (D( )/ d-1) S Introduce U. V. cutoff short ~ 1/L distances
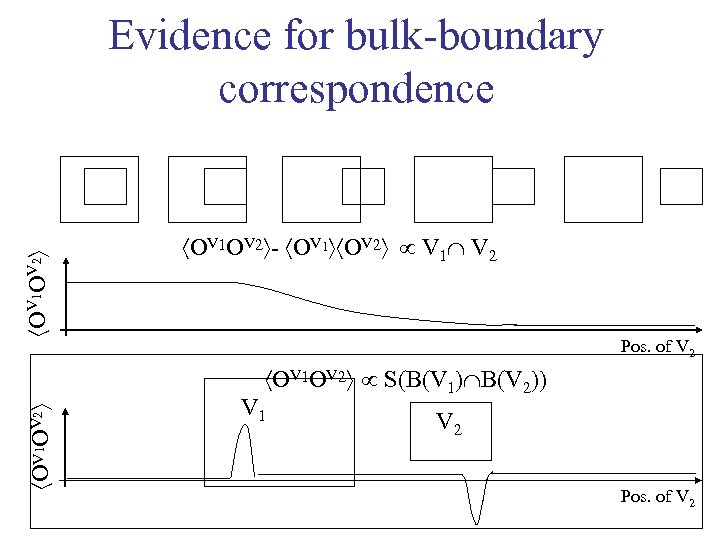 OV 1 OV 2 Evidence for bulk-boundary correspondence OV 1 OV 2 - OV 1 OV 2 V 1 V 2 Pos. of V 2 OV 1 OV 2 S(B(V 1) B(V 2)) V 1 V 2 Pos. of V 2
OV 1 OV 2 Evidence for bulk-boundary correspondence OV 1 OV 2 - OV 1 OV 2 V 1 V 2 Pos. of V 2 OV 1 OV 2 S(B(V 1) B(V 2)) V 1 V 2 Pos. of V 2
 A working example Large N limit
A working example Large N limit
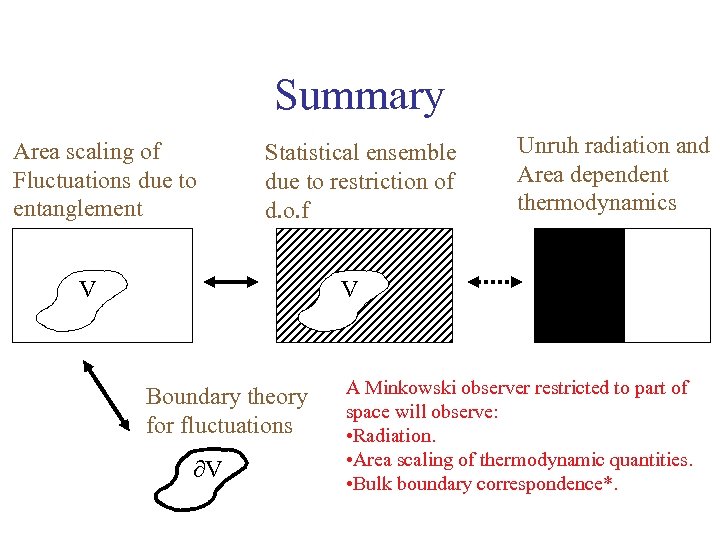 Summary Area scaling of Fluctuations due to entanglement Statistical ensemble due to restriction of d. o. f V Unruh radiation and Area dependent thermodynamics V Boundary theory for fluctuations V A Minkowski observer restricted to part of space will observe: • Radiation. • Area scaling of thermodynamic quantities. • Bulk boundary correspondence*.
Summary Area scaling of Fluctuations due to entanglement Statistical ensemble due to restriction of d. o. f V Unruh radiation and Area dependent thermodynamics V Boundary theory for fluctuations V A Minkowski observer restricted to part of space will observe: • Radiation. • Area scaling of thermodynamic quantities. • Bulk boundary correspondence*.
 Future directions • • Kruskal observer Ad. S observer Entanglement of a single string Experimental verification
Future directions • • Kruskal observer Ad. S observer Entanglement of a single string Experimental verification
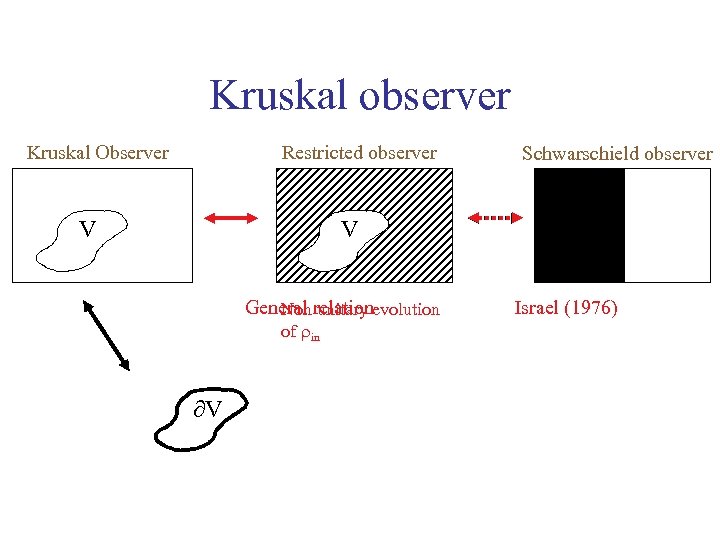 Kruskal observer Restricted observer Kruskal Observer V Schwarschield observer V General relationevolution Non unitary of in V Israel (1976)
Kruskal observer Restricted observer Kruskal Observer V Schwarschield observer V General relationevolution Non unitary of in V Israel (1976)
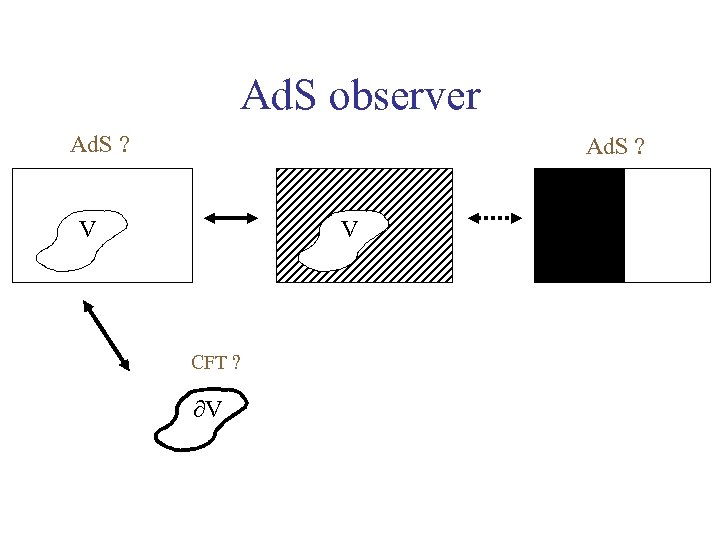 Ad. S observer Ad. S ? V V CFT ? V
Ad. S observer Ad. S ? V V CFT ? V
 Experimental verification • Prepare a pure quantum state. • Make repetitive measurements. • Measure part of the system.
Experimental verification • Prepare a pure quantum state. • Make repetitive measurements. • Measure part of the system.
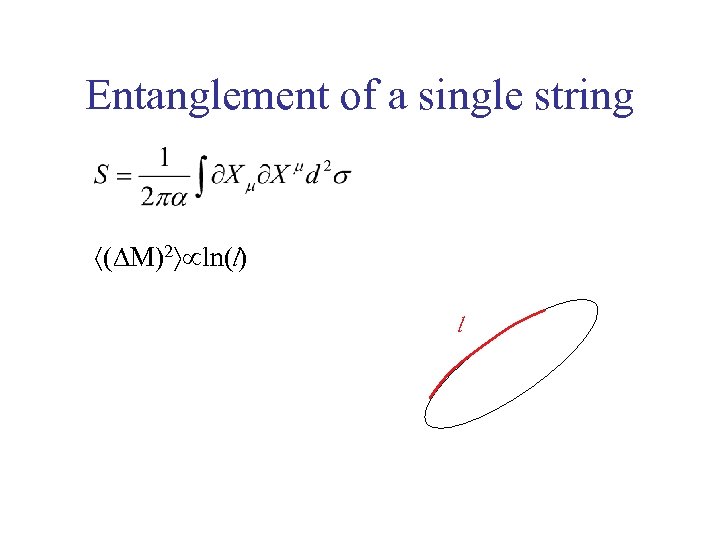 Entanglement of a single string (DM)2 ln(l) l
Entanglement of a single string (DM)2 ln(l) l
 Summary • Radiation, area scaling laws and a bulkboundary correspondence may be attributed to entanglement. • It is unclear whether gravity alone is responsible for area dependent quantities or if it is supplemented by quantum entanglement.
Summary • Radiation, area scaling laws and a bulkboundary correspondence may be attributed to entanglement. • It is unclear whether gravity alone is responsible for area dependent quantities or if it is supplemented by quantum entanglement.