3b32608cb3ebd8d1fb6bd418c5aab522.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 On Recent Climate Change and Modeling Future Climate Scenarios Branko Grisogono Dept. of Geophysics, Faculty of Science Thanks to: Č. Branković & I. Güttler Croatian Weather Service (DHMZ)
On Recent Climate Change and Modeling Future Climate Scenarios Branko Grisogono Dept. of Geophysics, Faculty of Science Thanks to: Č. Branković & I. Güttler Croatian Weather Service (DHMZ)
 OUTLINE Ø Data: Global Past, Present →? → Future Ø Numerical Models ( Simulators) Ø Climate vs. Weather Ø More of Current Results: Present → Future Ø Regional Climate Change Ø Tentative Conclusions → Discussion
OUTLINE Ø Data: Global Past, Present →? → Future Ø Numerical Models ( Simulators) Ø Climate vs. Weather Ø More of Current Results: Present → Future Ø Regional Climate Change Ø Tentative Conclusions → Discussion
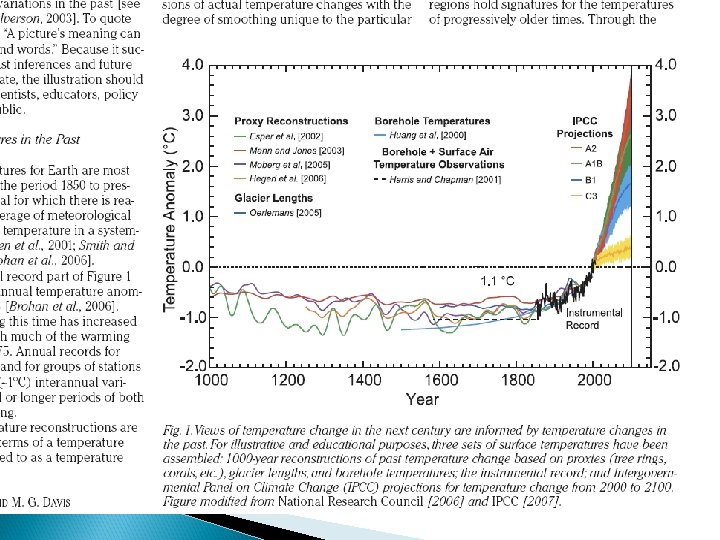
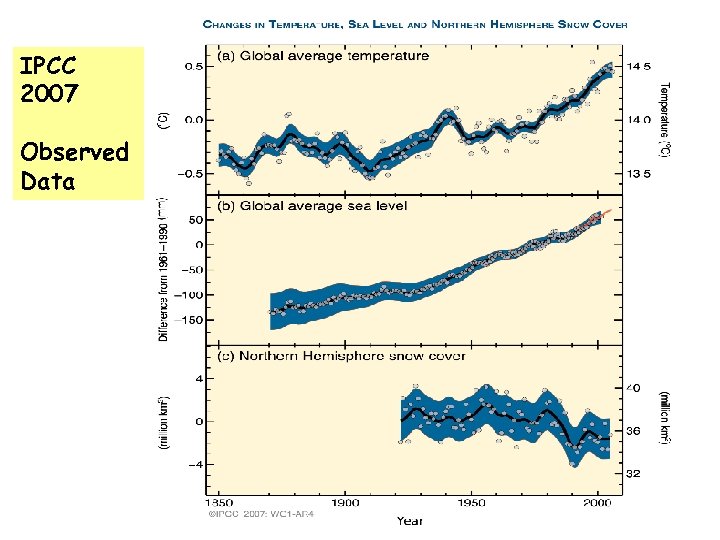 IPCC 2007 Observed Data
IPCC 2007 Observed Data
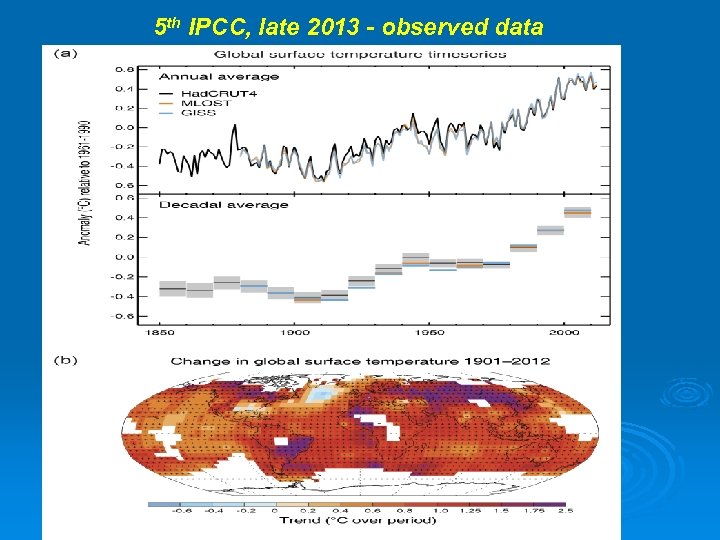 5 th IPCC, late 2013 - observed data
5 th IPCC, late 2013 - observed data
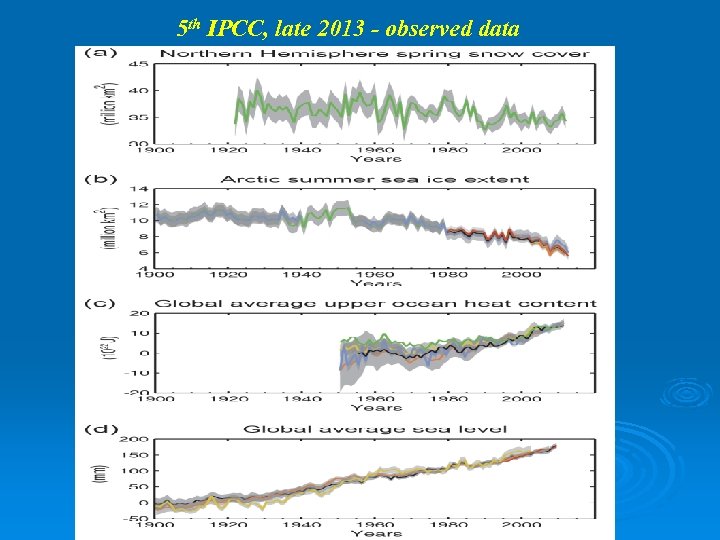 5 th IPCC, late 2013 - observed data
5 th IPCC, late 2013 - observed data
 Meteorology, Oceanography, Glaciology, Vulcanology, … Climatology BASIC ISSUES: - MEASUREMENTS, WITH THEIR ERRORS, ARE SPARSE IN SPACE & TIME. THUS, INITIAL STATE OF THE ATMOSPHERE & OCEAN IS ONLY KNOWN PARTLY - NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION (NWP) & CLIMATE MODELS CAN'T FULLY RESOLVE IN SPACE & TIME ALL THE RELEVANT PHYSICAL PROCESSES (ASIDE APPROXIMATIONS) - ATMOSPHERES & OCEANS ARE INHERENTLY CHAOTIC BESIDES STRONG DETERMINISTIC COMPONENTS
Meteorology, Oceanography, Glaciology, Vulcanology, … Climatology BASIC ISSUES: - MEASUREMENTS, WITH THEIR ERRORS, ARE SPARSE IN SPACE & TIME. THUS, INITIAL STATE OF THE ATMOSPHERE & OCEAN IS ONLY KNOWN PARTLY - NUMERICAL WEATHER PREDICTION (NWP) & CLIMATE MODELS CAN'T FULLY RESOLVE IN SPACE & TIME ALL THE RELEVANT PHYSICAL PROCESSES (ASIDE APPROXIMATIONS) - ATMOSPHERES & OCEANS ARE INHERENTLY CHAOTIC BESIDES STRONG DETERMINISTIC COMPONENTS
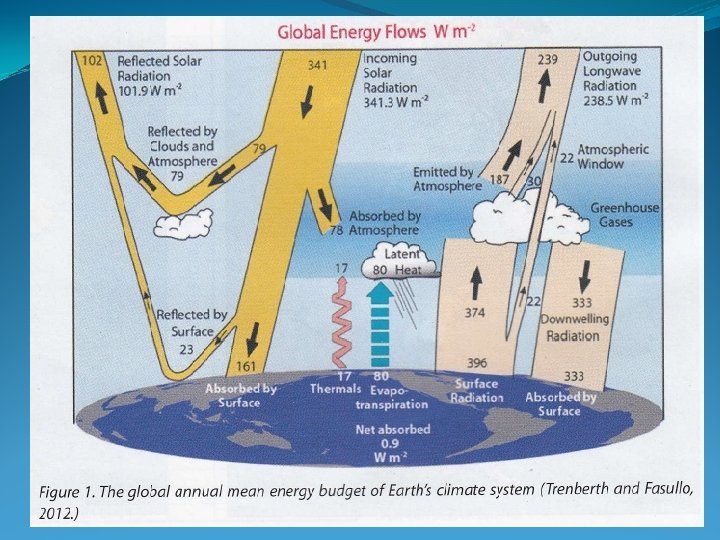
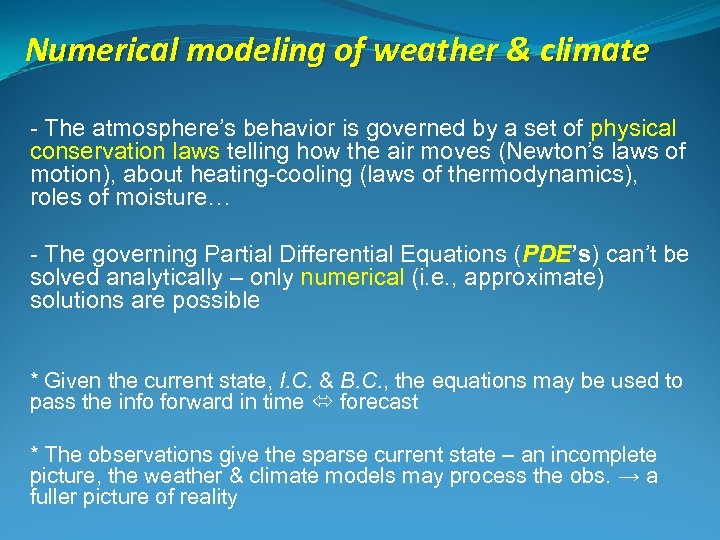 Numerical modeling of weather & climate - The atmosphere’s behavior is governed by a set of physical conservation laws telling how the air moves (Newton’s laws of motion), about heating-cooling (laws of thermodynamics), roles of moisture… - The governing Partial Differential Equations (PDE’s) can’t be solved analytically – only numerical (i. e. , approximate) solutions are possible * Given the current state, I. C. & B. C. , the equations may be used to pass the info forward in time forecast * The observations give the sparse current state – an incomplete picture, the weather & climate models may process the obs. → a fuller picture of reality
Numerical modeling of weather & climate - The atmosphere’s behavior is governed by a set of physical conservation laws telling how the air moves (Newton’s laws of motion), about heating-cooling (laws of thermodynamics), roles of moisture… - The governing Partial Differential Equations (PDE’s) can’t be solved analytically – only numerical (i. e. , approximate) solutions are possible * Given the current state, I. C. & B. C. , the equations may be used to pass the info forward in time forecast * The observations give the sparse current state – an incomplete picture, the weather & climate models may process the obs. → a fuller picture of reality
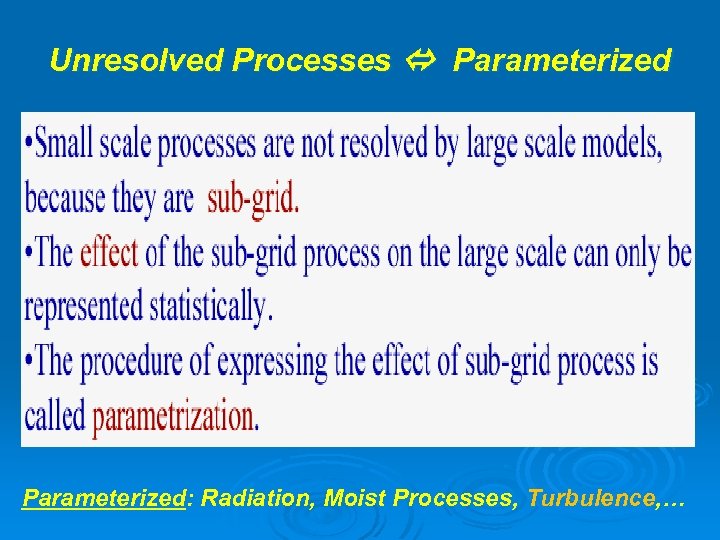 Unresolved Processes Parameterized: Radiation, Moist Processes, Turbulence, …
Unresolved Processes Parameterized: Radiation, Moist Processes, Turbulence, …
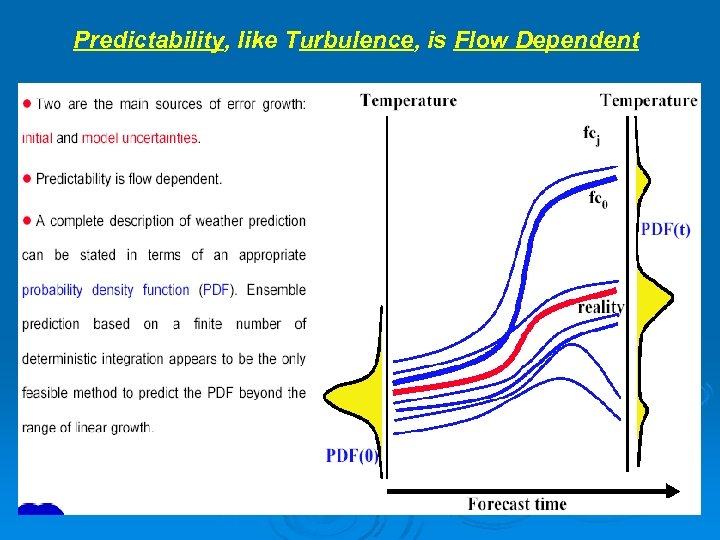 Predictability, like Turbulence, is Flow Dependent
Predictability, like Turbulence, is Flow Dependent
 Weather vs. Climate Models • Resolution & integration length of the governing PDE’s (motion, mass, thermodynamics, spicies) • Parameterizations (different space - & time-scales) e. g. , weather models might have slight drift (may avoid some feedbacks, etc. ) …climate modes not! • Sometimes numerics, due to numerous couplings (feedbacks) being modeled differently, etc. • Oceans, soil, biosphere, ice, … treated differently
Weather vs. Climate Models • Resolution & integration length of the governing PDE’s (motion, mass, thermodynamics, spicies) • Parameterizations (different space - & time-scales) e. g. , weather models might have slight drift (may avoid some feedbacks, etc. ) …climate modes not! • Sometimes numerics, due to numerous couplings (feedbacks) being modeled differently, etc. • Oceans, soil, biosphere, ice, … treated differently
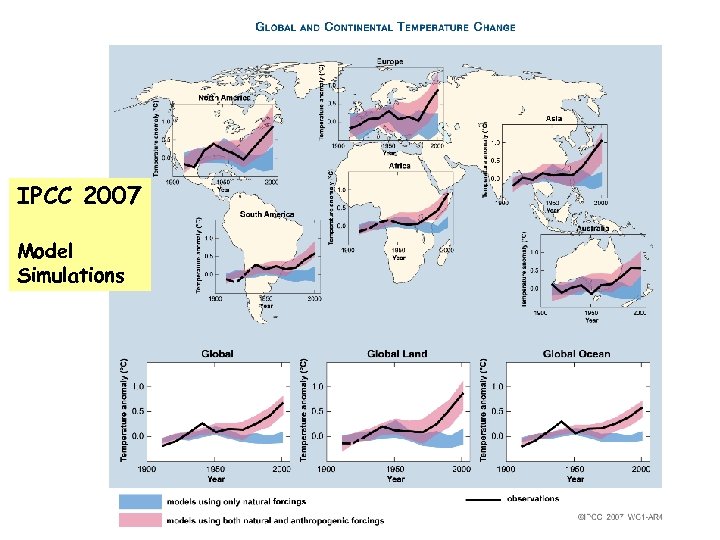 IPCC 2007 Model Simulations
IPCC 2007 Model Simulations
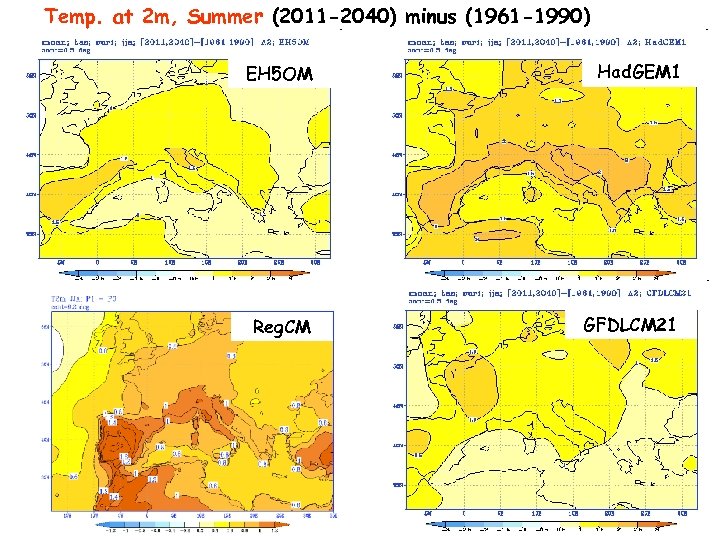 Temp. at 2 m, Summer (2011 -2040) minus (1961 -1990) EH 5 OM Had. GEM 1 Reg. CM GFDLCM 21 srednjak ansambla
Temp. at 2 m, Summer (2011 -2040) minus (1961 -1990) EH 5 OM Had. GEM 1 Reg. CM GFDLCM 21 srednjak ansambla
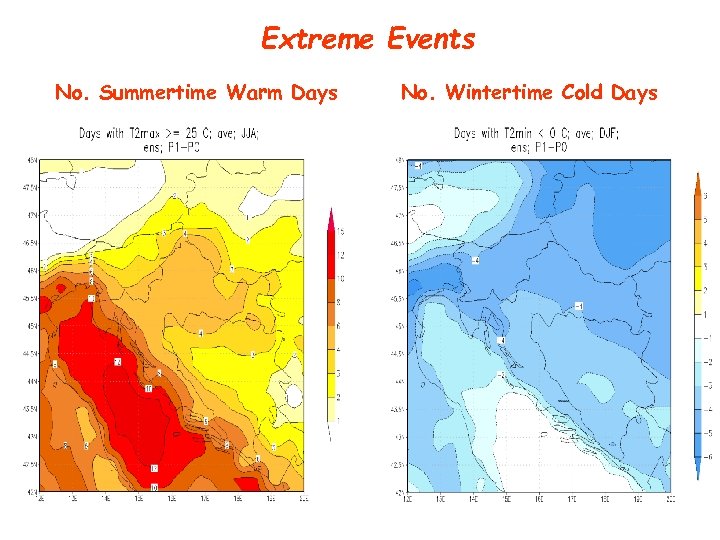 Extreme Events No. Summertime Warm Days No. Wintertime Cold Days
Extreme Events No. Summertime Warm Days No. Wintertime Cold Days
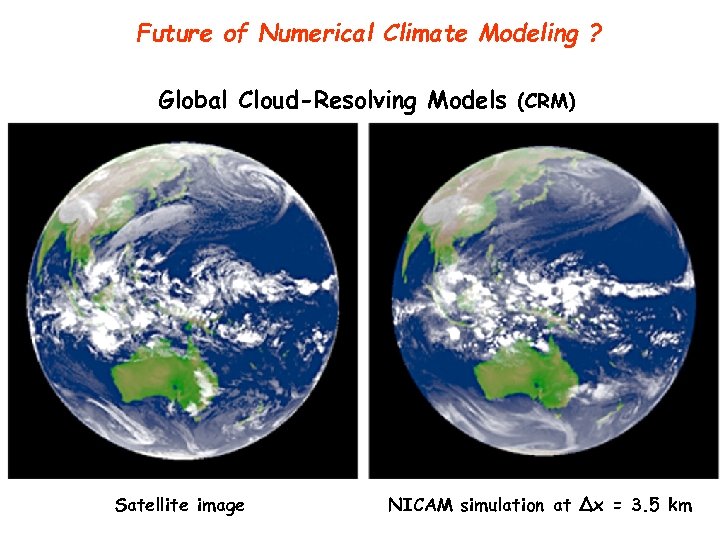 Future of Numerical Climate Modeling ? Global Cloud-Resolving Models (CRM) Satellite image NICAM simulation at Δx = 3. 5 km
Future of Numerical Climate Modeling ? Global Cloud-Resolving Models (CRM) Satellite image NICAM simulation at Δx = 3. 5 km
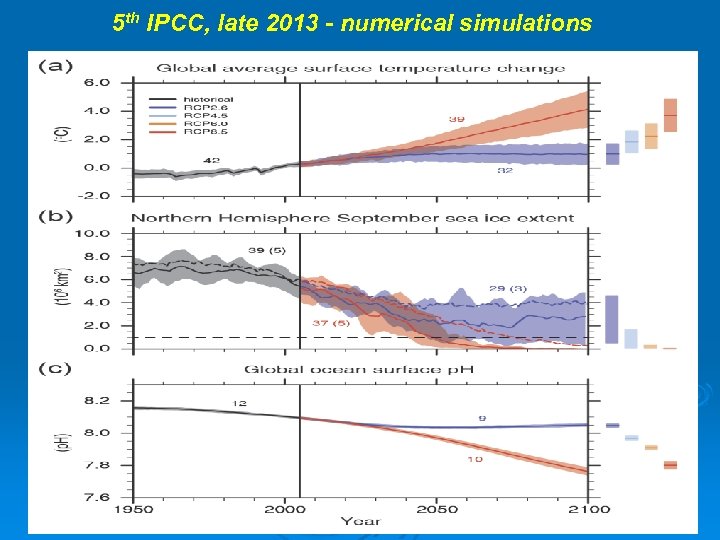 5 th IPCC, late 2013 - numerical simulations
5 th IPCC, late 2013 - numerical simulations
 TENTATIVE CONCLUSIONS Ø Current surface temp. upward trends & future predictions are unusual, unexplained by natural internal climate variability Ø “Predictions” are based on greenhouse gas emission scenarios & a link between the gases concentrations & temp. through modeling & simulations Ø Included: population growth, economic development, technol. change, social interactions Ø Besides large spatio-temporal variations, global warming is real, it exceeds in magnitude & pace natural changes over the last 10 3 yr.
TENTATIVE CONCLUSIONS Ø Current surface temp. upward trends & future predictions are unusual, unexplained by natural internal climate variability Ø “Predictions” are based on greenhouse gas emission scenarios & a link between the gases concentrations & temp. through modeling & simulations Ø Included: population growth, economic development, technol. change, social interactions Ø Besides large spatio-temporal variations, global warming is real, it exceeds in magnitude & pace natural changes over the last 10 3 yr.
 TENTATIVE CONCLUSIONS cont’d Ø Immediate changes seem needed: lowering emissions of greenhouse gasses to meet the scenario with global ~ +2 o. C in ≈ yr. 2100 Ø Targeting and promoting more human technologies, renewable energies, healthier food & water Humanistic approach needed! Ø It is wrong to deploy “instrumental rationalism” (max. efficiency only) & blind pragmatism based on e. g. , large resources & markets Ø Make reliable regional climate – economy projections for next few decades (agronomy, energy, tourism, education, etc. )
TENTATIVE CONCLUSIONS cont’d Ø Immediate changes seem needed: lowering emissions of greenhouse gasses to meet the scenario with global ~ +2 o. C in ≈ yr. 2100 Ø Targeting and promoting more human technologies, renewable energies, healthier food & water Humanistic approach needed! Ø It is wrong to deploy “instrumental rationalism” (max. efficiency only) & blind pragmatism based on e. g. , large resources & markets Ø Make reliable regional climate – economy projections for next few decades (agronomy, energy, tourism, education, etc. )
 … Za dalju diskusiju … * Klimatske promjene imaju utjecaj na gotovo sve oblike ljudske aktivnosti * Istraživanje meteoroloških aspekata klimatskih promjena - jedan od najvećih izazova suvremene klimatologije (kompleksnost, prediktabilnost, . . . ) * Istraživanje utjecaja klimatskih promjena na socio-ekonomske faktore (ublažavanje i prilagodba) * U istraživanje klimatskih promjena uključen je veliki broj institucija i znanstvenika * Važno definirati jasnu znanstvenu poziciju kako bi se moguće odluke zasnivale na znanstvenim činjenicama – primjer: potrebna je solidna znanstvena podloga kako bi se mogla opravdati novčana ulaganja u energiju iz obnovljivih izvora * Uloga klimatskog modeliranja i simuliranja nezaobilazna – jedini način kako “predvidjeti” klimatske promjene * Odgovornost institucija i grupa uključenih u klimatsko modeliranje * Poboljšanje i unaprijeđivanje globalnih i regionalnih klimatskih modela – vezano i vrlo ovisno o razvoju: primjenjene i numeričke matematike (PDE !), geofizike i računalne tehnologije
… Za dalju diskusiju … * Klimatske promjene imaju utjecaj na gotovo sve oblike ljudske aktivnosti * Istraživanje meteoroloških aspekata klimatskih promjena - jedan od najvećih izazova suvremene klimatologije (kompleksnost, prediktabilnost, . . . ) * Istraživanje utjecaja klimatskih promjena na socio-ekonomske faktore (ublažavanje i prilagodba) * U istraživanje klimatskih promjena uključen je veliki broj institucija i znanstvenika * Važno definirati jasnu znanstvenu poziciju kako bi se moguće odluke zasnivale na znanstvenim činjenicama – primjer: potrebna je solidna znanstvena podloga kako bi se mogla opravdati novčana ulaganja u energiju iz obnovljivih izvora * Uloga klimatskog modeliranja i simuliranja nezaobilazna – jedini način kako “predvidjeti” klimatske promjene * Odgovornost institucija i grupa uključenih u klimatsko modeliranje * Poboljšanje i unaprijeđivanje globalnih i regionalnih klimatskih modela – vezano i vrlo ovisno o razvoju: primjenjene i numeričke matematike (PDE !), geofizike i računalne tehnologije
 I’M AN AIR-CONDITIONED MIAOU-UU. . but soon maybe dead. . bgrisog@gfz. hr www. pmf. unizg. hr/geof
I’M AN AIR-CONDITIONED MIAOU-UU. . but soon maybe dead. . bgrisog@gfz. hr www. pmf. unizg. hr/geof
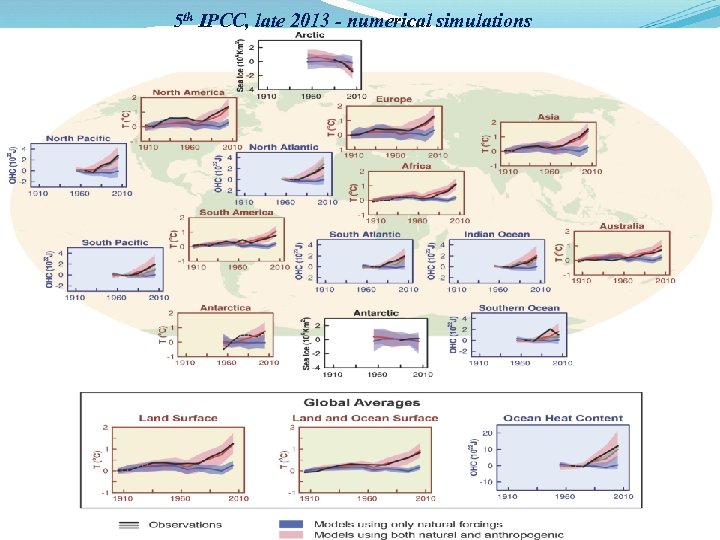 5 th IPCC, late 2013 - numerical simulations
5 th IPCC, late 2013 - numerical simulations
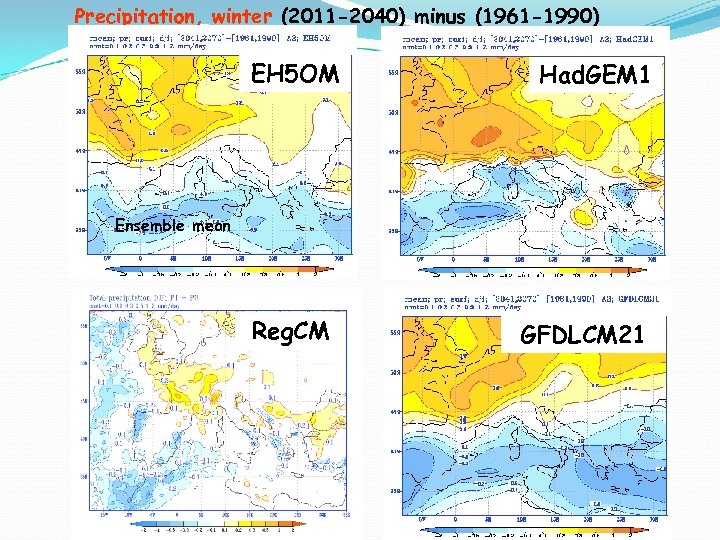 Precipitation, winter (2011 -2040) minus (1961 -1990) EH 5 OM Had. GEM 1 Ensemble mean Reg. CM GFDLCM 21
Precipitation, winter (2011 -2040) minus (1961 -1990) EH 5 OM Had. GEM 1 Ensemble mean Reg. CM GFDLCM 21


