Olga Romanenko The Brain.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Olga Romanenko SPP, gr. 1162
The brain is the central part of the nervous system. The human brain weighs about 1. 5 kg in adults. The Human Brain

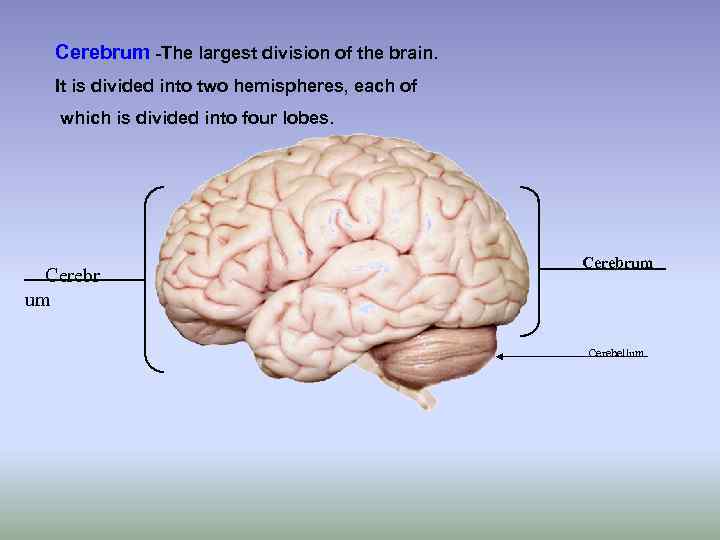
Cerebrum -The largest division of the brain. It is divided into two hemispheres, each of which is divided into four lobes. Cerebr um Cerebrum Cerebellum
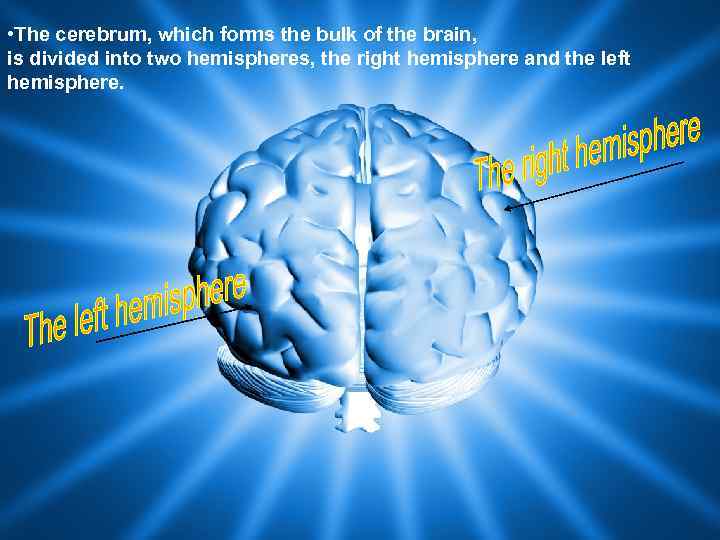
• The cerebrum, which forms the bulk of the brain, is divided into two hemispheres, the right hemisphere and the left hemisphere.
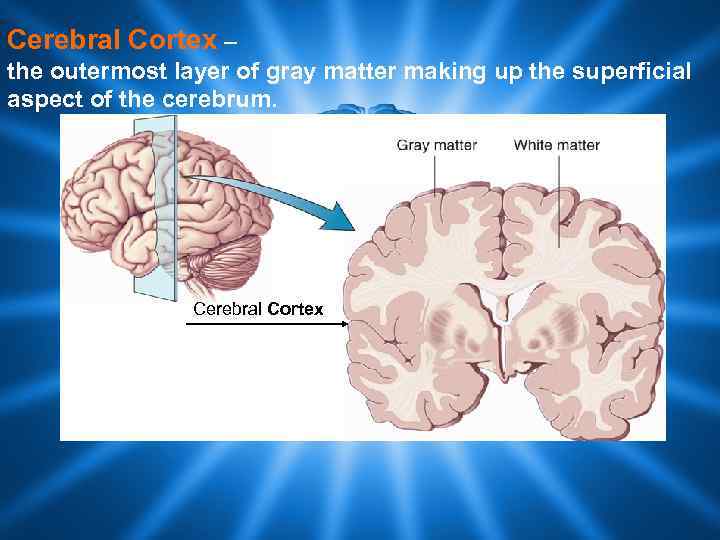
Cerebral Cortex – the outermost layer of gray matter making up the superficial aspect of the cerebrum. Cerebral Cortex
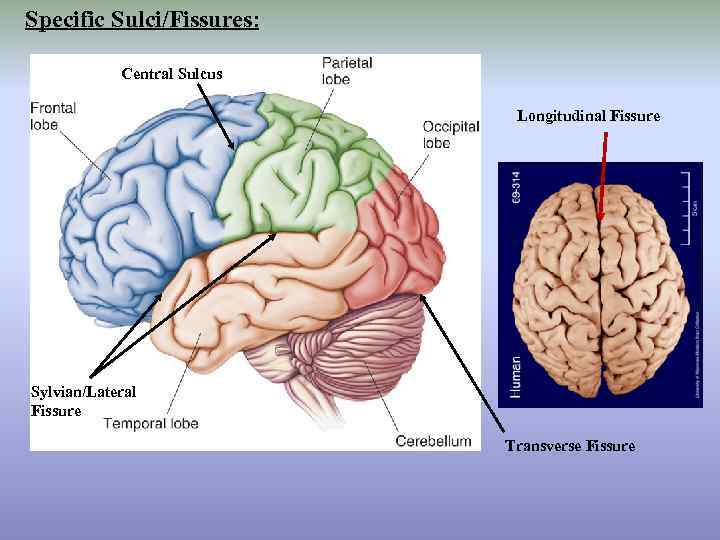
Specific Sulci/Fissures: Central Sulcus Longitudinal Fissure Sylvian/Lateral Fissure Transverse Fissure
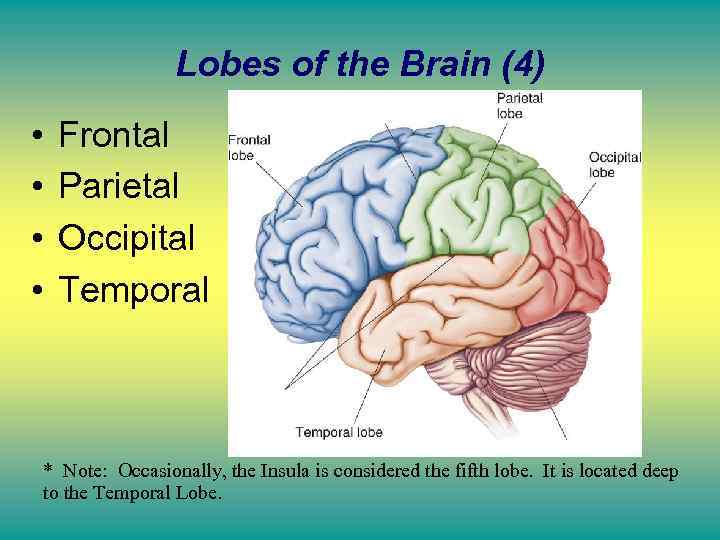
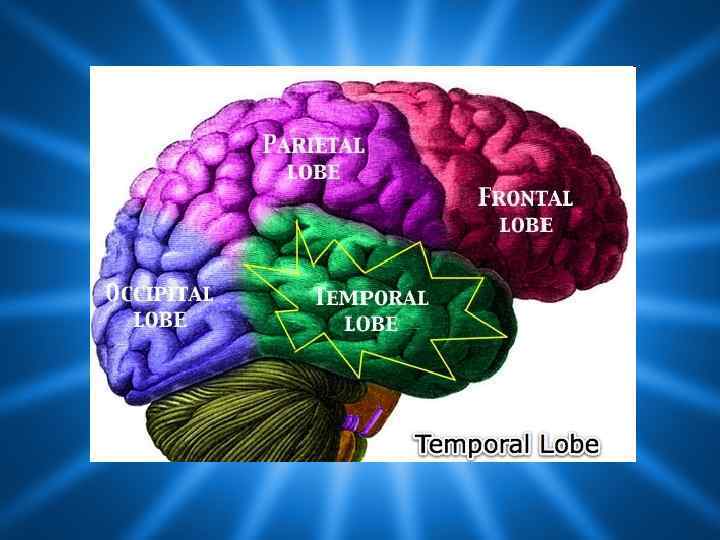
Lobes of the Brain (4) • • Frontal Parietal Occipital Temporal * Note: Occasionally, the Insula is considered the fifth lobe. It is located deep to the Temporal Lobe.
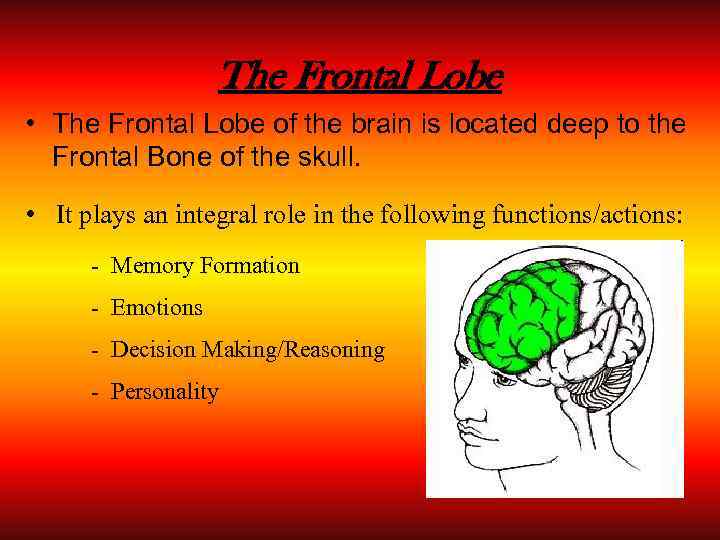
The Frontal Lobe • The Frontal Lobe of the brain is located deep to the Frontal Bone of the skull. • It plays an integral role in the following functions/actions: - Memory Formation - Emotions - Decision Making/Reasoning - Personality
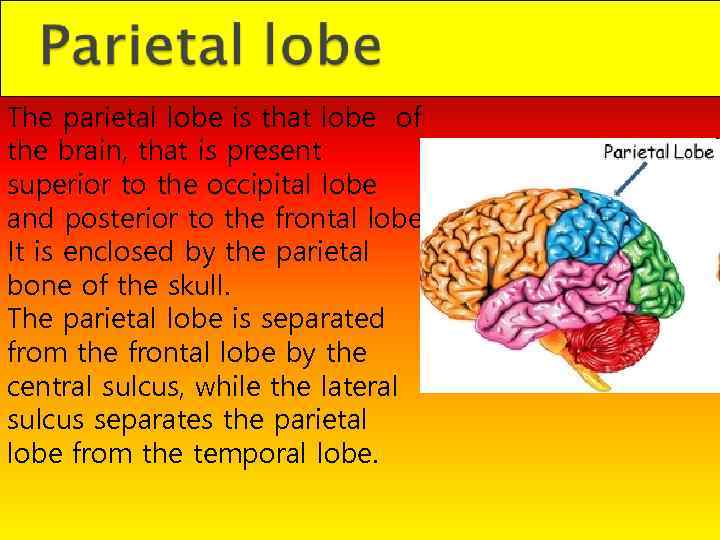
The parietal lobe is that lobe of the brain, that is present superior to the occipital lobe and posterior to the frontal lobe. It is enclosed by the parietal bone of the skull. The parietal lobe is separated from the frontal lobe by the central sulcus, while the lateral sulcus separates the parietal lobe from the temporal lobe.
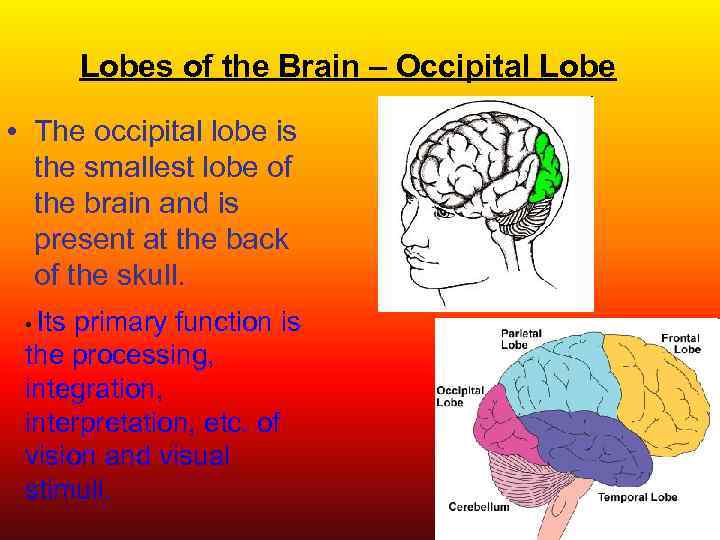
Lobes of the Brain – Occipital Lobe • The occipital lobe is the smallest lobe of the brain and is present at the back of the skull. • Its primary function is the processing, integration, interpretation, etc. of vision and visual stimuli.
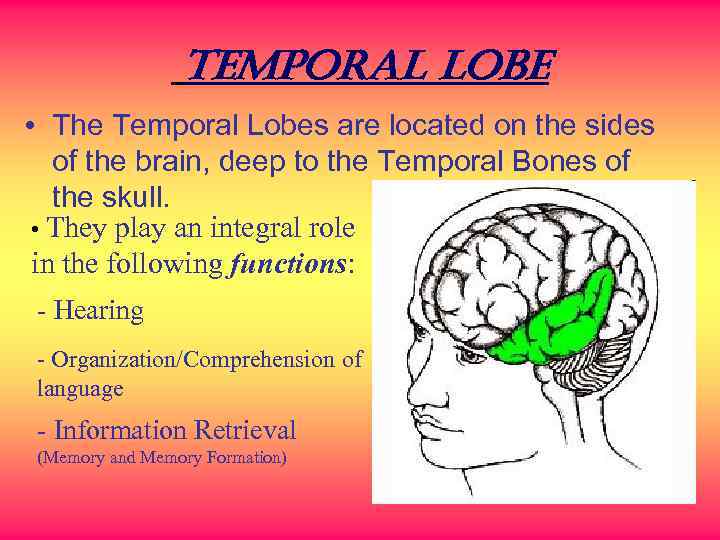
Temporal lobe • The Temporal Lobes are located on the sides of the brain, deep to the Temporal Bones of the skull. • They play an integral role in the following functions: - Hearing - Organization/Comprehension of language - Information Retrieval (Memory and Memory Formation)
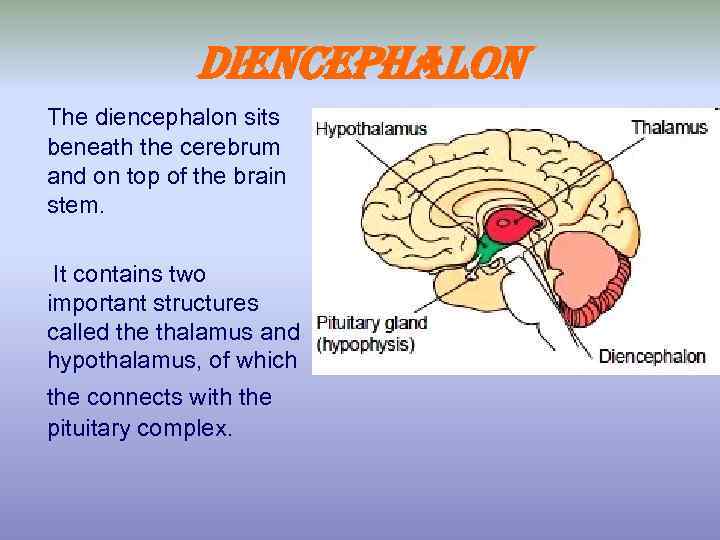
Diencephalon The diencephalon sits beneath the cerebrum and on top of the brain stem. It contains two important structures called the thalamus and hypothalamus, of which the connects with the pituitary complex.
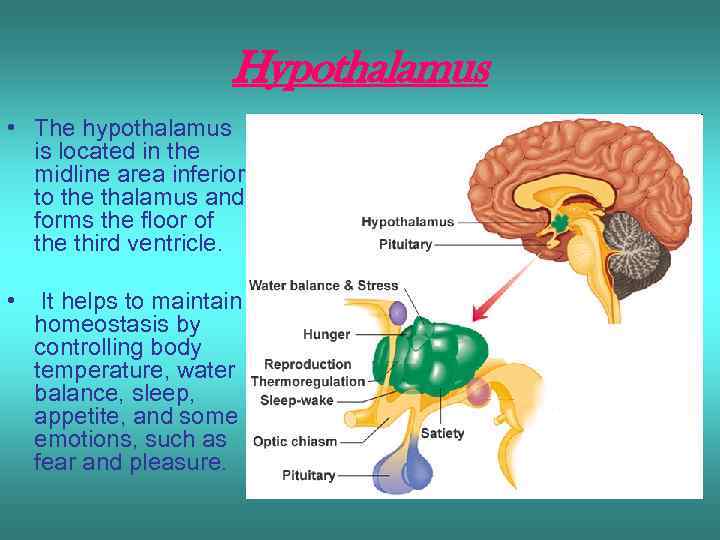
Hypothalamus • The hypothalamus is located in the midline area inferior to the thalamus and forms the floor of the third ventricle. • It helps to maintain homeostasis by controlling body temperature, water balance, sleep, appetite, and some emotions, such as fear and pleasure.
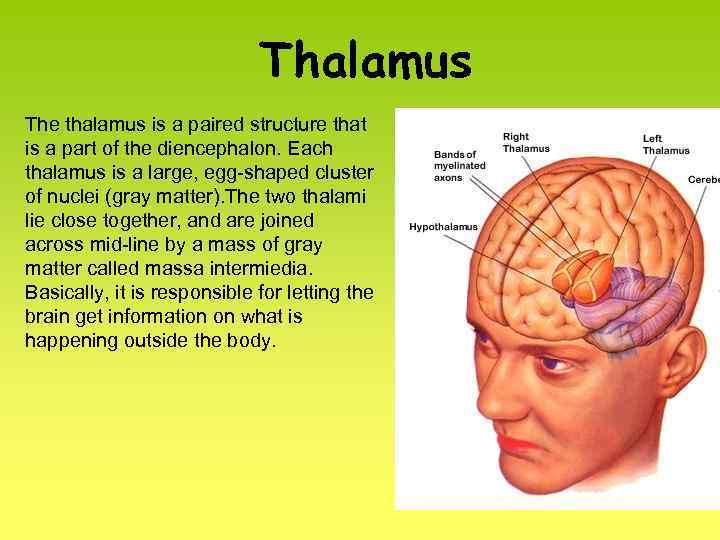
Thalamus The thalamus is a paired structure that is a part of the diencephalon. Each thalamus is a large, egg-shaped cluster of nuclei (gray matter). The two thalami lie close together, and are joined across mid-line by a mass of gray matter called massa intermiedia. Basically, it is responsible for letting the brain get information on what is happening outside the body.
Olga Romanenko The Brain.ppt