dd29cb3f1557bb5f17cff8013c773e23.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 OFFICE OF SCIENCE Isotope Program Office of Nuclear Physics Nuclear and Radiation Studies Board December 10, 2009 Jehanne Gillo Division Director, Facilities and Project Management Office of Science, U. S. Department of Energy
OFFICE OF SCIENCE Isotope Program Office of Nuclear Physics Nuclear and Radiation Studies Board December 10, 2009 Jehanne Gillo Division Director, Facilities and Project Management Office of Science, U. S. Department of Energy
 Nuclear Physics Program Mission: To discover, explore and understand all forms of nuclear matter; to understand how the fundamental particles, quarks and gluons, fit together and interact to create different types of matter in the universe, including those no longer found naturally Priorities: § To understand how quarks and gluons assemble into the various forms of matter and to search for yet undiscovered forms of matter § To understand how protons and neutrons combine to form atomic nuclei and how these nuclei have emerged during the 13. 7 billion years since the origin of the cosmos § To understand the fundamental properties of the neutron and develop a better understanding of the neutrino § To conceive, plan, design, construct, and operate national scientific user facilities; to develop new detector and accelerator technologies § To provide stewardship of isotope production and related technologies to advance important applications, research and tools for the nation § To foster integration of the research with the work of other organizations in 2
Nuclear Physics Program Mission: To discover, explore and understand all forms of nuclear matter; to understand how the fundamental particles, quarks and gluons, fit together and interact to create different types of matter in the universe, including those no longer found naturally Priorities: § To understand how quarks and gluons assemble into the various forms of matter and to search for yet undiscovered forms of matter § To understand how protons and neutrons combine to form atomic nuclei and how these nuclei have emerged during the 13. 7 billion years since the origin of the cosmos § To understand the fundamental properties of the neutron and develop a better understanding of the neutrino § To conceive, plan, design, construct, and operate national scientific user facilities; to develop new detector and accelerator technologies § To provide stewardship of isotope production and related technologies to advance important applications, research and tools for the nation § To foster integration of the research with the work of other organizations in 2
 Isotope Program Mission The mission of the DOE Isotope Program is threefold: § Produce and/or distribute radioactive and stable isotopes that are in short supply, associated byproducts, surplus materials and related isotope services. § Maintain the infrastructure required to produce and supply isotope products and related services. § Conduct R&D on new and improved isotope production and processing techniques which can make available new isotopes for research and applications. 3
Isotope Program Mission The mission of the DOE Isotope Program is threefold: § Produce and/or distribute radioactive and stable isotopes that are in short supply, associated byproducts, surplus materials and related isotope services. § Maintain the infrastructure required to produce and supply isotope products and related services. § Conduct R&D on new and improved isotope production and processing techniques which can make available new isotopes for research and applications. 3
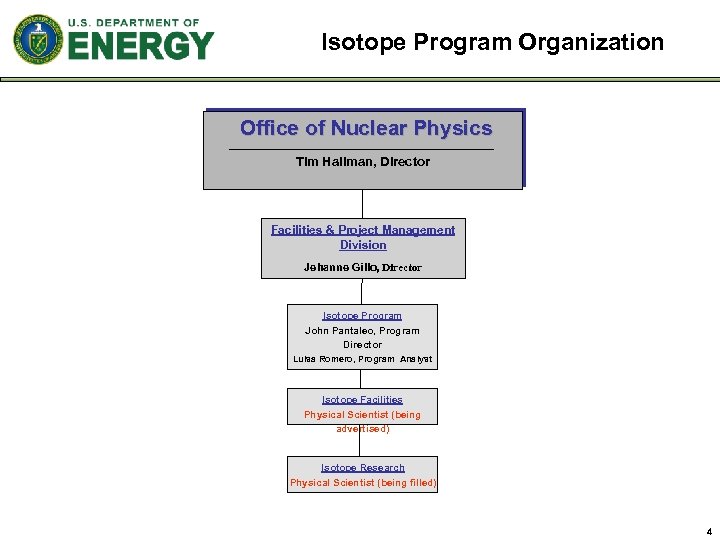 Isotope Program Organization Office of Nuclear Physics Tim Hallman, Director Facilities & Project Management Division Jehanne Gillo, Director Isotope Program John Pantaleo, Program Director Luisa Romero, Program Analyst Isotope Facilities Physical Scientist (being advertised) Isotope Research Physical Scientist (being filled) 4
Isotope Program Organization Office of Nuclear Physics Tim Hallman, Director Facilities & Project Management Division Jehanne Gillo, Director Isotope Program John Pantaleo, Program Director Luisa Romero, Program Analyst Isotope Facilities Physical Scientist (being advertised) Isotope Research Physical Scientist (being filled) 4
 Isotope Program • Transferred from the Office of Nuclear Energy to NP with the 2009 Appropriation. • Continues to produce, process, package and deliver isotopes for those isotopes not produced commercially. • Re-established research and development of isotope production techniques and the production of research isotopes • Pricing policy has been modified for research isotopes. Prices will be based on unit cost (e. g. , per millicurie) and not batch cost. Overall production cost was reduced. • Serves a broad community of Federal agencies in addition to DOE—NIH, NIST, EPA, NNSA, DHS… • Funding is from a combination of appropriations and sales—funds are deposited into the revolving fund which is externally audited annually. 5
Isotope Program • Transferred from the Office of Nuclear Energy to NP with the 2009 Appropriation. • Continues to produce, process, package and deliver isotopes for those isotopes not produced commercially. • Re-established research and development of isotope production techniques and the production of research isotopes • Pricing policy has been modified for research isotopes. Prices will be based on unit cost (e. g. , per millicurie) and not batch cost. Overall production cost was reduced. • Serves a broad community of Federal agencies in addition to DOE—NIH, NIST, EPA, NNSA, DHS… • Funding is from a combination of appropriations and sales—funds are deposited into the revolving fund which is externally audited annually. 5
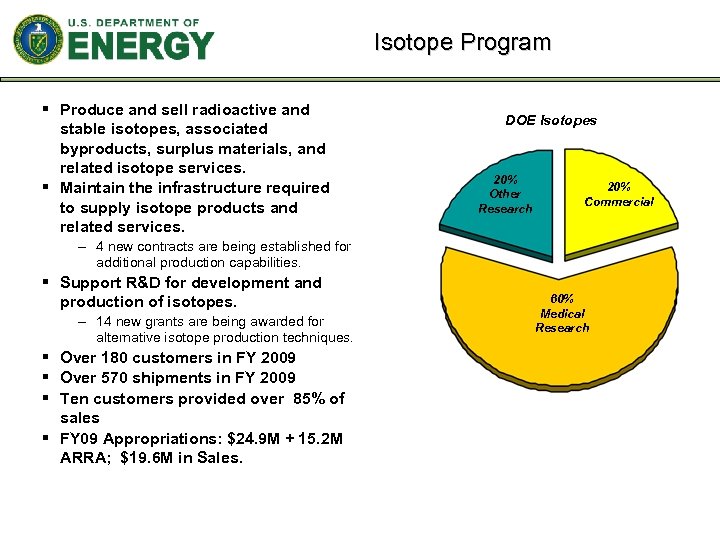 Isotope Program § Produce and sell radioactive and stable isotopes, associated byproducts, surplus materials, and related isotope services. § Maintain the infrastructure required to supply isotope products and related services. DOE Isotopes 20% Other Research 20% Commercial – 4 new contracts are being established for additional production capabilities. § Support R&D for development and production of isotopes. – 14 new grants are being awarded for alternative isotope production techniques. § Over 180 customers in FY 2009 § Over 570 shipments in FY 2009 § Ten customers provided over 85% of sales § FY 09 Appropriations: $24. 9 M + 15. 2 M ARRA; $19. 6 M in Sales. 60% Medical Research
Isotope Program § Produce and sell radioactive and stable isotopes, associated byproducts, surplus materials, and related isotope services. § Maintain the infrastructure required to supply isotope products and related services. DOE Isotopes 20% Other Research 20% Commercial – 4 new contracts are being established for additional production capabilities. § Support R&D for development and production of isotopes. – 14 new grants are being awarded for alternative isotope production techniques. § Over 180 customers in FY 2009 § Over 570 shipments in FY 2009 § Ten customers provided over 85% of sales § FY 09 Appropriations: $24. 9 M + 15. 2 M ARRA; $19. 6 M in Sales. 60% Medical Research
 Re-organizing the Isotope Program § Workshop held August 5 -7, 2008: The Nation's Needs for Isotopes: Present and Future Assembled representative stakeholders- federal, research and industrial to identify needs and challenges. § Establishing links of communications with federal agencies to understand needs and priorities Federal Working Group to discuss medical isotopes etc. (DOE BER, DOE NP and NIH); establishing NIH prioritization mechanism EOP Interagency Working Group to discuss He-3: NP/NNSA/DOD/DHS/CIA/FBI/Navy/Commerce/others Bi-national Working Group and OSTP Working Group on Mo-99 § Worked with industrial representatives to establish consortium and path forward for continuing Cf-252 production. Exploring other industrial opportunities. § Restructured the federal organization of the program – Federal vs contractor based. 7
Re-organizing the Isotope Program § Workshop held August 5 -7, 2008: The Nation's Needs for Isotopes: Present and Future Assembled representative stakeholders- federal, research and industrial to identify needs and challenges. § Establishing links of communications with federal agencies to understand needs and priorities Federal Working Group to discuss medical isotopes etc. (DOE BER, DOE NP and NIH); establishing NIH prioritization mechanism EOP Interagency Working Group to discuss He-3: NP/NNSA/DOD/DHS/CIA/FBI/Navy/Commerce/others Bi-national Working Group and OSTP Working Group on Mo-99 § Worked with industrial representatives to establish consortium and path forward for continuing Cf-252 production. Exploring other industrial opportunities. § Restructured the federal organization of the program – Federal vs contractor based. 7
 Re-organization continued § Restructuring the Isotope Business Office to National Isotope Data Center - Increased scope: coordinates and integrates multi-laboratory and university isotope production schedules; maintains isotope inventory balances and transportation container inventory and certifications; and conducts various outreach and societal activities. § Initiated R&D program on alternative isotope production techniques § Pricing policy has been modified for research isotopes. Prices will be based on unit cost and not batch cost. Overall production cost was reduced. § Established peer review mechanisms for facilities and initiatives § Establishing new production capabilities outside suite of NP/Isotope Program facilities – including other agency facilities and university facilities § Charged NSAC to set priorities for research opportunities and to 8
Re-organization continued § Restructuring the Isotope Business Office to National Isotope Data Center - Increased scope: coordinates and integrates multi-laboratory and university isotope production schedules; maintains isotope inventory balances and transportation container inventory and certifications; and conducts various outreach and societal activities. § Initiated R&D program on alternative isotope production techniques § Pricing policy has been modified for research isotopes. Prices will be based on unit cost and not batch cost. Overall production cost was reduced. § Established peer review mechanisms for facilities and initiatives § Establishing new production capabilities outside suite of NP/Isotope Program facilities – including other agency facilities and university facilities § Charged NSAC to set priorities for research opportunities and to 8
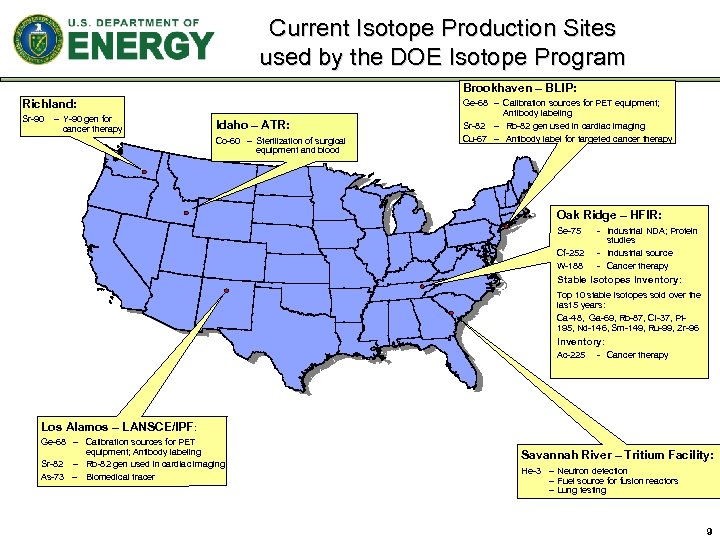 Current Isotope Production Sites used by the DOE Isotope Program Brookhaven – BLIP: Richland: Sr-90 – Y-90 gen for cancer therapy Idaho – ATR: Co-60 – Sterilization of surgical equipment and blood Ge-68 – Calibration sources for PET equipment; Antibody labeling Sr-82 – Rb-82 gen used in cardiac imaging Cu-67 – Antibody label for targeted cancer therapy Oak Ridge – HFIR: Se-75 Cf-252 W-188 - Industrial NDA; Protein studies - Industrial source - Cancer therapy Stable Isotopes Inventory: Top 10 stable isotopes sold over the last 5 years: Ca-48, Ga-69, Rb-87, Cl-37, Pt 195, Nd-146, Sm-149, Ru-99, Zr-96 Inventory: Ac-225 - Cancer therapy Los Alamos – LANSCE/IPF: Ge-68 – Calibration sources for PET equipment; Antibody labeling Sr-82 – Rb-82 gen used in cardiac imaging As-73 – Biomedical tracer Savannah River – Tritium Facility: He-3 – Neutron detection – Fuel source for fusion reactors – Lung testing 9
Current Isotope Production Sites used by the DOE Isotope Program Brookhaven – BLIP: Richland: Sr-90 – Y-90 gen for cancer therapy Idaho – ATR: Co-60 – Sterilization of surgical equipment and blood Ge-68 – Calibration sources for PET equipment; Antibody labeling Sr-82 – Rb-82 gen used in cardiac imaging Cu-67 – Antibody label for targeted cancer therapy Oak Ridge – HFIR: Se-75 Cf-252 W-188 - Industrial NDA; Protein studies - Industrial source - Cancer therapy Stable Isotopes Inventory: Top 10 stable isotopes sold over the last 5 years: Ca-48, Ga-69, Rb-87, Cl-37, Pt 195, Nd-146, Sm-149, Ru-99, Zr-96 Inventory: Ac-225 - Cancer therapy Los Alamos – LANSCE/IPF: Ge-68 – Calibration sources for PET equipment; Antibody labeling Sr-82 – Rb-82 gen used in cardiac imaging As-73 – Biomedical tracer Savannah River – Tritium Facility: He-3 – Neutron detection – Fuel source for fusion reactors – Lung testing 9
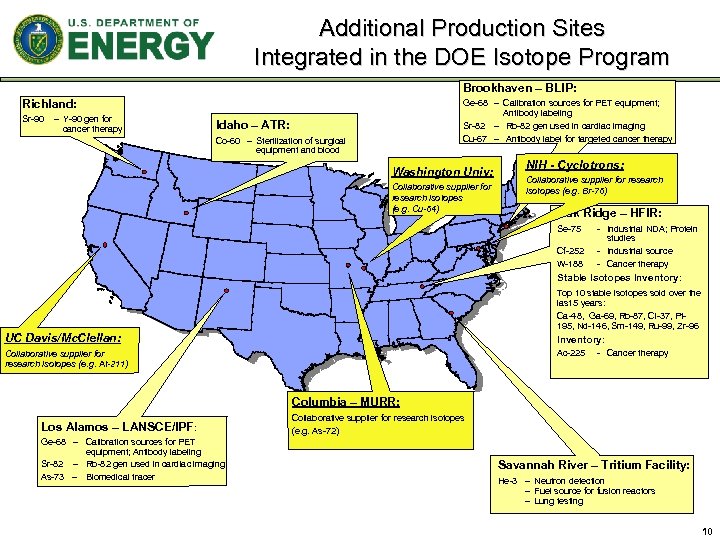 Additional Production Sites Integrated in the DOE Isotope Program Brookhaven – BLIP: Richland: Sr-90 – Y-90 gen for cancer therapy Ge-68 – Calibration sources for PET equipment; Antibody labeling Sr-82 – Rb-82 gen used in cardiac imaging Cu-67 – Antibody label for targeted cancer therapy Idaho – ATR: Co-60 – Sterilization of surgical equipment and blood Washington Univ: Collaborative supplier for research isotopes (e. g. Cu-64) NIH - Cyclotrons: Collaborative supplier for research isotopes (e. g. Br-76) Oak Ridge – HFIR: Se-75 Cf-252 W-188 - Industrial NDA; Protein studies - Industrial source - Cancer therapy Stable Isotopes Inventory: Top 10 stable isotopes sold over the last 5 years: Ca-48, Ga-69, Rb-87, Cl-37, Pt 195, Nd-146, Sm-149, Ru-99, Zr-96 UC Davis/Mc. Clellan: Inventory: Collaborative supplier for research isotopes (e. g. At-211) Ac-225 - Cancer therapy Columbia – MURR: Los Alamos – LANSCE/IPF: Ge-68 – Calibration sources for PET equipment; Antibody labeling Sr-82 – Rb-82 gen used in cardiac imaging As-73 – Biomedical tracer Collaborative supplier for research isotopes (e. g. As-72) Savannah River – Tritium Facility: He-3 – Neutron detection – Fuel source for fusion reactors – Lung testing 10
Additional Production Sites Integrated in the DOE Isotope Program Brookhaven – BLIP: Richland: Sr-90 – Y-90 gen for cancer therapy Ge-68 – Calibration sources for PET equipment; Antibody labeling Sr-82 – Rb-82 gen used in cardiac imaging Cu-67 – Antibody label for targeted cancer therapy Idaho – ATR: Co-60 – Sterilization of surgical equipment and blood Washington Univ: Collaborative supplier for research isotopes (e. g. Cu-64) NIH - Cyclotrons: Collaborative supplier for research isotopes (e. g. Br-76) Oak Ridge – HFIR: Se-75 Cf-252 W-188 - Industrial NDA; Protein studies - Industrial source - Cancer therapy Stable Isotopes Inventory: Top 10 stable isotopes sold over the last 5 years: Ca-48, Ga-69, Rb-87, Cl-37, Pt 195, Nd-146, Sm-149, Ru-99, Zr-96 UC Davis/Mc. Clellan: Inventory: Collaborative supplier for research isotopes (e. g. At-211) Ac-225 - Cancer therapy Columbia – MURR: Los Alamos – LANSCE/IPF: Ge-68 – Calibration sources for PET equipment; Antibody labeling Sr-82 – Rb-82 gen used in cardiac imaging As-73 – Biomedical tracer Collaborative supplier for research isotopes (e. g. As-72) Savannah River – Tritium Facility: He-3 – Neutron detection – Fuel source for fusion reactors – Lung testing 10
 FY 2010 Research Isotopes Capabilities § Actinium-225 § § § § § Arsenic-72 Arsenic-73 Berkelium-247 Beryllium-7 Bromine-86 Californium-252 Copper-64 Copper-67 Holmium-166 Iron-52 § § § Lead-203 Lutetium-177 Magnesium-28 Samarium-153 Selenium-72 Silicon-32 Radium-223/Th-227 Rubidium-83 Tungsten-188/Rhenium-188 Yttrium-86 Zirconium-89 Develop a coordinated production plan based on facility availability and customer deliveries. 11
FY 2010 Research Isotopes Capabilities § Actinium-225 § § § § § Arsenic-72 Arsenic-73 Berkelium-247 Beryllium-7 Bromine-86 Californium-252 Copper-64 Copper-67 Holmium-166 Iron-52 § § § Lead-203 Lutetium-177 Magnesium-28 Samarium-153 Selenium-72 Silicon-32 Radium-223/Th-227 Rubidium-83 Tungsten-188/Rhenium-188 Yttrium-86 Zirconium-89 Develop a coordinated production plan based on facility availability and customer deliveries. 11
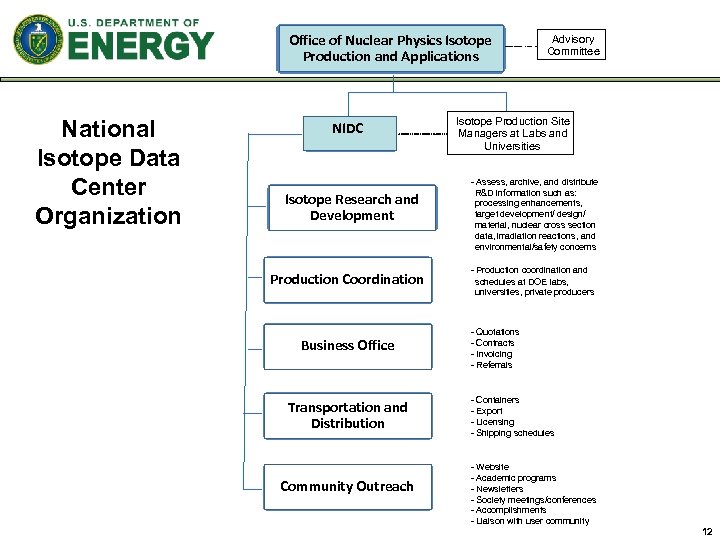 Office of Nuclear Physics Isotope Production and Applications National Isotope Data Center Organization NIDC Isotope Research and Development Production Coordination Business Office Transportation and Distribution Community Outreach Advisory Committee Isotope Production Site Managers at Labs and Universities - Assess, archive, and distribute R&D information such as: processing enhancements, target development/ design/ material, nuclear cross section data, irradiation reactions, and environmental/safety concerns - Production coordination and schedules at DOE labs, universities, private producers - Quotations - Contracts - Invoicing - Referrals - Containers - Export - Licensing - Shipping schedules - Website - Academic programs - Newsletters - Society meetings/conferences - Accomplishments - Liaison with user community 12
Office of Nuclear Physics Isotope Production and Applications National Isotope Data Center Organization NIDC Isotope Research and Development Production Coordination Business Office Transportation and Distribution Community Outreach Advisory Committee Isotope Production Site Managers at Labs and Universities - Assess, archive, and distribute R&D information such as: processing enhancements, target development/ design/ material, nuclear cross section data, irradiation reactions, and environmental/safety concerns - Production coordination and schedules at DOE labs, universities, private producers - Quotations - Contracts - Invoicing - Referrals - Containers - Export - Licensing - Shipping schedules - Website - Academic programs - Newsletters - Society meetings/conferences - Accomplishments - Liaison with user community 12
 NSAC Research Isotope Recommendations Compelling Research Opportunities using Isotopes § Invest in new production approaches of alpha-emitting radionuclides, e. g. Ac-225, At-211. § Invest in coordination of production capabilities and supporting research. § Produce isotopes of the heavy elements, e. g. Cf, Ra, TRU. § Focused study and R&D on new or increased production of He-3. § Re-establish domestic production and supply of stable isotopes. § Robust investment into education and training. 13
NSAC Research Isotope Recommendations Compelling Research Opportunities using Isotopes § Invest in new production approaches of alpha-emitting radionuclides, e. g. Ac-225, At-211. § Invest in coordination of production capabilities and supporting research. § Produce isotopes of the heavy elements, e. g. Cf, Ra, TRU. § Focused study and R&D on new or increased production of He-3. § Re-establish domestic production and supply of stable isotopes. § Robust investment into education and training. 13
 NSAC Long Range Plan Recommendations Isotopes for the Nation's Future A Long Range Plan § Maintain a continuous dialogue with all interested federal agencies and commercial isotope customers to forecast and match realistic isotope demand achievable production capabilities. § Coordinate production capabilities and supporting research to facilitate networking among existing DOE, commercial, and academic facilities. § Support a sustained research program in the base budget to enhance the capabilities of the isotope program in the production and supply of isotopes generated from reactors, accelerators, and separators. § Devise processes for the isotope program to better communicate with users, researchers, customers, students, and the public and to seek advice from experts: § Encourage the use of isotopes for research through reliable availability at affordable prices. § Increase the robustness and agility of isotope transportation both nationally and internationally. § Invest in workforce development in a multipronged approach, reaching out to students, post-doctoral fellows, and faculty through professional training, curriculum development, and meeting/workshop participation. § Construct and operate an electromagnetic isotope separator facility for stable 14
NSAC Long Range Plan Recommendations Isotopes for the Nation's Future A Long Range Plan § Maintain a continuous dialogue with all interested federal agencies and commercial isotope customers to forecast and match realistic isotope demand achievable production capabilities. § Coordinate production capabilities and supporting research to facilitate networking among existing DOE, commercial, and academic facilities. § Support a sustained research program in the base budget to enhance the capabilities of the isotope program in the production and supply of isotopes generated from reactors, accelerators, and separators. § Devise processes for the isotope program to better communicate with users, researchers, customers, students, and the public and to seek advice from experts: § Encourage the use of isotopes for research through reliable availability at affordable prices. § Increase the robustness and agility of isotope transportation both nationally and internationally. § Invest in workforce development in a multipronged approach, reaching out to students, post-doctoral fellows, and faculty through professional training, curriculum development, and meeting/workshop participation. § Construct and operate an electromagnetic isotope separator facility for stable 14
 Isotope Program Funding Opportunities § Request for proposals to domestically produce and separate stable and radioactive research isotopes that are needed for a wide variety of research topics, including medicine, physics, life sciences, material sciences, agriculture, and homeland security (June 2009) § Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA) for R&D on alternative isotope production techniques (May 2009) § Continue awards in FY 2010 of peer-reviewed FOA applications of alternative isotope production techniques § Continue developing capability for research isotope production in FY 2010 15
Isotope Program Funding Opportunities § Request for proposals to domestically produce and separate stable and radioactive research isotopes that are needed for a wide variety of research topics, including medicine, physics, life sciences, material sciences, agriculture, and homeland security (June 2009) § Funding Opportunity Announcement (FOA) for R&D on alternative isotope production techniques (May 2009) § Continue awards in FY 2010 of peer-reviewed FOA applications of alternative isotope production techniques § Continue developing capability for research isotope production in FY 2010 15
 Isotope Update § Actinium-225 – Continue to process the Th-229 for Ac-225; about 550 m. Ci per year. – ORNL is conducting R&D to assess alternative methods for the production of Th-229 and is exploring potential methods to overcome current barriers in separation and production. ORNL is also assessing the use of ionic liquids as solvents for improved production of radioisotopes. – LANL is conducting R&D to assess feasibility of an accelerator-based production route. – R&D conducted by North. Star is being supported for production of Ac-225 via high energy proton induced spallation. § Actinium-227 – R&D to separate and purify Ac-227 from surplus actinium-beryllium neutron sources at ORNL and other from legacy Ac-227 at PNNL. When completed, the Ac-227 can be used as a source (cow) for the decay production of very high purity Th-227 and Ra-223, important alphaemitting isotopes for medicine. § Astatine-211 16
Isotope Update § Actinium-225 – Continue to process the Th-229 for Ac-225; about 550 m. Ci per year. – ORNL is conducting R&D to assess alternative methods for the production of Th-229 and is exploring potential methods to overcome current barriers in separation and production. ORNL is also assessing the use of ionic liquids as solvents for improved production of radioisotopes. – LANL is conducting R&D to assess feasibility of an accelerator-based production route. – R&D conducted by North. Star is being supported for production of Ac-225 via high energy proton induced spallation. § Actinium-227 – R&D to separate and purify Ac-227 from surplus actinium-beryllium neutron sources at ORNL and other from legacy Ac-227 at PNNL. When completed, the Ac-227 can be used as a source (cow) for the decay production of very high purity Th-227 and Ra-223, important alphaemitting isotopes for medicine. § Astatine-211 16
 Isotope Update (continued) § Americium-241 – In the past, DOE provided Am-241 from inventory stored at LANL. Inventory is depleted, currently no domestic production of Am-241. – Jointly working with NNSA to define path forward. – Proposal will be peer reviewed by NP/NNSA. – Assumption is to develop purchase order contract with each customer or establish consortium with buyers similar to the Cf-252 contract. § Californium-252 – Capacity of production is maintained and within cost and schedule. – Capacity exists for additional future Cf-252 production as demand requires. 17
Isotope Update (continued) § Americium-241 – In the past, DOE provided Am-241 from inventory stored at LANL. Inventory is depleted, currently no domestic production of Am-241. – Jointly working with NNSA to define path forward. – Proposal will be peer reviewed by NP/NNSA. – Assumption is to develop purchase order contract with each customer or establish consortium with buyers similar to the Cf-252 contract. § Californium-252 – Capacity of production is maintained and within cost and schedule. – Capacity exists for additional future Cf-252 production as demand requires. 17
 Isotope Update (continued) § Copper-67 – R&D to produce Cu-67 at BLIP in quantity and quality suitable for clinical research. Current irradiation tests improved specific activity 3 fold to ~12 m. Ci/μg but further increase desirable. – Small quantities could be produced at universities. § Gadolinium-153 – Establish production capability of High-Specific-Activity Gd-153 at the INL with processing at PNNL. – The scope of work includes several staged tasks necessary to provide the ATR’s irradiation services, including capsule design and analysis, fabrication and assembly, irradiation, post-irradiation inspection, and handling and shipping. – The anticipated target insertion date into the ATR is May 29, 2010 for a 49 day irradiation cycle. INL and PNNL are still working out the details of capsule design and delivery. INL and PNNL representatives are meeting on Dec. 14 th to finalize the schedule. 18
Isotope Update (continued) § Copper-67 – R&D to produce Cu-67 at BLIP in quantity and quality suitable for clinical research. Current irradiation tests improved specific activity 3 fold to ~12 m. Ci/μg but further increase desirable. – Small quantities could be produced at universities. § Gadolinium-153 – Establish production capability of High-Specific-Activity Gd-153 at the INL with processing at PNNL. – The scope of work includes several staged tasks necessary to provide the ATR’s irradiation services, including capsule design and analysis, fabrication and assembly, irradiation, post-irradiation inspection, and handling and shipping. – The anticipated target insertion date into the ATR is May 29, 2010 for a 49 day irradiation cycle. INL and PNNL are still working out the details of capsule design and delivery. INL and PNNL representatives are meeting on Dec. 14 th to finalize the schedule. 18
 Isotope Update (continued) § Stable Isotopes – ORNL stable isotope purchase to replenish inventory of research isotopes such as Lu-176, Mo-100, Ni-62, W-186, and others. – ORNL is conducting R&D on technology for integrating gas centrifugation and electromagnetic isotope separation for preparation of stable isotopes. § Yttrium-86 – Developing large scale production of radioisotope Y-86 at BLIP in quantity and quality suitable for shipment to customers. Y-86 is a 14. 7 h positron emitter of interest to perform PET imaging study to optimize dose prior to therapeutic use of Y-90. 19
Isotope Update (continued) § Stable Isotopes – ORNL stable isotope purchase to replenish inventory of research isotopes such as Lu-176, Mo-100, Ni-62, W-186, and others. – ORNL is conducting R&D on technology for integrating gas centrifugation and electromagnetic isotope separation for preparation of stable isotopes. § Yttrium-86 – Developing large scale production of radioisotope Y-86 at BLIP in quantity and quality suitable for shipment to customers. Y-86 is a 14. 7 h positron emitter of interest to perform PET imaging study to optimize dose prior to therapeutic use of Y-90. 19
 Isotope Update (continued) § Molybdenum-99 – Within the DOE, NNSA has the lead on developing domestic Mo-99 supply based on LEU technology. – NP has been working closely with NNSA on this topic. – NP provides technical expertise as needed. – NP represented on Bi-national Working Group and OSTP Working Group. – SC considered capabilities at SC facilities for providing Mo-99 on shortterm emergency basis as part of Working Group exercises. – Focus was the High Flux Isotope Reactor stewarded by the Office of Basic Energy Sciences. – The U. S. Government is exploring international cooperation to mitigate potential shortages. – NNSA is investing in four LEU technologies for a domestic supply by 2013. 20
Isotope Update (continued) § Molybdenum-99 – Within the DOE, NNSA has the lead on developing domestic Mo-99 supply based on LEU technology. – NP has been working closely with NNSA on this topic. – NP provides technical expertise as needed. – NP represented on Bi-national Working Group and OSTP Working Group. – SC considered capabilities at SC facilities for providing Mo-99 on shortterm emergency basis as part of Working Group exercises. – Focus was the High Flux Isotope Reactor stewarded by the Office of Basic Energy Sciences. – The U. S. Government is exploring international cooperation to mitigate potential shortages. – NNSA is investing in four LEU technologies for a domestic supply by 2013. 20
 Isotope Update (continued) § Helium-3 Shortage – Established Integrated Project Team in March 2009 • Working Groups: Demand, Supply, Alternative Technologies (neutron detection); and Policy. • Guided by the steering group chaired by the National Security Council. • Prioritized and allocated some He-3 in FY 2009; additional to be allocated in FY 2010. • In June 2009 a He-3 workshop to explore alternatives to He-3 for neutron detection technologies was hosted by the Savannah River National Laboratory on behalf of the NNSA Network of Senior Scientists. – Strategy to Reduce/Manage Demand • Pursue and employ alternative technologies for neutron detection. American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) workshop to be held February 11, 2010: http: //cstsp. aaas. org/Helium 3. html. • Prioritize use of the existing supply of He-3. • Prioritize upcoming projects that would be big users of He-3. – Increase Supply • Seek He-3 supply from foreign countries. • Encourage He-3 recycling and reuse. • Investigate techniques to increase He-3 extraction efficiency. 21
Isotope Update (continued) § Helium-3 Shortage – Established Integrated Project Team in March 2009 • Working Groups: Demand, Supply, Alternative Technologies (neutron detection); and Policy. • Guided by the steering group chaired by the National Security Council. • Prioritized and allocated some He-3 in FY 2009; additional to be allocated in FY 2010. • In June 2009 a He-3 workshop to explore alternatives to He-3 for neutron detection technologies was hosted by the Savannah River National Laboratory on behalf of the NNSA Network of Senior Scientists. – Strategy to Reduce/Manage Demand • Pursue and employ alternative technologies for neutron detection. American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) workshop to be held February 11, 2010: http: //cstsp. aaas. org/Helium 3. html. • Prioritize use of the existing supply of He-3. • Prioritize upcoming projects that would be big users of He-3. – Increase Supply • Seek He-3 supply from foreign countries. • Encourage He-3 recycling and reuse. • Investigate techniques to increase He-3 extraction efficiency. 21
 Conclusions § Isotope Program is synergistic with Nuclear Physics program § Isotope Program is undergoing significant change in terms of management, mission , scope and capabilities § There are continuous challenges that the program faces § Much progress has already been made in addressing NSAC goals § Communication with stakeholders – both in the community and at a federal level – has improved § A high priority goal is to develop a coordinated, national strategy to meet present and future demand for isotopes in short supply for research and applications 22
Conclusions § Isotope Program is synergistic with Nuclear Physics program § Isotope Program is undergoing significant change in terms of management, mission , scope and capabilities § There are continuous challenges that the program faces § Much progress has already been made in addressing NSAC goals § Communication with stakeholders – both in the community and at a federal level – has improved § A high priority goal is to develop a coordinated, national strategy to meet present and future demand for isotopes in short supply for research and applications 22


