1b5b9ef29c83ecd2db3773b1d11d193a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 OECD WORK ON PENSION STATISTICS On-going data collection Working Party on Financial Statistics Paris, 6 -7 October 2003 Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Jean-Marc Salou OECD Financial Markets Division
OECD WORK ON PENSION STATISTICS On-going data collection Working Party on Financial Statistics Paris, 6 -7 October 2003 Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Jean-Marc Salou OECD Financial Markets Division
 Why pension funds statistics? < Pension funds are the main source of long-term savings; < Broad interaction with capital markets; < Use in macro-economic, financial and social policy; < OECD activities through the Working Party on Private Pension and through the International Network of Pension Regulators and Supervisors (INPRS).
Why pension funds statistics? < Pension funds are the main source of long-term savings; < Broad interaction with capital markets; < Use in macro-economic, financial and social policy; < OECD activities through the Working Party on Private Pension and through the International Network of Pension Regulators and Supervisors (INPRS).
 Goal of the OECD pension project The Global Pension Statistics Project would develop a system of international pension statistics, collected from primary sources, using coherent statistical concepts, definitions and methodologies.
Goal of the OECD pension project The Global Pension Statistics Project would develop a system of international pension statistics, collected from primary sources, using coherent statistical concepts, definitions and methodologies.
 A tool for measuring private pensions with an international perspective < < < Get data internationally comparable; Provide data together with information on their coverage (metadata); Supply up-to date data. 4
A tool for measuring private pensions with an international perspective < < < Get data internationally comparable; Provide data together with information on their coverage (metadata); Supply up-to date data. 4
 Practical objectives < < < Evaluate pension data currently available and its related metadata; Improve the harmonisation of concepts, definitions, and compliance in line with the taxonomy developed through the OECD Working Party on Private Pensions; Collect and analyse the data.
Practical objectives < < < Evaluate pension data currently available and its related metadata; Improve the harmonisation of concepts, definitions, and compliance in line with the taxonomy developed through the OECD Working Party on Private Pensions; Collect and analyse the data.
 Pension fund taxonomy < “Autonomous” pension funds: - Funds without legal personality (Portugal, Spain, Italy -fondi aperti-, Poland) - Funds with legal personality (rest of countries) < The governing body: - Trustee (UK, Ireland, Australia, Canada) - Board (foundations - Holland, Switzerland; mutuals - Germany, Austria, Hungary) - Fiduciary (USA) - Pension fund administrator (Portugal, Spain, Italy - fondi aperti)
Pension fund taxonomy < “Autonomous” pension funds: - Funds without legal personality (Portugal, Spain, Italy -fondi aperti-, Poland) - Funds with legal personality (rest of countries) < The governing body: - Trustee (UK, Ireland, Australia, Canada) - Board (foundations - Holland, Switzerland; mutuals - Germany, Austria, Hungary) - Fiduciary (USA) - Pension fund administrator (Portugal, Spain, Italy - fondi aperti)
 The new OECD definition: private plans Occupational plans (employment link as a condition of membership) Personal plans (employment link not needed) Mandatory a) DB: Finland, Holand, a) Sweden (mutual Australia, Switzerland funds) b) DC: Australia, Denmark, b) Mexico, Hungary, Iceland Poland (pension funds) Voluntary a) DB: Germany, Japan b) DC/DB: UK, USA, Canada c) DC: Italy, Spain In all countries, but tax advantages are not universal.
The new OECD definition: private plans Occupational plans (employment link as a condition of membership) Personal plans (employment link not needed) Mandatory a) DB: Finland, Holand, a) Sweden (mutual Australia, Switzerland funds) b) DC: Australia, Denmark, b) Mexico, Hungary, Iceland Poland (pension funds) Voluntary a) DB: Germany, Japan b) DC/DB: UK, USA, Canada c) DC: Italy, Spain In all countries, but tax advantages are not universal.
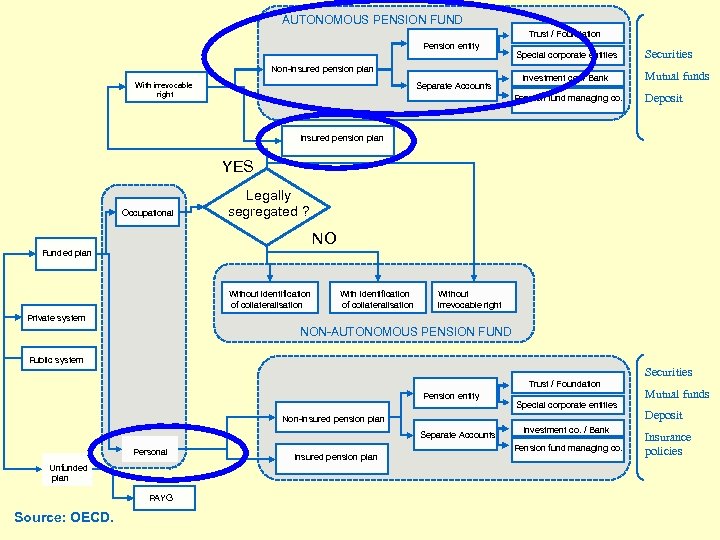 AUTONOMOUS PENSION FUND Trust / Foundation Pension entity Non-insured pension plan Separate Accounts With irrevocable right Special corporate entities Investment co. / Bank Pension fund managing co. Securities Mutual funds Deposit Insured pension plan YES Occupational Legally segregated ? NO Funded plan Without identification of collateralisation Without irrevocable right Private system NON-AUTONOMOUS PENSION FUND Public system Securities Trust / Foundation Pension entity Special corporate entities Non-insured pension plan Separate Accounts Personal Unfunded plan PAYG Source: OECD. Insured pension plan Investment co. / Bank Pension fund managing co. Mutual funds Deposit Insurance policies
AUTONOMOUS PENSION FUND Trust / Foundation Pension entity Non-insured pension plan Separate Accounts With irrevocable right Special corporate entities Investment co. / Bank Pension fund managing co. Securities Mutual funds Deposit Insured pension plan YES Occupational Legally segregated ? NO Funded plan Without identification of collateralisation Without irrevocable right Private system NON-AUTONOMOUS PENSION FUND Public system Securities Trust / Foundation Pension entity Special corporate entities Non-insured pension plan Separate Accounts Personal Unfunded plan PAYG Source: OECD. Insured pension plan Investment co. / Bank Pension fund managing co. Mutual funds Deposit Insurance policies
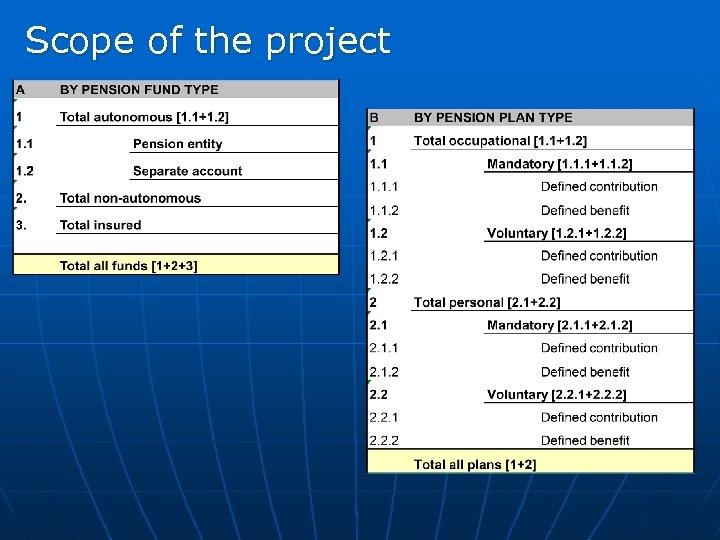 Scope of the project
Scope of the project
 Variables < Assets < Liabilities < Income < Expenditure < Membership
Variables < Assets < Liabilities < Income < Expenditure < Membership
 Where Are We? < < A common vocabulary: the Taxonomy and Glossary of pension terms; Design of a a statistical questionnaire based on a data availability exercise; Approval of the questionnaire by the Task Force on Pension Statistics and the Working Party on Private Pensions; First round of the on-going data collection (2001 and 2002 data). 11
Where Are We? < < A common vocabulary: the Taxonomy and Glossary of pension terms; Design of a a statistical questionnaire based on a data availability exercise; Approval of the questionnaire by the Task Force on Pension Statistics and the Working Party on Private Pensions; First round of the on-going data collection (2001 and 2002 data). 11
 Moving forward < < Preliminary results will be presented for the next Working Party on Private Pensions meeting in November; Taxonomy and glossary to be revised; Revisiting the methodology on the basis of the first round of data collection; Presentation of a set of financial indicators in June 2004. 12
Moving forward < < Preliminary results will be presented for the next Working Party on Private Pensions meeting in November; Taxonomy and glossary to be revised; Revisiting the methodology on the basis of the first round of data collection; Presentation of a set of financial indicators in June 2004. 12
 Issues to be address < Coherence with other datasets, - Autonomous vs. non-autonomous pension funds, - Funded vs. unfunded pension plans; < Coherence within the SNA framework (Taxonomy and Glossary); < Enhance data completeness; < Up-to-date data through the delivery of preliminary or estimates. 13
Issues to be address < Coherence with other datasets, - Autonomous vs. non-autonomous pension funds, - Funded vs. unfunded pension plans; < Coherence within the SNA framework (Taxonomy and Glossary); < Enhance data completeness; < Up-to-date data through the delivery of preliminary or estimates. 13
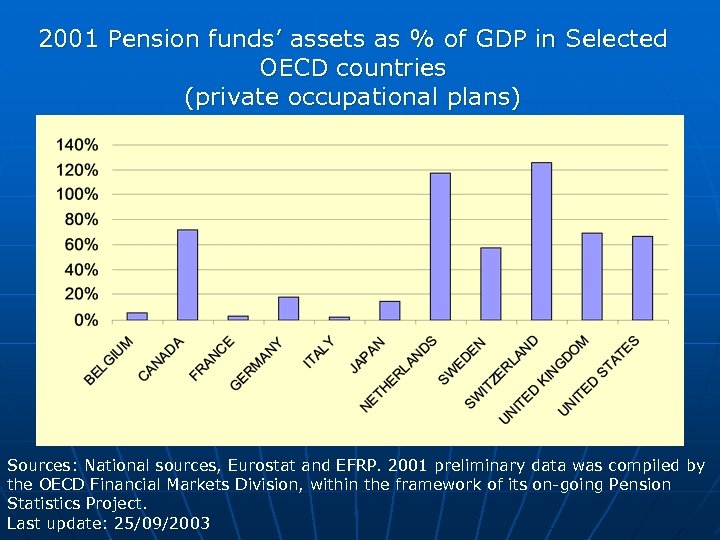 2001 Pension funds’ assets as % of GDP in Selected OECD countries (private occupational plans) Sources: National sources, Eurostat and EFRP. 2001 preliminary data was compiled by the OECD Financial Markets Division, within the framework of its on-going Pension Statistics Project. Last update: 25/09/2003
2001 Pension funds’ assets as % of GDP in Selected OECD countries (private occupational plans) Sources: National sources, Eurostat and EFRP. 2001 preliminary data was compiled by the OECD Financial Markets Division, within the framework of its on-going Pension Statistics Project. Last update: 25/09/2003
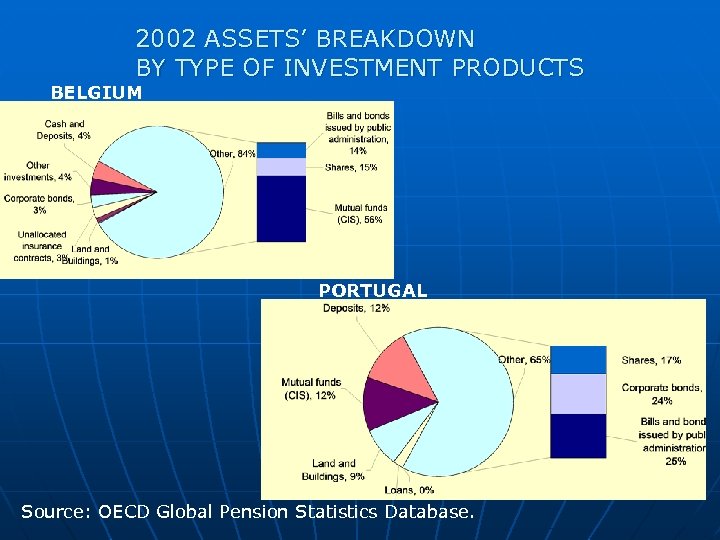 2002 ASSETS’ BREAKDOWN BY TYPE OF INVESTMENT PRODUCTS BELGIUM PORTUGAL Source: OECD Global Pension Statistics Database.
2002 ASSETS’ BREAKDOWN BY TYPE OF INVESTMENT PRODUCTS BELGIUM PORTUGAL Source: OECD Global Pension Statistics Database.
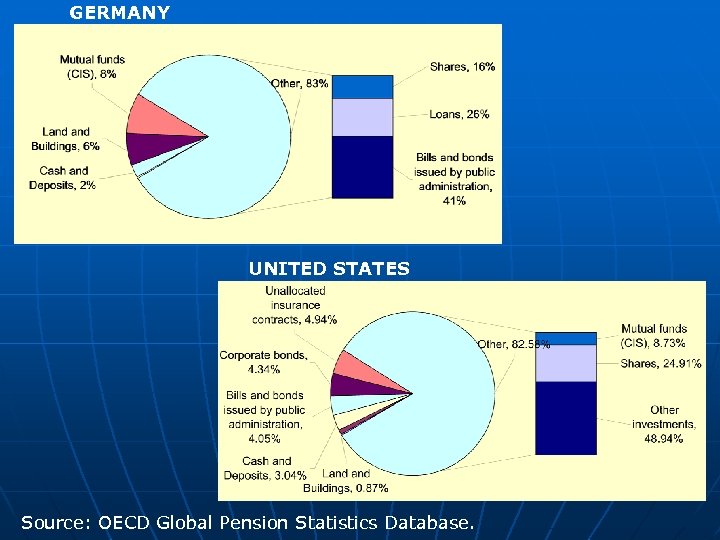 GERMANY UNITED STATES Source: OECD Global Pension Statistics Database.
GERMANY UNITED STATES Source: OECD Global Pension Statistics Database.
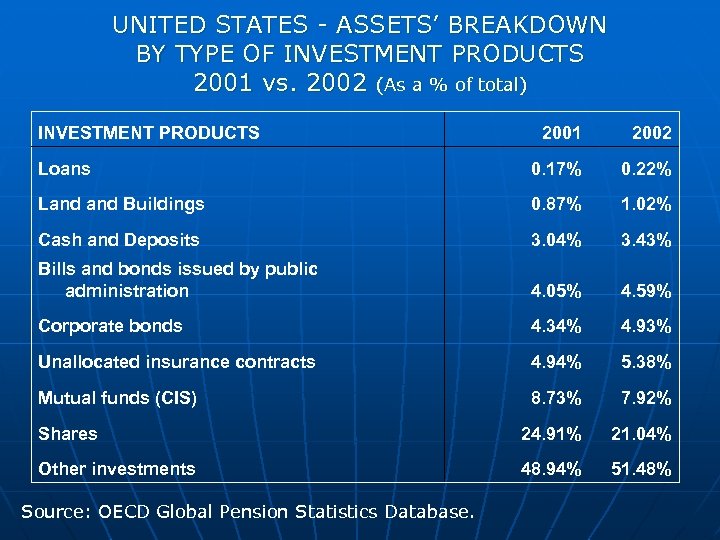 UNITED STATES - ASSETS’ BREAKDOWN BY TYPE OF INVESTMENT PRODUCTS 2001 vs. 2002 (As a % of total) INVESTMENT PRODUCTS 2001 2002 Loans 0. 17% 0. 22% Land Buildings 0. 87% 1. 02% Cash and Deposits 3. 04% 3. 43% Bills and bonds issued by public administration 4. 05% 4. 59% Corporate bonds 4. 34% 4. 93% Unallocated insurance contracts 4. 94% 5. 38% Mutual funds (CIS) 8. 73% 7. 92% Shares 24. 91% 21. 04% Other investments 48. 94% 51. 48% Source: OECD Global Pension Statistics Database.
UNITED STATES - ASSETS’ BREAKDOWN BY TYPE OF INVESTMENT PRODUCTS 2001 vs. 2002 (As a % of total) INVESTMENT PRODUCTS 2001 2002 Loans 0. 17% 0. 22% Land Buildings 0. 87% 1. 02% Cash and Deposits 3. 04% 3. 43% Bills and bonds issued by public administration 4. 05% 4. 59% Corporate bonds 4. 34% 4. 93% Unallocated insurance contracts 4. 94% 5. 38% Mutual funds (CIS) 8. 73% 7. 92% Shares 24. 91% 21. 04% Other investments 48. 94% 51. 48% Source: OECD Global Pension Statistics Database.


