6d069e5bf37ab99ca5e5a14a7f5952ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 OCULAR HYPERTENSION AFTER PENETRATING KERATOPLASTY F Orucov, E Strassman, D Landau, J Frucht-Pery and A Solomon, Department of Ophthalmology, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel Authors have no financial interests in any of the mentioned products or companies
OCULAR HYPERTENSION AFTER PENETRATING KERATOPLASTY F Orucov, E Strassman, D Landau, J Frucht-Pery and A Solomon, Department of Ophthalmology, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Jerusalem, Israel Authors have no financial interests in any of the mentioned products or companies
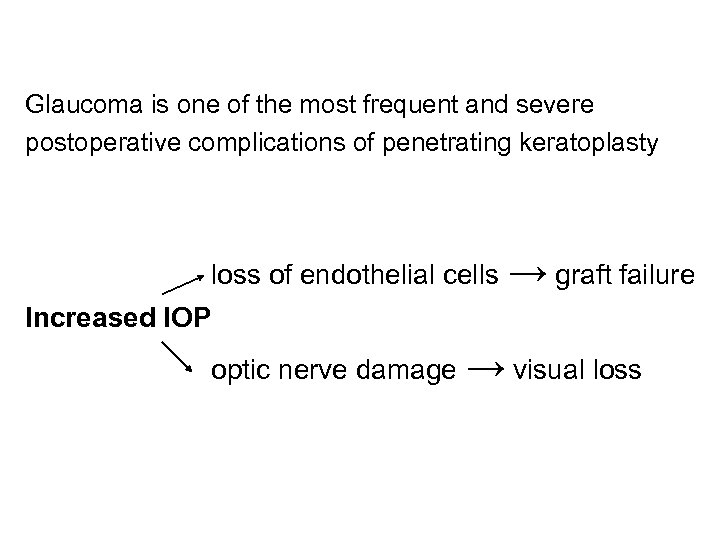 Glaucoma is one of the most frequent and severe postoperative complications of penetrating keratoplasty loss of endothelial cells → graft failure Increased IOP optic nerve damage → visual loss
Glaucoma is one of the most frequent and severe postoperative complications of penetrating keratoplasty loss of endothelial cells → graft failure Increased IOP optic nerve damage → visual loss
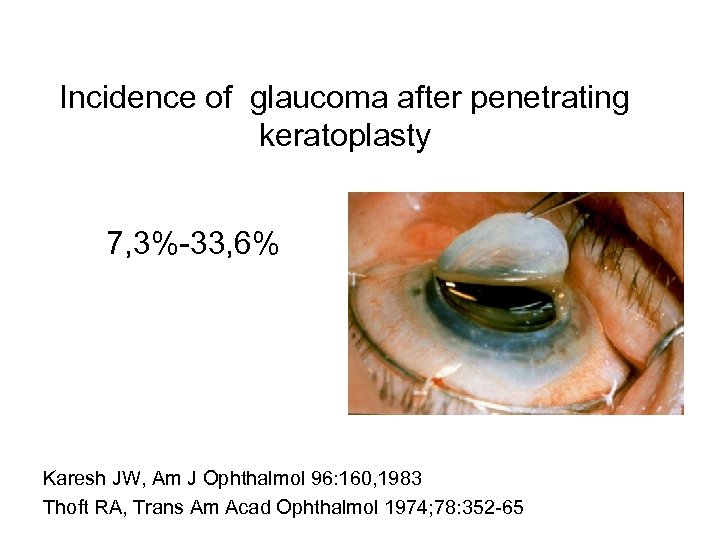 Incidence of glaucoma after penetrating keratoplasty 7, 3%-33, 6% Karesh JW, Am J Ophthalmol 96: 160, 1983 Thoft RA, Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol 1974; 78: 352 -65
Incidence of glaucoma after penetrating keratoplasty 7, 3%-33, 6% Karesh JW, Am J Ophthalmol 96: 160, 1983 Thoft RA, Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol 1974; 78: 352 -65
 PURPOSE This study evaluated the incidence and risk factors associated with Ocular Hypertension following penetrating keratoplasty
PURPOSE This study evaluated the incidence and risk factors associated with Ocular Hypertension following penetrating keratoplasty
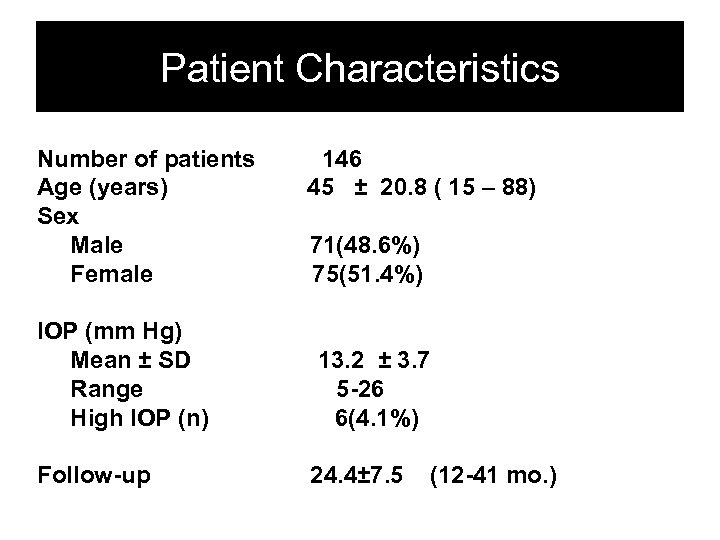 Patient Characteristics Number of patients Age (years) Sex Male Female IOP (mm Hg) Mean ± SD Range High IOP (n) Follow-up 146 45 ± 20. 8 ( 15 – 88) 71(48. 6%) 75(51. 4%) 13. 2 ± 3. 7 5 -26 6(4. 1%) 24. 4± 7. 5 (12 -41 mo. )
Patient Characteristics Number of patients Age (years) Sex Male Female IOP (mm Hg) Mean ± SD Range High IOP (n) Follow-up 146 45 ± 20. 8 ( 15 – 88) 71(48. 6%) 75(51. 4%) 13. 2 ± 3. 7 5 -26 6(4. 1%) 24. 4± 7. 5 (12 -41 mo. )
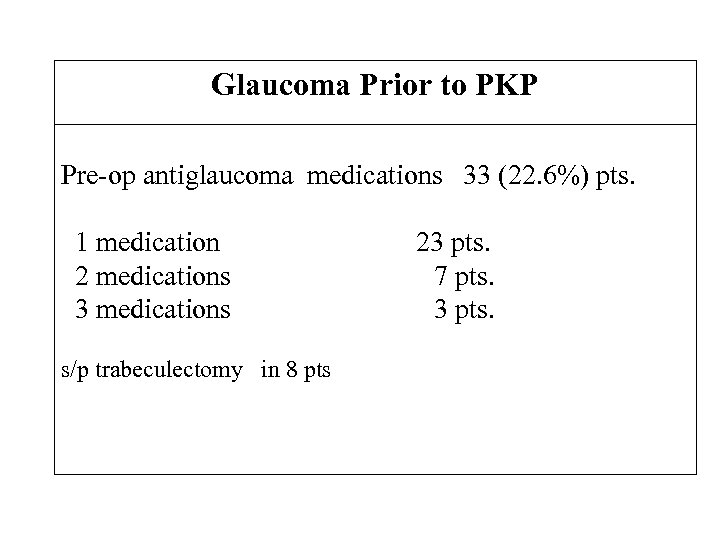 Glaucoma Prior to PKP Pre-op antiglaucoma medications 33 (22. 6%) pts. 1 medication 2 medications 3 medications s/p trabeculectomy in 8 pts 23 pts. 7 pts. 3 pts.
Glaucoma Prior to PKP Pre-op antiglaucoma medications 33 (22. 6%) pts. 1 medication 2 medications 3 medications s/p trabeculectomy in 8 pts 23 pts. 7 pts. 3 pts.
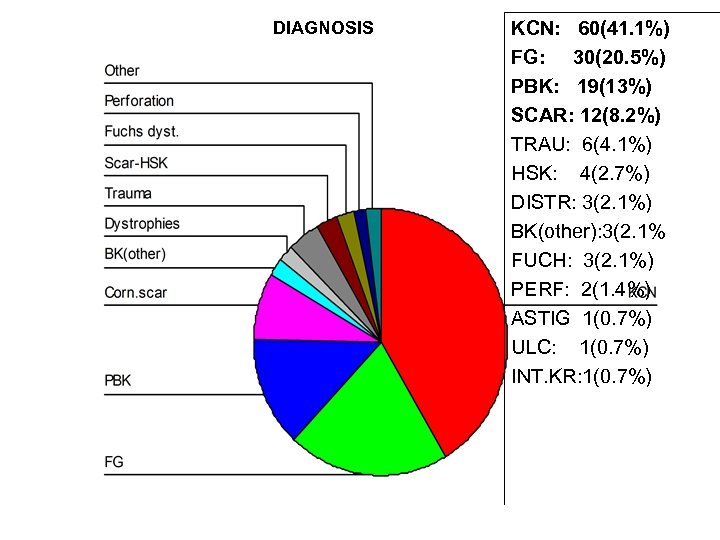 DIAGNOSIS KCN: 60(41. 1%) FG: 30(20. 5%) PBK: 19(13%) SCAR: 12(8. 2%) TRAU: 6(4. 1%) HSK: 4(2. 7%) DISTR: 3(2. 1%) BK(other): 3(2. 1% FUCH: 3(2. 1%) PERF: 2(1. 4%) ASTIG 1(0. 7%) ULC: 1(0. 7%) INT. KR: 1(0. 7%)
DIAGNOSIS KCN: 60(41. 1%) FG: 30(20. 5%) PBK: 19(13%) SCAR: 12(8. 2%) TRAU: 6(4. 1%) HSK: 4(2. 7%) DISTR: 3(2. 1%) BK(other): 3(2. 1% FUCH: 3(2. 1%) PERF: 2(1. 4%) ASTIG 1(0. 7%) ULC: 1(0. 7%) INT. KR: 1(0. 7%)
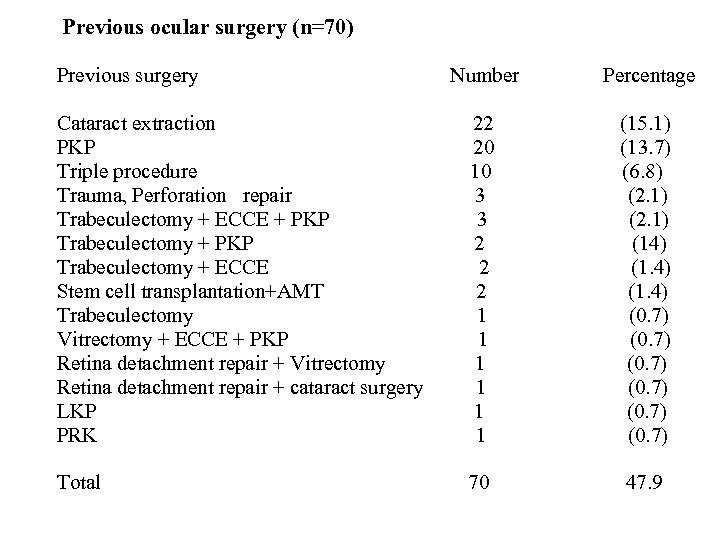 Previous ocular surgery (n=70) Previous surgery Number Percentage Cataract extraction PKP Triple procedure Trauma, Perforation repair Trabeculectomy + ECCE + PKP Trabeculectomy + ECCE Stem cell transplantation+AMT Trabeculectomy Vitrectomy + ECCE + PKP Retina detachment repair + Vitrectomy Retina detachment repair + cataract surgery LKP PRK 22 20 10 3 3 2 2 2 1 1 1 (15. 1) (13. 7) (6. 8) (2. 1) (14) (1. 4) (0. 7) Total 70 47. 9
Previous ocular surgery (n=70) Previous surgery Number Percentage Cataract extraction PKP Triple procedure Trauma, Perforation repair Trabeculectomy + ECCE + PKP Trabeculectomy + ECCE Stem cell transplantation+AMT Trabeculectomy Vitrectomy + ECCE + PKP Retina detachment repair + Vitrectomy Retina detachment repair + cataract surgery LKP PRK 22 20 10 3 3 2 2 2 1 1 1 (15. 1) (13. 7) (6. 8) (2. 1) (14) (1. 4) (0. 7) Total 70 47. 9
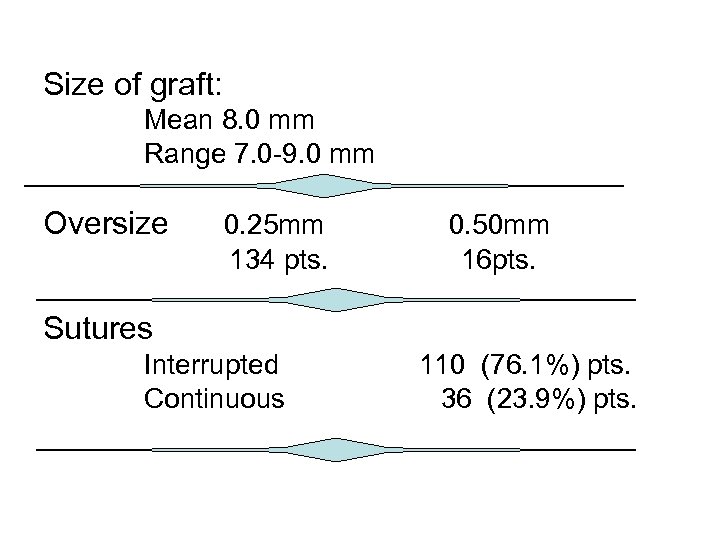 Size of graft: Mean 8. 0 mm Range 7. 0 -9. 0 mm Oversize 0. 25 mm 134 pts. 0. 50 mm 16 pts. Sutures Interrupted Continuous 110 (76. 1%) pts. 36 (23. 9%) pts.
Size of graft: Mean 8. 0 mm Range 7. 0 -9. 0 mm Oversize 0. 25 mm 134 pts. 0. 50 mm 16 pts. Sutures Interrupted Continuous 110 (76. 1%) pts. 36 (23. 9%) pts.
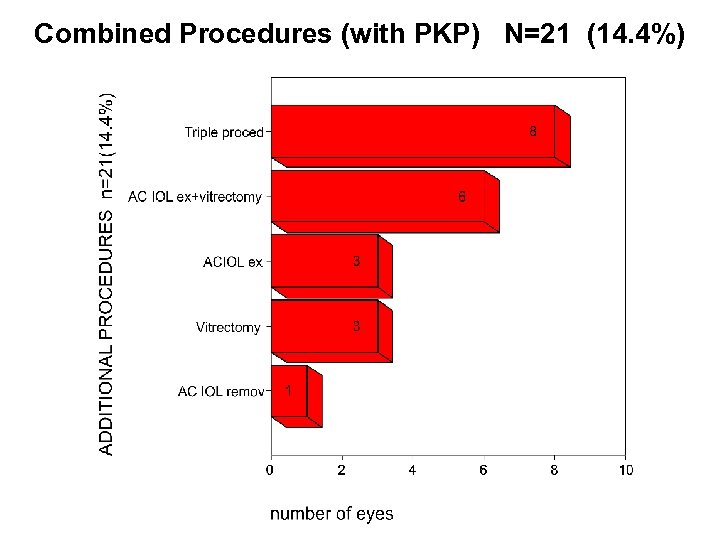 Combined Procedures (with PKP) N=21 (14. 4%)
Combined Procedures (with PKP) N=21 (14. 4%)
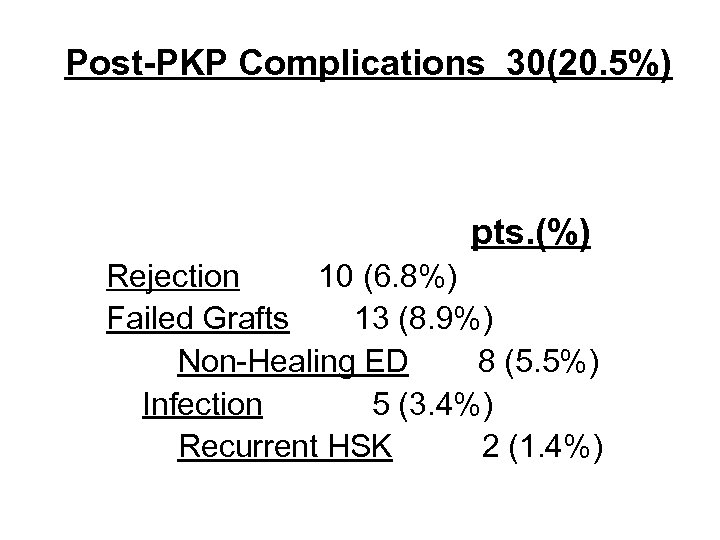 Post-PKP Complications 30(20. 5%) pts. (%) Rejection 10 (6. 8%) Failed Grafts 13 (8. 9%) Non-Healing ED 8 (5. 5%) Infection 5 (3. 4%) Recurrent HSK 2 (1. 4%)
Post-PKP Complications 30(20. 5%) pts. (%) Rejection 10 (6. 8%) Failed Grafts 13 (8. 9%) Non-Healing ED 8 (5. 5%) Infection 5 (3. 4%) Recurrent HSK 2 (1. 4%)
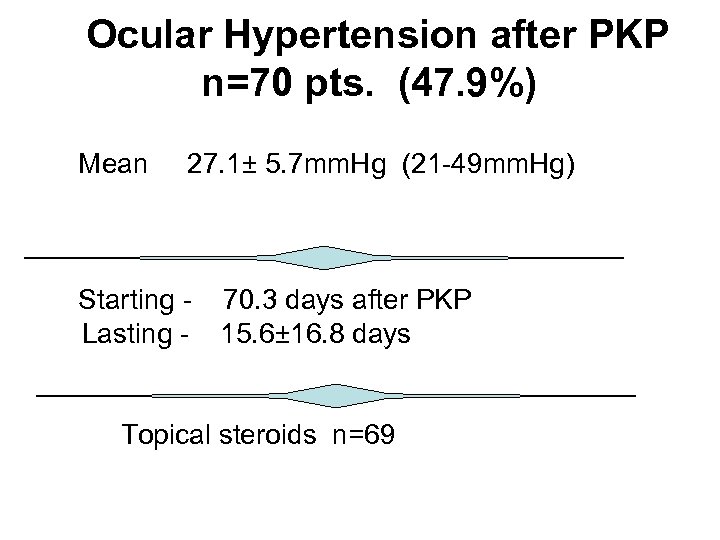 Ocular Hypertension after PKP n=70 pts. (47. 9%) Mean 27. 1± 5. 7 mm. Hg (21 -49 mm. Hg) Starting Lasting - 70. 3 days after PKP 15. 6± 16. 8 days Topical steroids n=69
Ocular Hypertension after PKP n=70 pts. (47. 9%) Mean 27. 1± 5. 7 mm. Hg (21 -49 mm. Hg) Starting Lasting - 70. 3 days after PKP 15. 6± 16. 8 days Topical steroids n=69
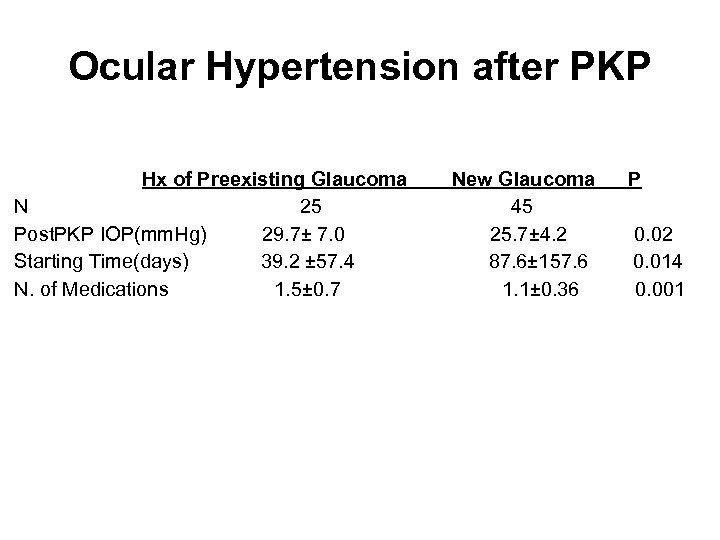 Ocular Hypertension after PKP Hx of Preexisting Glaucoma N 25 Post. PKP IOP(mm. Hg) 29. 7± 7. 0 Starting Time(days) 39. 2 ± 57. 4 N. of Medications 1. 5± 0. 7 New Glaucoma 45 25. 7± 4. 2 87. 6± 157. 6 1. 1± 0. 36 P 0. 02 0. 014 0. 001
Ocular Hypertension after PKP Hx of Preexisting Glaucoma N 25 Post. PKP IOP(mm. Hg) 29. 7± 7. 0 Starting Time(days) 39. 2 ± 57. 4 N. of Medications 1. 5± 0. 7 New Glaucoma 45 25. 7± 4. 2 87. 6± 157. 6 1. 1± 0. 36 P 0. 02 0. 014 0. 001
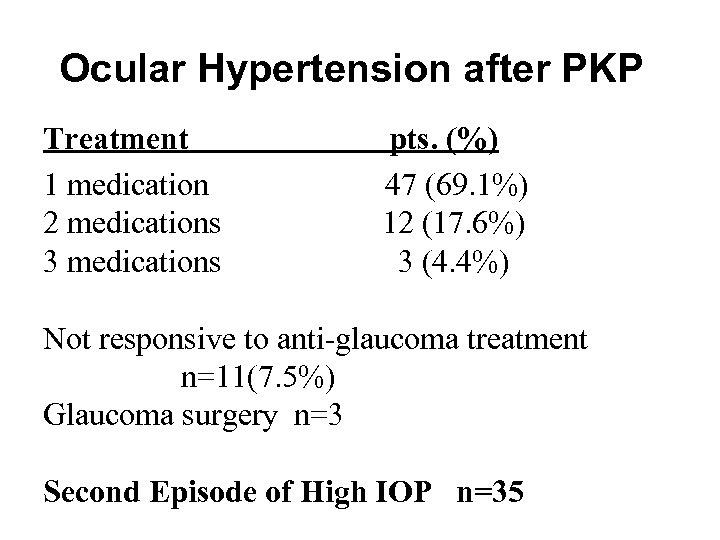 Ocular Hypertension after PKP Treatment 1 medication 2 medications 3 medications pts. (%) 47 (69. 1%) 12 (17. 6%) 3 (4. 4%) Not responsive to anti-glaucoma treatment n=11(7. 5%) Glaucoma surgery n=3 Second Episode of High IOP n=35
Ocular Hypertension after PKP Treatment 1 medication 2 medications 3 medications pts. (%) 47 (69. 1%) 12 (17. 6%) 3 (4. 4%) Not responsive to anti-glaucoma treatment n=11(7. 5%) Glaucoma surgery n=3 Second Episode of High IOP n=35
 Graft Failure in Patients with Postperative Glaucoma • 9 of 13 failed grafts (P=0. 107). • Pre-existing glaucoma was not a cause for graft failure (p=0. 152 chi-square test)
Graft Failure in Patients with Postperative Glaucoma • 9 of 13 failed grafts (P=0. 107). • Pre-existing glaucoma was not a cause for graft failure (p=0. 152 chi-square test)
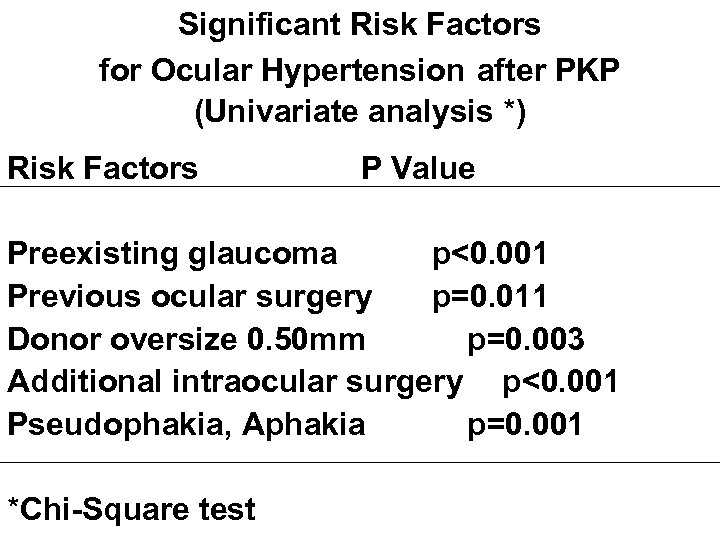 Significant Risk Factors for Ocular Hypertension after PKP (Univariate analysis *) Risk Factors P Value Preexisting glaucoma p<0. 001 Previous ocular surgery p=0. 011 Donor oversize 0. 50 mm p=0. 003 Additional intraocular surgery p<0. 001 Pseudophakia, Aphakia p=0. 001 *Chi-Square test
Significant Risk Factors for Ocular Hypertension after PKP (Univariate analysis *) Risk Factors P Value Preexisting glaucoma p<0. 001 Previous ocular surgery p=0. 011 Donor oversize 0. 50 mm p=0. 003 Additional intraocular surgery p<0. 001 Pseudophakia, Aphakia p=0. 001 *Chi-Square test
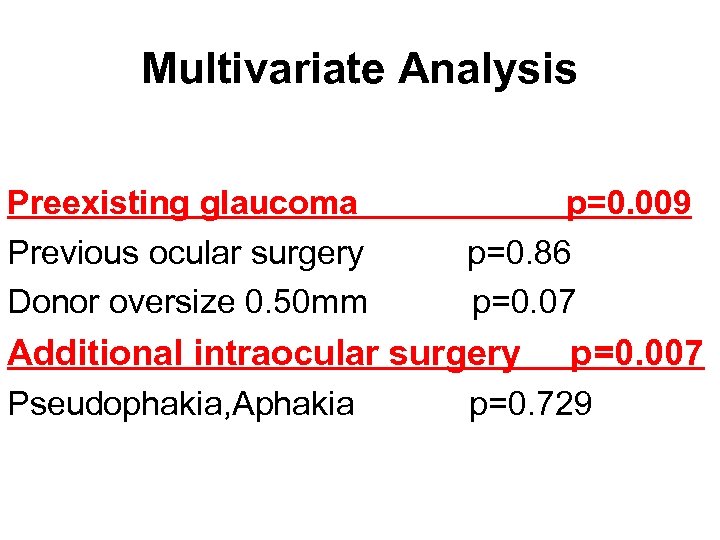 Multivariate Analysis Preexisting glaucoma Previous ocular surgery Donor oversize 0. 50 mm p=0. 009 p=0. 86 p=0. 07 Additional intraocular surgery Pseudophakia, Aphakia p=0. 007 p=0. 729
Multivariate Analysis Preexisting glaucoma Previous ocular surgery Donor oversize 0. 50 mm p=0. 009 p=0. 86 p=0. 07 Additional intraocular surgery Pseudophakia, Aphakia p=0. 007 p=0. 729
 Conclusions • Ocular Hypertension is Common in Patients Post-PKP • Pre-Operative Glaucoma and Additional Surgical Procedures are risk factors for Postoperative Ocular Hypertension • Monitoring of IOP During all Visits after PKP
Conclusions • Ocular Hypertension is Common in Patients Post-PKP • Pre-Operative Glaucoma and Additional Surgical Procedures are risk factors for Postoperative Ocular Hypertension • Monitoring of IOP During all Visits after PKP
 Summary The incidence of one episode of ocular hypertension after PKP is 47. 7% Starting after 70 days Second episode: 24% 7. 5% do not respond to topical management
Summary The incidence of one episode of ocular hypertension after PKP is 47. 7% Starting after 70 days Second episode: 24% 7. 5% do not respond to topical management


