2486fbee4022d38ab9ad33b5fd336a90.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 52

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Futuregazing: A presentation to the AUC staff Atlanta University Center staff retreat 16 July 2006 Atlanta, GA Eric Childress OCLC Research

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Outline § The Big Picture § Generations § Perceptions of Library Users § The Library Realm § OCLC – work underway § Q&A / Discussion

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center OCLC Reports http: //www. oclc. org/reports

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center The Big Picture

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Pattern recognition § Production anywhere, Global distribution § Make products anywhere, ship them everywhere § Offshore business processes & research centers § Network everywhere § Wi-fi, Bluetooth, cell phone towers, GPS § Big brands & mini channels § Mega-publishers, -media, -retailers, -search engines § Niche markets exploited via Ad. Words & affiliate programs § The “Attention Economy”

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Pattern recognition (cont’) § Portable devices, digital content, Net in your pocket § Devices (i. Pods, now with video; Are i. Phones next? ) § Audio (Ringtones, i. Tunes, Podcasts) & Video (Vlogs, Google § Self-service, micro-consumption § The “convenience” society – 24 x 7 stores, ATMs, click-n-buy § Disaggregation – consume by the news story, song, etc. § Intellectual property issues § Big business not-so-secretly wants all transactions billable § Open Source & Open Content rising (e. g. , Apache, Creative Commons)

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Me, mine, ours § Individual-driven content rising: § § Digital images/video (flickr, Picasa, You. Tube) § § Personal web pages/Blogs (a new one each second!) Bookmarks, etc. (e. g. , del. icio. us, furl, digg, technorati) The Network as community § § Community authorship - open content (Wikipedia), open source software § § Online gaming, VOIP, chat Myspace, Facebook, etc. personal presence services Instant verification: § § RSS, blogs, search engines, online news, opinion sites, fact-checking sites, etc. post and process news and opinion swiftly The Wisdom of the crowd § Google’s Page-Rank uses “link-love” to rank value § Amazon, etc. using buying decisions for recommendations, more
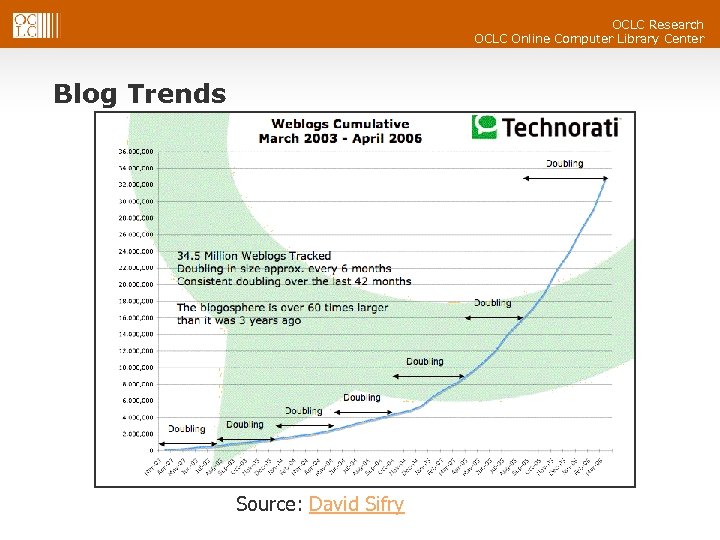
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Blog Trends Source: David Sifry

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center It’s all digital (or will be) § Content is now born digital § Editorial & publishing workflows are digital § Print is moving from default format to being a special-cases output option § Deep indexing: § Google, Yahoo, etc. print digitization initiatives § Amazon’s “Search inside” § On demand: Google Alerts, MSN RSS, etc. § Strong interest in digitizing older material (the “long tail”) § Google Print Library project / Yahoo & Open Content Alliance / Million Books project, Project Gutenberg, others. . § Other sources – Archives, museums, government agencies, NGO & university press publication backfiles, more… § Many, many digital library projects

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Techscape § Web 2. 0: § The Network spans all attached devices (i. Pods, phones, etc. ) § Software resides on the Net, not the workstation § “Participative Net” – social environment § Content mashed-up, reused, altered, re-released § System refactoring § Modularity (micro-services, remixing, multiple sources) § Layering (loosely-coupled systems) § Interoperability (low-friction, high reuse) § Lightweight protocols gaining favor (e. g. , SRW/SRU, microformats) § Machine-oriented services (Web services)

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Generations

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Recent generations (U. S. ) § Baby Boomers [1946 -64] § Technological bloom § Mass media, national brands, superstars § Social, cultural, political upheaval § Generation X [born 1965 -78] § Sometimes overshadowed by Boomers § Global brands, personal computing, electronic gaming § “Me” generation § Millennials [born 1979 -2000] § Net/Technology is woven into life § Close to parents § Group activity is natural § Ethnic/racial/cultural diversity is a given
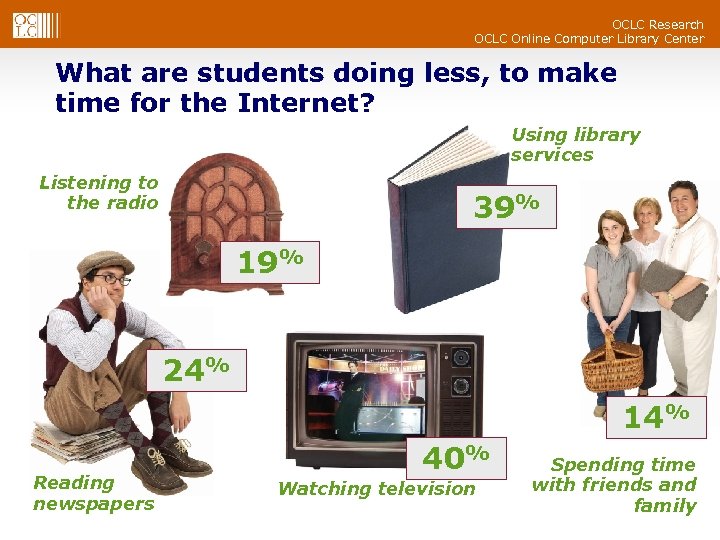
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center What are students doing less, to make time for the Internet? Using library services Listening to the radio 39% 19% 24% 14% Reading newspapers 40% Watching television Spending time with friends and family

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Perceptions of Users
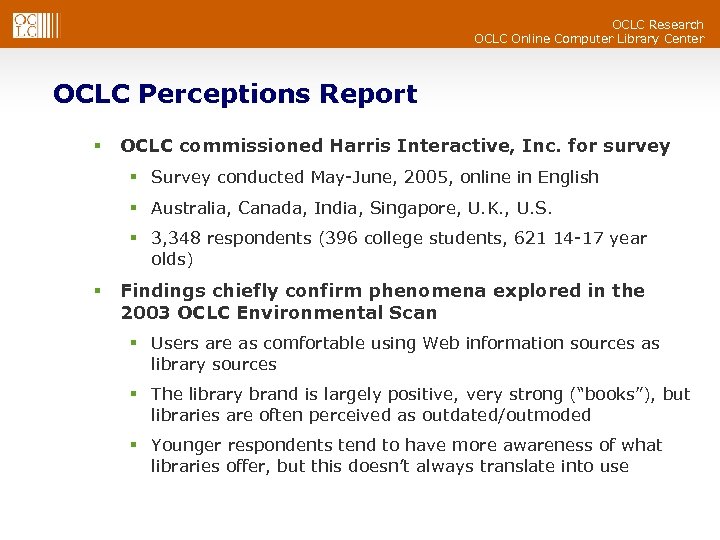
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center OCLC Perceptions Report § OCLC commissioned Harris Interactive, Inc. for survey § Survey conducted May-June, 2005, online in English § Australia, Canada, India, Singapore, U. K. , U. S. § 3, 348 respondents (396 college students, 621 14 -17 year olds) § Findings chiefly confirm phenomena explored in the 2003 OCLC Environmental Scan § Users are as comfortable using Web information sources as library sources § The library brand is largely positive, very strong (“books”), but libraries are often perceived as outdated/outmoded § Younger respondents tend to have more awareness of what libraries offer, but this doesn’t always translate into use
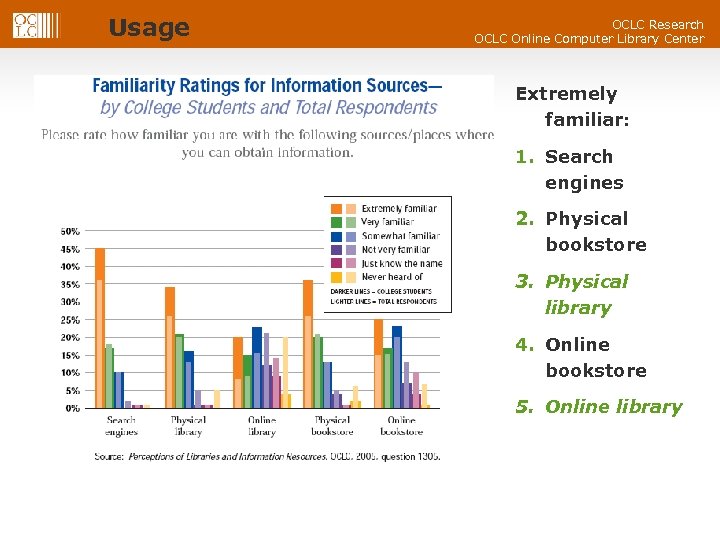
Usage Familiarity and Favorability OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Extremely familiar: 1. Search engines 2. Physical bookstore 3. Physical library 4. Online bookstore 5. Online library
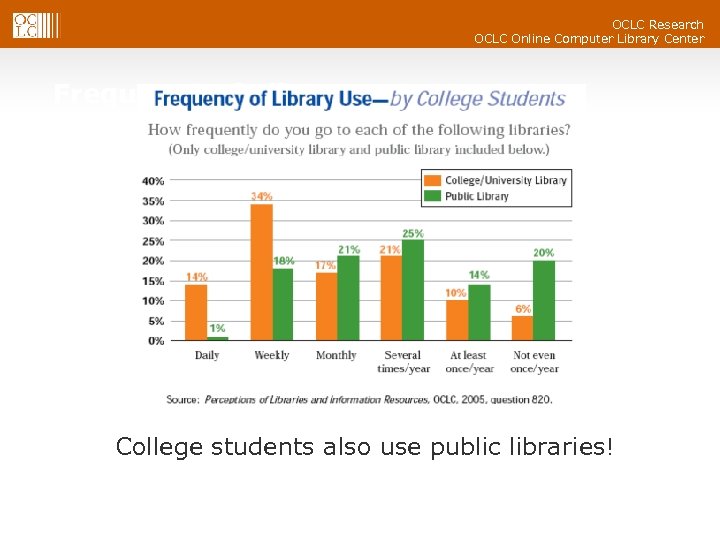
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Frequency of Library Use College students also use public libraries!
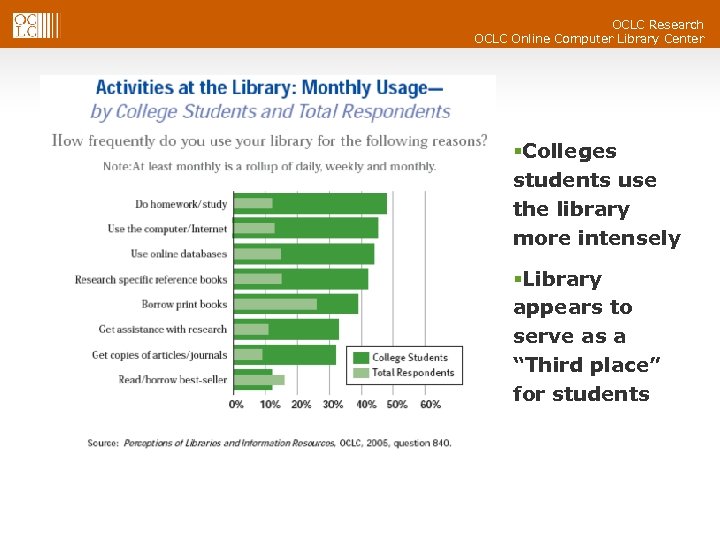
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Activities at the Library §Colleges students use the library more intensely §Library appears to serve as a “Third place” for students
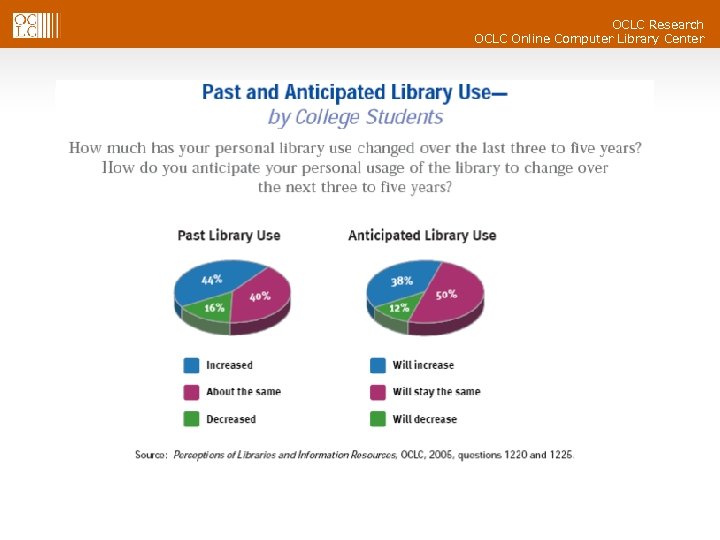
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Past and Anticipated Use by College Students
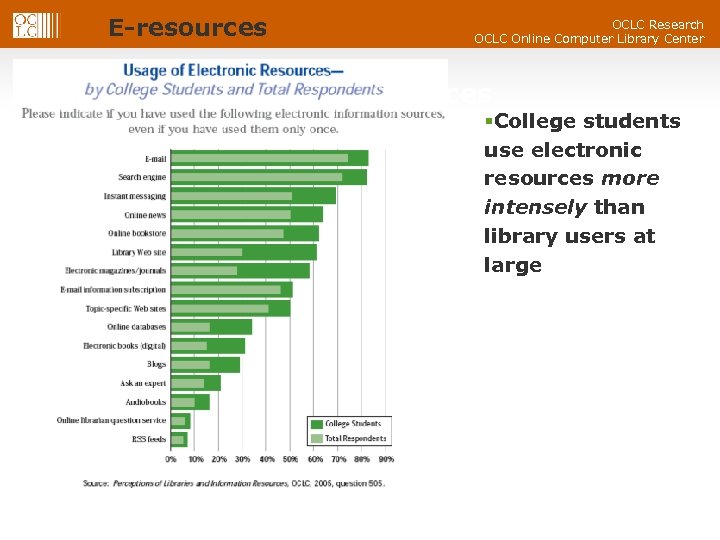
E-resources OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Usage of Electronic Resources §College students use electronic resources more intensely than library users at large
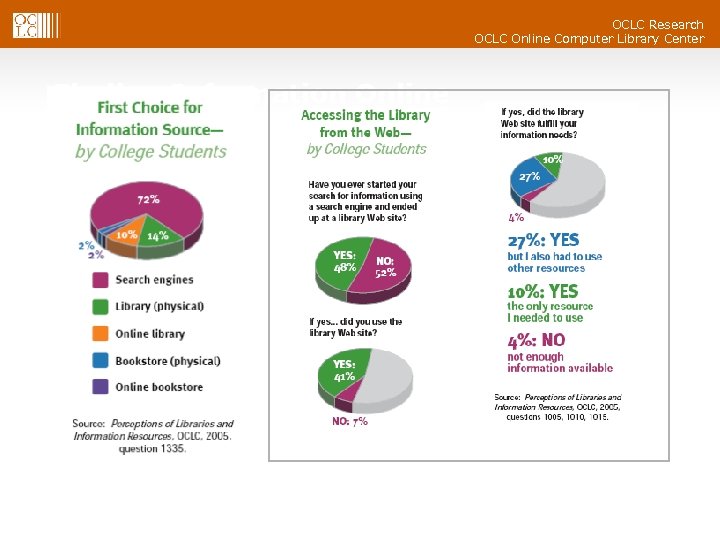
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Finding Information Online
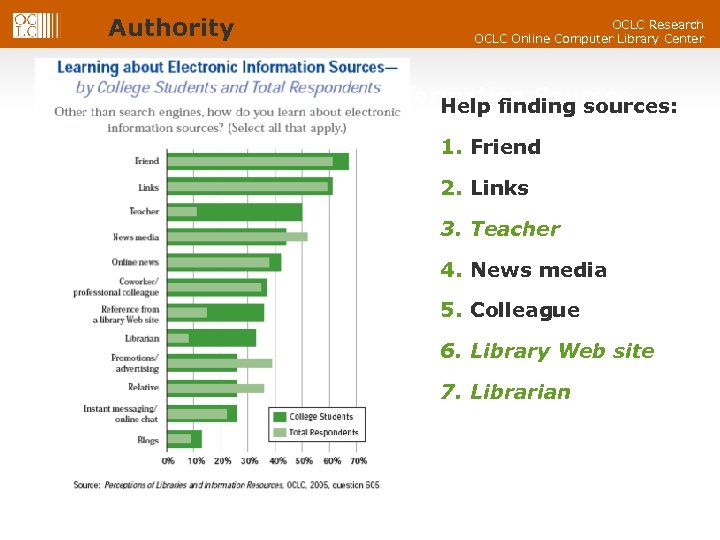
Authority OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Learning about Electronic Information Sources Help finding sources: 1. Friend 2. Links 3. Teacher 4. News media 5. Colleague 6. Library Web site 7. Librarian
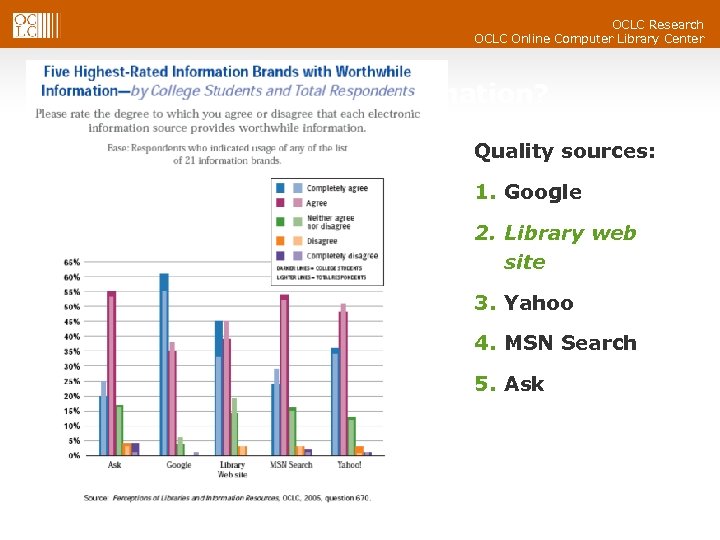
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Who has worthwhile information? Quality sources: 1. Google 2. Library web site 3. Yahoo 4. MSN Search 5. Ask
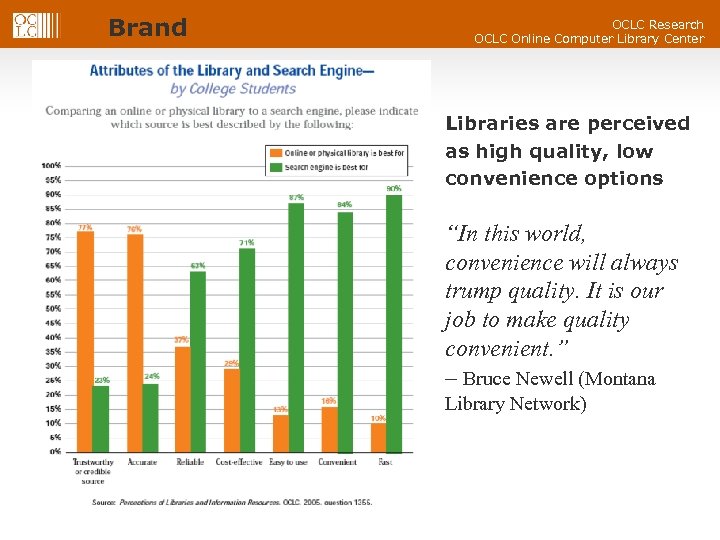
Brand OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Library vs. Search Engine Libraries are perceived as high quality, low convenience options “In this world, convenience will always trump quality. It is our job to make quality convenient. ” – Bruce Newell (Montana Library Network)
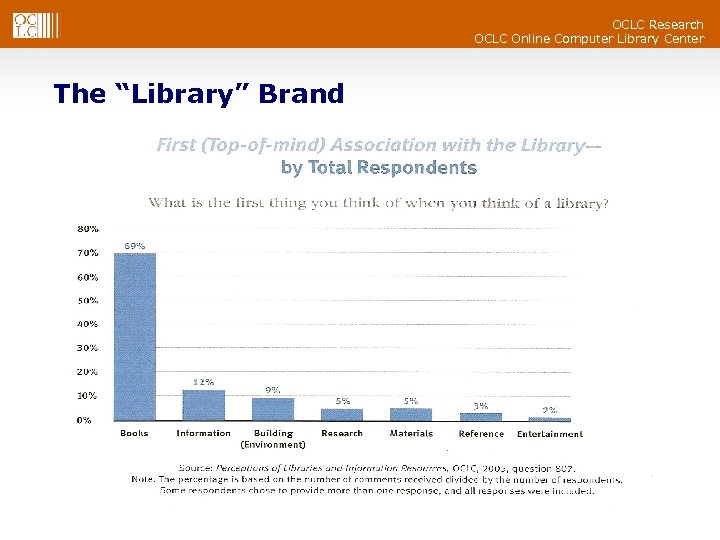
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center The “Library” Brand
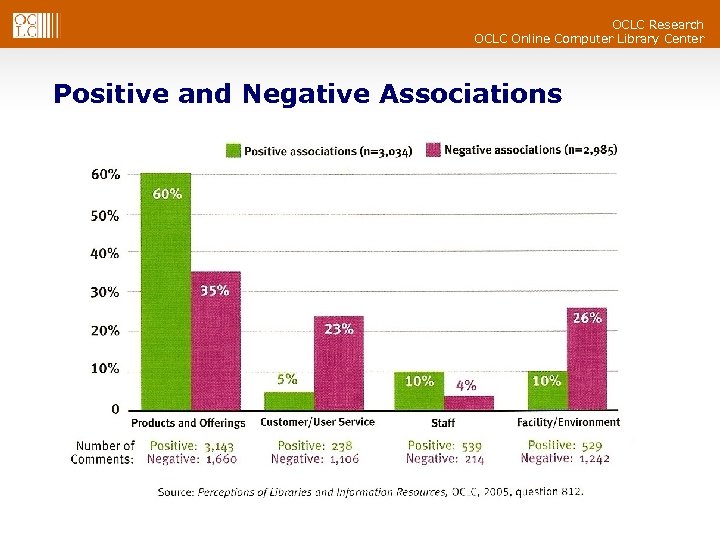
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Positive and Negative Associations
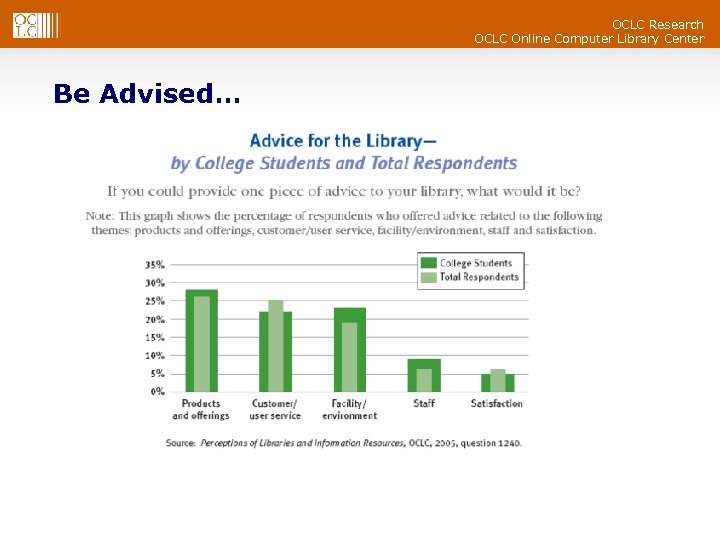
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Be Advised…

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center The Library Realm

Publishing OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Book Trade § A complex space gets more complex… § Web has had an impact on publishing & retail: § Give-electronic-to-sell-print model (e. g. , National Academies Press) § Newer players: Amazon, isbn. nu, others taking retail marketshare § Online books sales grew @34. 2% between 2003 -2004 (11% overall) § Bricks-and-mortar stores building web presence § Used is good § N. B. BISG estimates 2004 used book market = $2. 2 Billion (111 million books, 8. 4% total consumer spending on books. ) § E-books & e-audiobooks § Slowly developing momentum (esp. STM e-books) and acceptance § Novel approaches such as e-text into factual databases being tried § Pricing models & copyright/DRM (Digital Rights Mgt. ) still pose barriers

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Serial/media publishing § Publisher print-to-online transition accelerating § Self-aggregation § Article, news item, headline replacing journal, newspaper, magazine as unit of consumption § Newspapers, magazines, radio, TV: § More players – more TV channels, satellite radio, Internet radio, Web news sources, Google news, etc. § Audience shifting to online or alternatives (e. g. , Journalism alternatives such as news blogs, alternative news outlets) § Ad revenue offline not transitioning as fast as readers to online ; losing audience & revenue to Craigslist, other sales/classified ad channels § Business models = less subscription & more advertising § Experimentation with Wikis (Newsweek), web services (BBC), usercreated programming (KYOU)
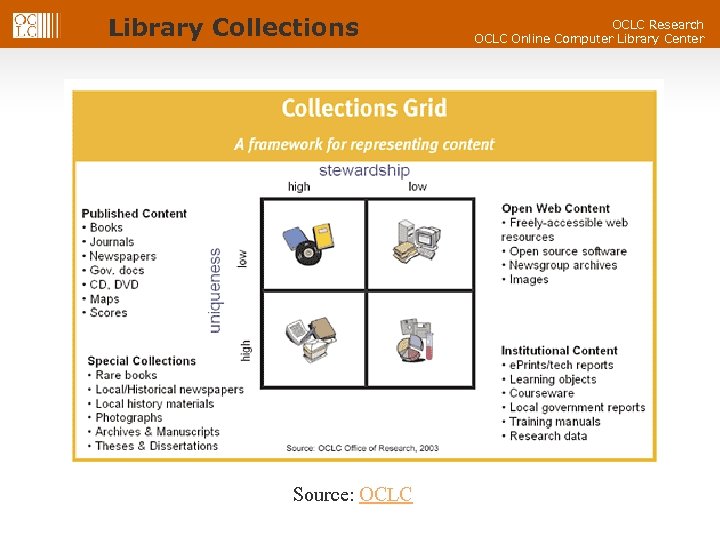
Library Collections Source: OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Published content space in libraries § Libraries originally established to collect and manage scarce content in physical containers § § § Now in a period of content abundance (the Web) Libraries still strongly text and physical container-based collection oriented Physical materials supply chain ever more automated § § Ordering, processing/cataloging, ready-to-shelve… Digital content continues to make inroads into libraries (spending up; users want it) § § E-audiobooks getting attention and interest from users § § E-books finally gaining some traction Strong trend to access published digital remotely rather than load locally Collection/selection process trends § New and improved selection tools from ILS vendors, jobbers, OCLC § Cooperative collection arrangements, cooperative remote storage
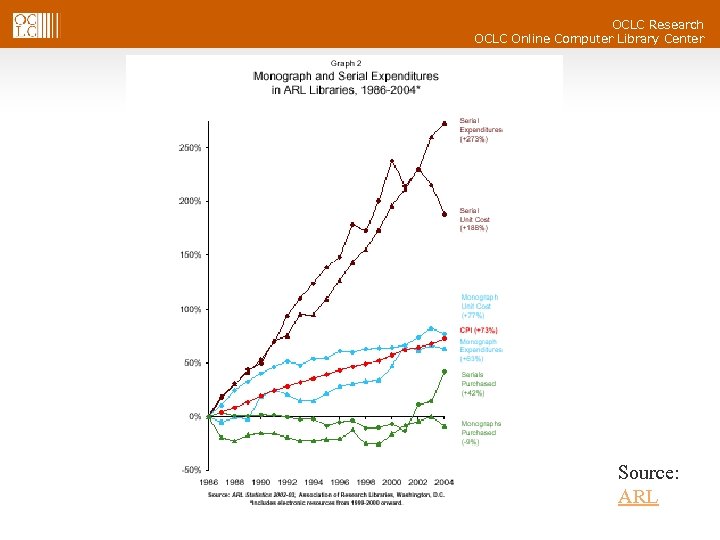
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Source: ARL

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Other parts of collections grid… § Special collections: § § § Often unique to single library -- typically high interest in digitizing, but not necessarily bandwidth/funding ARL’s “hidden collections” work (addressing cataloging backlog) Education/research products: § § § Opportunity for libraries to help scholarship & teaching, but not simple or inexpensive task Mostly poorly developed interfaces between systems, processes, practices in Course Mgt. Systems (CMS) & those in library services. Overlap with e-reserves? Library often invisible in CMS Open web: § Varied content (akin to Grey literature) & unclear what role(s) libraries should/can play vs. search engines, Internet Archive, etc. § Various slices-of-web projects: § Some libraries harvest all or some content from their country’s domain § Topical/period projects such as Library of Congress’ Election 2002 Web Archive
Platforms OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Libraries: Re-thinking, re-engineering § Library 2. 0 changes systems & services § Modularity in systems & data § Integration of data from many sources § User-contributed content § Supporting Library 2. 0 will mean change § More people space, fewer bookshelves § Library system as platform not monolith § Librarian 2. 0 (savvy, online, accessible, listening, contributing) § “Information is a conversation” -- Karen Schneider § Flowing the library into the Network § Surfacing on the Web: Open World. Cat, OAIster, etc. § Embedding the library in other systems (e. g. , Learning Mgt. ) § Networkflows – bend the library to users’ processes – Lorcan Dempsey

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Thinking aloud… § Michael Stephens on Library 2. 0: § The library is everywhere § The library has no barriers § The library invites participation § The library uses flexible, best-of-breed systems § The library encourages the heart § Cyril Oberlander on re-engineering: § Harness non-library sources (Amazon, Netflix…) § Streamline processes (how many steps are truly needed? ) § Deliver service first, sweat the small stuff later § acquire-choose-catalog vs. choose-acquire-catalog § Invest in staff (collaborate, educate, and innovate) § Intelligent business requires business intelligence

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center OCLC – work underway

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center OCLC at work § World. Cat. org [info] § Builds on Open World. Cat program that exposes World. Cat to Google, Yahoo, Microsoft, Ask, etc. § Search box/destination page for all of World. Cat § World. Cat expansion – continuing to load more data from more libraries worldwide § Registries & resolvers & data services § § Registry of Digital Masters – a central registry of digitization intent/work § § Open. URL resolver registry – helps patrons access e-resources from Google Scholar, etc. Institutional registry – information about OPACs, other data that helps library services be more exposed for creative applications (e. g. , mash-ups) Data services, etc. § OCLC Terminologies service – a simple side-pane for accessing vocabularies while doing cataloging and more § Prototyping various under-the-hood data services such as x. ISBN, FRBR (clustering of bibliographic records), more

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center OCLC Research § A unit within OCLC § Conducts and supports academic research on library-related topics § Active in standards work § Explores new ideas through prototyping, data mining, etc.

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Sample FRBR implementations § FRBR (Functional Requirements of Bibliographic Records) § Model for clustering related records together § Sample FRBR efforts § Top 1000 § x. ISBN § Fiction. Finder

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Top 10 works in WC by holdings #1 from OCLC Top 1000 #10

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center x. ISBN §OCLC Research prototype §Reveals all ISBNs associated with individual works in World. Cat §Web service: § URL syntax query (submit an ISBN) § Simple XML response (all ISBNs in workset) § Ex: Dune http: //labs. oclc. org/xisbn/0 441172717 §Users: § Various, loosely-coupled look-it-up applications § Copyright Clearance Center §OCLC Research team: § Thom Hickey (lead) § Jenny Toves § Jeff Young
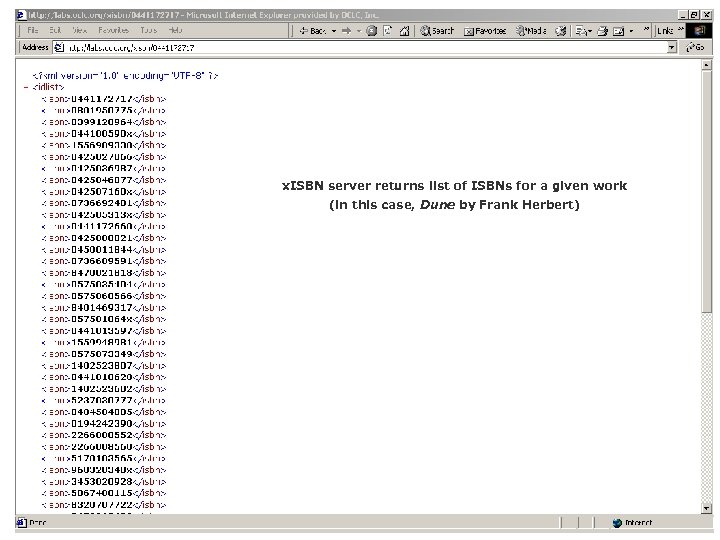
x. ISBN server returns list of ISBNs for a given work (in this case, Dune by Frank Herbert)

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Fiction. Finder §OCLC Research prototype §Supports searching & browsing of fiction materials cataloged in World. Cat §OCLC Research team: § Diane Vizine-Goetz (lead) § Fiction records — 2. 8 million § Roger Thompson § Unique works — 1. 4 million § Carol Hickey § Total holdings — 130 million § J. D. Shipengrover §Employs FRBR to: § Build a “work” view & cluster related records § Support the creation of special indexes §New version: § Available later in 2006 § Improved navigation & workbased displays
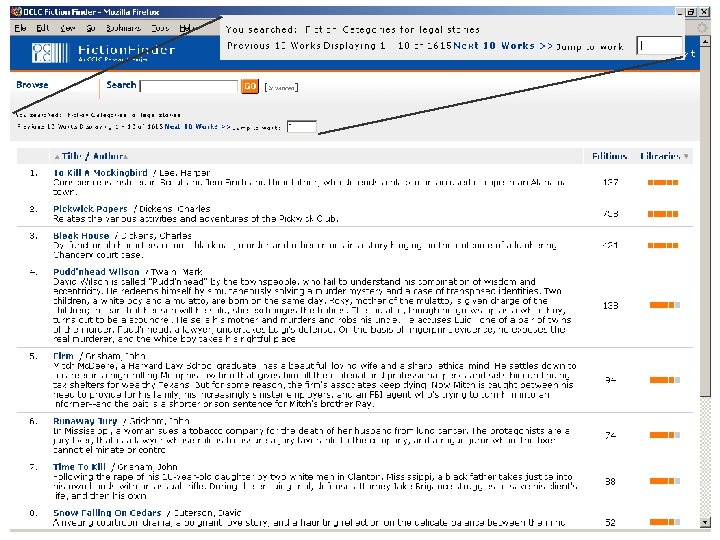
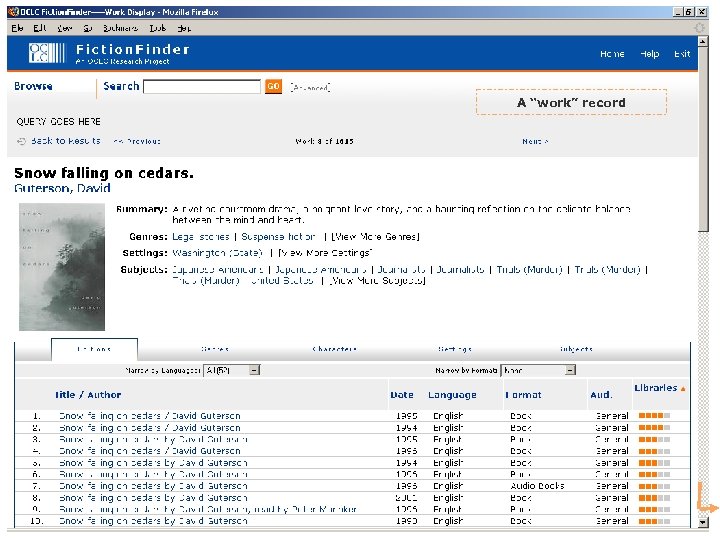
A “work” record
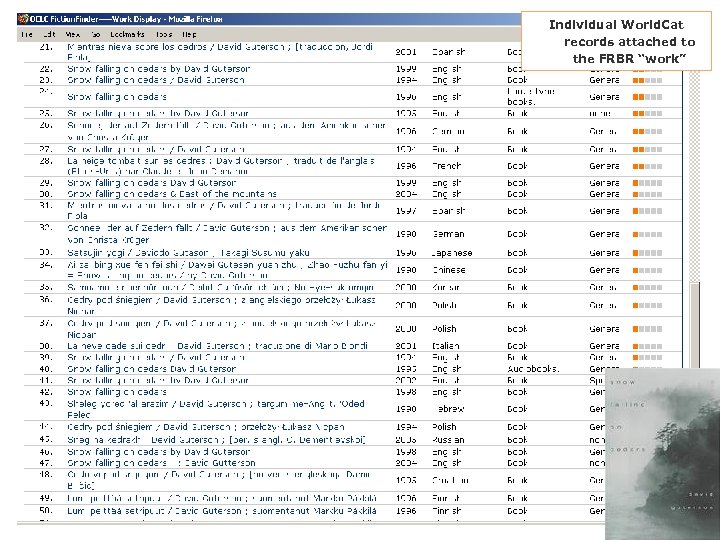
Individual World. Cat records attached to the FRBR “work”
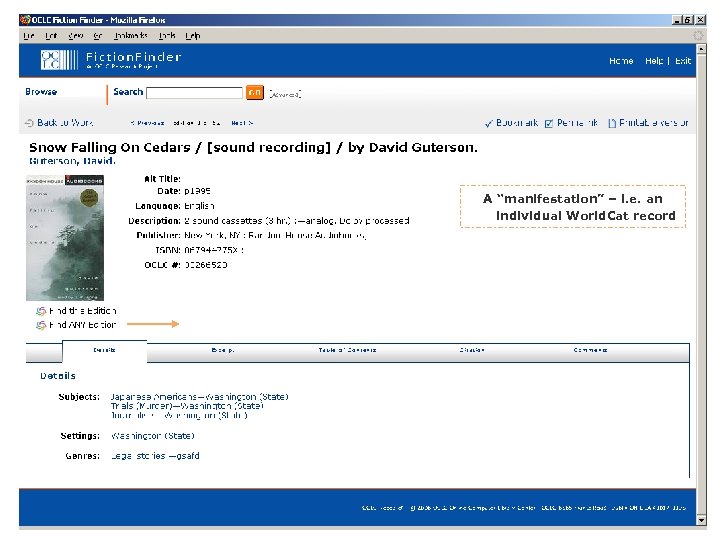
A “manifestation” – i. e. an individual World. Cat record

OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Further reading § OCLC Reports § http: //www. oclc. org/reports § OCLC Research § http: //www. oclc. org/research § OCLC-related blogs: § Lorcan Dempsey http: //orweblog. oclc. org § Thom Hickey http: //outgoing. typepad. com/outgoing § Stu Weibel http: //weibel-lines. typepad. com § It’s All Good http: //scanblogspot. com
OCLC Research OCLC Online Computer Library Center Thank you Eric Childress eric_childress@oclc. org
2486fbee4022d38ab9ad33b5fd336a90.ppt