PPH.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

Obstetrical bleedings

Importance of problem l There are post partum bleedings among 14 millions women in the word every year l 125 000 of patients are dead due to post partum bleedings every year l Risk of death from PB are : l 1 : 100 000 labor at England USA l 1 : 1 000 – at the few developed countries (at 100 times bigger) ВОЗ (1998)

Defects in treatment l Reasons of death from PB are : 1. Wrong assessment of blood lost 2. Not adequate fulfillment of blood lost volume 3. Delay of surgical treatment

l There are due to: 1. Absence of such services, as surgical and service of blood transfusion 2. Absence on the places rules to direct patients to specialistrs Contemporary OB/GYN Archive (2001)
Definition (1) l Post partum hemorrhage (PPH)- is loosing of not less, than 500 ml of blood from labor’s ways after a fetus delivery

l Primary post partum bleeding includes all cases PH during 24 hours after labor. l Secondary post partum bleeding includes all cases P. H. between 24 and 6 weeks after labor. WPHO(2000)
Definition 0 f post partum bleeding l Lost 500 ml of blood and more l Decreasing of hematocrit on 10%or necessity of blood transfusion l Any blood lost without compensation and leading to tissue injuring

Definition (2) l P. P. B. Any blood lost without compensation and leading to tissue injuring

Definition (2) l Volume of blood lost is severe not only due to quantity of loosing blood, but with counting increasing of blood volume due to pregnancy , individual physiologic reaction of woman: l not adequate increasing of blood lost in cases of preeclampsia l Difficulties in treatment in cases of anemia

Principles of treatment 1. Early recognizing and actions beginning: asking of help Restore of VCB 3. Primary assessment and supervision 2. 4. Looking of reason: stopping of bleeding

1. Early recognizing and actions beginning. There is blood lost till 1000 ml without symptoms of shock

1. Early recognation l There is blood lost 1000 and more ml with symptoms of shock
2. Treatment of blood lost l Put in i/v catheter of a big diameter ( № 16 or more) l Begin infusion of crystalloids l In cases of shock : put down a - Give oxygen l patient’s through head a mask
3. Primary assessment and supervision l Assessment of breathing ( respiratory ways, breathing), BP, pulse rate( Blood supply), color of skin l Catheterization of bladder (urine production) l Laboratory examination ( blood analysis, coagulability, checking of blood incompatibility )

4. Looking for a bleeding reason Reasons of primary post partum bleeding l Atonia of uterus - 90% l Trauma of sexual organs l Primary hematological disturbances l DIV syndrome ( rarely) l Uterine insertion (rarely) l The last 2 reasons more often lead to death l

Bleedings due to uterine atonia l In cases of retention of placenta l Massage of uterus should be done. If uterus is hard, attempts to remove of placenta should be done on the way of controlled tractions on umbilicus l If it is not possible , perform a vaginal examination , check , may be placenta is in cervical channel. Carefully , remove a placenta l On a contrary , perform an operation of manual removing of placenta l Surgical treatment in cases of placenta adherence WHO (2003)

Uterine atonia (bleeding) (2) l In cases of absence of placenta Palpation of uterus l Massage of uterus till it will be hard l Intramuscular introduction of oxytocinum (10 МЕ , or i/v 20 -40 МЕ in 1 000 ml of Na Cl , 40 -60 drops in minute) l l I/V like a bolus introduction of 5 ml oxytocinum may be reason of hypertension. WHO (2000)

Bleeding in cases of complete placenta removing l It should be checked possibility of rupture of vagina or uterine cervix l Assessment thoroughly and restore place l Laparotomy in cases of uterus rupture of rupture

Treatment in cases of atonia of uterus and absence reaction on oxytocinum l 0, 2 mg of methilergometrin, i/m till 5 dozes l It is contraindicated in cases of preeclampsia and PIH (Hemobat , PG F 2 ) on 250 μgr every 15 minutes till 8 times, i/m or in myometrium l Carboprost WHO (2000)

(1) Using of prostaglandins in refracted to oxytocinum cases l cases of refracted reaction to oxytocinum and alcoloids , frequency of effective results of prostaglandin’s F 2 using is 86% till 96%. In Canada (2000)

Using of prostaglandins at refracted cases (2) l Alternative drug is – mizoprostol l Introductiion per rectum l 800 – 1 000 мkgr or 4 -5 tablets l More effective as compare as another treatment: decrease possibility of another intervation (6% as compare as 34%), as compare as i/m injections of syntometrin or i/v injection of oxytocinum (ОР 0, 18; 95% ДИ от 0, 04 till 0, 67) Cochrane Library (2003)

Advantages of mizoprostolum l Small l Low l It quantity of side effects price is not necessary to store in fridge l Simple l Quick in using effect

Steadily bleeding In cases of reaction absence on previous treatment, it is necessary to make such thing, as: l ask of help l Make information at blood bank and department of intensive therapy l Prepare for operation ( the best is t o start early than late) l Local stopping bleeding l Manual pressure of aorta l Manual pressure of uterus WHO (2000) l
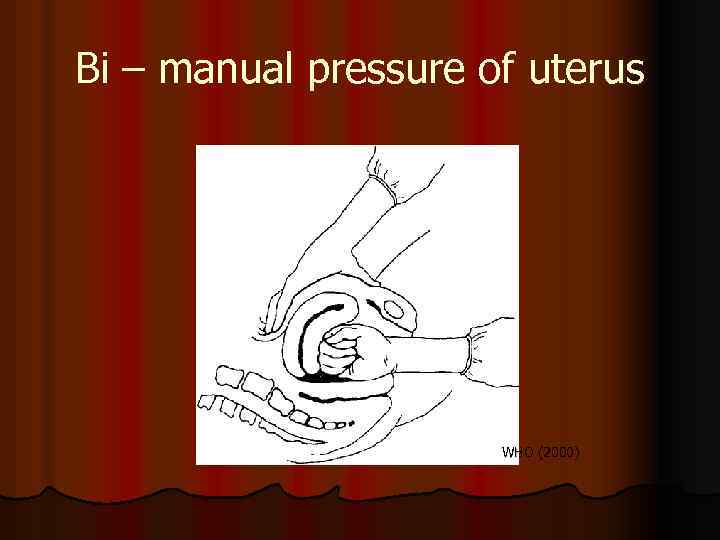
Bi – manual pressure of uterus WHO (2000)
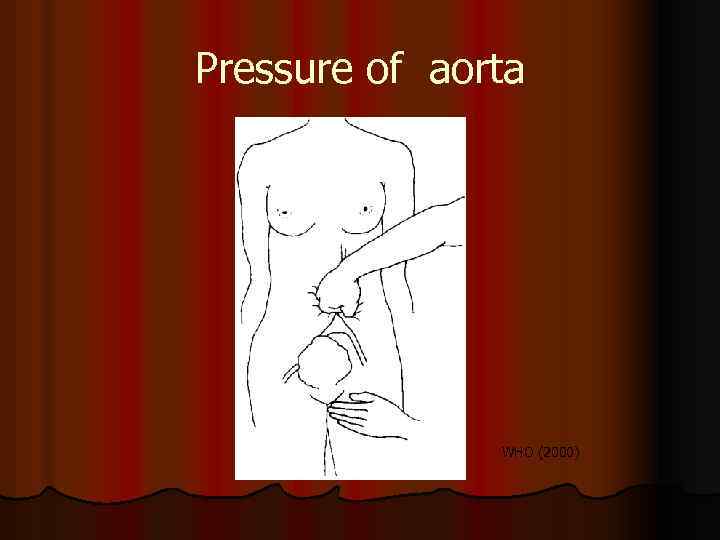
Pressure of aorta WHO (2000)

Arrest of bleeding (1) l If treatment without effect - surgical treatment l The best way is - early, than late l It is known, one of reason of bad results is too late management of surgical treatment Chamberlain (1992)
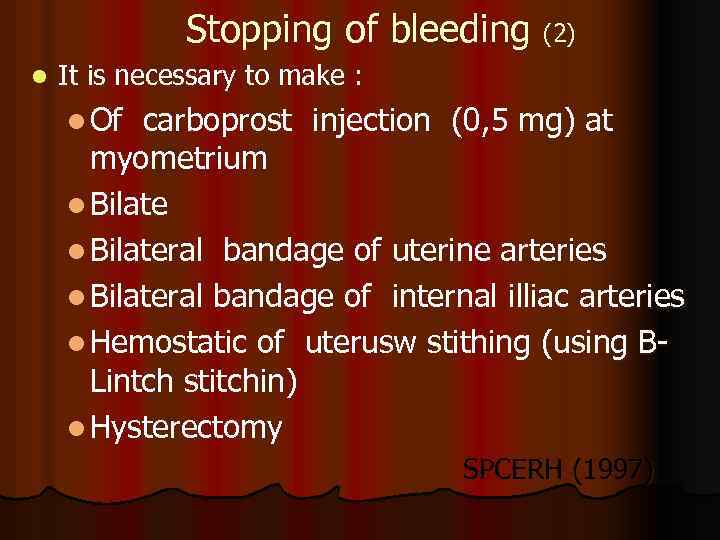
Stopping of bleeding (2) l It is necessary to make : l Of carboprost injection (0, 5 mg) at myometrium l Bilateral bandage of uterine arteries l Bilateral bandage of internal illiac arteries l Hemostatic of uterusw stithing (using BLintch stitchin) l Hysterectomy SPCERH (1997)

Bandage of uterine arteries l The more big examination by O Larry (65 patients, effect 96% l Another examination: 100 -% effect among 103 patients l There very absent serious complications , were cases of repeated pregnancies
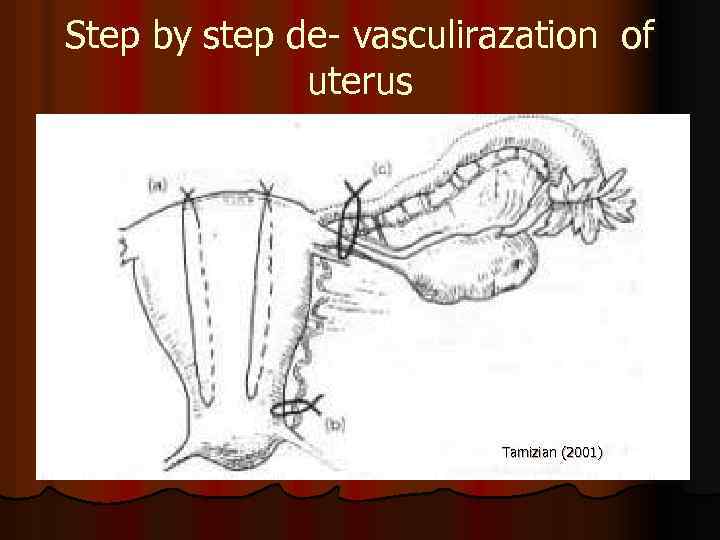
Step by step de- vasculirazation of uterus Tamizian (2001)

(1)Surgical - Bi- Linchi stitching l This stitch is known from 1997 year l There are description of 1300 случаев, in more cases hysterectomy was not done l It is possible to have pregnancy and labor after that. El-Hamamy E, B-Lynch C. (2005)
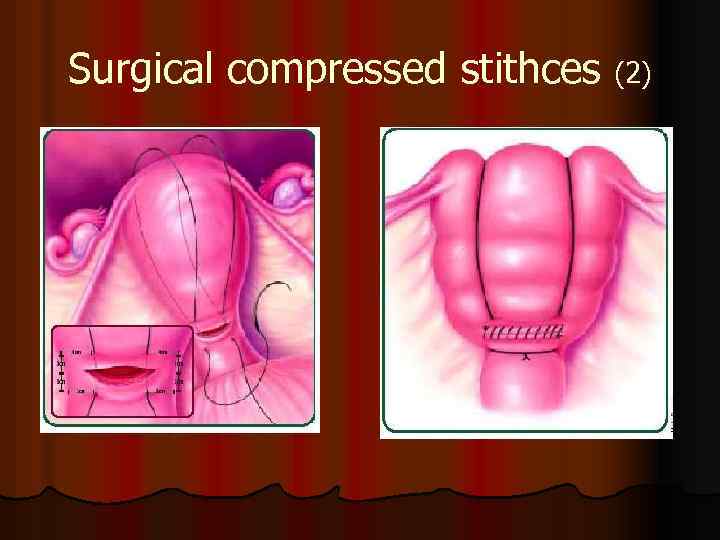
Surgical compressed stithces (2)

Hysterectomy l Hysterectomy are performing in 7 to 13 cases on 10000 labor ( 1: 1000 labor) l Indications for that- placenta adherence (49, 6%) l Previously date are an contrary ours date ( 1981 -1982), reason- uterine atonia. Stanco et al (1993)

Amputation of uterus or hysterectomy? l Amputation of uterus is performing at the most quantity of cases l Cervix should be removed in cases , when a source of bleeding is low of uterine segment)

BUT l Hysterectomy too late Duignan N (1991) should not be done Burke G,

Surgical conclusion l Laparotomy does not means hysteroctomy in all cases l Amputation of uterus is possible l Surgical treatment should be done in time

Infusion theprapy l It is better to use sol. Na. Cl o, 9 % ( in coordination 3: 1) l Colloid solution does not have more advantages l Exact indications for FFP and erythrocyte mass using. WHO (2000)

l Hydroxyethyl starch was compare with cristalloids at 10 randomized examination. ОР is 1, 16 (95% ДИ от 0, 68 till 1, 96)
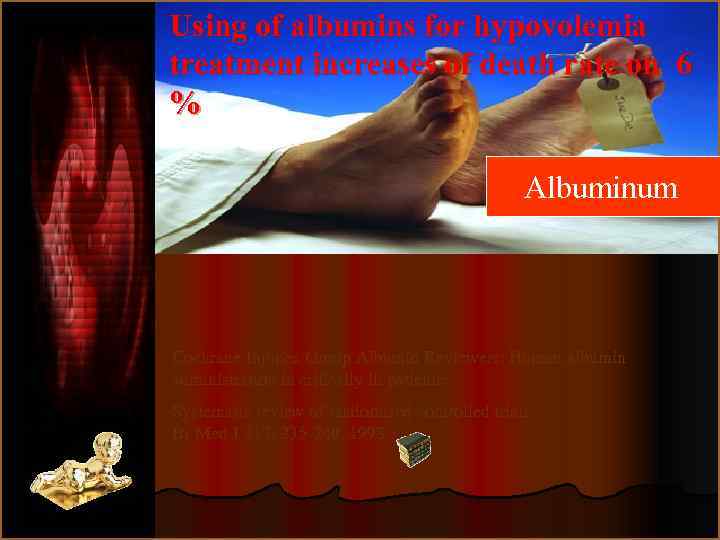
Using of albumins for hypovolemia treatment increases of death rate on 6 % Albuminum Cochrane Injuries Group Albumin Reviewers: Human albumin administration in critically ill patients: Systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Br Med J 317: 235 -240, 1998.

(2) l Compare colloids and cristalloids solutions ОР 0, 88 (95% ДИ from 0, 74 till 1, 05)

(3) l There is no the better effect due to that it is not necessary to use its for prolong time. P. (2004) Roberts I, Alderson
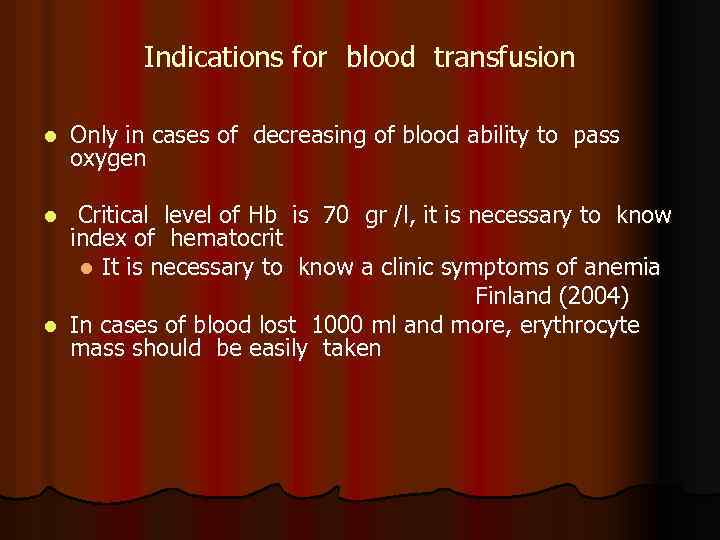
Indications for blood transfusion l Only in cases of decreasing of blood ability to pass oxygen l Critical level of Hb index of hematocrit l It is necessary to is 70 gr /l, it is necessary to know a clinic symptoms of anemia Finland (2004) l In cases of blood lost 1000 ml and more, erythrocyte mass should be easily taken

Indications for FFP Acute form of DIC syndrome after laboratory investigagtion l In cases of massive bleeding and using of more than 5 -6 packages of erythrocyte mass l it should be used not less, than 2 dozes just after making its fluid Lundberg G. D. (1994) l

Treatment of women with sever post partum bleeding (1) l It should be the clear protocol of treatment l Pregnant women should deliver at spetial departments with all necessary equipment and specialists There are such measures, as : 1. reanimation monitoring and laboratory investigations stopping of bleeding, it is not possible too late surgical treatment l l

l Early consultation of additional specialists l It should be all necessary drugs and equipment

Conclusion (1) l It is very important early detection of bleeding and its treatment l In many refracted cases it is dozen of oxytocinum in doze of 40 МЕ and prostaglandines l For temporary stopping of bleeding in cases of atonia it is possble to perform external and internal bi manual pressure of uterus and aorta. Another methods are not effective and we will loose a time.

Conclusion (2) l At every medical entities written form of instructions must be ( protocol) for prophylaxis and treatment of post partum bleedings, based on the principles of explanation ‘s medicine.

Conclusion (3) l Hysterectomy is not a single method of surgical treatment of massive bleedings , it is possible to perform a subtotal hysterectomy. является субтотальная гистерэктомия

Conclusion (4) l The first medicine for bleeding stopping is Na Cl 0, 9 %. l Sometimes hematransfusion is necessary ; but we should think about complications of these operation. Ther are strick indications for these operation.

Work at a small ghroup l Primary measures l Measures for a bleeding stopping before laparotomy l Indications and methodcs of finally hemostasis l Substitute therapy l Spreading of duties in cases of sever post partum bleeding
PPH.ppt